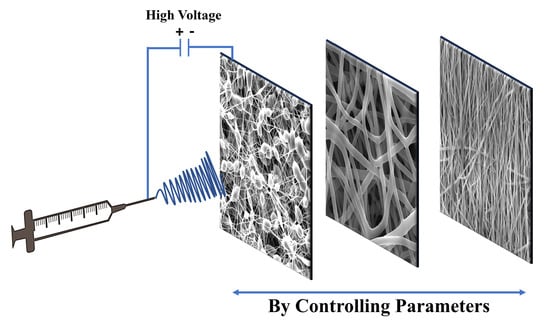
Electrospinning: Processes, Structures, and Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
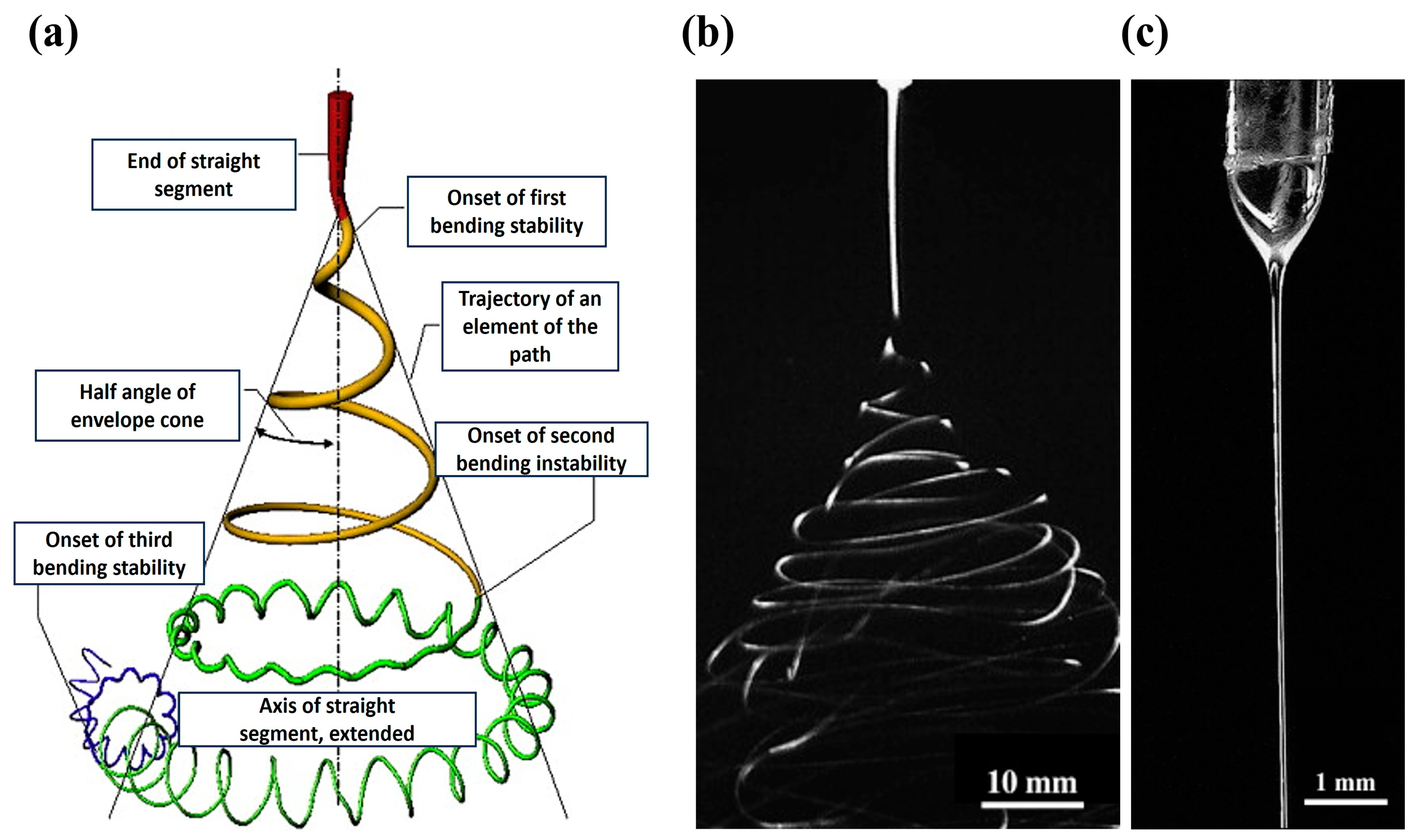
2. Principles of Solution Electrospinning
3. Parameters Related to Solution Electrospinning
- Solution parameters: polymer molecular weight (Mw), polymer concentration (C), solution conductivity (k), solution surface tension (γ), and type of solvent.
- Process parameters: flow rate (Q), applied voltage (V), distance between the needle and collector (d), needle diameter (D), and type of collector (fixed or mobile).
- Ambient parameters: temperature, relative humidity, and air velocity.
- The main effects of these parameters on the fiber morphology are discussed in Table 1, while a comprehensive explanation of each parameter is provided in the following section.
3.1. Solution Parameters
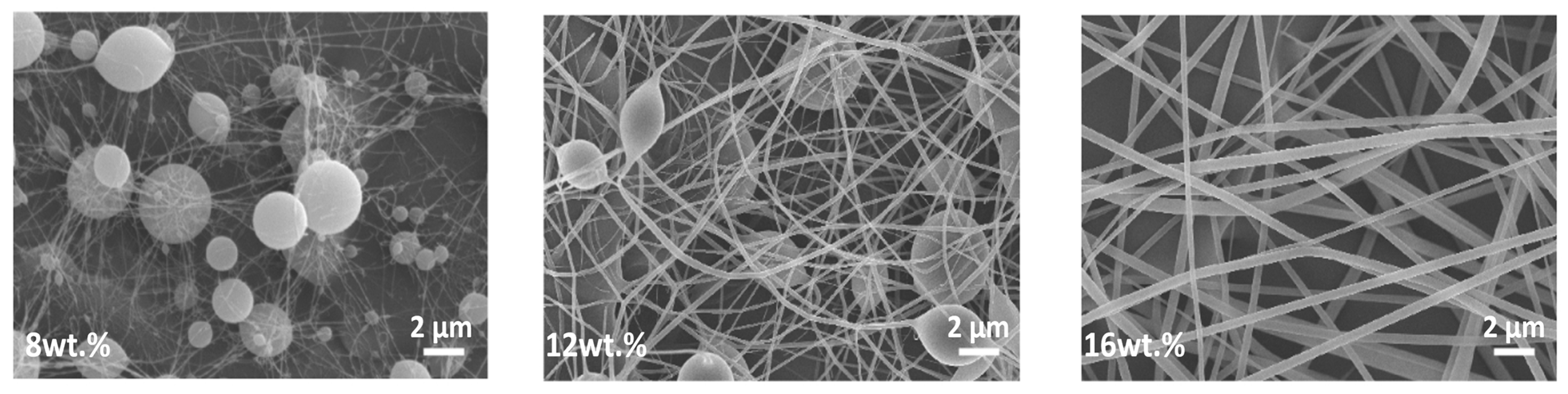
3.1.1. Concentration, Viscosity, and Molecular Weight
3.1.2. Surface Tension
3.1.3. Conductivity
3.1.4. Type of Solvent
3.2. Process Parameters
3.2.1. Voltage
3.2.2. Distance between the Needle and Collector
3.2.3. Flow Rate
3.2.4. Collector
3.3. Ambient Conditions
4. Structures/Morphologies
4.1. Aligned Structure
4.2. Core–Shell Structures
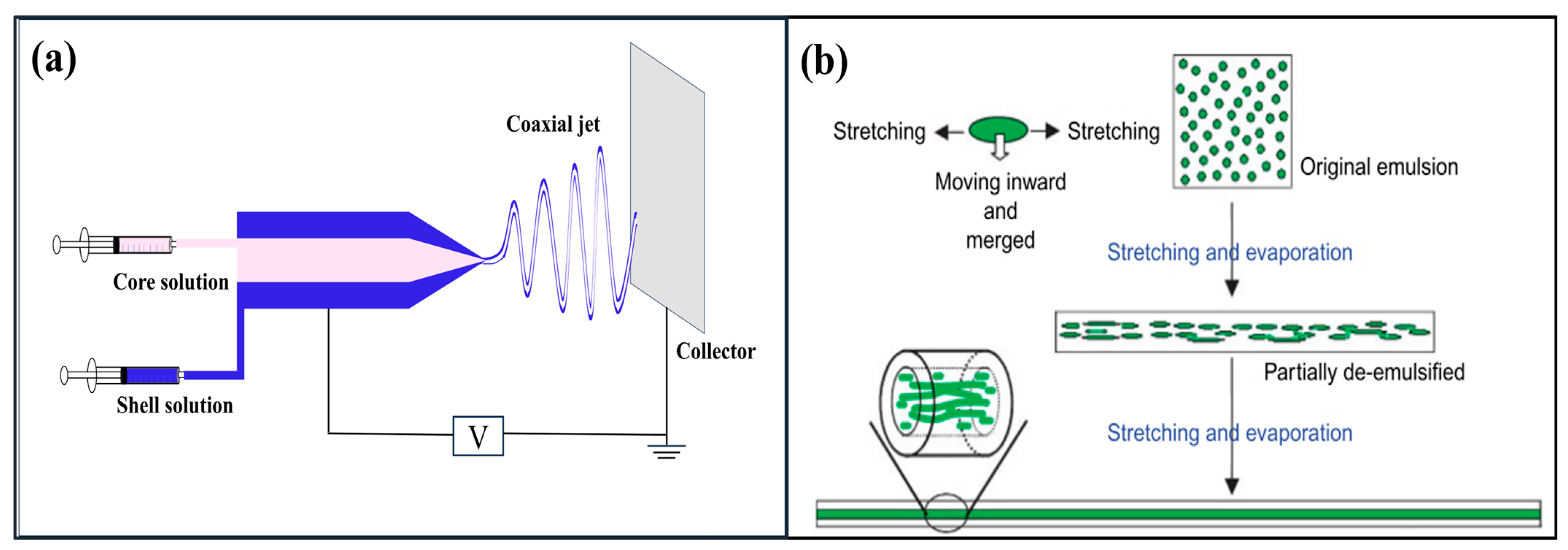
4.3. Hollow Fibers
4.4. Porous Structure
- (i)
- Breath figure: This mechanism is based on condensing water vapor on a cold surface during electrospinning [135]. As the solvent evaporates, it cools the fiber’s surface, leading to the condensation of water vapor. Then, the condensed water droplets create pores on the fiber’s surface and these pores become more pronounced as the water droplets evaporate. This mechanism requires high relative humidity and a significant temperature decrease. This is why volatile solvents (DCM, CF and THF) are used. Furthermore, this method is mainly used for hydrophobic polymers such as PS, PMMA, and PLA [135]. Huang and Thomas [136] produced porous PLA electrospun fibers using a chloroform (CF) solution. Circular pores were visible only on the fiber’s surface and not inside. They tested different solvents including acetone (ACe) and CF and found that CF, a water-immiscible solvent, created porous fibers, while ACe, a water-miscible solvent, resulted in smooth fibers. Water-immiscibility significantly affected the fiber morphology.
- (ii)
- Vapor-induced phase separation (VIPS): This process runs when a nonvolatile solvent slowly evaporates during electrospinning, allowing time for water vapor to diffuse into the charged jet [135]. The water vapor causes a liquid–liquid phase separation within the jet, resulting in an internal porous structure. VIPS is typically used for hydrophobic polymers dissolved in water-miscible solvents at high relative humidity. The low volatility of the solvent and environmental humidity are critical factors influencing the fiber’s structure [135]. Zheng et al. [137] fabricated electrospun porous PS fibers from a 25% PS/DMF solution at 60% relative humidity. They observed that the solvent properties and humidity levels were critical factors in shaping the fibers. The low volatility of DMF allowed water molecules to penetrate the polymer/solvent jet, leading to the formation of a porous structure through separation of the polymer-rich and polymer-lean phases.
- (iii)
- Non-solvent-induced phase separation (NIPS): This method creates porous fibers by combining a non-solvent with a polymer solution [138]. It is crucial to select a non-solvent with lower volatility than the solvent. The mixture forms a polymer-rich phase with most of the polymer and some solvent, as well as a polymer-lean phase with a blend of the remaining solvent, non-solvent, and a small portion of polymer. The polymer-lean phase evaporates during electrospinning, forming a porous structure, mostly on the surface [138]. Unlike the challenges of the breath figure method, NIPS offers better control, resulting in more uniform porous fibers and overcoming the issues of variable fiber diameter caused by low solvent dielectric constants [136]. Huang and Thomas [136] examined the changes in fiber morphology when varying the concentration of ethanol (EtOH) in PLA/CF. Using different EtOH content (5%, 10%, 20% and 30% v/v), they observed that 5% v/v EtOH produced elliptical pores on the surface. Increasing the EtOH content led to a transition from surface pores to a scalloped surface (shallow surface pores connected by ridges), eventually resulting in a smooth surface with some wrinkles. This progression was as follows: porous surface → scalloped surface → smooth fibers with minor wrinkles. Notably, all these fibers had a non-porous interior. They attributed these findings to the NIPS mechanism. The transition from scalloped to smooth surfaces was due to water droplets expanding on the fibers’ surface in a humid environment with high water–EtOH-miscibility.
- (iv)
- Thermally induced phase separation (TIPS): This method takes place when the electrospun jet faces a substantial temperature decrease during its travel to the collector [135]. The driving force to produce the porous structure is the temperature difference. Ye et al. [139] achieved a highly porous structure by integrating a high-temperature electrospinning process into a thermally induced phase separation. They increased the spinning solution temperature to 200 °C and the hot jet was quickly cooled as it reached the collector, leading to a thermally induced phase separation. This method produced porous fibers with over a 100-fold increase in specific surface area, which is a precise way of forming pores.
5. Electrospun Nanofibers Materials
5.1. Polymeric Nanofibers
5.1.1. Natural Polymers
Polysaccharide-Based Polymers
- Chitosan
- Alginate
- Cellulose
Protein-Based Polymers
- Collagen
- Gelatin
5.1.2. Synthetic Biodegradable Polymers
Polycaprolactone (PCL)
Polylactic acid (PLA)
Poly(butylene succinate) (PBS)
5.2. Carbon Nanofiber
5.3. Non-Polymeric Nanofibers
6. Fillers
6.1. Metal/Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
6.2. Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
6.3. Graphene and Graphene-Based Nanoparticles
7. Upscaling Electrospun Fibers’ Production
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAES | Alkyl ammonium ethyl sulfate |
| ACe | Acetone |
| al | Alcohol |
| AuNCs | Au nanocages |
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| BD | 1,4-butanediol |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| C | Concentration of the solution |
| CA | Cellulose acetate |
| CAB | Cellulose acetate butyrate |
| CF | Chloroform |
| CS | Chitosan |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| d | Distance between the needle and collector |
| D | Needle diameter |
| DMAc | Dimethylacetamide |
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DOX | Doxorubicin |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EMI | Electromagnetic interference |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| FA | Formic acid |
| GNPs | Graphene nanoplates |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| HAc | Acetic acid |
| HFIP | Hexafluoroisopropanol |
| IL | Ionic liquids |
| k | Conductivity of the solution |
| LIB | Lithium-ion batteries |
| MC | Methylene chloride |
| MNPs | Magnetic nanoparticles |
| MOF | Metal organic framework |
| Mw | Molecular weight |
| MWCNTs | Multiwalled carbon nanotubes |
| nHA | Nano-hydroxyapatite |
| NIPS | Non-solvent-induced phase separation |
| O/W | Oil-in-water |
| PA | Polyamide |
| PA6 | Nylon 6 |
| PAA | Poly(acrylic acid) |
| PAN | Poly(acrylonitrile) |
| PANI | Polyaniline |
| PBS | Polybutylene succinate |
| PBT | Polybutylene terephthalate |
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| PCL | Poly(ε-caprolactone)/Polycaprolactone |
| PCU | Poly(carbonate urethane) |
| PDLA | Poly(D,L-lactide)/poly D-lactic acid |
| PDLLA | Poly-D,L-lactic acid |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| PDT | Poly(dodecyl thiophene) |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| PEI | Polyethylenimine |
| PEN | Poly(ethylene naphthalate) |
| PEO | Poly(ethylene oxide) |
| PEOT | Poly(ethylene oxide terephthalate) |
| PEUU | Poly(ester urethane)urea |
| PGA | Polyglycolide |
| PHBV | Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) |
| PI | Polyimides |
| PLA | Poly(lactic acid)/polylactide |
| PLGA | Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) |
| PLLA | Poly(L-lactide)/poly-L-lactic acid |
| PLMC | Poly(D,L-lactide-co-trimethylene carbonate) |
| PMMA | Poly(methyl methacrylate) |
| PPS | Polyphenylsilane |
| PPy | Polypyrrole |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| PTT | Poly(trimethylene terephthalate) |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| PVA | Poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| PVDF | Poly(vinylidene fluoride) |
| PVDF-HFP | Poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) |
| PVP | Polyvinyl pyrrolidone |
| Q | Flow rate |
| rGO | Reduced graphene oxide |
| RhB | Rhodamine B |
| SA | Succinic acid |
| SAN | Poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SF | Silk |
| Si-NPs | Silica nanoparticles |
| SWCNTs | Single-walled carbon nanotubes |
| TEAB | Tetraethylammonium bromide |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| TFE | Trifluoroethanol |
| Tg | Glass transition temperature |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
| TIPS | Thermally induced phase separation |
| V | Applied voltage |
| VIPS | Vapor-induced phase separation |
| W/O | Water-in-oil |
| γ | Surface tension |
| η | Viscosity |
References
- Kenry; Lim, C.T. Nanofiber Technology: Current Status and Emerging Developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K. Electrospinning of Patterned and 3D Nanofibers. In Electrospun Nanofibers; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 399–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.J.; Stoyanov, S.D.; Stride, E.; Pelan, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Electrospinning versus Fibre Production Methods: From Specifics to Technological Convergence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4708–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Tekmen, C.; Pisignano, D. Industrial Upscaling of Electrospinning and Applications of Polymer Nanofibers: A Review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre Diameter Fibres of Polymer, Produced by Electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L.; Fong, H.; Koombhongse, S. Bending Instability of Electrically Charged Liquid Jets of Polymer Solutions in Electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4531–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zeng, L.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J. Fabrication of electrospun polymer nanofibers with diverse morphologies. Molecules 2019, 24, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltz, K.P.; Kalaf, E.A.G.; Chen, C.; Martin, R.S.; Sell, S.A. A review of electrospinning manipulation techniques to direct fiber deposition and maximize pore size. Electrospinning 2017, 1, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.S.M.; Kumar, K.S.; Rajini, N.; Siengchin, S.; Ayrilmis, N.; Rajulu, A.V. A comprehensive review of electrospun nanofibers: Food and packaging perspective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Xiao, C.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Electrospun polymer biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 90, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, W.; Ding, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Duan, G. A review of smart electrospun fibers toward textiles. Compos. Commun. 2020, 22, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Wong, S.C.; Abtahi, M.; Chen, P. Electrospinning of Polymer Nanofibers: Effects on Oriented Morphology, Structures and Tensile Properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, T.; Bhat, G.S.; Tock, R.W.; Parameswaran, S.; Ramkumar, S.S. Electrospinning of Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonakdar, M.A.; Hamdi, O.; Nazarenko, Y.; Ariya, P.A.; Rodrigue, D. Highly porous biobased membranes via electrospinning of PBS and CTAB. Polymer 2023, 280, 126045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.R.; Ahn, K.H.; Davis, F.J. The Potential of Electrospinning in Rapid Manufacturing Processes: The Fundamentals of Electrospinning, Key Process Parameters, Materials and Potential Application in Rapid Manufacturing Are Presented in This Paper. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2011, 6, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, K.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning Jets and Nanofibrous Structures. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 013403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballengee, J.; Pintauro, P. Morphological Control of Electrospun Nafion Nanofiber Mats. ECS Trans. 2010, 33, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.; Harris, D.; Beck Tan, N.C. The Effect of Processing Variables on the Morphology of Electrospun. Polymer 2001, 42, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, K.; Yu, D.G. From Taylor Cone to Solid Nanofiber in Tri-Axial Electrospinning: Size Relationships. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Kataphinan, W.; Theron, A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Nanofiber Garlands of Polycaprolactone by Electrospinning. Polymer 2002, 43, 6785–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgeson, M.E.; Grammatikos, K.N.; Deitzel, J.M.; Wagner, N.J. Theory and Kinematic Measurements of the Mechanics of Stable Electrospun Polymer Jets. Polymer 2008, 49, 2924–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Meng, N.; Xin, B. Effects of Jet Path on Electrospun Polystyrene Fibers. Polymers 2018, 10, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, W.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Experimental Study on Relationship between Jet Instability and Formation of Beaded Fibers during Electrospinning. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatov, Y.; Budyka, A.; Kirichenko, V. Electrospinning of Micro-and Nanofibers: Fundamentals in Separation and Filtration Processes; Begell House, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning Jets and Polymer Nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Buckling of Jets in Electrospinning. Polymer 2007, 48, 6064–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, L.A.; Downes, S. Acetone, a Sustainable Solvent for Electrospinning Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Fibres: Effect of Varying Parameters and Solution Concentrations on Fibre Diameter. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.Y.; Ren, J. Process optimization and empirical modeling for electrospun poly(D,L-lactide) fibers using response surface methodology. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2005, 290, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhu, L.; Jin, X. Controlling the surface structure, mechanical properties, crystallinity, and piezoelectric properties of electrospun PVDF nanofibers by maneuvering molecular weight. Soft Mater. 2019, 17, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L.; Han, Y.; Sheng, J. Study on morphology of electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) mats. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwiiri, F.K.; Daniels, R. Influence of PVA molecular weight and concentration on electrospinnability of birch bark extract-loaded nanofibrous scaffolds intended for enhanced wound healing. Molecules 2020, 25, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Shivkumar, S. Bead-to-fiber transition in electrospun polystyrene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A Fascinating Fiber Fabrication Technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korotcenkov, G. Electrospun metal oxide nanofibers and their conductometric gas sensor application. Part 1: Nanofibers and features of their forming. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q. Effect of salt concentration in spinning solution on fiber diameter and mechanical property of electrospun styrene-butadiene-styrene tri-block copolymer membrane. Polymer 2018, 153, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Z.; Hou, H.; Schaper, A.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Poly-L-lactide nanofibers by electrospinning—Influence of solution viscosity and electrical conductivity on fiber diameter and fiber morphology. E-Polymers 2003, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.; Stylios, G. Effect of Experimental Parameters on the Morphology of Electrospun Nylon 6 Fibres. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Megelski, S.; Stephens, J.S.; Bruce Chase, D.; Rabolt, J.F. Micro- and Nanostructured Surface Morphology on Electrospun Polymer Fibers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8456–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmati, A.H.; Rashidi, A.; Ghazisaeidi, R.; Drean, J.Y. Effect of Needle Length, Electrospinning Distance, and Solution Concentration on Morphological Properties of Polyamide-6 Electrospun Nanowebs. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1452–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargham, S.; Bazgir, S.; Tavakoli, A.; Rashidi, A.S.; Damerchely, R. The Effect of Flow Rate on Morphology and Deposition Area of Electrospun Nylon 6 Nanofiber. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 155892501200700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vrieze, S.; Van Camp, T.; Nelvig, A.; Hagström, B.; Westbroek, P.; De Clerck, K. The Effect of Temperature and Humidity on Electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Stachewicz, U. The impact of relative humidity on electrospun polymer fibers: From structural changes to fiber morphology. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 286, 102315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Içoǧlu, H.I.; Oǧulata, R.T. Effect of ambient parameters on morphology of electrospun polyetherimide (PEI) fibers. Tekst. ve Konfeksiyon. 2013, 23, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Elkins, C.; Long, T.E.; Wilkes, G.L. Electrospinning of Linear Homopolymers of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate): Exploring Relationships between Fiber Formation, Viscosity, Molecular Weight and Concentration in a Good Solvent. Polymer 2005, 46, 4799–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ang, B.C.; Andriyana, A.; Afifi, A.M. A Review on Fabrication of Nanofibers via Electrospinning and Their Applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.J.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Electrospinning Process and Structure Relationship of Biobased Poly(butylene succinate) for Nanoporous Fibers. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5547–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajavi, R.; Abbasipour, M. Controlling Nanofiber Morphology by the Electrospinning Process. In Electrospun Nanofibers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Higashi, S.; Hirai, T.; Matsubara, M.; Yoshida, H.; Beniya, A. Dynamic Viscosity Recovery of Electrospinning Solution for Stabilizing Elongated Ultrafine Polymer Nanofiber by TEMPO-CNF. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, V.; Anandjiwala, R.D.; Maaza, M. The Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Structural Morphology and Diameter of Electrospun Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, M.; Wilkes, G.; Colby, R.; Long, T. Correlations of Solution Rheology with Electrospun Fiber Formation of Linear and Branched Polyesters. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amariei, N.; Manea, L.R.; Bertea, A.P.; Bertea, A.; Popa, A. The Influence of Polymer Solution on the Properties of Electrospun 3D Nanostructures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 209, 012096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi, A.K.; Akbari, M. Trends in Electrospinning of Natural Nanofibers. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 2007, 204, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, C.E.; Wei, Y. Influence of Solvents on the Formation of Ultrathin Uniform Poly(Vinyl Pyrrolidone) Nanofibers with Electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 3721–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castkova, K.; Kastyl, J.; Sobola, D.; Petrus, J.; Stastna, E. Structure—Properties Relationship of Electrospun PVDF Fibers. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Kang, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Effects of Surfactants on the Formation of Gelatin Nanofibres for Controlled Release of Curcumin. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanger, J.; Tucker, N.; Kirwan, K.; Staiger, M.P. Effect of Charge Density on the Taylor Cone in Electrospinning. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2009, 23, 1956–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klairutsamee, W.; Supaphol, P.; Jangchud, I. Electrospinnability of Poly(Butylene Succinate): Effects of Solvents and Organic Salt on the Fiber Size and Morphology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Abdulhamid, M.A.; Holtzl, T.; Szekely, G. Nanofiber Engineering of Microporous Polyimides through Electrospinning: Influence of Electrospinning Parameters and Salt Addition. Mater. Des. 2021, 198, 109280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartetamrongsutt, K.; Chase, G.G. The Influence of Salt and Solvent Concentrations on Electrospun Polyvinylpyrrolidone Fiber Diameters and Bead Formation. Polymer 2013, 54, 2166–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mit-Uppatham, C.; Nithitanakul, M.; Supaphol, P. Ultrafine Electrospun Polyamide-6 Fibers: Effect of Solution Conditions on Morphology and Average Fiber Diameter. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2004, 205, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Kim, K.; Fang, D.; Ran, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and Process Relationship of Electrospun Bioabsorbable Nanofiber Membranes. Polymer 2002, 43, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.Y.; Zhuang, M.F.; Yu, Z.J.; Zheng, G.F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, D.H. The Effect of Surfactants on the Diameter and Morphology of Electrospun Ultrafine Nanofiber. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, P.; Harlin, A. Electrospinning of Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Solution: Effect of Conductive Additive and Filler on the Process. Express Polym. Lett. 2009, 3, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, H.; Li, G.; Cho, H.; Jiang, M.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X. Developments of Advanced Electrospinning Techniques: A Critical Review. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarusuwannapoom, T.; Hongrojjanawiwat, W.; Jitjaicham, S.; Wannatong, L.; Nithitanakul, M.; Pattamaprom, C.; Koombhongse, P.; Rangkupan, R.; Supaphol, P. Effect of solvents on electro-spinnability of polystyrene solutions and morphological appearance of resulting electrospun polystyrene fibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Shi, Z.; Fan, L.; Liang, Y.; Kang, W.; Cheng, B. Preparation of Elastomeric Tree-like Nanofiber Membranes Using Thermoplastic Polyurethane by One-Step Electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2017, 205, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Moghadam, B.H.; Abatari, M.H.M.; Haghi, A.K. On the Production Optimization of Polyacrylonitrile Electrospun Nanofiber. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2013, 45, 178–190. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.; Stylios, G.K. Analysis of the Effect of Experimental Parameters on the Morphology of Electrospun Polyethylene Oxide Nanofibres and on Their Thermal Properties. J. Text. Inst. 2012, 103, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, S.S.S.; Fong, K.C.; Eleyas, A.; Nazeri, M.F.M. Effect of Voltage and Flow Rate Electrospinning Parameters on Polyacrylonitrile Electrospun Fibers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 318, 012076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Fan, J.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.-Y. Effect of Applied Voltage on Diameter and Morphology of Ultrafine Fibers in Bubble Electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ju, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Ke, H.; He, J. Electrospun Jets Number and Nanofiber Morphology Effected by Voltage Value: Numerical Simulation and Experimental Verification. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmatulu, R.; Khan, W.S. Historical Background of the Electrospinning Process. In Synthesis and Applications of Electrospun Nanofibers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 17–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mazoochi, T.; Hamadanian, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Jabbari, V. Investigation on the Morphological Characteristics of Nanofiberous Membrane as Electrospun in the Different Processing Parameters. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Choi, K.H.; Ghim, H.D.; Kim, S.S.; Chun, D.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Lyoo, W.S. Role of Molecular Weight of Atactic Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) (PVA) in the Structure and Properties of PVA Nanofabric Prepared by Electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, X.X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M. Electrospinning; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 21–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.-Y.; Liu, H.-Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.-W.; Zheng, G.-F.; Sun, D.-H. Electrohydrodynamic Direct-Write Orderly Micro/Nanofibrous Structure on Flexible Insulating Substrate. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 708186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomavičiute, E.; Stanys, S. Formation of Electrospun PVA Mats on Different Types of Support Materials Using Various Kinds of Grounded Electrodes. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2011, 87, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.Z.; Li, H.P.; Yang, J.H.; Wan, J.; Yu, D.G. Influence of Working Temperature on The Formation of Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Janković, B.; Baumgartner, S.; Kocbek, P. The Impact of Relative Humidity during Electrospinning on the Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezarati, R.M.; Eifert, M.B.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Effects of Humidity and Solution Viscosity on Electrospun Fiber Morphology. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 19, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, G.; Hong, J.P.; Rhee, J.M.; Leo, D.J.; Nah, C. Preparation and Anisotropic Mechanical Behavior of Highly-Oriented Electrospun Poly(Butylene Terephthalate) Fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Compound Core-Shell Polymer Nanofibers by Co-Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1929–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Direct Fabrication of Composite and Ceramic Hollow Nanofibers by Electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezabeigi, E.; Wood-Adams, P.M.; Demarquette, N.R. Complex Morphology Formation in Electrospinning of Binary and Ternary Poly(Lactic Acid) Solutions. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 4094–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cao, X.; Jiang, L. Bio-mimic multichannel microtubes by a facile method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 764–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, N.; Di, J.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Nanowire-in-Microtube Structured Core/Shell Fibers via Multifluidic Coaxial Electrospinning. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11291–11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koombhongse, S.; Liu, W.; Reneker, D.H. Flat Polymer Ribbons and Other Shapes by Electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 2598–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, D.; Kang, D.; Jiang, X. Fabrication of necklace-like structures via electrospinning. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z. “Firecracker-Shaped” ZnO/Polyimide Hybrid Nanofibers via Electrospinning and Hydrothermal Process. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4427–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Shen, H.; Yuan, G.; Lin, K.; Su, J. The Effects of Alignment and Diameter of Electrospun Fibers on the Cellular Behaviors and Osteogenesis of BMSCs. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, M.; Khorrami, M.; Yi, N.; Majd, S.; Abidian, M.R. Electrospinning of Highly Aligned Fibers for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Puyana, V.; Wieringa, P.; Yuste, Y.; de la Portilla, F.; Guererro, A.; Romero, A.; Moroni, L. Fabrication of Hybrid Scaffolds Obtained from Combinations of PCL with Gelatin or Collagen via Electrospinning for Skeletal Muscle Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021, 109, 1600–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, B.S.; Colello, R.J.; Bowman, J.R.; Sell, S.A.; Lee, K.D.; Bigbee, J.W.; Bowlin, G.L.; Chow, W.N.; Mathern, B.E.; Simpson, D.G. Two Pole Air Gap Electrospinning: Fabrication of Highly Aligned, Three-Dimensional Scaffolds for Nerve Reconstruction. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.; Chou, M.H.; Zeng, W.Y. Piezoelectric Response of Aligned Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Carbon Nanotube Nanofibrous Membranes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, C.M.; Amoroso, N.J.; Amini, R.; Ungchusri, E.; Hong, Y.; D’Amore, A.; Sacks, M.S.; Wagner, W.R. Fabrication of Elastomeric Scaffolds with Curvilinear Fibrous Structures for Heart Valve Leaflet Engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 3101–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, X.; Lipner, J.; Manning, C.N.; Schwartz, A.G.; Thomopoulos, S.; Xia, Y. “Aligned-to-Random” Nanofiber Scaffolds for Mimicking the Structure of the Tendon-to-Bone Insertion Site. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindell, R.K.; Busselle, L.P.; Holloway, J.L. Magnetic Fields Enable Precise Spatial Control over Electrospun Fiber Alignment for Fabricating Complex Gradient Materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2023, 111, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Tian, F.; Shang, Y.; Wang, F.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z. Co-axial electrospun polystyrene/polyurethane fibres for oil collection from water surface. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2745–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Xue, J.; Geng, H.; Gu, H.; Chen, D.; Shi, R.; Zhang, L. Fibrous guided tissue regeneration membrane loaded with anti-inflammatory agent prepared by coaxial electrospinning for the purpose of controlled release. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 335, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Ai, H.; Lv, L.; Guo, Y.; Han, T.; Dong, L. Novel smart coaxial electrospinning textiles for efficient thermal interface management and electromagnetic compatibility in electronics. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 144854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaui, R.; Zussman, E.; Khalfin, R.; Semiat, R.; Cohen, Y. Polymeric microtubes for water filtration by co-axial electrospinning technique. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2017, 28, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.L.; Hubbard, P.L.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Parker, G.J.M. Coaxially electrospun axon-mimicking fibers for diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6311–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Electrospun porous structure fibrous film with high oil adsorption capacity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, L.; Licht, R.; de Boer, J.; de Wijn, J.R.; van Blitterswijk, C.A. Fiber diameter and texture of electrospun PEOT/PBT scaffolds influence human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and morphology, and the release of incorporated compounds. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4911–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A.J.; Pérez-Nava, A.; Ali, S.C.; González-Campos, J.B.; Holloway, J.L.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E.M. Comparative Analysis of Fiber Alignment Methods in Electrospinning. Matter 2021, 4, 821–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beachley, V.; Katsanevakis, E.; Zhang, N.; Wen, X. Highly aligned polymer nanofiber structures: Fabrication and applications in tissue engineering. In Biomedical Applications of Polymeric Nanofibers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 246, pp. 171–212. [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa, N.; Kimura, S.; Hotta, A. Mechanical Properties of Poly(Butylene Succinate) Composites with Aligned Cellulose-Acetate Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro De Prá, M.A.; Ribeiro-do-Valle, R.M.; Maraschin, M.; Veleirinho, B. Effect of Collector Design on the Morphological Properties of Polycaprolactone Electrospun Fibers. Mater. Lett. 2017, 193, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y. Improving Fiber Alignment during Electrospinning. In Electrospun Nanofibers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 125–147. [Google Scholar]
- Courtney, T.; Sacks, M.S.; Stankus, J.; Guan, J.; Wagner, W.R. Design and Analysis of Tissue Engineering Scaffolds That Mimic Soft Tissue Mechanical Anisotropy. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3631–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Y.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Aligned Biodegradable Nanofibrous Structure: A Potential Scaffold for Blood Vessel Engineering. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning Nanofibers as Uniaxially Aligned Arrays and Layer-by-Layer Stacked Films. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dzenis, Y.A. Analysis of the Effects of the Residual Charge and Gap Size on Electrospun Nanofiber Alignment in a Gap Method. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 355307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, P.; Alessandro, M.; Ramsier, R.D.; Chase, G.G. Continuous Electrospinning of Aligned Polymer Nanofibers onto a Wire Drum Collector. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Lu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, X. Fabrication of Aligned Fibrous Arrays by Magnetic Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3702–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, L. Preparation and Formation Mechanism of Highly Aligned Electrospun Nanofibers Using a Modified Parallel Electrode Method. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arras, M.M.L.; Grasl, C.; Bergmeister, H.; Schima, H. Electrospinning of Aligned Fibers with Adjustable Orientation Using Auxiliary Electrodes. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2012, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, B.S.; Yu, W.R. Recent Progress in Coaxial Electrospinning: New Parameters, Various Structures, and Wide Applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, B.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J. Drug Delivery Applications of Core-Sheath Nanofibers Prepared by Coaxial Electrospinning: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghe, A.K.; Gupta, B.S. Co-Axial Electrospinning for Nanofiber Structures: Preparation and Applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Chung, O.H.; Park, J.S. Coaxial Electrospun Poly(Lactic Acid)/Chitosan (Core/Shell) Composite Nanofibers and Their Antibacterial Activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaerkitcha, N.; Chuangchote, S.; Hachiya, K.; Sagawa, T. Influence of the Viscosity Ratio of Polyacrylonitrile/Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Solutions on Core–Shell Fibers Prepared by Coaxial Electrospinning. Polym. J. 2017, 49, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Guo, X.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wei, Z. Biodegradable Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) Nanofibrous Membrane with Core-Shell Structure and High Density for Improved Mechanical Properties. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, W.; Jiang, H.; Zimba, B.L.; Chen, L.; Wan, J.; Wu, Q. Preparation of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Graphene Oxide Nanofiber Membranes with Different Structures by Electrospinning for Drug Delivery. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16619–16625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, J.; Yu, G.; Cardenas, R.; Wei, S.; Wujcik, E.K.; Guo, Z. Coaxial Electrospun Fibers: Applications in Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2016, 8, 654–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atila, D.; Hasirci, V.; Tezcaner, A. Coaxial Electrospinning of Composite Mats Comprised of Core/Shell Poly(Methyl Methacrylate)/Silk Fibroin Fibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 128, 105105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupančič, Š. Core-Shell Nanofibers as Drug Delivery Systems. Acta Pharm. 2019, 69, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Jing, X. Preparation of Core-Sheath Composite Nanofibers by Emulsion Electrospinning. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. Electrospinning of Polycaprolactone/Chitosan Core-Shell Nanofibers by a Stable Emulsion System. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 583, 123956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Song, J.C.; Yoon, K.B. Controlled Wall Thickness and Porosity of Polymeric Hollow Nanofibers by Coaxial Electrospinning. Macromol. Res. 2010, 18, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-S.; Park, K.-M.; Yu, W.-R.; Youk, J.H. An Effective Method for Manufacturing Hollow Carbon Nanofibers and Microstructural Analysis. Macromol. Res. 2012, 20, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, R.; Abbasipour, M. Electrospinning as a Versatile Method for Fabricating Coreshell, Hollow and Porous Nanofibers. Sci. Iran. 2012, 19, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Thomas, N.L. Fabrication of Porous Fibers via Electrospinning: Strategies and Applications. Polym. Rev. 2020, 60, 595–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Thomas, N.L. Fabricating Porous Poly(Lactic Acid) Fibres via Electrospinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Han, C.C. Construction of Hierarchical Structures by Electrospinning or Electrospraying. Polymer 2012, 53, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezabeigi, E.; Sta, M.; Swain, M.; McDonald, J.; Demarquette, N.R.; Drew, R.A.L.; Wood-Adams, P.M. Electrospinning of Porous Polylactic Acid Fibers during Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.-Y.; Lin, F.-W.; Huang, X.-J.; Liang, H.-Q.; Xu, Z.-K. Polymer Fibers with Hierarchically Porous Structure: Combination of High Temperature Electrospinning and Thermally Induced Phase Separation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 13851–13858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhahebi, A.M.; Ling, J.; Krishnan, S.G.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Elumalai, N.K.; Saheed, M.S.M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Jose, R. Electrospinning Research and Products: The Road and the Way Forward. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 011319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.J.; Stride, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Mapping the Influence of Solubility and Dielectric Constant on Electrospinning Polycaprolactone Solutions. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4669–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.J.; Nangrejo, M.; Edirisinghe, M. A Novel Method of Selecting Solvents for Polymer Electrospinning. Polymer 2010, 51, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Singh, H.; Mishra, N.C. Natural Polymer Based Electrospun Systems for Wound Management. In Natural Polymers in Wound Healing and Repair; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 167–186. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan, L. An Overview on Electrospinning and Its Advancement toward Hard and Soft Tissue Engineering Applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2022, 300, 875–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Lu, T.; Cui, J.; Samal, S.K.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Bio-Based Electrospun Nanofiber as Building Blocks for a Novel Eco-Friendly Air Filtration Membrane: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, N.; Li, S.; Yan, F.; Kong, L. Recent Advances in Electrospinning of Nanofibers from Bio-Based Carbohydrate Polymers and Their Applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 120, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K.; Zia, K.M.; Zuber, M.; Salman, M.; Anjum, M.N. Recent Developments in Curcumin and Curcumin Based Polymeric Materials for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tian, H.; Mao, J.; Ma, F.; Zhang, M.; Chen, F.; Yang, P. Preparation and application of chitosan-based medical electrospun nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.B.; Zafar, M.S.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Shah, A.H.; Husain, S.; Rehman, I.U. Electrospinning of chitosan-based solutions for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbasizadeh, B.; Motasadizadeh, H.; Foroughi-Nia, B.; Farhadnejad, H. Tripolyphosphate-crosslinked chitosan/poly (ethylene oxide) electrospun nanofibrous mats as a floating gastro-retentive delivery system for ranitidine hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 153, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Xu, Q.; Lu, F.; Nie, J. Electrospun water-soluble carboxyethyl chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous membrane as potential wound dressing for skin regeneration. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Wang, J.P.; Sun, X.B.; Wang, X.X.; Jiang, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Li, P.; Qu, C.-H.; Long, Y.-Z.; Yu, G.-F. Ultra uniform metal−organic framework-5 loading along electrospun chitosan/polyethylene oxide membrane fibers for efficient PM2.5 removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombin, A.D.J.; Dunne, N.J.; McCarthy, H.O. Electrospinning of natural polymers for the production of nanofibres for wound healing applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 110994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taemeh, M.A.; Shiravandi, A.; Korayem, M.A.; Daemi, H. Fabrication challenges and trends in biomedical applications of alginate electrospun nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 228, 115419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhena, T.C.; Mochane, M.J.; Mtibe, A.; John, M.J.; Sadiku, E.R.; Sefadi, J.S. Electrospun alginate nanofibers toward various applications: A review. Materials 2020, 13, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daemi, H.; Mashayekhi, M.; Modaress, M.P. Facile fabrication of sulfated alginate electrospun nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Li, C.; Yu, C.; Xie, H.; Shi, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Lu, L. A novel electrospun membrane based on moxifloxacin hydrochloride/poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate for antibacterial wound dressings in practical application. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwald, J.; Junior, C.F.d.M.; Freitas, E.D.; Segundo, J.d.D.P.d.M.; Vieira, R.S.; Beppu, M.M. Cellulose-Based Electrospun Nanofibers: A Review. Cellulose 2022, 29, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Schauer, C.L. A Review: Electrospinning of Biopolymer Nanofibers and Their Applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 317–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ni, J.; Chen, J.; Xue, W.; Wang, J.; Na, H.; Zhu, J. Activation of Corn Cellulose with Alcohols to Improve Its Dissolvability in Fabricating Ultrafine Fibers via Electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaño-Leyva, B.; Rodriguez-Felix, F.; Torres-Chávez, P.; Ramirez-Wong, B.; López-Cervantes, J.; Sanchez-Machado, D. Preparation and Characterization of Durum Wheat (Triticum Durum) Straw Cellulose Nanofibers by Electrospinning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Dai, G.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. The Evolution Behavior and Dissolution Mechanism of Cellulose in Aqueous Solvent. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Hu, D.H.; Hong, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H. Effect of Co-Solvent on the Spinnability and Properties of Electrospun Cellulose Nanofiber. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, D.G.; Wang, G.; Williams, G.R.; Zhang, Z. Tunable Drug Release from Nanofibers Coated with Blank Cellulose Acetate Layers Fabricated Using Tri-Axial Electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Rangel, A.; Martin-Martinez, E.S. Collagen Based Electrospun Materials for Skin Wounds Treatment. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021, 109, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackstone, B.N.; Gallentine, S.C.; Powell, H.M. Collagen-Based Electrospun Materials for Tissue Engineering: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, G.; Hussain, T.; Chauhan, G.; Garg, T.; Goyal, A.K. Collagen Nanofiber Containing Silver Nanoparticles for Improved Wound-Healing Applications. J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Jiang, P.; Lin, T.; Li, X.; Sun, D. Characterization and Cell Response of Electrospun Rana Chensinensis Skin Collagen/Poly(L-Lactide) Scaffolds with Different Fiber Orientations. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N.; Sousa, S.R.; Van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Moroni, L.; Monteiro, F.J. A Biocomposite of Collagen Nanofibers and Nanohydroxyapatite for Bone Regeneration. Biofabrication 2014, 6, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Jobaer, M.; Mahedi, S.I.; Ali, A. Protein–based electrospun nanofibers: Electrospinning conditions, biomedical applications, prospects, and challenges. J. Text. Inst. 2023, 114, 1592–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, R.; Abbasipour, M.; Bahador, A. Electrospun Biodegradable Nanofibers Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sun, M.; Wu, S. State-of-the-art review of electrospun gelatin-based nanofiber dressings for wound healing applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Chwee, T.L.; Ramakrishna, S.; Huang, Z.M. Electrospinning of gelatin fibers and gelatin/PCL composite fibrous scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 72, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okutan, N.; Terzi, P.; Altay, F. Affecting parameters on electrospinning process and characterization of electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T. Electrospinning and mechanical characterization of gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 5361–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunarbekova, M.; Shynzhyrbai, K.; Mataev, M.; Bexeitova, K.; Kudaibergenov, K.; Sailaukhanuly, Y.; Azat, S.; Askaruly, K.; Tuleshov, Y.; Zhantikeyev, S.U.; et al. Biopolymers Synthesis and Application. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, S.; Sneha, C.; Mathew, B. Bioplastics: Its Timeline Based Scenario & Challenges. J. Polym. Biopolym. Phys. Chem. 2014, 2, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Liao, S.; Ngiam, M.; Chan, C.K.; Ramakrishna, S. Degradation Behaviors of Electrospun Resorbable Polyester Nanofibers. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2009, 15, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.G.B.; Diba, M.; Kersten, M.; Jansen, J.A.; van den Beucken, J.J.J.P.; Yang, F. Development of a PCL-Silica Nanoparticles Composite Membrane for Guided Bone Regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 85, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Pan, Z. Porous Bead-on-String Poly(Lactic Acid) Fibrous Membranes for Air Filtration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 441, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Hu, T.G.; Wang, H.; Zong, M.H.; Wu, H.; Wen, P. Electrospinning of PLA Nanofibers: Recent Advances and Its Potential Application for Food Packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8207–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimkhoei, V.; Padervand, M.; Hedayat, M.; Seidi, F.; Dawi, E.A.; Akbari, A. Biomedical Applications of Electrospun Polycaprolactone-Based Carbohydrate Polymers: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayilswamy, N.; Prakash, N.J.; Kandasubramanian, B. Design and Fabrication of Biodegradable Electrospun Nanofibers Loaded with Biocidal Agents. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2023, 72, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Coaxial Electrospinning of (Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-Conjugated Bovine Serum Albumin)-Encapsulated Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Nanofibers for Sustained Release. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.; Gonçalves, I.C.; Magalhães, F.D.; Pinto, A.M. Poly(Lactic Acid) Composites Containing Carbon-Based Nanomaterials: A Review. Polymers 2017, 9, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlotta, D. A Literature Review of Poly(Lactic Acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentano, I.; Bitinis, N.; Fortunati, E.; Mattioli, S.; Rescignano, N.; Verdejo, R.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Kenny, J.M. Multifunctional Nanostructured PLA Materials for Packaging and Tissue Engineering. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1720–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.S.; Schreck, K.M.; Hillmyer, M.A. Toughening Polylactide. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmaz, D.; Toprakci, H.A.K.; Olmez, H.; Toprakci, O. Electrospun Polylactic Acid Based Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Sci. Res. India 2018, 15, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, D.; Moyano, D.; Alvarez, F.; Grande-Tovar, C.D.; Valencia-Llano, C.H.; Peponi, L.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Zapata, P.A. Preparation and Characterization of Novel Poly (Lactic Acid)/Calcium Oxide Nanocomposites by Electrospinning as a Potential Bone Tissue Scaffold. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 153, 213578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, F.; Ahmed, S.; Liu, Y. Physico-Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties of PLA/TiO2 Composite Materials Synthesized via Electrospinning and Solution Casting Processes. Coatings 2019, 9, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigli, M.; Fabbri, M.; Lotti, N.; Gamberini, R.; Rimini, B.; Munari, A. Poly(Butylene Succinate)-Based Polyesters for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 431–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guo, B.-H. Microbial Succinic Acid, Its Polymer Poly(Butylene Succinate), and Applications. In Plastics from Bacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 347–388. [Google Scholar]
- Barletta, M.; Aversa, C.; Ayyoob, M.; Gisario, A.; Hamad, K.; Mehrpouya, M.; Vahabi, H. Poly(Butylene Succinate) (PBS): Materials, Processing, and Industrial Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2022, 132, 101579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtibe, A.; Muniyasamy, S.; Mokhena, T.C.; Ofosu, O.; Ojijo, V.; John, M. Recent Insight into the Biomedical Applications of Polybutylene Succinate and Polybutylene Succinate-Based Materials. Express Polym. Lett. 2023, 17, 2–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, G.; Soccio, M.; Posati, T.; Sotgiu, G.; Tiboni, M.; Barbalinardo, M.; Valle, F.; Casettari, L.; Zamboni, R.; Lotti, N.; et al. Regenerated Wool Keratin-Polybutylene Succinate Nanofibrous Mats for Drug Delivery and Cells Culture. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 179, 109272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliko, K.; Aldakhlalla, M.B.; Leslie, L.J.; Worthington, T.; Topham, P.D.; Theodosiou, E. Poly(Butylene Succinate) Fibrous Dressings Containing Natural Antimicrobial Agents. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 6948S–6967S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonakdar, M.A.; Chen, X.Y.; Sarbanha, A.A.; Rodrigue, D. Polybutylene Succinate Auxetic Membrane Produced by Solution Electrospinning. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2300699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiriyawirut, M.; Sarapat, K.; Sirima, S.; Prasertchol, A. Porous Electrospun Nanofiber from Biomass-Based Polyester Blends of Polylactic Acid and Polybutylene Succinate. Open J. Polym. Chem. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, N.; Paneva, D.; Mincheva, R.; Toncheva, A.; Manolova, N.; Dubois, P.; Rashkov, I. Poly(l-Lactide) and Poly(Butylene Succinate) Immiscible Blends: From Electrospinning to Biologically Active Materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 41, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Aboagye, A.; Kelkar, A.; Lai, C.; Fong, H. A Review: Carbon Nanofibers from Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile and Their Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Li, L.; Lee, J.K.Y.; Tian, L.; Srinivasan, M.; Adams, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun Carbon Nanofibers and Their Hybrid Composites as Advanced Materials for Energy Conversion and Storage. Nano Energy 2016, 22, 361–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.; Ismail, A.; Mustafa, A. A Review of Heat Treatment on Polyacrylonitrile Fiber. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.N.; Naraghi, M.; Chasiotis, I. Strong Carbon Nanofibers from Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile. Carbon 2011, 49, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Centrone, A.; Chen, L.; Simeon, F.; Hatton, T.A.; Rutledge, G.C. Highly Porous Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)-Based Carbon Fiber. Carbon. 2011, 49, 3395–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatema, U.K.; Uddin, A.J.; Uemura, K.; Gotoh, Y. Fabrication of Carbon Fibers from Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofibers. Text. Res. J. 2011, 81, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-H.; Yang, S.; Woo, H.-G. Electrochimica Acta Physical and Electrochemical Studies of Polyphenylsilane-Derived Porous Carbon Nanofibers Produced via Electrospinning. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 59, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-H.; Yang, S.; Kim, Y.A.; Kim, Y.J.; An, B.; Oshida, K. Solvent-Induced Porosity Control of Carbon Nanofiber Webs for Supercapacitor. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 10496–10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallave, M.; Bedia, J.; Ruiz-Rosas, R.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T.; Otero, J.C.; Marquez, M.; Barrero, A.; Loscertales, I.G. Filled and Hollow Carbon Nanofibers by Coaxial Electrospinning of Alcell Lignin without Binder Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4292–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, T.; Bohr, C.; Queraltó, A.; Frohnhoven, R.; Fischer, T.; Mathur, S. Inorganic Nanofibers by Electrospinning Techniques and Their Application in Energy Conversion and Storage Systems. In Semiconductors and Semimetals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 98, pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.A.M.; Kim, B.; Kim, H.Y. Production of Smooth and Pure Nickel Metal Nanofibers by the Electrospinning Technique: Nanofibers Possess Splendid Magnetic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Kong, D.; Ruan, Z.; Hsu, P.C.; Wang, S.; Yu, Z.; Carney, T.J.; Hu, L.; Fan, S.; Cui, Y. A Transparent Electrode Based on a Metal Nanotrough Network. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Fabrication of Titania Nanofibers by Electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh Kumar, P.; Syed Nizar, S.A.; Sundaramurthy, J.; Ragupathy, P.; Thavasi, V.; Mhaisalkar, S.G.; Ramakrishna, S. Tunable Hierarchical TiO2 Nanostructures by Controlled Annealing of Electrospun Fibers: Formation Mechanism, Morphology, Crystallographic Phase and Photoelectrochemical Performance Analysis. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9784–9790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, E.N.; Jose, R.; Archana, P.S.; Vijila, C.; Yusoff, M.M.; Ramakrishna, S. High Performance Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells with Record Open Circuit Voltage Using Tin Oxide Nanoflowers Developed by Electrospinning. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5401–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malwal, D.; Gopinath, P. Efficient Adsorption and Antibacterial Properties of Electrospun CuO-ZnO Composite Nanofibers for Water Remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.; Zhao, K.; Miao, P.; Kong, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, F.; Tang, Y. Microwave Absorption Performance of SiC/ZrC/SiZrOC Hybrid Nanofibers with Enhanced High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10490–10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.D.A.; Wang, C.; Shao, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhu, S.; Yuan, H.; Chen, J. Polymer-Free Electrospun Separator Film Comprising Silica Nanofibers and Alumina Nanoparticles for Li-Ion Full Cell. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 42, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. One-Dimensional Composite Nanomaterials: Synthesis by Electrospinning and Their Applications. Small 2009, 5, 2349–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Yu, S.-H. Nanoparticles Meet Electrospinning: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4423–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tang, Y.; Vlahovic, B. A Review on Preparation and Applications of Silver-Containing Nanofibers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, K.A.; Fouad, H.; Elsarnagawy, T.; Almajhdi, F.N. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun PLGA/Silver Composite Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 3483–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Wu, H.-C.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-C. Plasmon-Enhanced Polymer Photovoltaic Device Performance Using Different Patterned Ag/PVP Electrospun Nanofibers. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tobías, H.; Morales, G.; Grande, D. Comprehensive Review on Electrospinning Techniques as Versatile Approaches toward Antimicrobial Biopolymeric Composite Fibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, S.; Wang, X.; Kang, S.; Yu, D.; Wang, P.; Jiang, Q. Gold Nanoparticles-Loaded Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Ethylcellulose Coaxial Electrospun Nanofibers with Enhanced Osteogenic Capability for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Mater. Des. 2021, 212, 110240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjumeena, R.; Elakkiya, T.; Duraibabu, D.; Ahamed, A.F.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Venkatesan, R. “Green” Biocompatible Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Electrospun Nanofibers for Potential Biomedical Applications. J. Biomater. Appl. 2015, 29, 1039–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.C.; Liu, C.L.; Chen, W.C. Flexible Nonvolatile Transistor Memory Devices Based on One-Dimensional Electrospun P3HT:Au Hybrid Nanofibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4960–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiding, Q.; Cui, W. Functional Nanoparticles in Electrospun Fibers for Biomedical Applications. Nano Sel. 2022, 3, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.M.; Simončič, B.; Tomšič, B. Recent Advances in TiO2-Functionalized Textile Surfaces. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 22, 100890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Pathak, D.; Patil, D.S.; Dhiman, N.; Bhullar, V.; Mahajan, A. Electrospun PVP/TiO2 Nanofibers for Filtration and Possible Protection from Various Viruses like COVID-19. Technologies 2021, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palierne, J.F. Linear Rheology of Viscoelastic Emulsions with Interfacial Tension. Rheol. Acta 1990, 29, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniatto, T.V.; Rodrigues, B.V.M.; Marsi, T.C.O.; Ricci, R.; Marciano, F.R.; Webster, T.J.; Lobo, A.O. Nanostructured Poly (Lactic Acid) Electrospun Fiber with High Loadings of TiO2 Nanoparticles: Insights into Bactericidal Activity and Cell Viability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-H.; Su, J.; Liu, Y.-M.; Yu, Y.; Su, Y.; Xie, G.-X.; Jiang, L.-L.; Zhou, L.-N.; Zhu, D.-Y.; Chen, S.-H.; et al. Recent Advances in Electrospun Magnetic Nanofibers and Their Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 4072–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhu, J.; Fan, H. Magnetic Fibrous Sorbent for Remote and Efficient Oil Adsorption. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, X.; Cai, Z.; Ning, X.; Alshehri, S.M.; Ahamad, T.; Xu, X.; Yamauchi, Y.; Long, Y. Magnetic-Electrospinning Synthesis of γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticle—Embedded Flexible Nanofibrous Films for Electromagnetic Shielding. Polymers 2020, 12, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durga Prasad, P.; Hemalatha, J. Dielectric and Energy Storage Density Studies in Electrospun Fiber Mats of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)/Zinc Ferrite (ZnFe2O4) Multiferroic Composite. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2019, 573, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.D.; Beatrice, C.A.G. Polymer Nanocomposites with Different Types of Nanofiller. In Nanocomposites Recent Evolutions; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 103–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, K.S.; Nirmala, R.; Navamathavan, R.; Kim, H.Y. Mechanical Behavior of Electrospun Nylon66 Fibers Reinforced with Pristine and Treated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Fillers. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 8199–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, G.; Hong, J.P.; Rhee, J.M.; Lee, H.S.; Nah, C. Preparation and Characterization of Properties of Electrospun Poly(Butylene Terephthalate) Nanofibers Filled with Carbon Nanotubes. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macossay, J.; Sheikh, F.A.; Cantu, T.; Eubanks, T.M.; Salinas, M.E.; Farhangi, C.S.; Ahmad, H.; Hassan, M.S.; Khil, M.; Maffi, S.K.; et al. Imaging, Spectroscopic, Mechanical and Biocompatibility Studies of Electrospun Tecoflex® EG 80A Nanofibers and Composites Thereof Containing Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 321, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diouri, N.; Baitoul, M. Effect of Carbon Nanotubes Dispersion on Morphology, Internal Structure and Thermal Stability of Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Carbon Nanotubes Nanofibers. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2014, 46, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.Y.; Chen, N.; Peng, S.; Li, L.; Tian, L.; Thakor, N.; Ramakrishna, S. Polymer-Based Composites by Electrospinning: Preparation & Functionalization with Nanocarbons. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 86, 40–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Cebe, P. Poly(Lactides) Co-Electrospun with Carbon Nanotubes: Thermal and Cell Culture Properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Cho, J.W. Core-Sheath Polyurethane-Carbon Nanotube Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning. Fibers Polym. 2011, 12, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, K.; Oolo, M.; Savest, N.; Krumme, A. A Review on Graphene-Based Electrospun Conductive Nanofibers, Supercapacitors, Anodes, and Cathodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2019, 44, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Chegini, Z.; Seifalian, A.; Arabestani, M.R. Graphene-Based Materials for Inhibition of Wound Infection and Accelerating Wound Healing. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storti, E.; Lojka, M.; Lencová, S.; Hubálková, J.; Jankovský, O.; Aneziris, C.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Graphene Nanoplatelets-Containing Fibers by Electrospinning. Open Ceram. 2023, 15, 100395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.J.; Pillai, S.C.; Hehir, S.; McAfee, M.; Breen, A. Biomedical Applications of Electrospun Graphene Oxide. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1278–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhai, T.; Wang, X.; Dan, Y.; Turng, L.-S. The Surface Grafting of Graphene Oxide with Poly(Ethylene Glycol) as a Reinforcement for Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanocomposite Scaffolds for Potential Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 53, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Sahoo, S.; Wang, N.; Huczko, A. Graphene Research and Their Outputs: Status and Prospect. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2020, 5, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, E.; Dorati, R.; Pisani, S.; Bruni, G.; Rizzi, L.G.; Conti, B.; Modena, T.; Genta, I. Graphene Nanoplatelets for the Development of Reinforced PLA-PCL Electrospun Fibers as the next-Generation of Biomedical Mats. Polymers 2020, 12, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Han, N.; Zhang, X. Poly-L-Lactic Acid/Graphene Electrospun Composite Nanofibers for Wearable Sensors. Energy Technol. 2020, 8, 1901252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardeshirzadeh, B.; Anaraki, N.A.; Irani, M.; Rad, L.R.; Shamshiri, S. Controlled Release of Doxorubicin from Electrospun PEO/Chitosan/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Nanofibrous Scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Ding, G.; Xie, X.; Jiang, M. Preparation and Characterization of Graphene Oxide/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Composite Nanofibers via Electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 3026–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, H.R.; Park, C.H.; Tijing, L.D.; Amarjargal, A.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, C.S. Bimodal Fiber Diameter Distributed Graphene Oxide/Nylon-6 Composite Nanofibrous Mats via Electrospinning. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 407, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, P.; Szabó, E.; Domokos, A.; Hirsch, E.; Galata, D.; Farkas, B.; Démuth, B.; Andersen, S.K.; Vigh, T.; Verreck, G.; et al. Scale-up of electrospinning technology: Applications in the pharmaceutical industry. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 12, e1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omer, S.; Forgách, L.; Zelkó, R.; Sebe, I. Scale-up of Electrospinning: Market Overview of Products and Devices for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Purposes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vass, P.; Hirsch, E.; Kóczián, R.; Démuth, B.; Farkas, A.; Fehér, C.; Szabó, E.; Németh, Á.; Andersen, S.K.; Vigh, T.; et al. Scaled-Up Production and Tableting of Grindable Electrospun Fibers Containing a Protein-Type Drug. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partheniadis, I.; Nikolakakis, I.; Laidmäe, I.; Heinämäki, J. A Mini-Review: Needleless Electrospinning of Nanofibers for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Processes 2020, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Yao, J. A Review on Existing Technology of Electrospinning at Large Scale. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Information Technology and Scientific Management, Tianjin, China, 20–21 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sirc, J.; Kubinova, S.; Hobzova, R.; Stranska, D.; Kozlik, P.; Bosakova, Z.; Marekova, D.; Holan, V.; Sykova, E.; Michalek, J. Controlled gentamicin release from multi-layered electrospun nanofibrous structures of various thicknesses. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5315–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai-Tang, R.; Utarak, H.; Yoovidhya, T.; Intasanta, V.; Wongsasulak, S. Fabrication and antifungal activity of cellulose acetate-based fibers encapsulating natural neem seed oil. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 747, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Needleless electrospinning: Influences of fibre generator geometry. J. Text. Inst. 2012, 103, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, H.A.; Khan, K.R. Study on the various types of needles based and needleless electrospinning system for nanofiber production. Int. J. Text. Sci. 2017, 6, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; He, J.; Xu, L.; Yu, J. Bubble-electrospinning for fabricating nanofibers. Polymer 2009, 50, 5846–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

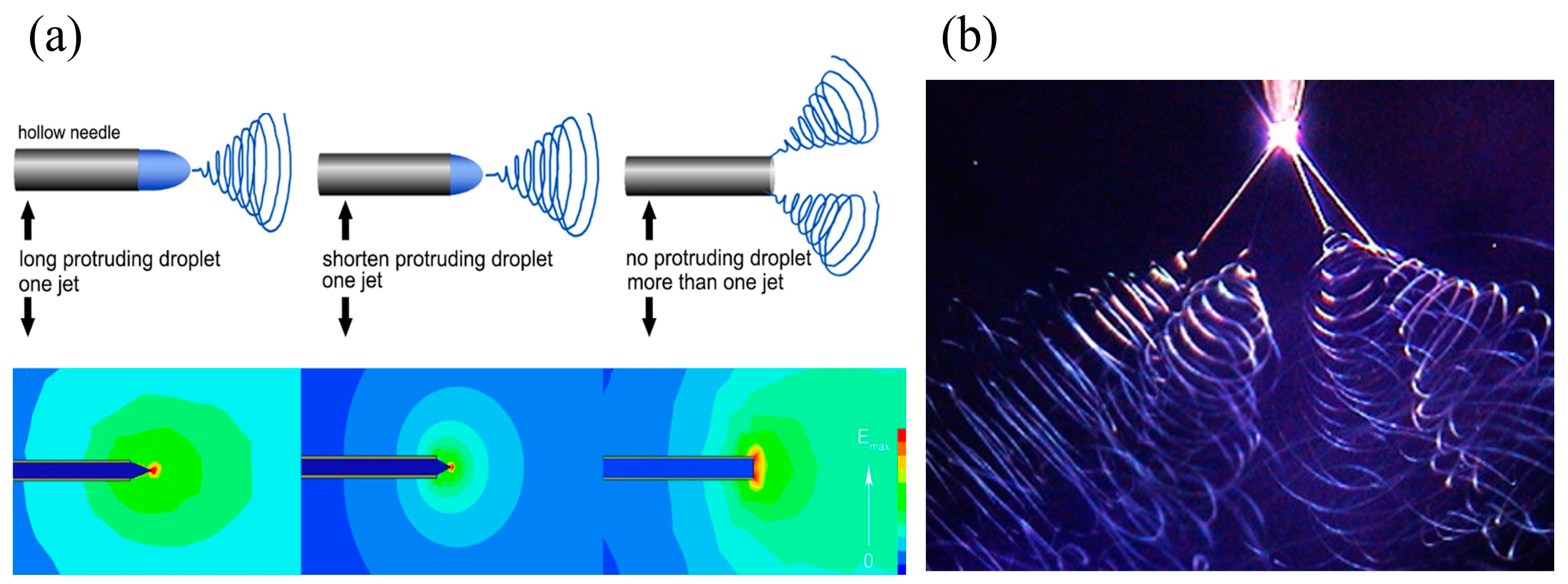

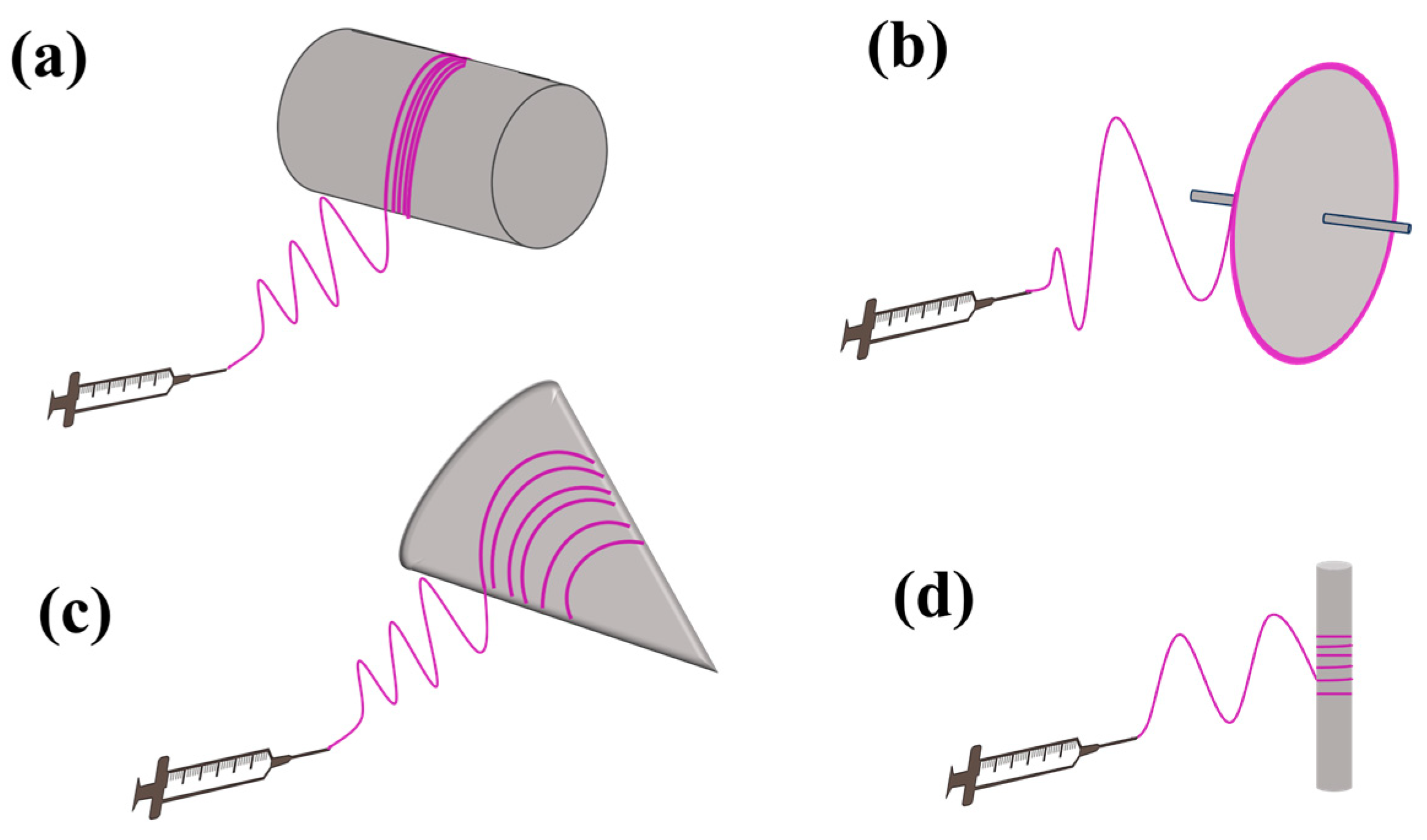
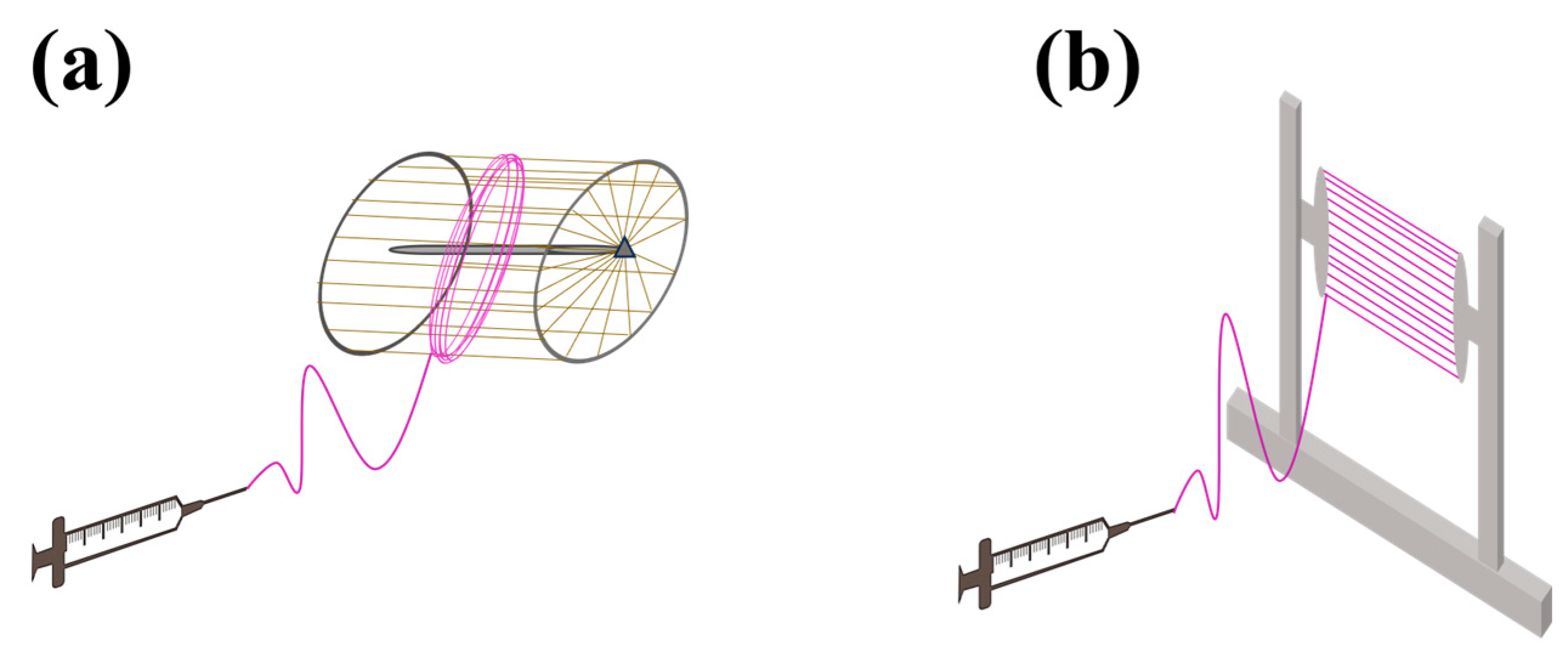
| Parameters * | Effect | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solution parameters | Concentration ↑ | ↑ fiber diameter, beads disappear | [28,29] |
| Viscosity ↑ | ↑ fiber diameter, beads disappear | [30,31] | |
| Molecular weight ↑ | beads disappear | [32,33] | |
| Surface tension ↓ | fiber formation | [34,35] | |
| Conductivity ↑ | ↓ fiber diameter, beads disappear | [36,37] | |
| Process parameters | Voltage ↑ | ↓ fiber diameter | [38,39] |
| Distance between the needle and collector ↑ | ↓ fiber diameter, beads disappear | [38,40] | |
| Flow rate ↑ | ↑ fiber diameter | [38,41] | |
| Ambient parameters | Temperature ↑ | ↓ fiber diameter | [42] |
| Humidity ↑ | Controversial effect on fiber diameter (dependence on polymer hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity) | [43,44] | |
| Fiber Structure | Materials | Spinneret | Collector | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aligned | PLLA | Single needle | Rotating Wire drum | Bone tissue engineering | [92] |
| PLGA | Single needle | Rotating drum | Drug delivery | [93] | |
| PCL/Gelatin | Single needle | Rotating mandrel collector | Skeletal muscle tissue engineering | [94] | |
| PCL | Single needle | Rotating two poles parallel collector | Scaffolds for nerve reconstruction | [95] | |
| PVDF/CNT | Single needle | Rotating drum | Piezoelectric sensor | [96] | |
| PEUU | Single needle | Rotating conical mandrel | Curvilinear scaffolds for heart valve leaflet engineering | [97] | |
| Aligned-to-random | PLGA | Single needle | Parallel electrodes | Gradient scaffold for bone tissue engineering | [98] |
| PCL, PEO, PEG, CA | Single needle | Magnetic collector | Complex gradient materials for tissue engineering | [99] | |
| Core/shell | PU/PS | Coaxial needle | Rotating mandrel | Oil sorbent | [100] |
| PCL/gelatin | Coaxial needle | Grounded collector | Drug delivery | [101] | |
| PEO/PVA/Fe3O4 | Coaxial needle | Grounded collector | Thermal interface management | [102] | |
| Hollow | PVDF-HFP | Coaxial needle | Rotating drum | Polymeric microtubes for water filtration | [103] |
| PCL | Coaxial needle | Grounded collector | Biomedical application | [104] | |
| Porous | PS | Single needle | Grounded collector | Oil sorbent | [105] |
| PEOT/PBT | Single needle | Grounded collector | Drug delivery | [106] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmadi Bonakdar, M.; Rodrigue, D. Electrospinning: Processes, Structures, and Materials. Macromol 2024, 4, 58-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4010004
Ahmadi Bonakdar M, Rodrigue D. Electrospinning: Processes, Structures, and Materials. Macromol. 2024; 4(1):58-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmadi Bonakdar, Mahboubeh, and Denis Rodrigue. 2024. "Electrospinning: Processes, Structures, and Materials" Macromol 4, no. 1: 58-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4010004
APA StyleAhmadi Bonakdar, M., & Rodrigue, D. (2024). Electrospinning: Processes, Structures, and Materials. Macromol, 4(1), 58-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4010004