The Case of a Patient with Limited Systemic Sclerosis and Interstitial Lung Disease Overlapping with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
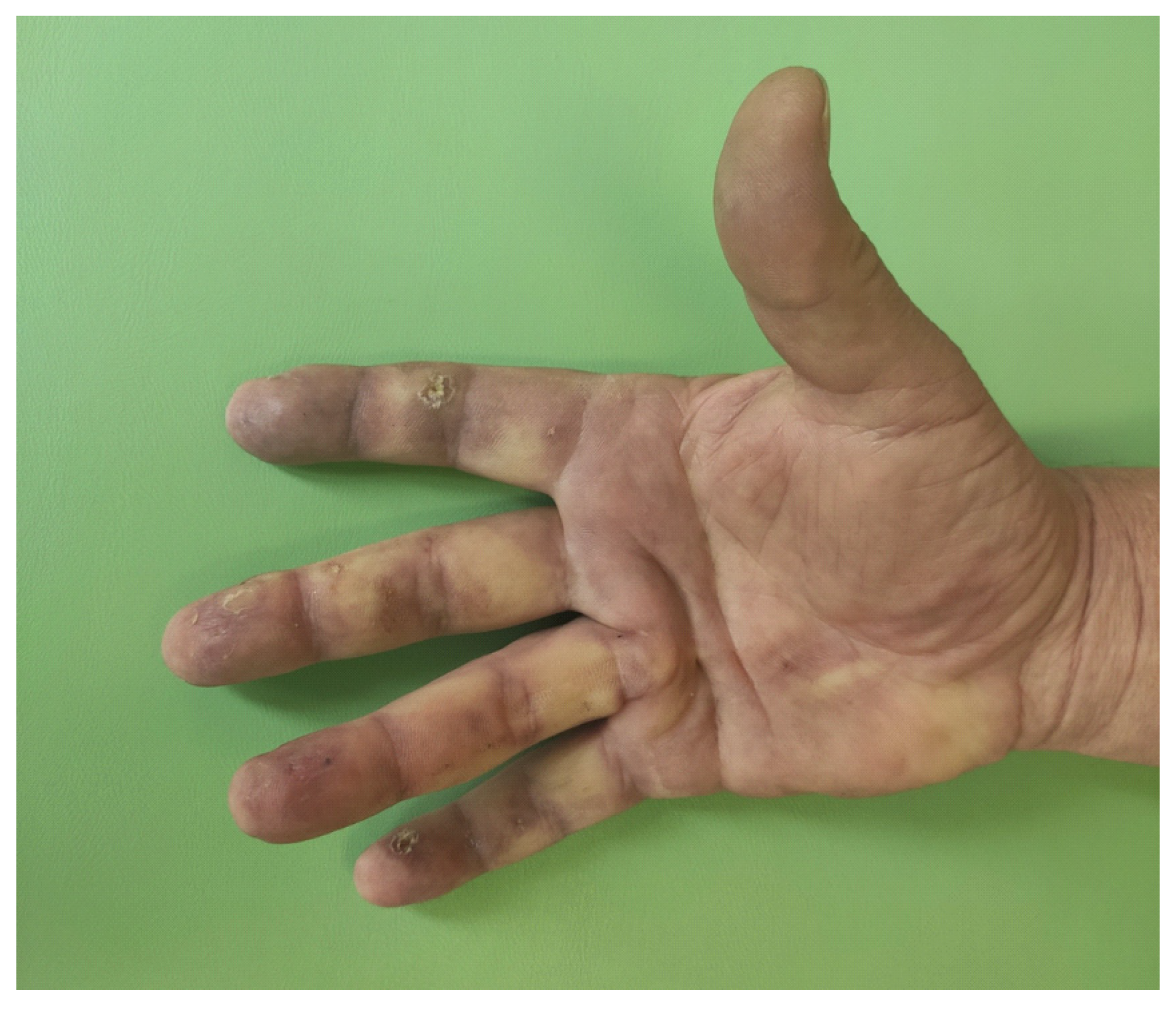
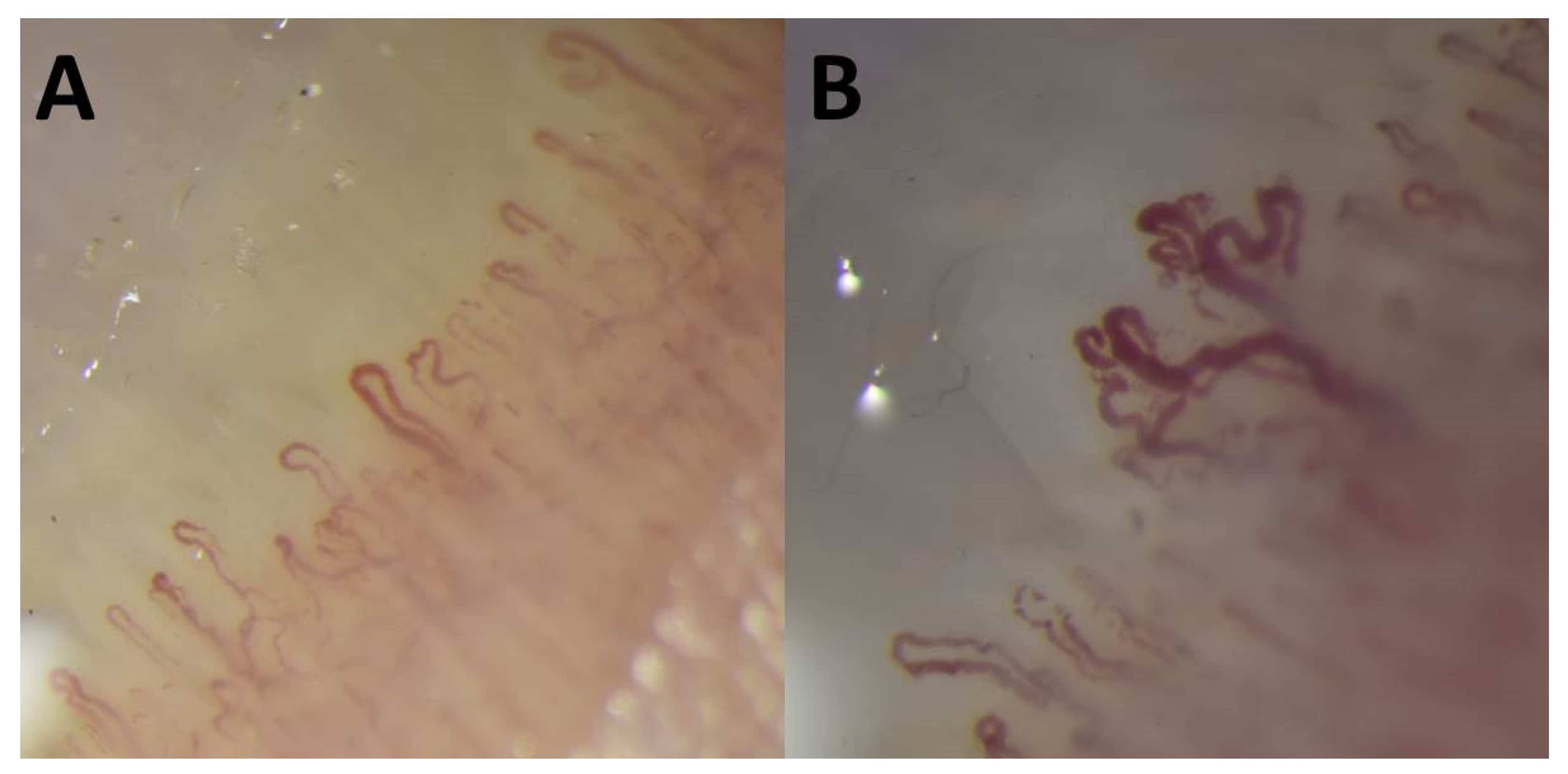
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelas, A.; Arrossi, A.V.; Highland, K.B. Pulmonary Manifestations of Systemic Sclerosis and Mixed Connective Tissue Disease. Clin. Chest Med. 2019, 40, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelas, A.; Silver, R.M.; Arrossi, A.V.; Highland, K.B. Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwee, T.C.; Kwee, R.M. Chest CT in COVID-19: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Radiographics 2020, 40, 1848–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestall, J.C.; Paul, E.A.; Garrod, R.; Garnham, R.; Jones, P.W.; Wedzicha, J.A. Usefulness of the Medical Research Council (MRC) dyspnoea scale as a measure of disability in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 1999, 54, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Furst, D.E.; Clements, P.J.; Allanore, Y.; Baron, M.; Czirjak, L.; Distler, O.; Foeldvari, I.; Kuwana, M.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; et al. Standardization of the modified Rodnan skin score for use in clinical trials of systemic sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2017, 2, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; du Bois, R. Interstitial lung disease in connective tissue disorders. Lancet 2012, 380, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.; Aalokken, T.M.; Gunther, A.; Mynarek, G.K.; Garen, T.; Lund, M.B.; Molberg, Ø. Pulmonary involvement in the antisynthetase syndrome: A comparative cross-sectional study. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fenlon, H.M.; Doran, M.; Sant, S.M.; Breatnach, E. High-resolution chest CT in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 166, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Rochwerg, B.; Zhang, Y.; Garcia, C.A.C.; Azuma, A.; Behr, J.; Brozek, J.; Collard, H.R.; Cunningham, W.; Homma, S.; et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline: Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An update of the 2011 clinical practice guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, e3–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Koyama, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Seki, S. State-of-the-art imaging of the lung for connective tissue disease (CTD). Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2015, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capobianco, J.; Grimberg, A.; Thompson, B.M.; Antunes, V.B.; Jasinowodolinski, D.; Meirelles, G.S. Thoracic manifestations of collagen vascular diseases. Radiographics 2012, 32, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Bruni, C.; Allanore, Y.; Clementi, M.; Dagna, L.; Damjanov, N.S.; de Paulis, A.; Distler, O.; Fox, D.; Furst, D.E.; et al. Systemic sclerosis and the COVID-19 pandemic: World Scleroderma Foundation preliminary advice for patient management. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, V.K.; Wirz, E.G.; Allanore, Y.; Rossbach, P.; Riemekasten, G.; Hachulla, E.; Distler, O.; Airò, P.; Carreira, P.E.; Balbir Gurman, A.; et al. Incidences and Risk Factors of Organ Manifestations in the Early Course of Systemic Sclerosis: A Longitudinal EUSTAR Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamasco, A.; Hartmann, N.; Wallace, L.; Verpillat, P. Epidemiology of systemic sclerosis and systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, A.; Davidyock, T.; Ferguson, L.T.; Ieong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Simms, R.W. Changes in forced vital capacity over time in systemic sclerosis: Application of group-based trajectory modelling. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, E.R. Natural History of Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: How to Identify a Progressive Fibrosing Phenotype. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2020, 5, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamanos, Y.; Tsifetaki, N.; Voulgari, P.V.; Siozos, C.; Tsamandouraki, K.; Alexiou, G.A.; Drosos, A.A. Epidemiology of systemic sclerosis in northwest Greece 1981 to 2002. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 34, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalles-Bonilla, J.G.; Martínez-Barrio, J.; López-Longo, F.; de la Torre, I.; González, C.; Valor, L.; Montoro-Άlvarez, M.; Aramburu, F.; Marín, C.; Martínez-Estupiñán, L.; et al. Survival, causes of death and mortality risk factors in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 71, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, J.; Popa-Diaconu, D.; Hesselstrand, R.; Carreira, P.; Valentini, G.; Beretta, L.; Airo, P.; Inanc, M.; Ullman, S.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; et al. Clinical prediction of 5-year survival in systemic sclerosis: Validation of a simple prognostic model in EUSTAR centres. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1788–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyndall, A.J.; Bannert, B.; Vonk, M.; Airò, P.; Cozzi, F.; Carreira, P.E.; Bancel, D.F.; Allanore, Y.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Distler, O.; et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: A study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Nagaraja, V.; Tseng, C.H.; Abtin, F.; Suh, R.; Kim, G.; Wells, A.; Furst, D.E.; Clements, P.J.; Roth, M.D.; et al. Predictors of lung function decline in scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease based on high-resolution computed tomography: Implications for cohort enrichment in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease trials. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Brown, M.; Elashoff, F.; Li, G.; Gjertson, D.W.; Lynch, D.A.; Strollo, D.C.; Kleerup, E.; Chong, D.; Shah, S.K.; et al. Quantitative texture-based assessment of one-year changes in fibrotic reticular patterns on HRCT in scleroderma lung disease treated with oral cyclophosphamide. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldin, J.G.; Kim, G.H.; Tseng, C.-H.; Volkmann, E.; Furst, D.; Clements, P.; Brown, M.; Roth, M.; Khanna, D.; Tashkin, D.P. Longitudinal changes in quantitative interstitial lung disease on computed tomography after immunosuppression in the Scleroderma Lung Study II. Ann. Am. Thorac Soc. 2018, 15, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, D.K.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, R. Post COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis- Is it reversible? Indian J. Tuberc. 2020, 68, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assassi, S.; Sharif, R.; Lasky, R.E.; McNearney, T.A.; Estrada-Y-Martin, R.M.; Draeger, H.; Nair, D.K.; Fritzler, M.J.; Reveille, J.D.; Arnett, F.C.; et al. Predictors of interstitial lung disease in early systemic sclerosis: A prospective longitudinal study of the GENISOS cohort. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domsic, R.T. Scleroderma: The role of serum autoantibodies in defining specific clinical phenotypes and organ system involvement. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2014, 26, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lauretis, A.; Sestini, P.; Pantelidis, P.; Hoyles, R.; Hansell, D.M.; Goh, N.S.; Zappala, C.J.; Visca, D.; Maher, T.M.; Denton, C.P.; et al. Serum interleukin 6 is predictive of early functional decline and mortality in interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mayes, M.D.; Pedroza, C.; Draeger, H.T.; Gonzalez, E.B.; Harper, B.E.; Reveille, J.D.; Assassi, S. Does C-reactive protein predict the long-term progression of interstitial lung disease and survival in patients with early systemic sclerosis? Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schupp, J.; Becker, M.; Günther, J.; Müller-Quernheim, J.; Riemekasten, G.; Prasse, A. Serum CCL18 is predictive for lung disease progression and mortality in systemic sclerosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1530–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiev, K.P.; Hua-Huy, T.; Kettaneh, A.; Gain, M.; Duong-Quy, S.; Tolédano, C.; Cabane, J.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T. Serum CC chemokine ligand-18 predicts lung disease worsening in systemic sclerosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann-Vold, A.-M.; Tennoe, A.H.; Garen, T.; Midtvedt, Ø.; Abraityte, A.; Aaløkken, T.M.; Lund, M.B.; Brunborg, C.; Aukrust, P.; Ueland, T.; et al. High level of chemokine CCL18 is associated with pulmonary function deterioration, lung fibrosis progression, and reduced survival in systemic sclerosis. Chest 2016, 150, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bon, L.; Affandi, A.J.; Broen, J.; Christmann, R.B.; Marijnissen, R.J.; Stawski, L.; Farina, G.A.; Stifano, G.; Mathes, A.L.; Cossu, M.; et al. Proteome-wide analysis and CXCL4 as a biomarker in systemic sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, G.A.; Kuwana, M.; Wu, M.; Estrada-Y-Martin, R.M.; Ying, J.; Charles, J.; Mayes, M.D.; Assassi, S. KL-6 but not CCL-18 is a predictor of early progression in systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, M.; Shirai, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Elevated serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 in early disease predicts subsequent deterioration of pulmonary function in patients with systemic sclerosis and interstitial lung disease. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabati, E.; Dehghani-Samani, A.; Mortazavimoghaddam, S.G. Association of COVID-19 and other viral infections with interstitial lung diseases, pulmonary fibrosis, and pulmonary hypertension: A narrative review. Can. J. Respir. Ther. 2020, 56, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, K.M.; Raghu, G.; Tzilas, V.; Bouros, D. Management of patients with interstitial lung disease in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. Respiration 2020, 99, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.W.; Fidler, L.; Marcoux, V.; Johannson, K.A.; Assayag, D.; Fisher, J.H.; Hambly, N.; Kolb, M.; Morisset, J.; Shapera, S.; et al. Practical considerations for the diagnosis and treatment of fibrotic interstitial lung disease during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Chest 2020, 158, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Papa, N.; Sambataro, G.; Minniti, A.; Maglione, W.; Pignataro, F.; Caminati, A.; Harari, S.; Sambataro, D.; Vitali, C.; Caporali, R.F. Impact of COVID-19 outbreak in an Italian cohort of patients with systemic sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2020, 12, 1759720X20953356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, T.M.; Docherty, A.B.; Harrison, E.M.; Quint, J.K.; Adamali, H.; Agnew, S.; Babu, S.; Barber, C.M.; Barratt, S.; Bendstrup, E. Outcome of Hospitalization for COVID-19 in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. An International Multicenter Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.S.; Zheng, J.P.; Mok, Y.W.; Li, Y.M.; Liu, Y.N.; Chu, C.M.; Ip, M.S. SARS: Prognosis, outcome and sequelae. Respirology 2003, 8, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.G. SARS Coronavirus and Lung Fibrosis. In Molecular Biology of the SARS-Coronavirus; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 247–258. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, B.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhao, H.; Chen, W. Dynamic changes of serum SARS-coronavirus IgG, pulmonary function and radiography in patients recovering from SARS after hospital discharge. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Han, N.; Ju, J.; Kou, Y.; Chen, L.; Jiang, M.; Pan, F.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Long-term bone and lung consequences associated with hospital-acquired severe acute respiratory syndrome: A 15-year follow-up from a prospective cohort study. Bone Res. 2020, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caso, F.; Costa, L.; Ruscitti, P.; Navarini, L.; Del Puente, A.; Giacomelli, R.; Scarpa, R. Could Sars-coronavirus-2 trigger autoimmune and/or autoinflammatory mechanisms in genetically predisposed subjects? Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani Cardoso, E.; Hundal, J.; Feterman, D.; Magaldi, J. Concomitant new diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus and COVID-19 with possible antiphospholipid syndrome. Just a coincidence? A case report and review of intertwining pathophysiology. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2811–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, S.; Xia, P.; Cao, W.; Jiang, W.; Chen, H.; Ding, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Coagulopathy and Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, R.Z.; Rio, A.P.T.D.; Reis, F. COVID-19 overlapping with systemic sclerosis. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop 2020, 53, e20200450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fineschi, S. Case Report: Systemic Sclerosis After COVID-19 Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 686699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, S.; Gonakoti, S.; Asemota, I.R.; Mba, B. A case of systemic lupus erythematosus flare triggered by severe coronavirus disease 2019. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 26, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Kaneko, Y.; Oshige, T. Exacerbation of immune thrombocytopaenia triggered by COVID-19 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 80, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, A.; Vyas-Lahar, A.; Rella, V.; Rudinskaya, A. Severe refractory thrombocytopenia in a woman positive for coronavirus disease 2019 with lupus and antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 2020, 29, 1472–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonometti, R.; Sacchi, M.C.; Stobbione, P.; Lauritano, E.C.; Tamiazzo, S.; Marchegiani, A.; Novara, E.; Molinaro, E.; Benedetti, I.; Massone, L.; et al. The first case of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) triggered by COVID-19 infection. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 9695–9697. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.Z.; Rogers, S.; Fatima, A.; Dawe, M.; Singh, R. A Flare of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease After COVID-19 Infection: A Case of Lupus Cerebritis. Cureus 2021, 13, e16104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, B.; Moeini Taba, S.M.; Shayestehpour, M. Systemic lupus erythematosus manifestation following COVID-19: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Paredes, J.L.; Niewold, T.B. COVID-19 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Lessons learned from the inflammatory disease. Transl. Res. 2021, 232, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami Fath, M.; Jahangiri, A.; Ganji, M.; Sefid, F.; Payandeh, Z.; Hashemi, Z.S.; Pourzardosht, N.; Hessami, A.; Mard-Soltani, M.; Zakeri, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Proteome Harbors Peptides Which Are Able to Trigger Autoimmunity Responses: Implications for Infection, Vaccination, and Population Coverage. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 705772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.; Anver, H.; Lwin, M.; Holroyd, C.; Faust, S.N.; Edwards, C.J. Lupus, vaccinations and COVID-19: What we know now. Lupus 2021, 30, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tale, S.; Ghosh, S.; Meitei, S.P.; Kolli, M.; Garbhapu, A.K.; Pudi, S. Post-COVID-19 pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis. QJM 2020, 113, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nune, A.; Iyengar, K.P.; Ish, P.; Varupula, B.; Musat, C.A.; Sapkota, H.R. Emergence of new onset SLE following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. QJM 2021, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, M.; Summer, R.; Roman, J. Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease as a Sequela of COVID-19 Pneumonia. Am. J. Med. Sci 2021, 361, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udwadia, Z.F.; Koul, P.A.; Dhooria, S. The impact of COVID-19 on patients with preexisting interstitial lung disease: High mortality in these high-risk patients. Lung India. 2021, 38, S1–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathar Hussain, M.R.; Kulasekaran, N.; Anand, A.M.; Danassegarane, P.R. COVID-19 causing acute deterioration of interstitial lung disease: A case report. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
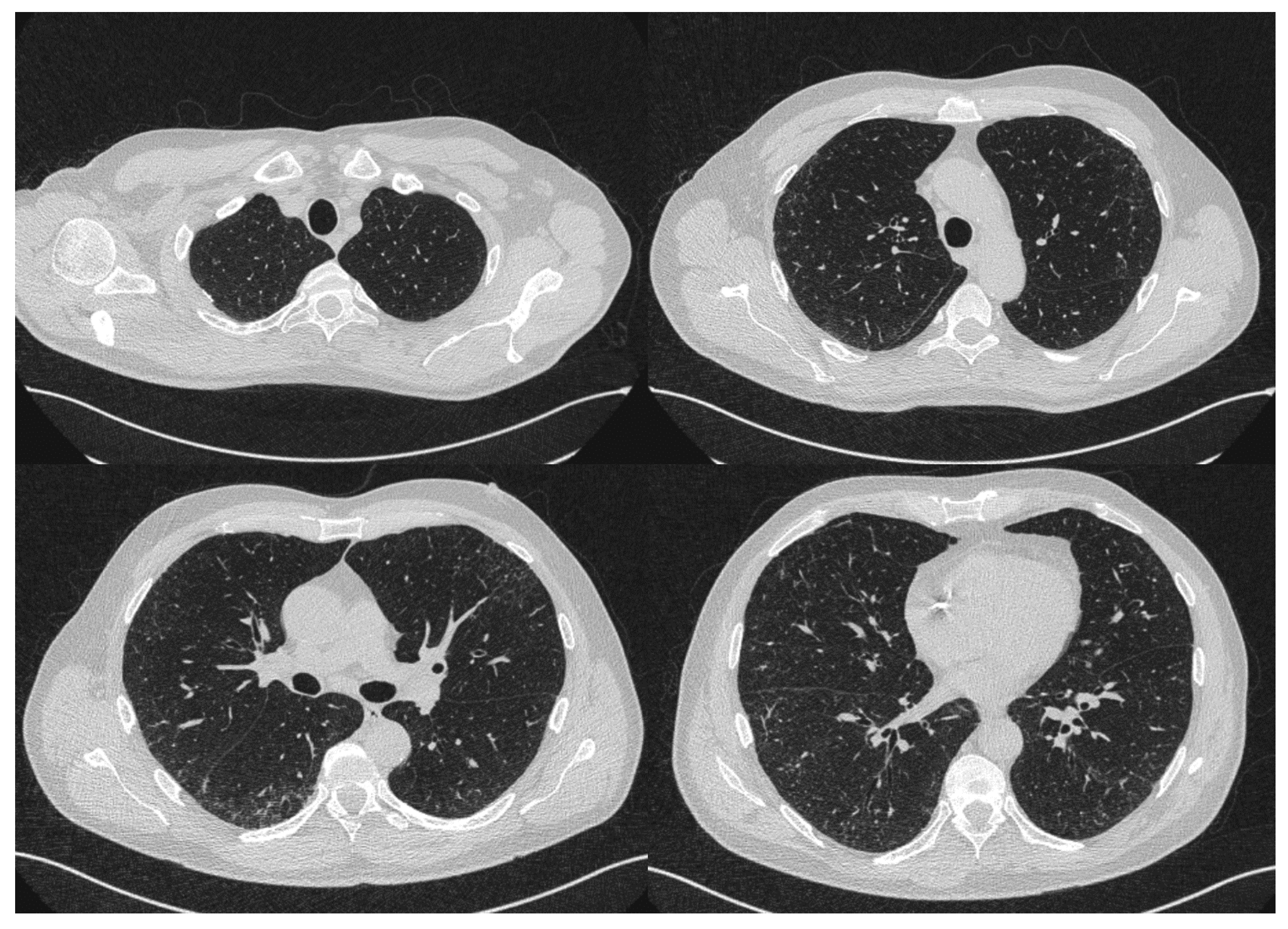
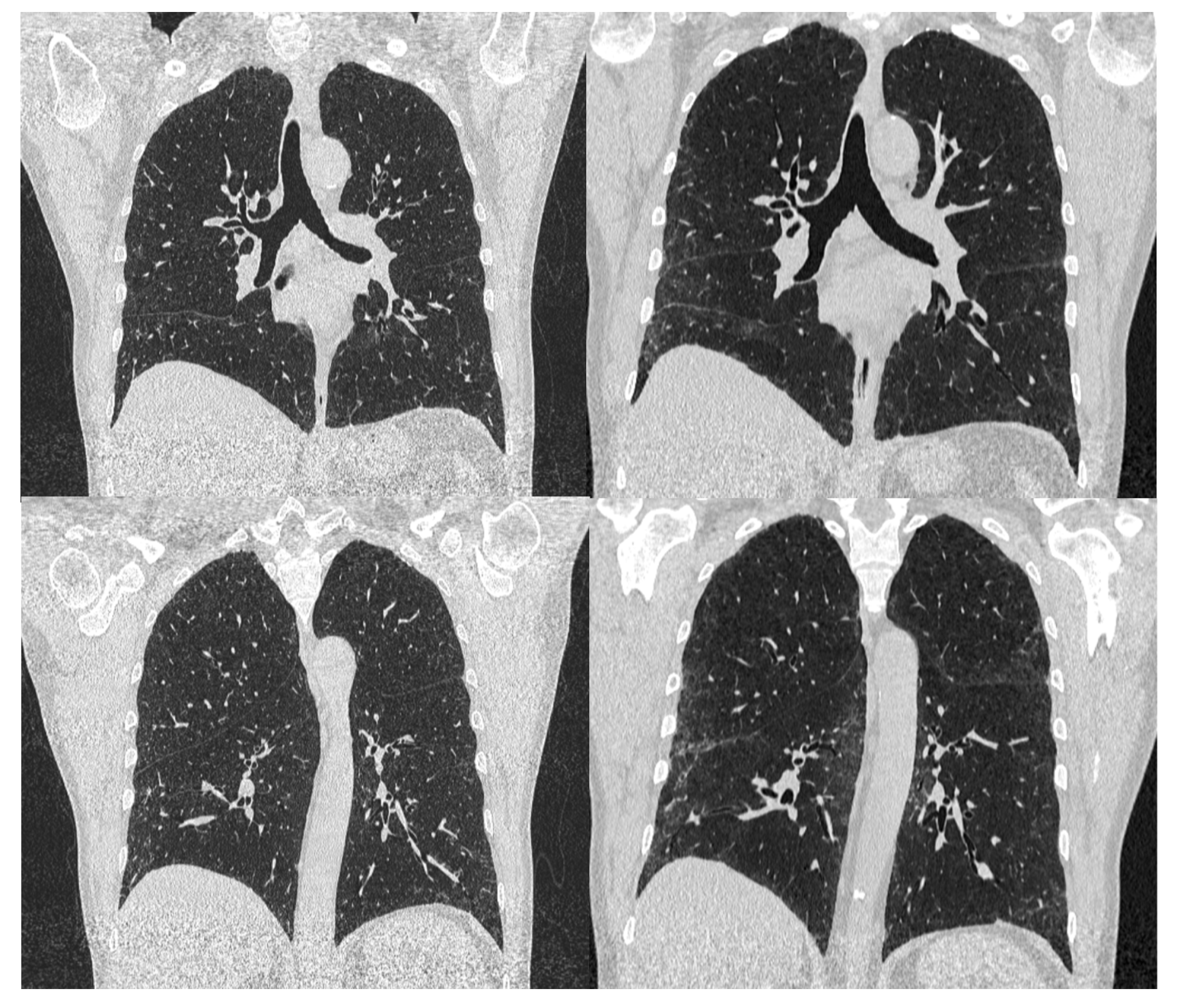
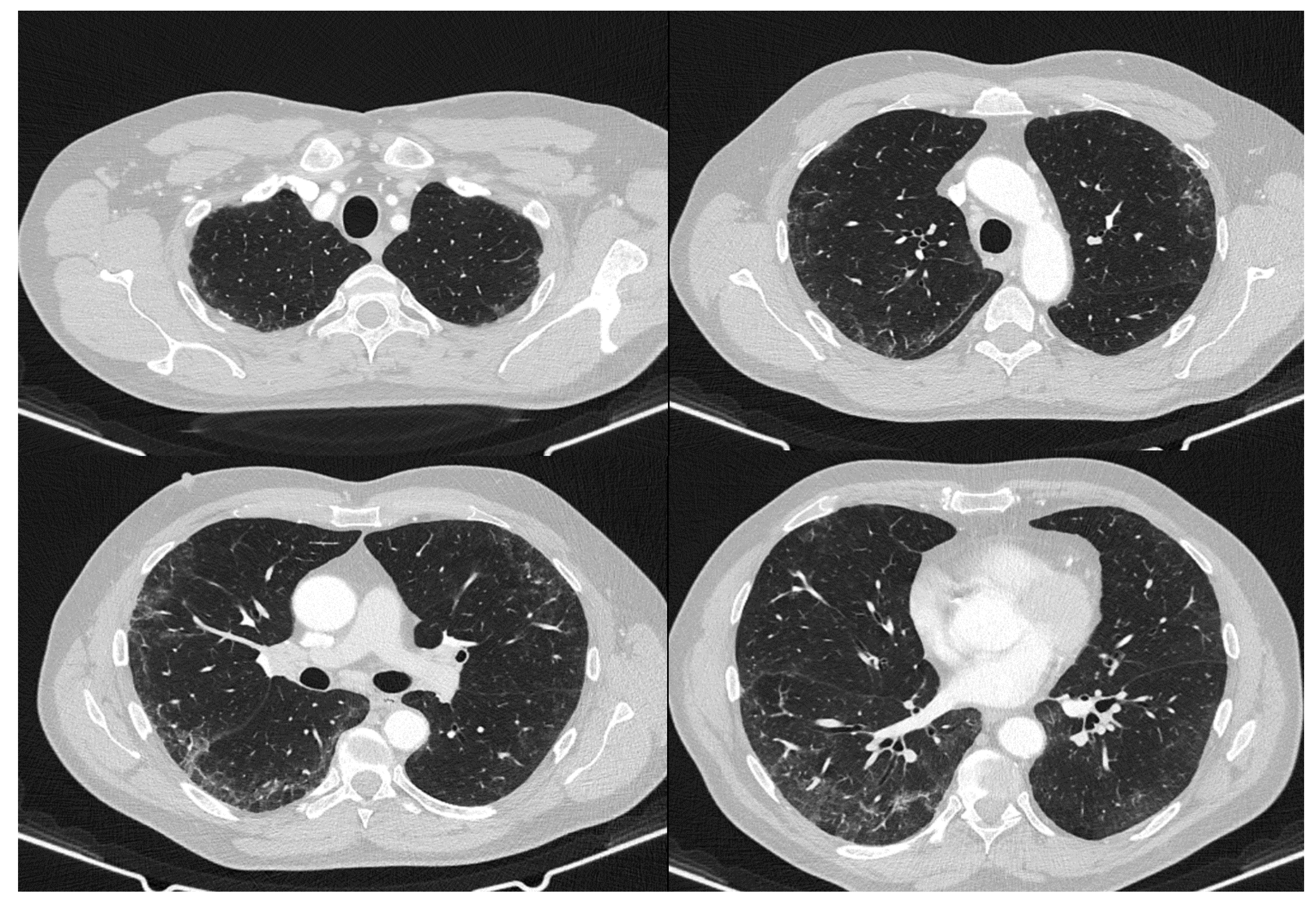
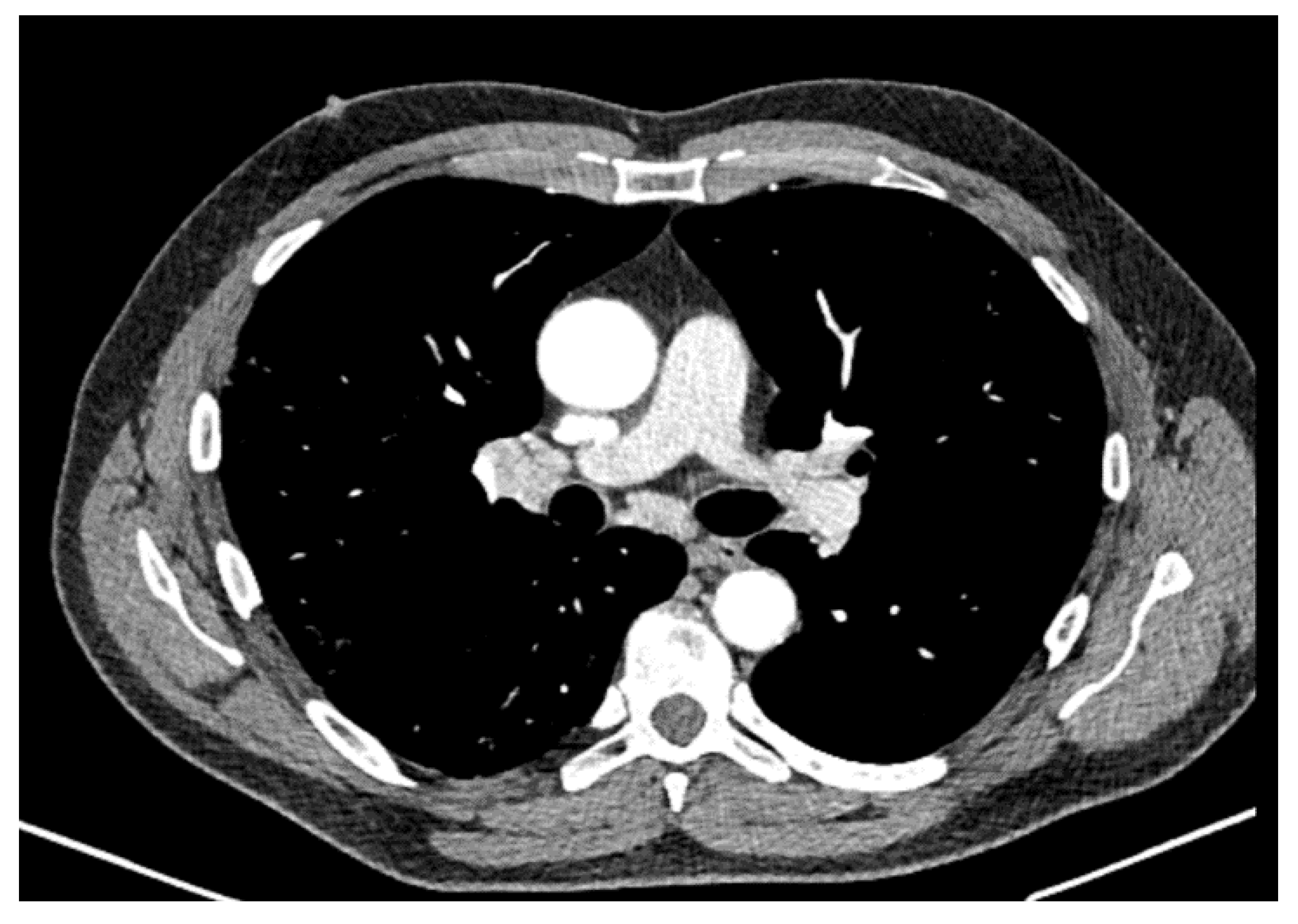

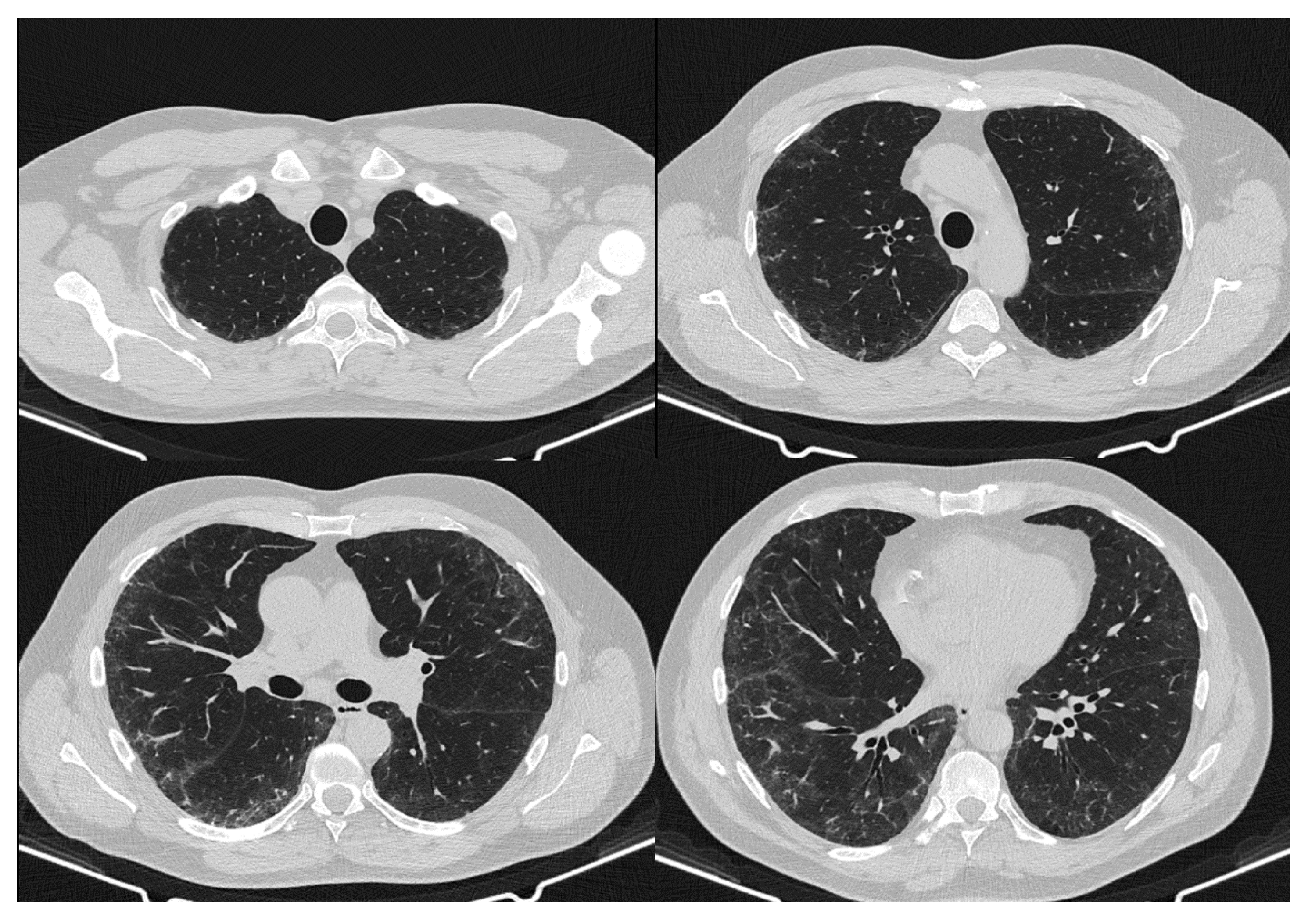
| May 2020 | September 2020 | February 2021 | Reference Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FVC% | 102.8 | 105 | 88.5 | 80–120 |
| TLC% | 127 | 113 | 103 | 80–120 |
| DLCO% | 86 | 93 | 77 | >60–<120 |
| EULAR ACR 2013 Classification Criteria for Systemic Sclerosis (For a Definite Classification a Total Score Greater than or Equal to 9 Is Needed) | EULAR ACR 2018 Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (For a Definite Classification a Total Score of 10 or More Is Needed if Entry Criterion Has Been Fulfilled) |
|---|---|
| Digital tip ulcers | Antinuclear antibodies at a titer of ≥1:80 on HEp-2 cells |
| Abnormal nailfold capillaries | Chilblain lupus erythematosus |
| Puffy fingers | Proteinuria > 0.5 g/24 h |
| Interstitial lung disease (ILD) | Anti-B2GP1 antibodies |
| Raynaud’s phenomenon | Low C4 |
| The patient has a total score of 11 | The patient has a total score of 13 and fulfills the entry criterion |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krawczyk, K.; Mazur, E.; Kargol, J.; Kijowski, R.; Reich, A. The Case of a Patient with Limited Systemic Sclerosis and Interstitial Lung Disease Overlapping with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Dermato 2021, 1, 59-70. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato1020009
Krawczyk K, Mazur E, Kargol J, Kijowski R, Reich A. The Case of a Patient with Limited Systemic Sclerosis and Interstitial Lung Disease Overlapping with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Dermato. 2021; 1(2):59-70. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato1020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrawczyk, Karolina, Ewelina Mazur, Jaromir Kargol, Robert Kijowski, and Adam Reich. 2021. "The Case of a Patient with Limited Systemic Sclerosis and Interstitial Lung Disease Overlapping with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" Dermato 1, no. 2: 59-70. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato1020009
APA StyleKrawczyk, K., Mazur, E., Kargol, J., Kijowski, R., & Reich, A. (2021). The Case of a Patient with Limited Systemic Sclerosis and Interstitial Lung Disease Overlapping with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Dermato, 1(2), 59-70. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato1020009







