Abstract
Despite advances in surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation treatments for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), 5-year survival rates remain at nearly 11%. Cholangiocarcinoma, while not as severe, also possesses similar survival rates. Fewer than 20% of patients are surgical candidates at time of diagnosis; therefore, it is imperative that alternative therapies are effective for non-surgical patients. There are several thermal ablative techniques, including radiofrequency ablation (RFA), high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), microwave ablation (MWA), alcohol ablation, stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), cryoablation, irreversible electroporation (IRE), biliary intraluminal brachytherapy, and biliary photodynamic therapy (PDT). Emerging literature in animal models and human patients has demonstrated that endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided RFA (EUS-RFA) prevents tumor progression through coagulative necrosis, protein denaturation, and activation of anticancer immunity in local and distant tumor tissue (abscopal effect). RFA treatment has been shown to not only reduce tumor-associated immunosuppressive cells but also increase functional T cells in distant tumor cells not treated with RFA. The remarkable ability to reduce tumor progression and promote tumor microenvironment (TME) remodeling makes RFA a very promising non-surgical therapy technique that has the potential to reduce mortality in this patient population. EUS-RFA offers superior precision and safety compared to other ablation techniques for pancreatic and biliary cancers, due to real-time imaging capabilities and minimally invasive nature. Future research should focus on optimizing RFA protocols, exploring combination therapies with chemotherapy or immunotherapy, and expanding its use in patients with metastatic disease. This review article will explore the current data and underlying pathophysiology of EUS-RFA while also highlighting the role of ablative therapies as a whole in immune activation response.
1. Introduction and Background of Ablation Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer has an insidious onset and destructive nature causing it to be one of the most difficult solid-organ cancers to detect and treat. Despite advancements in both surgical and non-surgical treatments, 5-year survival rates in the United States remain only at approximately 9% [1]. About half of patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer have metastatic disease by the time of diagnosis, making initial treatment selection challenging [2]. Additionally, cancer cells are often resistant to chemotherapy and radiation due to early recurrence and metastasis [3]. Surgical resection is a possible treatment method; however, less than 20% of pancreatic cancers are resectable [4]. It is thus imperative that viable non-surgical treatment options exist for those patients who are not surgical candidates.
There is a multimodal approach to pancreatic cancer involving systemic chemotherapy, surgical resection, and/or local ablation [5]. While chemotherapy, both adjuvant and neoadjuvant, and surgical resection have been mainstays for treating locally advanced pancreatic cancer, radiotherapy has been a controversial yet promising modality. Ablation by definition entails any procedure that involves the removal or destruction of a tissue. There are several thermal ablative techniques, including radiofrequency ablation (RFA), high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), microwave ablation (MWA), alcohol ablation, stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), cryoablation, irreversible electroporation (IRE), biliary intraluminal brachytherapy, and biliary photodynamic therapy (PDT). Many of these ablation techniques are guided by EUS. Specifically, EUS-RFA has shown to be a safe and feasible treatment option for treating pancreatic cancer [6]. EUS-guided ablative therapies are mainly described in the literature through case reports and observational studies, and have shown to be a promising rival to surgical management of pancreatic cancer treatment.
RFA produces an immune response through mechanisms such as distance coagulative necrosis protein denaturation, and activation of anticancer immunity in local and distant tumor tissue (abscopal effect) [7]. The alteration of the pancreatic tumor microenvironment (TME) through these processes is essential to the understanding of immune response and efficacy of ablative therapies. This review briefly summarizes current ablative therapy techniques and explores the role of ablative therapies in immune activation to treat pancreatic and biliary cancer.
2. Literature Review Methodology
Eligible studies for inclusion for this review met the following criteria: (1) original clinical investigations involving human or animal subjects undergoing various ablative therapies for pancreatic or biliary malignancies; (2) inclusion of data on clinical or immunological outcomes, such as tumor response, immune modulation, survival, or inflammatory markers; (3) availability of full-text articles in English; (4) clearly defined endpoints related to technical feasibility, safety, clinical impact, or therapeutic efficacy. Both prospective and retrospective study designs were considered. Studies were excluded if they focused solely on in vitro models, employed non-ablative techniques, or did not report immunological or clinically meaningful endpoints. Particular emphasis was placed on studies contributing to mechanistic insights and historical establishment of technique therapeutic success. A summary of the original research studies evaluating each of the ablation techniques is provided in Tables S1 and S2 along with brief highlighted advantages and disadvantages of each technique (Tables in Supplementary Materials).
3. Pancreatic Ablation Techniques and Indications
In pancreatic cancer, several modalities for ablative therapy exist including alcohol ablation, stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), microwave ablation (MWA), cryoablation, high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), irreversible electroporation (IFE), and RFA. Each therapy comes with its own advantages and disadvantages.
3.1. Alcohol Ablation
The first use of alcohol ablation in the management of pancreatic cystic lesions occurred in 2005 by Gan et al. who utilized EUS-guided ethanol ablation to treat a small cohort of 25 patients with pancreatic cystic lesions [8]. Of the cohort, eight patients had a complete response with the rest being partial or incomplete [8]. Given its abundance, ethanol has been widely used in the treatment of pancreatic neoplasms and cystic lesions. Through EUS guidance, cysts are visualized, drained, and then lavaged with alcohol for periods of 3–5 min (Figure 1). The alcohol solubilizes the cell membrane, altering protein structure and promoting cellular death through the lysis of cell membranes. Further studies continue to demonstrate the promising role that the alcohol solution has on cystic lesions and neuroendocrine tumors [9]. In the largest trial on ethanol usage in patients with pseudocysts, intrapapillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN), and mucinous cystic neoplasms (MCN), Park et al. evaluated a cohort of 91 patients and found a 50% success rate in treating cystic neoplasms and MCNS with a lower effect on IPMNs and uncategorized cysts [10]. Other smaller studies have demonstrated similar results with successful treatment largely depending on neoplasm characteristics. EUS-guided ethanol ablation for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET) has a treatment rate greater than 60% with minimal side effects across the current prospective studies [11]. While alcohol ablation is a generally well-tolerated procedure with decent success rates, the role beyond cystic lesions is fairly limited with no clear role in the treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
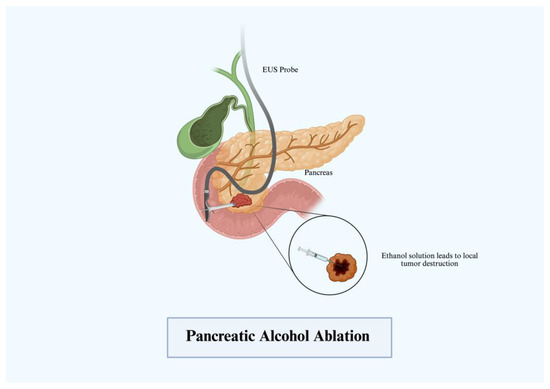
Figure 1.
Pancreatic alcohol ablation.
3.2. Microwave Ablation
Microwave ablation (MWA), along with RFA, produces coagulative necrosis via electromagnetic waves in the microwave energy spectrum. First used in the 2000s for the treatment of lung cancer, MWA has expanded its role in gastrointestinal malignancy [12]. The mechanism of therapy works by a microwave delivery system that consists of a generator, microwave antenna needle, and a flexible coaxial cable. An ablation probe connected to the generator is introduced to the target lesion delivering bursts of electromagnetic radiation at frequencies varying from 900 to 2450 MHz (Figure 2). This energy induces rapid oscillations increasing friction, heat generation, and subsequently coagulative necrosis of the surrounding tissue [13]. MWA treatment has gained traction and was first evaluated in 2007 by Lygidakis et al.; 15 patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC) underwent laparotomy with MWA with a 100% partial necrosis rate [14]. Currently, most studies have only evaluated MWA from the percutaneous and laparotomy-based approaches [15,16]. Evaluation of MWA in treating cystic lesions and mucinous neoplasms has only been conducted in small case series, but has shown successful results. Few case reports exist currently that show the success of EUS-guided MWA in achieving tumor necrosis without also leading to major complications [17]. More trials are needed to further evaluate its role in the endoscopic setting for gastroenterologists.
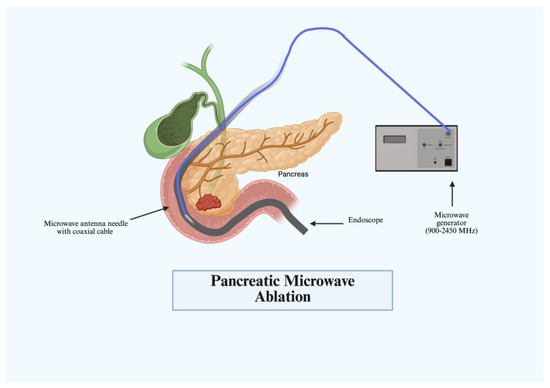
Figure 2.
Pancreatic microwave ablation (MWA).
3.3. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
Chemoradiotherapy for pancreatic cancer often involves months of treatment with frequent re-imaging and re-evaluation. Additionally, recent phase III trials demonstrated minimal or no effect on survival of chemoradiation in comparison to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in LAPC [18,19,20]. Even with the increasing success of current chemotherapeutic regimens, such as FOLFIRINOX, there is still an increasing need for local malignancy control. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) has been shown to play an increasingly prominent role. SBRT is a high-precision irradiation technique delivering high radiation doses directly to the tumor in a few treatment fractions. Using EUS-guided fiducial markers, fine needles are placed directly into the tumor, with frequent computed tomography (CT) and 3D examination to account for breathing patterns and organ movement (Figure 3). Most studies have evaluated these highly targeted doses at fractions varying between 25 Gy and 50 Gy [21]. Currently, SBRT is mainly utilized in patients with LAPC and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (BRPC). Initial studies demonstrated near 100% local control in LAPC when compared to conventional chemoradiotherapy regimens [22]. From this, subsequent studies have demonstrated that patients with BRPC who undergo SBRT in addition to aggressive induction chemotherapy are more likely to undergo resection and achieve higher rates of local control [21]. If resectable, median overall survival significantly improves and the highly targeted doses lead to minimal grade 3 and above toxicities in these populations [23]. One current prospective trial by Salas et al. has even observed that escalated doses of SBRT can achieve higher rates of freedom from local progression and higher survival rates at 1–2 years [24]. Additional emerging data show that SBRT provides a role in pain relief and in oligometastases to the liver [25]. Future prospective randomized control trials are currently underway to investigate and expand the role of SBRT in current LAPC and BRPC treatment.
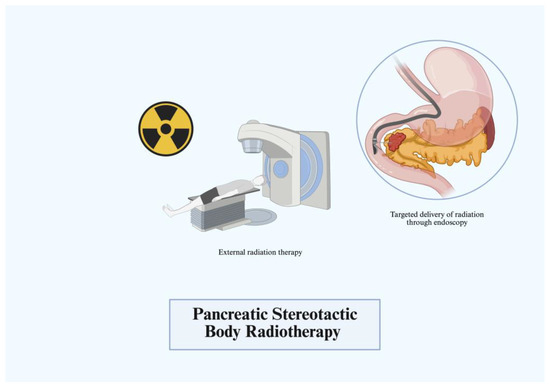
Figure 3.
Pancreatic stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT).
3.4. Cryoablation
Cryoablation is a more novel agent in the field of PDAC treatment. Cryoablation has advantages of shorter procedure times, reduced pain, and a decreased side effect profile. Changes in argon gas pressure generate freeze–thaw cycles and a catheter connected to a needle core is utilized to mediate cellular destruction, vascular damage, and tissue ischemia (Figure 4) [26]. The majority of current trials have used cryoablation as an adjunct to surgical intervention. One prospective trial has evaluated cryoablation in an EUS-guided approach; however, the conclusions were limited by lack of statistical power [27]. Porcine models have been explored, but no other current major trials exist evaluating EUS-guided cryoablation [28].
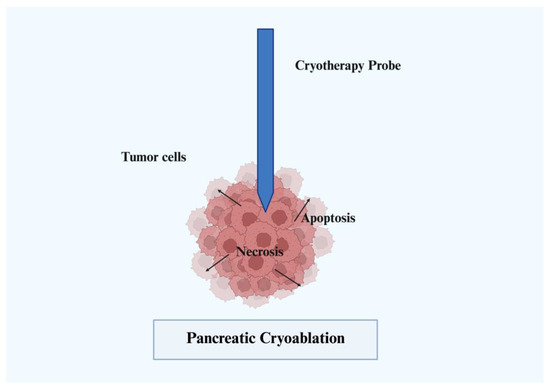
Figure 4.
Pancreatic cryoablation.
3.5. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
Similar to other therapies listed above, HIFU utilizes the vibrational waves of ultrasound to generate energy and heat. HIFU has the added benefit of acoustic cavitation alongside coagulative necrosis. Acoustic cavitation leads to local destruction of tissue from the high pressure and temperatures generated. HIFU has been evaluated in a non-endoscopic role directly delivered through the skin via transducer and water de-gasser (Figure 5) [29,30]. More recently, endoscopic HIFU has also been explored in combination with chemotherapy in treatment for advanced pancreatic cancer, leading to significant improvement in cancer pain [31]. Currently, FDA approval in the United States for HIFU is limited to bone metastases and uterine fibroid treatment, but use outside of the United States is being explored for other malignancies of prostate, breast, pancreas, and liver [32]. The function of HIFU in pancreatic cancer is predominantly palliative. In some small cohort retrospective trials, quality of life substantially improved and tumors near blood vessels, bowels, or stents were able to be successfully targeted [33]. One retrospective single study from Suining Central Hospital of 88 patients with advanced unresectable pancreatic cancer did not observe an effect on overall survival, but showed important results in tumor debulking and pain relief [34].
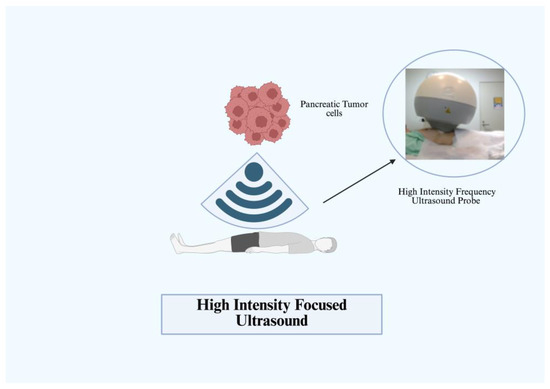
Figure 5.
Pancreatic high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) [30].
3.6. Irreversible Electroporation
More modern techniques such as irreversible electroporation (IRE) or NanoKnife apply a high-voltage pulsed electric field to change the transmembrane voltage, leading to nanometer-sized defects in cell membrane as well as cell death (Figure 6). Through high voltage electrical pulses, clinicians can deliver highly targeted non-thermal ablation to achieve tumor lysis and avoid collateral anatomical structures [8]. The most common application of IRE is in solid tumor malignancies such as liver and pancreatic cancer, with recent clinical trials demonstrating prolonged median survival and increased anti-tumor response [35]. First utilized in 2005, Davalos et al. established its use alongside surgery and chemotherapy for improved treatment results [36]. Initial in vitro studies demonstrated a significant decrease in proliferation of tumor cells in specific pancreatic cancer cell lines [37]. Furthermore, IRE causes controlled immune activation triggering cellular and humoral immune response to induce cell death. At higher frequencies of electrical pulse generation, a local antitumor immune response is generated without any distant tumor effect [38]. After approval from the FDA in 2009 for use in treating cancer, NanoKnife first demonstrated success in treating LAPC in 2012 [39]. Since then, studies conducted by Martin et al. and Sun et al. and others have demonstrated prolonged survival and progression-free survival in LAPC when combined with adjunctive chemotherapy [39,40]. A disadvantage of IRE in many of these trials is the higher adverse effect profile and severity of adverse events [35]. Additionally, a current prospective trial comparing IRE as a curative treatment to standard chemotherapeutic regimens for Stage III PDAC revealed no significant difference in outcomes [41]. This technique continues to demonstrate promise given the effects on local control, overall survival, and quality of life of patients with pancreatic malignancies.
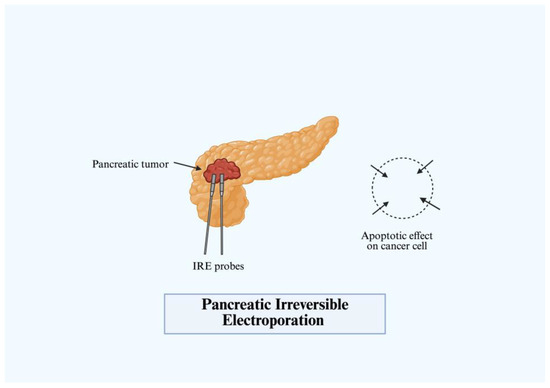
Figure 6.
Pancreatic irreversible electroporation (IRE).
3.7. Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) was introduced in 1931 by Martin Kirschner in experiments to treat trigeminal neuralgia [42]. Using radio waves to deliver targeted medium frequency alternating current energy to induce coagulative necrosis within cells, RFA has amazing versatility of applications. Development progressed significantly in the 1990s among patients undergoing ablation for unresectable liver malignancies [43]. In the early 2000s, RFA was first used in four patients with unresectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma and demonstrated prolonged periods of survival and even pain relief [44]. The current literature in both in vivo and ex vivo shows increased anti-tumor response and prolonged survival in patients with pancreatobiliary malignancies. It is the most studied ablative modality in the setting of pancreatic cancer.
A probe is inserted into tissue applying a current in a radio frequency range of 450–500 kHz (Figure 7) [45]. Similar to the mechanisms above, the high resistance to current produces heat and thus coagulative necrosis. Under endoscopic guidance, this technique has been applied to IPMNs, NETs, advanced pancreatic carcinomas, and others. EUS-RFA for pancreatic cystic lesions was first studied in 2015 by Pai et al., where six patients underwent RFA [46]. Two patients had complete resolution and three had partial tumor reduction [46]. Similar efficacy was seen in prospective studies by Barthet et al., where 64.7% of individuals achieved resolution at 12-month follow-up [47]. Younis et al. observed similar results in a smaller cohort of five patients [48]. Even in serous cystic neoplasms, a retrospective trial by Oh et al. demonstrated partial response in 8 of the 13 (62%) patients [49]. A wide clinical variety exists when evaluating pNETs, but clinical success with RFA has been more evident. A comparative trial by Crinò et al. in 2023 demonstrated EUS-RFA to be safer than surgery in 89 patients who underwent insulinoma treatment [50]. Despite the clinical variety and functionality of pNETs, most retrospective studies of EUS-RFA and pNETs demonstrate high success rates with a complete response rate of 86–96% [51]. Recently, Figueiredo et al. performed a large multicenter prospective trial in 29 patients with variable pancreatic tumors and saw a 73% response rate of pNETs and a 100% immediate response rate in functional pNETs [52].
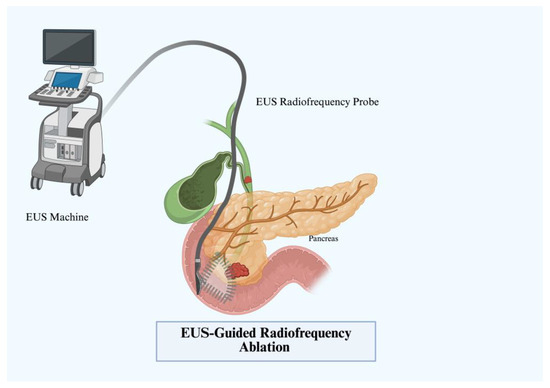
Figure 7.
EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA).
Spanning from the initial trials by Arcidiacono et al. to some of the most recent prospective single-center trials, technical success rates have grown to be 100% effective. Survival time in a very recent single center prospective study demonstrated a median survival rate of 20.5 months [53,54]. Previous studies in LAPC that had long-term follow-up demonstrated similar survival rates, even up to 24 months in patients who underwent EUS-RFA with adjunctive gemcitabine [49,55]. Not only is this procedure well-tolerated with a low serious adverse effect profile, but current data demonstrate the coagulative necrosis achieved through RFA releases cell debris-providing tumor antigens that can activate the adaptive tumor response to fight local and distal sites of malignancy [53]. Overall, RFA is the most studied ablative technique in the spectrum of pancreatic malignancies with the most evident benefit on survival and local and distant tumor control.
4. Biliary Ablation Techniques and Indications
Biliary malignancies most commonly are represented by cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), but can also represent gallbladder cancer, ampullary cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma. A majority of cases of CCA are unresectable at time of diagnosis. Survival rates at 5–10 years as stated above are less than 20% with a median survival duration of 3–9 months [55,56]. The breakdown of CCA is classified by intrahepatic or extrahepatic origin, presenting as locally advanced or metastatic in approximately 50–60% of patients [56]. The current standard of care of intraductal CCA is surgical resection and surgical resection plus neoadjuvant chemoradiation and liver transplant for perihilar CCA (pCCA) [57]. In distal CCA (dCCA), Whipple would be the primary curative procedure [57]. The majority of patients with CCA present at the time of already advanced disease, so chemotherapy is often the first-line treatment [57]. Gemcitabine cisplatin, based on the ABC-02 trial, has demonstrated superiority in median overall survival with limited benefit when adding radiation therapy, FOLFOX, or FOLFIRI [55].
This allows for an increased role for ablative therapies to deliver targeted cancer therapy and to challenge the current scope of treatment to further improve survival rates. Current ablation techniques are used in unresectable malignant biliary obstruction, and are often only able to provide palliative support. There are currently three modalities of ablative therapy that have been explored in CCA which include photodynamic therapy (PDT), intraluminal brachytherapy (IB), and RFA.
4.1. Biliary Intraluminal Brachytherapy
IB uses iridium-192 (192Ir) or iodine-125 (125I) on a ribbon placed endoscopically into the biliary tract trans-hepatically. After identifying the site of the tumor via endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), a guide wire is advanced through the structure with a naso-biliary tube passing over the wire. Fluoroscopy is used with radio-opaque markers to denote the intervals to position the tube to receive radioactive therapy. The trans-hepatic approach is usually preferred (Figure 8) due to the increased drainage access; however, direct cellular destruction is achieved regardless of method [56]. The first instance of this therapy was in 1981 by Fletcher et al. who demonstrated the use in palliation for hilar CCA [58]. Since then, multiple studies have attempted to recreate the treatment. A recent meta-analysis in 2021 by Taggar et al. evaluated 17 studies with variable characteristics and notably observed prolonged stent patency with IB in the range of 3.9–27.9 months (median 9.8 months) [59]. This is greater than that of the current standard of care, which is typically 6–7 months [59]. In clinical practice, however, IB is often not widely used due to the short half-life, poor side effect profile, and challenges in delivering the materials [60]. Thus, clinicians will often elect for PDT or RFA when treating CCA.
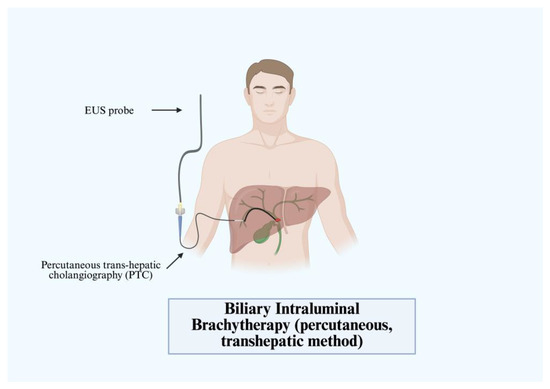
Figure 8.
Biliary intraluminal brachytherapy (percutaneous, transhepatic method).
4.2. Biliary Photodynamic Therapy
PDT relies on an intravenous photosensitizing agent to induce apoptosis through light-induced photoactivation. The most common agent in the United States is porfimer sodium, but a variety of agents are used in order to achieve the desired effect [61]. While not curative, patients with advanced CCA can benefit from stent placement and PDT. The substance gets absorbed by tissues at variable rates, and malignant biliary cells have a high predisposition. Subsequently, a diode laser fiber is positioned in the biliary tree across target stricture after ERCP with cholangiogram (Figure 9). Illumination to a targeted wavelength occurs, generating electron transfer mediated by the photosensitizer to create free radicals that lead to apoptosis and cell death [62]. Local tumor control is achieved through inflammatory cascades, vasoconstriction, and thrombosis. Given the risk of inflammatory damage, a stent is prophylactically placed to prevent cholangitis or obstruction.
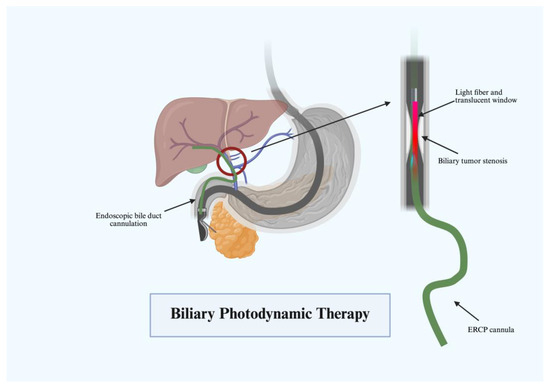
Figure 9.
Biliary photodynamic therapy.
Much of the use of PDT is founded on a landmark trial by Ortner et al. evaluating 39 patients who received stenting with PDT or stenting alone. Patients who underwent PDT with stenting demonstrated longer survival rates, increased biliary drainage, and improved quality of life [63]. Since then, several trials have been conducted exploring the role of PDT [64,65]. A meta-analysis by Chen et al. of 21 of the most current studies in this area demonstrated varying results in the efficacy of PDT [66]. Patients with biliary tract cancer who underwent PDT and stenting had slightly worse overall survival compared to stent placement alone (HR 1.56, 95% CI 1.00–2.43), but there was no significant different in 1-year and 2-year survival rates between these two groups [66]. Unclassified CCA with PDT and stent placement improved overall survival along with 2-year survival. PDT and stent placement improved both 1-and 2-year survival more than stenting alone in patients with hilar CCA. Two-year survival and overall survival were also improved in extrahepatic CCA cases with PDT and stent placement [66]. Future studies should seek to help elucidate the benefit of these treatments.
4.3. Biliary Radiofrequency Ablation
RFA applications in biliary malignancies have become increasingly common in the management of extrahepatic CCA, pCCA, ampullary neoplasms, and biliary strictures [64]. The only approved biliary RFA catheter currently in the United States is the Habib catheter (Boston Scientific, Natick, MA, USA). In 2011, Steele et al. introduced RFA for biliary decompression in unresectable malignant biliary obstruction. Six of these twenty-two patients in the open label trial had CCA and all patients received RFA and metal stent placement. Sixteen patients maintained stent patency at 90 days [67]. Cha et al. synthesized many of the current retrospective and randomized control trials evaluating RFA in biliary malignancy [68]. Pooling together seven trials, they determined RFA to have a significant impact on overall survival though few studies evaluated stent patency. Another recent review of nine studies investigated the outcomes of endoscopic or percutaneous RFA with stent placement in comparison to stent placement alone in 505 patients with malignant biliary strictures [69]. The RFA group had a longer stent patency of 50.6 days (95% CI: 32.83–68.48) and improved survival (hazard ratio, 1.395; 95% CI: 1.145–1.7; p < 0.001) [69]. Currently, a multicenter trial is underway to evaluate the efficacy of RFA versus PDT in unresectable biliary malignancy [70].
Other utilization for RFA includes benign biliary strictures and adenoma, although data surrounding these subjects are limited. Strictures can arise from surgical intervention, inflammation, or chronic pancreatitis induced by fibrous hyperplasia and subsequent duct lumen narrowing. Stents can be successful but due to risk of stricture formation, RFA can be employed when recurrent strictures occur. Only two current pilot studies exist for this therapy. From the nine-patient cohort of Hu et al., five achieved resolution of stricture and all six of the cohort of Akinci et al. had resolution, demonstrating the efficacy of RFA in limited stricture scenarios. Akinci et al. even noted the rather long time to re-evaluation, with an average of 430 days (270–575 days) [71,72]. Ampullary neoplasms have similarly limited data. Landim et al. pooled together the seven available retrospective and prospective trials surrounding RFA for low- and high-grade dysplasia in ampullary neoplasms [73]. Here, they found a high success rate of 75.7% (95% CI 65.0–88.0%) with the recurrence rate around 12 months to be nearly 24.3% (95% CI 16.0–35.0%) [73]. Given the variability of dysplasia and aggressive nature of CCA, it is easy to expect CCA to have a higher rate of recurrence. The surgical complications of duodenectomy and ampullectomy give rise to non-invasive forms of treatment, which RFA provides in the right clinical context. While RFA is an FDA-approved technology, the generalizability in CCA is limited by the small number of patients and variability in tumor types. Nonetheless, it has thus far shown to be an effective modality for improving stent patency and survival and merits further study.
After summarizing most of the past and current ablative therapies for pancreatic and biliary malignancies, it is easy to see the survival and treatment tolerability benefits of RFA. The effect of RFA on pancreatobiliary tumor cells is presently being uncovered and the success rates of treatment are already promising. The remainder of this review explores the unique and remarkable immunological reactions RFA treatment has on not only the targeted pancreatic tumor tissue, but also distant metastasis tissue.
5. Critical Evaluation of Different Ablation Techniques
The various ablation techniques employed to treat pancreatic and biliary cancers each have their own advantages and disadvantages. Alcohol ablation is an economical and relatively simple procedure; however, it is limited in targeting deeper or larger tumors and post-treatment pain can be significant [74]. Microwave ablation generates a higher temperature than RFA and is effective in treating larger tumors due to more efficient heat delivery. This can carry a higher risk of thermal injury to surrounding tissues and its use is limited by size and location of the tumor. SBRT is a non-invasive, high-precision technique especially for tumors that are difficult to reach with other modalities. Radiation-induced side effects such as skin reactions, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or less common strictures or bowel obstruction can occur and its effects may be delayed, making it less suitable for symptom management in the short term. Cryoablation uses extreme cold temperatures to induce tumor necrosis and has been found to be safe and effective in treating certain types of pancreatic cancers. Temperatures above −20 °C at the border of the ice ball may not be sufficient to kill all tumor cells leading to incomplete tumor destruction.
HIFU can be used both non-endoscopically and endoscopically with generally good tolerability, but is only limited to targeting well-localized and superficial tumors. IRE utilizes electric pulses to disrupt cell membranes, showing promise in treating tumors near large blood vessels or other critical structures where thermal techniques may fail. IRE is restricted to use in smaller tumors and its long-term effectiveness is still under investigation [75]. Biliary intraluminal brachytherapy delivers localized radiation directly to the tumor and has been effective in treating obstructive cholangiocarcinoma; however, it may lead to complications such as bile duct stenosis, strictures, and cholangitis [76]. Similarly, PDT offers symptom relief in cases of obstructive jaundice by using light to activate a photosensitizer, but its effectiveness is often restricted to superficial lesions and the need for an endoscopic light source insertion can complicate its application. Among these techniques, EUS-RFA offers advantages in terms of precision and safety, especially for tumors near critical structures such as blood vessels or ducts. Real-time imaging with EUS allows for accurate tumor targeting and minimal collateral damage to surrounding tissues, making it less prone to complications of thermal injury. There can be a heat–sink effect where blood flow dissipates heat, therefore reducing efficacy in larger or more vascularized tumors. Overall, EUS-RFA’s minimally invasive nature offers a favorable safety profile for palliative management without the limitations of other non-surgical ablative alternatives.
6. The Unique Tumor Microenvironment in Pancreaticobiliary Cancers
The tumor microenvironment (TME) refers to the complex and dynamic cellular, molecular, and vascular environment surrounding a tumor [77]. Common cellular components of the TME are cancer-associated fibroblasts, immune cells, extracellular matrix components, endothelial cells, and signaling molecules that all influence tumor growth, metastasis, and response to treatment [77]. Pancreatic cancer creates an immunosuppressive microenvironment that results in aggressive host anti-tumor immune invasion [78]. This leads to rapid cancer progression and poses challenges in treatment. The TME for pancreatic cancer includes cytokines, extracellular matrix, and cancer-associated fibroblasts that all play roles in tumor invasion, metastasis, and progression [78,79]. The stroma of PDAC comprised of these components creates a physical barrier that is responsible for treatment resistance [80]. Thus, understanding the pancreatic cancer TME can lead to the development of more targeted and potentially curative therapies.
One of the immune-suppressive aspects of pancreatic cancer is the low expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I which inhibits T-cell activation [79]. CD82 T cells are usually activated by interaction with MHC I antigen-presenting cells and attack cancer cells. These CD8 T cells play a critical role in antitumor response; however, there are some unique immunosuppressive mechanisms in pancreatic cancer cells. Some genetic mutations in pancreatic cancer cells lead to production of neoantigens which are presented on MHC class I receptors [81]. An effective immune response is not generated due to the immunosuppressive TME of PDAC where despite the presence of tumor neopeptides, T-cell activation is usually suppressed [82].
Other immunosuppressive mechanisms of pancreatic cancer TME include the upregulation of regulatory T cells (Tregs). Tregs primarily have an immune-suppressive function by upregulating immune-suppressive cytokines and inducing effector T-cell apoptosis [83,84]. It has been observed that higher concentrations of Tregs exist in patients with pancreatic cancer [84,85]. EUS-RFA has been shown to affect certain aspects of the pancreatic cancer TME in several human and animal studies. Many proinflammatory cytokines and genes are upregulated in RFA-treated tissue, illustrating the TME remodeling effects of this therapy [7].
Chemokines, particularly CXC13, are secreted by dendritic cells and myofibroblasts and have the function of recruiting T and B cells to maintain the antitumor response [86]. Interestingly, RFA has been shown to increase CXCL10, CXCL12, and CXCL13 expression in RFA-treated tumors compared to controls [7]. The increased presence of CXC13 is further support that RFA has a role in enhancing anti-tumor processes in activating adaptive immunity. Other immune modulators like CCL5, CD40, C5/C5a, ICAM, MIF, and SERPIN often increase after RFA, further illustrating the modulating effect RFA has on pancreatic TME [7].
Macrophages are important in regulation of the inflammatory processes, tissue remodeling, and surveillance of immune activities [87]. Macrophages can become activated by cytokines and can function to both activate or suppress immune reactions. M2 macrophages suppress the immune system and are activated by IL-4 and IL-13, and release cytokines that trigger a T-helper 2 immune response [88]. In the pancreatic cancer TME, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are reprogrammed to facilitate tumor angiogenesis and metastasis [89]. Dysplastic tumor cells secrete CCL2 which attracts inflammatory monocytes to the metastatic location [90]. CCL2 can stimulate CCL3 production by metastatic-associated macrophages (MAMs) which are essential in the spread of pancreatic tumor cells to the liver [91]. Therapeutic strategies targeting macrophages aiming to reduce the number of TAMs have their challenges due to the heterogenous nature of TAMs and their roles influenced by environmental conditions [92].
The TME in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is characterized by desmoplastic stroma with a high degree of heterogeneity among four main subtypes [93,94]. The immunogenic subtype in particular is characterized by an inflammatory TME with an over-expression of cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and PD-L1. The myeloid subtype describes increased expression of M2-macrophages and the mesenchymal subtype exhibits increased levels of activated fibroblasts [93]. T lymphocytes are the most common inflammatory cell in the CCA TME, particularly CD8+ [95]. Tumor-associated neutrophils also play a role in tumor development and progression; however, more needs to be discovered on understanding their roles as a potential target for therapy [96]. There are similarities in the cell types comprising both pancreatic and biliary malignancies. Therefore, treatment effects on these TMEs may be comparable.
7. Neutrophils Role in the Pancreatic Cancer TME Remodeling with RFA
Neutrophils play an important role in tumor antigen presentation to lymphocytes, activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells, and various chemokines that attract lytic cells to the target site. Additionally, neutrophils decrease myeloid-derived suppressor cell activity, preventing T-cell suppression and tumor growth. Tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) were elevated and peaked 24 h after tumor irradiation in a study conducted by Takeshima et al. In this study, CD11b + Gr-1 + cells (TANs) peak at 24 h after both 4T1 and EG7 irradiation therapy [97]. In fact, neutrophil-depleted mice had a significant increase in pancreatic tumor growth compared to tumor growth after radiation therapy, highlighting the crucial role neutrophils play in antitumor activity after radiation therapy. Cytokines and chemokines such as G-CSF, IL-1β, and KC can also help activate TANs. G-CSF levels have been observed to be significantly elevated after ablation therapy and similarly peaked 24 h post irradiation [97]. Thus, cytokines such as G-CSF can contribute to the infiltration of neutrophils after radiation.
There are several cytokines released by neutrophils in the host pro-inflammatory pathway in response to tumor invasion. Promising data exist that illustrate that RFA increases neutrophil infiltration which contributes to TME remodeling [98]. RFA-treated tumor tissue has been shown to have increased neutrophil infiltration as well as increased collagen deposition indicating TME remodeling [98]. Other tumor homogenates such as IL23, which is secreted by neutrophils, have been shown to be significantly increased after RFA treatment [98,99]. In addition to increasing the percentage of local neutrophils, RFA treatment has also been shown to reduce immunosuppressive cells such as regulatory T cells and tumor-associated macrophages [100]. Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) levels also remain elevated days after treatment in RFA-treated tumors, indicating the lasting effect RFA has on tumor cells and the potential concomitant role of immunotherapy for sustained inhibition of tumor growth [7].
8. RFA Effect on Distant TME-Abscopal Effect
The abscopal effect refers to a phenomenon where localized treatment, especially radiation therapy, of a tumor not only causes regression of the treated tumor, but also induces a therapeutic response to distant tumors [101]. As referenced earlier, RFA treatment induces coagulative necrosis through thermal energy leading to the release of cell debris. These necrotic components induce antigen response from the humoral immune system at both local and distant tumor sites [7].
Fei et al. further evaluated the translation of an RFA in vivo abscopal effect, exploring the role of distant immune effects [100]. Through single-cell RNA sequencing and single-cell T-cell receptor sequencing, clusters of immune cells were categorized and evaluated following RFA treatment in vivo. Increased immune response in distal tissues was present with the accumulation of CD8+PD-1+ clusters, which remained positive for 3 days in non-tumor cells. Additionally, the critical checkpoint inhibitors PD-1 and LAG-3 remained elevated along with macrophages, dendritic cells, and CD4+ cells. Levels of each cell peaked at 3 days and fell rapidly at 5–8 days [100]. While a majority were exhausted phenotypes, this can be suggestive of the increased activity tumor cells are placed under, both at the local and systemic level. Given the lack of sustained response, tumor suppression likely would not be achieved with RFA alone.
Neutrophils also have in important role in the abscopal effect. In neutrophil-depleted mice, tumor size was significantly increased in non-RFA-treated tumors compared to RFA-treated tumors [98]. RFA-treated neutrophil-depleted mice showed increased αSMA (a marker of myofibroblasts) expression only in distant non RFA-treated tumors. This highlights neutrophils’ role in an abscopal effect through modulation of myofibroblasts [98].
9. Discussion
The local and distant tumor-suppressive and immune-modulating effects of EUS-RFA indicate a promising role in pancreatobiliary malignancy treatment. For those who are not surgical candidates, ablation therapy can be effective in decreasing tumor size and also downregulating cancer immune reaction.
EUS-RFA is considered as a treatment option for patients with locally advanced, unresectable pancreatic tumors who might not be a good candidate for chemotherapy or radiation due to poor functional status or other factors. This treatment is most effective in patients with small tumors (typically < 3 cm) that are easily accessible through endoscopic ultrasound. It is also explored in patients with recurrent tumors that are confined to a single site or in a palliative setting among those who have recurrent obstructive symptoms such as jaundice and abdominal pain. For biliary tumors, EUS-RFA is commonly used for biliary obstruction or distal cholangiocarcinoma. Improvement in quality of life, reduction in pain, and alleviation of obstructive symptoms are all commonly observed outcomes to RFA, especially when combined with chemotherapy or stenting.
Some key considerations for patient selection include good performance status (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 0–2), a life expectancy of at least 3–6 months, and an absence of severe comorbidities such as uncontrolled coagulopathy, or active severe infection such as sepsis. RFA is usually contraindicated in patients with large tumors, extensive vascular involvement, poor performance status (ECOG ≥ 3), or those with distant metastases. Age and sex do not alter candidacy for RFA, but elderly patients or those with multiple debilitating comorbidities may require careful evaluation due to increased risks of the procedure itself and recovery. It is important to note that EUS-RFA can be considered as palliative therapy in patients with a poor prognosis with some of the above contraindications, and risk/benefit discussion should take place with the patient’s clinical care team. A multidisciplinary approach involving oncology, radiology, gastroenterology, and surgery teams is crucial in determining the appropriateness of EUS-RFA for many patients as the management of advanced pancreatic and biliary cancers can be complex.
There are historically several pancreatic and biliary ablative therapy techniques; however, EUS-RFA shows favorable outcomes in patients with pancreatobiliary malignancies. Both local and distant immune modulation has been observed after RFA treatment by affecting tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and other immune cells. Better knowledge of these immune mechanisms can also be used to create more targeted tumor-suppressive therapies. Overall, EUS-RFA demonstrates the capacity for an elevated immune response and could serve as an important adjunctive therapy to prevent progression and spread of malignancy. This review highlights the advantages of EUS-RFA therapy over other more invasive or inefficient ablation techniques and explores the remarkable immunological effects in reducing tumor size and improving patients’ quality of life. Additional prospective studies are warranted to further substantiate the mortality benefit of EUS-RFA in pancreatic cancer with and without metastatic disease.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/immuno5030030/s1, Table S1: Summary of Pancreatic Ablation Studies; Table S2: Summary of Biliary Ablation Studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, N.Q. and R.A.; writing—review and editing, supervision, N.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suker, M.; Beumer, B.R.; Sadot, E.; Marthey, L.; Faris, J.E.; Mellon, E.A.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Wang-Gillam, A.; Lacy, J.; Hosein, P.J.; et al. FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and patient-level meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.Y.; Wagner, T.D.; Fuss, M.; Thomas, C.R. Multimodality Approaches for Pancreatic Cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Farmer, W.; Hannon, G.; Ghosh, S.; Prina-Mello, A. Thermal ablation in pancreatic cancer: A scoping review of clinical studies. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1066990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraoni, E.Y.; Ju, C.; Robson, S.C.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Bailey-Lundberg, J.M. Purinergic and Adenosinergic Signaling in Pancreatobiliary Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 849258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, S.I.; Thompson, C.C.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Bounds, B.C.; Brugge, W.R. Ethanol lavage of pancreatic cystic lesions: Initial pilot study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 61, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Li, Z.S.; Jin, Z.D. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided ethanol ablation therapy for tumors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 3397–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Yim, Y.; Baek, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Shong, Y.K.; Lee, J.H. Ethanol ablation as a treatment strategy for benign cystic thyroid nodules: A comparison of the ethanol retention and aspiration techniques. Ultrasonography 2019, 38, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Paik, W.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.W.; Cho, I.R.; Ryu, J.K.; Kim, Y.T. Efficacy and predictive factors of endoscopic ultrasound-guided ethanol ablation in benign solid pancreatic tumors. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 5960–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Liu, W.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, F.; Zhai, B.; Shi, J.; Shi, G. Percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for lung cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2002, 24, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ardeshna, D.R.; Leupold, M.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Pawlik, T.M.; Cloyd, J.M.; Ejaz, A.; Shah, H.; Burlen, J.; Krishna, S.G. Advancements in Microwave Ablation Techniques for Managing Pancreatic Lesions. Life 2023, 13, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lygidakis, N.J.; Sharma, S.K.; Papastratis, P.; Zivanovic, V.; Kefalourous, H.; Koshariya, M.; Lintzeris, I.; Porfiris, T.; Koutsiouroumba, D. Microwave ablation in locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma—A new look. Hepatogastroenterology 2007, 54, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carrafiello, G.; Ierardi, A.M.; Fontana, F.; Petrillo, M.; Floridi, C.; Lucchina, N.; Cuffari, S.; Dionigi, G.; Rotondo, A.; Fugazzola, C. Microwave ablation of pancreatic head cancer: Safety and efficacy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, T.J.; Panahi, B.; Albrecht, M.H.; Naguib, N.N.N.; Nour-Eldin, N.E.A.; Gruber-Rouh, T.; Thompson, Z.M.; Basten, L.M. Microwave ablation of pancreatic tumors. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2018, 27, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Medranda, C.; Arevalo-Mora, M.; Oleas, R.; Alcivar-Vasquez, J.; Del Valle, R. Novel EUS-guided microwave ablation of an unresectable pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. VideoGIE 2022, 7, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammel, P.; Huguet, F.; Van Laethem, J.L.; Goldstein, D.; Glimelius, B.; Artru, P.; Borbath, I.; Bouché, O.; Shannon, J.; André, T.; et al. Effect of chemoradiotherapy vs chemotherapy on survival in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer controlled after 4 months of gemcitabine with or without erlotinib the LAP07 randomized clinical trial. JAMA—J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 315, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loehrer, P.J.; Feng, Y.; Cardenes, H.; Wagner, L.; Brell, J.M.; Cella, D.; Flynn, P.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Crane, C.H.; Alberts, S.R.; et al. Gemcitabine alone versus gemcitabine plus radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: An Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4105–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauffert, B.; Mornex, F.; Bonnetain, F.; Rougier, P.; Mariette, C.; Bouché, O.; Bosset, J.F.; Aparicio, T.; Mineur, L.; Azzedine, A.; et al. Phase III trial comparing intensive induction chemoradiotherapy (60 Gy, infusional 5-FU and intermittent cisplatin) followed by maintenance gemcitabine with gemcitabine alone for locally advanced unresectable pancreatic cancer. Definitive results of the 2000-01 FFCD/SFRO study. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkoň, P.; Trna, J.; Slávik, M.; Němeček, R.; Kazda, T.; Pospíšil, P.; Dastych, M.; Eid, M.; Novotný, I.; Procházka, T.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) of Pancreatic Cancer—A Critical Review and Practical Consideration. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koong, A.C.; Le, Q.T.; Ho, A.; Fong, B.; Fisher, G.; Cho, C.; Ford, J.; Poen, J.; Gibbs, I.C.; Mehta, V.K.; et al. Phase I study of stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 58, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, A.; Kaiser, A.; Regine, W.F.; Chuong, M.D. The expanding role of stereotactic body radiation therapy for pancreatic cancer: A review of the literature. Transl. Cancer Res. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, B.; Ferrera-Alayón, L.; Espinosa-López, A.; Vera-Rosas, A.; Salcedo, E.; Kannemann, A.; Alayon, A.; Chicas-Sett, R.; Lloret, M.; Lara, P.C. Dose-escalated SBRT for borderline and locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Feasibility, safety and preliminary clinical results of a multicenter study. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 45, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.M.; Hoffman, J.P.; Thayer, S.P.; Wolff, R.A. Management of the primary tumor and limited metastases in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. JNCCN J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2015, 13, e29–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erinjeri, J.P.; Clark, T.W.I. Cryoablation: Mechanism of action and devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, S187–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testoni, S.G.G.; Petrone, M.C.; Reni, M.; Rossi, G.; Barbera, M.; Nicoletti, V.; Gusmini, S.; Balzano, G.; Linzenbold, W.; Enderle, M.; et al. Efficacy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided ablation with the hybridtherm probe in locally advanced or borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: A phase ii randomized controlled trial. Cancers 2021, 13, 4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baust, J.M.; Robilotto, A.; Raijman, I.; Santucci, K.L.; Van Buskirk, R.G.; Baust, J.G.; Snyder, K.K. The Assessment of a Novel Endoscopic Ultrasound-Compatible Cryocatheter to Ablate Pancreatic Cancer. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F. High intensity focused ultrasound: A noninvasive therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16480–16488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofuni, A.; Asai, Y.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tanaka, R.; Tonozuka, R.; Honjo, M.; Mukai, S.; Nagai, K.; Yamamoto, K.; et al. Novel Therapeutic Method for Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer—The Impact of the Long-Term Research in Therapeutic Effect of High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4845–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, G.; Wang, D.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ji, Y.; Zhong, B.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Z.; et al. Concurrent gemcitabine and high-intensity focused ultrasound therapy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2010, 21, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, M.; Schiraldi, L.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Memeo, R.; Mutter, D.; Pessaux, P.; Marescaux, J. High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) applied to hepato-bilio-pancreatic and the digestive system—Current state of the art and future perspectives. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2016, 5, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinova, M.; Feradova, H.; Gonzalez-Carmona, M.A.; Conrad, R.; Tonguc, T.; Thudium, M.; Becher, M.U.; Kun, Z.; Gorchev, G.; Tomov, S.; et al. Improving quality of life in pancreatic cancer patients following high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) in two European centers. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 5818–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.; Wan, L.I.; Wu, Y. Analysis of the results of high-intensity focused ultrasound for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. 2023, 40, 2250586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajewska-Naryniecka, A.; Szwedowicz, U.; Łapińska, Z.; Rudno-Rudzińska, J.; Kielan, W.; Kulbacka, J. Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreatic Cancer—An Evolving Experimental and Clinical Method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davalos, R.V.; Mir, L.M.; Rubinsky, B. Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutiani, N.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Pandit, H.; Shi, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Pulliam, Z.R.; Tan, M.; Martin, R.C.G. Electrochemotherapy with Irreversible Electroporation and FOLFIRINOX Improves Survival in Murine Models of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 4348–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercadal, B.; Beitel-White, N.; Aycock, K.N.; Castellví, Q.; Davalos, R.V.; Ivorra, A. Dynamics of Cell Death After Conventional IRE and H-FIRE Treatments. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 48, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.C.G.; McFarland, K.; Ellis, S.; Velanovich, V. Irreversible electroporation therapy in the management of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2012, 215, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Liu, Y.; He, C.; Hu, W.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Wu, J.; Xie, F.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Combining NanoKnife with M1 oncolytic virus enhances anticancer activity in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021, 502, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.C.G.; White, R.R.; Bilimoria, M.M.; Kluger, M.D.; Iannitti, D.A.; Polanco, P.M.; Hammil, C.W.; Cleary, S.P.; Heithaus, R.E.; Welling, T.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Irreversible Electroporation When Used for the Ablation of Stage 3 Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Initial Results from the DIRECT Registry Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhitny, V.P.; Jannoud, R.; Young, J.P.; Dixon, B.; Bungart, B.; Phillips, L.; Sutin, K.; Bernstein, J.; Issa, M. Radiofrequency Ablation: Honoring the Pioneers of Modern Therapeutic Innovations. Cureus 2024, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curley, S.A.; Izzo, F. Radiofrequency ablation of primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 7, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, Y.; Nakagawa, A.; Kamiyama, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Kubo, N.; Nakase, Y. Selective thermocoagulation of unresectable pancreatic cancers by using radiofrequency capacitive heating. Pancreas 2000, 20, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaneethan, U.; Thosani, N.; Goodman, A.; Manfredi, M.; Pannala, R.; Parsi, M.A.; Smith, Z.L.; Sullivan, S.A.; Banerjee, S.; Maple, J.T. Radiofrequency ablation devices. VideoGIE 2017, 2, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, M.; Habib, N.; Senturk, H.; Lakhtakia, S.; Reddy, N.; Cicinnati, V.R.; Kaba, I.; Beckebaum, S.; Drymousis, P.; Kahaleh, M.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound guided radiofrequency ablation, for pancreatic cystic neoplasms and neuroendocrine tumors. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2015, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthet, M.; Giovannini, M.; Lesavre, N.; Boustiere, C.; Napoleon, B.; Koch, S.; Gasmi, M.; Vanbiervliet, G.; Gonzalez, J.M. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and pancreatic cystic neoplasms: A prospective multicenter study. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, F.; Ben-Ami Shor, D.; Lubezky, N.; Geva, R.; Osher, E.; Shibolet, O.; Phillips, A.; Scapa, E. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation of premalignant pancreatic-cystic neoplasms and neuroendocrine tumors: Prospective study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 34, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.; Ko, S.W.; Seo, D.W.; Hong, S.M.; Kim, J.H.; Song, T.J.; Park, D.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, M.H. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation of pancreatic microcystic serous cystic neoplasms: A retrospective study. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crinò, S.F.; Napoleon, B.; Facciorusso, A.; Lakhtakia, S.; Borbath, I.; Caillol, F.; Do-Cong Pham, K.; Rizzatti, G.; Forti, E.; Palazzo, L.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Radiofrequency Ablation Versus Surgical Resection for Treatment of Pancreatic Insulinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 2834–2843.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.C.S.; Adler, D.G. EUS-radiofrequency ablation for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Is there a promising future? Endosc. Ultrasound 2024, 13, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo Ferreira, M.; Garces-Duran, R.; Eisendrath, P.; Devière, J.; Deprez, P.; Monino, L.; Van Laethem, J.-L.; Borbath, I. EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation of pancreatic/peripancreatic tumors and oligometastatic disease: An observational prospective multicenter study. Endosc. Int. Open 2022, 10, E1380–E1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moond, V.; Maniyar, B.; Harne, P.S.; Bailey-Lundberg, J.M.; Thosani, N.C. Harnessing endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation to reshape the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma microenvironment and elicit systemic immunomodulation. Explor. Target. Antitumor Ther. 2024, 5, 1056–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thosani, N.; Cen, P.; Rowe, J.; Guha, S.; Bailey-Lundberg, J.M.; Bhakta, D.; Patil, P.; Wray, C.J. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA) for advanced pancreatic and periampullary adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zori, A.G.; Yang, D.; Draganov, P.V.; Cabrera, R. Advances in the management of cholangiocarcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, I.S.; Mcpherson, G.A.D.; Blumgart, L.H. IRIDIUM-192 WIRE FOR HILAR CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA. Lancet 1981, 318, 582–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A.; Wege, H.; Caca, K.; Nashan, B.; Neumann, U. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Cholangiocarcinoma. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2014, 111, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fletcher, M.S.; Brinkley, D.; Dawson, J.L.; Nunnerley, H.; Williams, R. Treatment of hilar carcinoma by bile drainage combined with internal radiotherapy using 192iridium wire. Br. J. Surg. 1983, 70, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggar, A.S.; Mann, P.; Folkert, M.R.; Aliakbari, S.; Myrehaug, S.D.; Dawson, L.A. A systematic review of intraluminal high dose rate brachytherapy in the management of malignant biliary tract obstruction and cholangiocarcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 165, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowronek, J.; Zwierzchowski, G. Brachytherapy in the treatment of bile duct cancer—A tough challenge. J. Contemp. Brachytherapy 2017, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, Y.K. Recent advances of photodynamic therapy for biliary tract cancer. Int. J. Gastrointest. Interv. 2021, 10, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talreja, J.P.; DeGaetani, M.; Ellen, K.; Schmitt, T.; Gaidhane, M.; Kahaleh, M. Photodynamic therapy in unresectable cholangiocarcinoma: Not for the uncommitted. Clin. Endosc. 2013, 46, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortner, M.A.E.J.; Liebetruth, J.; Schreiber, S.; Hanft, M.; Wruck, U.; Fusco, V.; Muller, J.M.; Hortnagl, H.; Lochs, H.; Nishioka, N.S. Photodynamic therapy of nonresectable cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, E.S.; Tarnasky, P.R.; Kedia, P. Ablative therapies of the biliary tree. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.Y.; Cheon, Y.K.; Shim, C.S.; Cho, Y.D. Photodynamic therapy prolongs metal stent patency in patients with unresectable hilar cholangiocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 5589–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Umbrella review of adjuvant photodynamic therapy for cholangiocarcinoma palliative treatment. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2025, 51, 104472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, A.W.; Postgate, A.J.; Khorsandi, S.; Nicholls, J.; Jiao, L.; Vlavianos, P.; Habib, N.; Westaby, D. Endoscopically applied radiofrequency ablation appears to be safe in the treatment of malignant biliary obstruction. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 73, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, B.H.; Jang, M.J.; Lee, S.H. Survival benefit of intraductal radiofrequency ablation for malignant biliary obstruction: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Clin. Endosc. 2021, 54, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, A.A.; Khan, M.A.; Das, A.; Sachdev, M.; Khuder, S.; Nawras, A.; Lee, W. Radiofrequency ablation combined with biliary stent placement versus stent placement alone for malignant biliary strictures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 944–951.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.; Zapf, A.; Ozga, A.K.; Canbay, A.; Denzer, U.; De Toni, E.N.; Lohse, A.W.; Schulze, K.; Rösch, T.; Stein, A.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation via catheter and transpapillary access in patients with cholangiocarcinoma (ACTICCA-2 trial)—A multicenter, randomized, controlled, open-label investigator-initiated trial. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Gao, D.J.; Wu, J.; Wang, T.T.; Yang, X.M.; Ye, X. Intraductal radiofrequency ablation for refractory benign biliary stricture: Pilot feasibility study. Dig. Endosc. 2014, 26, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinci, D.; Unal, E.; Ciftci, T.T.; Kyendyebai, S.; Abbasoglu, O.; Akhan, O. Endobiliary radiofrequency ablation in the percutaneous management of refractory benign bilioenteric anastomosis strictures. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, W83–W91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landim, D.L.; de Moura, D.T.H.; Hirsch, B.S.; de Oliveira, G.H.P.; Veras, M.d.O.; Nunes, F.G.; Cavassola, P.R.P.; Bernardo, W.M.; Mahmood, S.; de Moura, E.G.H. Radiofrequency ablation for ampullary neoplasia with intraductal extension after endoscopic papillectomy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2024, 12, E440–E447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, W.H.; Seo, D.W.; Dhir, V.; Wang, H.P. Safety and efficacy of EUS-guided ethanol ablation for treating small solid pancreatic Neoplasm. Medicine 2016, 95, e2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, Q.D.; Schmitges, J.; Sun, M.; Sukumar, S.; Sammon, J.; Shariat, S.F.; Jeldres, C.; Bianchi, M.; Tian, Z.; Perrotte, P.; et al. Improvement of racial disparities with respect to the utilization of minimally invasive radical prostatectomy in the United States. Cancer 2012, 118, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosla, D.; Zaheer, S.; Gupta, R.; Madan, R.; Goyal, S.; Kumar, N.; Kapoor, R. Role of intraluminal brachytherapy in palliation of biliary obstruction in cholangiocarcinoma: A brief review. World J. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the Crime: Functions of Cells Recruited to the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, T.; Hiroshima, Y.; Matsuyama, R.; Homma, Y.; Hoffman, R.M.; Endo, I. Role of the tumor microenvironment in pancreatic cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2019, 3, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryschich, E.; Cebotari, O.; Fabian, O.V.; Autschbach, F.; Kleeff, J.; Friess, H.; Bierhaus, A.; Büchler, M.W.; Schmidt, J. Loss of heterozygosity in the HLA class I region in human pancreatic cancer. Tissue. Antigens. 2004, 64, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratticò, F.; Garajová, I. Focus on Pancreatic Cancer Microenvironment. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Forget, M.A.; Lucas, F.A.S.; Alvarez, H.A.; Haymaker, C.; Chattopadhyay, C.; Kim, S.H.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Grimm, E.A.; et al. Exploiting the neoantigen landscape for immunotherapy of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignali, D.A.A.; Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Sakaguchi, S. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Nakazawa, M.; Matsuyama, R.; Mori, R.; Takeda, K.; Ichikawa, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Endo, I. Changes in the immune cell population and cell proliferation in peripheral blood after gemcitabine-based chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 16, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazanietz, M.G.; Durando, M.; Cooke, M. CXCL13 and its receptor CXCR5 in cancer: Inflammation, immune response, and beyond. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Leng, X.; Zhang, Q. The Current State of Nanoparticle-Induced Macrophage Polarization and Reprogramming Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyken, S.J.; Locksley, R.M. Interleukin-4- and Interleukin-13-Mediated Alternatively Activated Macrophages: Roles in Homeostasis and Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, B.Z.; Pollard, J.W. Macrophage Diversity Enhances Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Cell 2010, 141, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonapace, L.; Coissieux, M.M.; Wyckoff, J.; Mertz, K.D.; Varga, Z.; Junt, T.; Bentires-Alj, M. Cessation of CCL2 inhibition accelerates breast cancer metastasis by promoting angiogenesis. Nature 2014, 515, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrilovich, D. Fatal attraction: How macrophages participate in tumor metastases. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorestani, P.; Dashti, M.; Nejati, N.; Habibi, M.A.; Askari, M.; Robat-Jazi, B.; Ahmadpour, S.; Tavakolpour, S. The complex role of macrophages in pancreatic cancer tumor microenvironment: A review on cancer progression and potential therapeutic targets. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Job, S.; Rapoud, D.; Dos Santos, A.; Gonzalez, P.; Desterke, C.; Pascal, G.; Elarouci, N.; Ayadi, M.; Adam, R.; Azoulay, D.; et al. Identification of Four Immune Subtypes Characterized by Distinct Composition and Functions of Tumor Microenvironment in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2020, 72, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulpice, L.; Rayar, M.; Desille, M.; Turlin, B.; Fautrel, A.; Boucher, E.; Llamas-Gutierrez, F.; Meunier, B.; Boudjema, K.; Clément, B.; et al. Molecular profiling of stroma identifies osteopontin as an independent predictor of poor prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1992–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goeppert, B.; Frauenschuh, L.; Zucknick, M.; Stenzinger, A.; Andrulis, M.; Klauschen, F.; Joehrens, K.; Warth, A.; Renner, M.; Mehrabi, A.; et al. Prognostic impact of tumour-infiltrating immune cells on biliary tract cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaul, M.E.; Fridlender, Z.G. Tumour-associated neutrophils in patients with cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshima, T.; Pop, L.M.; Laine, A.; Iyengar, P.; Vitetta, E.S.; Hannan, R. Key role for neutrophils in radiation-induced antitumor immune responses: Potentiation with G-CSF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11300–11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraoni, E.Y.; O’Brien, B.J.; Strickland, L.N.; Osborn, B.K.; Mota, V.; Chaney, J.; Atkins, C.L.; Cen, P.; Rowe, J.; Cardenas, J.; et al. Radiofrequency Ablation Remodels the Tumor Microenvironment and Promotes Neutrophil-Mediated Abscopal Immunomodulation in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023, 11, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chu, Z.; Yang, T.; Sun, H.X.; Yang, F.; Wang, W.; Hou, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Characterization and biological significance of IL-23-induced neutrophil polarization. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Q.; Pan, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.; Hou, Z.; Yu, X.; Lin, X.; Lin, R.; Lu, F.; et al. High-dimensional single-cell analysis delineates radiofrequency ablation induced immune microenvironmental remodeling in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grass, G.D.; Krishna, N.; Kim, S. The immune mechanisms of abscopal effect in radiation therapy. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2016, 40, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).