Abstract
Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-based soft elastomers, bearing tertiary amine and hydroxyl groups, were synthesized in bulk from the epoxy–amine reaction between poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDE) and a poly(etherdiamine), Jeffamine ED600. High gel fractions (≥0.95) and low glass transition temperatures (Tg ≈ −50 °C) were attained after complete curing of the systems in bulk. The amphiphilicity of the network allowed the swelling of the materials in both aqueous solutions and a variety of organic solvents. Magnetic nanocomposites were synthesized by in situ coprecipitation of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) in the elastomeric matrix. The obtained materials were processed by cryogenic milling to obtain powders that were tested as potential magnetic adsorbents and that showed a fast and strong response to the action of a permanent magnet. These materials showed removal rates of at least 50% in 10 min when used in the adsorption of Cu+2 ions from an aqueous solution, making them interesting candidates for the design of magnetically separable metal ion adsorbents.
1. Introduction
The epoxy–amine chemistry has proven to be a versatile route for the design of polymer networks with a wide variety of properties [1,2]. The oxirane group can react with both electrophilic and nucleophilic species, which makes it susceptible to attack by a huge variety of reagents. Epoxy–amine reactions take place as polyadditions, with reactivity being controlled by the nature of both monomers. The epoxy ring reacts with the hydrogens of amines in a one-to-one ratio. Hence, the reaction of a diepoxy (a difunctional monomer) with a diamine (a tetrafunctional monomer) results in the formation of a crosslinked network [3,4,5,6]. Epoxy networks are very well known as crosslinked matrices used in the design of adhesives, coatings and high-performance composites [1,7]. However, the use of the epoxy–amine reaction for the synthesis of soft elastomeric matrices that can swell in both water and organic solvents has been much less reported. An interesting aspect of this chemistry is that the opening of the oxirane ring by the amine conducts the formation of a polymer bearing tertiary amine and secondary hydroxyl groups [3]. These groups have proved to be interesting anchor sites for the capture of metallic ions and used, for example, as covalently linked reducing agents for the generation of metal nanoparticles (NPs) [8]. Hence, both the versatility of the epoxy–amine chemistry and the possibility of creating a functionalized network in a one-step process make this chemistry very interesting for the development of elastomer gels with the ability to swell in a variety of solvents and coordinate with metallic ions. Epoxy–amine reactions have been barely used for the synthesis of amphiphilic gels, despite their versatility, with most examples dealing with the special, although very interesting, synthesis of hydrogels with shape-persistent dendritic junctions [4,6] physical crosslinks [9] or systems based on interpenetrated networks obtained by coupling reactions within a gel network [10]. For obtaining soft elastomers that can be swollen in water using the epoxy–amine chemistry, hydrophilic and flexible monomers (or oligomers) are the ideal choice. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is an interesting candidate for the design of these materials because of its innocuous character and biocompatibility. Many elastomeric matrices and hydrogels have been developed by polymerization of functionalized poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) [11,12,13]. As the polyether linkage shows high affinity to a variety of organic solvents, networks with the ability to swell in both water and organic solvents could be ideally obtained. At the same time, the presence of coordinating groups and affinity to aqueous solutions opens up the possibility of using these matrices as hosts of inorganic precursors for the in situ synthesis of inorganic nanostructures. In situ coprecipitation of iron salts, for example, could be a convenient way of forming magnetic nanocomposites with strong magnetic responses and great perspectives in actuation ([14,15,16], magnetorheological elastomer (MRE)-based devices [17] and soft robotics [18,19]. The affinity of these matrices to metal ions could also be used for ion capturing and water remediation. A balanced combination of these last two characteristics could be used for the design of magnetically separable/recyclable metal adsorbents for the cleaning of water bodies [20,21,22,23]
In this work, an epoxy–amine reaction is used for obtaining low-modulus elastomers with high affinity to metal ions and the ability to swell in both water and organic solvents. A simple one-pot synthesis strategy that does not require any solvents is proposed. The capacity of these samples to be infiltrated with iron salt solutions is analyzed, and the potentiality of these systems as precursors of ferrogels studied. These materials’ magnetic properties are also measured to determine the possibility of using them as remotely activated materials. Finally, the ability of the obtained elastomers and nanocomposites in the capturing of copper ions from an aqueous solution is evaluated as a preliminary assessment of the adsorption capacities of the materials.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDE, average Mn = 500, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and an aliphatic polyetherdiamine (Jeffamine® ED600 type, Huntsman Corporation, The Woodlands, TX, USA) were used as monomers. For the nanocomposite synthesis, Fe (II) and Fe (III) salts (SO4Fe·7H2O and FeCl3·6H2O, respectively, from Biopack) were employed and used as received. The ethanol, chloroform and acetone used were analytical-grade and also from Biopack. MiliQTM water was used in all cases.
2.2. Synthesis of the Elastomer
“The crosslinked elastomer (E) was obtained by reaction in bulk of PEGDE and Jeffamine ED600. More specifically, the calculated amounts of reagents were weighted in a ratio of 1 g of PEGDE to 684 mg of Jeffamine ED600. The monomers were poured on an aluminum mold and mixed by gentle stirring with a glass bar at 80 °C on a hot plate for a few minutes. After the blend was clear, curing was performed in a convection oven at 80 °C on an uncovered aluminum mold (Figure 1). The variables of the curing schedule (PEG/ED600 mass ratio, temperature and time) were selected in order to attain full con-version of the stoichiometric formulation; conditions were obtained from FT-NIR measurements (see discussion below)”.
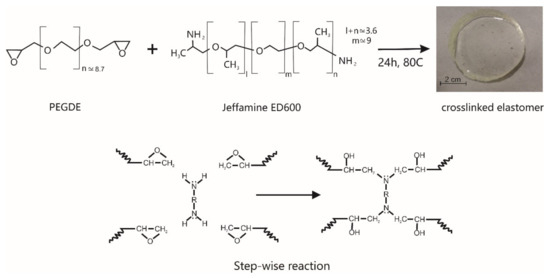
Figure 1.
Scheme showing the reagents’ structure and the chemical reaction between PEGDE and Jeffamine ED600.
2.3. Nanocomposite Synthesis
A magnetic elastomer (ME) was obtained by in situ coprecipitation of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) in a crosslinked matrix. In this procedure, the cured sample was first introduced to an ammonia solution for 24 h at room temperature (Figure 2a) and then changed to a stirred aqueous solution of iron salts (12.22 g FeSO4·7H2O + 18.83 g FeCl3·6H2O in 150 mL H2O) at 60 °C for 24 h (Figure 2b). The solution pH was adjusted to 7. Following that, the system was immersed again in ammonia solution for 24 h at 60 °C (Figure 2c) to optimize the formation of the magnetic phase (Figure 2d). Finally, the product was washed in water. An ME powder was obtained by cryo-milling using liquid nitrogen and a mortar.

Figure 2.
Photographs showing the steps of nanocomposite formation. (a) Elastomer swollen in ammonia for 24 h. (b) The system after immersion in aqueous solution of iron salts for 24 h. (c) The material after coprecipitation of magnetic nanoparticles by swelling in ammonia for 24 h. (d) Response of the obtained material to a magnet.
2.4. FT-NIR Characterization
Fourier-transformed near-infrared spectroscopy (FT-NIR) was used to determine the evolution of the reaction between PEGDE and Jeffamine ED600. A Nicolet 6700 Thermo Scientific instrument was used in the range of 4000–8000 cm−1 using 32 co-added scans and 4 cm−1 of resolution.
2.5. Gel Fraction Determination
The gel fraction () was obtained by following a classical procedure. Pieces of approximately 150 mg of the elastomer or nanocomposite were allowed to dry for 24 h at 40 °C. Once dried, they were weighed and introduced to chloroform for 5 days (120 h). At the end of this time, they were withdrawn from the solvent, dried for 24 h at 40 °C and weighed. The gel fraction was calculated as:
where is the initial mass of the samples after drying for 24 h at 40 °C, and is the final mass of the sample after 5 days in chloroform.
2.6. Swelling (Mt) Degree Assays
The swelling degree () was determined for elastomer and nanocomposites samples using water, chloroform, ethanol and acetone as solvents for 24 h (1440 min). was calculated with the following equation:
where is the final mass of the swollen sample after 24 h of being immersed in the solvents, and is the initial mass of the samples after drying for 24 h at 40 °C
2.7. Thermal Characterization
The amount of iron oxide formed in the nanocomposites by the in situ coprecipitation of iron salts was determined using thermogravimetric (TGA) analysis with a TA Q500 v20.13 (New Castle, DE) instrument. Measurements were performed under air flow using approximately 15 mg of the dried sample and heating it to between 25 and 900 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min.
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was carried out using a Perkin Elmer Pyris 1 device. Scans were performed between −60 and 120 °C at 10 °C/min.
2.8. X-ray Diffraction
A Panalytical X-ray diffractometer (XRD) X’pert PRO model with Cu K-alpha radiation was used. Diffraction patterns were obtained between 2 and 70° .
2.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
MNPs were characterized using a JEOL JEM-2100 microscope with a B6La filament at 200 KV. Samples were prepared by dispersing in ethanol a fine powder of the cryogenically ground nanocomposite followed by deposition of a droplet of this suspension on a carbon-coated copper grid coated with Formvar.
2.10. Magnetic Characterization
The magnetic response of MNPs in the ME matrix was measured on a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) LakeShore 7004 until a maximum magnetic field of about 1.6 × 106 A/m at room temperature. Results were analyzed using the function:
where is the magnetization as a function of the applied field and temperature , is the mean volume of MNP, is the Bohr magneton, is the Boltzmann constant, is the MNP magnetic moment, is the Langevin function, is the log-normal distribution of MNP magnetic moments, C is a constant factor which takes into account contributions from diamagnetic–paramagnetic phases, and B is an additive constant from the experimental offset. The quantity retrieved from this analysis was the MNP mean magnetic moment , with and being the values obtained from fitting with the distributed Langevin function. cycles were normalized with the sample iron oxide content mean value obtained from TGA measurements.
2.11. Rheological Measurements
Rheological measurements were carried out using an Anton Paar Physica MCR 301 rheometer. Specimens with rectangular cross sections (12 mm × 6 mm × 2 mm) were tested under torsion mode. Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) tests were performed at a heating rate of 5 °C/min from −70 to 150 °C with a fixed frequency of 1 Hz.
2.12. Adsorption Kinetics in Copper Solutions
The equilibrium adsorption capacity () of the sample (E, ME, ME powder) was evaluated by measuring the adsorption of Cu+2 ions in aqueous solution by UV-Vis spectrophotometry. An Agilent 8453 UV-Vis spectrophotometer was used. Spectra were taken in the 300 to 1000 nm range. The absorbance of the peak at 808 nm was followed as a function of time [24]. The solutions were prepared by using solid CuSO4·5H2O (from Ciccarelli) in water at initial concentrations of 20, 30, 40, 60 and 80 mM Cu+2.
The adsorption kinetics were evaluated and analyzed through:
where is the metal ion concentration of the initial solution, is the equilibrium metal ion concentration, is the volume of the solution, and is the sample mass (E, ME or ME powder).
The removal percentage () was calculated as follows:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Elastomers
Clear, rubbery crosslinked polymers were obtained by curing the reactive blends for 24 h at 80 °C. The reaction took place through the well-known stepwise polymerization involving opening of the oxirane ring by the amine group. A polyetheramine (an aliphatic polyether diamine derived from a propylene oxide-capped polyethylene glycol, Jeffamine ED600) was used with the idea of including flexible segments in the network. The long times required for reaching full conversion are related to the lower reactivity of aliphatic epoxies towards nucleophilic compounds (like amines) when compared with most commonly used diglycidylether of bisphenol A-based resins [25,26]. However, conversions close to 1 could be reached after 24 h of reaction in absence of any accelerator, and gel fractions measured gravimetrically yield values around 95 wt% for all the obtained samples.
Figure 3 shows the FT-NIR spectra corresponding to the PEGDE, the ED600 and the reaction product after 24 h of reaction. As can be clearly seen, the characteristic peaks associated with the epoxy group at 4530 cm−1 and 6070 cm−1 in the PEGDE disappeared after reaction. The first of these peaks is assigned to a combination band of the second overtone of the epoxy ring stretch at 916 cm−1, with the fundamental C–H stretch at 2725 cm−1, whereas the second one can be assigned to the first overtone of the terminal CH2 stretching mode [27]. A similar change is observed in the case of the amine groups in ED600. The doublet located between 6530–6480 cm−1, assigned to the N-H stretching first overtone, and the band at 4936 cm−1, assigned to the combination of N-H stretching and bending, also disappeared after 24 h of curing. No bands associated with the presence of secondary amines could be observed in the product, confirming the complete reaction of the amine groups in the formulation and the formation of tertiary amines. The formation of hydroxyl groups was also proven by the appearance of the broad band located around 4760 cm−1 (combination band of O-H stretching and bending) and the absorption around 7000 cm−1 (O-H overtones). Hence, the reaction of the monomers during 24 h of curing at 80 °C yields a fully cured elastomer bearing tertiary amine and hydroxyl groups. The peak at 5197 cm−1 was assigned to the presence of low amounts of water in the matrix. As cooling of the sample was not carried out in a vacuum, water absorption took place, as evidenced by the presence of this peak and confirmed by thermogravimetric analysis (Figure 4). This well-defined and intense band has been successfully used to monitor the water absorption of crosslinked epoxies [28] and is a clear indication of the presence of water in this sample. High affinity of these matrices to water is then evidenced since the first moments after their synthesis.
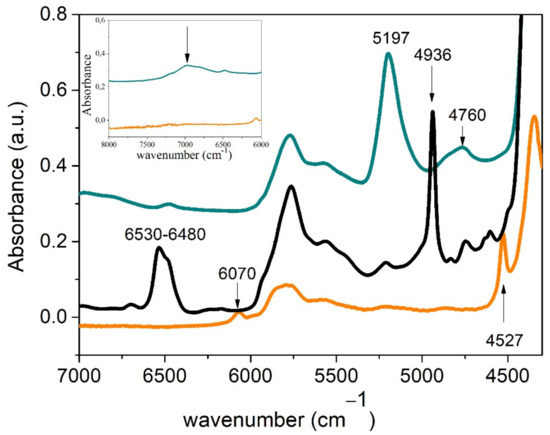
Figure 3.
FT-NIR spectra of both monomers (PEGDE orange line, ED600 black line) and the product of polymerization after 24 h at 80 °C (green line).
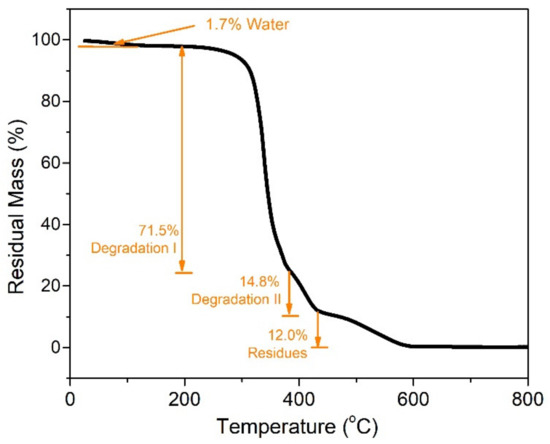
Figure 4.
TGA curve for the gel obtained by curing of a stoichiometric blend of PEGDE and ED600 for 24 h at 80 °C.
The presence of a broad and low glass transition temperature, Tg, located around −40 °C and −50 °C was inferred from the corresponding features observed by both rheometry (tanδ peak) and DSC. This transition is indicative of a heterogeneous network with a low crosslinking density and flexible chain segments arising from the polyether structure of PEGDE and ED600 (Figures S1 and S2 in Supplementary Materials).
Determinations of the storage modulus, G’, of the elastomer were performed at room temperature using rheometry. A G’ value of 48 kPa ± 16 kPa was determined, showing the soft nature the of the synthesized material.
The swelling behavior of the elastomer both in water and in organic solvents was analyzed. A very significant increase in size was verified in samples immersed in water and, to a higher degree, in chloroform. The reproducibility of this behavior was checked in several samples, pointing to the higher swelling degree of the elastomers in these two solvents. Quantitative determination of the swelling degree was performed gravimetrically and can be observed in Figure 5. All the measurements were performed after 24 h of immersion to attain equilibrium values. Plotting the swelling degree against the solubility parameter of the solvents (Figure 5) showed that the maximum swelling was attained for HCCl3, with a Hildebrand solubility parameter of δ = 19 (MPa)1/2, which would indicate that this value is near the δ value of the elastomeric matrix. However, acetone, with δ = 20 (MPa)1/2, showed the lowest swelling degree (86.7%), whereas water gave a swelling value of 226.9% with δ = 47.8 (MPa)1/2 [29]. These results seem to show that the compatibility of the obtained polymer with solvents is not possible to understand in terms of a single component Hildebrand parameter. This is due to the relative contribution of dispersion, polar and hydrogen bonding components to the total solubility parameters of these solvents. In fact, the highest swelling ability was found for a solvent with a high dispersion force component (δD = 17.8 (MPa)1/2) and low polarity (δP = 3.1 (MPa)1/2) and hydrogen bonding (δH = 5.7 (MPa)1/2) components. This behavior matches well with a polymer in which intermolecular forces are primarily due to dispersion forces. However, a rather high amount of swelling in water could also be measured, a solvent with a high hydrogen bonding component of the solubility parameter (δH = 42.3 (MPa)1/2), quite high polar forces component (δP = 16 (MPa)1/2) and moderate dispersion contribution (δD = 15.6 (MPa)1/2). Solvents with intermediate polarity and hydrogen bonding capacity, like acetone or ethanol, showed the worst compatibility with the matrix. Hence, these results seem to reflect the rather amphiphilic character of the gel, with chains mainly interacting through dispersion forces but, at the same time, with the ability to present strong hydrogen bonding between polar functional groups. These properties confer to the matrix versatility and interesting potentiality as a host of ions and molecules present in both organic and aqueous solvents. In the following section, the use of this versatility in the synthesis of magnetic nanocomposites and the capturing of metal ions will be analyzed.
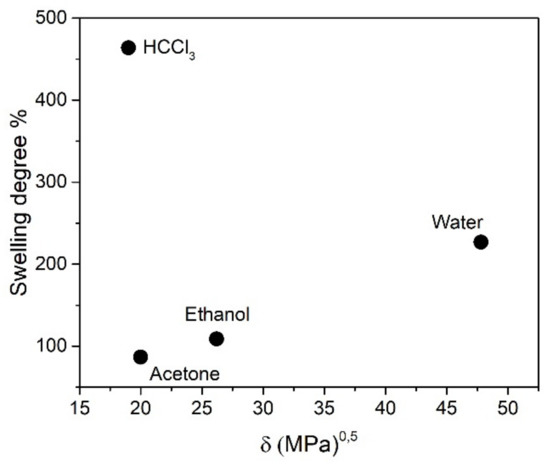
Figure 5.
Percentage of swelling degree as a function of the Hildebrand parameter of the solvent.
3.2. Nanocomposites Synthesis and Characterization
The ability of the obtained elastomers to swell in aqueous solutions was used to synthesize magnetic nanocomposites through an in situ technique. Tertiary amine and hydroxyl groups can act as anchor sites for metal ions like iron, working as complexing agents until precipitation. As the increase of the pH inside the matrix can be a slow process, the elastomers were first immersed in a solution of ammonia to prepare the environment for immediate precipitation and to avoid the formation of other non-magnetic iron phases [30]. After this step, the gels were impregnated in an iron salt solution and then placed in a solution of ammonia again to complete the conversion of the precursors into the iron oxide magnetic phase (magnetite and/or maghemite). Figure 2 shows optical photographs of the synthesis process and the response of the obtained final dark ferrogel to a permanent magnet. TEM micrographs showed clearly the presence of a polydisperse population of MNPs distributed in the matrix (Figure 6). The average diameter was 7.5 ± 2.7 nm (inset in Figure 6). The average size of the magnetic NP core was determined using at least two images and employing more than 100 particles/image. The small diameter of the MNPs was attributed to the restrictions imposed by the polymer matrix during coprecipitation [31]. Similar results have been obtained in the case of ferrogels fabricated by in situ precipitation of magnetite nanoparticles in a polyacrylamide hydrogel. The monodispersity of these magnetite nanoparticles, with an average size of 3–5 nm, has been confirmed by transmission electron microscopy [32]. MNPs have also been synthesized inside a chitosan hydrogel under ambient conditions. In this case, a mean diameter of about 16 nm was obtained [33]. Hence, previous work has shown that it is possible to obtain a range of sizes and monodispersities depending on the conditions of precipitation and the nature of the polymer matrix. Thermogravimetric curves showed that the approximate content of the magnetic phase, calculated as Fe2O3, is 5 wt%.
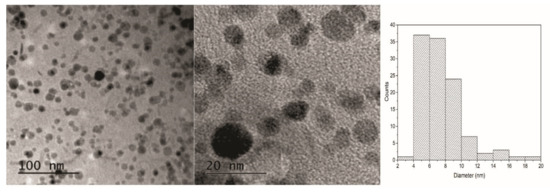
Figure 6.
TEM micrographs of MNPs in the elastomeric matrix and the histogram corresponding to the MNPs’ distribution.
Thermal characterization of the obtained product showed barely any influence of the synthesized MNPs on the Tg of the matrix (Figure S1, Supplementary Materials). However, the measured G’ value at room temperature was 88 ± 24 kPa, almost the double the value found for the neat matrix, indicating that the nanostructured phase can act as a mechanical reinforcement of the elastomeric phase. However, both the elastomer and the nanocomposites can still be considered soft materials with a low elastic modulus.
The presence of the magnetic phase was corroborated by XRD. X-ray diagrams showed a broad peak between 15–28° 2θ (Figure S3 in Supplementary Materials) attributed to the amorphous matrix and peaks assigned to the typical reflections of magnetite (Reference code: 00-002-1035) and maghemite (Reference code: 00-004-0755).
Magnetization vs. the intensity of the magnetic field () cycles (Figure 7) were determined by VSM. The obtained curve shows the absence of a coercivity field (inset in Figure 7), pointing to the superparamagnetic response of the synthesized MNPs at room temperature (RT). Retrieved parameters from magnetization vs. the intensity of the magnetic field cycle analysis with Equation (3) are displayed in Table 1.
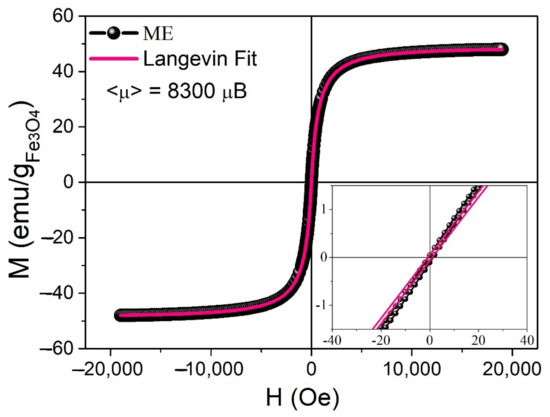
Figure 7.
VSM, cycle normalized with the sample iron oxide content and fitted with a magnetic moment-distributed Langevin function. Inset: low field range showing almost no coercivity, i.e., .

Table 1.
Obtained parameters from Langevin fit performed on the cycle M vs. H. Mean magnetic moment , magnetic saturation , mean magnetic diameter and standard deviation .
The magnetic diameter (7.6 nm) was in agreement with the diameter measured by TEM microscopy (7.5 nm). As is known, the presence of either a superparamagnetic or a ferromagnetic phase can be used to confer the materials with the ability to be removed from a liquid medium using a magnet, which is important when these materials are used in adsorption processes. This removal efficiency can be optimized by increasing the available contact surface, which can be accomplished by transforming the bulk material into a powder. Below Tg, both the elastomer and the nanocomposite were brittle, enabling the use of cryo-milling to obtain ME powders that can be easily removed from an aqueous solution using a magnet (Figure 8).
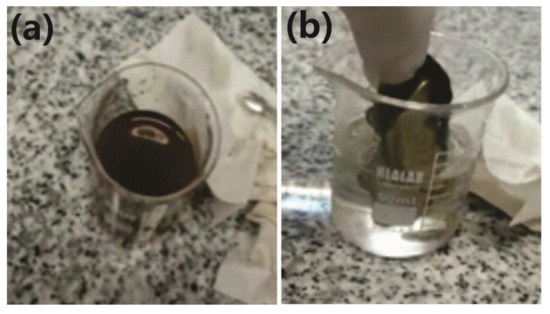
Figure 8.
(a) Powdered ME suspended in an aqueous solution. (b) Aqueous solution before complete removal of FG powder using a permanent magnet.
Comparison between the swelling capabilities of E and ME materials in different solvents was performed in order to determine their potentiality as adsorbents and the influence of the nanostructured phase on the ME’s behavior towards solvents. Water, acetone and ethanol were used for comparison due to their wide use as industrial solvents.
Figure 9 shows the swelling curves as a function of time (up to 24 h) for ME samples in the different solvents. High swelling values were attained after only 30–40 min of contact of the ME with the three solvents, pointing to the good wettability and open structure of the networks. When compared with the values plotted in Figure 5, no significant differences could be found between the maximum swelling values of the E and ME in acetone and ethanol. However, the magnetic elastomers exhibited lower swelling in water than those devoid of NPs. These results point to the presence of a specific kind of interaction between water and the pendant groups of the network that could be hindered in the ferrogel. Interactions of the polymer segments with the ions and the formed NPs, in addition to altering the chemical compatibility with the solvent, might also lead to the formation of low-mobility regions [34]. In brief, the reduction in the degree of water uptake upon the formation of MNPs in the elastomer could be due to several effects, and it is an important aspect to consider for applications of the materials as adsorbents or cleaners [35]. Further work will be necessary to elucidate the actual nature of this type of interaction.
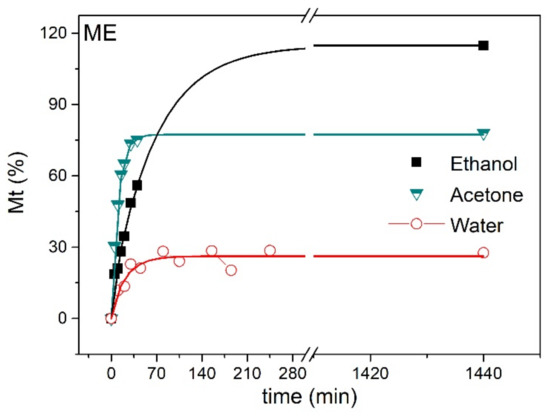
Figure 9.
ME swelling curves in water, acetone and ethanol.
3.3. Adsorption Measurements
As is currently well known, increasing heavy metal ion contamination has become a critical environmental problem. The main ecological concern is related to metal ions’ accumulation and non-degradability in soil and water bodies. Nanostructured magnetic iron oxides have proved to be economical and inert materials with good ion-adsorption properties. In fact, magnetic adsorption has demonstrated promising potential for replacing conventional water treatment methods [36]. An inherent drawback of magnetic remediation relies on the impossibility of recycling magnetic nanoparticles of very small size, especially in a continuous flowing system. This problem can be avoided by using an adequate matrix with the ability to encapsulate or contain these particles that can be attracted and separated by a permanent magnet. In addition to this advantage, the matrix can also be useful to protect the magnetic NPs against oxidation [22].
The most frequently found transition metals and metalloids in waste water include arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper, lead, nickel and zinc, all of which can produce illness in human beings and risks for the environment [37]. As a way to evaluate the potential use of the synthesized ME in the removal of metal ions of environmental importance, adsorption measurements with Cu+2 were performed.
As a first test, maximum adsorption values attained after 72 h for E and ME samples were determined. The maximum Cu+2 recovery ratios from an 80 mM solution (5224 ppm) were 8.3 and 42.8 for ME and E samples respectively, whereas for the ME powder, the adsorption was 75.8 mg/g. The higher adsorption capacity of the ME powder compared to the ME in bulk was attributed to the higher surface area of the cryogenically milled material. It is known that the particle size of hydrogels influences directly their adsorption efficiency. Hydrogel microparticles (or microgels) with small volume and large specific surface area [38] have been considered a good option for the preparation of high-efficiency adsorbents. On the other hand, due to their high specific surface area and fast stimulus responsiveness, hydrogel microspheres have been also used as efficient adsorbents [39]. These values are in good agreement with the expected adsorption range for materials with potential applications as adsorbers [40]. Despite the lower swelling capacity of the ME in water compared to the neat elastomer, the best adsorption performance was found for the ME powder, possibly due to the higher available surface area of this material and to the presence of the magnetic iron oxide phase. The selectiveness of magnetite in the adsorption of Cd+2 and Cu+2 ions has been previously explained by the formation of coordinated bonds between Fe and the pollutant [41]. Hence, the affinity of copper ions to the magnetic phase can explain the high efficiency found for these magnetic elastomers.
Removal curves as a function of time were obtained for ME powders in order to determine the efficiency of this material in environments of variable metal ion concentrations. Figure 10a shows the Cu+2 adsorption isotherm, whereas Figure 10b presents the removal of Cu+2 by the ME powder as a function of time at different initial ion concentrations. As clearly observed in Figure 10a, the adsorption process takes place quickly, with the adsorption equilibrium being reached after 2 h of contact between the material and the ion solution. The Qe values varied from 21–79 mg/g, which can be considered an excellent adsorption capacity when compared with other reported adsorbents [40]. In the review of Crini [40], which includes several references from other authors and presents a complete comparison between natural adsorbers, some examples of Qe values for Cu+2 ions were 200 mg/g for alumina/chitosan composites, 21.5 mg/g for activated carbon and 5.1 mg/g for a zeolite sample. Paulino et al. [41] have also used a chitosan hydrogel for Cu+2 adsorption, obtaining Qe values of 90 mg/g at pH = 5 and 25 °C. It is also important to remark that, in all cases, the ME powder was completely recovered from the solution using a permanent magnet.
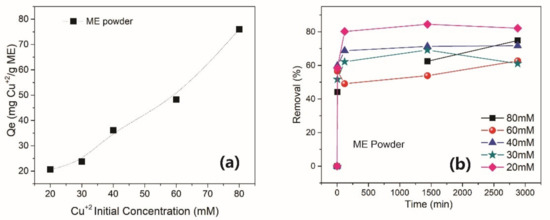
Figure 10.
Adsorption behavior of ME powders: (a) Cu+2 adsorption isotherm (b) Removal % as a function of time for variable concentrations of Cu+2.
4. Conclusions
PEG-based, amphiphilic, low-modulus elastomers with a high gel fraction and affinity to water and organic solvents were fabricated by a simple one-pot synthesis strategy that does not require any solvents. Thanks to the coordinating ability of pendant groups present in the network structure and to the high swelling capacity of the neat elastomers, it was possible to generate magnetic nanocomposites through an in situ coprecipitation procedure that generates magnetic nanoparticles that display superparamagnetic behavior at room temperature. The efficiency of these materials as adsorbents of Cu+2 ions from model aqueous solutions was determined, as well as the possibility of producing magnetic powdered adsorbents that can be easily removed from water bodies using a permanent magnet. The uptake of other types of ions and pollutants is currently under study.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/macromol2030027/s1, Figure S1: DSC scan for the E and the ME obtained. Figure S2: G’, G’’ and tanδ curves obtained for the E and the ME. Figure S3: X-ray diagrams for E, ME and Magnetite/Maghemite phases.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S.G. and C.E.H.; methodology, M.L.A.V.; investigation, M.L.A.V., J.S.G. and C.E.H.; data curation, M.L.A.V.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.A.V.; writing—review and editing, J.S.G. and C.E.H.; project administration, J.S.G. and C.E.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We thank the CONICET (Research Council of Argentina, PUE 22920170100090CO and PIP Nº 0594), Agency I+d+i (PICT18-2309, PICT16-1905) and the UNMdP (15/G524) for financial support of this research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Vanesa Muñoz for TEM images, Andres Torres Nicolini for TGA and DSC measurements and Ulises Casado for helping with the rheology measurements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pascault, J.-P.; Williams, R.J.J. Epoxy Polymers New Materials and Innovations, 1st ed.; Sons, J.W., Ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; ISBN 3527628711. [Google Scholar]
- Auvergne, R.; Caillol, S.; David, G.; Boutevin, B.; Pascault, J.P. Biobased Thermosetting Epoxy: Present and Future. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1082–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascault, J.-P.; Sautereau, H.; Verdu, J.; Williams, R.J.J. Thermosetting Polymers; Dekker, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; Chapter 2; ISBN 0824706706. [Google Scholar]
- Gitsov, I.; Zhu, C. Amphiphilic Hydrogels Constructed by Poly(ethylene glycol) and Shape-Persistent Dendritic Fragments. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8418–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchet, J.; Pascault, J.P. Do Epoxy-Amine Networks Become Inhomogeneous at the Nanometric Scale? J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 2422–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Hard, C.; Lin, C.; Gitsov, I. Novel Materials for Bioanalytical and Biomedical Applications: Environmental Response and Binding/Release Capabilities of Amphiphilic Hydrogels with Shape-Persistent Dendritic Junctions. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 4017–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tess, R.W. Epoxy Resins Chemistry and Technology; May, C.A., Dekker, M., Eds.; Springer Science: New York, NY, USA, 1988; ISBN 1351449966. [Google Scholar]
- Ledo-Suárez, A.; Puig, J.; Zucchi, I.A.; Hoppe, C.E.; Gómez, M.L.; Zysler, R.; Ramos, C.; Marchi, M.C.; Bilmes, S.A.; Lazzari, M.; et al. Functional Nanocomposites Based on the Infusion or in Situ Generation of Nanoparticles into Amphiphilic Epoxy Gels. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 10135–10145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, J.; Zucchi, I.A.; Hoppe, C.E.; Ṕerez, C.J.; Galante, M.J.; Williams, R.J.J.; Rodríguez-Abreu, C. Epoxy Networks with Physical Cross-Links Produced by Tail-to-Tail Associations of Alkyl Chains. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 9344–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, A.Y.; Qiao, G.G.; Solomon, D.H. Interpenetrating Amphiphilic Polymer Networks of Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) and Poly(ethylene oxide). Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 5650–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naga, N.; Sato, M.; Mori, K.; Nageh, H.; Nakano, T. Synthesis of Network Polymers by Means of Addition Reactions of Multifunctional-Amine and Poly(ethylene glycol) Diglycidyl Ether or Diacrylate Compounds. Polymers 2020, 12, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin-Gibson, S.; Bencherif, S.; Cooper, J.A.; Wetzel, S.J.; Antonucci, J.M.; Vogel, B.M.; Horkay, F.; Washburn, N.R. Synthesis and Characterization of PEG Dimethacrylates and Their Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocke, N.A.; Zhang, X.; Hilt, J.Z.; DeRouchey, J.E. Transport in PEG-Based Hydrogels: Role of Water Content at Synthesis and Crosslinker Molecular Weight. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2017, 218, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirkiai, A.; Abrisham, M.; Panahi-Sarmad, M.; Xiao, X.; Alimardani, A.; Sadri, M. Tracing Evolutions of Elastomeric Composites in Shape Memory Actuators: A Comprehensive Review. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 102658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, J.; Koch, K.; Hess, M.; Schmidt, A.M. Magneto-Mechanical Coupling of Single Domain Particles in Soft Matter Systems. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2020. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, J.; Hoppe, C.E.; Fasce, L.A.; Pérez, C.J.; Piñeiro-Redondo, Y.; Bañobre-López, M.; López-Quintela, M.A.; Rivas, J.; Williams, R.J.J. Superparamagnetic Nanocomposites Based on the Dispersion of Oleic Acid-Stabilized Magnetite Nanoparticles in a Diglycidylether of Bisphenol A-Based Epoxy Matrix: Magnetic Hyperthermia and Shape Memory. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 13421–13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, A.K.; Ang, E.; Paudel, M.; Li, L. Soft Hybrid Magnetorheological Elastomer: Gap Bridging between MR Fluid and MR Elastomer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 583, 123975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, Fabrication and Control of Soft Robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Bai, H.; Shepherd, R.F.; Zhao, H. Bio-inspired Design and Additive Manufacturing of Soft Materials Machines Robots and Haptic Interfaces. Angew. Chem. 2019, 58, 11182–11204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.S.; Hoppe, C.E.; Williams, R.J.J. Elastomers Obtained by Crosslinking of α,ω-Bis(Glycidylether) Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) as Versatile Platforms for Functional Materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 87, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, M.F.; Pizzano, A.; Spetter, C.; Lassalle, V. Magnetic Nanotechnological Devices as Efficient Tools to Improve the Quality of Water: Analysis on a Real Case. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28185–28194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areal, M.P.; Arciniegas, M.L.; Horst, F.; Lassalle, V.; Sánchez, F.H.; Alvarez, V.A.; Gonzalez, J.S. Water Remediation: PVA-Based Magnetic Gels as Efficient Devices to Heavy Metal Removal. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3129–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.M.; Ollier, R.P.; Gonzalez, J.S.; Alvarez, V.A. Nanocomposite Materials for Dyes Removal; Hussain, C.M., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 9780128133514. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, R.M.; Freeman, J.J.; Lytle, F.W. Characterization of Cu Al2O3 Catalysts. J. Catal. 1978, 55, 10–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.J.; Kong, F.M.; Walkup, C.M. Structure-Property Relations of Polyethertriamine-Cured Bisphenol-A-Diglycidyl Ether Epoxies. Polymers 1984, 25, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Bauer, R.S. Curing Reactions. In Epoxy Resins; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 285–463. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez Gonzalez, M.; Cabanelas, J.C.; Baselga, J. Applications of FTIR on Epoxy Resins-Identification, Monitoring the Curing Process, Phase Separation and Water Uptake. In Infrared Spectroscopy: Materials Science, Engineering and Technology; Theophile, T., Ed.; National Technical University of Athens: Athens, Greece, 2012; pp. 261–284. [Google Scholar]
- Linde, E.; Giron, N.H.; Celina, M.C. Water Diffusion with Temperature Enabling Predictions for Sorption and Transport Behavior in Thermoset Materials; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 153, ISBN 5058449781. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, A.F. CRC Handbook of Solubility Parameters and Other Cohesion Parameters, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781315140575. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, T.; Kim, J.H.; Yang, H.M.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, J.D. Formation Pathways of Magnetite Nanoparticles by Coprecipitation Method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 6069–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.S.; Hoppe, C.E.; Zélis, P.M.; Arciniegas, L.; Pasquevich, G.A.; Sánchez, F.H.; Alvarez, V.A. Simple and Efficient Procedure for the Synthesis of Ferrogels Based on Physically Cross-Linked PVA. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivudu, K.S.; Rhee, K.Y. Preparation and Characterization of PH-Responsive Hydrogel Magnetite Nanocomposite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 349, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, D. Chitosan-Induced Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles via Iron Ions Assembly. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.; Namdeo, M.; Mohan, Y.M.; Bajpai, S.K.; Bajpai, M. Review on Polymer, Hydrogel and Microgel Metal Nanocomposites: A Facile Nanotechnological Approach. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 45, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katime, I.; Rodríguez, E. Absorption of Metal Ions and Swelling Properties of Poly(Acrylic Acid-Co-Itaconic Acid) Hydrogels. J. Macromol. Sci.-Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 38 A, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wei, S.; Chen, M.; Gu, H.; Rapole, S.B.; Pallavkar, S.; Ho, T.C.; Hopper, J.; Guo, Z. Magnetic Nanocomposites for Environmental Remediation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, K.; Kumar, V.; Choudhary, S.; Mankotia, P.; Kumar, B.; Mishra, H.; Moulick, A.; Ekielski, A.; et al. A Review of Adsorbents for Heavy Metal Decontamination: Growing Approach to Wastewater Treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Z.; You, L.Q.; Wei, H.L.; Wang, G.F.; Chu, H.J.; Zhu, J.; He, J. Preparation and Characterization of PH-Sensitive Hydrogel Microspheres Based on Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chu, H.; Wei, H.; Zhu, H.; Wang, G.; Zhu, J.; He, J. Facile Fabrication of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium/Graphene Oxide Hydrogel Microparticles for Water Purification. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50061–50069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Recent Developments in Polysaccharide-Based Materials Used as Adsorbents in Wastewater Treatment. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 38–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, A.T.; Belfiore, L.A.; Kubota, L.T.; Muniz, E.C.; Almeida, V.C.; Tambourgi, E.B. Effect of Magnetite on the Adsorption Behavior of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Cu(II) in Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Desalination 2011, 275, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).