Dynamics of Peripheral Lymphocyte Subsets from Birth until Old Age
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Blood Sampling
2.4. Lymphocyte Subset Enumeration and Phenotyping
2.5. Measurement of Serum Cytokine Levels
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
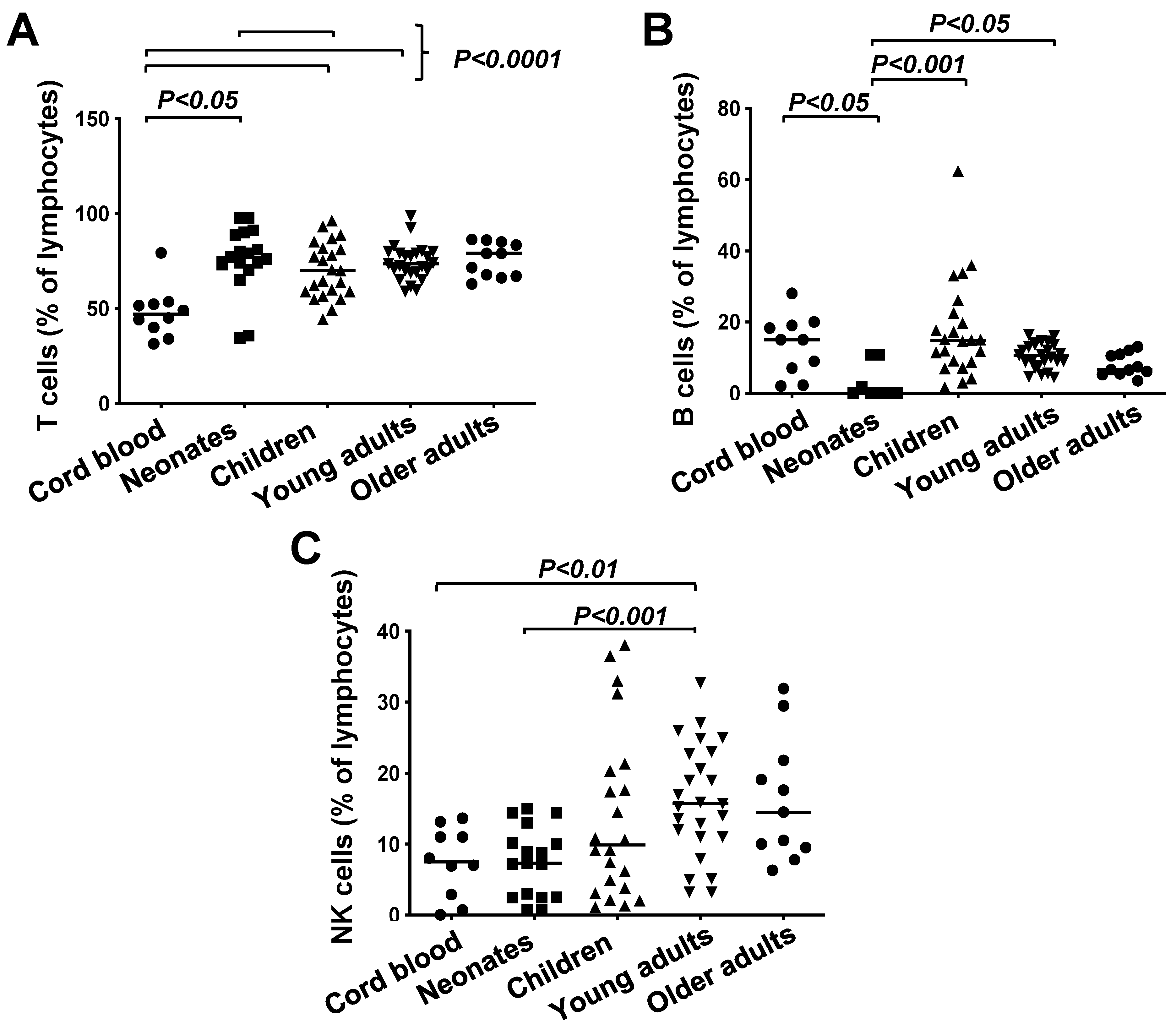
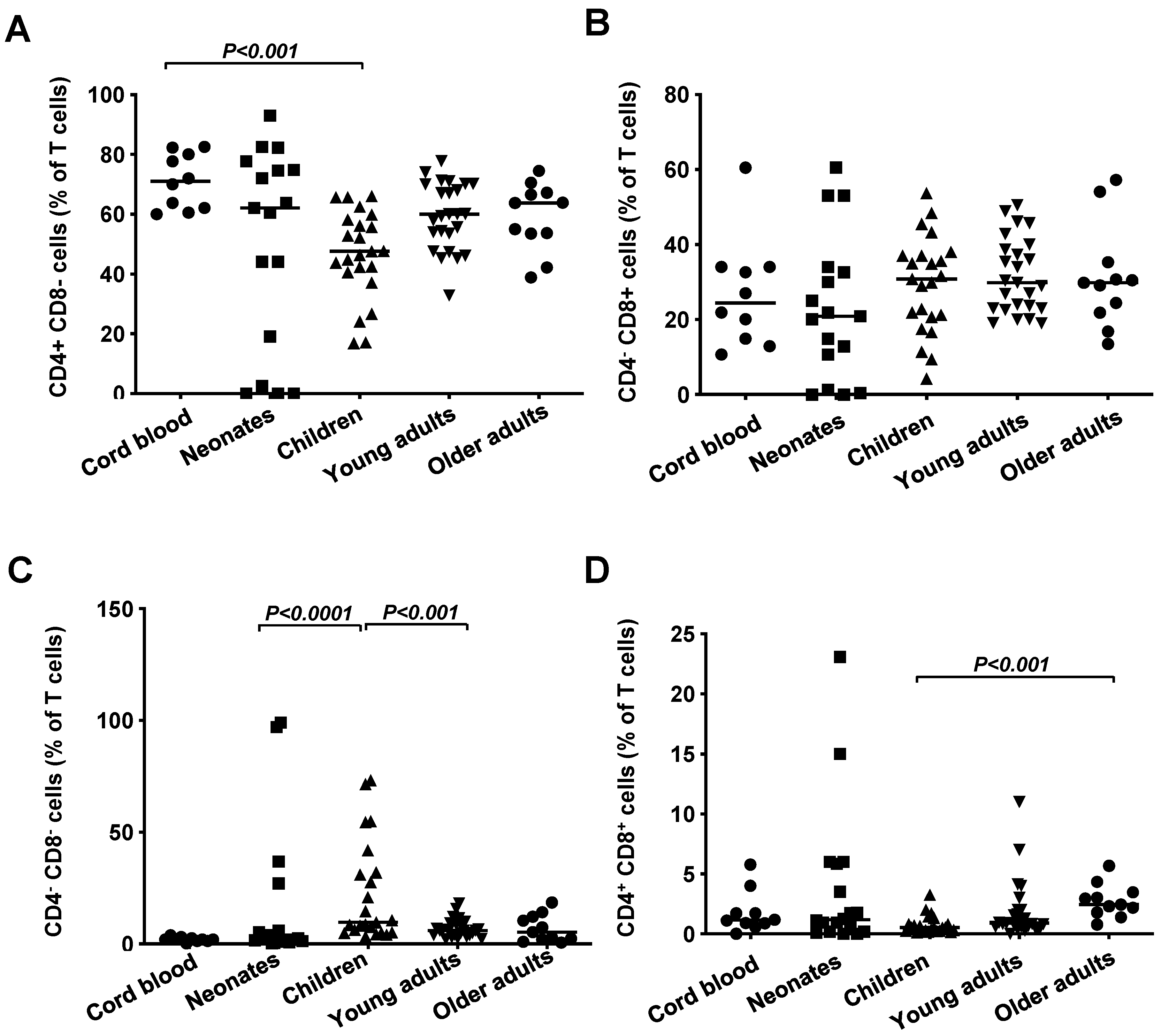
3.1. Frequencies of T Cells, B Cells and NK Cells in Healthy Subjects Grouped According to Age
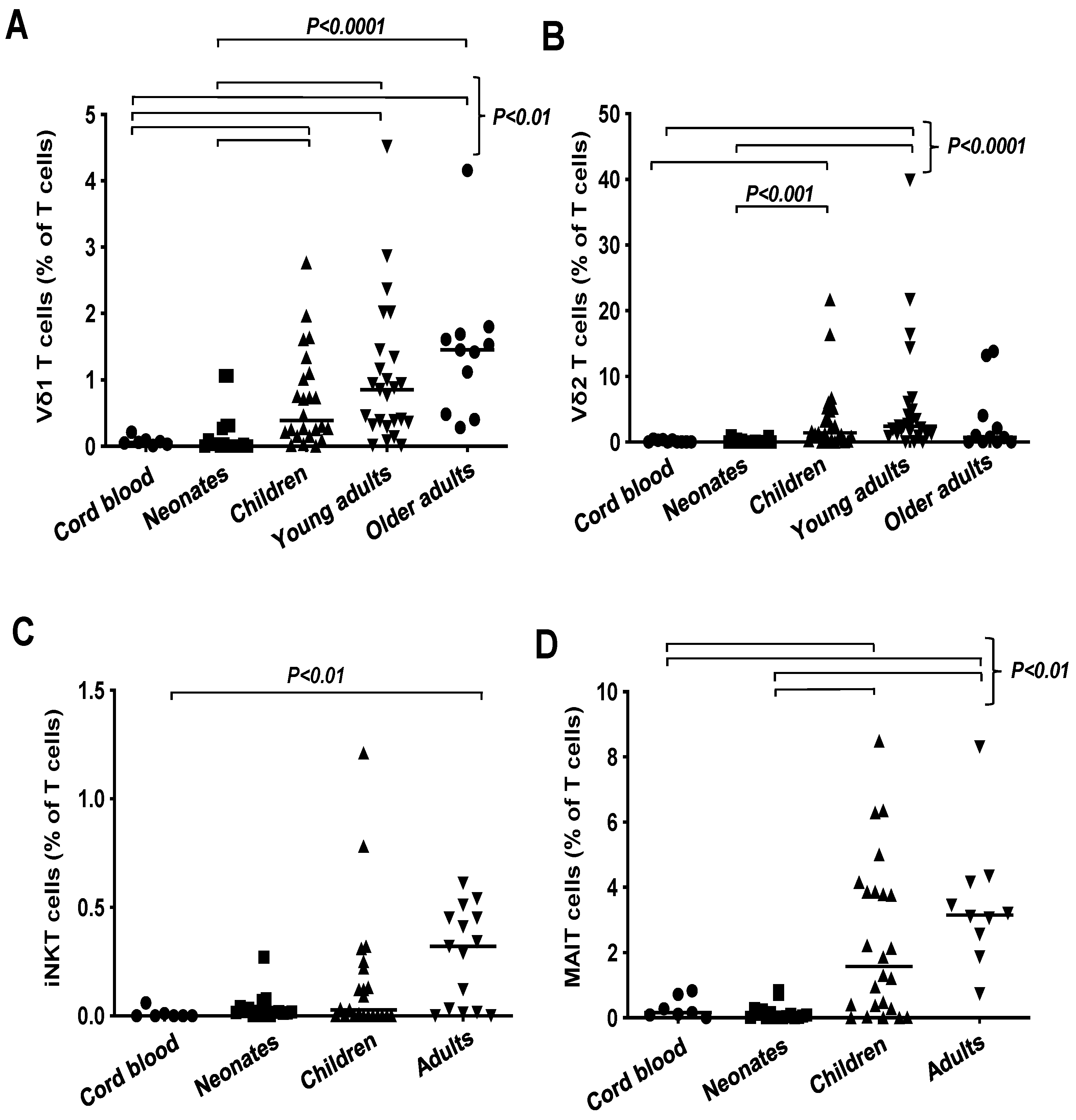
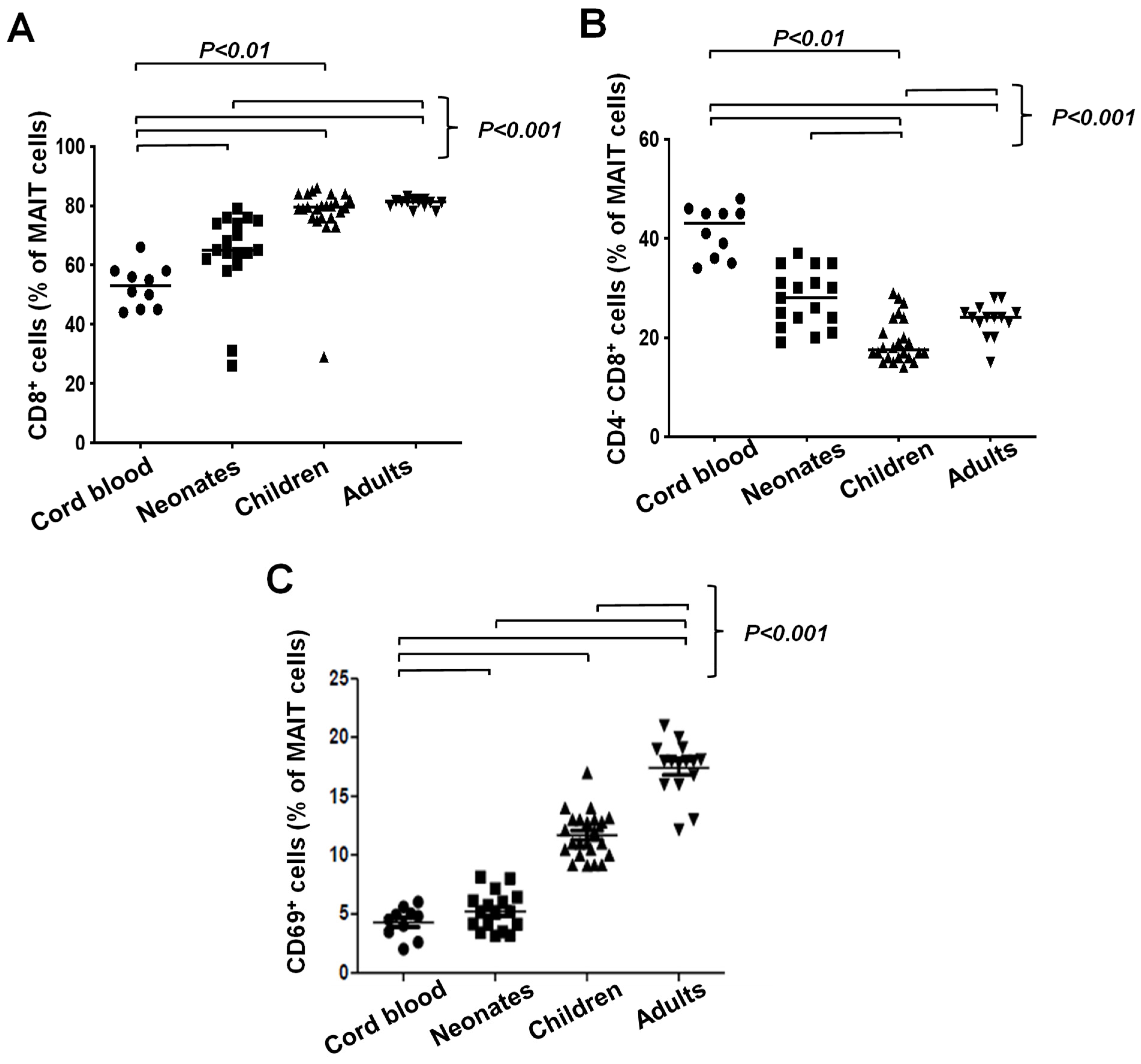
3.2. Unconventional T Cell Frequencies in Healthy Donors Grouped According to Age
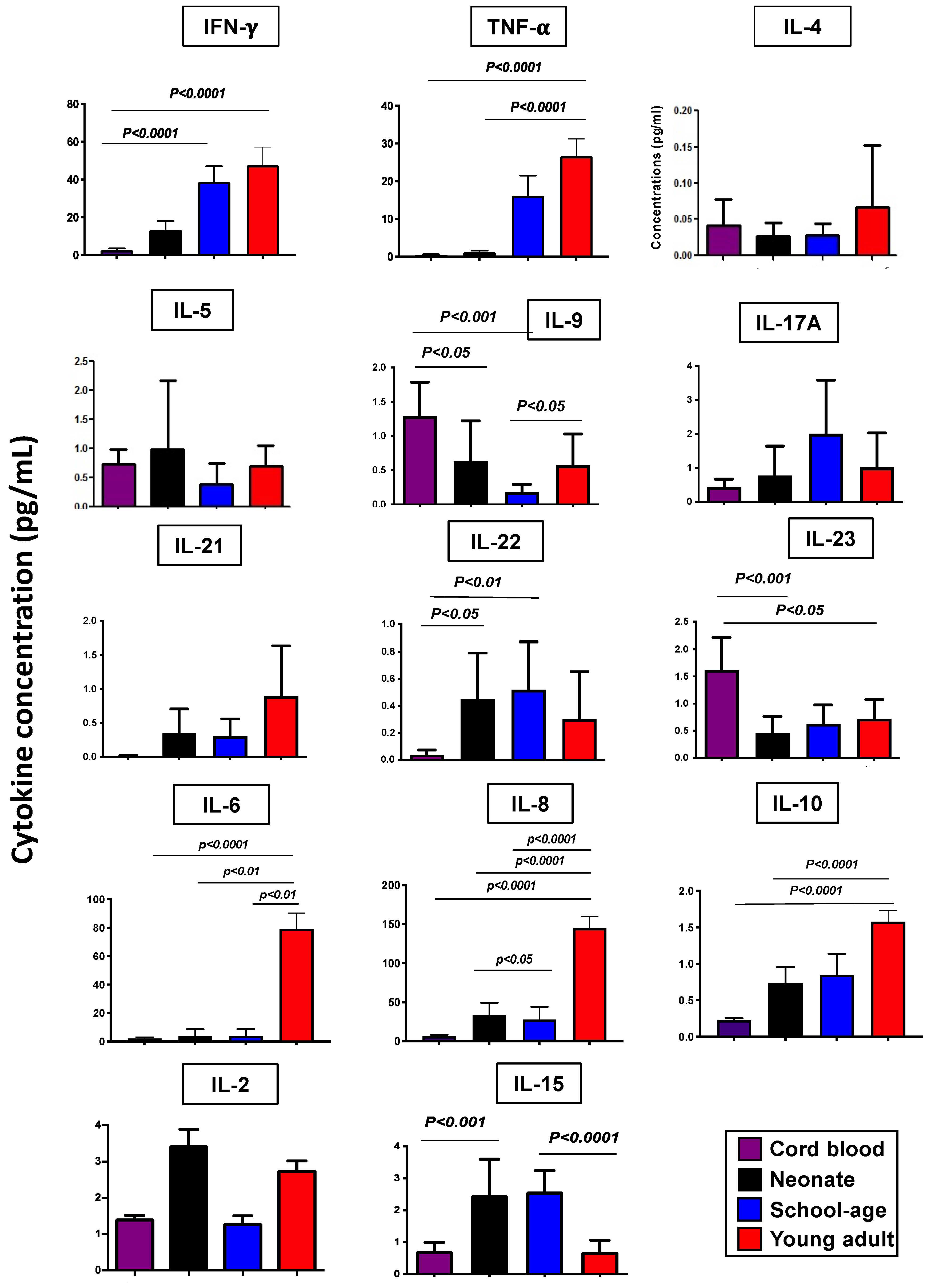
3.3. Serum Cytokine Levels in Healthy Subjects Grouped According to Age
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DN | double negative |
| DP | double positive |
| FcR | Fc receptor |
| FSC | forward scatter |
| γδ T cell | gamma delta T cell |
| IFN-γ | interferon-gammaq |
| Ig | immunoglobulin |
| IL | interleukin |
| iNKT cell | invariant natural killer T cell |
| mAb | monoclonal antibody |
| MAIT cell | mucosa-associated invariant T cell |
| NFκB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| NK | natural killer |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| SSC | side scatter |
| Th cell | helper T cell |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| Treg cell | regulatory T cell |
References
- Simon, A.K.; Hollander, G.A.; McMichael, A. Evolution of the immune system in humans from infancy to old age. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20143085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besedovsky, L.; Lange, T.; Haack, M. The sleep-immune crosstalk in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1325–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.; Christian, L.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J. Stress, age, and immune function: Toward a lifespan approach. J. Behav. Med. 2006, 29, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpert, A.; Pickman, Y.; Leipold, M.; Rosenberg-Hasson, Y.; Ji, X.; Gaujoux, R.; Rabani, H.; Starosvetsky, E.; Kveler, K.; Schaffert, S.; et al. A clinically meaningful metric of immune age derived from high-dimensional longitudinal monitoring. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourkochristou, E.; Triantos, C.; Mouzaki, A. The influence of nutritional factors on immunological outcomes. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 665968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N. The early life education of the immune system: Moms, microbes and (missed) opportunities. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1824564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecino-Rodriguez, E.; Berent-Maoz, B.; Dorshkind, K. Causes, consequences, and reversal of immune system aging. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawelec, G. Age and immunity: What is “immunosenescence”? Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 105, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Weyand, C.; Goronzy, J. Hallmarks of the aging T-cell system. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 7123–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgountzou, A.; Papadopoulos, N. Postnatal innate immune development: From birth to adulthood. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.; Fabbri, E. Inflammageing: Chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, K.; Wu, Y.; Barnett, Y.; Duggan, O.; Vaughan, R.; Kondeatis, E.; Nilsson, B.; Wikby, A.; Kipling, D.; Dunn-Walters, D. B-cell diversity decreases in old age and is correlated with poor health status. Aging Cell 2009, 8, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangrazzi, L.; Weinberger, B. T cells, aging and senescence. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 134, 110887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahata, Y.; Nomura, A.; Takada, H.; Ohga, S.; Furuno, K.; Hikino, S.; Nakayama, H.; Sakaguchi, S.; Hara, T. CD25+CD4+ T cells in human cord blood: An immunoregulatory subset with naive phenotype and specific expression of forkhead box p3 (Foxp3) gene. Exp. Hematol. 2004, 32, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mold, J.; Venkatasubrahmanyam, S.; Burt, T.; Michaëlsson, J.; Rivera, J.; Galkina, S.; Weinberg, K.; Stoddart, C.; McCune, J. Fetal and adult hematopoietic stem cells give rise to distinct T cell lineages in humans. Science 2010, 330, 1695–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridings, J.; Dinan, L.; Williams, R.; Roberton, D.; Zola, H. Somatic mutation of immunoglobulin VH6 genes in human infants. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 114, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Chowdhury, S.; Greenspan, N.; Schreiber, J. Decreased expression of tumor necrosis factor family receptors involved in humoral immune responses in preterm neonates. Blood 2007, 110, 2948–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlgren, M.; Friedli, M.; Tougne, C.; Rochat, A.; Lambert, P.; Siegrist, C. Reduced ability of neonatal and early-life bone marrow stromal cells to support plasmablast survival. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons; Haque, S.; Silberzahn, T.; Hamilton, K.; Langford, C.; Ellis, P.; Carr, R.; Hayday, A. Neonates harbour highly active γδ T cells with selective impairments in preterm infants. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1794–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeansyah, E.; Loh, L.; Nixon, D.F.; Sandberg, J.K. Acquisition of innate-like microbial reactivity in mucosal tissues during human fetal MAIT-cell development. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, G.B.; Tourret, M.; Salou, M.; Ghazarian, L.; Houdouin, V.; Mondot, S.; Mburu, Y.; Lambert, M.; Azarnoush, S.; Diana, J.S.; et al. Ontogeny of human mucosal-associated invariant T cells and related T cell subsets. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.; Thomas, P. A Cell for the Ages: Human γδ T cells across the lifespan. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Fichtner, A.S.; Bruni, E.; Odak, I.; Sandrock, I.; Bubke, A.; Borchers, A.; Schultze-Florey, C.; Koenecke, C.; Förster, R.; et al. A fetal wave of human type 3 effector γδ cells with restricted TCR diversity persists into adulthood. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabf0125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.; Guimiot, F.; Six, E.; Jourquin, F.; Setterblad, N.; Kahn, E.; Yagello, M.; Schiffer, C.; Andre-Schmutz, I.; Cavazzana-Calvo, M.; et al. Dynamics of thymus-colonizing cells during human development. Immunity 2006, 24, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotoff, D.A.; Schwarz, B.A.; Bhandoola, A. The long road to the thymus: The generation, mobilization, and circulation of T-cell progenitors in mouse and man. Semin. Immunopathol. 2008, 30, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, J.; Toapanta, F. B and T cell immunity in tissues and across the ages. Vaccines 2021, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgin, H.; Wherry, E.; Ahmed, R. Redefining chronic viral infection. Cell 2009, 138, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bektas, A.; Schurman, S.H.; Sen, R.; Ferrucci, L. Human T cell immunosenescence and inflammation in aging. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-López, J.; Martín-Antonio, B. Inflammaging, an imbalanced immune response that needs to be restored for cancer prevention and treatment in the elderly. Cells 2021, 10, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, K.; Li, G.; Vallejo, A.; Lee, W.; Koetz, K.; Bryl, E.; Witkowski, J.; Fulbright, J.; Weyand, C.; Goronzy, J. The influence of age on T cell generation and TCR diversity. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 7446–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bektas, A.; Zhang, Y.; Lehmann, E.; Wood, W.; Becker, K.; Madara, K.; Ferrucci, L.; Sen, R. Age-associated changes in basal NF-κB function in human CD4+ T lymphocytes via dysregulation of PI3 kinase. Aging 2014, 6, 957–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocchegiani, E.; Malavolta, M. NK and NKT cell functions in immunosenescence. Aging Cell 2004, 3, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, L.; Guilbert, L.J.; Wegmann, T.G.; Belosevic, M.; Mosmann, T.R. T helper 1 response against Leishmania major in pregnant C57BL/6 mice increases implantation failure and fetal resorptions. Correlation with increased IFN-gamma and TNF and reduced IL-10 production by placental cells. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghupathy, R. Th1-type immunity is incompatible with successful pregnancy. Immunol. Today 1997, 18, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, A.; Henckel, E.; Chen, Y.; Lakshmikanth, T.; Pou, C.; Mikes, J.; Gustafsson, A.; Bernhardsson, A.K.; Zhang, C.; Bohlin, K.; et al. Stereotypic immune system development in newborn children. Cell 2018, 174, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, N.A.; Kelly, L.A.; Al-Harbi, A.I.; O’Dea, M.I.; Zareen, Z.; Ryan, E.; Molloy, E.J.; Doherty, D.G. Altered distributions and functions of natural killer T cells and γδ T cells in neonates with neonatal encephalopathy, in school-age children at follow-up, and in children with cerebral palsy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 356, 577597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ygberg, S.; Nilsson, A. The developing immune system—From foetus to toddler. Acta Paediatr. 2012, 101, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansoni, P.; Cossarizza, A.; Brianti, V.; Fagnoni, F.; Snelli, G.; Monti, D.; Marcato, A.; Passeri, G.; Ortolani, C.; Forti, E.; et al. Lymphocyte subsets and natural killer cell activity in healthy old people and centenarians. Blood 1993, 82, 2767–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentsch-Ullrich, K.; Koenigsmann, M.; Mohren, M.; Franke, A. Lymphocyte subsets’ reference ranges in an age- and gender-balanced population of 100 healthy adults—A monocentric German study. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademokun, A.; Wu, Y.C.; Dunn-Walters, D. The ageing B cell population: Composition and function. Biogerontology 2010, 11, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasca, D.; Diaz, A.; Romero, M.; Landin, A.M.; Blomberg, B.B. Age effects on B cells and humoral immunity in humans. Ageing Res. Rev. 2011, 10, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, M.; Zamai, L.; Neri, L.M.; Galanzi, A.; Facchini, A.; Rana, R.; Cataldi, A.; Papa, S. The impairment of natural killer function in the healthy aged is due to a postbinding deficient mechanism. Cell Immunol. 1992, 145, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego, F.; Alonso, M.; Galiani, M.D.; Carracedo, J.; Ramirez, R.; Ostos, B.; Peña, J.; Solana, R. NK phenotypic markers and IL2 response in NK cells from elderly people. Exp. Gerontol. 1999, 34, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chidrawar, S.M.; Khan, N.; Chan, Y.L.; Nayak, L.; Moss, P.A. Ageing is associated with a decline in peripheral blood CD56bright NK cells. Immun. Ageing 2006, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Garff-Tavernier, M.; Béziat, V.; Decocq, J.; Siguret, V.; Gandjbakhch, F.; Pautas, E.; Debré, P.; Merle-Beral, H.; Vieillard, V. Human NK cells display major phenotypic and functional changes over the life span. Aging Cell 2010, 9, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehniger, T.A.; Cooper, M.A.; Nuovo, G.J.; Cella, M.; Faccetti, F.; Colonna, M.; Caligiuri, M.A. CD56bright natural killer cells are present in human lymph nodes and are activated by T cell derived IL-2: A potential new link between adaptive and innate immunity. Blood 2003, 101, 3052–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.S.; Willcox, C.R.; Joyce, S.P.; Ladell, K.; Kasatskaya, S.A.; McLaren, J.E.; Hunter, S.; Salim, M.; Mohammed, F.; Price, D.A.; et al. Clonal selection in the human Vδ1 T cell repertoire indicates γδ TCR-dependent adaptive immune surveillance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravens, S.; Fichtner, A.S.; Willers, M.; Torkornoo, D.; Pirr, S.; Schöning, J.; Deseke, M.; Sandrock, I.; Bubke, A.; Wilharm, A.; et al. Microbial exposure drives polyclonal expansion of innate γδ T cells immediately after birth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18649–18660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimova, T.; Brouwer, M.; Gosselin, F.; Tassignon, J.; Leo, O.; Donner, C.; Marchant, A.; Vermijlen, D. Effector Vγ9Vδ2 T cells dominate the human fetal γδ T-cell repertoire. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E556–E565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, M.; Tieppo, P.; McGovern, N.; Gosselin, F.; Chan, J.K.Y.; Goetgeluk, G.; Dauby, N.; Cogan, A.; Donner, C.; Ginhoux, F.; et al. TCR Sequencing Reveals the Distinct Development of Fetal and Adult Human Vγ9Vδ2 T Cells. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 1468–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, E.; Brouwer, M.; Dimova, T.; Goldman, M.; Willems, F.; Vermijlen, D. IL-23R and TCR signaling drives the generation of neonatal Vγ9Vδ2 T cells expressing high levels of cytotoxic mediators and producing IFN-gamma and IL-17. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.; Boudova, S.; Mvula, G.; Divala, T.H.; Rach, D.; Mungwira, R.G.; Boldrin, F.; Degiacomi, G.; Manganelli, R.; Laufer, M.K.; et al. Age-related changes in PD-1 expression coincide with increased cytotoxic potential in Vδ2 T cells during infancy. Cell Immunol. 2021, 359, 104244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, S.B.; Rathore, D.K.; Nair, D.; Chaudhary, A.; Raza, S.; Kanodia, P.; Sopory, S.; George, A.; Rath, S.; Bal, V.; et al. Comparison of human neonatal and adult blood leukocyte subset composition phenotypes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salio, M.; Silk, J.D.; Jones, E.Y.; Cerundolo, V. Biology of CD1- and MR1-restricted T cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 323–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, D.I.; Uldrich, A.P.; McCluskey, J.; Rossjohn, J.; Moody, D.B. The burgeoning family of unconventional T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszak, T.; An, D.; Zeissig, S.; Vera, M.P.; Richter, J.; Franke, A.; Glickman, J.N.; Siebert, R.; Baron, R.M.; Kasper, D.L.; et al. Microbial exposure during early life has persistent effects on natural killer T cell function. Science 2012, 336, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.J.; Kang, Y.H.; Smith, M.O.; Tharmalingham, H.; Ramamurthy, N.; Fleming, V.M.; Sahgal, N.; Leslie, A.; Oo, Y.; Geremia, A.; et al. Human MAIT and CD8αα cells develop from a pool of type-17 precommitted CD8+ T cells. Blood 2012, 119, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Deng, W.; Li, D.; Zeng, T.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; Duan, D.; et al. Circulating mucosal-associated invariant T cells in a large cohort of healthy Chinese Individuals from rewborn to elderly. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.-J.; Cho, Y.-N.; Kee, S.-J.; Kim, M.-J.; Jin, H.-M.; Lee, S.-J.; Park, K.-J.; Kim, T.-J.; Lee, S.-S.; Kwon, Y.-S.; et al. Circulating mucosal-associated invariant T cell levels and their cytokine levels in healthy adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 49, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, R.H.; Cordle, C.T.; Thomas, D.J.; Winship, T.R.; Schaller, J.P.; Dugle, J.E. Longitudinal study of intracellular T cell cytokine production in infants compared to adults. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 128, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparoni, A.; Ciardelli, L.; Avanzini, A.; Castellazzi, A.M.; Carini, R.; Rondini, G.; Chirico, G. Age-related changes in intracellular TH1/TH2 cytokine production, immunoproliferative T lymphocyte response and natural killer cell activity in newborns, children and adults. Biol. Neonate 2003, 84, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeljeli, M.; Khourouj, V.G.-E.; Pédron, B.; Gressens, P.; Sibony, O.; Sterkers, G. Ontogeny of cytokine responses to PHA from birth to adulthood. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 86, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angkasekwinai, P.; Dong, C. IL-9-producing T cells: Potential players in allergy and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Huan, C.; Yang, Y. The relationship between umbilical cord blood IL-22 level and infantile eczema at 42 days. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1376706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, G.; Marcuzzi, A.; Zanin, V.; Monasta, L.; Zauli, G. Cytokine levels in the serum of healthy subjects. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, M.L.; Grobusch, M.P.; Ritz, N. Influence of age and other factors on cytokine expression profiles in healthy children-A systematic review. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taher, N.A.B.; Isaza-Correa, J.M.; Melo, A.M.; Kelly, L.A.; Al-Harbi, A.I.; O’Dea, M.I.; Zareen, Z.; Ryan, E.; Omer, M.; Townsend, L.; et al. Dynamics of Peripheral Lymphocyte Subsets from Birth until Old Age. Immuno 2024, 4, 358-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040023
Taher NAB, Isaza-Correa JM, Melo AM, Kelly LA, Al-Harbi AI, O’Dea MI, Zareen Z, Ryan E, Omer M, Townsend L, et al. Dynamics of Peripheral Lymphocyte Subsets from Birth until Old Age. Immuno. 2024; 4(4):358-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040023
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaher, Nawal A. B., Johana M. Isaza-Correa, Ashanty M. Melo, Lynne A. Kelly, Alhanouf I. Al-Harbi, Mary I. O’Dea, Zunera Zareen, Emer Ryan, Murwan Omer, Liam Townsend, and et al. 2024. "Dynamics of Peripheral Lymphocyte Subsets from Birth until Old Age" Immuno 4, no. 4: 358-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040023
APA StyleTaher, N. A. B., Isaza-Correa, J. M., Melo, A. M., Kelly, L. A., Al-Harbi, A. I., O’Dea, M. I., Zareen, Z., Ryan, E., Omer, M., Townsend, L., Molloy, E. J., & Doherty, D. G. (2024). Dynamics of Peripheral Lymphocyte Subsets from Birth until Old Age. Immuno, 4(4), 358-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040023




