Ohmic Heating Nixtamalization Modifies Maize Starch and Affects the Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Instant Masa Flours †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Material
2.2. Production of Instant Masa Flours
2.2.1. Traditional Nixtamalization Process
2.2.2. Nixtamalization Process Using Ohmic Heating
2.3. Characterization of Starch Changes on Instant Flours
2.3.1. Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Viscosity Profile Analysis
2.3.3. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
2.3.4. Thermal Properties
2.3.5. Statistical Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
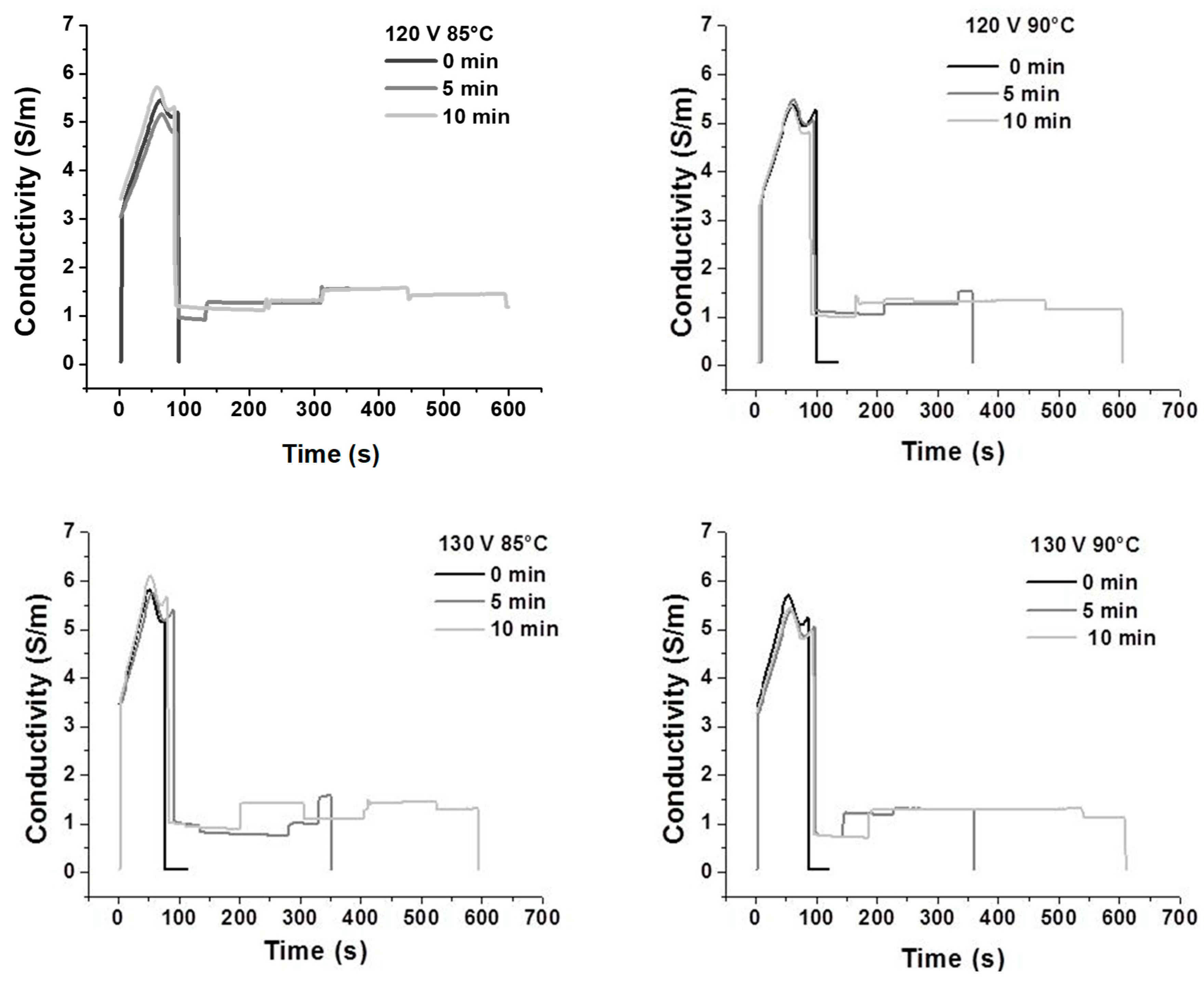
3.1. Electrical Conductivity
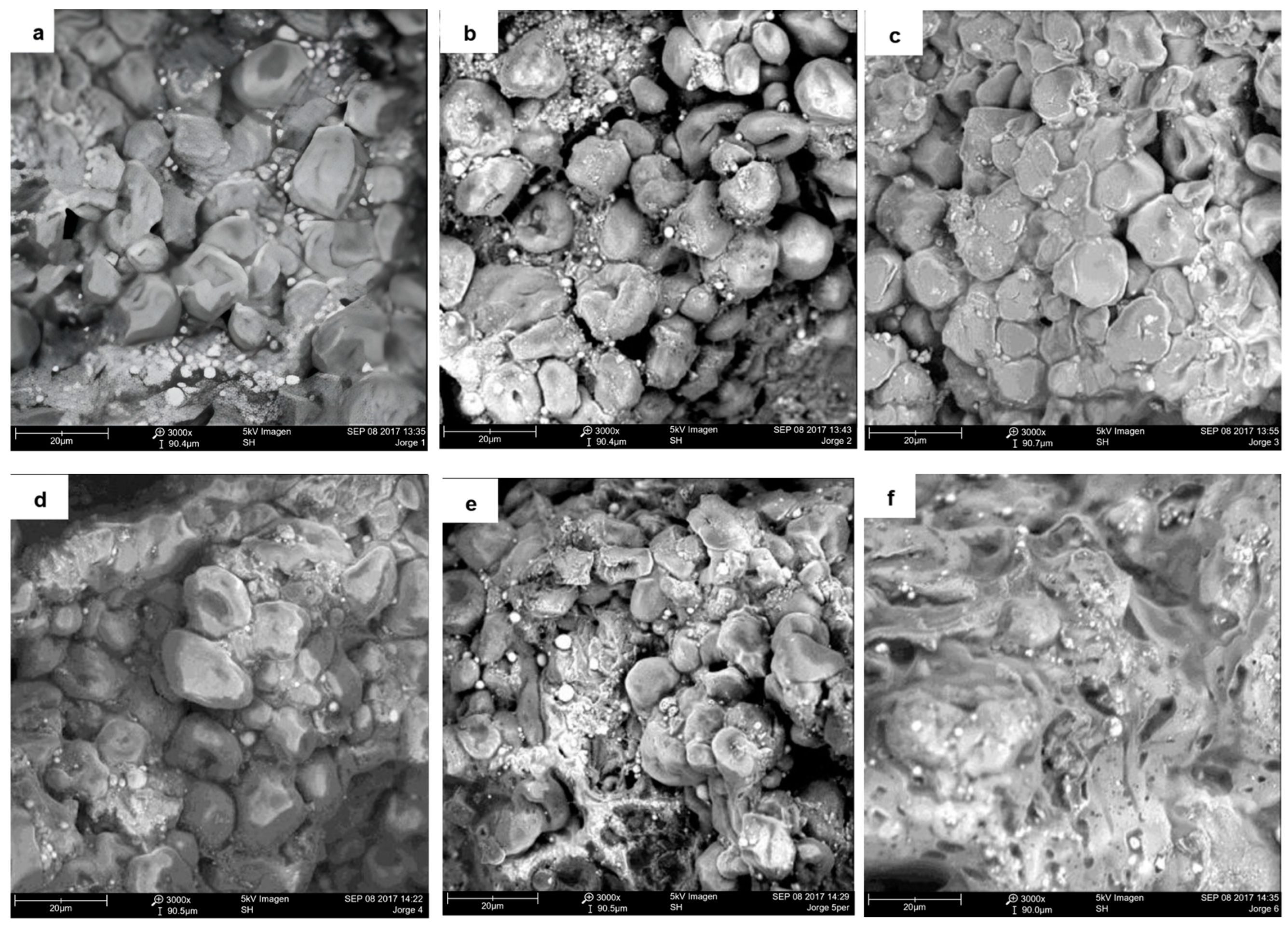
3.2. Changes in Microstructure
3.3. Thermal and Rheological Properties
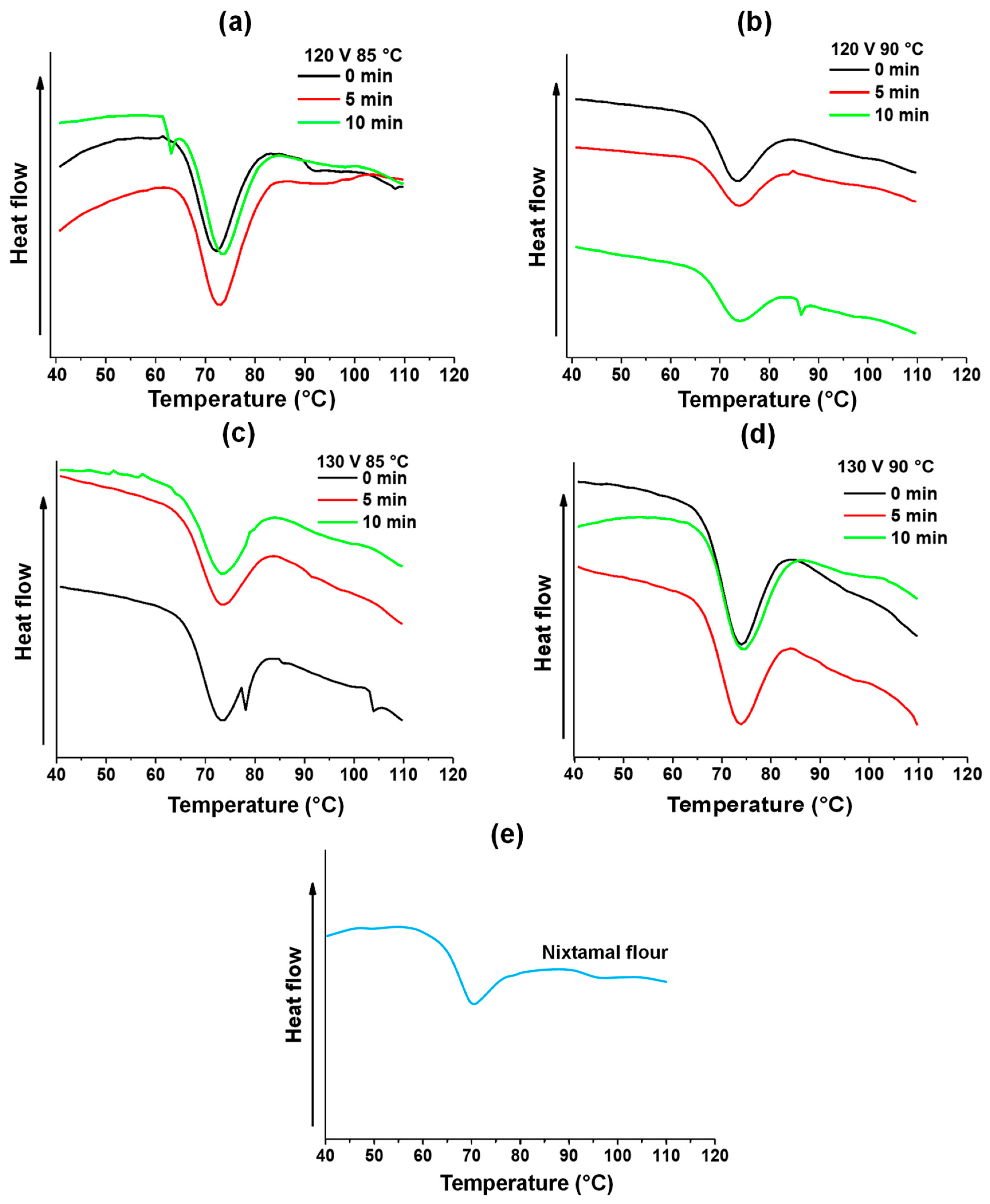
3.3.1. Thermal Parameters
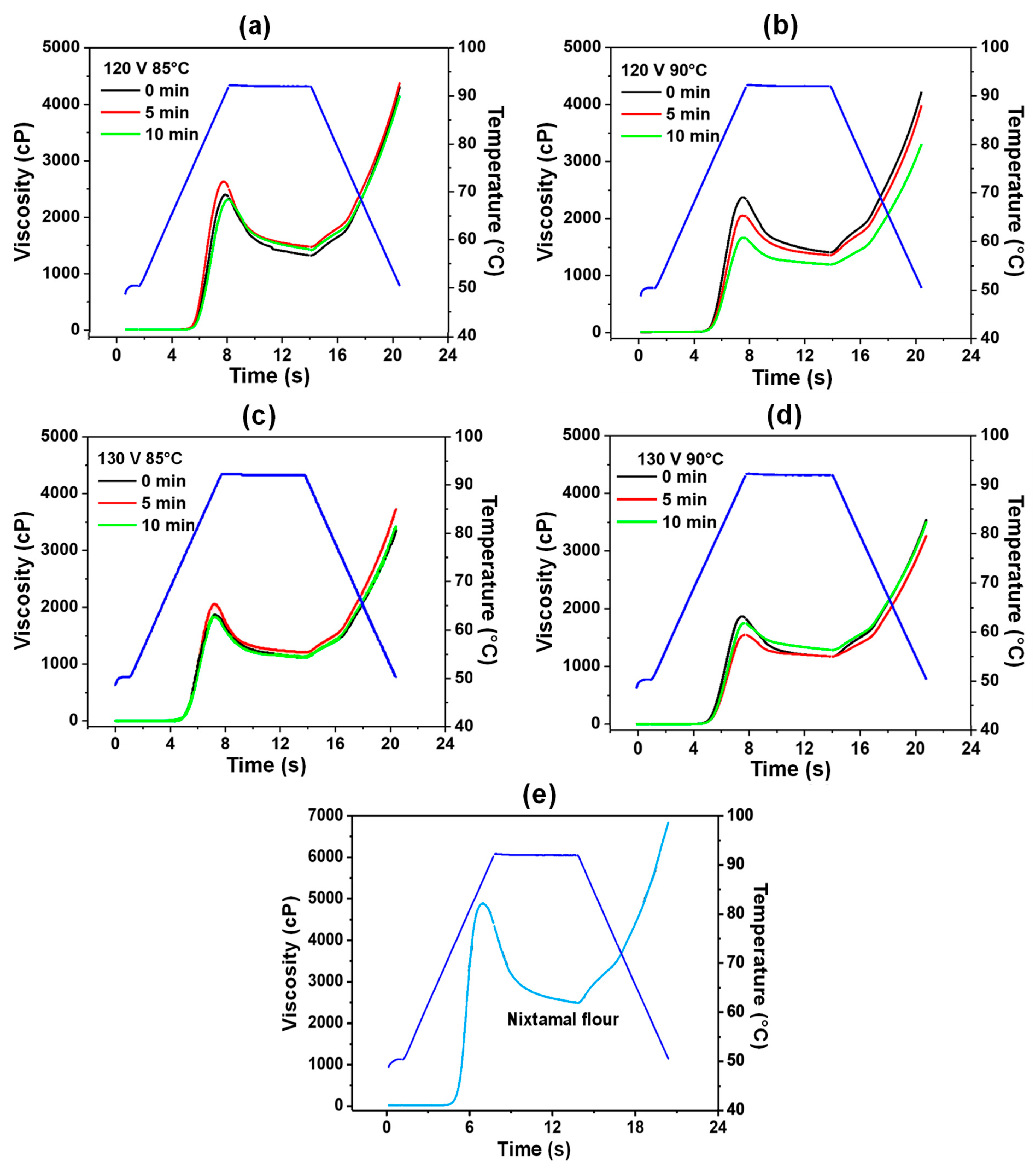
3.3.2. Viscosity Profile
3.3.3. X-Ray Diffraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanumihardjo, S.A.; McCulley, L.; Roh, R.; Lopez-Ridaura, S.; Palacios-Rojas, N.; Gunaratna, N.S. Maize Agro-Food Systems to Ensure Food and Nutrition Security in Reference to the Sustainable Development Goals. Glob. Food Sec 2020, 25, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Ramos, D.; de Dios Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.; Mariscal-Moreno, R.M.; Escalante-Aburto, A.; Ponce-García, N.; Véles-Medina, J.J. Physical and Chemical Changes Undergone by Pericarp and Endosperm during Corn Nixtamalization—A Review. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 81, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Saldivar, S.O.; Rooney, L.W. Chapter 13—Industrial Production of Maize Tortillas and Snacks. In Tortillas; Rooney, L.W., Serna-Saldivar, S.O., Eds.; AACC International Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2015; pp. 247–281. ISBN 978-1-891127-88-5. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán-Soria, D.; Taboada-González, P.; Aguilar-Virgen, Q.; Baltierra-Trejo, E.; Marquez-Benavides, L. Environmental Impact of Corn Tortilla Production: A Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Araujo, H.; Gaytán-Martínez, M.; Reyes-Vega, M.L. Alternative Technologies to the Traditional Nixtamalization Process: Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaytán-Martínez, M.; Figueroa, J.D.C.; Vázquez-Landaverde, P.A.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Martínez-Flores, H.E.; Reyes-Vega, M.L. Caracterización Fisicoquímica, Funcional y Química de Harinas Nixtamalizadas de Maíz Obtenidas Por Calentamiento Óhmico y Proceso Tradicional. CYTA J. Food 2012, 10, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménera-López, I.; Gaytán-Martínez, M.; Reyes-Vega, M.L.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Figueroa, J.D.C. Physico-Chemical Properties and Quality Assessment of Corn Flour Processed by a Continuous Ohmic Heating System and Traditional Nixtamalization. CYTA J. Food 2013, 11, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Jiménez, A.K.; Rangel-Hernández, J.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Gaytán-Martínez, M. Changes on the Phytochemicals Profile of Instant Corn Flours Obtained by Traditional Nixtamalization and Ohmic Heating Process. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Hernández, E.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.A.; Domínguez-Hernández, M.E.; Loarca-Piña, G.F.; Gaytán-Martínez, M. In Search of Better Snacks: Ohmic-heating Nixtamalized Flour and Amaranth Addition Increase the Nutraceutical and Nutritional Potential of Vegetable-enriched Tortilla Chips. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2773–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, N.; Singh, A.K. Ohmic Heating: Concept and Applications—A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2338–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F. Modifications of Starch by Electric Field Based Techniques. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jittanit, W.; Khuenpet, K.; Kaewsri, P.; Dumrongpongpaiboon, N.; Hayamin, P.; Jantarangsri, K. Ohmic Heating for Cooking Rice: Electrical Conductivity Measurements, Textural Quality Determination and Energy Analysis. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 42, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjanapongkul, K. Rice Cooking Using Ohmic Heating: Determination of Electrical Conductivity, Water Diffusion and Cooking Energy. J. Food Eng. 2017, 192, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniglia, B.C.; Castanha, N.; Le-Bail, P.; Le-Bail, A.; Augusto, P.E.D. Starch Modification through Environmentally Friendly Alternatives: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2482–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Bustos, F.; Martínez-Flores, H.E.; Sanmartín-Martínez, E.; Sánchez-Sinencio, F.; Chang, Y.K.; Barrera-Arellano, D.; Rios, E. Effect of the Components of Maize on the Quality of Masa and Tortillas during the Traditional Nixtamalisation Process. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.-H. Effect of Ohmic Heating on Thermal and Water Holding Property of Starches. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2014, 27, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-García, F.M.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Gaytán-Martínez, M.; de la Cruz, G.V.; del Carmen Méndez-Montealvo, M.G. Effect of Electric Field on Physicochemical Properties and Resistant Starch Formation in Ohmic Heating Processed Corn Starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Hernández, E.; Rangel-Hernández, J.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Gaytán-Martínez, M. Effect of Ohmic Heating Nixtamalization on the Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Instant Maize Flours and Their Relation to Starch Modifications. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2022, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón-Londoño, N.; Vega-Rojas, L.J.; Contreras-Padilla, M.; Acosta-Osorio, A.A.; Rodríguez-García, M.E. Analysis of the Pasting Profile in Corn Starch: Structural, Morphological, and Thermal Transformations, Part I. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Ramírez, J.E.; Cabrera-Ramirez, A.H.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Rodriguez-García, M.E.; de la Luz Reyes-Vega, M.; Ramírez-Jiménez, A.K.; Contreras-Jiménez, B.L.; Gaytán-Martínez, M. Amylose-Lipid Complex Formation from Extruded Maize Starch Mixed with Fatty Acids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, 116555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Sánchez, E.; Reyes-Vega, M.L.; Gaytán-Martínez, M.; Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.D.; Velázquez, G. Relationship between Electrical Conductivity and Water Activity of Starch-Water Composites. In Water Stress in Biological, Chemical, Pharmaceutical and Food Systems; Food Engineering Series; Gutiérrez-López, G., Alamilla-Beltrán, L., del Pilar Buera, M., Welti-Chanes, J., Parada-Arias, E., Barbosa-Cánovas, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY USA, 2015; pp. 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Jaimes, C.; Lobato-Calleros, C.; Sosa, E.; Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Vernon-Carter, E.J.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J. Electrochemical Characterization of Gelatinized Starch Dispersions: Voltammetry and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy on Platinum Surface. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 124, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, T.S.; Sastry, S.K.; Cristianini, M. Effect of Concentration and Consistency on Ohmic Heating. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhengbiao, G.U. Morphology of Modified Starches Prepared by Different Methods. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villada, J.A.; Sánchez-Sinencio, F.; Zelaya-Ángel, O.; Gutiérrez-Cortez, E.; Rodríguez-García, M.E. Study of the Morphological, Structural, Thermal, and Pasting Corn Transformation during the Traditional Nixtamalization Process: From Corn to Tortilla. J. Food Eng. 2017, 212, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.-A.; Hong, J. Modification of Plant Biopolymers by Pulsed Electric Fields. In Handbook of Electroporation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 1–4, pp. 2423–2438. [Google Scholar]
- Londoño-Restrepo, S.M.; Rincón-Londoño, N.; Contreras-Padilla, M.; Millan-Malo, B.M.; Rodriguez-Garcia, M.E. Morphological, Structural, Thermal, Compositional, Vibrational, and Pasting Characterization of White, Yellow, and Purple Arracacha Lego-like Starches and Flours (Arracacia xanthorrhiza). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinopoulou, A.; Papastergiadis, E.; Raphaelides, S.N.; Kontominas, M.G. Structural Characterization and Thermal Properties of Amylose-Fatty Acid Complexes Prepared at Different Temperatures. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 58, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Campos, F.G.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Cabrera-Ramírez, Á.H.; Martinez, M.M.; Rodríguez-García, M.E.; Gaytán-Martínez, M. High Amylose Starch Thermally Processed by Ohmic Heating: Electrical, Thermal, and Microstructural Characterization. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 87, 103417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deladino, L.; Schneider Teixeira, A.; Plou, F.J.; Navarro, A.S.; Molina-García, A.D. Effect of High Hydrostatic Pressure, Alkaline and Combined Treatments on Corn Starch Granules Metal Binding: Structure, Swelling Behavior and Thermal Properties Assessment. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 102, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovrlija, R.; Rondeau-Mouro, C. Hydrothermal Changes of Starch Monitored by Combined NMR and DSC Methods. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador-Rodríguez, K.Y.; Silos-Espino, H.; Valera-Montero, L.L.; Perales-Segovia, C.; Flores-Benítez, S.; Martínez-Bustos, F. Physico-Chemical, Thermal, and Rheological Properties of Nixtamalized Creole Corn Flours Produced by High-Energy Milling. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Z.; Yao, T.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, X.; Kong, X.; Ai, L. Effects of Heat-Moisture Treatment Reaction Conditions on the Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Maize Starch: Moisture and Length of Heating. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de los Ángeles Cornejo-Villegas, M.; Rincón-Londoño, N.; Del Real-López, A.; Rodríguez-García, M.E. The Effect of Ca2+ Ions on the Pasting, Morphological, Structural, Vibrational, and Mechanical Properties of Corn Starch–Water System. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Tatsumi, E.; Yin, L. Effects of Corn Fiber Gum (CFG) on the Pasting and Thermal Behaviors of Maize Starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valderrama Bravo, M.D.C.; Sánchez Lara, M.J.; Contreras Padilla, M.; Pahua Ramos, M.E.; Jiménez Ambriz, S. Effect of Wet Grinding and Drying of the Nixtamal on Physicochemical, Morphologic, and Vibrational Properties of Flours and Rheological Changes of Masa. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaytán-Martínez, M.; Figueroa, J.D.C.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Vázquez-Landaverde, P.A.; Martínez-Flores, H.E. Physicochemical Properties of Masa and Corn Tortilla Made by Ohmic Heating. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 16028–16036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teissie, J. Mechanistic Description of Membrane Electropermeabilization. In Handbook of Electroporation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 1–4, pp. 451–472. [Google Scholar]
- Kusnadi, C.; Sastry, S.K. Effect of Moderate Electric Fields on Salt Diffusion into Vegetable Tissue. J. Food Eng. 2012, 110, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo, C.; Rodríguez-Llamazares, S.; Bouza, R.; Barral, L.; Castaño, J.; Müller, N.; Restrepo, I. Study of the Structural Order of Native Starch Granules Using Combined FTIR and XRD Analysis. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Ramos, D.; de Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.D.; Véles-Medina, J.J.; Mariscal-Moreno, R.M. Changes in the Thermal and Structural Properties of Maize Starch during Nixtamalization and Tortilla-Making Processes as Affected by Grain Hardness. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 74, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; An, D.; Zeng, X.A.; Han, Z.; Zheng, X.; Cai, M.; Bian, K.; Aadil, R.M. Behaviors of Large A-Type and Small B-Type Wheat Starch Granules Esterified by Conventional and Pulsed Electric Fields Assisted Methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Zeng, X.A.; Buckow, R.; Han, Z.; Wang, M. sheng Nanostructure, Morphology and Functionality of Cassava Starch after Pulsed Electric Fields Assisted Acetylation. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariscal-Moreno, R.M.; de Dios Figueroa Cárdenas, J.; Santiago-Ramos, D.; Rayas-Duarte, P.; Veles-Medina, J.J.; Martínez-Flores, H.E. Nixtamalization Process Affects Resistant Starch Formation and Glycemic Index of Tamales. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Process | Treatment | Viscosity | Thermal Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Maximum (cP) | Setback (cP) | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Te (°C) | ΔT (°C) | ΔHgel (J∙g−1) | %SG | |
| Ohmic Heating | 120 | 85 | 0 | 2241 ab | 2789 a | 65.83 d | 72.45 d | 79.84 bc,A | 14.01 ab,A | 3.97 ab,A | 48.44 ab,A |
| 5 | 2381 a | 2772 ab | 66.14 cd | 72.63 cd | 80.83 abc | 14.69 a,A | 4.66 a,A | 39.49 b,A | |||
| 10 | 2114 abc | 2555 abc | 66.91 abc | 73.21 bdc | 81.35 ab | 14.44 ab,A | 4.21 ab,A | 45.39 ab,A | |||
| 90 | 0 | 2179 abc | 2622 abc | 66.73 abc | 73.3 abcd | 81.19 ab | 14.46 ab,A | 3.74 ab,A | 51.49 ab,A | ||
| 5 | 1903 abc | 2418 abc | 66.81 abc | 73.72 ab | 81.08 ab | 14.27 ab,A | 3.02 ab,A | 60.76 ab,A | |||
| 10 | 1699 c | 2190 c | 67.12 ab | 73.87 ab | 81.26 ab | 14.15 ab,A | 2.78 b | 63.94 a | |||
| 130 | 85 | 0 | 1882 abc | 2330 abc | 66.67 bcd | 73.04 bcd | 80.4 abc,A | 13.73 ab,A | 3.69 ab,A | 52.14 ab,A | |
| 5 | 1961 abc | 2416 abc | 66.17 cd | 73.22 bcd | 81.15 ab | 14.98 a,A | 3.28 ab,A | 57.39 ab,A | |||
| 10 | 1774 bc | 2254 abc | 66.65 bcd | 73.22 bcd | 79.01 c,A | 12.36 b,A | 3.17 ab,A | 58.88 ab,A | |||
| 90 | 0 | 1861 abc | 2381 abc | 67.36 ab | 73.81 ab | 80.88 abc | 13.53 ab,A | 3.48 ab,A | 54.86 ab,A | ||
| 5 | 1748 bc | 2274 abc | 66.72 abcd | 73.46 abc | 80.91 a | 14.19 ab,A | 3.02 ab,A | 60.76 ab,A | |||
| 10 | 1730 bc | 2217 bc | 67.56 a | 74.21 a | 82.3 a | 14.74 a,A | 4.38 ab,A | 43.19 ab,A | |||
| Traditional | Nixtamal instant flour (control) | 4887 A | 4281 A | 65.16 A | 70.98 A | 79.08 A | 13.91 A | 4.26 A | 44.70 A | ||
| Standard Error of the Mean | 104 | 110 | 0.159 | 0.186 | 0.387 | 0.422 | 0.325 | 4.22 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dominguez-Hernandez, E.; Rangel-Hernandez, J.; Morales-Sanchez, E.; Gaytan-Martinez, M. Ohmic Heating Nixtamalization Modifies Maize Starch and Affects the Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Instant Masa Flours. Macromol 2025, 5, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5010001
Dominguez-Hernandez E, Rangel-Hernandez J, Morales-Sanchez E, Gaytan-Martinez M. Ohmic Heating Nixtamalization Modifies Maize Starch and Affects the Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Instant Masa Flours. Macromol. 2025; 5(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleDominguez-Hernandez, Elisa, Jorge Rangel-Hernandez, Eduardo Morales-Sanchez, and Marcela Gaytan-Martinez. 2025. "Ohmic Heating Nixtamalization Modifies Maize Starch and Affects the Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Instant Masa Flours" Macromol 5, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5010001
APA StyleDominguez-Hernandez, E., Rangel-Hernandez, J., Morales-Sanchez, E., & Gaytan-Martinez, M. (2025). Ohmic Heating Nixtamalization Modifies Maize Starch and Affects the Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Instant Masa Flours. Macromol, 5(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5010001






