The Expanding Threat of Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever Virus: Role of Migratory Birds and Climate Change as Drivers of Hyalomma spp. Dispersal in Europe
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
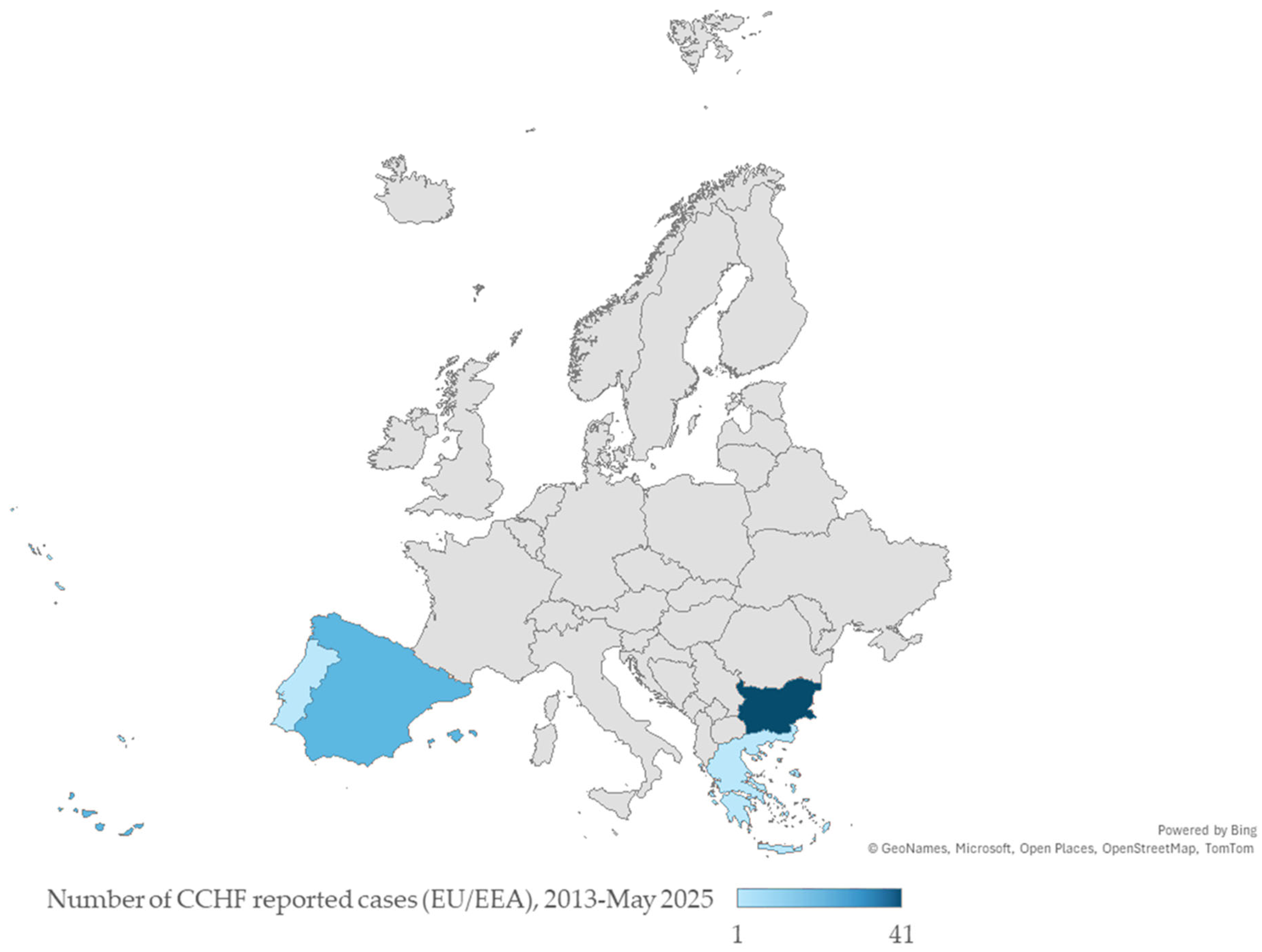
3. Evidence of Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever Virus (CCHFV) in Europe
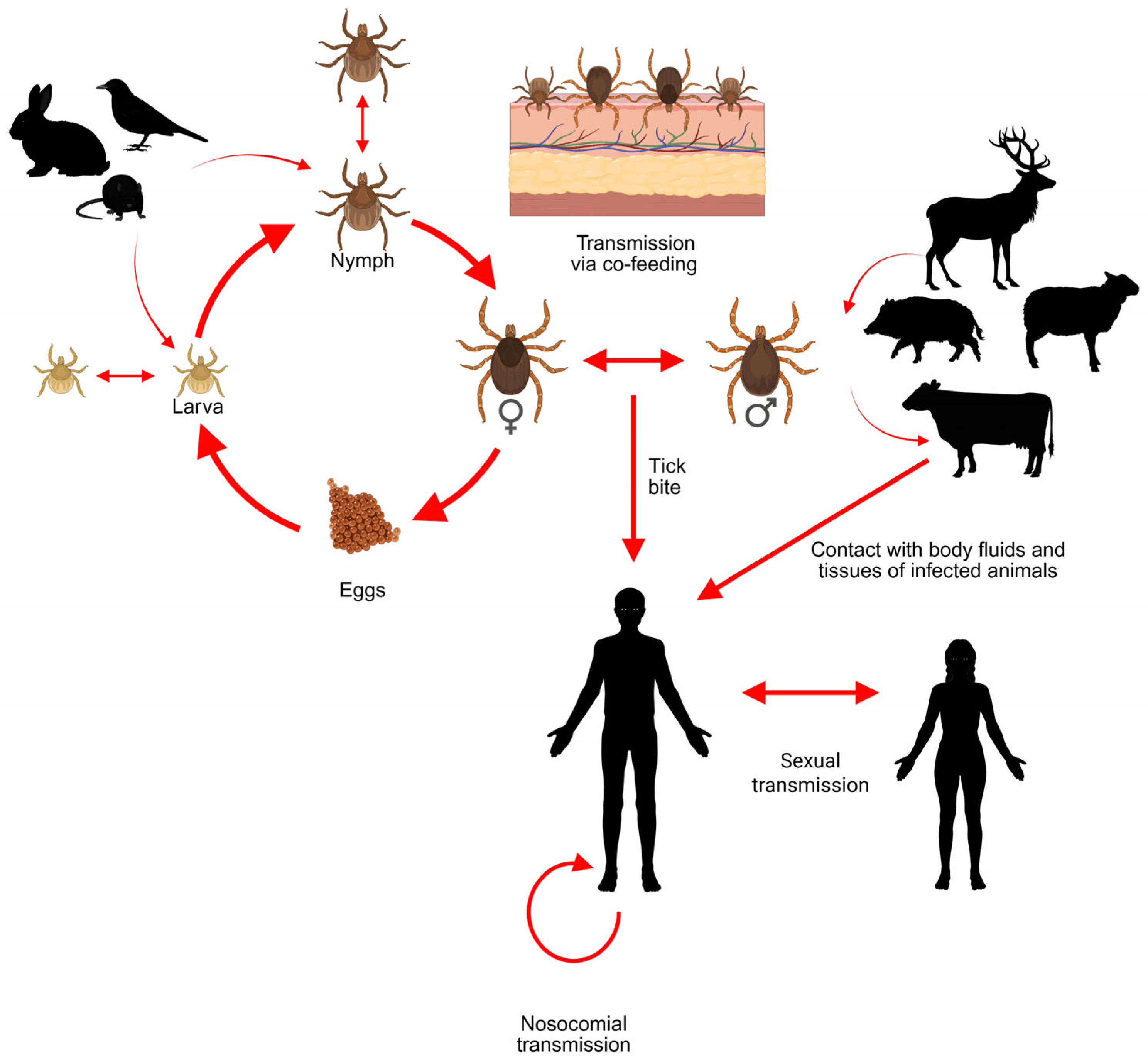
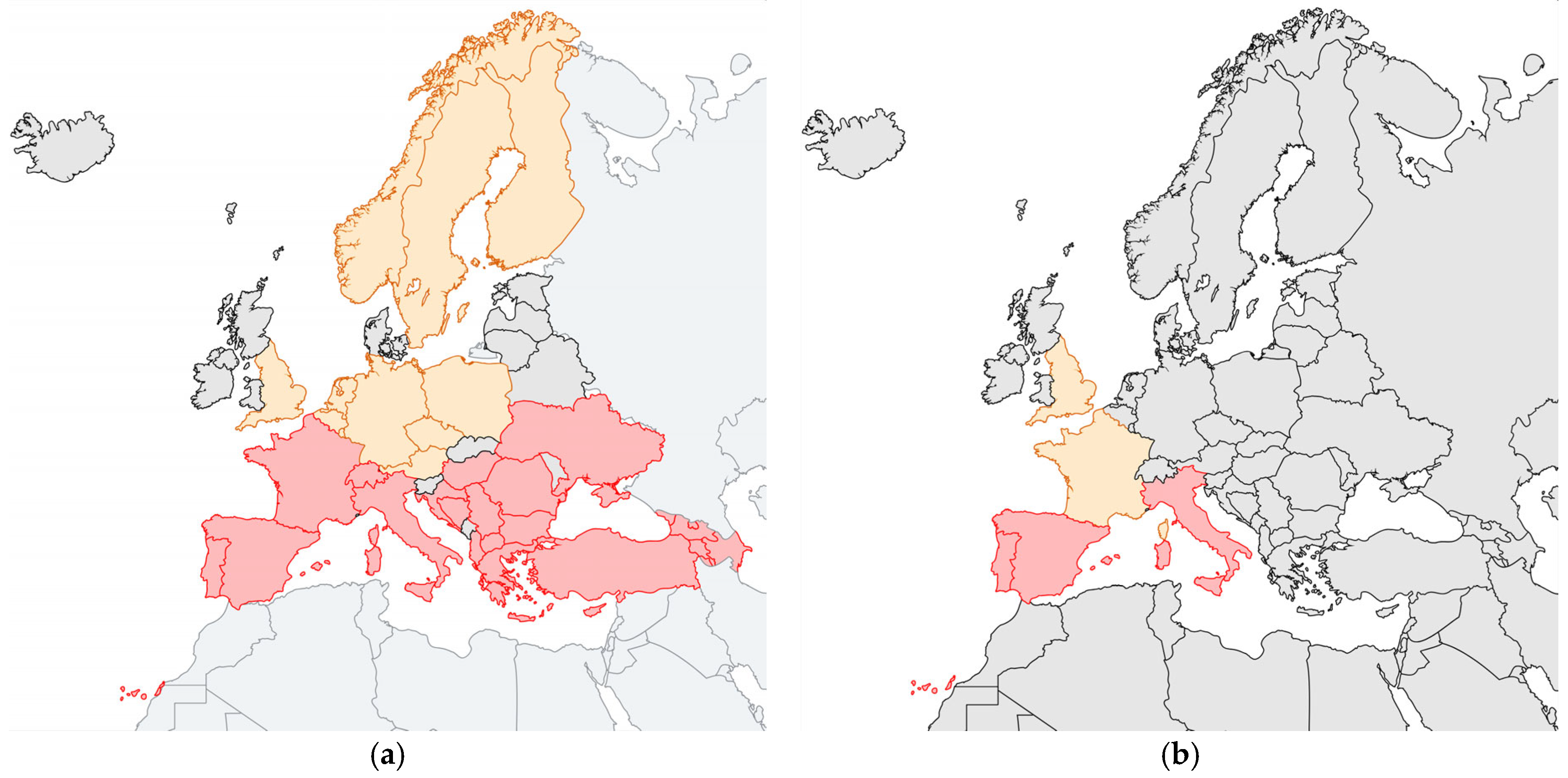
4. Hyalomma Ticks in Europe
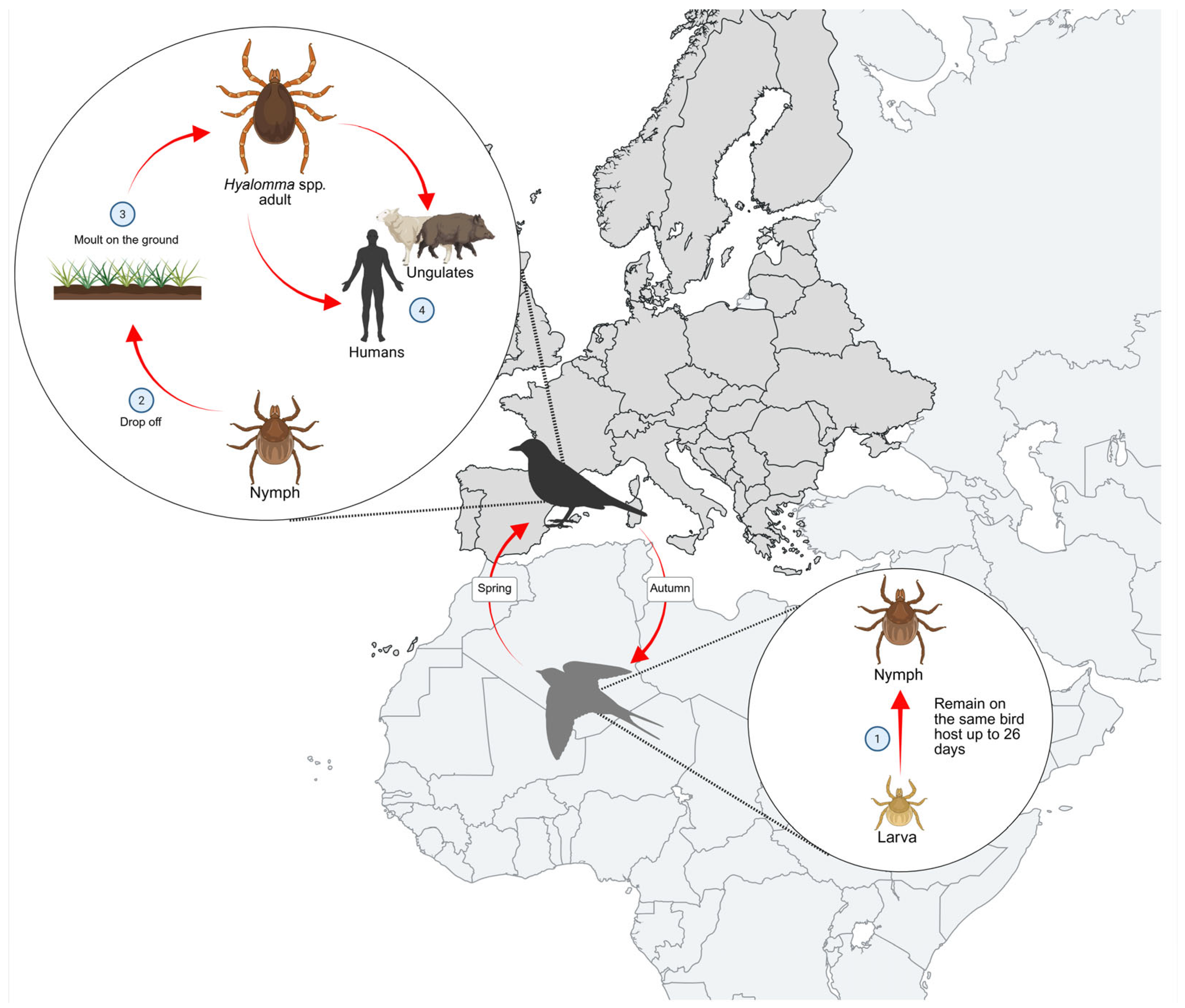
5. The Role of Migratory Birds in the Dispersal of Hyalomma spp. in Europe
5.1. Detection of Hyalomma spp. on Migratory Birds in Non-Endemic European Regions (2008–2022)
5.1.1. Northern Europe
5.1.2. Central Europe
5.2. Migratory Bird Species Infested by CCHFV-Positive Ticks
5.2.1. Great Reed Warbler (Acrocephalus arundinaceus)
5.2.2. Woodchat Shrike (Lanius senator)
5.2.3. Black-Eared Wheatear (Oenanthe hispanica)
5.2.4. Whinchat (Saxicola rubetra)
6. Climate Change and Its Effects on the Expansion of Hyalomma spp.
7. Limitations
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Baz-Flores, S.; Herraiz, C.; Peralbo-Moreno, A.; Barral, M.; Arnal, M.C.; Balseiro, A.; Cano-Terriza, D.; Castro-Scholten, S.; Cevidanes, A.; Conde-Lizarralde, A.; et al. Mapping the risk of exposure to Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in the Iberian Peninsula using Eurasian wild boar (Sus scrofa) as a model. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2024, 15, 102281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Addiego, J.; Wand, N.; Afrough, B.; Fletcher, T.; Kurosaki, Y.; Leblebicioglu, H.; Hewson, R. Recovery of complete genome sequences of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) directly from clinical samples: A comparative study between targeted enrichment and metagenomic approaches. J. Virol. Methods 2024, 323, 114833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juanes, H.M.L.; López-Bernus, A.; Vicente, B.; Alonso-Sardón, M.; Alonso, B.R.; Ulerio, J.P.; Soto, P.F.; Bellido, J.L.M.; Muro, A.; Belhassen-García, M. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus screening among African individuals in Spain: Lessons to learn. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 64, 102814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, Y.S.; Arun Prince Milton, A.; Ghatak, S.; Ghosh, S. Neglected Bird-Associated Viral Zoonotic Infections. In Role of Birds in Transmitting Zoonotic Pathogens, Livestock Diseases and Management; Malik, Y.S., Milton, A.A.P., Ghatak, S., Ghosh, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeborg, M.; Barboutis, C.; Ehrenborg, C.; Fransson, T.; Jaenson, T.G.; Lindgren, P.E.; Lundkvist, Å.; Nyström, F.; Salaneck, E.; Waldenström, J.; et al. Migratory birds, ticks, and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, T.; Carra, L.G.; Öhagen, P.; Fransson, T.; Barboutis, C.; Piacentini, D.; Figuerola, J.; Kiat, Y.; Onrubia, A.; Jaenson, T.G.; et al. Association between guilds of birds in the African-Western Palaearctic region and the tick species Hyalomma rufipes, one of the main vectors of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. One Health 2021, 13, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroșan, Ș.; Cozma, A.P.; Dascălu, M.A.; Crivei, L.A. Impact of recent and future climate change on vectorborne diseases: Viruses analyses. Lucr. Ştiinţ. Ser. Med. Vet. 2023, 66, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesmero-García, C.; Cabanero-Navalon, M.D.; Garcia-Bustos, V. The Importance and Impact of Francisella-like Endosymbionts in Hyalomma Ticks in the Era of Climate Change. Diversity 2023, 15, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, M.J.; Johnson, N.; Mansfield, K.L. Vectorial dynamics underpinning current and future tick-borne virus emergence in Europe. J. Gen. Virol. 2024, 105, 002041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celina, S.S.; Italiya, J.; Tekkara, A.O.; Černý, J. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in ticks, domestic, and wild animals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 11, 1513123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.; Munasinghe, T.; Tubbs, H.; Anyamba, A. Predicting Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Outbreaks via Multivariate Time-Series Classification of Climate Data. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Medical and Health Informatics 2022, Virtual Event, Japan, 13–15 May 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duygu, F.; Sari, T.; Kaya, T.; Tavsan, O.; Naci, M. The relationship between crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever and climate: Does climate affect the number of patients? Acta Clin. Croat. 2018, 57, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, A.; Buonavoglia, D. Risk of Crimean Congo haemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) introduction and spread in CCHF-free countries in southern and Western Europe: A semi-quantitative risk assessment. One Health 2021, 13, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayan, S.; Bokaean, M.; Shahrivar, M.R.; Chinikar, S. Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever. Lab. Med. 2015, 46, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capek, M.; Literak, I.; Kocianova, E.; Sychra, O.; Najer, T.; Trnka, A.; Kverek, P. Ticks of the Hyalomma marginatum complex transported by migratory birds into Central Europe. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celina, S.S.; Černý, J.; Samy, A.M. Mapping the potential distribution of the principal vector of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus Hyalomma marginatum in the Old World. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0010855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirian, H. Ticks infected with Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV): A decision approach systematic review and meta-analysis regarding their role as vectors. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 47, 102309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buczek, A.M.; Buczek, W.; Buczek, A.; Bartosik, K. The potential role of migratory birds in the rapid spread of ticks and tick-borne pathogens in the changing climatic and environmental conditions in Europe. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenson, T.G.T.; Jaenson, D.G.E.; Eisen, L.; Petersson, E.; Lindgren, E. Changes in the geographical distribution and abundance of the tick Ixodes ricinus during the past 30 years in Sweden. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameson, L.J.; Morgan, P.J.; Medlock, J.M.; Watola, G.; Vaux, A.G. Importation of Hyalomma marginatum, vector of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus, into the United Kingdom by migratory birds. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascucci, I.; Di Domenico, M.; Capobianco Dondona, G.; Di Gennaro, A.; Polci, A.; Capobianco Dondona, A.; Mancuso, E.; Cammà, C.; Savini, G.; Cecere, J.G.; et al. Assessing the role of migratory birds in the introduction of ticks and tick-borne pathogens from African countries: An Italian experience. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasle, G. Transport of ixodid ticks and tick-borne pathogens by migratory birds. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomar, A.M.; Santibáñez, P.; Mazuelas, D.; Roncero, L.; Santibáñez, S.; Portillo, A.; Oteo, J.A. Role of birds in dispersal of etiologic agents of tick-borne zoonoses, Spain, 2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foti, M.; Rinaldo, D.; Guercio, A.; Giacopello, C.; Aleo, A.; De Leo, F.; Fisichella, V.; Mammina, C. Pathogenic microorganisms carried by migratory birds passing through the territory of the island of Ustica, Sicily (Italy). Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; de la Fuente, J.; Latapia, T.; Ortega, C. The Impact of Climate Trends on a Tick Affecting Public Health: A Retrospective Modeling Approach for Hyalomma marginatum (Ixodidae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever: Surveillance—Cases in the EU Since 2013. 2024. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/crimean-congo-haemorrhagic-fever/surveillance/cases-eu-since-2013 (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control and European Food Safety Authority. Tick Maps [Internet]. Stockholm: ECDC. 2023. Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/en/disease-vectors/surveillance-and-disease-data/tick-maps (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- BirdLife International. BirdLife Data Zone. 2024. Available online: https://datazone.birdlife.org/ (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Okely, M.; Anan, R.; Gad-Allah, S.; Samy, A.M. Mapping the environmental suitability of etiological agent and tick vectors of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Acta Trop. 2020, 203, 105319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zé-Zé, L.; Nunes, C.; Sousa, M.; de Sousa, R.; Gomes, C.; Santos, A.S.; Alexandre, R.T.; Amaro, F.; Loza, T.; Blanco, M.; et al. Fatal Case of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever, Portugal, 2024. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2025, 31, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, I.; Mertens, M.; Mrenoshki, S.; Staubach, C.; Mertens, C.; Brüning, F.; Wernike, K.; Hechinger, S.; Berxholi, K.; Mitrov, D.; et al. Sheep and goats as indicator animals for the circulation of CCHFV in the environment. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2016, 68, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Liberato, C.; Frontoso, R.; Magliano, A.; Montemaggiori, A.; Autorino, G.L.; Sala, M.; Bosworth, A.; Scicluna, M.T. Moni-toring for the possible introduction of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in Italy based on tick sampling on migratory birds and serological survey of sheep flocks. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 149, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadrado-Matías, R.; Cardoso, B.; Sas, M.A.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Schuster, I.; González-Barrio, D.; Reiche, S.; Mertens, M.; Cano-Terriza, D.; Casades-Martí, L.; et al. Red deer reveal spatial risks of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus infection. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e630–e645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevidanes, A.; Barandika, J.F.; Aduriz, G.; Hurtado, A.; García-Pérez, A.L.; Barral, M. Exposure to Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus in Wild Ungulates in the Basque Country, Northern Iberian Peninsula. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 8553577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, H.G.; Cornet, J.-P.; Camicas, J.-L. Experimental Transmission of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus by West African Wild Ground-Feeding Birds to Hyalomma marginatum rufipes Ticks. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1994, 50, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Swanepoel, R.; Leman, P.A.; Shepherd, S.P. Field and laboratory investigation of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus (Nairovirus, family Bunyaviridae) infection in birds. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1987, 81, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergönül, O. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Manjunathachar, H.V.; Ghosh, S. A review on Hyalomma species infestations on human and animals and progress on management strategies. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, S.I.; Bertagnoli, S.; Falchi, A.; Figoni, J.; Fite, J.; Hoch, T.; Quillery, E.; Moutailler, S.; Raffetin, A.; René-Martellet, M.; et al. An update of evidence for pathogen transmission by ticks of the genus Hyalomma. Pathogens 2023, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Pena, A.; Bouattour, A.; Camicas, J.-L.; Walker, A.R. Ticks of Domestic Animals in the Mediterranean Region; University of Zaragoza: Zaragoza, Spain, 2004; 131p. [Google Scholar]
- Lesiczka, P.M.; Daněk, O.; Modrý, D.; Hrazdilová, K.; Votýpka, J.; Zurek, L. A New Report of Adult Hyalomma marginatum and Hyalomma rufipes in the Czech Republic. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Animal Health and Welfare. Scientific Opinion on the Role of Tick Vectors in the Epidemiology of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever and African Swine Fever in Eurasia. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallménius, K.; Barboutis, C.; Fransson, T.; Jaenson, T.G.; Lindgren, P.E.; Nyström, F.; Olsen, B.; Salaneck, E.; Nilsson, K. Spotted fever Rickettsia species in Hyalomma and Ixodes ticks infesting migratory birds in the European Mediterranean area. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, J.R.; Estrada-Peña, A. Host preferences support the prominent role of Hyalomma ticks in the ecology of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillâtre, P.; Revest, M.; Tattevin, E.P. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever: An update. Med. Mal. Infect. 2019, 49, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.W.; Linthicum, K.J.; Moulton, J. Transmission of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in two species of Hyalomma ticks from infected adults to cofeeding immature forms. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 48, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandi, G.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Choklikitumnuey, P.; Strube, C.; Springer, A.; Albihn, A.; Jaenson, T.G.; Omazic, A. First records of adult Hyalomma marginatum and H. rufipes ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Sweden. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakheit, M.; Latif, A.; Vatansever, Z.; Seitzer, U.; Ahmed, J. The huge risks due to Hyalomma ticks. In Arthropods as Vectors of Emerging Diseases; Mehlhorn, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Schaper, S.; Rieß, R.; Bitterwolf, K.; Frangoulidis, D.; Bestehorn, M.; Springer, A.; Oehme, R.; Drehmann, M.; Lindau, A.; et al. Imported Hyalomma ticks in Germany in 2018. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado-Matías, R.; Moraga-Fernández, A.; Peralbo-Moreno, A.; Negredo, A.I.; Sánchez-Seco, M.P.; Ruiz-Fons, F. Crimean–Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in questing non-Hyalomma spp. ticks in Northwest Spain, 2021. Zoonoses Public Health 2024, 71, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansford, K.M.; Carter, D.; Gillingham, E.L.; Hernández-Triana, L.M.; Chamberlain, J.; Cull, B.; McGinley, L.; Phipps, L.M.; Medlock, J.M. Hyalomma rufipes on an untraveled horse: Is this the first evidence of Hyalomma nymphs successfully moulting in the United Kingdom? Tick Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, I.; Vojtíšek, J.; Kejíková, R.; Šikutová, S.; Mendel, J.; Hubálek, Z.; Šikutová, S.; Estrada-Peña, A. Probable overwintering of adult Hyalomma rufipes in Central Europe. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duscher, G.G.; Hodžić, A.; Hufnagl, P.; Wille-Piazzai, W.; Schötta, A.M.; Markowicz, M.A.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Stanek, G.; Allerberger, F. Adult Hyalomma marginatum tick positive for Rickettsia aeschlimannii in Austria, October 2018. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 1800595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; D’Amico, G.; Fernández-Ruiz, N. Modelling the potential spread of Hyalomma marginatum ticks in Europe by migratory birds. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, E.; Toma, L.; Pascucci, I.; d’Alessio, S.G.; Marini, V.; Quaglia, M.; Riello, S.; Ferri, A.; Spina, F.; Serra, L.; et al. Direct and indirect role of migratory birds in spreading CCHFV and WNV: A multidisciplinary study on three stop-over islands in Italy. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, E.; Urach, K.; Hodžić, A.; Fusani, L.; Hufnagl, P.; Felsberger, G.; Ferroglio, E.; Duscher, G.G. Zoonotic pathogens in ticks from migratory birds, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornok, S.; Cutajar, B.; Takács, N.; Galea, N.; Attard, D.; Coleiro, C.; Galea, R.; Keve, G.; Sándor, A.D.; Kontschán, J. On the way between Africa and Europe: Molecular taxonomy of ticks collected from birds in Malta. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, F.; Toma, L.; Ciervo, A.; Di Luca, M.; Faggioni, G.; Lista, F.; Rezza, G. Virus investigation in ticks from migratory birds in Italy. New Microbiol. 2013, 36, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ivanova Aleksandrova, N.; Christova, I.; Dimitrov, D.; Marinov, M.P.; Panayotova, E.; Trifonova, I.; Taseva, E.; Gladnishka, T.; Kamenov, G.; Ilieva, M.; et al. Records of Ixodid ticks on wild birds in Bulgaria. Probl. Infect. Parasit. Dis. 2021, 27, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblebicioglu, H.; Eroglu, C.; Erciyas-Yavuz, K.; Hokelek, M.; Acici, M.; Yilmaz, H. Role of migratory birds in spreading Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Turkey. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, E.; Di Domenico, M.; Di Gialleonardo, L.; Menegon, M.; Toma, L.; Di Luca, M.; Casale, F.; Di Donato, G.; D’onofrio, L.; De Rosa, A.; et al. Tick species diversity and molecular identification of spotted fever group Rickettsiae collected from migratory birds arriving from Africa. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uiterwijk, M.; Ibáñez-Justicia, A.; van de Vossenberg, B.; Jacobs, F.; Overgaauw, P.; Nijsse, R.; Dabekaussen, C.; Stroo, A.; Sprong, H. Imported Hyalomma ticks in the Netherlands 2018–2020. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, M.E.; Phipps, P.; Medlock, J.M.; Atkinson, P.M.; Atkinson, B.; Hewson, R.; Gale, P. Hyalomma ticks on northward migrating birds in southern Spain: Implications for the risk of entry of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus to Great Britain. J. Vector Ecol. 2016, 41, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Keve, G.; Csörgő, T.; Benke, A.; Huber, A.; Mórocz, A.; Németh, Á.; Kalocsa, B.; Tamás, E.A.; Gyurácz, J.; Kiss, O.; et al. Ornithological and molecular evidence of a reproducing Hyalomma rufipes population under continental climate in Europe. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1147186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, L.; Stachurski, F.; Leblond, A.; Huber, K.; Vourc’h, G.; René-Martellet, M.; Desjardins, I.; Balança, G.; Grosbois, V.; Pradier, S.; et al. Strong evidence for the presence of the tick Hyalomma marginatum Koch, 1844 in southern continental France. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylen, D.; Fonville, M.; Docters van Leeuwen, A.; Stroo, A.; Duisterwinkel, M.; Van Wieren, S.; Diuk-Wasser, M.; de Bruin, A.; Sprong, H. Pathogen communities of songbird-derived ticks in Europe’s low countries. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, A.; Tischenkov, A.; Silaghi, C.; Proka, A.; Toderas, I.; Movila, A.; Frickmann, H.; Poppert, S. Prevalence of Bacterial and Protozoan Pathogens in Ticks Collected from Birds in the Republic of Moldova. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley-Fisher, M.; Phipps, P.; Medlock, J.M.; Atkinson, P.; Atkinson, B.; Hewson, R.; Gale, P. Ticks on northward migrating birds in southern Spain during Spring, 2011. J. Vector Ecol. 2012, 37, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumer, L.; Graser, E.; Hillebrand, T.; Talaska, T.; Dautel, H.; Mediannikov, O.; Roy-Chowdhury, P.; Sheshukova, O.; Mantke, O.D.; Niedrig, M. Rickettsia aeschlimannii in Hyalomma marginatum ticks, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trilar, T. Ticks (Acarina Ixodidae) on birds in Slovenia. Acrocephalus 2004, 25, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Briedis, M.; Wong, J.B.; Adamík, P.; Lislevand, T.; Funts, K.; Hromádka, M.; Hromádka, K.; Porkert, J.; Hahn, S. Seasonal variation in migration routes of Common Whitethroat Curruca communis. J. Ornithol. 2024, 166, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, M.M.; Jähnig, S.; Lisovski, S.; Mermillon, C.; Alba, R.; Rosselli, D.; Chamberlain, D. High nest failure but better nestling quality for early breeders in an alpine population of Northern Wheatear (Oenanthe oenanthe). Ibis 2023, 165, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinszke, A.; Remisiewicz, M. Long-term changes in autumn migration timing of Garden Warblers Sylvia borin at the southern Baltic coast in response to spring, summer and autumn temperatures. Eur. Zool. J. 2023, 90, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarán, A. Ruiseñor Común–Luscinia megarhynchos (Brehm, 1831); CSIC—Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales (MNCN): Madrid, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępniewska, K.; Ożarowska, A.; Busse, P.; Bobrek, R.; Zehtindjiev, P.; Ilieva, M.; Meissner, W. Autumn migration strategy of juvenile great reed warblers Acrocephalus arundinaceus on the eastern European flyway: A spatiotemporal pattern of accumulation and utilisation of energy stores. Eur. Zool. J 2020, 87, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.M.; Encarnação, V.; Fearon, P.; Gosler, A.G. Autumn migration of Savi’s Warblers Locustella luscinioides in Portugal: Differences in timing, fuel deposition rate and non-stop flight range between the age classes. Bird Study 2008, 55, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourcade, J.M.; Fontanilles, P.; Demongin, L. Fuel management, stopover duration and potential flight range of pied flycatcher Ficedula hypoleuca staying in South-West France during autumn migration. J. Ornithol. 2022, 163, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mérő, T.O.; Žuljević, A.; Kolykhanova, O.; Lengyel, S. Reuse of nests in the Great Reed Warbler Acrocephalus arundinaceus: A behavior to save time and energy and to deter nest parasites? Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasuelli, M.; Ilahiane, L.; Boano, G.; Cucco, M.; Galimberti, A.; Pavia, M.; Pioltelli, E.; Shafaeipour, A.; Voelker, G.; Pellegrino, I. Phylogeography of Lanius senator in its breeding range: Conflicts between alpha taxonomy, subspecies distribution and genetics. Eur. Zool. J. 2022, 89, 941–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloche, D.A.; Sapir, N. Breeding performance and nest-site selection of Woodchat Shrikes Lanius senator near the southern edge of their breeding distribution. J. Ornithol. 2024, 165, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, M.; Fulco, E.; Gustin, M.; Celada, C. Habitat preferences of the threatened Black-eared Wheatear Oenanthe hispanica in southern Italy. Bird Study 2013, 60, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanbury, A.J.; Tománková, I.; Teuten, E.L.; Douglas, D.J. No evidence that declining Whinchat Saxicola rubetra are currently limited by the availability of apparently suitable breeding habitat within the UK uplands. J. Ornithol. 2022, 163, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillingham, E.L.; Medlock, J.M.; Macintyre, H.; Phalkey, R. Modelling the current and future temperature suitability of the UK for the vector Hyalomma marginatum (Acari: Ixodidae). Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Martínez Avilés, M.; Muñoz Reoyo, M.J. A population model to describe the distribution and seasonal dynamics of the tick Hyalomma marginatum in the Mediterranean Basin. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2011, 58, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.S.; Dautel, H.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Kahl, O.; Lindgren, E. Effects of climate change on ticks and tick-borne diseases in Europe. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2009, 2009, 593232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y. The Effects of Climate Change on Birds and Approaches to Response. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth. Environ. Sci. 2022, 1011, 012054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; de la Fuente, J. The ecology of ticks and epidemiology of tick-borne viral diseases. Antivir. Res. 2014, 108, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, P.; Stephenson, B.; Brouwer, A.; Martinez, M.; De la Torre, A.; Bosch, J.; Foley-Fisher, M.; Bonilauri, P.; Lindström, A.; Ulrich, R.; et al. Impact of climate change on risk of incursion of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in livestock in Europe through migratory birds. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, A.; Schnitzler, J.C.; De Nardi, M.; Donachie, A.; Capua, I.; Lanave, G.; Buonavoglia, D.; Caceres-Soto, P.; Tizzani, P. Epidemic intelligence data of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever, European Region, 2012 to 2022: A new opportunity for risk mapping of neglected diseases. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Bird Species | Species of Collected Ticks | Country | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barn Swallow (Hirundo rustica) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [57] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | Italy, Malta | [56,58] | |
| Black Redstart (Phoenicuros ochruros) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [57] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | Italy | [56,57] | |
| Black-Eared Wheatear (Oenanthe hispanica) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33,56,59] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | Italy | [56] | |
| Citril Finch (Carduelis citrinella) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| Collared flycatcher (Ficedula albicollis) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [56] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy, Malta | [6,56,57,58] | |
| Common Chaffinch (Fringilla coelebs) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| Common Chiffchaff (Phylloscopus collybita) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [56] |
| Common Cuckoo (Cuculus canorus) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33] |
| Common Hoopoe (Upupa epops) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33,56] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Malta | [6,58] | |
| Common Kestrel (Falco tinnunculus) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain, Malta | [23,58] |
| Common Kingfisher (Alcedo atthis) | Hyalomma marginatum | Malta | [58] |
| Common Linnet (Linaria cannabina) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| Common Nightingale (Luscinia megarhynchos) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33,56,59] |
| Hyalomma marginatum s.l. | Czech Republic | [15] | |
| Hyalomma marginatum | African-Western Palaearctic region, Spain, Italy, Bulgaria | [6,23,56,60] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,56] | |
| Common Redstart (Phoenicurus phoenicurus) | Hyalomma spp. | United Kingdom, Italy, Turkey | [20,33,56,57,59,61] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | African-Western Palaearctic region, Greece, Italy | [6,44,56] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy, Malta | [6,56,57,58,62] | |
| Common Reed-Warbler (Acrocephalus scirpaceus) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [56] |
| Hyalomma marginatum s.l. | Czech Republic, Slovakia | [15] | |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy, Malta, Netherlands | [6,56,58,63] | |
| Common Whitethroat (Sylvia communis) | Hyalomma spp. | United Kingdom, Italy, Malta, Spain | [20,33,56,57,58,59,64] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy, Malta, Bulgaria | [6,56,58,60] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy, Malta, Hungary | [6,56,57,58,65] | |
| Dunnock (Prunella modularis) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [57] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Italy, France | [56,66] | |
| Eurasian Blackbird (Turdus merula) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [59] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] | |
| Eurasian Blackcap (Sylvia atricapilla) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [59] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, France | [6,66] | |
| Eurasian Blue Tit (Cyanistes caeruleus) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| Eurasian Buzzard (Buteo buteo) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [59] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] | |
| Eurasian Golden Oriole (Oriolus oriolus) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33,56] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Spain, Greece, Italy | [23,44,56] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,56] | |
| Eurasian Scops-Owl (Otus scops) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33,56] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Italy | [56] | |
| Eurasian Siskin (Spinus spinus) | Hyalomma marginatum | Greece | [44] |
| European Goldfinch (Carduelis carduelis) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [56] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Italy | [56] | |
| European Greenfinch (Chloris chloris) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| European Honey-Buzzard (Pernis apivorus) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [59] |
| European Nightjar (Caprimulgus europaeus) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [56] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,56] | |
| European Opied Flycatcher (Ficedula hypoleuca) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy, Hungary | [33,56,57,59,65] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy, Malta | [6,56,58] | |
| European Robin (Erithacus rubecula) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [56] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy, France | [6,56,66] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | Italy | [57] | |
| European Turtle-Dove (Streptopelia turtur) | Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region | [6] |
| Garden Warbler (Sylvia borin) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy, Netherlands/Belgium | [33,56,67] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,56] | |
| Great Reed-Warbler (Acrocephalus arundinaceus) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy, Turkey | [33,61] |
| Hyalomma marginatum s.l. | Czech Republic, Slovakia | [15] | |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Spain, Greece, Moldova | [23,44,68] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | Italy, Malta | [56,58] | |
| Great Tit (Parus major) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [56] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] | |
| House Sparrow (Passer domesticus) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| Icterine Warbler (Hippolais icterina) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33,56,57] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Italy | [56] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,56] | |
| Kentish Plover (Charadrius alexandrinus) | Hyalomma marginatum | African-Western Palaearctic region | [6] |
| Long-Tailed Tit (Aegithalos caudatus) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| Marsh Warbler (Acrocephalus palustris) | Hyalomma marginatum s.l. | Czech Republic | [15] |
| Hylomma marginatum | Bulgaria | [60] | |
| Melodious Warbler (Hippolais polyglotta) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [59] |
| Northern Wheatear (Oenanthe oenanthe) | Hyalomma spp. | United Kingdom, Italy | [20,33,56,57] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | African-Western Palaearctic region | [6] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,56,57] | |
| Ortolan Bunting (Emberiza hortulana) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| Red-Backed Shrike (Lanius collurio) | Hyalomma spp. | Turkey | [61] |
| Rock Bunting (Emberiza cia) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| Rock Sparrow (Petronia petronia) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| Rufous-Tailed Rock-Thrush (Monticola saxatilis) | Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region | [6] |
| Savi’s Warbler (Locustella luscinioides) | Hyalomma marginatum s.l. | Slovakia | [15] |
| Sedge Warbler (Acrocephalus schoenobaenus) | Hyalomma spp. | Malta, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain | [6,20,33,56,64] |
| Hyalomma marginatum s.l. | Slovakia | [15] | |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Greece, Malta | [44,58] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Greece, Italy, Malta, Hungary | [6,44,56,58,65] | |
| Song Thrush (Turdus philomelos) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [56,57] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Greece, Italy | [44,56] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | Italy | [56,57] | |
| Spanish Sparrow (Passer hispaniolensis) | Hyalomma lusitanicum | Malta | [58] |
| Spotted Flycatcher (Muscicapa striata) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33,56,59] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Italy | [56] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,56,57] | |
| Subalpine Warbler (Curruca cantillans) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33,57] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | Italy | [56] | |
| Thrush Nightingale (Luscinia luscinia) | Hyalomma spp. | Turkey | [61] |
| Tree Pipit (Anthus trivialis) | Hyalomma spp. | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,33,56,57,59] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,56] | |
| Western Olivaceous Warbler (Iduna opaca) | Hyalomma spp. | Spain | [64,69] |
| Western Subalpine Warbler (Curruca iberiae) | Hyalomma rufipes | Malta | [58] |
| Western yellow wagtail (Motacilla flava) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33,56,59] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy, Malta | [6,56,58] | |
| Whinchat (Saxicola rubetra) | Hyalomma spp. | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,33,56,57,59] |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy | [6,56,57,62] | |
| Willow Warbler (Phylloscopus trochilus) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy, Spain | [33,56,57,59,64] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Malta | [58] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | Italy, Malta | [56,58] | |
| Wood Warbler (Phylloscopus sibilatrix) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy, Malta | [33,56,57,58,62] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | Italy | [56] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy, Malta | [6,56,57,58,62] | |
| Woodchat Shrike (Lanius senator) | Hyalomma spp. | Italy | [33,56,59] |
| Hyalomma marginatum | African-Western Palaearctic region | [6] | |
| Hyalomma rufipes | African-Western Palaearctic region, Italy, Malta | [6,56,58,62] | |
| Woodlark (Lullula arborea) | Hyalomma marginatum | Spain | [23] |
| Infested Migratory Bird | CCHFV-Positive Tick | Hyalomma Life Stage | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Great Reed Warbler (Acrocephalus arundinaceus) | Hyalomma spp. | Nymph (n = 1) | Turkey | [61] |
| Woodchat Shrike (Lanius senator) | Hyalomma marginatum | Nymph (n = 3) | Greece | [5] |
| Western Black-Eared Wheatear (Oenanthe hispanica) | Hyalomma rufipes | Larva (n = 1) | Italy | [56] |
| Whinchat (Saxicola rubetra) | Hyalomma rufipes | Nymph (n = 1) | Italy | [56] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves Rodrigues, M.; Lesiczka, P.; Fontes, M.d.C.; Cardoso, L.; Coelho, A.C. The Expanding Threat of Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever Virus: Role of Migratory Birds and Climate Change as Drivers of Hyalomma spp. Dispersal in Europe. Birds 2025, 6, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds6020031
Alves Rodrigues M, Lesiczka P, Fontes MdC, Cardoso L, Coelho AC. The Expanding Threat of Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever Virus: Role of Migratory Birds and Climate Change as Drivers of Hyalomma spp. Dispersal in Europe. Birds. 2025; 6(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds6020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves Rodrigues, Melissa, Paulina Lesiczka, Maria da Conceição Fontes, Luís Cardoso, and Ana Cláudia Coelho. 2025. "The Expanding Threat of Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever Virus: Role of Migratory Birds and Climate Change as Drivers of Hyalomma spp. Dispersal in Europe" Birds 6, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds6020031
APA StyleAlves Rodrigues, M., Lesiczka, P., Fontes, M. d. C., Cardoso, L., & Coelho, A. C. (2025). The Expanding Threat of Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever Virus: Role of Migratory Birds and Climate Change as Drivers of Hyalomma spp. Dispersal in Europe. Birds, 6(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds6020031








