An Advanced Optimization Method to Minimize the Detection Limit of Liquid Scintillation Counter to Measure Low-Level Tritium Activity in Groundwater
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
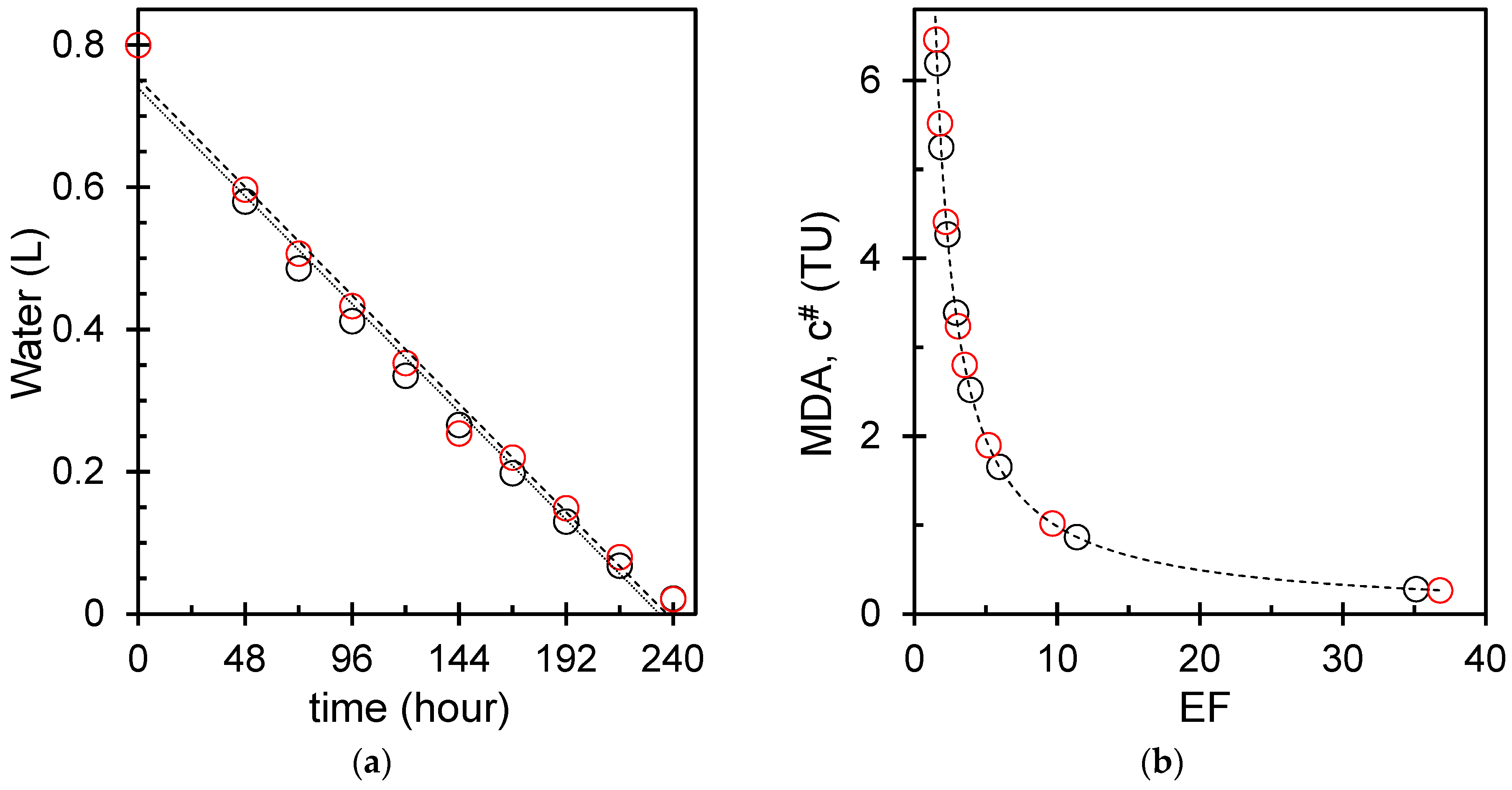
2.2. Electrolytic Enrichment
2.3. Tritium Activity Measurement
2.4. Mathematical Formulation
2.5. Data Validation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Enrichment of Tritium Concentration
3.2. Counting Efficiency and Background Radiation
3.3. Counting Time-Dependent Decision Threshold, Detection Limit, and Standard Uncertainty
3.4. Effect of the Volume Ratio of Water Sample with Scintillation Cocktail
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wanke, C.; Kossert, K.; Nähle, O.J. Investigations on TDCR measurements with the HIDEX 300 SL using a free parameter model. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 70, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noakes, J. Low Background Liquid Scintillation Counters. In Liquid Scintillation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976; p. 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al- Sudani, Z.; Fleifil, S.; Mohammed, M. Measurement of Tritium Activity Concentrations in Water Samples of Al-Amara City in Misan Province-Iraq, using Liquid Scintillation Counter. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2023, 20, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizman, S.; Mukhtarli, O. Tritium concentrations and consequent doses in bottled natural and mineral waters sold in Turkey and Azerbaijan. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Chen, B.; Zhao, C.; He, L.; Tang, F.; Zhuo, W. Application of a liquid scintillation system with 100-ml counting vials for environmental tritium determination: Procedure optimization, performance test, and uncertainty analysis. J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 225, 106427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Done, L.; Ioan, M.R. Minimum Detectable Activity in gamma spectrometry and its use in low level activity measurements. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2016, 114, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.; Manjón, G. Low-level measurements of tritium in water. Appl. Radiat. Isot. Incl. Data Instrum. Methods Use Agric. Ind. Med. 2004, 61, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.B.; Lee, J.-M.; Park, T.; Lee, S.; Jeong, M.; Lee, M.-K. Clarification of the calculation of minimum detectable activity in low-level radioactivity measurements. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2015, 109, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S. Review of the new edition of ISO 13528. Accredit. Qual. Assur. 2016, 21, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequang, V.; Vo, N.; Huynh Dinh, C.; Lau, P.; Thanh, T.; Tao, C. Study of the minimum detectable activity in gamma-ray spectrometry with various shielding configurations. Sci. Technol. Dev. J.-Nat. Sci. 2017, 1, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Yu, T.; Yu, W.; Ni, J.; Lin, L. Electrolytic enrichment method for tritium determination in the Arctic Ocean using liquid scintillation counter. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jiang, H.; Chen, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hou, X. Determination of tritium in large volume of seawater using electrolytic enrichment and LSC and its application for the East China Sea water. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2023, 332, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastino, W.; Chereji, I.; Cuna, S.; Kaihola, L.; De Felice, P.; Lupsa, N.; Balas, G.; Mirel, V.; Berdea, P.; Baciu, C. Tritium in water electrolytic enrichment and liquid scintillation counting. Radiat. Meas. 2007, 42, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, G.T.; Passo, C.J.; Carter, B. 5-Environmental Liquid Scintillation Analysis. In Handbook of Radioactivity Analysis, L’Annunziata, M.F., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 331–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestlund, H.G.; Werner, E. The Electrolytic Enrichment of Tritium and Deuterium for Natural Tritium Measurements; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Rittirong, A.; Noithong, P.; Hazama, R.; Sakuma, Y.; Saenboonruang, K.; Sudprasert, W. Determination of tritium levels in tap waters collected from various regions in Thailand using liquid scintillation counting. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1285, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorsson, P. A review of low-level tritium systems and sensitivity requirements. Appl. Radiat. Isot. Incl. Data Instrum. Methods Use Agric. Ind. Med. 1999, 50, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, B.; Viswanathan, S.; Venkatesan, S.; Jose, M.T.; Balasubramaniam, V. Study of Triple to Double Coincidence Method for Tritium Measurements. Radiochemistry 2021, 63, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, R. A review of the triple-to-double coincidence ratio (TDCR) method for standardizing radionuclides. Appl. Radiat. Isot. Incl. Data Instrum. Methods Use Agric. Ind. Med. 2003, 58, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, R.; Maletka, K. The Tdcr Method as An Important Tool in Radionuclide Metrology; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun, A.; Alazmi, A.S. Advancement of a Liquid Scintillation Counter and Semiconductor Alpha Spectroscopy Detector to Estimate the Radon Concentration in Groundwater. Water 2022, 14, 3849. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun, A.; Alazmi, A.S. Risk Assessment of Radon Exposure by Ingestion and Inhalation of Groundwater Within Different Age Groups. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2023, 43, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plassin, S.; Koch, J.; Paladino, S.; Friedman, J.R.; Spencer, K.; Vaché, K.B. A socio-environmental geodatabase for integrative research in the transboundary Rio Grande/Río Bravo basin. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korun, M.; Petrovič, T.; Vodenik, B.; Zorko, B. Calculation of decision thresholds according to the standard ISO 11929-3 in case of presence of the peaked background. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2023, 193, 110682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyles, T. Decision Thresholds; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaloud, K.B.; ElBatouti, M. Statistical analysis of 222Rn concentration in Zamzam and other water sources in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choppin, G.R.; Liljenzin, J.-O.; Rydberg, J.A.N. CHAPTER 5-Radionuclides in Nature. In Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Choppin, G.R., Liljenzin, J.-O., Rydberg, J.A.N., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Woburn, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 94–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.L.; Unterweger, M.P. Comprehensive Review and Critical Evaluation of the Half-Life of Tritium. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2000, 105, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadros, C.V.; Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J.; Hollins, S.E.; Chisari, R. Tritium in Australian precipitation: A 50 year record. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 262–273. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio Lucena, C.; Martins, M.; Sousa, W. Detection limit calculation according to ISO 11929 for in vitro 210Pb radiobioassay determinations by LSC. Braz. J. Radiat. Sci. 2023, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, L. Limits for qualitative detection and quantitative determination. Application to radiochemistry. Anal. Chem. 1968, 40, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Collani, E. A Critical Note on the Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement (GUM). Econ. Qual. Control 2008, 23, 123–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample ID | Spiked Activity (TU) | ±Error (TU) |
|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 8500 | 604.4 |
| Sample 2 | 4250 | 182.7 |
| Sample 3 | 850 | 166.2 |
| Sample 4 | 425 | 133.4 |
| Sample 5 | 85 | 12.29 |
| Sample 6 | 43 | 5.254 |
| Sample 7 | 8.50 | 4.661 |
| Sample 8 | 4.25 | 1.271 |
| Sample 9 | 0.85 | 0.297 |
| Sample 10 | 0.45 | 0.085 |
| Sample 11 | 0.15 | 0.127 |
| Sample 12 | 0.08 | 0.085 |
| Sample ID | Measured Activity, C (TU) | ±Error (TU) | Z |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 8760 | 560.9 | −0.315 |
| Sample 2 | 4124 | 264.1 | 0.392 |
| Sample 3 | 820 | 52.42 | 0.175 |
| Sample 4 | 395 | 25.29 | 0.222 |
| Sample 5 | 89.5 | 5.740 | −0.333 |
| Sample 6 | 40.3 | 2.590 | 0.372 |
| Sample 7 | 10.7 | 0.694 | −0.458 |
| Sample 8 | 3.73 | 0.253 | 0.401 |
| Sample 9 | 0.69 | 0.081 | 0.508 |
| Sample 10 | 0.42 | 0.061 | 0.278 |
| Sample 11 | <MDA | ||
| Sample 12 | <MDA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamun, A. An Advanced Optimization Method to Minimize the Detection Limit of Liquid Scintillation Counter to Measure Low-Level Tritium Activity in Groundwater. Radiation 2023, 3, 138-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation3030012
Mamun A. An Advanced Optimization Method to Minimize the Detection Limit of Liquid Scintillation Counter to Measure Low-Level Tritium Activity in Groundwater. Radiation. 2023; 3(3):138-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation3030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamun, Al. 2023. "An Advanced Optimization Method to Minimize the Detection Limit of Liquid Scintillation Counter to Measure Low-Level Tritium Activity in Groundwater" Radiation 3, no. 3: 138-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation3030012
APA StyleMamun, A. (2023). An Advanced Optimization Method to Minimize the Detection Limit of Liquid Scintillation Counter to Measure Low-Level Tritium Activity in Groundwater. Radiation, 3(3), 138-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation3030012






