Orchestration of Immune Cells Contributes to Fibrosis in IgG4-Related Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Clinical Features
2. Targeted Therapy Has Proven the Contribution of B Cell Lineages to IgG4-RD
2.1. Plasmablasts
2.2. Other B Cell Subsets
3. Therapeutic Drugs That Might Change the Treatment of IgG4-RD
4. CD4+ T Cells
4.1. Tfh Cells
4.2. Th2 Cells
4.3. CD4+CTLs
4.4. CD8+ T Cells
5. What Is the Target of T Cells with a Cytotoxic Phenotype?
6. M2 Macrophages Participate in the Pathogenesis of IgG4-RD
7. The Role of IgG4 in IgG4-RD
8. Potential Triggers of IgG4-RD: Autoantigens
9. Playing Fibrosis in IgG4-RD
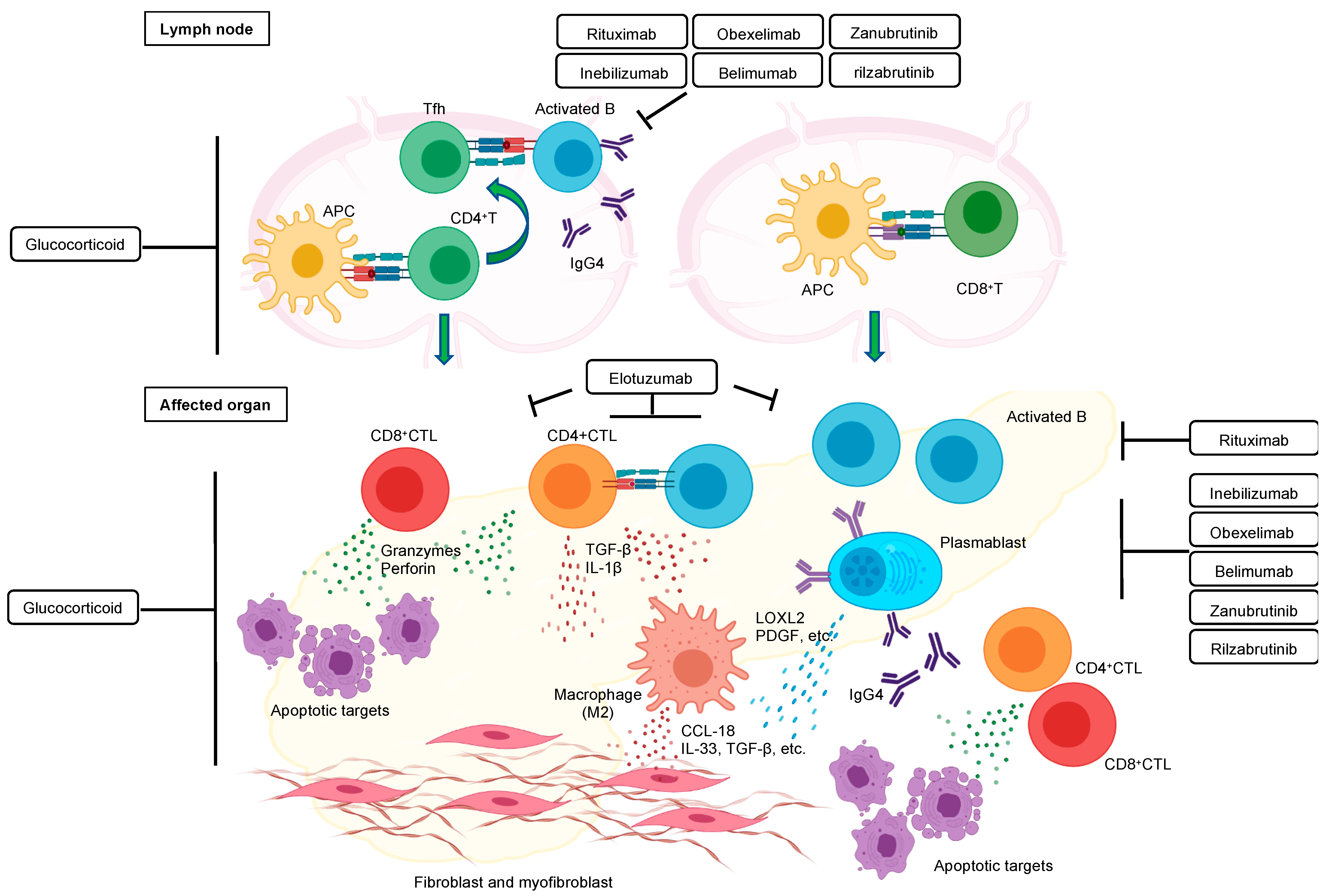
10. Orchestration of Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis of IgG4-RD
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carruthers, M.N.; Stone, J.H.; Khosroshahi, A. The latest on IgG4-RD: A rapidly emerging disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2012, 24, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.H.; Khosroshahi, A.; Deshpande, V.; Chan, J.K.; Heathcote, J.G.; Aalberse, R.; Azumi, A.; Bloch, D.B.; Brugge, W.R.; Carruthers, M.N.; et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheumathol. 2012, 64, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, V.; Zen, Y.; Chan, J.K.; Yi, E.E.; Sato, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Klöppel, G.; Heathcote, J.G.; Khosroshahi, A.; Ferry, J.A.; et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okazaki, K.; Uchida, K.; Koyabu, M.; Miyoshi, H.; Takaoka, M. Recent advances in the concept and diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroshahi, A.; Stone, J.H. A clinical overview of IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.H.; Zen, Y.; Deshpande, V. IgG4-related disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umehara, H.; Okazaki, K.; Masaki, Y.; Kawano, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Saeki, T.; Matsui, S.; Sumida, T.; Mimori, T.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): General concept and details. Mod. Rheumatol. 2012, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Stone, J.H. An update on IgG4-related disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2015, 27, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zen, Y.; Nakanuma, Y. IgG4-related disease: A cross-sectional study of 114 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1812–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugino, C.A.; Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Maehara, T.; Wallace, Z.S.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. Emerging treatment models in rheumatology: IgG4-related disease: Insights into human immunology and targeted therapies. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehara, T.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H.; Nakamura, S. Clinical features and mechanistic insights regarding IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis: A review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, S.; Perugino, C.; Kaneko, N. Immune mechanisms of fibrosis and inflammation in IgG4-related disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2020, 32, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamekura, R.; Takahashi, H.; Ichimiya, S. New insights into IgG4-related disease: Emerging new CD4+ T-cell subsets. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perugino, C.A.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease: An update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M. B cell targeted therapy for immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Immunol. Med. 2021, 44, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yin, W.; Westerberg, L.S.; Lee, P.; Gong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Dong, L.; Liu, C. Immune dysregulation in IgG(4)-related disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 738540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.C.; Shen, C.Y.; Liao, H.T.; Chen, M.H.; Wu, C.H.; Li, K.J.; Lu, C.S.; Kuo, Y.M.; Tsai, H.C.; Tsai, C.Y.; et al. The cellular and molecular bases of allergy, inflammation and tissue fibrosis in patients with IgG4-related disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Shimosegawa, T.; Okazaki, K.; Nishino, T.; Watanabe, H.; Kanno, A.; Okumura, F.; Nishikawa, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Ichiya, T.; et al. Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2009, 58, 1504–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Zen, Y.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease. Lancet 2015, 385, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, D.W.; Cidlowski, J.A. Immune regulation by glucocorticoids. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, Y.; Matsui, S.; Saeki, T.; Tsuboi, H.; Hirata, S.; Izumi, Y.; Miyashita, T.; Fujikawa, K.; Dobashi, H.; Susaki, K.; et al. A multicenter phase II prospective clinical trial of glucocorticoid for patients with untreated IgG4-related disease. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masamune, A.; Nishimori, I.; Kikuta, K.; Tsuji, I.; Mizuno, N.; Iiyama, T.; Kanno, A.; Tachibana, Y.; Ito, T.; Kamisawa, T.; et al. Randomised controlled trial of long-term maintenance corticosteroid therapy in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2017, 66, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimosegawa, T.; Chari, S.T.; Frulloni, L.; Kamisawa, T.; Kawa, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Kim, M.H.; Klöppel, G.; Lerch, M.M.; Löhr, M.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: Guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas 2011, 40, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Naden, R.P.; Chari, S.; Choi, H.; Della-Torre, E.; Dicaire, J.F.; Hart, P.A.; Inoue, D.; Kawano, M.; Khosroshahi, A.; et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khosroshahi, A.; Wallace, Z.S.; Crowe, J.L.; Akamizu, T.; Azumi, A.; Carruthers, M.N.; Chari, S.T.; Della-Torre, E.; Frulloni, L.; Goto, H.; et al. International Consensus Guidance Statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroshahi, A.; Bloch, D.B.; Deshpande, V.; Stone, J.H. Rituximab therapy leads to rapid decline of serum IgG4 levels and prompt clinical improvement in IgG4-related systemic disease. Arthritis Rheumathol. 2010, 62, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroshahi, A.; Carruthers, M.N.; Deshpande, V.; Unizony, S.; Bloch, D.B.; Stone, J.H. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: Lessons from 10 consecutive patients. Medicine 2012, 91, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, M.N.; Topazian, M.D.; Khosroshahi, A.; Witzig, T.E.; Wallace, Z.S.; Hart, P.A.; Deshpande, V.; Smyrk, T.C.; Chari, S.; Stone, J.H. Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: A prospective, open-label trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.C.; Cambridge, G. B-cell targeting in rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, J.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Oliver, J.A.; Ravetch, J.V.; Poe, J.C.; Haas, K.M.; Tedder, T.F. The innate mononuclear phagocyte network depletes B lymphocytes through Fc receptor-dependent mechanisms during anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gaetano, N.; Cittera, E.; Nota, R.; Vecchi, A.; Grieco, V.; Scanziani, E.; Botto, M.; Introna, M.; Golay, J. Complement activation determines the therapeutic activity of rituximab in vivo. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teeling, J.L.; French, R.R.; Cragg, M.S.; van den Brakel, J.; Pluyter, M.; Huang, H.; Chan, C.; Parren, P.W.; Hack, C.E.; Dechant, M.; et al. Characterization of new human CD20 monoclonal antibodies with potent cytolytic activity against non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood 2004, 104, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Q.; Ou, Q.; Ye, S.; Lee, W.P.; Cornelius, J.; Diehl, L.; Lin, W.Y.; Hu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Importance of cellular microenvironment and circulatory dynamics in B cell immunotherapy. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Mattoo, H.; Carruthers, M.; Mahajan, V.S.; Della Torre, E.; Lee, H.; Kulikova, M.; Deshpande, V.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Torre, E.; Feeney, E.; Deshpande, V.; Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.; Kulikova, M.; Wallace, Z.S.; Carruthers, M.; Chung, R.T.; Pillai, S.; et al. B-cell depletion attenuates serological biomarkers of fibrosis and myofibroblast activation in IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 2236–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Della-Torre, E.; Sekigami, Y.; Carruthers, M.; Wallace, Z.S.; Deshpande, V.; Stone, J.H.; Pillai, S. De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Della-Torre, E.; Rigamonti, E.; Perugino, C.; Baghai-Sain, S.; Sun, N.; Kaneko, N.; Maehara, T.; Rovati, L.; Ponzoni, M.; Milani, R.; et al. B lymphocytes directly contribute to tissue fibrosis in patients with IgG(4)-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 968–981.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sumimoto, K.; Uchida, K.; Kusuda, T.; Mitsuyama, T.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Fukui, T.; Matsushita, M.; Takaoka, M.; Nishio, A.; Okazaki, K. The role of CD19+ CD24high CD38high and CD19+ CD24high CD27+ regulatory B cells in patients with type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2014, 14, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.; Jin, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q.; Fei, Y.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. B cell subsets and dysfunction of regulatory B cells in IgG4-related diseases and primary Sjögren’s syndrome: The similarities and differences. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanzillotta, M.; Della-Torre, E.; Milani, R.; Bozzolo, E.; Bozzalla-Cassione, E.; Rovati, L.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Partelli, S.; Falconi, M.; Ciceri, F.; et al. Effects of glucocorticoids on B-cell subpopulations in patients with IgG4-related disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S118), 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Nowosad, C.R.; Spillane, K.M.; Tolar, P. Germinal center B cells recognize antigen through a specialized immune synapse architecture. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sacquin, A.; Gador, M.; Fazilleau, N. The strength of BCR signaling shapes terminal development of follicular helper T cells in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Ishigami, K.; Yajima, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Tabeya, T.; Matsui, M.; Suzuki, C.; Naishiro, Y.; Imai, K.; et al. Relapse patterns in IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Kulikova, M.; Lu, L.; Deshpande, V.; Choi, H.K.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. Predictors of disease relapse in IgG4-related disease following rituximab. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hart, P.A.; Kamisawa, T.; Brugge, W.R.; Chung, J.B.; Culver, E.L.; Czakó, L.; Frulloni, L.; Go, V.L.; Gress, T.M.; Kim, M.H.; et al. Long-term outcomes of autoimmune pancreatitis: A multicentre, international analysis. Gut 2013, 62, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamisawa, T.; Ohara, H.; Kim, M.H.; Kanno, A.; Okazaki, K.; Fujita, N. Role of endoscopy in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Dig. Endosc. 2014, 26, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q. Bispecific antibodies for autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: Clinical progress to date. BioDrugs 2020, 34, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzillotta, M.; Mancuso, G.; Della-Torre, E. Advances in the diagnosis and management of IgG4 related disease. BMJ 2020, 369, m1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szili, D.; Cserhalmi, M.; Bankó, Z.; Nagy, G.; Szymkowski, D.E.; Sármay, G. Suppression of innate and adaptive B cell activation pathways by antibody coengagement of FcγRIIb and CD19. mAbs 2014, 6, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, M.; Aochi, S.; Suzuki, C.; Nakamura, S.; Murakami, R.; Ogawa, Y.; Takahashi, H. A case with good response to belimumab for lupus nephritis complicated by IgG4-related disease. Lupus 2019, 28, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, V.S.; Mattoo, H.; Deshpande, V.; Pillai, S.S.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 315–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.; Tangye, S.G.; Mackay, C.R. T follicular helper (TFH) cells in normal and dysregulated immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotty, S. T follicular helper cell differentiation, function, and roles in disease. Immunity 2014, 41, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeannin, P.; Lecoanet, S.; Delneste, Y.; Gauchat, J.F.; Bonnefoy, J.Y. IgE versus IgG4 production can be differentially regulated by IL-10. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 3555–3561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morita, R.; Schmitt, N.; Bentebibel, S.E.; Ranganathan, R.; Bourdery, L.; Zurawski, G.; Foucat, E.; Dullaers, M.; Oh, S.; Sabzghabaei, N.; et al. Human blood CXCR5(+)CD4(+) T cells are counterparts of T follicular cells and contain specific subsets that differentially support antibody secretion. Immunity 2011, 34, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akiyama, M.; Suzuki, K.; Yamaoka, K.; Yasuoka, H.; Takeshita, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Kondo, H.; Kassai, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Morita, R.; et al. Number of circulating follicular helper 2 T cells correlates with IgG4 and interleukin-4 levels and plasmablast numbers in IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2476–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maehara, T.; Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Murphy, S.J.; Yuen, G.J.; Ishiguro, N.; Ohta, M.; Moriyama, M.; Saeki, T.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. The expansion in lymphoid organs of IL-4(+) BATF(+) T follicular helper cells is linked to IgG4 class switching in vivo. Life Sci. Alliance 2018, 1, e201800050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
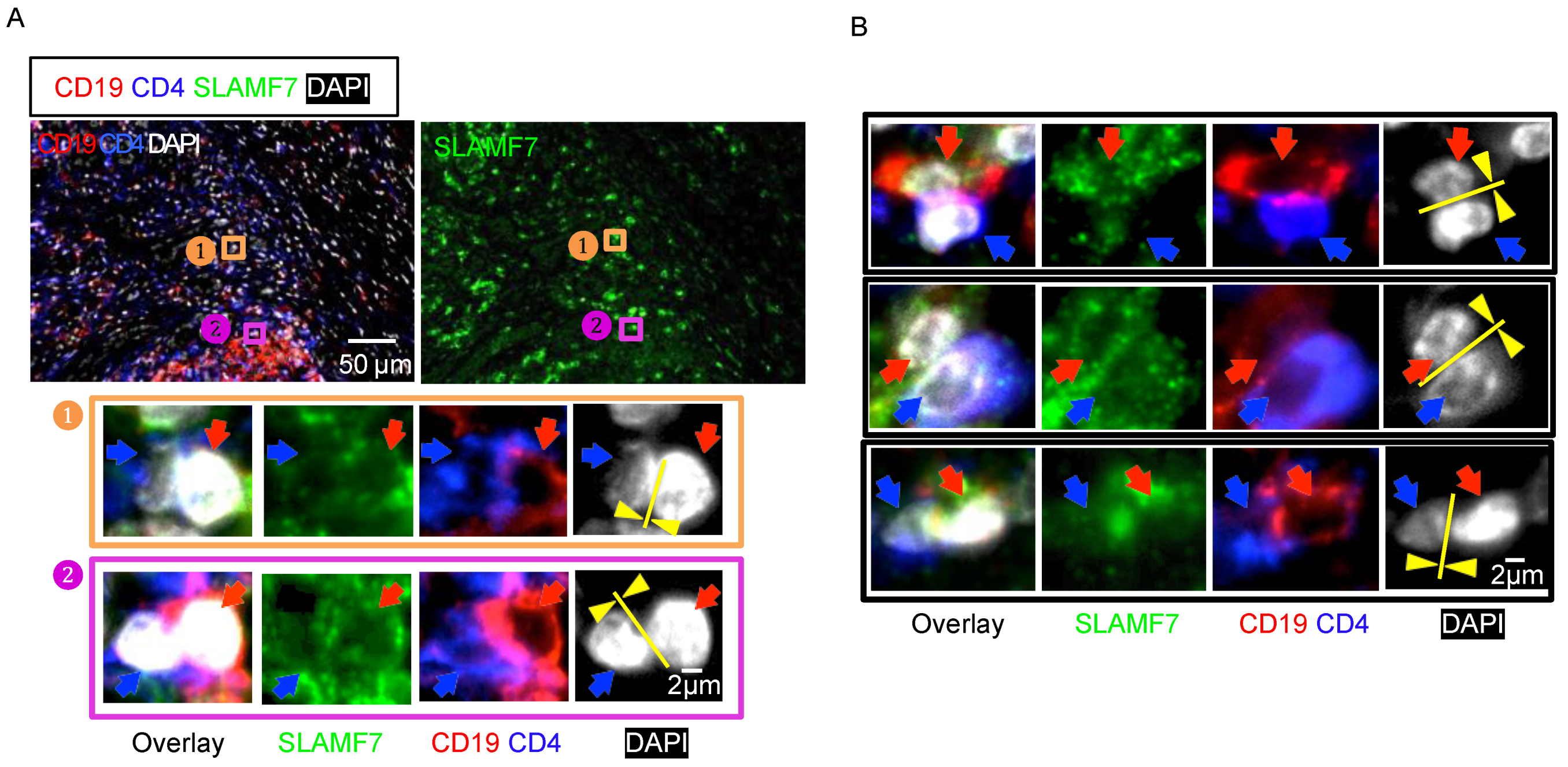
- Higashioka, K.; Ota, Y.; Maehara, T.; Moriyama, M.; Ayano, M.; Mitoma, H.; Akahoshi, M.; Arinobu, Y.; Horiuchi, T.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Association of circulating SLAMF7+Tfh1 cells with IgG4 levels in patients with IgG4-related disease. BMC Immunol. 2020, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, P.T.; Sharpe, A.H. T follicular regulatory cells in the regulation of B cell responses. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, F.; Kamekura, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Takano, K.; Takaki, H.; Yabe, H.; Ikegami, I.; Shigehara, K.; Himi, T.; Takahashi, H.; et al. IL-10(+) T follicular regulatory cells are associated with the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 207, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zen, Y.; Fujii, T.; Harada, K.; Kawano, M.; Yamada, K.; Takahira, M.; Nakanuma, Y. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis and cholangitis. Hepatology 2007, 45, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Moriyama, M.; Nakashima, H.; Miyake, K.; Hayashida, J.N.; Maehara, T.; Shinozaki, S.; Kubo, Y.; Nakamura, S. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions contribute to IgG4 production and the initiation of Mikulicz disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2012, 64, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.; Beutler, C.; Picó, A.H.; Otten, M.; Dürr, A.; Al-Abadi, H.; Guckelberger, O.; Meyer zum Büschenfelde, D.; Jöhrens, K.; Volkmann, M.; et al. Increased T-helper 2 cytokines in bile from patients with IgG4-related cholangitis disrupt the tight junction-associated biliary epithelial cell barrier. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeringa, J.J.; Karim, A.F.; van Laar, J.A.M.; Verdijk, R.M.; Paridaens, D.; van Hagen, P.M.; van Zelm, M.C. Expansion of blood IgG(4)(+) B, T(H)2, and regulatory T cells in patients with IgG(4)-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1831–1843.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattoo, H.; Della-Torre, E.; Mahajan, V.S.; Stone, J.H.; Pillai, S. Circulating Th2 memory cells in IgG4-related disease are restricted to a defined subset of subjects with atopy. Allergy 2014, 69, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Maehara, T.; Deshpande, V.; Della-Torre, E.; Wallace, Z.S.; Kulikova, M.; Drijvers, J.M.; Daccache, J.; Carruthers, M.N.; et al. Clonal expansion of CD4(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maehara, T.; Mattoo, H.; Ohta, M.; Mahajan, V.S.; Moriyama, M.; Yamauchi, M.; Drijvers, J.; Nakamura, S.; Stone, J.H.; Pillai, S.S. Lesional CD4+ IFN-gamma+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Della-Torre, E.; Bozzalla-Cassione, E.; Sciorati, C.; Ruggiero, E.; Lanzillotta, M.; Bonfiglio, S.; Mattoo, H.; Perugino, C.A.; Bozzolo, E.; Rovati, L.; et al. A CD8α-Subset of CD4+SLAMF7+ Cytotoxic T cells is expanded in patients with IgG4-related disease and decreases following glucocorticoid treatment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugino, C.A.; Kaneko, N.; Maehara, T.; Mattoo, H.; Kers, J.; Allard-Chamard, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Liu, H.; Della-Torre, E.; Murphy, S.J.H.; et al. CD4+ and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes may induce mesenchymal cell apoptosis in IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehara, T.; Kaneko, N.; Perugino, C.A.; Mattoo, H.; Kers, J.; Allard-Chamard, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Liu, H.; Murphy, S.J.; Ghebremichael, M.; et al. Cytotoxic CD4+ T lymphocytes may induce endothelial cell apoptosis in systemic sclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2451–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allard-Chamard, H.; Alsufyani, F.; Kaneko, N.; Xing, K.; Perugino, C.; Mahajan, V.S.; Wheat, J.L.; Deepe, G.S., Jr.; Loyd, J.; Pillai, S. CD4(+)CTLs in fibrosing mediastinitis linked to histoplasma capsulatum. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skapenko, A.; Leipe, J.; Lipsky, P.E.; Schulze-Koops, H. The role of the T cell in autoimmune inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7 (Suppl. S2), S4–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sospedra, M.; Martin, R. Immunology of multiple sclerosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 683–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hellings, N.; Raus, J.; Stinissen, P. Insights into the immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Res. 2002, 25, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.O.; Sica, A.; Mantovani, A.; Locati, M. Macrophage activation and polarization. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, X.; Min, S.N.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; Yu, G.Y.; Wu, L.L.; Yang, H.Y. TNF-α suppresses autophagic flux in acinar cells in IgG4-related sialadenitis. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Moriyama, M.; Miyake, K.; Nakashima, H.; Tanaka, A.; Maehara, T.; Iizuka-Koga, M.; Tsuboi, H.; Hayashida, J.N.; Ishiguro, N.; et al. Interleukin-33 produced by M2 macrophages and other immune cells contributes to Th2 immune reaction of IgG4-related disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, N.; Moriyama, M.; Furusho, K.; Furukawa, S.; Shibata, T.; Murakami, Y.; Chinju, A.; Haque, A.; Gion, Y.; Ohta, M.; et al. Activated M2 macrophages contribute to the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease via toll-like receptor 7/interleukin-33 signaling. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovati, L.; Kaneko, N.; Pedica, F.; Monno, A.; Maehara, T.; Perugino, C.; Lanzillotta, M.; Pecetta, S.; Stone, J.H.; Doglioni, C.; et al. Mer tyrosine kinase (MerTK) as a possible link between resolution of inflammation and tissue fibrosis in IgG4-related disease. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 4929–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Moriyama, M.; Maehara, T.; Gion, Y.; Furukawa, S.; Tanaka, A.; Hayashida, J.N.; Yamauchi, M.; Ishiguro, N.; Mikami, Y.; et al. DNA microarray analysis of submandibular glands in IgG4-related disease indicates a role for MARCO and other innate immune-related proteins. Medicine 2016, 95, e2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawakami, T.; Mizushima, I.; Yamada, K.; Fujii, H.; Ito, K.; Yasuno, T.; Izui, S.; Yamagishi, M.; Huard, B.; Kawano, M. Abundant a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL)-producing macrophages contribute to plasma cell accumulation in immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, S.; Moriyama, M.; Tanaka, A.; Maehara, T.; Tsuboi, H.; Iizuka, M.; Hayashida, J.N.; Ohta, M.; Saeki, T.; Notohara, K.; et al. Preferential M2 macrophages contribute to fibrosis in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis, so-called Mikulicz’s disease. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 156, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, I.Y.; Park, C.; Harrison, K.; Kehrl, J.H. TLR4 signaling augments B lymphocyte migration and overcomes the restriction that limits access to germinal center dark zones. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2641–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, T.; Yamashita, K.; Fujikawa, S.; Sakurai, T.; Kudo, M.; Shiokawa, M.; Kodama, Y.; Uchida, K.; Okazaki, K.; Chiba, T. Involvement of activation of toll-like receptors and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors in enhanced IgG4 responses in autoimmune pancreatitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2012, 64, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinju, A.; Moriyama, M.; Kakizoe-Ishiguro, N.; Chen, H.; Miyahara, Y.; Rafiul Haque, A.S.M.; Furusho, K.; Sakamoto, M.; Kai, K.; Kibe, K.; et al. CD163+ M2 macrophages promote fibrosis in IgG4-related disease via TLR7/IRAK4/NF-kB signaling. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Deshpande, V.; Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Kulikova, M.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease: Clinical and laboratory features in one hundred twenty-five patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2466–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Neut Kolfschoten, M.; Schuurman, J.; Losen, M.; Bleeker, W.K.; Martínez-Martínez, P.; Vermeulen, E.; den Bleker, T.H.; Wiegman, L.; Vink, T.; Aarden, L.A.; et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of human IgG4 antibodies by dynamic Fab arm exchange. Science 2007, 317, 1554–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergoossen, D.L.E.; Plomp, J.J.; Gstöttner, C.; Fillié-Grijpma, Y.E.; Augustinus, R.; Verpalen, R.; Wuhrer, M.; Parren, P.; Dominguez-Vega, E.; van der Maarel, S.M.; et al. Functional monovalency amplifies the pathogenicity of anti-MuSK IgG4 in myasthenia gravis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020635118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalberse, R.C.; Stapel, S.O.; Schuurman, J.; Rispens, T. Immunoglobulin G4: An odd antibody. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampert, D.C.; Hubers, L.M.; van de Graaf, S.F.J.; Beuers, U. On the role of IgG4 in inflammatory conditions: Lessons for IgG4-related disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalberse, R.C.; van der Gaag, R.; van Leeuwen, J. Serologic aspects of IgG4 antibodies. I. Prolonged immunization results in an IgG4-restricted response. J. Immunol. 1983, 130, 722–726. [Google Scholar]
- Shiokawa, M.; Kodama, Y.; Kuriyama, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Tomono, T.; Morita, T.; Kakiuchi, N.; Matsumori, T.; Mima, A.; Nishikawa, Y.; et al. Pathogenicity of IgG in patients with IgG4-related disease. Gut 2016, 65, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Yajima, T.; Shimaoka, T.; Ogawa, S.; Saito, T.; Yamaoka, K.; Takeuchi, T.; Kubo, M. Synergistic effect of IgG4 antibody and CTLs causes tissue inflammation in IgG4-related disease. Int. Immunol. 2019, 32, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Shi, L.; Chen, P.; Yang, W.; Xun, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, G. Prohibitin is involved in patients with IgG4 related disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubers, L.M.; Vos, H.; Schuurman, A.R.; Erken, R.; Oude Elferink, R.P.; Burgering, B.; van de Graaf, S.F.J.; Beuers, U. Annexin A11 is targeted by IgG4 and IgG1 autoantibodies in IgG4-related disease. Gut 2018, 67, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiokawa, M.; Kodama, Y.; Sekiguchi, K.; Kuwada, T.; Tomono, T.; Kuriyama, K.; Yamazaki, H.; Morita, T.; Marui, S.; Sogabe, Y.; et al. Laminin 511 is a target antigen in autoimmune pancreatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaaq0997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perugino, C.A.; AlSalem, S.B.; Mattoo, H.; Della-Torre, E.; Mahajan, V.; Ganesh, G.; Allard-Chamard, H.; Wallace, Z.; Montesi, S.B.; Kreuzer, J.; et al. Identification of galectin-3 as an autoantigen in patients with IgG(4)-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 736–745.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarrell, J.A.; Baker, M.C.; Perugino, C.A.; Liu, H.; Bloom, M.S.; Maehara, T.; Wong, H.H.; Lanz, T.V.; Adamska, J.Z.; Kongpachith, S.; et al. Neutralizing anti-IL-1 receptor antagonist autoantibodies induce inflammatory and fibrotic mediators in IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, A.; Yoshifuji, H.; Ito, S.; Kitagori, K.; Kiso, K.; Yamada, N.; Nakajima, T.; Haga, H.; Tsuruyama, T.; Miyagawa-Hayashino, A. High expression of galectin-3 in patients with IgG4-related disease: A proteomic approach. Pathol. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9312142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.C.; Li, J.; Gao, J. Functions of galectin-3 and its role in fibrotic diseases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 351, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, S. T cells in fibrosis and fibrotic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaneko, N.; Moriyama, M.; Maehara, T.; Chen, H.; Miyahara, Y.; Nakamura, S. Orchestration of Immune Cells Contributes to Fibrosis in IgG4-Related Disease. Immuno 2022, 2, 170-184. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2010013
Kaneko N, Moriyama M, Maehara T, Chen H, Miyahara Y, Nakamura S. Orchestration of Immune Cells Contributes to Fibrosis in IgG4-Related Disease. Immuno. 2022; 2(1):170-184. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaneko, Naoki, Masafumi Moriyama, Takashi Maehara, Hu Chen, Yuka Miyahara, and Seiji Nakamura. 2022. "Orchestration of Immune Cells Contributes to Fibrosis in IgG4-Related Disease" Immuno 2, no. 1: 170-184. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2010013
APA StyleKaneko, N., Moriyama, M., Maehara, T., Chen, H., Miyahara, Y., & Nakamura, S. (2022). Orchestration of Immune Cells Contributes to Fibrosis in IgG4-Related Disease. Immuno, 2(1), 170-184. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2010013





