Mechanisms of Immune Evasion in PTEN Loss Prostate Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PTEN Molecular Pathway
2.1. PTEN. Overview and Biological Functions
2.2. PTEN Loss in Prostate Cancer
2.3. Mechanisms of PTEN Inactivation
2.4. Treatment Strategies for PTEN Loss Prostate Cancer
2.4.1. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Inhibition
2.4.2. Restoring PTEN Function
2.4.3. Targeting PTEN Regulators
3. Immune Alterations in PTEN Loss Prostate Cancer
3.1. Role of Immune Infiltration in PCa
3.2. Immune Alterations in PTEN Loss PCa During Tumor Initiation
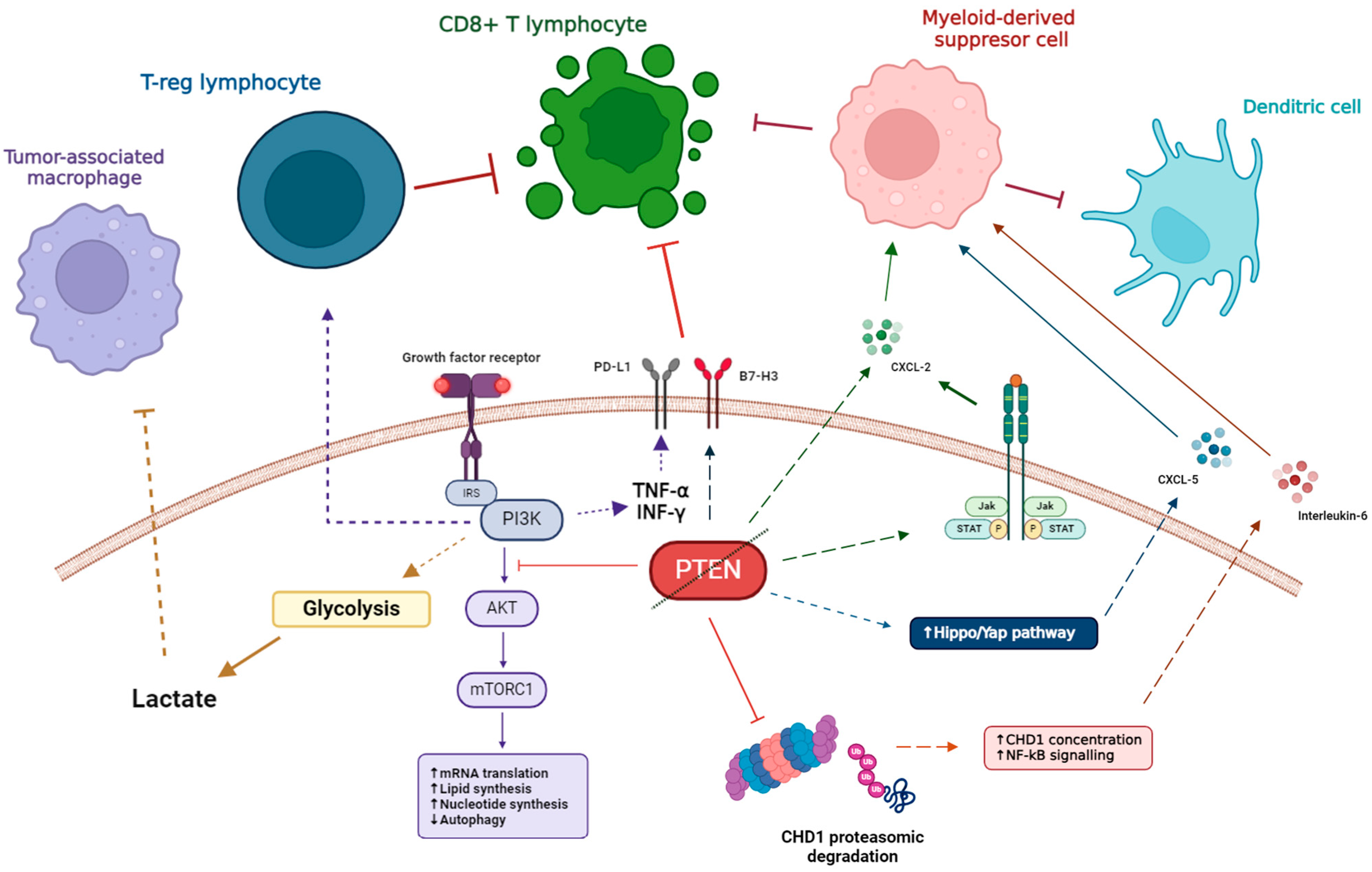
3.3. Immune Alterations of PTEN Loss PCa During Tumor Progression
4. Strategies to Overcome Treatment Resistance in PTEN Loss PCa and Future Directions
4.1. Resistance to Androgen Receptor Signaling Inhibitors and Taxane Chemotherapy
4.2. Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| ADT | Androgen deprivation therapy |
| AR | Androgen receptor |
| ARSI | Androgen receptor signaling inhibitors |
| bRFS | Biochemical-failure free recurrence free survival |
| CDK12 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 12 |
| CRPC | Castration-resistant prostate cancer |
| DC | Dendritic cells |
| DMFS | Distant-metastases free survival |
| FISH | Fluorescent in situ hybridization |
| HG-PIN | High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia |
| HSPC | Hormone-sensitive prostate cancer |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| IDO | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LOH | Loss of heterozygosity |
| MDSC | Myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| MMR | Mismatch-repair |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PCa | Prostate cancer |
| PI3K | phosphatydilinositol-4,5 biphosphate 3-kinase |
| PIP2 | phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| PIP3 | phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| rPFS | Radiographic progression-free survival |
| TAM | Tumor-associated macrophage |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas. |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.; Moore, C.M.; Chiong, E.; Beltran, H.; Bristow, R.G.; Williams, S.G. Prostate Cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeshouse, A.; Ahn, J.; Akbani, R.; Ally, A.; Amin, S.; Andry, C.D.; Annala, M.; Aprikian, A.; Armenia, J.; Arora, A.; et al. The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaspishvili, T.; Berman, D.M.; Ross, A.E.; Scher, H.I.; De Marzo, A.M.; Squire, J.A.; Lotan, T.L. Clinical Implications of PTEN Loss in Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfanos, K.S.; Hempel, H.A.; De Marzo, A.M. The Role of Inflammation in Prostate Cancer. In Inflammation and Cancer; Aggarwal, B.B., Sung, B., Gupta, S.C., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 816, pp. 153–181. ISBN 978-3-0348-0836-1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yen, C.; Liaw, D.; Podsypanina, K.; Bose, S.; Wang, S.I.; Puc, J.; Miliaresis, C.; Rodgers, L.; McCombie, R.; et al. PTEN, a Putative Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Gene Mutated in Human Brain, Breast, and Prostate Cancer. Science 1997, 275, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.S.; Salmena, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. The Functions and Regulation of the PTEN Tumour Suppressor. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, W.-C.; Li, P.; Guo, H.; Poh, S.-B.; Brady, S.W.; Xiong, Y.; Tseng, L.-M.; Li, S.-H.; Ding, Z.; et al. Combating Trastuzumab Resistance by Targeting SRC, a Common Node Downstream of Multiple Resistance Pathways. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.-P. PTEN Coordinates G1 Arrest by Down-Regulating Cyclin D1 via Its Protein Phosphatase Activity and up-Regulating P27 via Its Lipid Phosphatase Activity in a Breast Cancer Model. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.H.; Balajee, A.S.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Eng, C.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Yin, Y. Essential Role for Nuclear PTEN in Maintaining Chromosomal Integrity. Cell 2007, 128, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, C.; Ho, J.; Srikumar, T.; Dowling, R.J.O.; Gorrini, C.; Miller, S.J.; Mak, T.W.; Neel, B.G.; Raught, B.; Stambolic, V. Nuclear PTEN Controls DNA Repair and Sensitivity to Genotoxic Stress. Science 2013, 341, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.F.; Lawrence, M.S.; Demichelis, F.; Drier, Y.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.Y.; Sboner, A.; Esgueva, R.; Pflueger, D.; Sougnez, C.; et al. The Genomic Complexity of Primary Human Prostate Cancer. Nature 2011, 470, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Cunha, I.W.; Coudry, R.A.; Fonseca, F.P.; Torres, C.H.; Soares, F.A.; Squire, J.A. FISH Analysis of 107 Prostate Cancers Shows That PTEN Genomic Deletion Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, P.; Okami, K.; Halachmi, S.; Halachmi, N.; Esteller, M.; Herman, J.G.; Jen, J.; Isaacs, W.B.; Bova, G.S.; Sidransky, D. Frequent Inactivation of PTEN/MMAC1 in Primary Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4997–5000. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wu, Y.-M.; Schultz, N.; Lonigro, R.J.; Mosquera, J.-M.; Montgomery, B.; Taplin, M.-E.; Pritchard, C.C.; Attard, G.; et al. Integrative Clinical Genomics of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.H.M.; Attard, G.; Brewer, D.; Miranda, S.; Riisnaes, R.; Clark, J.; Hylands, L.; Merson, S.; Vergis, R.; Jameson, C.; et al. Novel, Gross Chromosomal Alterations Involving PTEN Cooperate with Allelic Loss in Prostate Cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.J.; Karnes, R.J.; Kosari, F.; Castellar, B.E.R.P.; Kipp, B.R.; Johnson, S.H.; Terra, S.; Harris, F.R.; Halling, G.C.; Klein, J.L.S.; et al. Integrated Analysis of the Genomic Instability of PTEN in Clinically Insignificant and Significant Prostate Cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibeawuchi, C.; Schmidt, H.; Voss, R.; Titze, U.; Abbas, M.; Neumann, J.; Eltze, E.; Hoogland, A.; Jenster, G.; Brandt, B.; et al. Exploring Prostate Cancer Genome Reveals Simultaneous Losses of PTEN, FAS and PAPSS2 in Patients with PSA Recurrence after Radical Prostatectomy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3856–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nip, H.; Dar, A.A.; Saini, S.; Colden, M.; Varahram, S.; Chowdhary, H.; Yamamura, S.; Mitsui, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Kato, T.; et al. Oncogenic microRNA-4534 Regulates PTEN Pathway in Prostate Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68371–68384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doldi, V.; El Bezawy, R.; Zaffaroni, N. MicroRNAs as Epigenetic Determinants of Treatment Response and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Añazco-Guenkova, A.M.; Monteagudo-García, Ó.; Blanco, S. Epigenetic and Epitranscriptomic Control in Prostate Cancer. Genes 2022, 13, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, H.; Yelensky, R.; Frampton, G.M.; Park, K.; Downing, S.R.; MacDonald, T.Y.; Jarosz, M.; Lipson, D.; Tagawa, S.T.; Nanus, D.M.; et al. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing of Advanced Prostate Cancer Identifies Potential Therapeutic Targets and Disease Heterogeneity. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, N.R.; Foti, M. Non-Genomic Loss of PTEN Function in Cancer: Not in My Genes. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismar, T.A.; Yoshimoto, M.; Vollmer, R.T.; Duan, Q.; Firszt, M.; Corcos, J.; Squire, J.A. PTEN Genomic Deletion Is an Early Event Associated with ERG Gene Rearrangements in Prostate Cancer. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICGC Prostate UK Group; Gundem, G.; Van Loo, P.; Kremeyer, B.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Tubio, J.M.C.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Brewer, D.S.; Kallio, H.M.L.; Högnäs, G.; et al. The Evolutionary History of Lethal Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Nature 2015, 520, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnham, D.J.; Bullock, N.; Dass, M.S.; Staffurth, J.N.; Pearson, H.B. The PTEN Conundrum: How to Target PTEN-Deficient Prostate Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting PI3K in Cancer: Mechanisms and Advances in Clinical Trials. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Cerniglia, G.J.; Mick, R.; Ahmed, M.S.; Bakanauskas, V.J.; Muschel, R.J.; McKenna, W.G. Radiation Sensitization of Human Cancer Cells in Vivo by Inhibiting the Activity of PI3K Using LY294002. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 56, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maira, S.-M.; Pecchi, S.; Huang, A.; Burger, M.; Knapp, M.; Sterker, D.; Schnell, C.; Guthy, D.; Nagel, T.; Wiesmann, M.; et al. Identification and Characterization of NVP-BKM120, an Orally Available Pan-Class I PI3-Kinase Inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Rowley, B.R.; Bull, C.O.; Schneider, C.; Haegebarth, A.; Schatz, C.A.; Fracasso, P.R.; Wilkie, D.P.; Hentemann, M.; Wilhelm, S.M.; et al. BAY 80-6946 Is a Highly Selective Intravenous PI3K Inhibitor with Potent P110α and P110δ Activities in Tumor Cell Lines and Xenograft Models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, A.; Nguyen, H.G.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Meng, M.V.; Carroll, P.; Friedlander, T.W.; Zhang, L.; Thomas, M.; Febbo, P.G.; Feng, F.Y.-C.; et al. A Pharmacodynamic Study of Pre-Prostatectomy Buparlisib in Men with High-Risk, Localized Prostate Cancer. JCO 2016, 34, e14110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Halabi, S.; Healy, P.; Alumkal, J.J.; Winters, C.; Kephart, J.; Bitting, R.L.; Hobbs, C.; Soleau, C.F.; Beer, T.M.; et al. Phase II Trial of the PI3 Kinase Inhibitor Buparlisib (BKM-120) with or without Enzalutamide in Men with Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 81, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Billalabeitia, E.; Seitzer, N.; Song, S.J.; Song, M.S.; Patnaik, A.; Liu, X.-S.; Epping, M.T.; Papa, A.; Hobbs, R.M.; Chen, M.; et al. Vulnerabilities of PTEN—TP53 -Deficient Prostate Cancers to Compound PARP–PI3K Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Chaudagar, K.; Sharma-Saha, S.; Bynoe, K.; Maillat, L.; Heiss, B.; Leung, K.; Krishnan, Y.; Stadler, W.; Patnaik, A. Abstract 1685: PARP/PI3K Inhibitor Combination Therapy Eradicates c-MYC-Driven Murine Prostate Cancers via cGAS/STING Pathway Activation within Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Velasco, M.A.; Kura, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Nishio, K.; Davies, B.R.; Uemura, H. Efficacy of Targeted AKT Inhibition in Genetically Engineered Mouse Models of PTEN -Deficient Prostate Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15959–15976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, N.; Mellado, B.; Shah, S.; Hauke, R.; Costin, D.; Adra, N.; Cullberg, M.; Teruel, C.F.; Morris, T. A Phase I Study of Capivasertib in Combination With Abiraterone Acetate in Patients With Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2023, 21, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, C.; Bracarda, S.; Sternberg, C.N.; Chi, K.N.; Olmos, D.; Sandhu, S.; Massard, C.; Matsubara, N.; Alekseev, B.; Parnis, F.; et al. Ipatasertib plus Abiraterone and Prednisolone in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (IPATential150): A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, A.C.; Liu, Y.; Edlind, M.P.; Ingolia, N.T.; Janes, M.R.; Sher, A.; Shi, E.Y.; Stumpf, C.R.; Christensen, C.; Bonham, M.J.; et al. The Translational Landscape of mTOR Signalling Steers Cancer Initiation and Metastasis. Nature 2012, 485, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Birle, D.C.; Tannock, I.F. Effects of the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitor CCI-779 Used Alone or with Chemotherapy on Human Prostate Cancer Cells and Xenografts. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2825–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhao, L.; Siemann, D.W. Abstract B59: Dual mTOR Kinase Inhibitor Reverses Rapamycin Resistance in Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, B59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guertin, D.A.; Sabatini, D.M. Defining the Role of mTOR in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sheng, J.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lv, T.; Hu, S.; Jin, J.; Yu, W.; Song, Y. Potent Antitumour of the mTORC1/2 Dual Inhibitor AZD2014 in Docetaxel-sensitive and Docetaxel-resistant Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Cell Mol. Medi 2021, 25, 2436–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, M.H.; Gordon, M.S.; Mita, M.; Rini, B.; Makker, V.; Macarulla, T.; Smith, D.C.; Cervantes, A.; Puzanov, I.; Pili, R.; et al. Phase 1 Study of mTORC1/2 Inhibitor Sapanisertib (TAK-228) in Advanced Solid Tumours, with an Expansion Phase in Renal, Endometrial or Bladder Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altınoğlu, S.A.; Wang, M.; Li, K.Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q. Intracellular Delivery of the PTEN Protein Using Cationic Lipidoids for Cancer Therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Fan, H. The Effect of Nanoparticle Mediated Phosphatase and Tensin Homologue on Chromosome Ten on Prostate Cancer. J. Biomater Tissue Eng. 2018, 8, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavictoire, S.J.; Gont, A.; Julian, L.M.; Stanford, W.L.; Vlasschaert, C.; Gray, D.A.; Jomaa, D.; Lorimer, I.A.J. Engineering PTEN-L for Cell-Mediated Delivery. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2018, 9, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Hodakoski, C.; Barrows, D.; Mense, S.M.; Parsons, R.E. PTEN Function: The Long and the Short of It. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, J.-X.; Shao, Z.-Q. miR-21 Targets and Inhibits Tumor Suppressor Gene PTEN to Promote Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion: An Experimental Study. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, C.; Nugent, F.; Waryah, C.B.; Garcia-Bloj, B.; Harvey, A.R.; Blancafort, P. Activating PTEN Tumor Suppressor Expression with the CRISPR/dCas9 System. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 14, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, W.H.; Zitvogel, L.; Sautès–Fridman, C.; Kroemer, G. The Immune Contexture in Cancer Prognosis and Treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Attwood, K.; Bshara, W.; Mohler, J.L.; Guru, K.; Xu, B.; Kalinski, P.; Chatta, G. High Intratumoral CD8 + T-cell Infiltration Is Associated with Improved Survival in Prostate Cancer Patients Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy. Prostate 2021, 81, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, N.; Andersen, S.; Valkov, A.; Nordby, Y.; Donnem, T.; Al-Saad, S.; Busund, L.-T.; Bremnes, R.M.; Richardsen, E. Infiltration of CD8+ Lymphocytes Is an Independent Prognostic Factor of Biochemical Failure-Free Survival in Prostate Cancer: CD8+ Lymphocytes in Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2014, 74, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitprez, F.; Fossati, N.; Vano, Y.; Freschi, M.; Becht, E.; Lucianò, R.; Calderaro, J.; Guédet, T.; Lacroix, L.; Rancoita, P.M.V.; et al. PD-L1 Expression and CD8+ T-Cell Infiltrate Are Associated with Clinical Progression in Patients with Node-Positive Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus. 2019, 5, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.G.; Lehrer, J.; Chang, S.L.; Das, R.; Erho, N.; Liu, Y.; Sjöström, M.; Den, R.B.; Freedland, S.J.; Klein, E.A.; et al. The Immune Landscape of Prostate Cancer and Nomination of PD-L2 as a Potential Therapeutic Target. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidotto, T.; Saggioro, F.P.; Jamaspishvili, T.; Chesca, D.L.; Picanço De Albuquerque, C.G.; Reis, R.B.; Graham, C.H.; Berman, D.M.; Siemens, D.R.; Squire, J.A.; et al. PTEN-deficient Prostate Cancer Is Associated with an Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment Mediated by Increased Expression of IDO1 and Infiltrating FoxP3+ T Regulatory Cells. Prostate 2019, 79, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, R.; Li, S.; Liu, J. IDO1: An Important Immunotherapy Target in Cancer Treatment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 47, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigos, A.S.; Pasam, A.; Banks, P.; Wallace, R.; Guo, C.; Keam, S.; Thorne, H.; kConFab; Mitchell, C.; Lade, S.; et al. Tumor Immune Microenvironment of Primary Prostate Cancer with and without Germline Mutations in Homologous Recombination Repair Genes. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pavlovitz, B.; Tull, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, F.-M.; Fuller, C. Detection of TMPRSS2 Gene Deletions and Translocations in Carcinoma, Intraepithelial Neoplasia, and Normal Epithelium of the Prostate by Direct Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2010, 19, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Cutz, J.-C.; Nuin, P.A.S.; Joshua, A.M.; Bayani, J.; Evans, A.J.; Zielenska, M.; Squire, J.A. Interphase FISH Analysis of PTEN in Histologic Sections Shows Genomic Deletions in 68% of Primary Prostate Cancer and 23% of High-Grade Prostatic Intra-Epithelial Neoplasias. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2006, 169, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, J.; Lei, Q.; Rozengurt, N.; Pritchard, C.; Jiao, J.; Thomas, G.V.; Li, G.; Roy-Burman, P.; Nelson, P.S.; et al. Prostate-Specific Deletion of the Murine Pten Tumor Suppressor Gene Leads to Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.J.; Ruscetti, M.; Arenzana, T.L.; Tran, L.M.; Bianci-Frias, D.; Sybert, E.; Priceman, S.J.; Wu, L.; Nelson, P.S.; Smale, S.T.; et al. Pten Null Prostate Epithelium Promotes Localized Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Expansion and Immune Suppression during Tumor Initiation and Progression. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priceman, S.J.; Sung, J.L.; Shaposhnik, Z.; Burton, J.B.; Torres-Collado, A.X.; Moughon, D.L.; Johnson, M.; Lusis, A.J.; Cohen, D.A.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L.; et al. Targeting Distinct Tumor-Infiltrating Myeloid Cells by Inhibiting CSF-1 Receptor: Combating Tumor Evasion of Antiangiogenic Therapy. Blood 2010, 115, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Krelin, Y.; Dvorkin, T.; Bjorkdahl, O.; Segal, S.; Dinarello, C.A.; Voronov, E.; Apte, R.N. CD11b+/Gr-1+ Immature Myeloid Cells Mediate Suppression of T Cells in Mice Bearing Tumors of IL-1β-Secreting Cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 8200–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condamine, T.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Differentiation and Function. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mitri, D.; Toso, A.; Chen, J.J.; Sarti, M.; Pinton, S.; Jost, T.R.; D’Antuono, R.; Montani, E.; Garcia-Escudero, R.; Guccini, I.; et al. Tumour-Infiltrating Gr-1+ Myeloid Cells Antagonize Senescence in Cancer. Nature 2014, 515, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dart, D.A.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Jiang, W.G. Prostate-Specific PTen Deletion in Mice Activates Inflammatory microRNA Expression Pathways in the Epithelium Early in Hyperplasia Development. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augello, M.A.; Liu, D.; Deonarine, L.D.; Robinson, B.D.; Huang, D.; Stelloo, S.; Blattner, M.; Doane, A.S.; Wong, E.W.P.; Chen, Y.; et al. CHD1 Loss Alters AR Binding at Lineage-Specific Enhancers and Modulates Distinct Transcriptional Programs to Drive Prostate Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 603–617.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Cai, L.; Lu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Ittmann, M.; Shang, X.; Jiang, S.; Li, H.; et al. Chromatin Regulator CHD1 Remodels the Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment in PTEN-Deficient Prostate Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1374–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toso, A.; Revandkar, A.; Di Mitri, D.; Guccini, I.; Proietti, M.; Sarti, M.; Pinton, S.; Zhang, J.; Kalathur, M.; Civenni, G.; et al. Enhancing Chemotherapy Efficacy in Pten -Deficient Prostate Tumors by Activating the Senescence-Associated Antitumor Immunity. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Yang, X. Inhibition of Transforming Growth Factor Beta/ SMAD Signal by MiR-155 Is Involved in Arsenic Trioxide-induced Anti-angiogenesis in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Majeti, B.K.; Acevedo, L.M.; Murphy, E.A.; Mukthavaram, R.; Scheppke, L.; Huang, M.; Shields, D.J.; Lindquist, J.N.; Lapinski, P.E.; et al. MicroRNA-132–Mediated Loss of p120RasGAP Activates the Endothelium to Facilitate Pathological Angiogenesis. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezhong, L.; Xiaoyi, Z.; Xianlian, L.; Hongyan, Z.; Guohua, Z.; Bo, S.; Lian, Z. miR-150 Is a Factor of Survival in Prostate Cancer Patients. J. Buon. 2015, 20, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Sartor, O.; De Bono, J.S. Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkadakrishnan, V.B.; Presser, A.G.; Singh, R.; Booker, M.A.; Traphagen, N.A.; Weng, K.; Voss, N.C.E.; Mahadevan, N.R.; Mizuno, K.; Puca, L.; et al. Lineage-Specific Canonical and Non-Canonical Activity of EZH2 in Advanced Prostate Cancer Subtypes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebello, R.J.; Oing, C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Loeb, S.; Johnson, D.C.; Reiter, R.E.; Gillessen, S.; Van Der Kwast, T.; Bristow, R.G. Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shen, M.M. Prostate Cancer Cell Heterogeneity and Plasticity: Insights from Studies of Genetically-Engineered Mouse Models. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 82, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzi, M.; Seitzer, N.; Ishikawa, T.; Reschke, M.; Chen, M.; Wang, G.; Mitchell, C.; Ng, C.; Katon, J.; Lunardi, A.; et al. Diverse Genetic-Driven Immune Landscapes Dictate Tumor Progression through Distinct Mechanisms. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzon, B.; Zhao, S.G.; Haffner, M.C.; Takhar, M.; Erho, N.; Yousefi, K.; Hurley, P.; Bishop, J.L.; Tosoian, J.; Ghabili, K.; et al. Correlation of B7-H3 with Androgen Receptor, Immune Pathways and Poor Outcome in Prostate Cancer: An Expression-Based Analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017, 20, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Kim, J.J.; Li, H.; Meng, C.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Mak, D.H.; Van, V.; et al. Immune Checkpoint B7-H3 Is a Therapeutic Vulnerability in Prostate Cancer Harboring PTEN and TP53 Deficiencies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadf6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Mei, C.; Yao, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Qi, J.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; et al. Sp1 Is Involved in Regulation of Cystathionine γ-Lyase Gene Expression and Biological Function by PI3K/Akt Pathway in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wu, C.-J.; Chu, G.C.; Xiao, Y.; Ho, D.; Zhang, J.; Perry, S.R.; Labrot, E.S.; Wu, X.; Lis, R.; et al. SMAD4-Dependent Barrier Constrains Prostate Cancer Growth and Metastatic Progression. Nature 2011, 470, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitchison, A.A.; Veerakumarasivam, A.; Vias, M.; Kumar, R.; Hamdy, F.C.; Neal, D.E.; Mills, I.G. Promoter Methylation Correlates with Reduced Smad4 Expression in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2008, 68, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lu, X.; Dey, P.; Deng, P.; Wu, C.C.; Jiang, S.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, K.; Konaparthi, R.; Hua, S.; et al. Targeting YAP-Dependent MDSC Infiltration Impairs Tumor Progression. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Tretiakova, M.S.; Silvis, M.R.; Lucas, J.; Klezovitch, O.; Coleman, I.; Bolouri, H.; Kutyavin, V.I.; Morrissey, C.; True, L.D.; et al. ERG Activates the YAP1 Transcriptional Program and Induces the Development of Age-Related Prostate Tumors. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Thompson, C.B. The Emerging Hallmarks of Cancer Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhou, G.; Cui, C.; Weng, Y.; Liu, W.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Perez-Neut, M.; et al. Metabolic Regulation of Gene Expression by Histone Lactylation. Nature 2019, 574, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeraerts, X.; Fernández-Garcia, J.; Hartmann, F.J.; De Goede, K.E.; Martens, L.; Elkrim, Y.; Debraekeleer, A.; Stijlemans, B.; Vandekeere, A.; Rinaldi, G.; et al. Macrophages Are Metabolically Heterogeneous within the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 110171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zou, J.X.; Xue, X.; Cai, D.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, Z.; Xiang, Q.; Yang, J.C.; Louie, M.C.; Borowsky, A.D.; et al. ROR-γ Drives Androgen Receptor Expression and Represents a Therapeutic Target in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcinotto, A.; Spataro, C.; Zagato, E.; Di Mitri, D.; Gil, V.; Crespo, M.; De Bernardis, G.; Losa, M.; Mirenda, M.; Pasquini, E.; et al. IL-23 Secreted by Myeloid Cells Drives Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Nature 2018, 559, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priulla, M.; Calastretti, A.; Bruno, P.; Amalia, A.; Paradiso, A.; Canti, G.; Nicolin, A. Preferential Chemosensitization of PTEN-mutated Prostate Cells by Silencing the Akt Kinase. Prostate 2007, 67, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescigno, P.; Lorente, D.; Dolling, D.; Ferraldeschi, R.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Riisnaes, R.; Miranda, S.; Bianchini, D.; Zafeiriou, Z.; Sideris, S.; et al. Docetaxel Treatment in PTEN- and ERG-Aberrant Metastatic Prostate Cancers. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 1, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M. Mechanisms of Docetaxel Resistance in Prostate Cancer: The Key Role Played by miRNAs. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2021, 1875, 188481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.N.; Burotto, M.; Fong, P.C.; Pook, D.; Zurawski, B.; Kopp, R.M.; Salinas, J.E.; Bylow, K.; Kramer, G.; Ratta, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab (Pembro) plus Enzalutamide (Enza) for Patients (Pts) with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC): Randomized Double-Blind Phase III KEYNOTE-641 Study. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratzke, C.J.; Ozguroglu, M.; Peer, A.; Sendur, M.a.N.; Retz, M.; Goh, J.C.H.; Loidl, W.C.; Jayram, G.; Byun, S.-S.; Kwak, C.; et al. Pembrolizumab (Pembro) plus Enzalutamide (Enza) and Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) for Patients (Pts) with Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer (mHSPC): Randomized Double-Blind Phase III KEYNOTE-991 Study. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S957–S958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrylak, D.P.; Ratta, R.; Matsubara, N.; Korbenfeld, E.P.; Gafanov, R.; Mourey, L.; Todenhöfer, T.; Gurney, H.; Kramer, G.; Bergman, A.M.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Docetaxel for Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC): Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 3 KEYNOTE-921 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.S.; Montgomery, B.; Cheng, H.H.; Yu, E.Y.; Nelson, P.S.; Pritchard, C.; Erickson, S.; Alva, A.; Schweizer, M.T. Mismatch Repair Deficiency in Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Response to PD-1 Blockade and Standard Therapies. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sena, L.A.; Fountain, J.; Isaacsson Velho, P.; Lim, S.J.; Wang, H.; Nizialek, E.; Rathi, N.; Nussenzveig, R.; Maughan, B.L.; Velez, M.G.; et al. Tumor Frameshift Mutation Proportion Predicts Response to Immunotherapy in Mismatch Repair-Deficient Prostate Cancer. Oncologist 2021, 26, e270–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.-N.; Jin, Y.; He, M.-M.; Liu, Z.-X.; Xu, R.-H. Evaluation of POLE and POLD1 Mutations as Biomarkers for Immunotherapy Outcomes Across Multiple Cancer Types. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1504–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Isaacsson Velho, P.; Fu, W.; Wang, H.; Agarwal, N.; Sacristan Santos, V.; Maughan, B.L.; Pili, R.; Adra, N.; Sternberg, C.N.; et al. CDK12-Altered Prostate Cancer: Clinical Features and Therapeutic Outcomes to Standard Systemic Therapies, Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibitors, and PD-1 Inhibitors. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Yuen, K.C.; Gillessen, S.; Kadel, E.E.; Rathkopf, D.; Matsubara, N.; Drake, C.G.; Fizazi, K.; Piulats, J.M.; Wysocki, P.J.; et al. Atezolizumab with Enzalutamide vs Enzalutamide Alone in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, C.; Malu, S.; Creasy, C.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Xu, C.; McKenzie, J.A.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; et al. Loss of PTEN Promotes Resistance to T Cell–Mediated Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zou, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, W.; Li, C.; Liu, N.; Wu, H. Overcoming Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Therapy in PTEN-Null Prostate Cancer by Intermittent Anti-PI3Kα/β/δ Treatment. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudagar, K.; Hieromnimon, H.M.; Khurana, R.; Labadie, B.; Hirz, T.; Mei, S.; Hasan, R.; Shafran, J.; Kelley, A.; Apostolov, E.; et al. Reversal of Lactate and PD-1–Mediated Macrophage Immunosuppression Controls Growth of PTEN/P53-Deficient Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 1952–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Tian, T.; Kalland, K.-H.; Ke, X.; Qu, Y. Targeting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling for Cancer Immunotherapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.K.; Danila, D.C.; Lin, C.-C.; Lee, J.-L.; Matsubara, N.; Ward, P.J.; Armstrong, A.J.; Pook, D.; Kim, M.; Dorff, T.B.; et al. Xaluritamig, a STEAP1 × CD3 XmAb 2+1 Immune Therapy for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Results from Dose Exploration in a First-in-Human Study. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danila, D.C.; Szmulewitz, R.Z.; Vaishampayan, U.; Higano, C.S.; Baron, A.D.; Gilbert, H.N.; Brunstein, F.; Milojic-Blair, M.; Wang, B.; Kabbarah, O.; et al. Phase I Study of DSTP3086S, an Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of Prostate 1, in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. JCO 2019, 37, 3518–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.S.; Sundar, R.; Wong, A.; Yong, W.-P.; Soo, R.; Chee, C.E.; Lee, S.C.; Goh, B.C.; Dent, R.; Jeraj, S.D.N.; et al. 515MO A Phase I Trial of Durvalumab (Durv) in Combination with Olaparib (Ola) and Capivasertib (Cap) in Patients (Pts) with Advanced or Metastatic Cancers (Ca) (MEDIPAC). Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S585–S586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Nowecki, Z.; Im, S.-A.; Chung, W.-P.; Lord, S.; Armstrong, A.; Ma, C.X.; Huisden, R.; Stewart, R.; Kumar, R.; et al. Abstract PD10-03: BEGONIA: Phase 1b/2 Study of Durvalumab (D) Combinations in Locally Advanced/Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): Results from Arm 1 D + Paclitaxel (P), Arm 2 D+P + Capivasertib (C), and Arm 5 D+P + Oleclumab (O). Cancer Res. 2022, 82, PD10-03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.B.; Bentley, J.; Jeffery, Z.; DeMarzo, A.M. Heterogeneity of PTEN and ERG Expression in Prostate Cancer on Core Needle Biopsies: Implications for Cancer Risk Stratification and Biomarker Sampling. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, T.L.; Wei, W.; Ludkovski, O.; Morais, C.L.; Guedes, L.B.; Jamaspishvili, T.; Lopez, K.; Hawley, S.T.; Feng, Z.; Fazli, L.; et al. Analytic Validation of a Clinical-Grade PTEN Immunohistochemistry Assay in Prostate Cancer by Comparison with PTEN FISH. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, T.L.; Heumann, A.; Rico, S.D.; Hicks, J.; Lecksell, K.; Koop, C.; Sauter, G.; Schlomm, T.; Simon, R. PTEN Loss Detection in Prostate Cancer: Comparison of PTEN Immunohistochemistry and PTEN FISH in a Large Retrospective Prostatectomy Cohort. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 65566–65576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahearn, T.U.; Pettersson, A.; Ebot, E.M.; Gerke, T.; Graff, R.E.; Morais, C.L.; Hicks, J.L.; Wilson, K.M.; Rider, J.R.; Sesso, H.D.; et al. A Prospective Investigation of PTEN Loss and ERG Expression in Lethal Prostate Cancer. JNCI J. 2015, 108, djv346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraldeschi, R.; Nava Rodrigues, D.; Riisnaes, R.; Miranda, S.; Figueiredo, I.; Rescigno, P.; Ravi, P.; Pezaro, C.; Omlin, A.; Lorente, D.; et al. PTEN Protein Loss and Clinical Outcome from Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Treated with Abiraterone Acetate. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabb, S.J.; Griffiths, G.; Marwood, E.; Dunkley, D.; Downs, N.; Martin, K.; Light, M.; Northey, J.; Wilding, S.; Whitehead, A.; et al. Pan-AKT Inhibitor Capivasertib With Docetaxel and Prednisolone in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase II Trial (ProCAID). JCO 2021, 39, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabb, S.J.; Ye, D.-W.; Uemura, H.; Morris, T.; Gresty, C.; Logan, J.; Rooney, C.; Foxley, A.; Carducci, M.A. CAPItello-280: A Phase III Study of Capivasertib and Docetaxel versus Placebo and Docetaxel in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. JCO 2023, 41, TPS287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; George, D.J.; De Santis, M.; Clarke, N.; Fay, A.P.; Uemura, H.; Grinsted, L.; Rooney, C.; Verheijen, R.B.; Anjum, R.; et al. A Phase III Trial of Capivasertib and Abiraterone versus Placebo and Abiraterone in Patients with de Novo Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer Characterized by PTEN Deficiency (CAPItello-281). JCO 2021, 39, TPS178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.D. PTEN-PI3K Pathway Alterations in Advanced Prostate Cancer and Clinical Implications. Prostate 2022, 82, S60–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, N.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, D.; Rivera, A.A.; Li, D.; Lee, C.; Haywood, S.; Chen, X.; Chang, Q.; et al. Defining the Therapeutic Selective Dependencies for Distinct Subtypes of PI3K Pathway-Altered Prostate Cancers. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yang, J.; Saleh, N.; Chen, S.-C.; Ayers, G.D.; Abramson, V.G.; Mayer, I.A.; Richmond, A. Inhibition of the PI3K/mTOR Pathway in Breast Cancer to Enhance Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, L.M.; Yuzugullu, H.; Zhao, J.J. PI3K in Cancer: Divergent Roles of Isoforms, Modes of Activation and Therapeutic Targeting. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschweiler, S.; Ramírez-Suástegui, C.; Li, Y.; King, E.; Chudley, L.; Thomas, J.; Wood, O.; Von Witzleben, A.; Jeffrey, D.; McCann, K.; et al. Intermittent PI3Kδ Inhibition Sustains Anti-Tumour Immunity and Curbs irAEs. Nature 2022, 605, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, A.; Khan, S.A.; MacNeil, I.A.; Rich, B.E.; Molden, J.S.; Davis, L.N.; Rossetti, S.; Broege, A.M.; Laing, L.G. Therapeutic Effect of Gedatolisib, a Pan-PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor, on Prostate Cancer Models with PI3K or PTEN Mutational Status. JCO 2023, 41, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial Number | Drug | Phase |
|---|---|---|
| NCT04317105 | Copanlisib Nivolumab +/− Ipilimumab | I/II |
| NCT03673787 | Ipatasertib Atezolizumab | I |
| NCT03842228 | Copanlisib Olaparib +/− Durvalumab | I |
| NCT04975958 | Buparlisib Atezolizumab AN2025/AN2005 | I |
| NCT03772561 | Capivasertib Olaparib Atezolizumab | I |
| NCT02637531 | Eganelisib Nivolumab | I |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esteban-Villarrubia, J.; Ballesteros, P.A.; Martín-Serrano, M.; Vico, M.R.; Funes, J.M.; de Velasco, G.; Castro, E.; Olmos, D.; Castellano, D.; González-Billalabeitia, E. Mechanisms of Immune Evasion in PTEN Loss Prostate Cancer. Immuno 2024, 4, 444-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040028
Esteban-Villarrubia J, Ballesteros PA, Martín-Serrano M, Vico MR, Funes JM, de Velasco G, Castro E, Olmos D, Castellano D, González-Billalabeitia E. Mechanisms of Immune Evasion in PTEN Loss Prostate Cancer. Immuno. 2024; 4(4):444-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040028
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsteban-Villarrubia, Jorge, Pablo Alvarez Ballesteros, Miguel Martín-Serrano, María Ruiz Vico, Juan M Funes, Guillermo de Velasco, Elena Castro, David Olmos, Daniel Castellano, and Enrique González-Billalabeitia. 2024. "Mechanisms of Immune Evasion in PTEN Loss Prostate Cancer" Immuno 4, no. 4: 444-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040028
APA StyleEsteban-Villarrubia, J., Ballesteros, P. A., Martín-Serrano, M., Vico, M. R., Funes, J. M., de Velasco, G., Castro, E., Olmos, D., Castellano, D., & González-Billalabeitia, E. (2024). Mechanisms of Immune Evasion in PTEN Loss Prostate Cancer. Immuno, 4(4), 444-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040028







