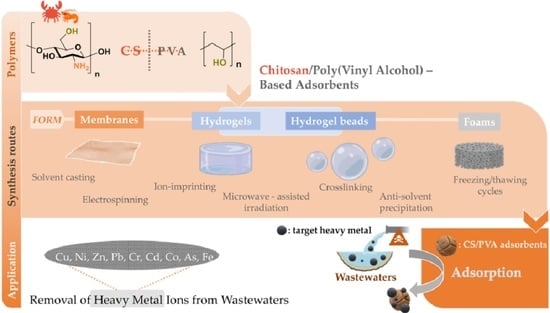
Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewaters by Using Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Adsorbents: A Review
Abstract
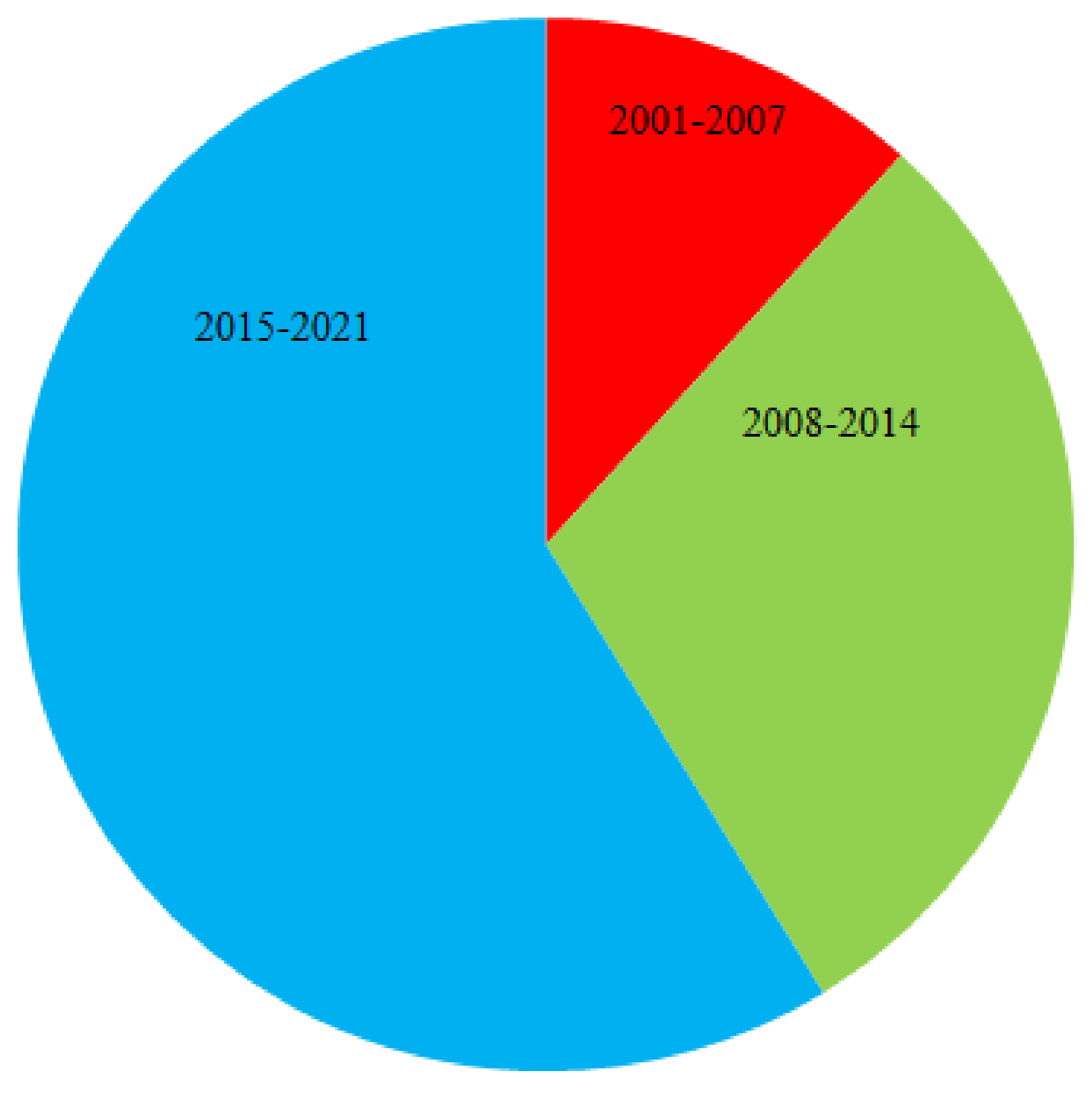
:1. Introduction
2. Synthesis Routes and Characterization of CS/PVA-Based Adsorbents
2.1. Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Based Membranes
2.1.1. Solvent Casting
2.1.2. Electrospinning
2.2. Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Hydrogels
2.2.1. Hydrogels
2.2.2. Beads
2.3. Other CS/PVA Composites (The Case of Foams and Fixed-Bed Columns)
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Xu, J.; Yuvaraja, G.; Zhang, W. Application of chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/CuO (CS/PVA/CuO) beads as an adsorbent material for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous environment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 149, 184–195. [Google Scholar]
- Sherlala, A.I.A.; Raman, A.A.A.; Bello, M.M.; Asghar, A. A review of the applications of organo-functionalized magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposites for heavy metal adsorption. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 1004–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihsanullah, A.A.; Al-Amer, A.M.; Laoui, T.; Al-Marri, M.J.; Nasser, M.S.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M.A. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution by advanced carbon nanotubes: Critical review of adsorption applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.; Cases, F.; Moretto, L.M. Graphene-based materials for the electrochemical determination of hazardous ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 946, 9–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinisik, A.; Yurdakoc, K. Chitosan-/PVA-coated magnetic nanoparticles for Cu(II) ions adsorption. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 18463–18474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghami, S.; Mohammadi, T.; Kazemimoghadam, M. Adsorption Behavior of Cu(II) Ions on Crosslinked Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol Ion Imprinted Membrane. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Afifi, A.M.; Salleh, A.; Ang, B.C. Chitosan/(polyvinyl alcohol)/zeolite electrospun compositenanofibrous membrane for adsorption of Cr6+, Fe3+ and Ni2+. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Tan, S. Adsorption of Cd2+ and Ni2+ from Aqueous Single-Metal Solutions on Graphene Oxide-Chitosan-Poly(vinyl alcohol) Hydrogels. Langmuir 2019, 35, 4481–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebjamee, N.; Soltanieh, M.; Mousavi, S.M.; Heydarinasab, A. Removal of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ ions from aqueous solution using a novel chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol adsorptive membrane. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 210, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, D. Hydrophilic PVA-co-PE nanofiber membrane functionalized with iminodiacetic acid by solid-phase synthesis for heavy metal ions removal. React. Funct. Polym. 2014, 82, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ye, Z. Preparation and characterization of new foam adsorbents of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan composites and their removal for dye and heavy metal from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaer, H.; Kaya, I. Synthesis, characterization and using at the copper adsorption of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol magnetic composite. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H. Eco-friendly polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels reinforced with graphene oxide and bentonite for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 185, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, G. Constructing biodegradable nanochitin-contained chitosan hydrogel beads for fast and efficient removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikkaliotis, D.G.; Christoforidis, A.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Adsorption of copper ions onto chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) beads functionalized with poly(ethylene glycol). Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlou, N.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Deliyanni, E.A. Graphite oxide/chitosan composite for reactive dye removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 217, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chung, Y.S.; Lyoo, W.S.; Min, B.G. Preparation and properties of chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend foams for copper adsorption. Polym. Int. 2006, 55, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, T.; Kumar, P.S.; Kumar, K.S. Binding of Zn(II) Ions to Chitosan–PVA Blend in Aqueous Environment: Adsorption Kinetics and Equilibrium Studies. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2014, 34, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, T.; Kumar, P.S.; Kumar, K.S.; Sriram, K.; Ahmed, J.F. Biosorption of lead(II) ions onto nano-sized chitosan particle blended polyvinyl alcohol (PVA): Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and equilibrium studies. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 13711–13721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, E.; Madaeni, S.S.; Rajabi, L.; Derakhshan, A.A.; Daraei, S.; Vatanpour, V. Static and dynamic adsorption of copper ions on chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol thin adsorptive membranes: Combined effect of polyethylene glycol and aminated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
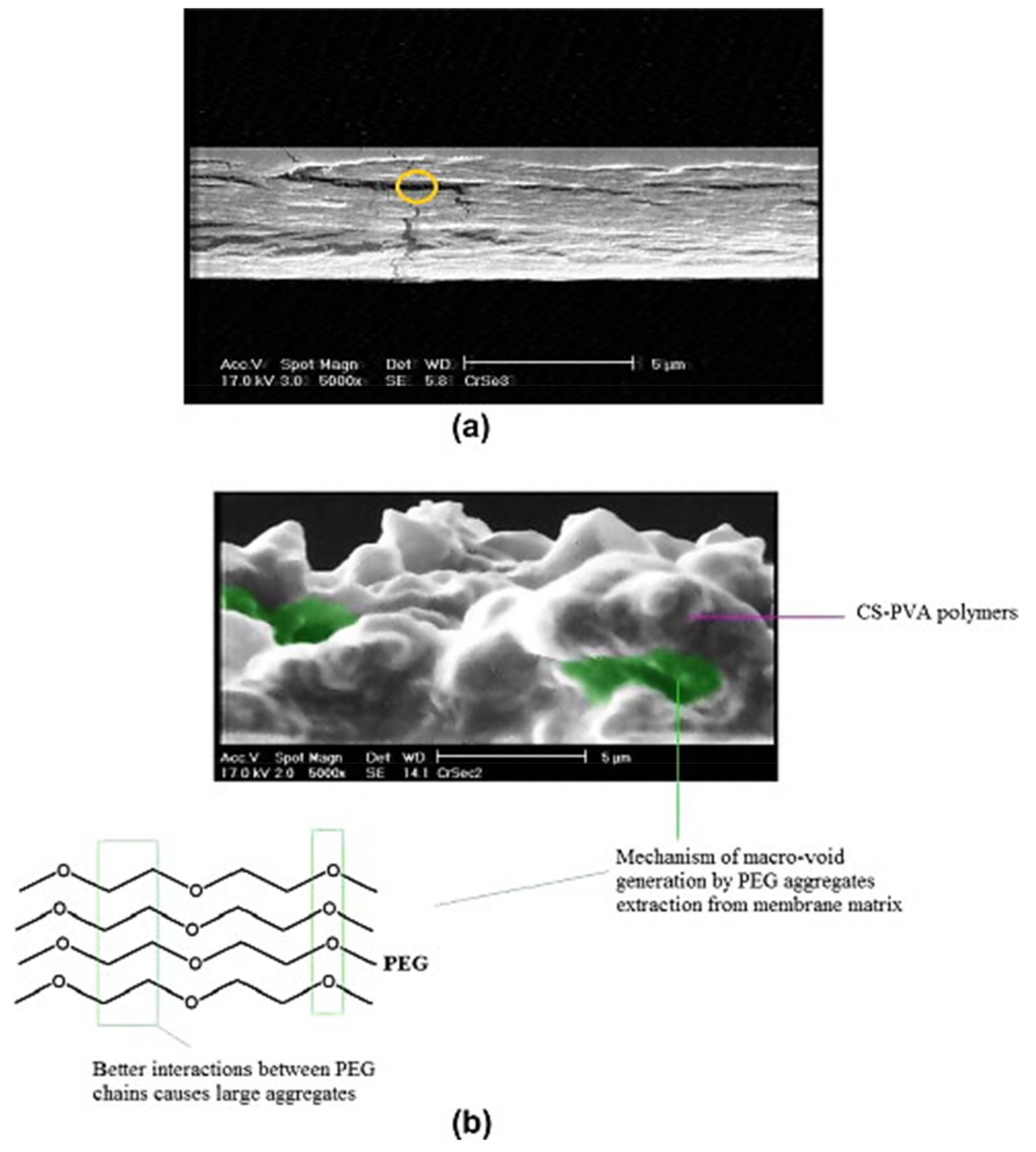
- Salehi, E.; Madaeni, S.S. Influence of poly(ethylene glycol) as pore-generator on morphology and performance of chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) membrane adsorbents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 288, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Siddique, T.A.; Joo, T.C.; Salleh, A.; Ang, B.C.; Afifi, A.M. Synthesis of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/zeolite composite for removal of methyl orange, Congo red and chromium(VI) by flocculation/adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habiba, U.; Siddique, T.A.; Talebian, S.; Lee, J.J.L.; Salleh, A.; Ang, B.C.; Afifi, A.M. Effect of deacetylation on property of electrospun chitosan/PVA nanofibrous membrane and removal of methyl orange, Fe(III) and Cr(VI) ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, K.; Afifi, A.M. Novel chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/talc composite for adsorption of heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solution. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Salehi, E.; Sahebjamee, N.; Ashrafi, M. Novel chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol thin membrane adsorbents modified with detonation nanodiamonds: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption performance. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 13, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Saied, M.A.; Wycisk, R.; Abbassy, M.M.; El-Naim, G.A.; El-Demerdash, F.; Youssef, M.E.; Bassuony, H.; Pintauro, P.N. Sulfated chitosan/PVA absorbent membrane for removal of copper and nickel ions from aqueous solutions—Fabrication and sorption studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajitha, P.; Vijayalakshmi, K.; Saranya, M.; Gomathi, T.; Rani, K.; Sudha, P.N.; Anil, S. Removal of toxic heavy metal lead (II) using chitosan oligosaccharide-graft-maleic anhydride/polyvinyl alcohol/silk fibroin composite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1469–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Shawky, H.A. Synthesis of Ion-Imprinting Chitosan/PVA Crosslinked Membrane for Selective Removal of Ag(I). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 2608–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.; Yahya, W.Z.N.; Wirzal, M.D.H. Crosslinked chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers functionalized by ionic liquid for heavy metal ions removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 195, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.; Aijaz, M.O.; Alharth, N.H.; Alharbi, H.F.; Al-Mubaddel, F.S.; Awual, M.R. Composite nanofibers membranes of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan for selective lead(II) and cadmium(II) ions removal from wastewater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Beni, A.A. A novel fixed-bed reactor design incorporating an electrospun PVA/chitosan nanofiber membrane. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebian, S.; Afifi, A.M.; Khanlou, H.M. Fabrication and characterisation of chitosan/poly vinyl alcohol nanofibres via electrospinning. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, K.; Afiffi, A.M.; Salleh, A.; Mohamad, E.N.; Izadiyan, Z. Evaluation of heavy metals removal by cross-linked (polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan/magnetic) nano fibrous membrane prepared by electro spinning technique. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 98, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koushkbaghi, S.; Zakialamdari, A.; Pishnamazi, M.; Ramandi, H.F.; Aliabadi, M.; Irani, M. Aminated-Fe3O4 nanoparticles filled chitosan/PVA/PES dual layers nanofibrous membrane for the removal of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions in adsorption and membrane processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 337, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.P.; Luo, J.J.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhen, B.; Dong, C.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Shen, J.; Cheng, Y.T.; Chen, H.P. A novel electrospun β-CD/CS/PVA nanofiber membrane for simultaneous and rapid removal of organic micropollutants and heavy metal ions from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassanapukdee, Y.; Prayongpan, P.; Songsrirote, K. Removal of heavy metal ions from an aqueous solution by CS/PVA/PVP composite hydrogel synthesized using microwaved-assisted irradiation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, X.; Hua, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pang, C.; Wang, Y. Selective adsorption of uranyl ion on ion-imprinted chitosan/PVA cross-linked hydrogel. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; He, G.; Ning, X.; Wang, C.; Fan, L.; Yin, Y.; Cai, W. Hydroxypropyl chitosan-based dual self-healing hydrogel for adsorption of chromium ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 174, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.S.W.; Kamari, A.; Koay, Y.J. Equilibrium and kinetics studies of adsorption of copper (II) on chitosan and chitosan/PVA beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2004, 34, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Bai, R. Mechanisms of Lead Adsorption on Chitosan/PVA Hydrogel Beads. Langmuir 2002, 18, 9765–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tripathi, B.P.; Shahi, V.K. Crosslinked chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol blend beads for removal and recovery of Cd(II) from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamnongkan, T.; Mongkholrttanasit, R.; Wattanakornsiri, A.; Wachirawongsakorn, P.; Takatsuka, Y.; Hara, T. Green adsorbents for copper (II) biosorption from waste aqueous solution based on hydrogel-beads of biomaterials. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 35, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Ye, Z. Preparation of macroporous bead adsorbents based on poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan and their adsorption properties for heavy metals from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 178, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, P.; Bai, H.; Dong, W.; Chen, M. Preparation of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan hydrogel compounded with graphene oxide to enhance the adsorption properties for Cu(II) in aqueous solution. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Xiao, C. Formation and cleaning function of physically cross-linked dual strengthened water-soluble chitosan-based core-shell particles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gutha, Y.; Zhang, W. Antibacterial property and biocompatibility of Chitosan/Poly(vinylalcohol)/ZnO (CS/PVA/ZnO) beads as an efficient adsorbent for Cu(II) removal from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 156, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Hirase, N.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. Pb (II) Remediation from Aqueous Environment Using Chitosan-Activated Carbon-Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Beads. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Gao, Y.; Li, M. Xanthate-modified magnetic chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) adsorbent: Preparation, characterization, and performance of Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, J. Removal of Co2+ from radioactive wastewater by polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/chitosan magnetic composite. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2014, 71, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; TYao, B.; Zang, Y.; Du, X.; Dong, L. Xanthate-Modified Magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2-Based Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Composite Material for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water. Polymers 2022, 14, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, H.; Levit, M.V. Use of carboxylated cellulose nanofibrils-filled magnetic chitosan hydrogel beads as adsorbents for Pb(II). Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

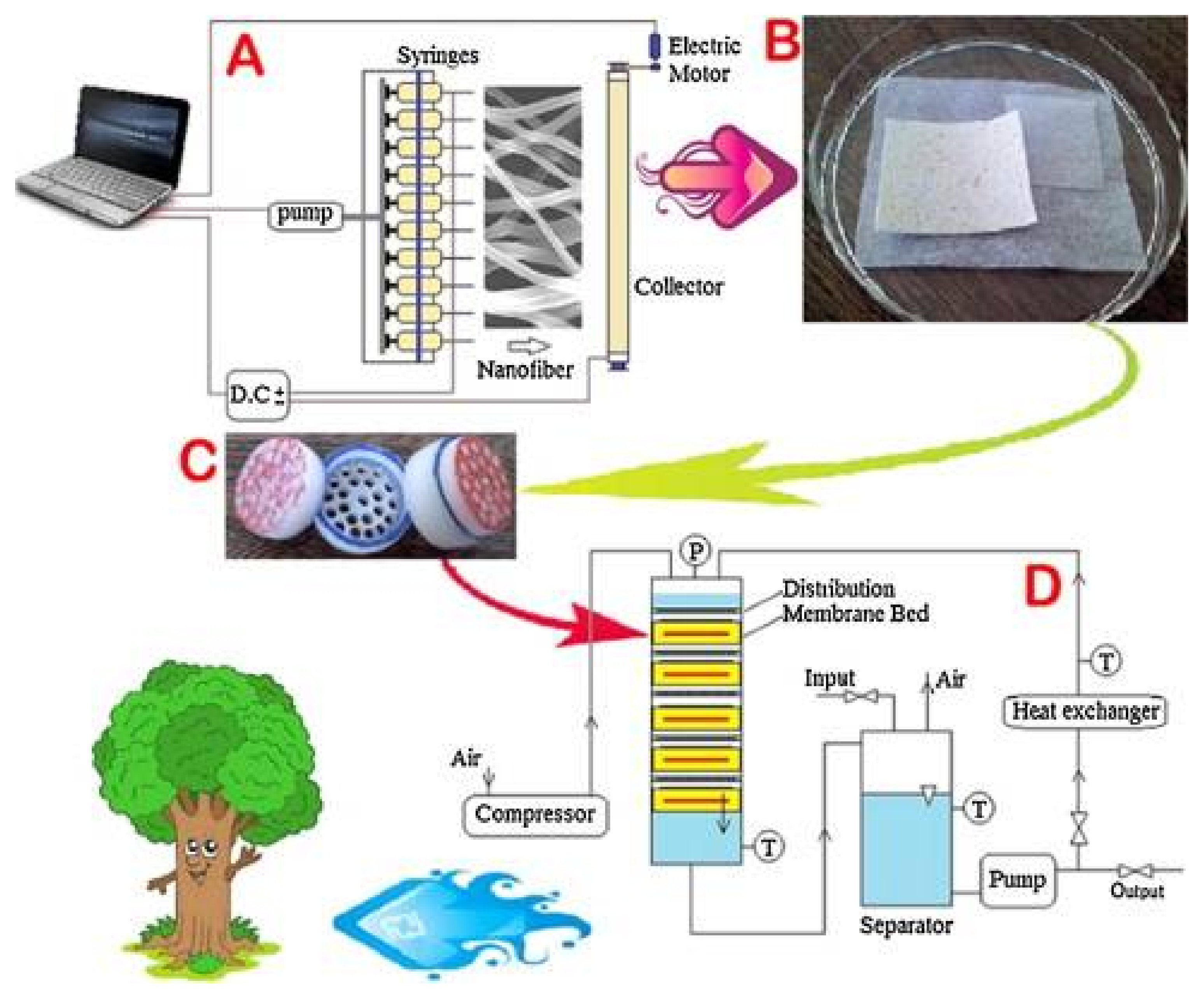
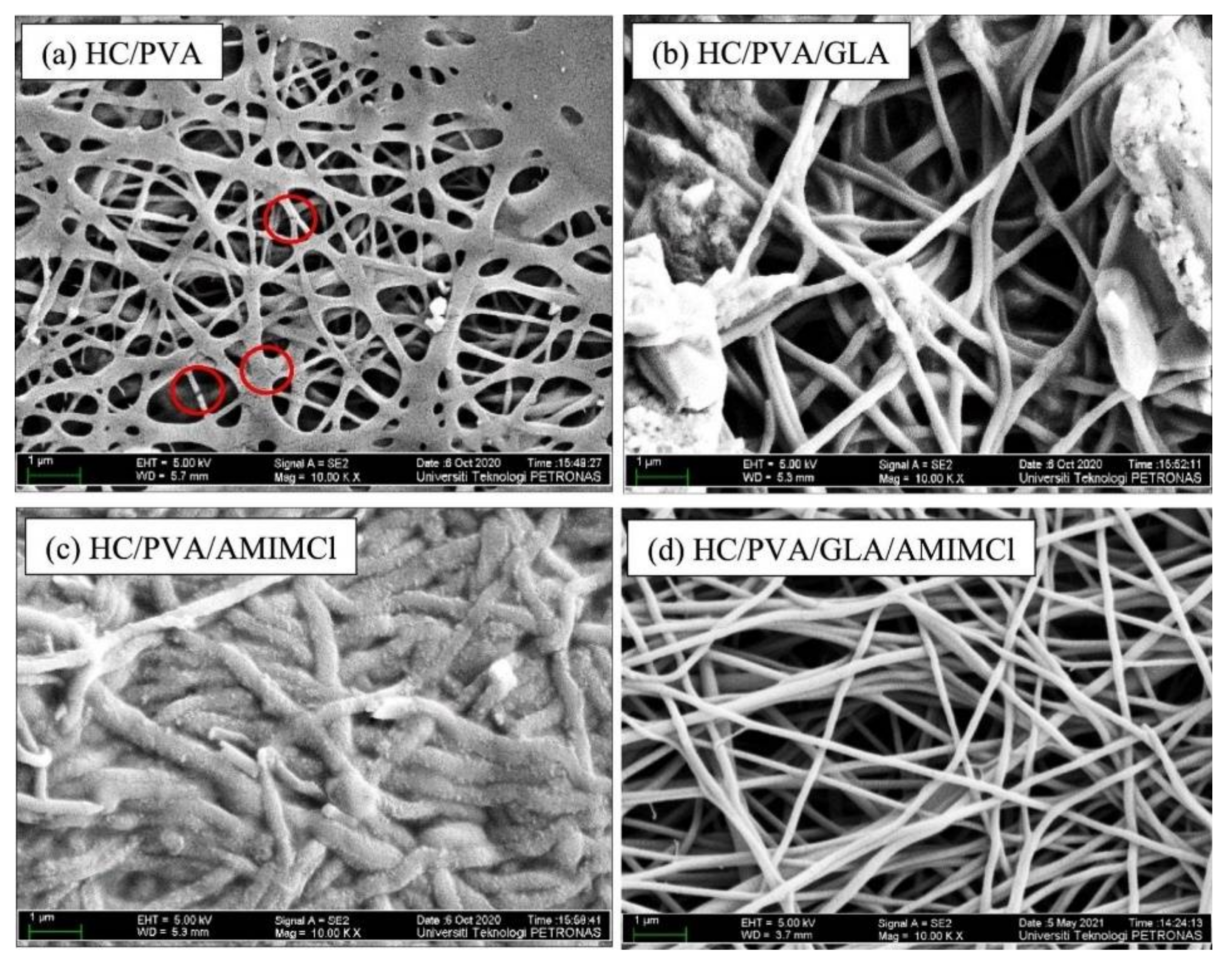

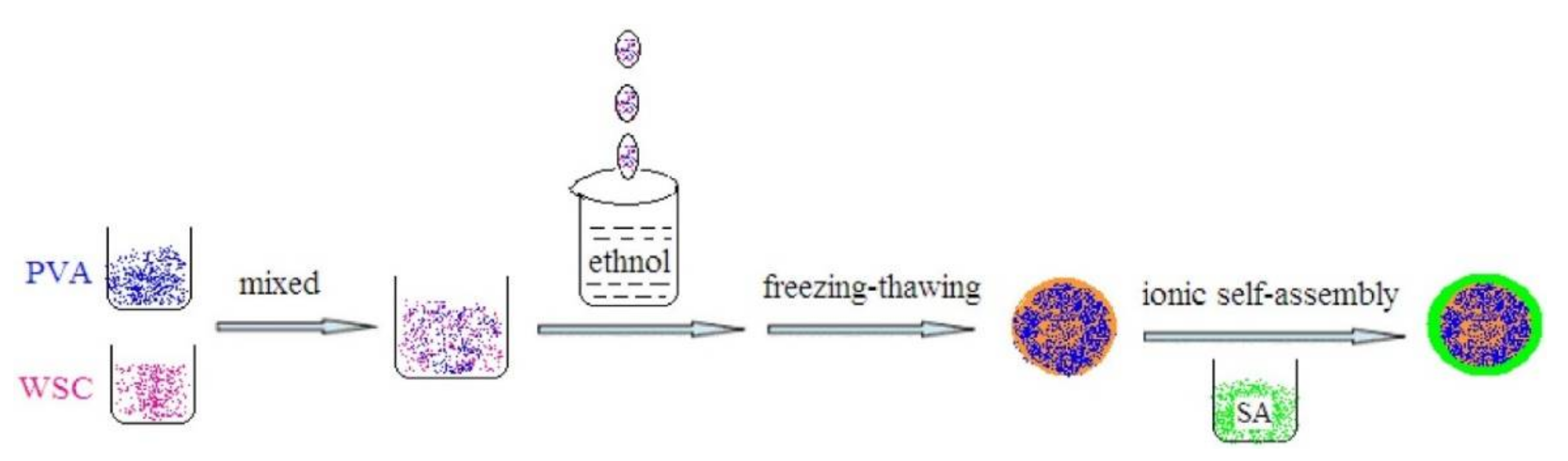
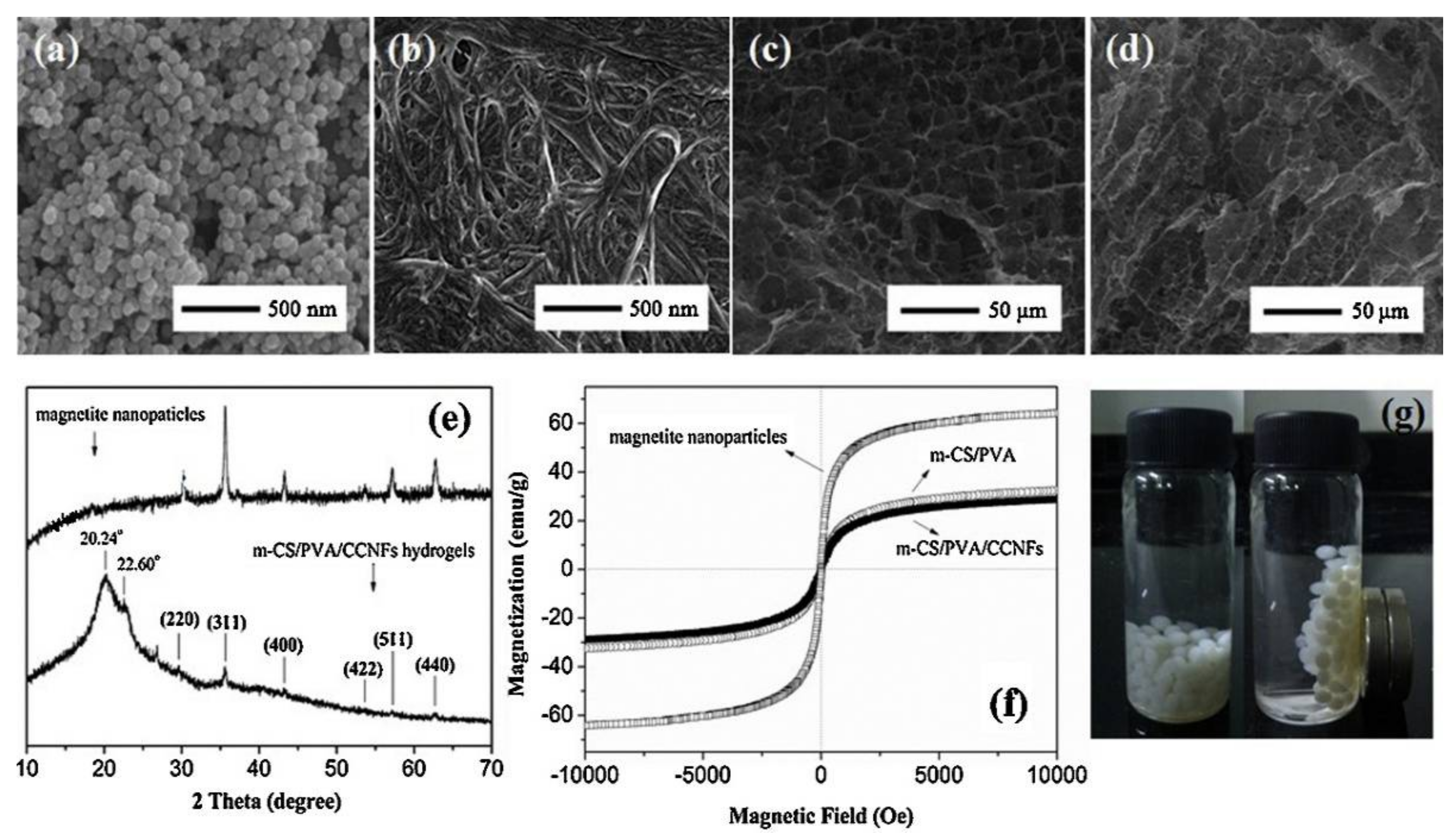
| Heavy Metal | Maximum Industrial Effluent Discharge Standard (mg/L) | Drinking Water (mg/L) | Health Effects | Sources | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA | Malaysian (DOE) | WHO | ||||
| Standard A | Standard B | |||||
| Lead | 0.015 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.01 | High risk of lower IQ, impaired intellectual ability and behavioral problems such as hyperactivity in children. May cause slow growth, mental retardation, hearing and anemia problems in children. Causes cardiovascular effects, nervous system damage, increased blood pressure and hypertension in adults. Cancer and renal kidney disease. | Metal plating, mining activities, paint-manufacture industries, pesticides, smoking, automobile emissions, burning of coal |
| Arsenic | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.01 | Carcinogenic, dermatological, cardiorenal and gastrointestinal effects. Skin cancers, lungs, bladder and kidney, cancer and other internal tumors. Vascular diseases and diabetes, infant mortality and weight loss of newborn babies. Hearing loss, reproductive toxicity, hematologic disorders, neurological diseases, developmental abnormalities and neurobehavioral disorders. | Mining, smelting of arsenic-bearing minerals, pesticides, fungicides, sedimentary rocks, geothermal water and from weathered volcanic rocks. Human activities such as manufacturing, metallurgy and wood preservation. |
| Nickel | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1 | 0.07 | DNA damage, eczema, phyototoxicity, respiratory cancer, dry cough, bone nose, and lung cancer. Cyanosis, rapid respiration, shortness of breath, tightness of the chest, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, dizziness and headache. | Metal plating, mining, fertilizers, tanneries, batteries, paper, pesticides, electronics, petrochemical, textile, production of some alloys, printing and silver refineries. |
| Chromium | 0.05 a 0.10 b | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.05 | Lung cancer, dermatitis, severe diarrhea, vomiting, pulmonary congestion, liver and kidney damage. | Plastic, pigment, wood preservative, electroplating, leather tanning, cement, mining, dyeing and fertilizer. |
| Copper | 1.3 | 0.2 | 1 | 2 | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, weakness, cramps, increased blood pressure and respiratory rates, kidney and liver damages, convulsions, vomiting or even death. | Mining, refining ores, fertilizer and pesticides industries, tanneries, batteries and paper industries. |
| Zinc | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 | Abdominal pain, phytotoxic, anemia, nausea, skin irritations, cramps and vomiting. | Pharmaceuticals, galvanizing, paints, pigments, insecticides, cosmetics, brass platting, wood-pulp production, ground and newsprint-paper production, zinc and brass metal works, refineries and plumbing. |
| Cadmium | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.003 | Detrimental effects on kidney, lungs, liver, heart and bones of human being. Cancers, bronchiolitis, emphysema, fibrosis and skeletal damage. | Metal plating, mining activities, paint-manufacture industries, steel and plastics industries, electroplating and coating operations. Nickel–cadmium batteries, Cd-Te thin-film solar cells and pigments. Welding, fertilizers and nuclear emission plants. |
| Mercury | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.05 | 0.001 | Harmful effects on nervous, digestive and immune systems, lungs and kidneys. Corrosive to the skin, eyes and gastrointestinal tract, and may induce kidney toxicity if ingested. Damage to the brain, reproductive, hematologic, cardiovascular and respiratory systems. | Coal-fired power stations, residential coal burning for heating and cooking, industrial processes, waste incinerators, mining for mercury, gold and other metals. Mineral deposits, fossil fuel or ores, pesticides, batteries and paper industry. |
| Adsorbent | Crosslinker | Synthetical Pathway | Characterization Techniques | Target Heavy Metal Ions | Isotherms and Kinetics | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | Qmax (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS/PVA [29] | GLA | Electrospinning technique | FESEM-EDX, FTIR | Pb2+ | L, F *, T Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | - | 166.34 |
| β-CD/CS/PVA [35] | ECH | Electrospinning process—crosslinking | FTIR, SEM | Pb2+ | L, F * Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | - | 13.44 |
| CS/PVA [30] | n.r. | Electrospinning technique | FE-SEM | Pb2+, Cd2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | - | 266.12 148.79 |
| CS/PVA/ Zeolite [7] | GLA | Electrospinning technique | FE-SEM, XRD, FTIR, swelling test | Cr6+, Fe3+, Ni2+ | L Ps1 *, Ps2 *, Intra | - | 8.84 6.14 1.76 |
| CS/PVA [31] | - | Electrospinning technique—thermal crosslinking | BET, SEM, FTIR | Ni2+, Co2+ | L, F, D-R * Ps1 *, Ps2 | 16.05 25.72 | 54.12 13.26 |
| Cs/PVA [23] | GLA | Electrospinning technique | FE-SEM, FTIR, XRD, TGA, tensile and weight loss testing | Fe3+ Cr6+ | L *, F | - | 11.3 117 |
| PVA/CS/ A-Fe3O4 [34] | GLA | -PES membranes: solvent casting -PVA/CS/A-Fe3O4 membrane: electrospinning process | SEM, TEM and AFM analysis | Cr6+, Pb2+ | L *, F, D-R Ps1 *, Ps2, Intra | - | 509.7 525.8 |
| CS/PVA/ DNDs [25] | NaOH | Crosslinking and solvent casting | SEM, FTIR | Pb2+ | L *, F - | 3.77 | 92 |
| CS/PVA/PEI [9] | Thermal crosslinking (50 °C for 48 h) and NaOH | Solvent casting | FTIR, SEM, swelling degree and BET | Cu2+, Cd2+, Ni2+ | L *, F, D-R, T Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | −6.15 −7.31 −10.07 | 86.08 112.13 75.5 |
| CS/PVA/ Talc [24] | NaOH | Solvent casting | FTIR, FE- SEM, XRD, TGA, weight-loss experiments | Pb2+ Cr6+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 * | - | 430 479 |
| (COS-g-MAH)/PVA/SF [27] | - | Solvent casting | FTIR, XRD | Pb2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | - | 168.93 |
| CS/PVA/ Zeolite [22] | Thermal crosslinking (70 °C for 2h) and NaOH | Solvent casting | FE-SEM, FTIR, XRD, TGA, water loss | Cr6+ | L, F * Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | - | 450 |
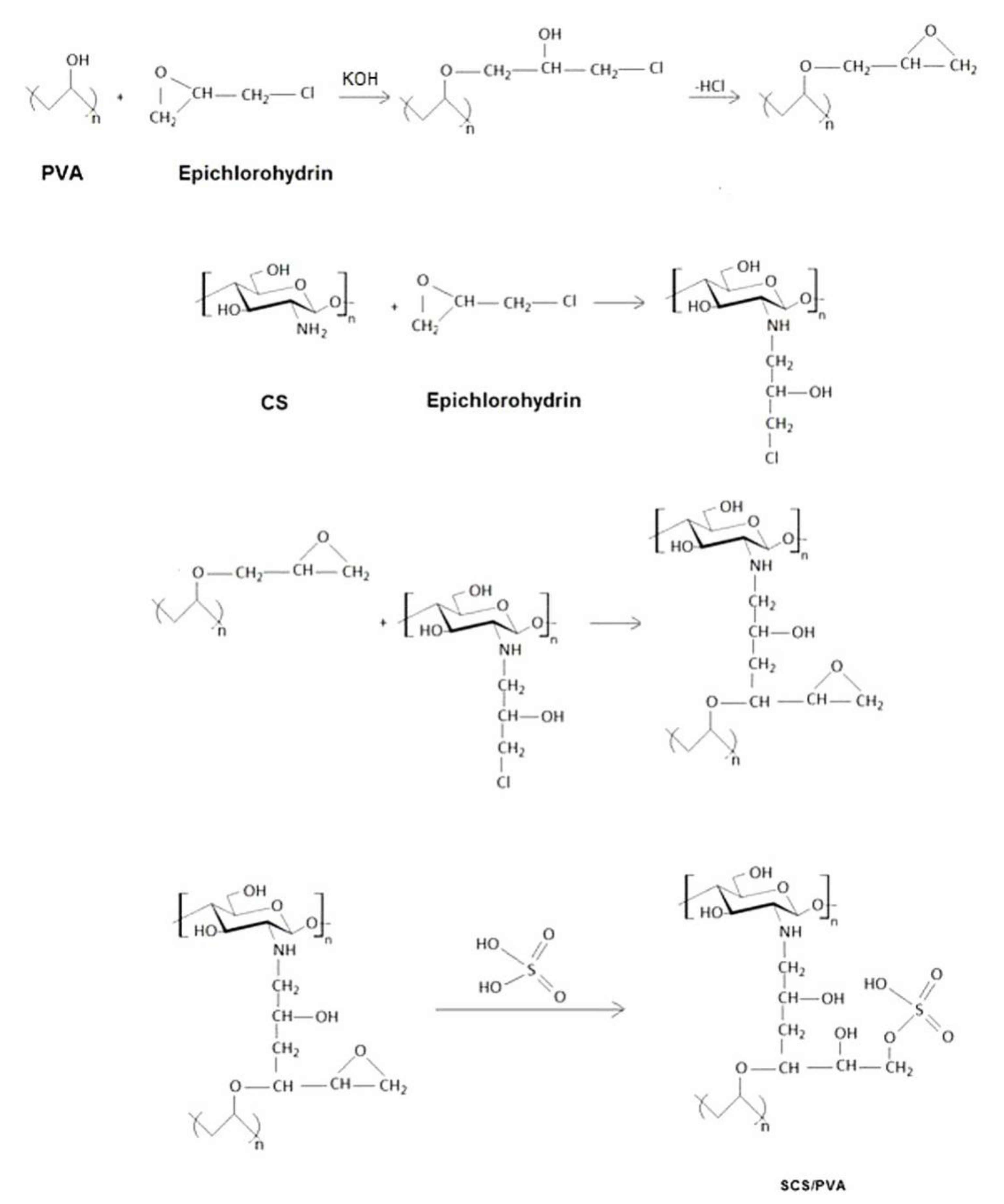
| SCS/PVA [26] | ECH | Solvent casting | FTIR, SEM, XRD and TGA analyses | Cu2+ Ni2+ | L, F* Ps2 * | - | 80.6 35.5 |
| CS/PVA [19] | GLA | Solvent casting | SEM | Pb2+ | L, F *,T Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra, Boyd | −8.54 | 14.24 |
| CS/PVA [6] | GLA | Crosslinking of blended CS/PVA | SEM | Cu2+ | L, F * Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | - | 55.55 |
| CS/PVA/PEG [21] | NaOH | Solvent casting | SEM, AFM, and wettability analyses | Cu2+ | - | 9.12 | 26 |
| CS/PVA [18] | GLA | Blending and solvent casting | SEM, TEM, XRD | Zn2+ | L, F * Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra, Boyd | - | 2.19 |
| CS/PVA/PEG/ MWCNT-NH2 [20] | Thermal (48 h at 50 °C) | Solvent casting | Water content, AFM, SEM | Cu2+ | Ps1, Ps2 * | 8.40 | 35 |
| CS/PVA [28] | GLA | Solution casting | FTIR | Ag+ | - | - | 125 |
| Absorbent Composition | Crosslinker | Synthetical Pathway | Characterization Techniques | Target Heavy Metal Ions | Isotherms and Kinetics | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | Qmax (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogel HPCS/PAM/ PVA [38] | Crosslinking agent (OSA, H3BO3) and NaOH | Polymerization and crosslinking process | FTIR, TGA, SEM, swelling test | Cr6+ | L *, F Ps1 *, Ps2 | - | 95.31 |
| Hydrogel CS/PVA/PVP [36] | ECH | Microwave-assisted irradiation | Swelling tests, gel fraction measurements, FTIR, SEM-XPS, XAS | Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Cd2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 * | - | 80.02 33.07 15.13 8.36 |
| Hydrogel CS/PVA [37] | EGDE | Gelation process | BET, FTIR | UO2+ | L *, F Ps2 | - | 132 |
| Beads CS/PVA [42] | GLA | Precipitation into an antisolvent using a prototype instrumentation | FTIR, SEM-EDX, swelling testing | Cu2+ | Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | - | 41 |
| Beads CS/AC/PVA [47] | NaOH | Crosslinking | FE-SEM, EDS, XRD, BET | Pb2+ | L, F *, T Ps1, Ps2 * | - | 9.51 |
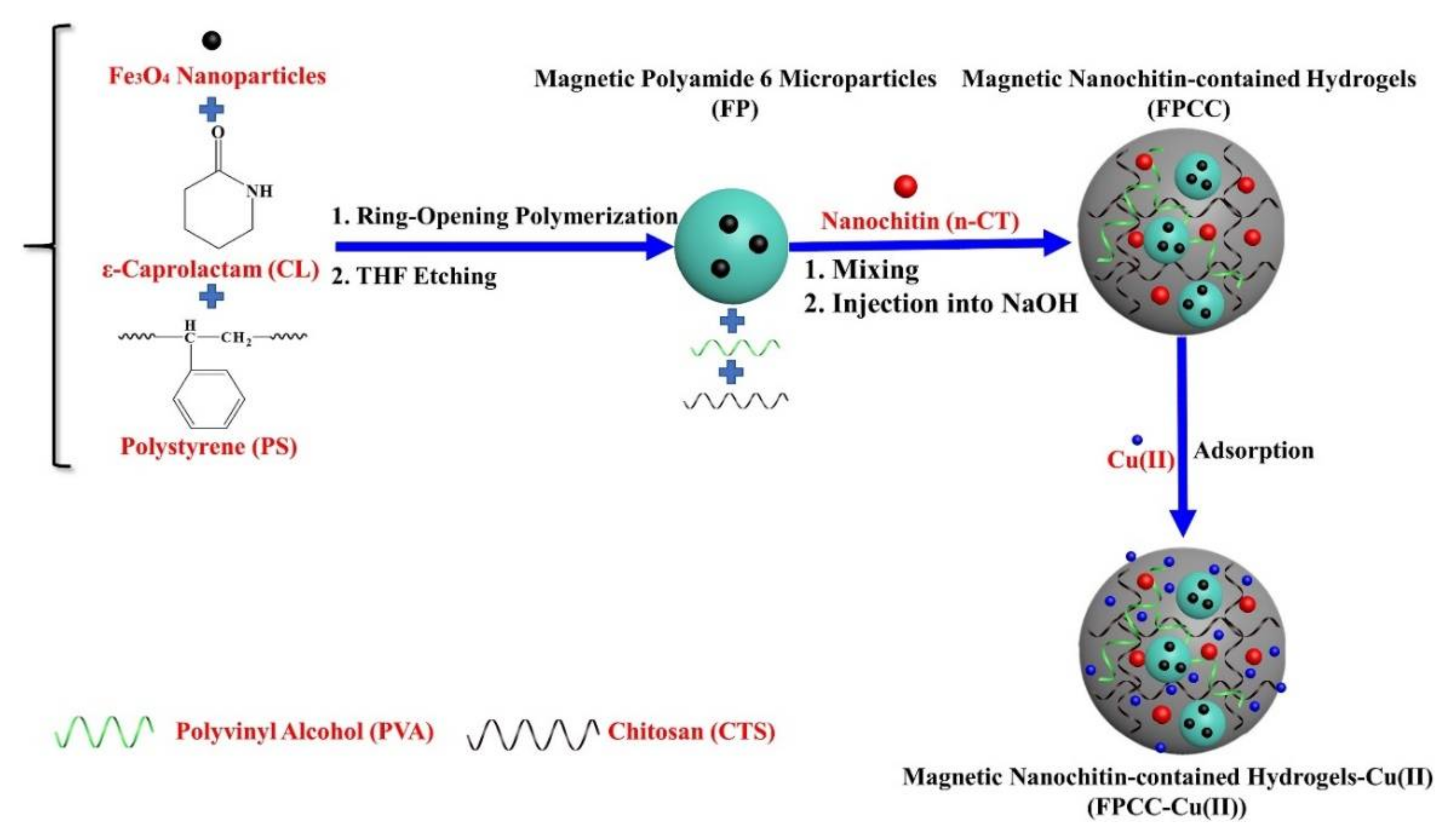
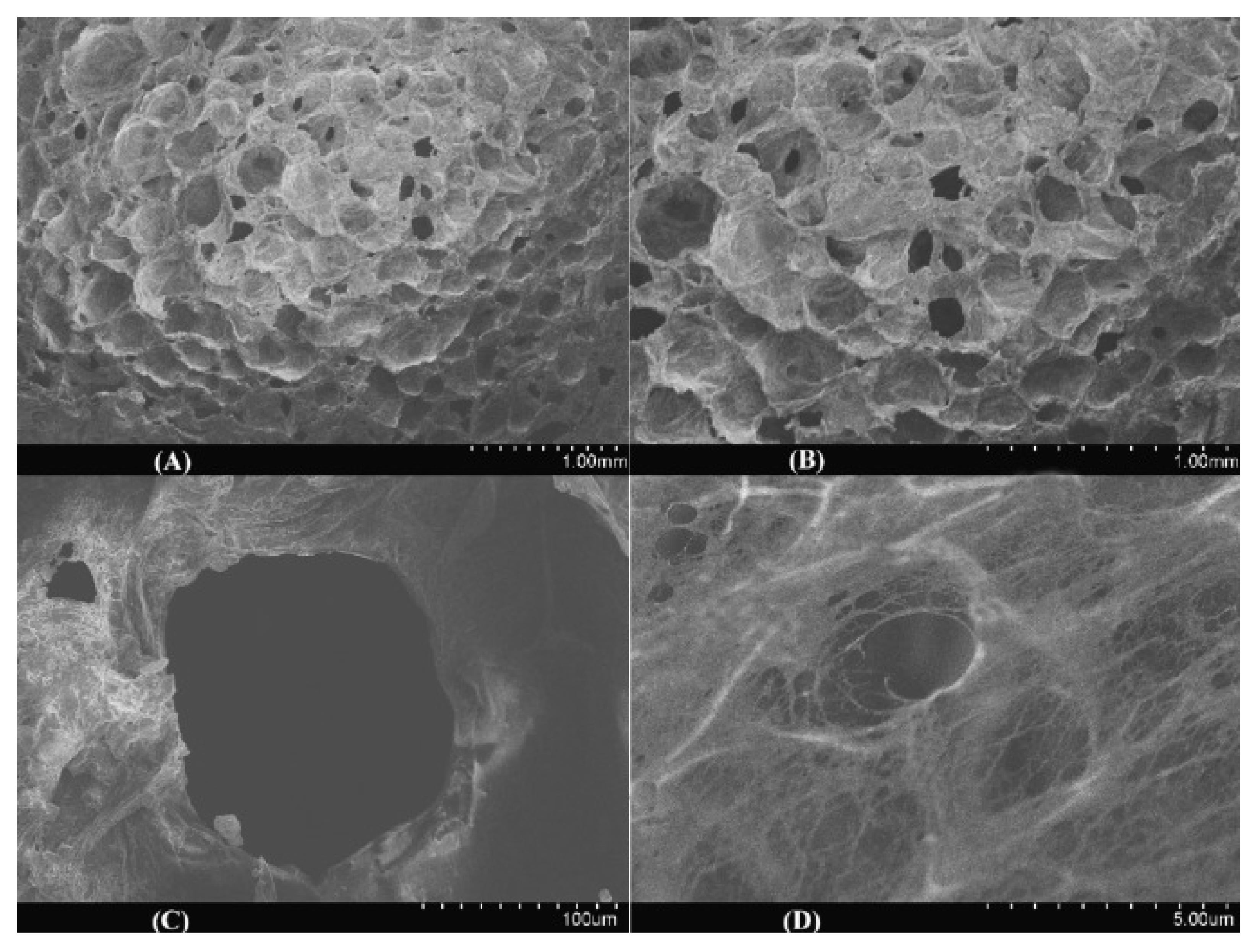
| Beads Fe3O4-NPs-contained polyamide 6 (PA 6) microparticles (FP) encapsulated into PVA-CS hybrids (PVA/CTS) [14] | NaOH | In situ encapsulation of FP microparticles and n-CT nanoparticles into PVA-enhanced CTS hydrogels | SEM, TEM, FTIR, EDS, DLS, compression testing | Cu2+ | L *, F, D-R Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | - | 100.9 |
| Beads CS/SA/PVA particles [45] | SA | Precipitation into an antisolvent | FTIR, TGA, DMTA, SEM/EDS | Pb2+, Cu2+ | - | - | 39.28 26.03 |
| Beads XMMCP/PVA [48] | GLA | Instantaneous gelation method | FTIR, XRD, SEM, BET, swelling tests | Pb2+ | - | - | 35 |
| Beads XMPC [50] | GLA | Instantaneous gelation method | FTIR, Raman, SEM, TGA, DSC, BET, XRD | Pb2+, Cu2+ Cd2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | 6.56 1.13 0.44 | 67 100 307 |
| Beads CS/PVA/ZnO [46] | NaOH | Precipitation into antisolvent | XRD, FTIR, SEM, TEM, antibacterial properties | Cu2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | 27.75 | 90.90 |
| Beads CS/PVA/CuO [1] | Thermal (320 K for 12 h), NaOH | Precipitation into antisolvent | XRD, FTIR, SEM-EDS, TEM | Pb2+ | L *, F, D-R Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | 11.62 | 116.84 |
| Beads CS/PVA–Fe3O4 [12] | Thermal (24h at 40 °C), NaOH | Instantaneous gelation method | FTIR, SEM-EDX, TEM, BET, DLS, TGA, DSC, swelling tests | Cu2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra, Arrhenius | 65 | 143.39 |
| Beads Magnetic CS/PVA [5] | NaOH | Fe3O4 nanoparticles: coprecipitation method CS/PVA beads: precipitation into an antisolvent | XRD, SEM, FTIR, TGA, BET | Cu2+ | L *, F, D-R, BET Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra, Elovich | 127.4 | 502.5 |
| Beads PVA/CS/GO [44] | CaCl2-saturated boric acid solution | Instantaneous gelation method | SEM, TGA, BET, XRD | Cu2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | 26.56 | 162 |
| Beads Magnetic CS/PVA [49] | NaOH | Gelation method | FTIR, SEM-EDX | Co2+ | L, F * Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | 8.5 | 14.39 |
| Beads m-CS/PVA/ CCNFs [51] | NaOH | Instantaneous gelation method | SEM, XRD, TGA | Pb2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | - | 171 |
| Beads CS/PVA [43] | CaCl2-saturated boric acid solution | Precipitation into an antisolvent/Crosslinking | BET, EDS, XRD, SEM, swelling tests | Cu2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Cd2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 * | 187.94 101.57 88.6 91.98 | 238.45 166.44 74.18 126.06 |
| Beads CS/PVA [41] | GLA | Suspension into an antisolvent | FTIR, XRD, SEM | Cd2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 * | 40.32 | 142.9 |
| Beads CS/PVA [39] | NaOH | Precipitation into an antisolvent | Swelling freeze–thaw cycles | Cu2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 * | - | 47.85 |
| Beads CS/PVA [40] | NaOH | Precipitation in antisolvent | SEM, FTIR, XPS | Pb2+ | - | - | 0.9 |
| Absorbent Composition | Crosslinker | Synthetical Pathway | Characterization Techniques | Target Heavy Metal Ions | Isotherms and Kinetics | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | Qmax (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS/PVA [11] | HCl | Blending and application of multiple freeze–thaw cycles | BET, EDS, TGA, SEM, swelling tests | Cu2+ | L *, F Ps1, Ps2 *, Intra | 64.52 | 193.39 |
| CS/PVA [17] | GLA | Blending, addition of HCl, HCHO and drying | Swelling tests, SEM | Cu2+ | - | - | 27.38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trikkaliotis, D.G.; Ainali, N.M.; Tolkou, A.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Kyzas, G.Z. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewaters by Using Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Adsorbents: A Review. Macromol 2022, 2, 403-425. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2030026
Trikkaliotis DG, Ainali NM, Tolkou AK, Mitropoulos AC, Lambropoulou DA, Bikiaris DN, Kyzas GZ. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewaters by Using Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Adsorbents: A Review. Macromol. 2022; 2(3):403-425. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrikkaliotis, Dimitrios G., Nina Maria Ainali, Athanasia K. Tolkou, Athanasios C. Mitropoulos, Dimitra A. Lambropoulou, Dimitrios N. Bikiaris, and George Z. Kyzas. 2022. "Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewaters by Using Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Adsorbents: A Review" Macromol 2, no. 3: 403-425. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2030026
APA StyleTrikkaliotis, D. G., Ainali, N. M., Tolkou, A. K., Mitropoulos, A. C., Lambropoulou, D. A., Bikiaris, D. N., & Kyzas, G. Z. (2022). Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewaters by Using Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Adsorbents: A Review. Macromol, 2(3), 403-425. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2030026