A Randomised Controlled CBT Intervention for Maladaptive Perfectionism: Outcome and Predictors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
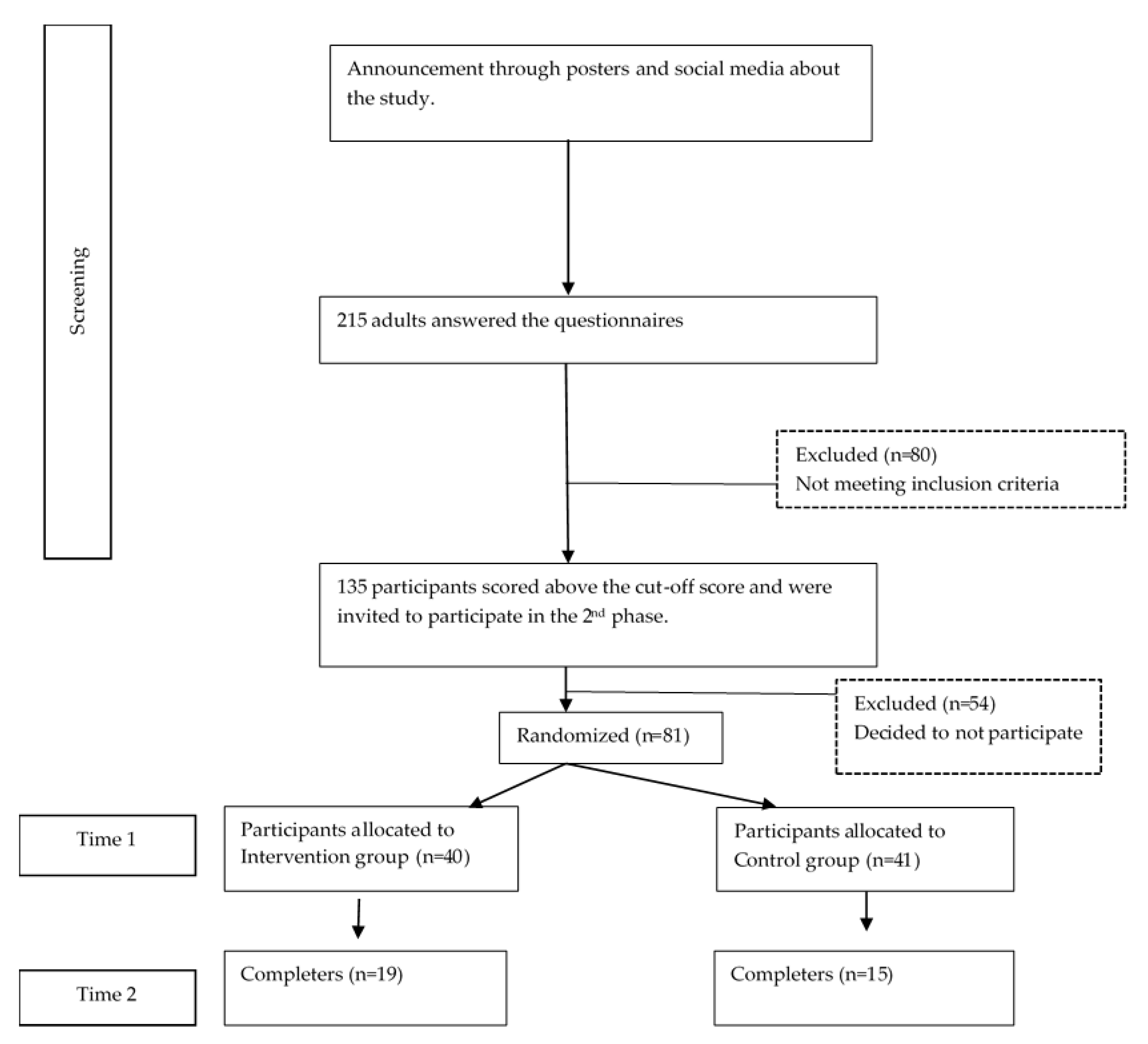
2.3. Procedures
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics in Time 1
3.2. Correlations
3.3. Regression Analysis in Time 1
3.4. Analysis of Intervention Effect
3.5. Regression Analysis in Time 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding

Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frost, R.; Marten, P.; Lahart, C.; Rosenblate, R. The Dimensions of Perfectionism. Cognit. Ther. Res. 1990, 14, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, P.; Flett, G. Perfectionism in the Self and Social Contexts: Conceptualization, Assessment, and Association with Psychopathology. J. Pers. Soc. Behav. Psychol. 1991, 60, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkley, D.; Zuroff, D.; Blankstein, K. Self-Critical Perfectionism and Daily Affect: Dispositional and Situational Influences on Stress and Coping. J. Pers. Soc. Behav. Psychol. 2003, 84, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeber, J.; Otto, K. Positive Conceptions of Perfectionism: Approaches, Evidence, Challenges. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 2006, 10, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, K.; Richardson, C.; Ray, M. Perfectionism in Academic Settings. Perfect. Health Well-Being 2015, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, L.; Miracco, M.; Galarregui, M.; Keegan, E. Perfectionism and Rumination in Depression. Curr. Psychol. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flett, G.L.; Hewitt, P.L.; Oliver, J.M.; Macdonald, S. Perfectionism in Children and Their Parents: A Developmental Analysis. Perfect. Theory Res. Treat. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.C.; Kearney, C.A. Parent Perfectionism and Psychopathology Symptoms and Child Perfectionism. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2014, 70, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, K.L.; Serena Shim, S.; Wang, C. Perfectionistic Concerns Mediate the Relationship between Psychologically Controlling Parenting and Achievement Goal Orientations. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2012, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speirs Neumeister, K.L. Factors Influencing the Development of Perfectionism in Gifted College Students. Gift. Child Q. 2004, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, A.J.; Yates, G.C.R. Maternal Goal Factors in Adaptive and Maladaptive Childhood Perfectionism. Educ. Psychol. 2008, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcardle, S.; Duda, J.L. Exploring the Etiology of Perfectionism and Perceptions of Self-Worth in Young Athletes. Soc. Dev. 2008, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, K.G.; Tucker, C.M.; Desmond, F.F. Perfectionism and Depression among Low-Income Chronically Ill African American and White Adolescents and Their Maternal Parent. J. Clin. Psychol. Med. Settings 2008, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumrind, D. Current Patterns of Parental Authority. Dev. Psychol. 1971, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumrind, D. Rearing Competent Children. In Child Development Today and Tomorrow; The Jossey-Bass Social and Behavioral Science Series; Jossey-Bass/Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1989; pp. 349–378. [Google Scholar]
- Maccoby, E.E.; Martin, J. Socialization in the Context of the Family: Parent-Child Interaction. In Handbook of Child Psychology; Mussen, P.H., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 1–101. [Google Scholar]
- Power, T.G. Parenting Dimensions and Styles: A Brief History and Recommendations for Future Research. Child. Obes. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basirion, Z.; Majid, R.A.; Jelas, Z.M. Big Five Personality Factors, Perceived Parenting Styles, and Perfectionism among Academically Gifted Students. Asian Soc. Sci. 2014, 10, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbard, D.R.; Walton, G.E. Exploring the Development of Perfectionism: The Influence of Parenting Style and Gender. Soc. Behav. Pers. 2014, 42, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.L.; Lambert, A.D.; Neumeister, K.L.S. Parenting Style, Perfectionism, and Creativity in High-Ability and High-Achieving Young Adults. J. Educ. Gift. 2012, 35, 344–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros, L.B.; Iuorno, O.; Serppe, M. Child Perfectionism and Its Relationship with Personality, Excessive Parental Demands, Depressive Symptoms and Experience of Positive Emotions. Span. J. Psychol. 2017, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flett, G.L.; Hewitt, P.L.; Singer, A. Perfectionism and Parental Authority Styles. Individ. Psychol. 1995, 51, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, R.O.; Lahart, C.M.; Rosenblate, R. The Development of Perfectionism: A Study of Daughters and Their Parents. Cognit. Ther. Res. 1991, 15, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, K.G.; Ashby, J.S.; Preusser, K.J. Perfectionism, Relationships with Parents, and Self-Esteem. Individ. Psychol. 1996, 52, 246. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, K.Y.; Frost, R.O.; Harmatz, M.G. The Relationship of Perceived Parenting Styles to Perfectionism. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2002, 32, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.M.; Sherry, S.B.; Gautreau, C.M.; Mushquash, A.R.; Saklofske, D.H.; Snow, S.L. The Intergenerational Transmission of Perfectionism: Fathers’ Other-Oriented Perfectionism and Daughters’ Perceived Psychological Control Uniquely Predict Daughters’ Self-Critical and Personal Standards Perfectionism. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2017, 119, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.; Wade, T.; Shafran, R. Perfectionism as a Transdiagnostic Process: A Clinical Review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2011, 31, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricuțoiu, L.; Măgurean, S.; Tulbure, B. Perfectionism in a Transdiagnostic Context. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2020, 36, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, P.; Flett, G. Perfectionism and Depression: A Multidimensional Analysis. J. Soc. Behav. Pers. 1990, 5, 423–438. [Google Scholar]
- Enns, M.; Cox, B.; Borger, S. Correlates Of Analogue and Clinical Depression: A Further Test of The Phenomenological Continuity Hypothesis. J. Affect. Disord. 2001, 66, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huprich, S.; Porcerelli, J.; Keaschuk, R.; Binienda, J.; Engle, B. Depressive Personality Disorder, Dysthymia, and Their Relationship to Perfectionism. Depress. Anxiety 2008, 25, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Sherry, S.; Ge, S.; Hewitt, P.; Flett, G.; Baggley, D. Multidimensional Perfectionism Turns 30: A Review of Known Knowns and Known Unknowns. Can. Psychol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, A.; Marques, M.; Pereira, A. Perfectionism and Psychological Distress: A Review of the Cognitive Factors. Int. J. Clin. Neurosci. Ment. Health 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Flett, G.; Hewitt, P.; Blankstein, K.; Solnik, M.; Van Brunschot, M. Perfectionism, Social Problem-Solving Ability, and Psychological Distress. J. Ration. Emot. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 1996, 14, 245–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, M.; Purdon, C.; Huta, V.; Richard, P. Swinson. Dimensions of Perfectionism across the Anxiety Disorders. Behav. Res. Ther. 1998, 36, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboonchi, F.; Lundh, L.; Öst, L. Perfectionism and Self-Consciousness in Social Phobia and Panic Disorder with Agoraphobia. Behav. Res. Ther. 1999, 37, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, S.; Battista, S.; Sherry, S.; Stewart, S. Perfectionistic Self-Presentation Predicts Social Anxiety Using Daily Diary Methods. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2014, 56, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepon, T.; Flett, G.; Hewitt, P.; Molnar, D. Perfectionism, Negative Social Feedback, and Interpersonal Rumination in Depression and Social Anxiety. Can. J. Behav. Sci. 2011, 43, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iketani, T.; Kiriike, N.; Stein, M.; Nagao, K.; Nagata, T.; Minamikawa, N.; Shidao, A.; Fukuhara, H. Relationship Between Perfectionism, Personality Disorders And Agoraphobia In Patients With Panic Disorder. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2002, 106, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handley, A.; Egan, S.; Kane, R.; Rees, C. The Relationships between Perfectionism, Pathological Worry and Generalised Anxiety Disorder. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flett, G.; Endler, N.; Tassone, C.; Hewitt, P. Perfectionism and Components of State and Trait Anxiety. Curr. Psychol. 1994, 13, 326–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.; Steketee, G. Perfectionism in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Patients. Behav. Res. Ther. 1997, 35, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obsessive Compulsive Cognitions Working Group. Psychometric Validation Of The Obsessive Belief Questionnaire And Interpretation Of Intrusions Inventory—Part 2: Factor Analyses and Testing Of A Brief Version. Behav. Res. Ther. 2005, 43, 1527–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melli, G.; Bulli, F.; Doron, G.; Carraresi, C. Maladaptive Beliefs in Relationship Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (ROCD): Replication and Extension in a Clinical Sample. J. Obs. Compuls. Relat. Disord. 2018, 18, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershuny, B.; Sher, K. Compulsive Checking and Anxiety in a Nonclinical Sample: Differences in Cognition, Behavior, Personality, and Affect. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 1995, 17, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallis, F. Compulsive Washing In the Absence of Phobic and Illness Anxiety. Behav. Res. Ther. 1996, 34, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.; Gross, R. The Hoarding of Possessions. Behav. Res. Ther. 1993, 31, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankstein, K.; Flett, G.; Hewitt, P.; Eng, A. Dimensions of Perfectionism and Irrational Fears: An Examination with the Fear Survey Schedule. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1993, 15, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieling, P.; Israeli, A.; Antony, M. Is Perfectionism Good, Bad, or Both? Examining Models Of The Perfectionism Construct. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2004, 36, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafran, R.; Cooper, Z.; Fairburn, C. Clinical Perfectionism: A Cognitive–Behavioural Analysis. Behav. Res. Ther. 2002, 40, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, M.; Bakhtiyari, M.; Masjedi Arani, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Saberi Isfeedvajani, M. The Comparison Between CBT Focused On Perfectionism And CBT Focused On Emotion Regulation For Individuals With Depression Anxiety Disorders And Dysfunctional Perfectionism: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, M.; Carlbring, P.; Andersson, G.; Berg, M.; Shafran, R.; Rozental, A. Internet-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy of Perfectionism: Comparing Regular Therapist Support And Support Upon Request. Internet Interv. 2019, 17, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, A.; Waite, S.; Egan, S.; Finnigan, J.; Handley, A.; Wade, T. Psycho-Education and Group Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy for Clinical Perfectionism: A Case-Series Evaluation. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2012, 41, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafran, R.; Egan, S.; Wade, T. Overcoming Perfectionism: A Self-Help Manual Using Cognitive-Behavioural Techniques; Robinson: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, D.; Brown, G.; Fairburn, C.; Shafran, R. A Preliminary Evaluation of Cognitive-Behaviour Therapy for Clinical Perfectionism: A Case Series. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 2007, 46, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, C.; Lee, M.; Cooper, Z.; Fairburn, C.; Shafran, R. A Randomised Controlled Trial of Cognitive-Behaviour Therapy for Clinical Perfectionism: A Preliminary Study. Behav. Res. Ther. 2007, 45, 2221–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lloyd, S.; Schmidt, U.; Khondoker, M.; Tchanturia, K. Can Psychological Interventions Reduce Perfectionism? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2014, 43, 705–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana, F.; Miracco, M.; Galarregui, M.; Keegan, E. A Brief Cognitive Behavioural Intervention for Maladaptive Perfectionism In Students: A Pilot Study. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2017, 45, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, J. The Frost Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale Revisited: More Perfect With Four (Instead Of Six) Dimensions. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1998, 24, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, B.; Pallant, J.; Harvey, D. An Evaluation of the Factor Structure of the Frost Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2004, 64, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, A.; Soares, M.; Pereira, A.; Bos, S.; Marques, M.; Valente, J.; Nogueira, V.; Azevedo, M.; Macedo, A. Frost Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale: The Portuguese Version. Arch. Clin. Psychiatry (São Paulo) 2013, 40, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pannhausen, S.; Klug, K.; Rohrmann, S. Never Good Enough: The Relation between the Impostor Phenomenon and Multidimensional Perfectionism. Curr. Psychol. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdon, C.; Antony, M.; Swinson, R. Psychometric Properties of the Frost Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale in a Clinical Anxiety Disorders Sample. J. Clin. Psychol. 1999, 55, 1271–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovibond, P.; Lovibond, S. The Structure of Negative Emotional States: Comparison of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression Anxiety Inventories. Behav. Res. Ther. 1995, 33, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, M.; Bieling, P.; Cox, B.; Enns, M.; Swinson, R. Psychometric Properties of the 42-Item and 21-Item Versions of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales in Clinical Groups and a Community Sample. Psychol. Assess. 1998, 10, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyrakos, G.; Arvaniti, C.; Smyrnioti, M.; Kostopanagiotou, G. Translation and Validation Study of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale in the Greek General Population and in a Psychiatric Patient’s Sample. Eur. Psychiatry 2011, 26, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, C. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory for Adults. PsycTESTS Dataset 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulakis, K.; Papadopoulou, M.; Kleanthous, S.; Papadopoulou, A.; Bizeli, V.; Nimatoudis, I.; Iacovides, A.; Kaprinis, G. Reliability and psychometric properties of the Greek translation of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory form Y: Preliminary data. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, G.; Roussos, J.; Hadzi-Pavlovic, D.; Mitchell, P.; Wilhelm, K.; Austin, M. The Development of a Refined Measure of Dysfunctional Parenting And Assessment Of Its Relevance In Patients With Affective Disorders. Psychol. Med. 1997, 27, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozental, A.; Shafran, R.; Wade, T.; Egan, S.; Nordgren, L.; Carlbring, P.; Landström, A.; Roos, S.; Skoglund, M.; Thelander, E.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Internet-Based Cognitive Behavior Therapy For Perfectionism Including An Investigation Of Outcome Predictors. Behav. Res. Ther. 2017, 95, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafran, R.; Wade, T.; Egan, S.; Kothari, R.; Allcott-Watson, H.; Carlbring, P.; Rozental, A.; Andersson, G. Is The Devil In The Detail? A Randomised Controlled Trial of Guided Internet-Based CBT for Perfectionism. Behav. Res. Ther. 2017, 95, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberschatz, G.; Aafjes-van Doorn, K. Pathogenic Beliefs Mediate the Relationship between Perceived Negative Parenting and Psychopathology Symptoms. J. Aggress. Maltreatment Trauma 2017, 26, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craddock, A.E.; Church, W.; Sands, A. Family of Origin Characteristics as Predictors of Perfectionism. Aust. J. Psychol. 2009, 61, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeister, K.L.S.; Finch, H. Perfectionism in High-Ability Students: Relational Precursors and Influences on Achievement Motivation. Gift. Child Q. 2006, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Sherry, S.; Ray, C.; Hewitt, P.; Flett, G. Is Perfectionism a Vulnerability Factor for Depressive Symptoms, a Complication of Depressive Symptoms, or Both? A Meta-Analytic Test of 67 Longitudinal Studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 84, 101982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damian, L.; Stoeber, J.; Negru, O.; Băban, A. On the Development of Perfectionism in Adolescence: Perceived Parental Expectations Predict Longitudinal Increases in Socially Prescribed Perfectionism. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2013, 55, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.; Shafran, R.; Lee, M.; Fairburn, C.; Cooper, Z.; Doll, H.; Palmer, R.; Watson, H. The Reliability and Validity of the Clinical Perfectionism Questionnaire in Eating Disorder and Community Samples. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2015, 44, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotardi, V.; Dubien, D. Perfectionism, Wellbeing, and University Performance: A Sample Validation of the Frost Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale (FMPS) in New Zealand. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2019, 143, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| M | SD | |
|---|---|---|
| FMPS—Total | 96.83 | 11.79 |
| DASS—Anxiety | 6.42 | 4.55 |
| DASS—Stress | 11.42 | 4.94 |
| DASS—Depression | 9.11 | 6.22 |
| STAI—State | 54.03 | 9.55 |
| STAI—Trait | 53.76 | 8.53 |
| MOPS—Father Indifference | 12.89 | 8.88 |
| MOPS—Father Abuse | 10.80 | 7.81 |
| MOPS—Father Overcontrol | 8.25 | 4.54 |
| MOPS—Mother Indifference | 12.69 | 10.59 |
| MOPS—Mother Abuse | 10.71 | 7.76 |
| MOPS—Mother Overcontrol | 7.34 | 3.79 |
| FMPS Total | FMPS CM | FMPS PS | FMPS PE | FMPS PC | FMPS D | FMPS O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DASS—Anxiety | 0.459 ** | 0.384 ** | 0.246 * | 0.159 | 0.183 | 0.335 ** | −0.030 |
| DASS—Stress | 0.475 ** | 0.384 ** | 0.258 * | 0.155 | 0.210 | 0.361 ** | −0.055 |
| DASS—Depression | 0.482 ** | 0.394 ** | 0.101 | 0.167 | 0.284 * | 0.455 ** | −0.155 |
| STAI—State | 0.331 ** | 0.343 ** | 0.148 | 0.046 | 0.076 | 0.301 ** | −0.134 |
| STAI—Trait | 0.477 ** | 0.447 ** | 0.211 | 0.046 | 0.128 | 0.538 ** | −0.119 |
| MOPS—Father Indifference | 0.493 ** | 0.546 ** | 0.194 | 0.215 | 0.152 | 0.168 | 0.095 |
| MOPS—Father Abuse | 0.391 ** | 0.448 ** | 0.133 | 0.110 | 0.173 | 0.155 | 0.098 |
| MOPS—Father Overcontrol | 0.279 * | 0.329 ** | 0.106 | 0.030 | 0.087 | 0.188 | 0.040 |
| MOPS—Mother Indifference | 0.398 ** | 0.452 ** | 0.142 | 0.107 | 0.163 | 0.180 | 0.177 |
| MOPS—Mother Abuse | 0.441 ** | 0.520 ** | 0.184 | 0.122 | 0.153 | 0.154 | 0.102 |
| MOPS—Mother Overcontrol | 0.345 ** | 0.475 ** | 0.098 | 0.012 | 0.058 | 0.224 | 0.045 |
| Time 1 | Time 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IG (n = 19) | CG (n = 15) | IG (n =19) | CG (n = 15) | F | p | η2 | Cohen’s d [95% CI] | |
| FMPS—Total | 94.00 (13.15) | 80.11 (16.86) | 89.33 (12.66) | 83.87 (6.98) | 4.64 | 0.04 | 0.12 | −0.92 [−1.86, 0.27] |
| FMPS—Concerns over Mistakes | 28 (4.89) | 21 (7.08) | 25.27 (4.80) | 24.47 (4.67) | 10.14 | 0.00 | 0.24 | −1.15 [−2.12, −0.18] |
| FMPS—Personal Standards | 27 (4.19) | 24 (3.57) | 26.07 (3.51) | 24 (2.85) | 0.71 | 0.41 | 0.02 | −0.77 [−1.70, 0.161] |
| FMPS—Parental Expectations | 14.79 (5.05) | 13.68 (5.93) | 15.53 (4.19) | 14.67 (3.15) | 0.04 | 0.83 | 0.00 | −0.20 [−1.10,−0.7] |
| FMPS—Parental Criticism | 10.11 (3.65) | 9.26 (3.75) | 9.67 (2.89) | 8.67 (1.67) | 0.04 | 0.83 | 0.00 | −0.23 [−1.25, 0.79] |
| FMPS—Doubts about action | 14.1 (3.15) | 12.15 (3.18) | 12.8 (3.18) | 12.07 (3.69) | 1.11 | 0.30 | 0.03 | −0.62 [−1.65, 0.42] |
| FMPS—Organisation | 23.15 (3.25) | 21.84 (3.67) | 25.07 (2.25) | 23.93 (3.57) | 0.023 | 0.88 | 0.00 | −0.38 [−1.40, 0.64] |
| DASS—Depression | 8.26 (5.59) | 5.74 (4.55) | 5.33 (5.57) | 6.87 (6.16) | 8.94 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.49 [−1.41, 0.42] |
| DASS—Anxiety | 6.00 (4.47) | 3.79 (3.81) | 4.33 (4.75) | 5.27 (5.34) | 4.65 | 0.04 | 0.13 | −0.53 [−1.45, 0.38] |
| DASS—Stress | 12.05 (4.55) | 8.47 (4.58) | 8.47 (5.46) | 7.87 (4.84) | 4.82 | 0.04 | 0.13 | −0.77 [−1.71, 0.16] |
| STAI—State | 51.84 (8.91) | 48.05 (11.69) | 50.33 (8.59) | 46.87 (10.12) | 0.00 | 0.93 | 0.00 | −0.37 [−1.27, 0.54] |
| STAI—Trait | 54.16 (7.50) | 49.05 (9.17) | 49.93 (9.89) | 48.07 (7.14) | 2.18 | 0.15 | 0.06 | −0.61 [−1.53, 0.31] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zikopoulou, O.; Nisyraiou, A.; Simos, G. A Randomised Controlled CBT Intervention for Maladaptive Perfectionism: Outcome and Predictors. Psychiatry Int. 2021, 2, 287-299. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint2030022
Zikopoulou O, Nisyraiou A, Simos G. A Randomised Controlled CBT Intervention for Maladaptive Perfectionism: Outcome and Predictors. Psychiatry International. 2021; 2(3):287-299. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint2030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleZikopoulou, Olga, Anna Nisyraiou, and Gregoris Simos. 2021. "A Randomised Controlled CBT Intervention for Maladaptive Perfectionism: Outcome and Predictors" Psychiatry International 2, no. 3: 287-299. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint2030022
APA StyleZikopoulou, O., Nisyraiou, A., & Simos, G. (2021). A Randomised Controlled CBT Intervention for Maladaptive Perfectionism: Outcome and Predictors. Psychiatry International, 2(3), 287-299. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint2030022






