Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Deep-Sea Mineral Water on LPS-Induced Inflammation in Raw 264.7 Murine Macrophage Cells and Zebrafish Larvae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Acquisition of Seawater
2.2. Cell Maintenance and Media Preparation
2.3. Cells Cytotoxicity Analysis
2.4. NO Assay
2.5. Cytokine Induction Analysis in Raw 264.7 Cells
2.6. In Vivo Survival Assay for Zebrafish Eggs and Larvae
2.7. Analysis of DSW Effect on Macrophage and Neutrophil Recruitment to the Amputated Fin Fold of Zebrafish Larvae
2.8. Cytokine Induction Analysis in Zebrafish Larvae
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
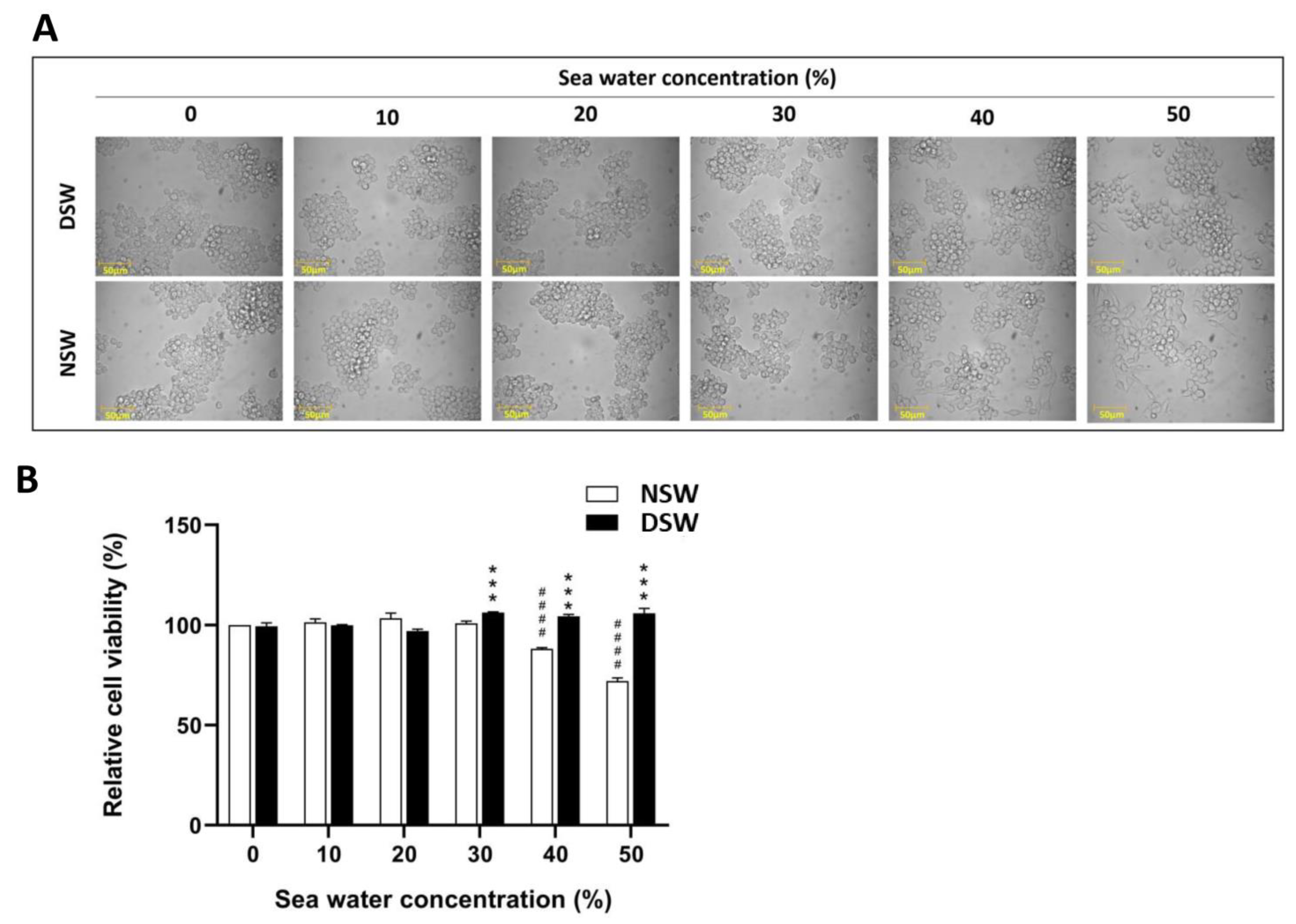
3.1. DSW Enhances the Viability of RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells
3.2. DSW Reduces LPS-Induced Apoptosis in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells
3.3. DSW Suppresses LPS-Induced NO Production and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Induction
3.4. DSW Shows Less Lethal Effect on Zebrafish Larvae
3.5. DSW Reduces the Macrophage and Neutrophil Recruitment to the Amputated Fin Fold
3.6. DSW Reduces LPS-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pahwa, R.; Goyal, A.; Jialal, I. Chronic Inflammation. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, N.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophages in Inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets—Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunarathne, W.A.H.M.; Lee, K.T.; Choi, Y.H.; Jin, C.-Y.; Kim, G.-Y. Anthocyanins Isolated from Hibiscus Syriacus L. Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Endotoxic Shock by Inhibiting the TLR4/MD2-Mediated NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Phytomedicine 2020, 76, 153237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, E.M.; McGinity, C.; Wink, D.A.; McVicar, D.W. Nitric Oxide in Macrophage Immunometabolism: Hiding in Plain Sight. Metabolites 2020, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Clermont, G.; Vodovotz, Y.; Chow, C.C. The Dynamics of Acute Inflammation. J. Theor. Biol. 2004, 230, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Ahn, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.-K. Inhibitory Activity of Plant Extracts on Nitric Oxide Synthesis in LPS-Activated Macrophages. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yin, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Dong, H.; Bai, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Feng, S.; et al. LPS-induced Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Macrophages via NF-κB, STAT3 or AP-1 Activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5484–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-B.; Lee, Y.-J.; Park, S.K.; Kim, H.-C.; Bae, H.; Kim, H.M.; Ko, S.-G.; Choi, H.Y.; Oh, M.S.; Park, W. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Scutellaria Baicalensis Water Extract on LPS-Activated RAW 264.7 Macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 125, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelpoel, L.T.C.; Baeten, D.L.P.; de Jong, E.C.; den Dunnen, J. Control of Cytokine Production by Human Fc Gamma Receptors: Implications for Pathogen Defense and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matz, H.; Orion, E.; Wolf, R. Balneotherapy in Dermatology. Dermatol. Ther. 2003, 16, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S.; Chun, S.-Y.; Lee, M.-G.; Kim, S.; Jang, T.-J.; Nam, K.-S. The Prevention of TNF-α/IFN-γ Mixture-Induced Inflammation in Human Keratinocyte and Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions in Nc/Nga Mice by Mineral-Balanced Deep Sea Water. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.-Y.; Lee, K.-S.; Nam, K.-S. Refined Deep-Sea Water Suppresses Inflammatory Responses via the MAPK/AP-1 and NF-κB Signaling Pathway in LPS-Treated RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.; Kim, K.J.; Park, G.; Kim, B.G.; Jeong, G.-H.; Jeon, J.; Hurh, B.S.; Kim, J.Y. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Mineral-Balanced Deep Sea Water in In-Vitro and In-Vivo Models of Inflamed Intestinal Epithelium. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, M.-J.; Chou, P.-Y.; Lin, W.-H.; Pan, C.-H.; Chien, Y.-C.; Chung, Y.-L.; Liu, F.-C.; Wu, C.-H. Deep Sea Water Modulates Blood Pressure and Exhibits Hypolipidemic Effects via the AMPK-ACC Pathway: An in vivo Study. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2183–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Hao, J.; Peng, W.; Qiu, P.; Li, C.; Guan, H. Modulation of Lipid Metabolism by Deep-Sea Water in Cultured Human Liver (HepG2) Cells. Mar. Biotechnol. 2014, 16, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.-L.; Hsu, T.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hsu, J.-D.; Yang, L.-C.; Tsai, F.-J.; Li, C.-C.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Tzang, B.-S. Effects of Deep-Sea Water on Cardiac Abnormality in High-Cholesterol Dietary Mice: Cardiac Protective Effects of Deep-Sea Water. J. Food Biochem. 2012, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuda, S.; Yasukawa, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyake, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Katahira, K.; Mohri, M.; Shimizu, T.; Hazama, A. Deep-Sea Water Improves Cardiovascular Hemodynamics in Kurosawa and Kusanagi-Hypercholesterolemic (KHC) Rabbits. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, B.G.; Park, J.; Shin, E.J.; Shon, Y.H. Effects of Balanced Deep-sea Water on Adipocyte Hypertrophy and Liver Steatosis in High-fat, Diet-induced Obese Mice. Obesity 2014, 22, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of Cell Viability by the MTT Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 2018, pdb-rot095505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanaka, K.A.S.N.; Jung, S.; Madushani, K.P.; Wijerathna, H.M.S.M.; Neranjan Tharuka, M.D.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, J. Generation of Viperin-Knockout Zebrafish by CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Genome Engineering and the Effect of This Mutation under VHSV Infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 131, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Alexander, M.; Misharin, A.V.; Budinger, G.R.S. The Role of Macrophages in the Resolution of Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maehira, F.; Iinuma, Y.; Eguchi, Y.; Miyagi, I.; Teruya, S. Effects of Soluble Silicon Compound and Deep-Sea Water on Biochemical and Mechanical Properties of Bone and the Related Gene Expression in Mice. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2008, 26, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.J.; Ruckerl, D.; Cook, P.C.; Jones, L.H.; Finkelman, F.D.; van Rooijen, N.; MacDonald, A.S.; Allen, J.E. Local Macrophage Proliferation, Rather than Recruitment from the Blood, Is a Signature of T H 2 Inflammation. Science 2011, 332, 1284–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valledor, A.F.; Comalada, M.; Santamaría-Babi, L.F.; Lloberas, J.; Celada, A. Macrophage Proinflammatory Activation and Deactivation: A Question of Balance. Adv. Immunol. 2010, 108, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xaus, J.; Comalada, M.; Valledor, A.F.; Lloberas, J.; López-Soriano, F.; Argilés, J.M.; Bogdan, C.; Celada, A. LPS Induces Apoptosis in Macrophages Mostly through the Autocrine Production of TNF-α. Blood 2000, 95, 3823–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.-S.; Shin, J.-S.; Choi, H.-E.; Cho, Y.-W.; Bang, M.-H.; Baek, N.-I.; Lee, K.-T. Fucosterol Isolated from Undaria Pinnatifida Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Production of Nitric Oxide and pro-Inflammatory Cytokines via the Inactivation of Nuclear Factor-κB and P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.N.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S.S. Role of Nitric Oxide in Inflammatory Diseases. Inflammopharmacol 2007, 15, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teame, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Xie, M.; Gao, C.; Ye, Y.; Duan, M.; et al. The Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) as Biomedical Models. Anim. Front. 2019, 9, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, T.-Y.; Choi, T.-I.; Lee, Y.-R.; Choe, S.-K.; Kim, C.-H. Zebrafish as an Animal Model for Biomedical Research. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, H.S. Water Quality For Zebrafish Culture. In The Zebrafish in Biomedical Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 321–335. ISBN 978-0-12-812431-4. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Meijer, A.H.; Schaaf, M.J.M. Modeling Inflammation in Zebrafish for the Development of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 620984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.R.; Gelaleti, G.B.; Moschetta, M.G.; Maschio-Signorini, L.B.; Zuccari, D.A.P.D.C. Proinflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines Mediated by NF- κ B Factor as Prognostic Markers in Mammary Tumors. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Bi, W.; Xiao, S.; Lan, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Neuroinflammation Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Causes Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.S.; Kim, H.A.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, J.W. Anti-Obesity and Antidiabetic Effects of Deep Sea Water on Ob/Ob Mice. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewicki, S.; Zdanowski, R.; Krzyżowska, M.; Lewicka, A.; Dębski, B.; Niemcewicz, M.; Goniewicz, M. The Role of Chromium III in the Organism and Its Possible Use in Diabetes and Obesity Treatment. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2014, 21, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Type of Seawater | Na+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) | K+ (mg/L) | Salinity (ppt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep-sea mineral water (Desalinated concentrate, DSW) | 70.6 | 1175.2 | 448.0 | 19.4 | 18 |
| Normal seawater (NSW) (Salinity adjusted to 18 ppt) | 5484.4 | 582.6 | 175.2 | 164.9 | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wijerathna, H.M.S.M.; Vileka Jayamali, B.P.M.; Moon, D.-S.; Kim, C.-G.; Jung, S.; Lee, J. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Deep-Sea Mineral Water on LPS-Induced Inflammation in Raw 264.7 Murine Macrophage Cells and Zebrafish Larvae. Immuno 2024, 4, 344-357. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040022
Wijerathna HMSM, Vileka Jayamali BPM, Moon D-S, Kim C-G, Jung S, Lee J. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Deep-Sea Mineral Water on LPS-Induced Inflammation in Raw 264.7 Murine Macrophage Cells and Zebrafish Larvae. Immuno. 2024; 4(4):344-357. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040022
Chicago/Turabian StyleWijerathna, Hitihami M. S. M., Bulumulle P. M. Vileka Jayamali, Deok-Soo Moon, Choong-Gon Kim, Sumi Jung, and Jehee Lee. 2024. "Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Deep-Sea Mineral Water on LPS-Induced Inflammation in Raw 264.7 Murine Macrophage Cells and Zebrafish Larvae" Immuno 4, no. 4: 344-357. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040022
APA StyleWijerathna, H. M. S. M., Vileka Jayamali, B. P. M., Moon, D.-S., Kim, C.-G., Jung, S., & Lee, J. (2024). Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Deep-Sea Mineral Water on LPS-Induced Inflammation in Raw 264.7 Murine Macrophage Cells and Zebrafish Larvae. Immuno, 4(4), 344-357. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040022






