Pathogenic Mechanisms of Collagen TypeⅦA1 (COL7A1) and Transporter Protein Transport and Golgi Organization 1 (TANGO1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A New Therapeutic Target
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. Western Blot (WB) and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) in Plasma Samples
2.3. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Isolation, RNA Isolation, and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.4. In Vitro Analysis
2.4.1. Cell Culture and In Vitro Knockdown of COL7A1
2.4.2. WB Analysis and qRT-PCR
2.5. In Silico Analysis
2.5.1. Screening of COL7A1- and TANGO1-Interacting Proteins and Association with RA
2.5.2. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Construction of Selected Proteins
2.5.3. Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment Analysis of Selected Proteins
2.5.4. Pathway Enrichment Analysis of Selected Proteins
2.5.5. Preparation of Target Proteins for Molecular Docking
2.5.6. Preparation of Ligands
2.5.7. Active Binding Site Prediction
2.5.8. Molecular Docking
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
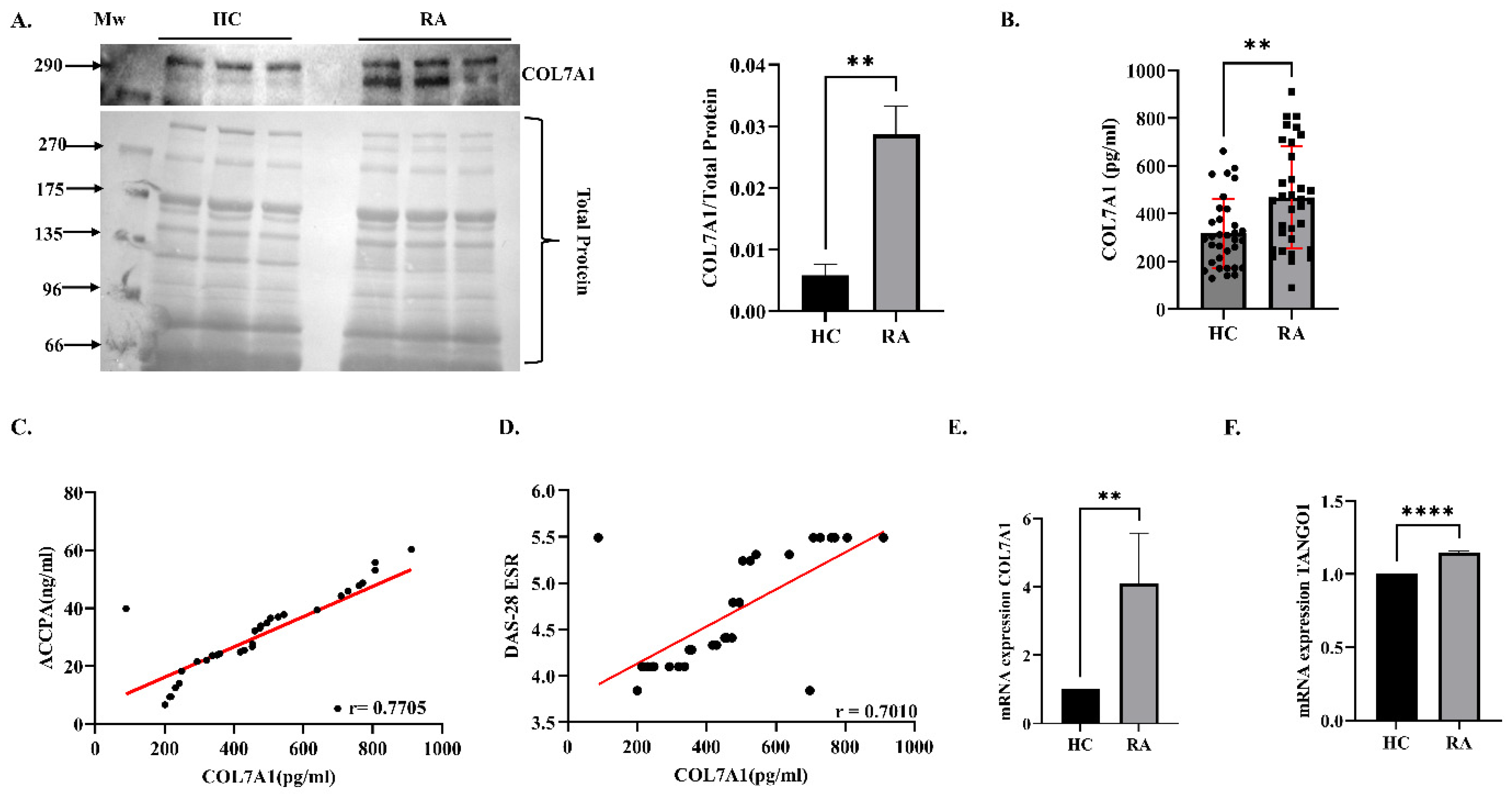
3.1. Expression Analysis of COL7A1 in Plasma and PBMCs
3.2. Effect of Knockdown of COL7A1 on Inflammation in SW982 Cells (In Vitro Analysis)
3.3. Targeted Therapeutic Approach of COL7A1-Associated Proteins in RA (In Silico Analysis)
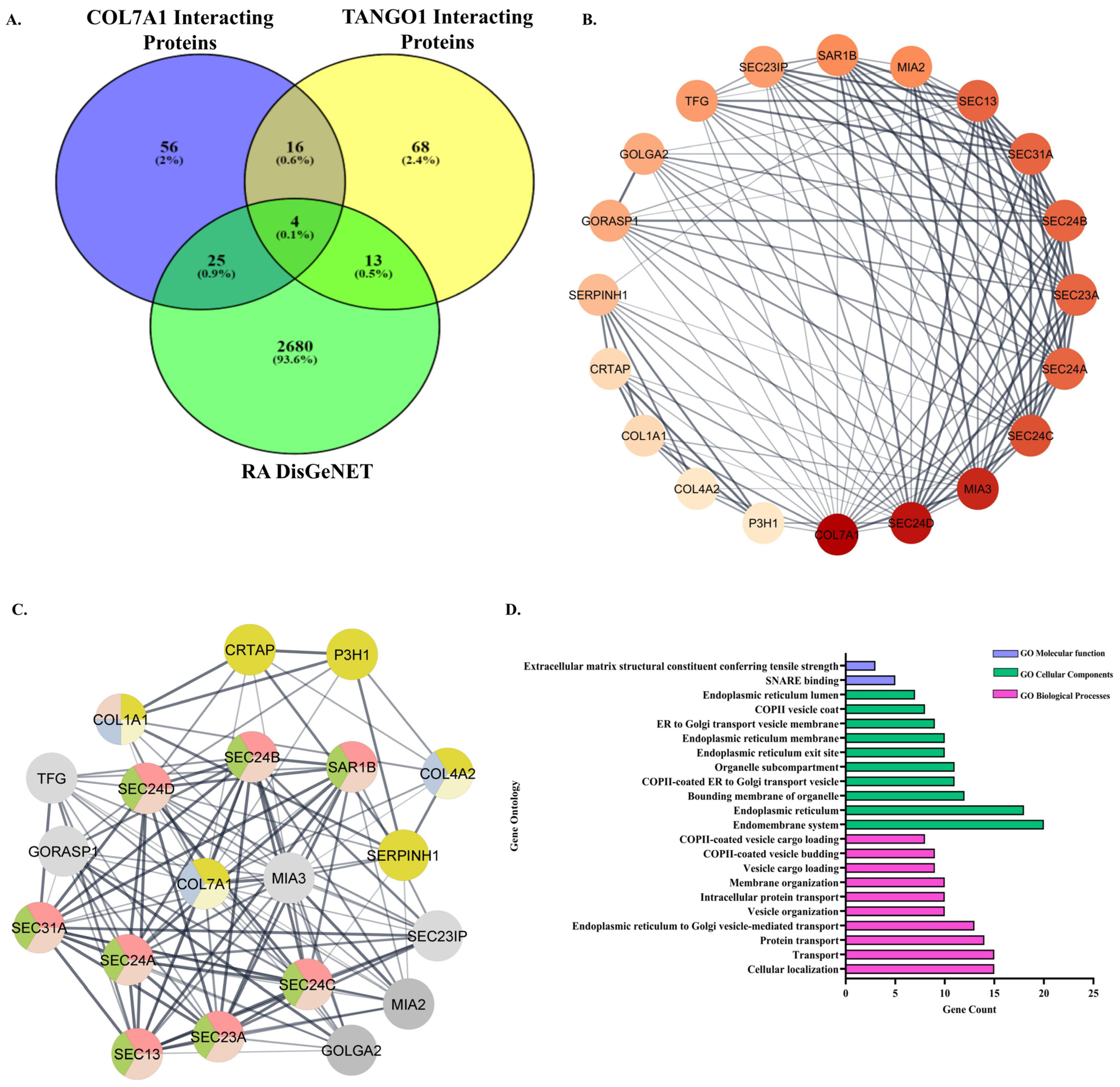
3.3.1. Retrieval of Common Interacting Proteins of COL7A1 and TANGO1 and Association with RA
3.3.2. PPI Network of the Common Interacting Proteins of COL7A1 and TANGO1
3.3.3. Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment Analysis
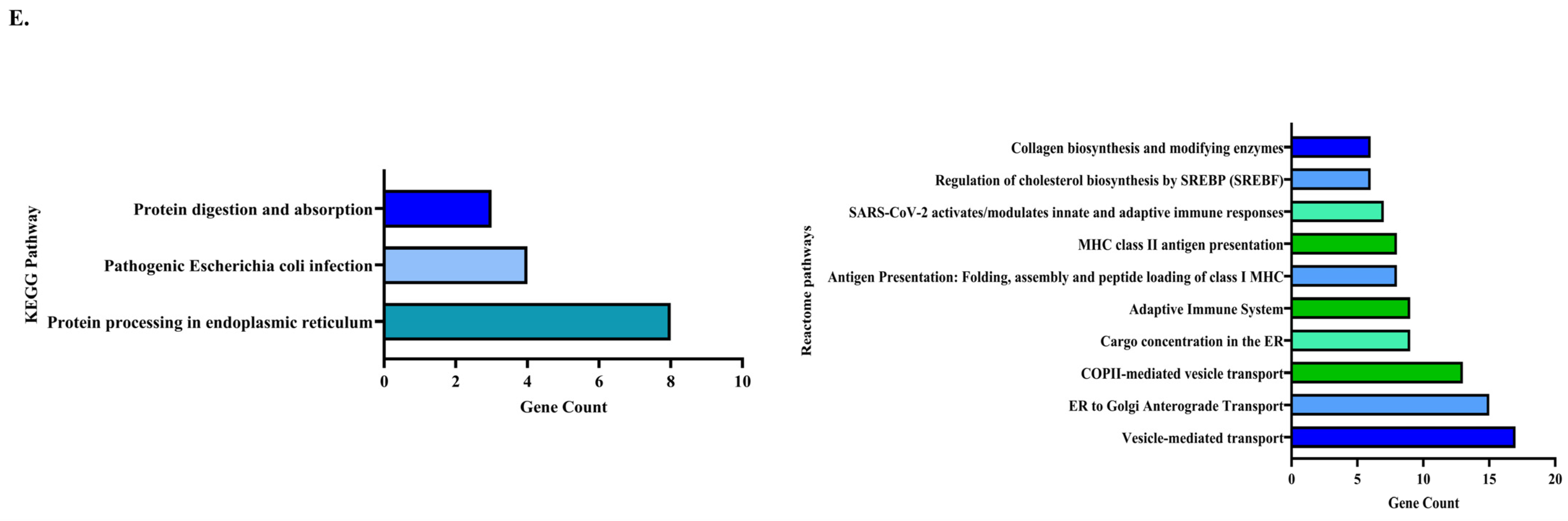
3.3.4. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.3.5. Molecular Docking of COL7A1 and TANGO1
3.3.6. Docked Complex Preparation of Drugs with TANGO1
3.3.7. Molecular Docking of COL7A1 with TANGO–Drug Complexes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Elango, J.; Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Ge, B.; Hou, C.; Pan, Z.; Bao, B.; Pérez Albacete Martínez, C.; Granero Marín, J.M.; Maté Sánchez de Val, J.E.; Wu, W. Paradoxical Duel Role of Collagen in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Cause of Inflammation and Treatment. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rannou, F.; François, M.; Corvol, M.-T.; Berenbaum, F. Cartilage breakdown in rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2006, 73, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, J.M.; Huffstutter, E.H.; Townes, A.S.; Kang, A.H. Incidence and specificity of antibodies to types I, II, III, IV, and V collagen in rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic diseases as measured by 125I-radioimmunoassay. Arthritis Rheum. 1983, 26, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelse, K.; Pöschl, E.; Aigner, T. Collagens—Structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.J.; Uitto, J. Type VII collagen: The anchoring fibril protein at fault in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Dermatol. Clin. 2010, 28, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Wei, W. Extracellular matrix in synovium development, homeostasis and arthritis disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 121, 110453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptashekas, R.S.; Vaĭtkene, D.I. Formation of collagen fibrils in the synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis (electron microscope study). Arkhiv Anat. Gistol. I Embriol. 1983, 84, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- García-Bermúdez, M.; López-Mejías, R.; González-Juanatey, C.; Corrales, A.; Castañeda, S.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; González-Gay, M.A. Association Study of MIA3 rs17465637 Polymorphism with Cardiovascular Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. DNA Cell Biol. 2012, 31, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, A.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates collagen VII expression by cutaneous cells in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 117, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidwell, R.U.; Yates, R.; Atherton, D. Dilated cardiomyopathy in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Arch. Dis. Child. 2000, 83, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küttner, V.; Mack, C.; Gretzmeier, C.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Dengjel, J. Loss of collagen VII is associated with reduced transglutaminase 2 abundance and activity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2381–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, A.; Velati, D.; Mittapalli, V.R.; Fritsch, A.; Kern, J.S.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. Collagen VII plays a dual role in wound healing. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3498–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küttner, V.; Mack, C.; Rigbolt, K.T.G.; Kern, J.S.; Schilling, O.; Busch, H.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Dengjel, J. Global remodelling of cellular microenvironment due to loss of collagen VII. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2013, 9, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Maeda, M. Not just a cargo receptor for large cargoes; an emerging role of TANGO1 as an organizer of ER exit sites. J. Biochem. 2019, 166, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Chen, M.; Bard, F.; Chen, S.; Zhou, H.; Woodley, D.; Polischuk, R.; Schekman, R.; Malhotra, V. TANGO1 Facilitates Cargo Loading at Endoplasmic Reticulum Exit Sites. Cell 2009, 136, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.G.; Phamluong, K.; Li, L.; Sun, M.; Cao, T.C.; Liu, P.S.; Modrusan, Z.; Sandoval, W.N.; Rangell, L.; Solloway, M.J. Global defects in collagen secretion in a Mia3/TANGO1 knockout mouse. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemyn, B.; Nampoothiri, S.; Syx, D.; Malfait, F.; Symoens, S. Loss of TANGO1 Leads to Absence of Bone Mineralization. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasahira, T.; Kirita, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Ueda, N.; Kurihara, M.; Matsushima, S.; Bhawal, U.K.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Kuniyasu, H. Transport and Golgi organisation protein 1 is a novel tumour progressive factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Sharma, S.; Saroha, A.; Bhakuni, D.S.; Malhotra, R.; Zahur, M.; Oellerich, M.; Das, H.R.; Asif, A.R. Identification of novel autoantigen in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients using an immunoproteomics approach. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monu Agnihotri, P.; Saquib, M.; Sarkar, A.; Chakraborty, D.; Kumar, U.; Biswas, S. Transthyretin and Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Product’s Differential Levels Associated with the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 5581–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Chakraborty, D.; Kumar, V.; Malhotra, R.; Biswas, S. Upregulation of leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein: A key regulator of inflammation and joint fibrosis in patients with severe knee osteoarthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1028994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venn, J.I. On the diagrammatic and mechanical representation of propositions and reasonings. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1880, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihaiti, Y.; Tuerhong, X.; Ye, J.-T.; Ren, X.-Y.; Xu, P. Identification of pivotal genes and pathways in the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis through integrated bioinformatic analysis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3513–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Malik, S.; Ideker, T.; et al. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, D.; Sarkar, A.; Mann, S.; Monu Agnihotri, P.; Saquib, M.; Biswas, S. Estrogen-mediated differential protein regulation and signal transduction in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2022, 69, R25–R43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, D.; Gupta, K.; Biswas, S. Potential role of Bavachin in Rheumatoid arthritis: Informatics approach for rational based selection of phytoestrogen. J. Herb. Med. 2023, 38, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Chan, H.C.S.; Hu, Z. Using PyMOL as a platform for computational drug design. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2017, 7, e1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloni, D.; Chakraborty, D.; Tiwari, A.; Biswas, S. In silico studies on the phytochemical components of Murraya koenigii targeting TNF-α in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Herb. Med. 2020, 24, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Chen, C.; Lei, X.; Zhao, J.; Liang, J. CASTp 3.0: Computed atlas of surface topography of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W363–W367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Xia, B.; Porter, K.A.; Padhorny, D.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Vajda, S. The ClusPro web server for protein–protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseenko, A.; Ignatov, M.; Jones, G.; Sabitova, M.; Kozakov, D. Protein–protein and protein–peptide docking with ClusPro server. Protein Struct. Predict. 2020, 157–174. [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple Ligand–Protein Interaction Diagrams for Drug Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaide-Ruggiero, L.; Molina-Hernández, V.; Granados, M.M.; Domínguez, J.M. Main and Minor Types of Collagens in the Articular Cartilage: The Role of Collagens in Repair Tissue Evaluation in Chondral Defects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhaj Mahmoud, D.; Kaabachi, W.; Sassi, N.; Mokhtar, A.; Ben Ammar, L.; Rekik, S.; Tarhouni, L.; Kallel-Sellami, M.; Cheour, E.; Laadhar, L.; et al. Expression of extracellular matrix components and cytokine receptors in human fibrocytes during rheumatoid arthritis. Connect. Tissue Res. 2021, 62, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.; Murrell, D.F. Mutation analysis and characterization of COL7A1 mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

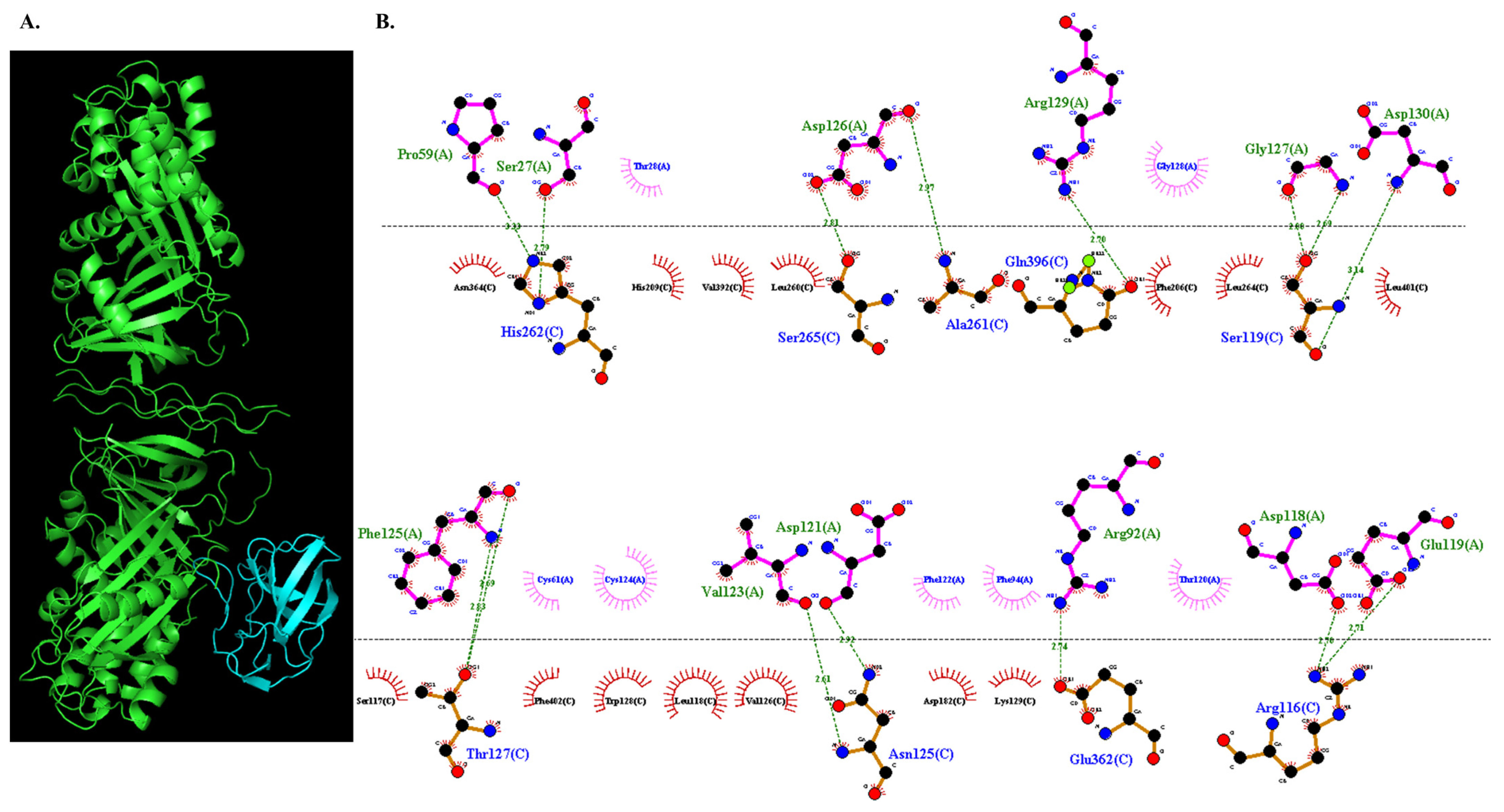
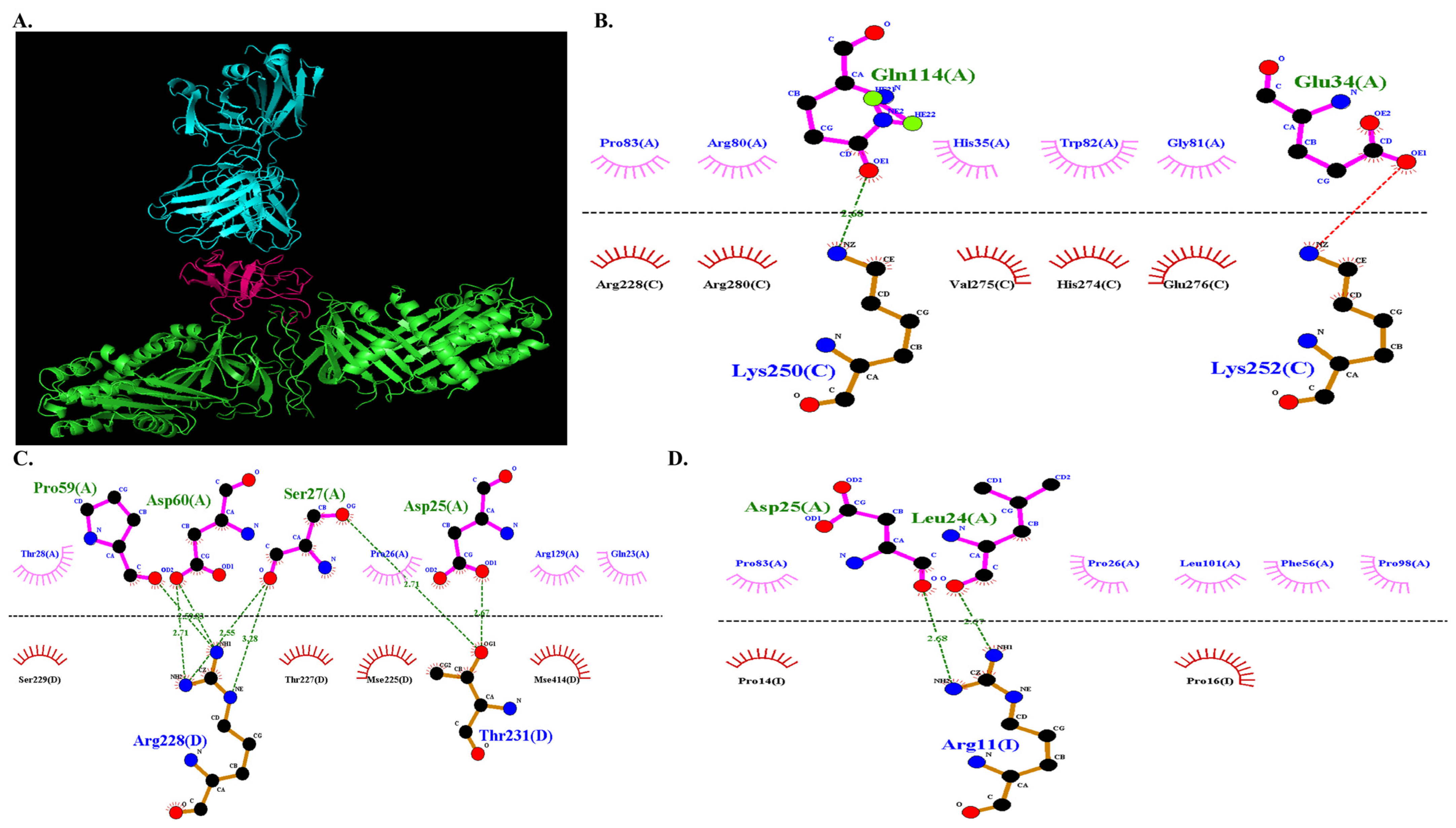
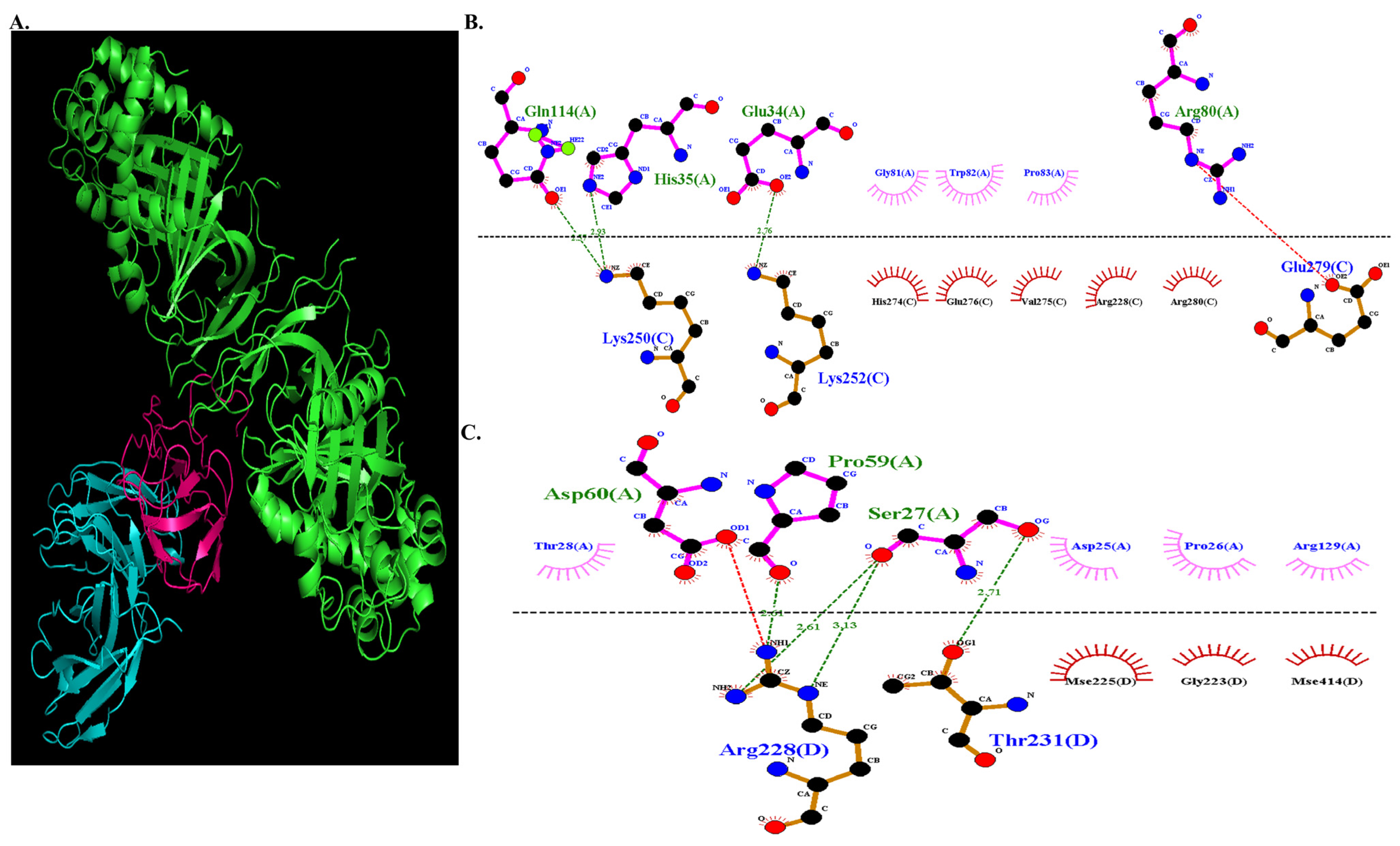
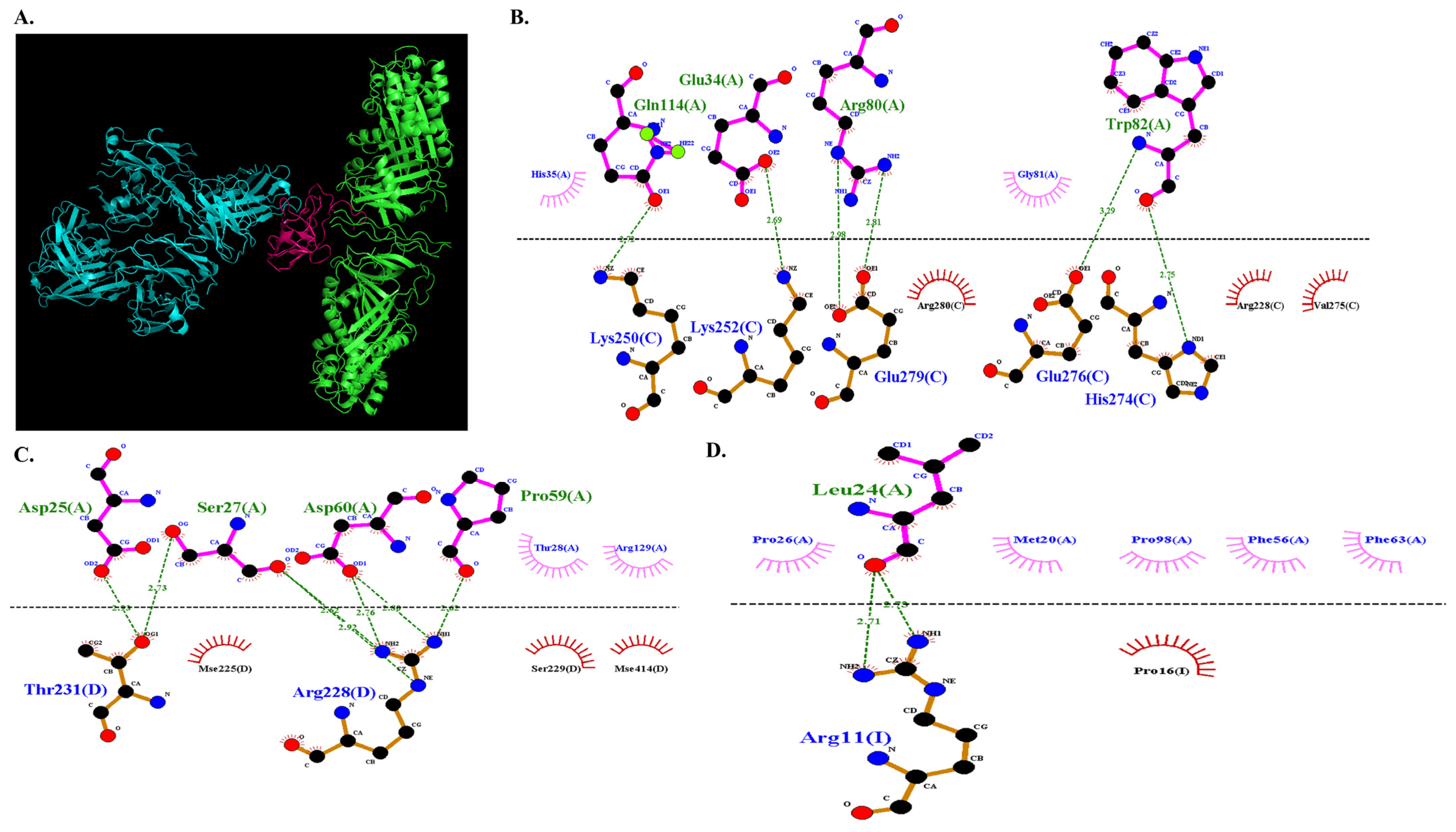
| Proteins | Lowest Binding Energy | TANGO1 (Chain A) | COL7A1 (Chain C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| COL7A1-TANGO1 | −1013.4 | Asp 118 | Arg 116 |
| Glu 119 | Arg 116 | ||
| Asp 130 | Ser 119 | ||
| Gly 127 | Ser 119 | ||
| Gly 127 | Ser 119 | ||
| Asp 121 | Asn 125 | ||
| Val 123 | Asn 125 | ||
| Phe 125 | Thr 127 | ||
| Phe 125 | Thr 127 | ||
| Pro 59 | His 262 | ||
| Ser 27 | His 262 | ||
| Asp 126 | Ala 261 | ||
| Asp 126 | Ser 265 | ||
| Arg 92 | Glu 362 | ||
| Arg 129 | Gln 396 |
| DMARDs | Lowest Binding Energy | TANGO1 (Chain A) | COL7A1 (Chain C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −674.7 | Gln 114 | Lys 250 |
| TANGO1 (Chain A) | COL7A1 (Chain D) | ||
| Pro 59 | Arg 228 | ||
| Asp 60 | Arg 228 | ||
| Asp 60 | Arg 228 | ||
| Ser 27 | Arg 228 | ||
| Ser 27 | Arg 228 | ||
| Ser 27 | Thr 231 | ||
| Asp 25 | Thr 231 | ||
| TANGO1 (Chain A) | COL7A1 (Chain I) | ||
| Asp 25 | Arg 11 | ||
| Leu 24 | Arg 11 | ||
| −679.5 | TANGO1 (Chain A) | COL7A1 (Chain C) |
| Gln 114 | Lys 250 | ||
| His 35 | Lys 250 | ||
| Glu 34 | Lys 252 | ||
| TANGO1 (Chain A) | COL7A1 (Chain D) | ||
| Pro 59 | Arg 228 | ||
| Ser 27 | Arg 228 | ||
| Ser 27 | Arg 228 | ||
| Ser 27 | Thr 231 | ||
| −670.6 | TANGO1 (Chain A) | COL7A1 (Chain C) |
| Gln 114 | Lys 250 | ||
| Glu 34 | Lys 252 | ||
| Trp 82 | His 274 | ||
| Trp 82 | Glu 276 | ||
| Arg 80 | Glu 279 | ||
| Arg 80 | Glu 279 | ||
| TANGO1 (Chain A) | COL7A1 (Chain D) | ||
| Ser 27 | Arg 228 | ||
| Ser 27 | Thr 231 | ||
| Asp 60 | Arg 228 | ||
| Asp 60 | Arg 228 | ||
| Pro 59 | Arg 228 | ||
| Asp 25 | Thr 231 | ||
| TANGO1 (Chain A) | COL7A1 (Chain I) | ||
| Leu 24 | Arg 11 | ||
| Leu 24 | Arg 11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chakraborty, D.; Agnihotri, P.; Joshi, L.; Saquib, M.; Malik, S.; Kumar, U.; Biswas, S. Pathogenic Mechanisms of Collagen TypeⅦA1 (COL7A1) and Transporter Protein Transport and Golgi Organization 1 (TANGO1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A New Therapeutic Target. Immuno 2024, 4, 461-478. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040029
Chakraborty D, Agnihotri P, Joshi L, Saquib M, Malik S, Kumar U, Biswas S. Pathogenic Mechanisms of Collagen TypeⅦA1 (COL7A1) and Transporter Protein Transport and Golgi Organization 1 (TANGO1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A New Therapeutic Target. Immuno. 2024; 4(4):461-478. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040029
Chicago/Turabian StyleChakraborty, Debolina, Prachi Agnihotri, Lovely Joshi, Mohd Saquib, Swati Malik, Uma Kumar, and Sagarika Biswas. 2024. "Pathogenic Mechanisms of Collagen TypeⅦA1 (COL7A1) and Transporter Protein Transport and Golgi Organization 1 (TANGO1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A New Therapeutic Target" Immuno 4, no. 4: 461-478. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040029
APA StyleChakraborty, D., Agnihotri, P., Joshi, L., Saquib, M., Malik, S., Kumar, U., & Biswas, S. (2024). Pathogenic Mechanisms of Collagen TypeⅦA1 (COL7A1) and Transporter Protein Transport and Golgi Organization 1 (TANGO1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A New Therapeutic Target. Immuno, 4(4), 461-478. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040029






