How Does Food Enrichment and the Presence of Visitors Affect the Behaviour of Two Species of Freshwater Fish in a Public Aquarium?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Note
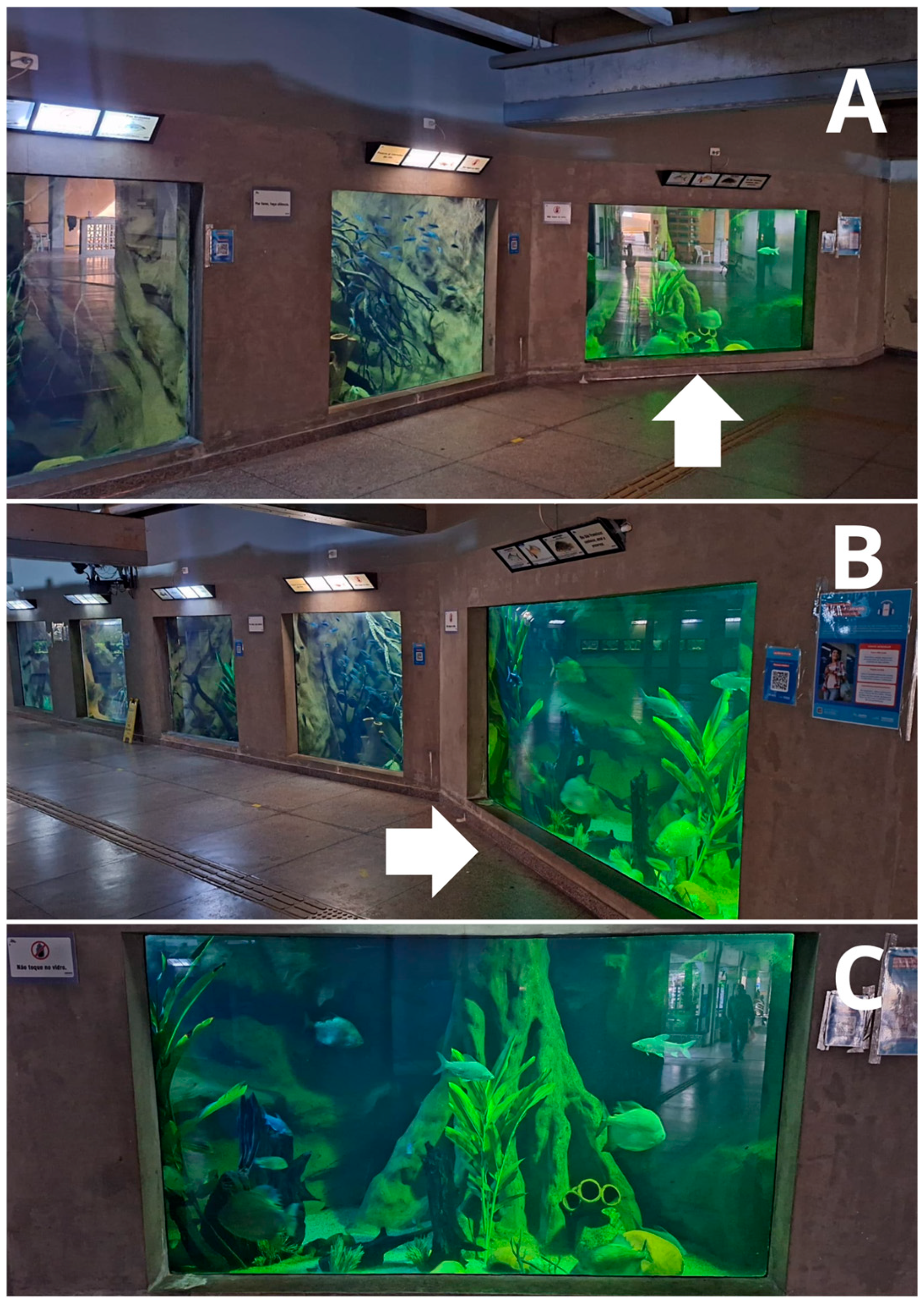
2.2. Study Place, Fish Species, and Maintenance
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Declaration of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
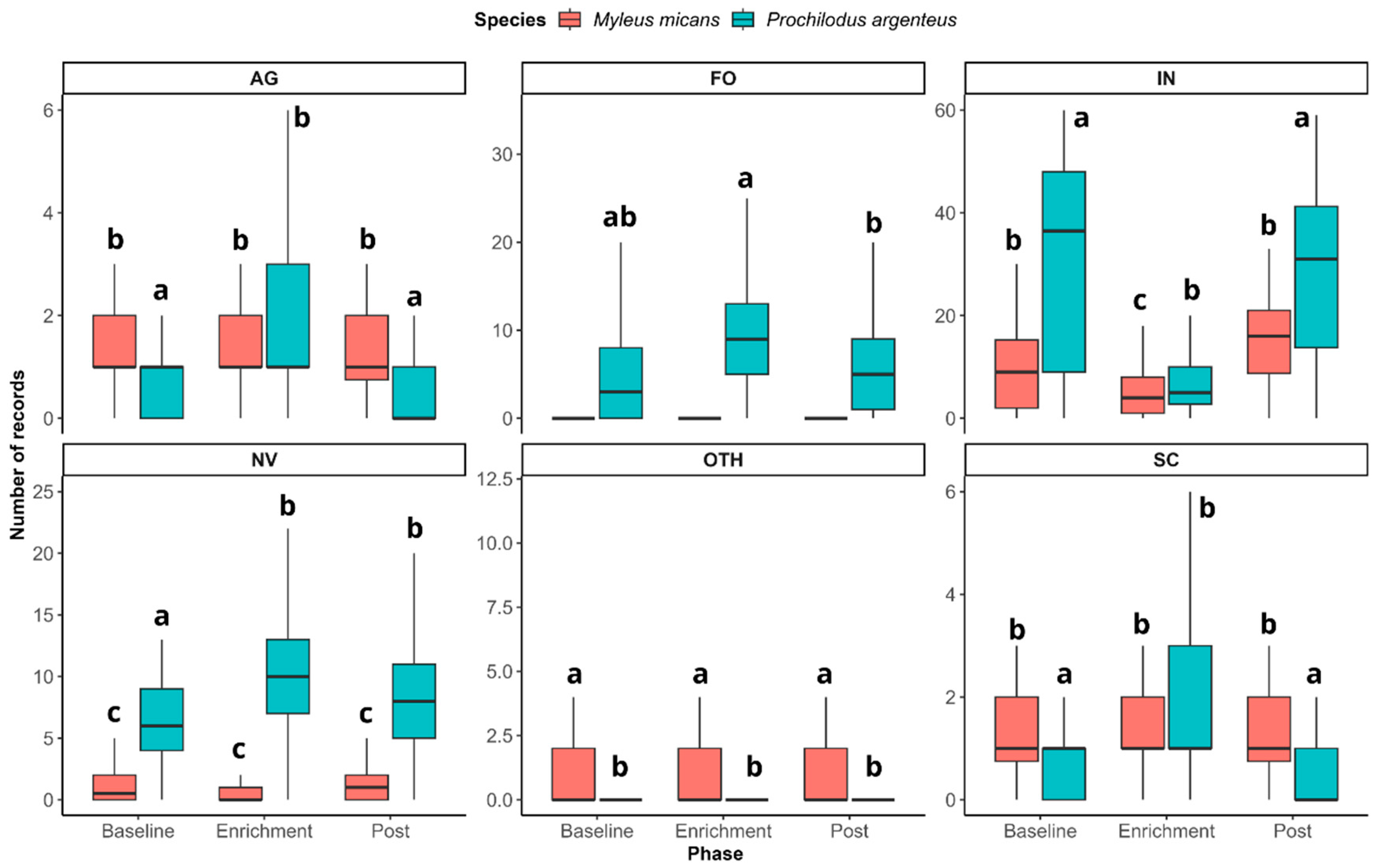
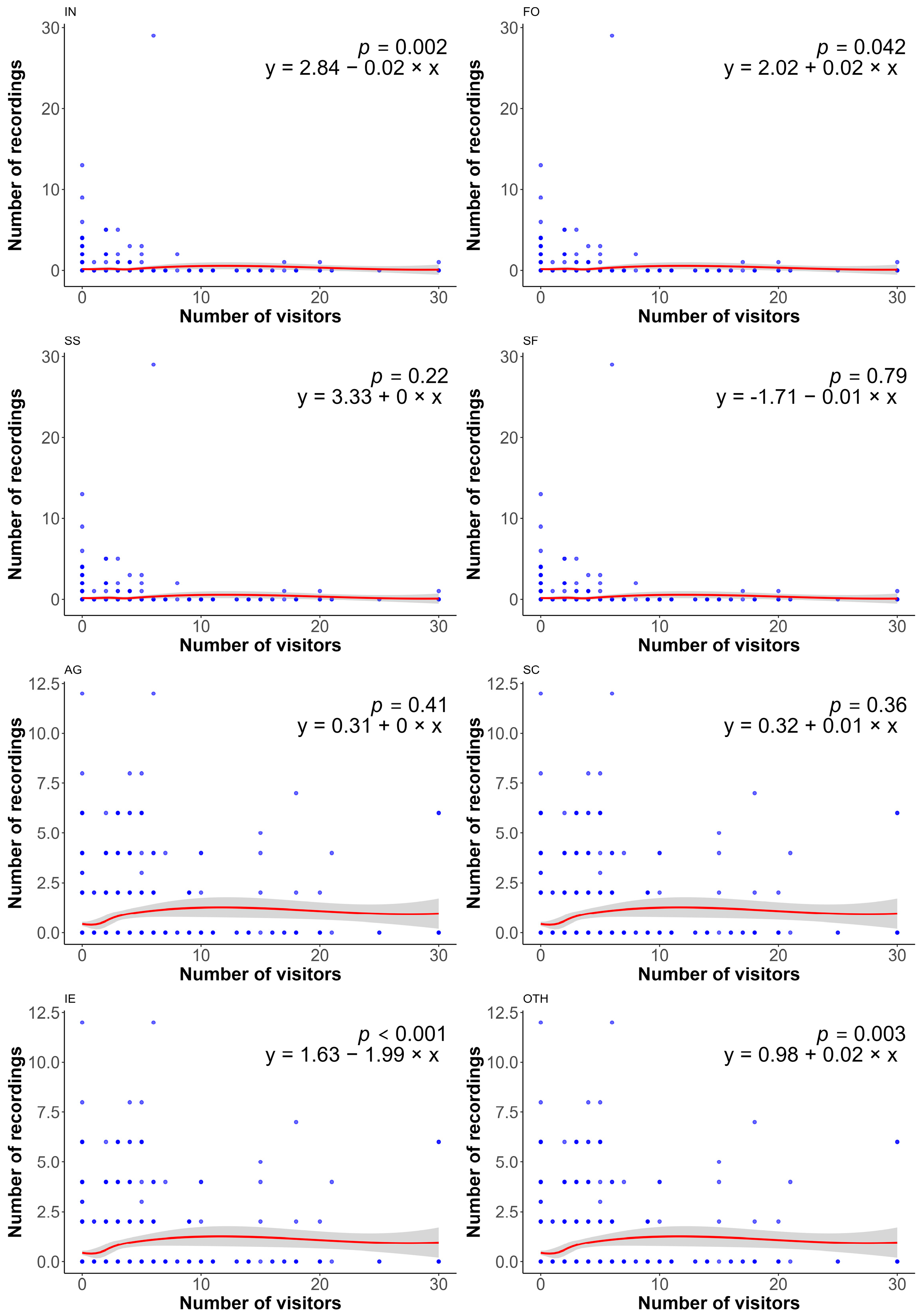
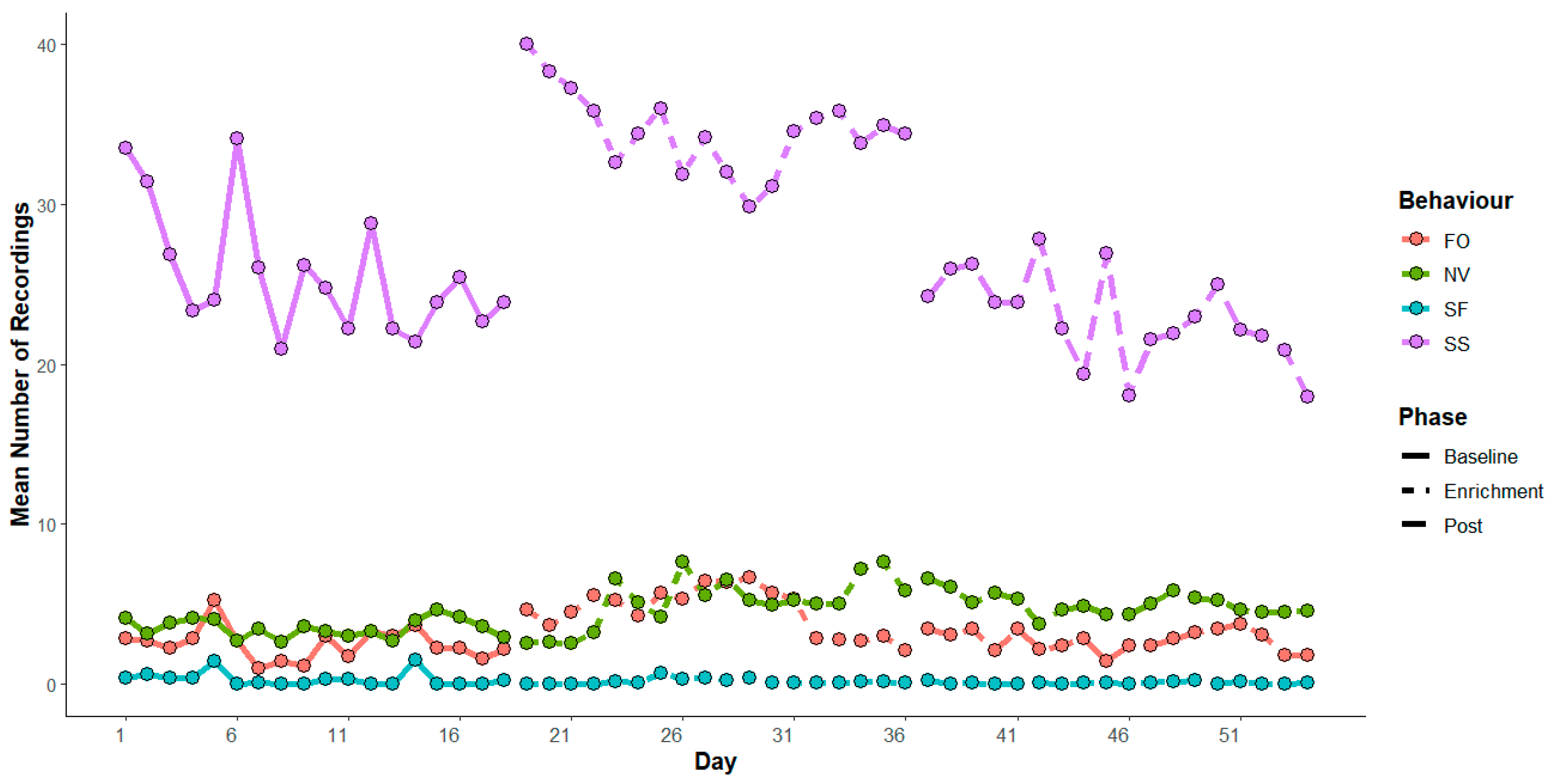
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, R.J. Environmental Enrichment for Captive Animals, 1st ed.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, D.J.; Beausoleil, N.J.; Littlewood, K.E.; McLean, A.N.; McGreevy, P.D.; Jones, B.; Wilkins, C. The 2020 Five Domains Model: Including Human–Animal Interactions in Assessments of Animal Welfare. Animals 2020, 10, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampton, J.O.; Hemsworth, L.M.; Hemsworth, P.H.; Hyndman, T.H.; Sandøe, P. Rethinking the Utility of the Five Domains Model. Anim. Welf. 2023, 32, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, K.; Bryant, J.; Staley, M.; Whitham, J.C.; Miller, L.J. Behavioural Diversity as a Potential Welfare Indicator for Professionally Managed Chimpanzees (Pan Troglodytes): Exploring Variations in Calculating Diversity Using Species-Specific Behaviours. Anim. Welf. 2021, 30, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzutto, C.S.; Sgai, M.G.F.G.; Guimarães, M.A.B.V. O Enriquecimento Ambiental Como Ferramenta Para Melhorar a Reprodução e o Bem-Estar de Animais Cativos: Uma Revisão. Rev. Bras. De. Reprodução Anim. 2009, 33, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, A.; Azevedo, C. Efeitos Do Enriquecimento Ambiental Na Diminuição de Comportamentos Anormais Exibidos Por Papagaios-Verdadeiros (Amazona Aestiva, Psittacidae) Cativos. Rev. Bras. Ornitol. 2011, 19, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, C.S.; Cipreste, C.F.; Pizzutto, C.S. Fundamentos Do Enriquecimento Ambiental, 1st ed.; Editora Payá: São Paulo, Brazil, 2022; ISBN 9786558546610. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, A.; Lima, M.R.; Meletti, P.C.; Jerep, F.C. Impact of Environmental Enrichment and Social Group Size in the Aggressiveness and Foraging Activity of Serrapinnus Notomelas. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2020, 224, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavala-Lopez, P.; Cabrera-Álvarez, M.J.; Maia, C.M.; Saraiva, J.L. Environmental Enrichment in Fish Aquaculture: A Review of Fundamental and Practical Aspects. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 704–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, J.E. Challenges and Directions in Zoo and Aquarium Food Presentation Research: A Review. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2020, 1, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, J.E. Size Matters: A Review of the Effect of Pellet Size on Animal Behaviour and Digestion. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 7, 090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Davidson, T.; Laland, K. Environmental Enrichment and Prior Experience of Live Prey Improve Foraging Behaviour in Hatchery-reared Atlantic Salmon. J. Fish Biol. 2003, 63, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderman, I.R.; Clayton, L.A. Fish Behavior. In Clinical Guide to Fish Medicine; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Young, R.J. The Importance of Food Presentation for Animal Welfare and Conservation. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1997, 56, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, I.B.; de Azevedo, C.S.; Cipreste, C.F.; Reisfeld, L.C.; Suzana, T.; Capriolli, R.G.; Pizzutto, C.S. The Impact of Food Enrichment on the Behavior of Cownose Ray (Rhinoptera Bonasus) Kept under Human Care. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2024, 5, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, M.; Persson, A. The Effects of Spatial Food Distribution and Group Size on Foraging Behaviour in a Benthic Fish. Behav. Process. 2005, 70, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.; Barr, Y.; McKeown, S.; Scheun, J.; Tay, C.; O’Riordan, R. An International Investigation of the Prevalence of Negative Visitor Behaviour in the Zoo. Animals 2023, 13, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Hunton, V.; Hosey, G.; Ward, S.J. The Impact of Visitors on Non-Primate Species in Zoos: A Quantitative Review. Animals 2023, 13, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, S.P.; Litzgus, J.D.; Lesbarrères, D. Limited Evidence for Negative Effects of Highway Widening on North American Large Mammals. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2020, 66, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truax, J.; Vonk, J.; Meri, E.; Troxell-Smith, S.M. Aquarium Visitors Catch Some Rays: Rays Are More Active in the Presence of More Visitors. Animals 2023, 13, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.P.; Byk, J.; Del-Claro, K. Influência de Técnicas de Enriquecimento Ambiental No Aumento Do Bem-Estar de Callithrix Penicillata (E. Geoffroy, 1812) (Primates: Callitrichidae). Biotemas 2011, 24, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eslamloo, K.; Akhavan, S.R.; Fallah, F.J.; Henry, M.A. Variations of Physiological and Innate Immunological Responses in Goldfish (Carassius Auratus) Subjected to Recurrent Acute Stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 37, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portz, D.E.; Woodley, C.M.; Cech, J.J. Stress-Associated Impacts of Short-Term Holding on Fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish 2006, 16, 125–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulart, V.D.; Azevedo, P.G.; van de Schepop, J.a.; Teixeira, C.P.; Barçante, L.; Azevedo, C.S.; Young, R.J. GAPs in the Study of Zoo and Wild Animal Welfare. Zoo Biol. 2009, 28, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachetti, É.d.S.; Viol, L.Y.; Viana-Junior, A.B.; Young, R.J.; de Azevedo, C.S. Global Overview of Environmental Enrichment Studies: What Has Been Done and Future Directions. Animals 2024, 14, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melfi, V.A. There Are Big Gaps in Our Knowledge, and Thus Approach, to Zoo Animal Welfare: A Case for Evidence-based Zoo Animal Management. Zoo Biol. 2009, 28, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binding, S.; Farmer, H.; Krusin, L.; Cronin, K. Status of Animal Welfare Research in Zoos and Aquariums: Where Are We, Where to Next? J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2020, 8, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, P.; Riley, L. The Use of Qualitative Behavioural Assessment in Zoo Welfare Measurement and Animal Husbandry Change. Res. Artic. J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2019, 7, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Näslund, J.; Aarestrup, K.; Thomassen, S.T.; Johnsson, J.I. Early Enrichment Effects on Brain Development in Hatchery-Reared Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar): No Evidence for a Critical Period. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvanes, A.G.V.; Moberg, O.; Ebbesson, L.O.E.; Nilsen, T.O.; Jensen, K.H.; Braithwaite, V.A. Environmental Enrichment Promotes Neural Plasticity and Cognitive Ability in Fish. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20131331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePasquale, C.; Neuberger, T.; Hirrlinger, A.M.; Braithwaite, V.A. The Influence of Complex and Threatening Environments in Early Life on Brain Size and Behaviour. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20152564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näslund, J.; Rosengren, M.; Del Villar, D.; Gansel, L.; Norrgård, J.R.; Persson, L.; Winkowski, J.J.; Kvingedal, E. Hatchery Tank Enrichment Affects Cortisol Levels and Shelter-Seeking in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 70, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pounder, K.C.; Mitchell, J.L.; Thomson, J.S.; Pottinger, T.G.; Buckley, J.; Sneddon, L.U. Does Environmental Enrichment Promote Recovery from Stress in Rainbow Trout? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 176, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzina, A.; Karakatsouli, N. The Presence of Substrate as a Means of Environmental Enrichment in Intensively Reared Gilthead Seabream Sparus Aurata: Growth and Behavioral Effects. Aquaculture 2012, 370–371, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, D.; Utne-Palm, A.; Jakobsen, P.; Braithwaite, V.; Jensen, K.; Salvanes, A. Enrichment Promotes Learning in Fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 412, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodewald, P.; Hyvärinen, P.; Hirvonen, H. Wild Origin and Enriched Environment Promote Foraging Rate and Learning to Forage on Natural Prey of Captive Reared Atlantic Salmon Parr. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2011, 20, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengren, M.; Kvingedal, E.; Näslund, J.; Johnsson, J.I.; Sundell, K. Born to Be Wild: Effects of Rearing Density and Environmental Enrichment on Stress, Welfare, and Smolt Migration in Hatchery-Reared Atlantic Salmon. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.J.; Møller, D. Yolk Absorption, Yolk Sac Constrictions, Mortality, and Growth During First Feeding of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar) Incubated on Astro-Turf. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1985, 42, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzina, A.; Dalla, C.; Papadopoulou-Daifoti, Z.; Karakatsouli, N. Effects of Environmental Enrichment on Growth, Aggressive Behaviour and Brain Monoamines of Gilthead Seabream Sparus Aurata Reared under Different Social Conditions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2014, 169, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiber, A.; Stomp, M.; Rouby, M.; Ferreira, V.H.B.; Bégout, M.-L.; Benhaïm, D.; Labbé, L.; Tocqueville, A.; Levadoux, M.; Calandreau, L.; et al. Cognitive Enrichment to Increase Fish Welfare in Aquaculture: A Review. Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monreal_Pawlowsky, T.; Vaicekauskaite, R.; Membrive, G.; Delfour, F.; Manteca, X. Goal-Oriented Behavioural and Environmental Enrichment in Aquarium Species. J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2021, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holanda, P.; Furtado-Neto, M.A.A.; Cabral, N. An Evaluation of Public Aquariums in São Paulo (Brazil) in Light of the Global Aquarium Strategy for Conservation and Sustainability. Arq. Ciências Mar. 2015, 48, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, C.S.; Barçante, L. Enriquecimento Ambiental Em Zoológicos Brasileiros: Em Busca Do Bem-Estar Animal. Rev. Bras. Zoociências 2018, 19, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabb, G.B. The Evolution of Zoos from Menageries to Centers of Conservation and Caring. Curator Mus. J. 2004, 47, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R.; Escribano, N.; Casas, M.; Pino-del-Carpio, A.; Villarroya, A. The Role of Zoos and Aquariums in a Changing World. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2023, 11, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prefeitura de Belo Horizonte Aquário Do Rio São Francisco. Available online: https://prefeitura.pbh.gov.br/fundacao-de-parques-e-zoobotanica/aquario-rio-sao-francisco?__goc_wbp__=01548700249x6sf4VqYlv3POpt8HKuwa-2PE (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Peressin, A.; de Magalhães Lopes, J.; Wouters, L.; Andrade Neto, F.R.; Alves, C.B.M.; Pompeu, P.S. Migratory Behavior of Prochilodus argenteus in the São Francisco River Basin, Brazil. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2024, 31, e12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.M.C.; Vari, R.P. Detritivores of the South American Fish Family Prochilodontidae (Teleostei:Ostariophysi:Characiformes): A Phylogenetic and Revisionary Study; Smithsonian Books: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, H.; Godinho, A. Águas, Peixes e Pescadores Do São Francisco Das Minas Gerais; Godinho, H., Godinho, A., Eds.; Editora Puc-Minas: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, E.M.; Amaral, D.F. Peixes Do Rio São Francisco Nativos, Endêmicos e Exóticos; Souza, E.M., Amaral, D.F., Eds.; IFSertãoPE: Petrolina, Brazil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, L.C.; Faustino, F.; Paes, M.C.F.; Beraldo-Massoli, M.C.; Cardozo, M.V.; Schocken-Iturrino, R.P.; Nakaghi, L.S.O. Morfologia e Quantificação Da Microbiota Intestinal Do Curimbatá (Prochilodus Lineatus) e Do Cascudo Cinza (Pterygoplichthys Anisitsi) Cultivados Em Cativeiro. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2012, 64, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britski, H.A.; Sato, Y.; Rosa, A.B.S. Manual de Identificação de Peixes Da Região de Três Marias, 3rd ed.; CODEVASF: Brasilia, Brazil, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- CONCEA-Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal. Guia Brasileiro de Produção, Manutenção Ou Utilização de Animais Em Atividades de Ensino Ou Pesquisa Científica, 1st ed.; Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação: Brasília, Brazil, 2023; pp. 384–458.
- Altmann, J. Observational Study of Behavior: Sampling Methods. Behaviour 1974, 49, 227–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, P.; Martin, P. Measuring Behaviour, 4th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; ISBN 9780511810893. [Google Scholar]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Gerlai, R. Zebrafish as an Emerging Model for Studying Complex Brain Disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, R.G.; Thal, J.E.; Das, P.; Zarlinga, N.J.; Lukas, K.E.; Wark, J.D. Agonistic Behavior and Feeding Competition in the Largest Piranha Species, Pygocentrus Piraya, in a Zoo. J. Ethol. 2023, 41, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barçante, L.; Azevedo, C.S.; Pizzutto, C.S.; Vasconcellos, A.d.S. A Importância Do Estudo Do Comportamento Para a Avaliação Da Eficácia Do Enriquecimento Ambiental. In Fundamentos do Enriquecimento Ambiental. In Fundamentos do Enriquecimento Ambiental; Azevedo, C.S., Cipreste, C.F., Pizzutto, C.S., Eds.; Paya: São Paulo, Brazil, 2022; pp. 271–292. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 9 January 2025).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M. GlmmTMB Balances Speed and Flexibility among Packages for Zero-Inflated Generalized Linear Mixed Modeling. R. J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R.V.; Bolker, B.; Buerkner, P.; Giné-Vázquez, I.; Herve, M.; Jung, M.; Love, J.; Miguez, F.; Piaskowiski, J.; Riebl, H.; et al. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means. R Package Version 4.0-3. 2024. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, L.; Vicino, G.; Sheftel, J.; Lauderdale, L. Behavioral Diversity as a Potential Indicator of Positive Animal Welfare. Animals 2020, 10, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, J.; Fernandez, E. Which Index Should I Use? A Comparison of Indices for Enclosure Use Studies. Anim. Behav. Cogn. 2022, 9, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.A.R.; Webster, M.M.; Salvanes, A.G.V. Physical Enrichment Research for Captive Fish: Time to Focus on the DETAILS. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 99, 704–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.R.; Cabrera-Alvarez, M.J.; Soares, F.; Diáz-Gil, C.; Candeias-Mendes, A.; Saraiva, J.L.; Arechavala-Lopez, P. Structural Enrichment Promotes Natural Behaviour and Welfare of Captive Gilthead Seabream Broodstock. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2024, 275, 106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Zuberi, A.; Khan, K.U.; Ahmad, S.; Thörnqvist, P.-O.; Winberg, S. Effects of Enrichment on the Development of Behaviour in an Endangered Fish Mahseer (Tor Putitora). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2017, 186, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpaz, R.; Schneidman, E. Social Interactions Drive Efficient Foraging and Income Equality in Groups of Fish. Elife 2020, 9, e56196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Cruze, N.; Khan, S.; Carder, G.; Megson, D.; Coulthard, E.; Norrey, J.; Groves, G. A Global Review of Animal–Visitor Interactions in Modern Zoos and Aquariums and Their Implications for Wild Animal Welfare. Animals 2019, 9, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlbeck Bergendahl, I.; Salvanes, A.G.V.; Braithwaite, V.A. Determining the Effects of Duration and Recency of Exposure to Environmental Enrichment. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 176, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Mo, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W. A Global Synthesis of Environmental Enrichment Effect on Fish Stress. Fish Fish. 2025, 26, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbachini, H.; Pizzutto, C.S.; de Souza Mesquita, L.M.; Gadig, O.B.F. Environmental Enrichment Effects on the Reproductive Behavior of Captive Nurse Sharks Ginglymostoma Cirratum. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2021, 104, 471–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.; Esson, M. Visitor Interest in Zoo Animals and the Implications for Collection Planning and Zoo Education Programmes. Zoo Biol. 2010, 29, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbachini, H.; Mello, H.E.S.d.O. Enriquecimento Ambiental e a Sua Relevância Para a Educação Ambiental. In Fundamentos do Enriquecimento Ambiental. In Fundamentos do Enriquecimento Ambiental; Editora Payá: São Paulo, Brazil, 2022; pp. 284–293. ISBN 978-65-5854-661-0. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, M.A.; Winder, L.A.; Watt, P.J. Enrichment Increases Aggression in Zebrafish. Fishes 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, R.E.; Carvalho, G.G.A.; Volpato, G.L. The Aggressive Behavior of Nile Tilapia Introduced into Novel Environments with Variation in Enrichment. Zoology 2011, 114, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, S.T. Aggression in Aquatic Environments and Its Relevance in Aquaculture and Conservation Efforts. Discov. Anim. 2024, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barley, A.J.; Coleman, R.M. Habitat Structure Directly Affects Aggression in Convict Cichlids Archocentrus Nigrofasciatus. Curr. Zool. 2010, 56, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallas-Lopes, M.; Benvenutti, R.; Donzelli, N.I.Z.; Marcon, M. A Systematic Review of the Impact of Environmental Enrichment in Zebrafish. Lab. Anim. 2023, 52, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Behaviour (Acronym) | Description |
|---|---|
| Foraging (FO) | Looking for and/or eating food in the tank. |
| Inactive (IN) | Standing still, with no locomotion movements, only the pectoral fin and operculum movement. |
| Swimming slowly (SS) | Slow locomotion, smooth movement of the fins. |
| Swimming fast (SF) | Fast locomotion, energetic caudal fin movement in one direction (maximum of two trips back and forth in the tank). |
| Abnormal swim (AS) | Swimming sideways, backwards, upside down, diagonally, spiralling or convulsing; swimming from side to side, forming a figure of eight (more than two trips back and forth in the tank). |
| Aggression (AG) | Chasing, biting, and flicking, where the fish swim towards each other, clash mouth-to-mouth, and swim away to the opposite side. |
| Escaping from agonistic encounters (SC) | Swimming away fast from an aggressive individual. |
| Abnormal behaviours (AB) | Keeping mouth open for a long time or too often, slack-jawed, banging head and eyes on the glass, trembling. |
| Freezing (FRE) | Completely inert at the bottom of the aquarium except for its eyes and operculum. |
| Carousel (CAR) | Two individuals swimming in tight circles around each other. |
| Interacting with enrichment (IE) | Interacting directly with the enrichment item placed in the tank. |
| Not visible (NV) | Outside the researcher’s field of vision. |
| Other behaviours (OTH) | New behaviours not previously described in the ethogram. |
| Response | Explanatory Variables | Estimate | SE | z-Value | Pr (>|z|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aggression | Phase Enrichment | 0.362 | 0.068 | 5.306 | <0.001 |
| Phase Post-Enrichment | −0.060 | 0.074 | −0.817 | 0.413 | |
| Species curimba | −0.340 | 0.057 | −5.894 | <0.001 | |
| Foraging | Phase Enrichment | 0.216 | 0.128 | 1.682 | 0.092 |
| Phase Post-Enrichment | −0.187 | 0.131 | −1.418 | 0.156 | |
| Species curimba | 4.561 | 0.178 | 25.535 | <0.001 | |
| Inactive | Phase Enrichment | −1.144 | 0.073 | −15.621 | <0.001 |
| Phase Post-Enrichment | 0.113 | 0.069 | 1.634 | 0.102 | |
| Species curimba | 0.700 | 0.050 | 13.960 | <0.001 | |
| Not visible | Phase Enrichment | 0.266 | 0.076 | 3.499 | <0.001 |
| Phase Post-Enrichment | 0.2780 | 0.075 | 3.673 | <0.001 | |
| Species curimba | 2.062 | 0.051 | 39.756 | <0.001 | |
| Other behaviours | Phase Enrichment | −0.362 | 0.143 | −2.523 | 0.011 |
| Phase Post-Enrichment | −0.063 | 0.131 | −0.486 | 0.626 | |
| Species curimba | −2.699 | 0.212 | −12.710 | <0.001 | |
| Escaping from agonistic encounters | Phase Enrichment | 0.349 | 0.068 | 5.102 | <0.001 |
| Phase Post-Enrichment | −0.066 | 0.0.74 | −0.889 | 0.373 | |
| Species curimba | −0.322 | 0.057 | −5.570 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.A.; Azevedo, C.S.d.; Cipreste, C.F.; Pizzutto, C.S.; Eskinazi Sant’Anna, E.M. How Does Food Enrichment and the Presence of Visitors Affect the Behaviour of Two Species of Freshwater Fish in a Public Aquarium? J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2025, 6, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg6030035
Silva AA, Azevedo CSd, Cipreste CF, Pizzutto CS, Eskinazi Sant’Anna EM. How Does Food Enrichment and the Presence of Visitors Affect the Behaviour of Two Species of Freshwater Fish in a Public Aquarium? Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens. 2025; 6(3):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg6030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Arthur Afeitos, Cristiano Schetini de Azevedo, Cynthia Fernandes Cipreste, Cristiane Schilbach Pizzutto, and Eneida Maria Eskinazi Sant’Anna. 2025. "How Does Food Enrichment and the Presence of Visitors Affect the Behaviour of Two Species of Freshwater Fish in a Public Aquarium?" Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens 6, no. 3: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg6030035
APA StyleSilva, A. A., Azevedo, C. S. d., Cipreste, C. F., Pizzutto, C. S., & Eskinazi Sant’Anna, E. M. (2025). How Does Food Enrichment and the Presence of Visitors Affect the Behaviour of Two Species of Freshwater Fish in a Public Aquarium? Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens, 6(3), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg6030035








