Is Bronchiectasis (BE) Properly Investigated in Patients with Severe Asthma? A Real-Life Report from Eight Italian Centers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
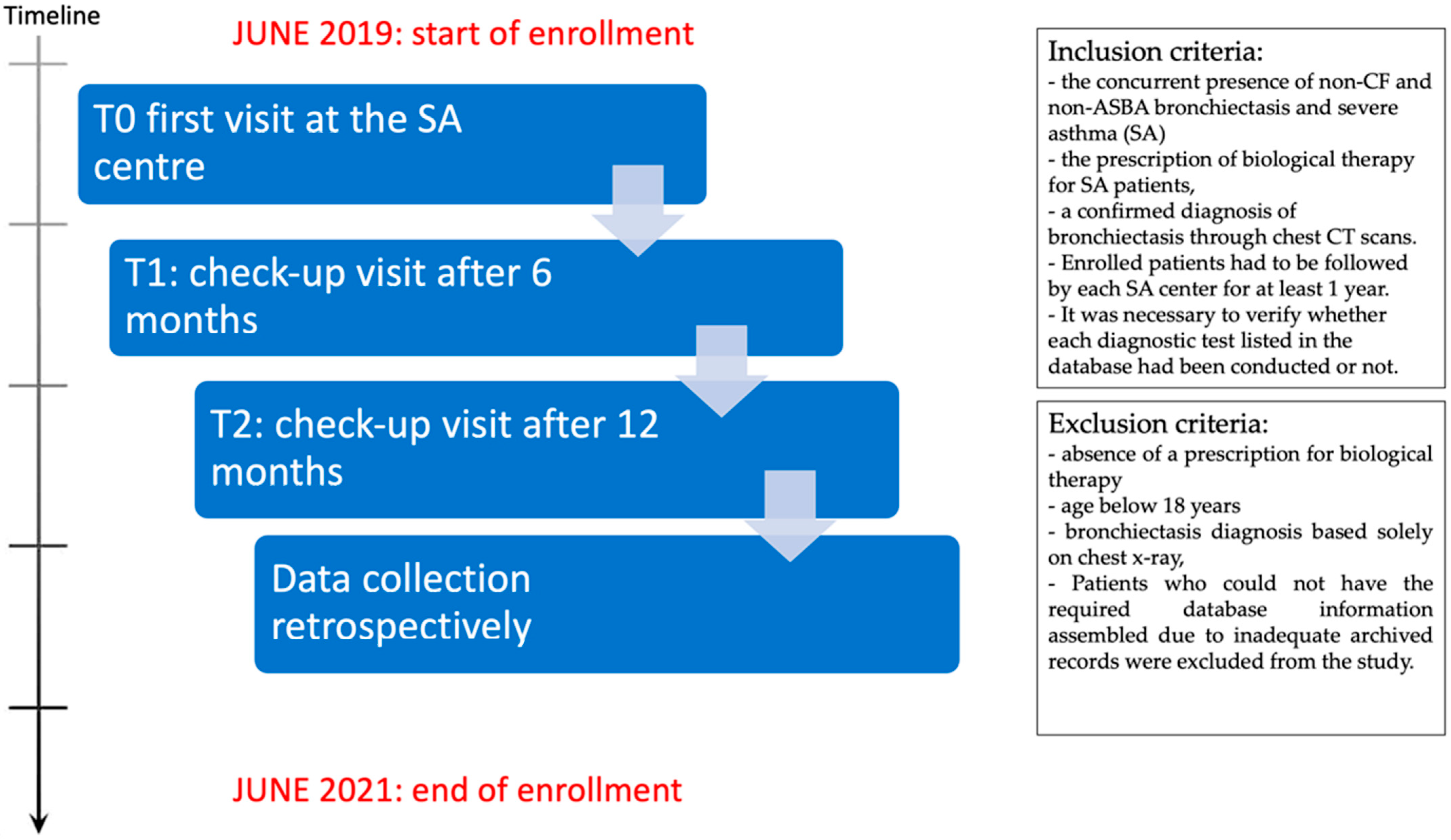
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
Methods
| Clinical Features | |
|---|---|
| Age (n = 92) | 58.8 ± 12.1 |
| Female | 51.9% |
| Former smoker | 22.2% |
| Current smoker | 7.4% |
| Family History of Asthma | 75% |
| Atopy | 69.1% |
| Bilateral Bronchiectasis | 79.5% |
| Chronic bronchial Infection by P. Aeruginosa | 2.4% |
| NMT colonization | 0.0% |
| TBC | 0.0% |
| Comorbidities (88.9% of all patients) | |
| Rhinitis | 63.1% |
| Nasal polyposis | 61.7% |
| Rhinosinusitis | 50.0% |
| GERD | 42.0% |
| Autoimmune disease | 14.6% |
| ASA intolerance | 12.2% |
| Vasculitis | 9.8% |
| Urticaria | 9.8% |
| OSAS | 7.3% |
| Dermatitis | 7.3% |
| Infertility | 0.0% |
| Main Diagnostic Evaluations | |
| ACT (n = 83) | 14.21 ± 4.93 |
| BSI (n = 34) | 5.64 ± 3.90 |
| % FEV1 (n = 92) | 64.66 ± 21.60 |
| % FVC (n = 92) | 82.35 ± 15.55 |
| FeNO 50 (n = 33) | 70.15 ± 72.84 |
| IgE (n = 75) | 672.53 ± 235.67 |
| Blood Eosinophilia (n = 58) | 858.43 ± 640.00 |
| Home Therapy | |
| ICS-LABA | 100% |
| LAMA | 72.5% |
| OCS | 69.1% |
| Moderate dose ICS | 56.6% |
| High dose ICS | 43.4% |
| Anti-LTRA | 33.8% |
| Mucolytics | 26.8% |
| Number of antibiotic cycles/year | 2.87 ± 2.00 |
| Omalizumab | 32.1% |
| Mepolizumab | 38.3% |
| Benralizumab | 29.6% |
| LUNG FUNCTION TESTS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | |
| Spirometry% | 100.0 | 64.2 | 43.0 |
| Bronchodilator Reversibility Testing% | 64.3 | 17.1 | 0.0 |
| TLC% | 16.7 | 21.0 | 0.0 |
| DLCO% | 16.0 | 13.6 | 8.9 |
| RADIOLOGY | |||
| Chest X-ray% | 28.4 | 7.4 | 11.1 |
| Chest CT scan% | 100.0 | 4.9 | 3.7 |
| MICROBIOLOGY | |||
| Sputum culture, % | 29.6 | 3.7 | 3.7 |
| BAL culture, % | 11.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| LABORATORY DIAGNOSTICS | |||
| Blood Count% | 63.0 | 27.2 | 27.2 |
| Blood eosinophilia% | 63.0 | 27.2 | 27.2 |
| Sputum eosinophilia% | 2.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Total S-IgE% | 81.5 | 16.0 | 12.3 |
| Nasal cytology% | 28.4 | 0.0 | 2.5 |
| ESR% | 8.6 | 8.6 | 0.0 |
| CRP% | 50.6 | 11.1 | 0.0 |
| ANA, ANCA% | 20.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| FRACTIONAL EXHALED NITRIC OXIDE (FeNO) TEST | |||
| FeNO50% | 35.8 | 39.5 | 39.5 |
| FeNO350% | 8.6 | 16.0 | 9.9 |
| OTHER DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS | |||
| A1AT genotyping% | 17.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Ciliary motility test% | 2.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| QUESTIONNAIRES | |||
| ACT% | 90.1 | 67.9 | 61.7 |
| ACQ% | 28.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| AQLQ% | 21.0 | 19.8 | 25.9 |
| Compliance to therapy% | 96.3 | 97.6 | 82.5 |
| BSI% | 37.0 | 11.0 | 8.6 |
| FACED score% | 9.9 | 0.0 | 7.4 |
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results


4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crimi, C.; Ferri, S.; Crimi, N. Bronchiectasis and asthma: A dangerous liaison? Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 19, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Hong, Y.K.; Kim, C.W.; Choe, K.O.; Hong, C.S. High-resolution computed tomography in patients with bronchial asthma: Correlation with clinical features, pulmonary functions and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 1997, 7, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paganin, F.; Seneterre, E.; Chanez, P.; Daurés, J.P.; Bruel, J.M.; Michel, F.B.; Bousquet, J. Computed tomography of the lungs in asthma: Influence of disease severity and etiology. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimakou, K.; Gousiou, A.; Toumbis, M.; Kaponi, M.; Chrysikos, S.; Thanos, L.; Triantafillidou, C. Investigation of bronchiectasis in severe uncontrolled asthma. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverino, E.; Goeminne, P.C.; McDonnell, M.J.; Aliberti, S.; Marshall, S.E.; Loebinger, M.R.; Murris, M.; Cantón, R.; Torres, A.; Dimakou, K.; et al. European Respiratory Society guidelines for the management of adult bronchiectasis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsbjerg, C.; Menzies-Gow, A. Comorbidities in severe asthma: Clinical impact and management. Respirology 2017, 22, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malipiero, G.; Paoletti, G.; Blasi, F.; Paggiaro, P.; Senna, G.; Latorre, M.; Caminati, M.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Crimi, N.; Spanevello, A.; et al. Clinical features associated with a doctor-diagnosis of bronchiectasis in the Severe Asthma Network in Italy (SANI) registry. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021, 15, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luján, M.; Gallardo, X.; Amengual, M.J.; Bosque, M.; Mirapeix, R.M.; Domingo, C. Prevalence of bronchiectasis in asthma according to oral steroid requirement: Influence of immunoglobulin levels. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 109219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendien, S.A.; van Loon-Kooij, S.; Kramer, G.; Huijgen, W.; Altenburg, J.; Ten Brinke, A.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H. Bronchiectasis in Severe Asthma: Does It Make a Difference? Respiration 2021, 99, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Kay, S.; Pike, J.; Williams, A.; Rosenzweig, J.R.C.; Hillyer, E.V.; Price, D. The Asthma Control Test (ACT) as a predictor of GINA guideline-defined asthma control: Analysis of a multinational cross-sectional survey. Prim. Care Respir. J. 2009, 18, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juniper, E.F.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Guyatt, G.H.; Ferrie, P.J.; King, D.R. Development and validation of a questionnaire to measure asthma control. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 14, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juniper, E.F.; Guyatt, G.H.; Epstein, R.S.; Ferrie, P.J.; Jaeschke, R.; Hiller, T.K. Evaluation of impairment of health related quality of life in asthma: Development of a questionnaire for use in clinical trials. Thorax 1992, 47, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza, V.; Fernández-Rodríguez, C.; Melero, C.; Cosío, B.G.; Entrenas, L.M.; de Llano, L.P.; Gutiérrez-Pereyra, F.; Tarragona, E.; Palomino, R.; López-Viña, A.; et al. Validation of the ‘Test of the Adherence to Inhalers’ (TAI) for Asthma and COPD Patients. J. Aerosol. Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2016, 29, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, J.D.; Goeminne, P.; Aliberti, S.; McDonnell, M.J.; Lonni, S.; Davidson, J.; Poppelwell, L.; Salih, W.; Pesci, A.; Dupont, L.J.; et al. The bronchiectasis severity index. An international derivation and validation study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martınez, M.; Gracia, J.; Vendrell, M.; Giron, R.; Maiz, L.; Carrillo, D.; Olveira, C. Multidimensional approach to BQNFQ the FACED score. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- “Diagnosis and Management of Difficult-to-Treat and Severe Asthma”, Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention 2019. Available online: http://www.ginasthma.org.GINA2019 (accessed on 27 June 2019).
- Israel, E.; Reddel, H.K. Severe and difficult-to-treat asthma in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, C.; Jin, K.; Cho, S.; Kang, H. Severe asthma phenotypes classified by site of airway involvement and remodeling via chest CT scan. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 28, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisaccioni, C.; Aun, M.V.; Cajuela, E.; Kalil, J.; Agondi, R.C.; Giavina-Bianchi, P. Comorbidities in severe asthma: Frequency of rhinitis, nasal polyposis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, vocal cord dysfunction and bronchiectasis. Clinics 2009, 64, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Siddiqui, S.; Haldar, P.; Raj, J.V.; Entwisle, J.J.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Bradding, P.; Pavord, I.D.; Green, R.H.; Brightling, C.E. Qualitative analysis of high-resolution CT scans in severe asthma. Chest 2009, 136, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, I.; Pola-Bibian, B.; Barranco, P.; Vila-Nadal, G.; Dominguez-Ortega, J.; Romero, D.; Villasante, C.; Quirce, S. Bronchiectasis in severe asthma: Clinical features and outcomes. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 120, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyton, R.J.; Reynolds, C.J.; Quigley, K.J.; Altmann, D.M. Immune mechanisms and the impact of the disrupted lung microbiome in chronic bacterial lung infection and bronchiectasis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 171, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H. Bronchiectasis in severe asthma and asthmatic components in bronchiectasis. Respir. Investig. 2022, 60, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Thomas, C.M.; Chana, K.K.; Gibeon, D.; Barnes, P.J.; Chung, K.F.; Bhavsar, P.K.; Donnelly, L.E. Impaired macrophage phagocytosis of bacteria in severe asthma. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Illing, R.; Hui, C.K.; Downey, K.; Carr, D.; Stearn, M.; Alshafi, K.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Zhong, N.; Chung, K.F. Bacteria in sputum of stable severe asthma and increased airway wall thickness. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Galo, A.; Olveira, C.; Fernández de Rota-Garcia, L.; Marco-Galve, I.; Plata, A.J.; Alvarez, A.; Rivas-Ruiz, F.; Carmona-Olveira, A.; Cebrian-Gallardo, J.J.; Martinez-Garcia, M.A. Factors associated with bronchiectasis in patients with uncontrolled asthma; the NOPES score: A study in 398 patients. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, M.J.; Jary, H.R.; Perry, A.; MacFarlane, J.G.; Hester, K.L.; Small, T.; Molyneux, C.; Perry, J.D.; Walton, K.E.; De Soyza, A. Non cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis: A longitudinal retrospective observational cohort study of Pseudomonas persistence and resistance. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loebinger, M.R.; Wells, A.U.; Hansell, D.M.; Chinyanganya, N.; Devaraj, A.; Meister, M.; Wilson, R. Mortality in bronchiectasis: A long-term study assessing the factors influencing survival. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upham, J.W.; Le Lievre, C.; Jackson, D.J.; Masoli, M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Price, D.B.; Panel, D. Defining a severe asthma super-responder: Findings from a Delphi process. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 3997–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, J.E.; D’ancona, G.; Elstad, M.; Green, L.; Fernandes, M.; Thomson, L.; Roxas, C.; Dhariwal, J.; Nanzer, A.M.; Kent, B.D.; et al. Real-world effectiveness and the characteristics of a “super-responder” to mepolizumab in severe eosinophilic asthma. Chest 2020, 158, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.S.; Langton, D.; Katelaris, C.; Stevens, S.; Farah, C.S.; Gillman, A.; Harrington, J.; Hew, M.; Kritikos, V.; Radhakrishna, N.; et al. Mepolizumab effectiveness and identification of super-responders in severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1902420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupani, H.; Hew, M. Super-Responders to Severe Asthma Treatments: Defining a New Paradigm. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 4005–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-García, M.Á.; Méndez, R.; Olveira, C.; Girón, R.; García-Clemente, M.; Máiz, L.; Sibila, O.; Golpe, R.; Rodríguez-Hermosa, J.L.; Barreiro, E.; et al. The U-Shaped Relationship Between Eosinophil Count and Bronchiectasis Severity: The Effect of Inhaled Corticosteroids. Chest 2023, 164, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keir, H.R.; Shoemark, A.; Dicker, A.J.; Perea, L.; Pollock, J.; Giam, Y.H.; Suarez-Cuartin, G.; Crichton, M.L.; Lonergan, M.; Oriano, M.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps, disease severity, and antibiotic response in bronchiectasis: An international, observational, multicohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanduzzi, A.; Ciasullo, E.; Capitelli, L.; Sanduzzi Zamparelli, S.; Bocchino, M. Alpha-1-Antitrypsin Deficiency and Bronchiectasis: A Concomitance or a Real Association? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carpagnano, G.E.; Quaranta, V.N.; Crimi, C.; Santus, P.; Menzella, F.; Pelaia, C.; Scioscia, G.; Caruso, C.; Bargagli, E.; Scichilone, N.; et al. Is Bronchiectasis (BE) Properly Investigated in Patients with Severe Asthma? A Real-Life Report from Eight Italian Centers. J. Respir. 2023, 3, 178-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor3040017
Carpagnano GE, Quaranta VN, Crimi C, Santus P, Menzella F, Pelaia C, Scioscia G, Caruso C, Bargagli E, Scichilone N, et al. Is Bronchiectasis (BE) Properly Investigated in Patients with Severe Asthma? A Real-Life Report from Eight Italian Centers. Journal of Respiration. 2023; 3(4):178-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor3040017
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarpagnano, Giovanna Elisiana, Vitaliano Nicola Quaranta, Claudia Crimi, Pierachille Santus, Francesco Menzella, Corrado Pelaia, Giulia Scioscia, Cristiano Caruso, Elena Bargagli, Nicola Scichilone, and et al. 2023. "Is Bronchiectasis (BE) Properly Investigated in Patients with Severe Asthma? A Real-Life Report from Eight Italian Centers" Journal of Respiration 3, no. 4: 178-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor3040017
APA StyleCarpagnano, G. E., Quaranta, V. N., Crimi, C., Santus, P., Menzella, F., Pelaia, C., Scioscia, G., Caruso, C., Bargagli, E., Scichilone, N., & Polverino, E. (2023). Is Bronchiectasis (BE) Properly Investigated in Patients with Severe Asthma? A Real-Life Report from Eight Italian Centers. Journal of Respiration, 3(4), 178-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor3040017












