The Multifaceted Profile of Thyroid Disease in the Background of DICER1 Germline and Somatic Mutations: Then, Now and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Syndromic and Non-Syndromic DICER1 Alterations and Mutations in Relation to Thyroid Manifestations
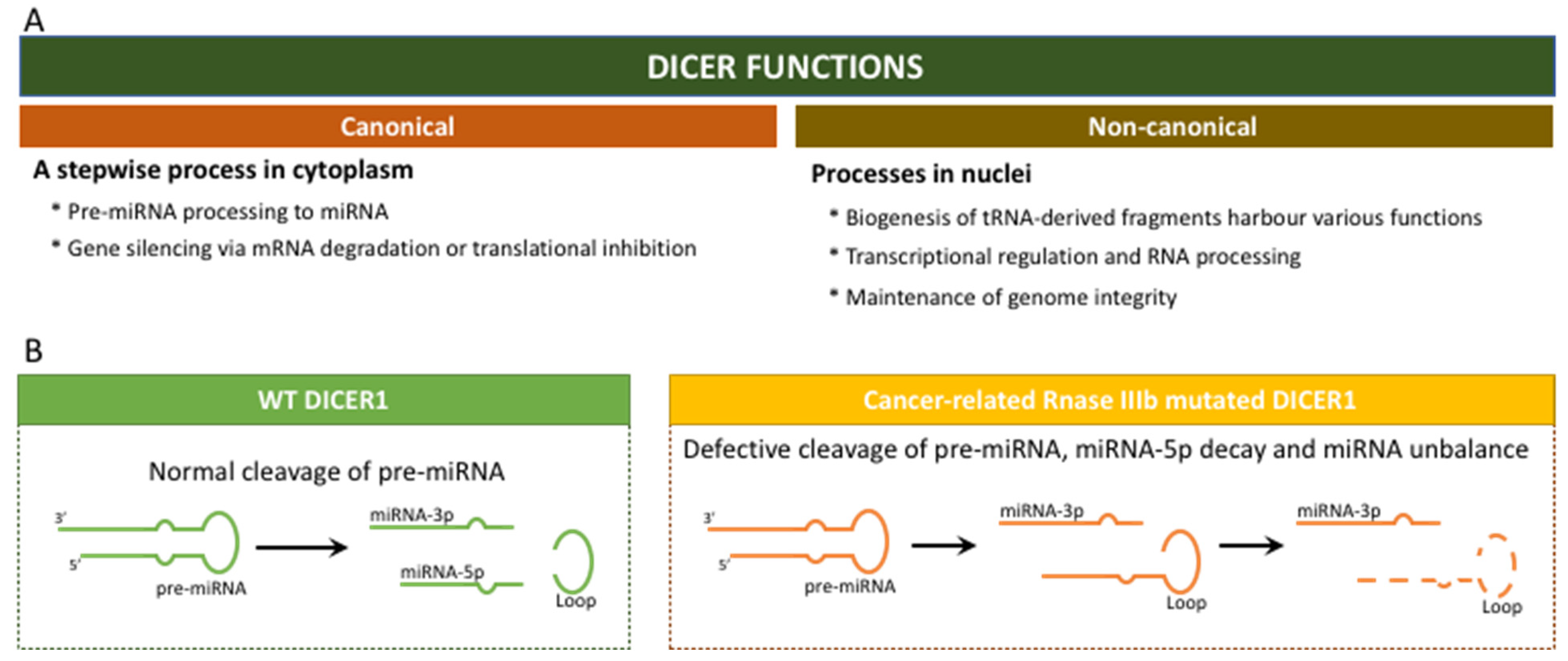
2.1. “The Gene DICER1” and the “Enzyme DICER”
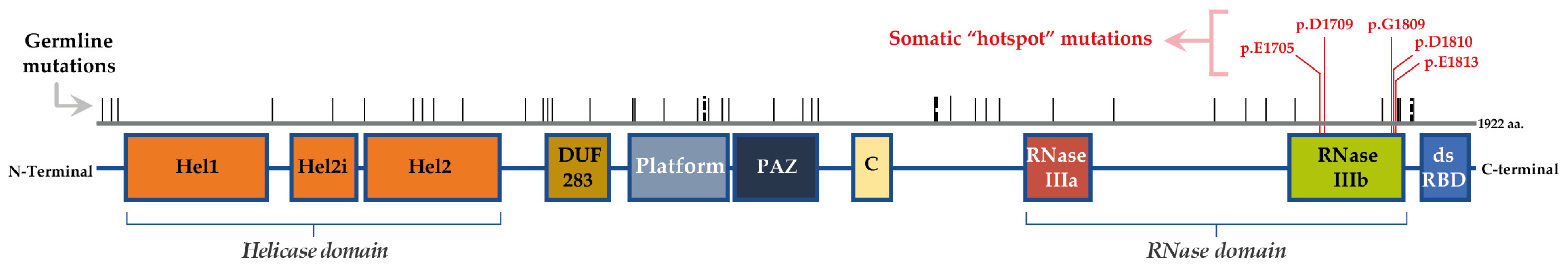
2.2. Mutations/Alterations of DICER1
2.3. Thyroid Neoplasm in the Context of DICER1 Syndromic and Non-Syndromic Mutations
| Thyroid Lesion(s) | Age (yo) | Other Known Lesions (age) | Germline Mutations | Somatic Mutations (Thyroid Lesions) | Ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA Mutation(s) | Protein Alteration(s) | DNA Mutation(s) | Protein Alteration(s) | ||||
| Invasive FVPTC | 9 | PPB type II (1.9; 4.3); MNG (7) | c.3505dupT * mother carrier | p.S1169F,fs*8 | c.5439G>T | p.E1813D | [30] |
| FVPTC | 7 | PPB type I (1.3); cataracts (6), CBME (6.1) | c.3579_3580delCA | p.N1193K,fs*41 | c.5438A>G | p.E1813G | |
| Bilateral PTC within an FA | 11.5 | Type II PPB & CN (2.7) | c.2379T>G | p.Y793X | c.5113G>A | p.E1705K | |
| PTC within encapsulated follicular nodules | NA | SLCT, cystic nephroma, MNG | c.5441C>T | p.S1814L | c.5126A>G | p.D1709G | [31] |
| PTC within encapsulated follicular nodules | NA | NA | c.5425G>A | p.G1809R | |||
| Follicular nodule with papillary hyperplasia, focal PTC | NA | NA | c.5126A>G (left node) c.5428G>C (right node) | p.D1709G p.D1810H | |||
| MNG | NA | NA | Without hotspot mutations | ||||
| Follicular hyperplasia | 18.0 (a) | NA | c.1329_1344_del16 | p.C443W,fs*10 | c.5438A>G | p.E1813G | [8] |
| Nodular hyperplasia | 36.5 (a) | NA | c.1408G>T | p.E470* | c.5126A>G | p.D1709G | |
| Nodular hyperplasia | 13.7 (a) | NA | c.1525C>T | p.R509* | c.5125G>A | p.D1709N | |
| Nodular hyperplasia | 14.2 (a) | NA | c.1525C>T | p.R509* | c.5428G>C | p.D1810H | |
| MNG | 41.6 (a) | c.1870C.T | p.R624 | c.5126A>G (2 lesions) c.5429A>T (1 lesion) c.5437G>C (1 lesion) | p.D1709G p.D1810V p.E1813Q | ||
| Nodular hyperplasia | 21.0 (a) | NA | c.2062C>T | p.R688* | c.5428G>T | p.D1810Y | |
| Nodular hyperplasia | 37 (a) | NA | c.2062C>T | p.R688* | c.5429A>T | p.D1810V | |
| Multinodular hyperplasia | 15.5 (a) | NA | c.2247C>A | p.Y749* | c.5429A>T | p.D1810V | |
| Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | 20.6 (a) | NA | c.2247C>A | p.Y749* | None | None | |
| Nodular hyperplasia | 13.6 (a) | NA | c.2650+1G>T | Splice site variant | None | None | |
| Nodular hyperplasia | 21.0 (a) | NA | c.2830C>T | p.R944* | c.5126A>G | p.D1709G | |
| Nodular hyperplasia | 21.9 (a) | NA | c.3019C>T | p.Q1007* | c.5113G>A | p.E1705K | |
| Nodular hyperplasia with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | 32.4 (a) | c.3515_3525del11insA | c.5126A>G (2 lesions) c.5429A>T (1 lesion) None (1 lesion) | p.D1709G p.D1810V - | |||
| Thyroid carcinoma, papillary, macrofollicular | 30.6 (a) | NA | c.3675C>G | p.Y1225 | c.5113G>A (1 lesion) c.5126A>G (1 lesion) | p.E1705K p.D1709G | |
| PTC, follicular variant | 18.6 (a) | PPB type II (4.1), MNG (18) | c.3726C>A | p.Y1242 | c.5426G.A | p.G1809E | |
| Nodular hyperplasia with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | 60.9 (a) | NA | c.4812C>A | p.C1604* | None | None | |
| MNG | 15 | SLCT (13) | c.4207-41_5364+1034del | Loss of exons 23 and 24 | c.5113G>C+c.5114A>T | p.E1705Q + p.E1705V | [32] |
| MNG | 15, 56 | NA | c.5126A>G | p.D1709G | |||
| MNG | 13 | NA | c.5429A>T | p.D1810V | |||
| MNG | 7, 26 | NA | ND | - | |||
| MNG and DTC (papillary) | 70 | NA | No | - | ND | - | |
| FVPTC | 13 | ERMS, SLCT, MNG | c.5504_5507delATCC | p.Y1835S,fs*2 | c.5113G>A | p.E1705K | |
| Encapsulated cPTC | 16.5 | None | c.2875A>T c.5125G>A | p.K959 * p.D1709N | [33] | ||
| Minimally invasive, encapsulated FVPTC | 14 | None | c.1124C>G | p.P375R (rs148758903) | c.5428G>T, LOH (del chr14:94,043,795-104,822,229) | p.D1810Y | |
| Infiltrative classical PTC | 11.7 | ALL, TBI, HSCT | c.5439G>C LOH (del chr14:78,529,021-100,616,514) | p.E1813D | |||
| Classical PTC with focal hobnail and tall cell change | 10 | None | c.4260_4262delGGA (b) | p.E1420del (rs544960260) (probably benign) | |||
| Minimally invasive solid-variant PTC | 15 | ALL, TBI | c.2997T>G | p.L999L (rs12018992) | Silent | ||
| Minimally invasive FVPTC and miPTC | 17.4 | ALL, | c.20A>G (b) | p.Q7R (rs117358479) | |||
| Follicular Nodular Disease, multifocal | 12 | None | c.2535_2539del + insAATCAACTTCAAGCATT | p.T847del + insNFKHS | c.5438A>G | p.E1813G | |
| Follicular Nodular Disease | 16 | None | c.84dupT | p.G29W,fs*11 | c.5125G>A | p.D1709N | |
| FVPTC | 9 | PPB type II (2), PPB metastasis (4), MNG (7) | c.3505insT * mother carrier | p.S1169F,fs*8 | c.5438A>G | p.E1813G | [14] (c) |
| NIFTP | 7 | PPB type I (1), CBME (6) | c.3579_3580delCA | p.N1193K,fs*41 | c.5438A>G | p.E1813G | [14] (d) |
| PTC | 11 | PPB type II (2), CN (2), Askin tumour (13) | c.2379T>G | p.Y793* | c.5113G>A | p.E1705K | |
| PDTC | 10 | Bilateral renal and lung cysts (2), pineoblastoma (7), bilateral SLCT (13,15), CBME (17) | c.5437G>C | p.E1813Q | LOH | LOH | [14] (e) |
| FVPTC, NTH | 13 | None | c.1363del | p.V455fs | In 3 out of 5 lesions: c.5126A>G (tumour 1) c.5127T>G (tumour 2) c.5113G>A (NTH) | p.D1709G p.D1709E p.E1705K | [14] |
| NIFTP, NTH | 17 (NIFTP) | MNG (13) | c.1363del | p.V455fs | In 1 out of 2 NIFTP lesions: c.5427_5428del+insTT | p.D1810Y | |
| NIFTP | 15 | Lung cysts | c.3999C>A | p.C1333* | c.5437G>A | p.E1813K | |
| PDTC | 14 | None | c.2256+1G>C | Splice variant | c.5437G>C | p.E1813Q | |
| FVPTC, NTH | 23 (FVPTC) | None | c.988G>A | p.Q330* | c.5125G>A (T1a+T1b tumours) c.5126A>G (T2 tumour+NTH1) c.5437G>A (T3 tumor) c.5438A>T (NTH2) c.5428G>T (NTH3) c.5429A>T (NTH4) | p.D1709N p.D1709G p.E1813K p.E1813V p.D1810Y p.D1810V | |
| FVPTC, NTH | 28 (FVPTC) | None | c.988G>A | p.Q330* | c.5113G>A (NTH 1,2) c.5126A>G (NTH 3,4) c.5438A>T (tumour1+NTH 5–9) c.5429A>T (NTH 10) | p.E1705K p.D1709G p.E1813V p.D1810V | |
| eaFTC | 2.4 | None | c.3506C>G | p.S1169* | c.5437G>A | p.E1813K | [12] |
| wiFTC | 9.3 | PPB (2), Nodular hyperplasia | c.3505dupT | p.S1169fs | c.5439G>T | p.E1813D | |
| miFTC | 8.9 | Bronchogenic cyst or pulmonary parenchymal cyst; Nodular hyperplasia; FA | c.5378delA | p.E1793fs | c.5125G>A | p.D1709N | |
| wiFTC | 14 | None | c.5437G>C c.5465A>G | p.E1813Q p.D1822G | |||
| miFTC | 14.6 | PNET in lung; FA | c.2621C>A Copy number loss (chr1:96–106Mb/chr10:pter-10Mb) Copy number gain (chr9:121Mbqter) | p.S874* | c.5126A>G | p.D1709G | |
| miFTC | 18 | Lymphocytic thyroiditis | c.5437G>A | p.E1813K | |||
| miFTC | 18.3 | Nodular hyperplasia | c.3157dupT, c.5437G>A | p.C1053fs, p.E1813K | |||
| miFTC | 18.5 | Nodular hyperplasia | c.4273G>T c.5437G>A LOH (chr9/chr21q)d | p.E1425* p.E1813K | |||
| PDTC, encapsulated FVPTC | 14 (PDTC) | NA | c.5113G>A | p.E1705K | [11] | ||
| PDTC, encapsulated FVPTC | 14 (PDTC) | NA | c.5125G>A, c.3627dupA | p.D1709N, p.P1210Tfs*25 | |||
| PDTC | 19 | NA | c.5137G>T | p.D1713Y | |||
| PDTC | 17 | NA | c.735-8T>G | Splicing site affected | c.5437G>A | p.E1813K | |
| PDTC, PTC | 17 (PDTC) | NA | c.5437G>C, LOH | p.E1813Q, LOH | |||
| miFTC with multifocal capsular invasion; MNG | 12 | Sever’s disease | ND | ND | c.5113G>A | p.E1705K | [34] |
| miPTC, MNG | 37 | Heterozygous factor V Leiden mutation (24) | ND | ND | c.5113G>A | p.E1705K | |
| Minimally invasive FTC | 58 | Ovarian endometriosis | ND | ND | c.5113G>A | p.E1705K | |
| Adenomatoid nodules | 35 | Breast fibroadenoma and benign cysts | ND | ND | c.5126A>G | p.D1709G | |
| FTC with a focus on vascular invasion; MNG | 14 | Unknown | ND | ND | c.5428G>T | p.D1810Y | |
| PDTC | 17 | PPD+/CXR− (15) | ND | ND | c.5428G>T | p.D1810Y | |
| Classic PTC | 65 | Breast cancer (45), uterine cancer (52), schwannoma | ND | ND | c.5428G>T | p.D1810Y | |
| Classic PTC | 38 | NA | c.-3T>C | Promoter region | Not found | Not found | [2] |
| OV-PTC | 44 | NA | c.20A>G | p.Q7R | Not found | Not found | |
| OV-PTC | 65 | NA | c.59C>T | p.A20V | Not found | Not found | |
| Classic PTC-A | 63 | NA | c.1795A>G | p.T599A | Not found | Not found | |
| FVPTC | 53 | NA | c.1887G>A | p.T629T | Not found | Not found | |
| FVPTC | 44 | NA | c.1904A>G | p.N635S | Not found | Not found | |
| FVPTC | 25 | NA | c.2512T>G | p.L838V | Not found | Not found | |
| OV-PTC | 27 | NA | c.2557A>G | p.I853V | Not found | Not found | |
| Classic PTC-O | 45 | NA | c.2614G>A | p.A872T | Not found | Not found | |
| Classic PTC | 30 | NA | c.2951A>C | p.N984T | Not found | Not found | |
| Classic PTC | 31 | NA | Not found | Not found | |||
| FVPTC | 36 | NA | Not found | Not found | |||
| HV-PTC | 33 | NA | c.3778G>A | p.V1260I | Not found | Not found | |
| FVPTC | 88 | NA | c.4260_4262delGGA | p.E1420del | Not found | Not found | |
| OV-PTC | 51 | NA | c.4680G>A | p.A1560A | Not found | Not found | |
| OV_PTC | 65 | NA | c.4891T>G | p.S1631A | Not found | Not found | |
| OV-PTC | 26 | NA | c.5013G>C | p.K1671N | Not found | Not found | |
| FVPTC | 31 | NA | Not found | Not found | c.5428G>C | p.D1810H | |
| OV-PTC | 44 | NA | Not found | Not found | c.5438A>G | p.E1813G | |
| Classic PTC | 64 | NA | c.5507C>T | p.P1836H | Not found | Not found | |
| OV-PTC | 20 | NA | Not found | Not found | c.5718A>C | p.R1906S | |
2.4. DICER1 Somatic Hotspot Mutations and the Free Pass to Thyroid Malignancy
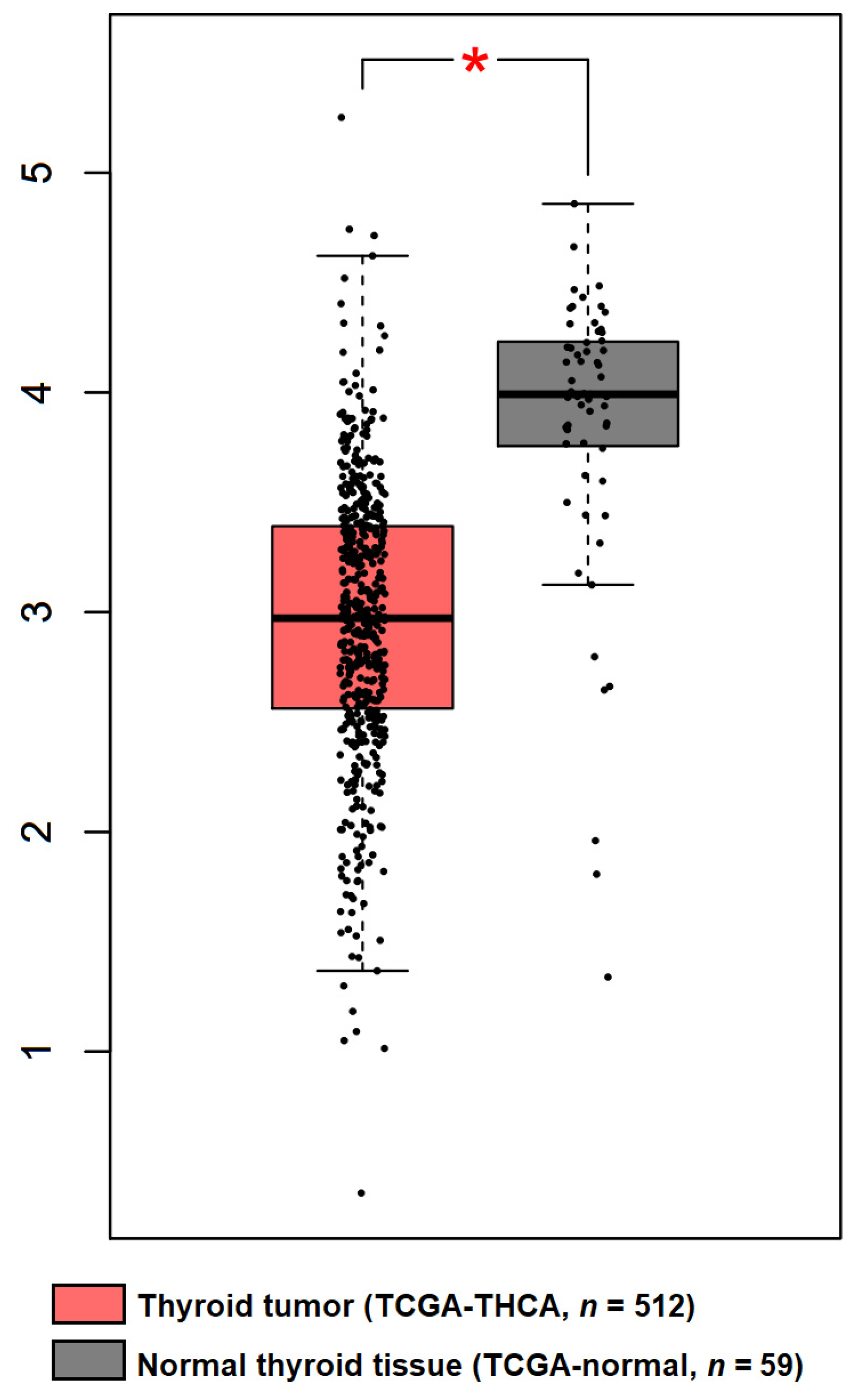
3. Regulation of DICER1 Expression in TC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Couch, R.M.; Hughes, I.A.; DeSa, D.J.; Schiffrin, A.; Guyda, H.; Winter, J.S. An autosomal dominant form of adolescent multinodular goiter. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1986, 39, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Canberk, S.; Ferreira, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Batista, R.; Vieira, A.F.; Soares, P.; Sobrinho Simoes, M.; Maximo, V. Analyzing the Role of DICER1 Germline Variations in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2021, 9, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.A.; Ivanovich, J.; Priest, J.R.; Gurnett, C.A.; Dehner, L.P.; Desruisseau, D.; Jarzembowski, J.A.; Wikenheiser-Brokamp, K.A.; Suarez, B.K.; Whelan, A.J.; et al. DICER1 mutations in familial pleuropulmonary blastoma. Science 2009, 325, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slade, I.; Bacchelli, C.; Davies, H.; Murray, A.; Abbaszadeh, F.; Hanks, S.; Barfoot, R.; Burke, A.; Chisholm, J.; Hewitt, M.; et al. DICER1 syndrome: Clarifying the diagnosis, clinical features and management implications of a pleiotropic tumour predisposition syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 48, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rio Frio, T.; Bahubeshi, A.; Kanellopoulou, C.; Hamel, N.; Niedziela, M.; Sabbaghian, N.; Pouchet, C.; Gilbert, L.; O’Brien, P.K.; Serfas, K.; et al. DICER1 mutations in familial multinodular goiter with and without ovarian Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors. JAMA 2011, 305, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thunders, M.; Delahunt, B. Gene of the month: DICER1: Ruler and controller. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 74, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver-Petit, I.; Bertozzi, A.I.; Grunenwald, S.; Gambart, M.; Pigeon-Kerchiche, P.; Sadoul, J.L.; Caron, P.J.; Savagner, F. Multinodular goitre is a gateway for molecular testing of DICER1 syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 2019, 91, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.E.; Bauer, A.J.; Schultz, K.A.P.; Doros, L.; Decastro, R.M.; Ling, A.; Lodish, M.B.; Harney, L.A.; Kase, R.G.; Carr, A.G.; et al. Quantification of Thyroid Cancer and Multinodular Goiter Risk in the DICER1 Syndrome: A Family-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kock, L.; Wu, M.K.; Foulkes, W.D. Ten years of DICER1 mutations: Provenance, distribution, and associated phenotypes. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 1939–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooper, L.M.; Bynum, J.P.; Miller, K.P.; Lin, M.T.; Gagan, J.; Thompson, L.D.R.; Bishop, J.A. Recurrent DICER1 Hotspot Mutations in Malignant Thyroid Gland Teratomas: Molecular Characterization and Proposal for a Separate Classification. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernock, R.D.; Rivera, B.; Borrelli, N.; Hill, D.A.; Fahiminiya, S.; Shah, T.; Chong, A.S.; Aqil, B.; Mehrad, M.; Giordano, T.J.; et al. Poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma of childhood and adolescence: A distinct entity characterized by DICER1 mutations. Mod. Pathol. Off. J. U. S. Can. Acad. Pathol. Inc 2020, 33, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Im, S.W.; Jung, K.C.; Chung, E.J.; Shin, C.H.; Kim, J.I.; Park, Y.J. Predominant DICER1 Pathogenic Variants in Pediatric Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas. Thyroid Off. J. Am. Thyroid Assoc. 2020, 30, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedanayagam, J.; Chatila, W.K.; Aksoy, B.A.; Majumdar, S.; Skanderup, A.J.; Demir, E.; Schultz, N.; Sander, C.; Lai, E.C. Cancer-associated mutations in DICER1 RNase IIIa and IIIb domains exert similar effects on miRNA biogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Tuin, K.; de Kock, L.; Kamping, E.J.; Hannema, S.E.; Pouwels, M.M.; Niedziela, M.; van Wezel, T.; Hes, F.J.; Jongmans, M.C.; Foulkes, W.D.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics May Alter Treatment Strategies of Thyroid Malignancies in DICER1 Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, M.S.; Rossi, J.J. Molecular mechanisms of Dicer: Endonuclease and enzymatic activity. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1603–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciechanowska, K.; Pokornowska, M.; Kurzynska-Kokorniak, A. Genetic Insight into the Domain Structure and Functions of Dicer-Type Ribonucleases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Jin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Valdmanis, P.N.; Kay, M.A. The loop position of shRNAs and pre-miRNAs is critical for the accuracy of dicer processing in vivo. Cell 2012, 151, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, P.W.; Guiley, K.Z.; De, N.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B.; MacRae, I.J. The molecular architecture of human Dicer. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pallante, P.; Battista, S.; Pierantoni, G.M.; Fusco, A. Deregulation of microRNA expression in thyroid neoplasias. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Moya, J.; Wert-Lamas, L.; Riesco-Eizaguirre, G.; Santisteban, P. Impaired microRNA processing by DICER1 downregulation endows thyroid cancer with increased aggressiveness. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5486–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.; Pester, R.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Lane, K.; Chin, C.; Lu, J.; Kirsch, D.G.; Golub, T.R.; Jacks, T. Dicer1 functions as a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 2700–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Field, A.; Schultz, K.A.P.; Hill, D.A.; Stewart, D.R. The prevalence of DICER1 pathogenic variation in population databases. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 2030–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caroleo, A.M.; De Ioris, M.A.; Boccuto, L.; Alessi, I.; Del Baldo, G.; Cacchione, A.; Agolini, E.; Rinelli, M.; Serra, A.; Carai, A.; et al. DICER1 Syndrome and Cancer Predisposition: From a Rare Pediatric Tumor to Lifetime Risk. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 614541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillerman, R.P.; Foulkes, W.D.; Priest, J.R. Imaging of DICER1 syndrome. Pediatr. Radiol. 2019, 49, 1488–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, R.V.; Osamura, R.Y.; Klöppel, G.; Rosai, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Lyon, France, 2017; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, D.R.; Best, A.F.; Williams, G.M.; Harney, L.A.; Carr, A.G.; Harris, A.K.; Kratz, C.P.; Dehner, L.P.; Messinger, Y.H.; Rosenberg, P.S.; et al. Neoplasm Risk Among Individuals With a Pathogenic Germline Variant in DICER1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.S.; Jung, S.H.; Hirokawa, M.; Bychkov, A.; Miyauchi, A.; Lee, S.; Chung, Y.J.; Jung, C.K. High Prevalence of DICER1 Mutations and Low Frequency of Gene Fusions in Pediatric Follicular-Patterned Tumors of the Thyroid. Endocr. Pathol. 2021, 32, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, A.S.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Condello, V.; Wald, A.I.; Nikiforova, M.N.; Foulkes, W.D.; Rivera, B. Prevalence and Spectrum of DICER1 Mutations in Adult-onset Thyroid Nodules with Indeterminate Cytology. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghossein, C.A.; Dogan, S.; Farhat, N.; Landa, I.; Xu, B. Expanding the spectrum of thyroid carcinoma with somatic DICER1 mutation: A survey of 829 thyroid carcinomas using MSK-IMPACT next-generation sequencing platform. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kock, L.; Sabbaghian, N.; Soglio, D.B.; Guillerman, R.P.; Park, B.K.; Chami, R.; Deal, C.L.; Priest, J.R.; Foulkes, W.D. Exploring the association Between DICER1 mutations and differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1072–E1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutter, M.M.; Jha, P.; Schultz, K.A.; Sheil, A.; Harris, A.K.; Bauer, A.J.; Field, A.L.; Geller, J.; Hill, D.A. DICER1 Mutations and Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Evidence of a Direct Association. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apellaniz-Ruiz, M.; de Kock, L.; Sabbaghian, N.; Guaraldi, F.; Ghizzoni, L.; Beccuti, G.; Foulkes, W.D. Familial multinodular goiter and Sertoli–Leydig cell tumors associated with a large intragenic in-frame DICER1 deletion. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, K11–K19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wasserman, J.D.; Sabbaghian, N.; Fahiminiya, S.; Chami, R.; Mete, O.; Acker, M.; Wu, M.K.; Shlien, A.; de Kock, L.; Foulkes, W.D. DICER1 Mutations Are Frequent in Adolescent-Onset Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Son, M.H.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Park, H.J.; Park, B.K. Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma Arising After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in a Child with Pleuropulmonary Blastoma. Thyroid Off. J. Am. Thyroid Assoc. 2012, 22, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kock, L.; Wang, Y.C.; Revil, T.; Badescu, D.; Rivera, B.; Sabbaghian, N.; Wu, M.N.; Weber, E.; Sandoval, C.; Hopman, S.M.J.; et al. High-sensitivity sequencing reveals multi-organ somatic mosaicism causing DICER1 syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darbinyan, A.; Morotti, R.; Cai, G.; Prasad, M.L.; Christison-Lagay, E.; Dinauer, C.; Adeniran, A.J. Cytomorphologic features of thyroid disease in patients with DICER1 mutations: A report of cytology-histopathology correlation in 7 patients. Cancer Cytopathol 2020, 128, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.C.; Jorcyk, C.L.; Oxford, J.T. DICER1 Syndrome: DICER1 Mutations in Rare Cancers. Cancers 2018, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agaimy, A.; Witkowski, L.; Stoehr, R.; Cuenca, J.C.C.; Gonzalez-Muller, C.A.; Brutting, A.; Bahrle, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Amin, R.M.S.; Hartmann, A.; et al. Malignant teratoid tumor of the thyroid gland: An aggressive primitive multiphenotypic malignancy showing organotypical elements and frequent DICER1 alterations-is the term "thyroblastoma" more appropriate? Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2020, 477, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, K.A.P.; Williams, G.M.; Kamihara, J.; Stewart, D.R.; Harris, A.K.; Bauer, A.J.; Turner, J.; Shah, R.; Schneider, K.; Schneider, K.W.; et al. DICER1 and Associated Conditions: Identification of At-risk Individuals and Recommended Surveillance Strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakhuizen, J.J.; Hanson, H.; van der Tuin, K.; Lalloo, F.; Tischkowitz, M.; Wadt, K.; Jongmans, M.C.J.; Group, S.H.G.W.; CanGene-CanVar Clinical Guideline Working, G.; Expert Network, M. Surveillance recommendations for DICER1 pathogenic variant carriers: A report from the SIOPE Host Genome Working Group and CanGene-CanVar Clinical Guideline Working Group. Fam. Cancer 2021, 20, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsson, J.O.; Wang, N.; Gao, J.; Stenman, A.; Zedenius, J.; Mu, N.; Lui, W.O.; Larsson, C.; Juhlin, C.C. GABPA-dependent down-regulation of DICER1 in follicular thyroid tumours. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Mu, N.; Wang, N.; Straat, K.; Sofiadis, A.; Guo, Y.; Stenman, A.; Li, K.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, L.; et al. GABPA inhibits invasion/metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma by regulating DICER1 expression. Oncogene 2019, 38, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestana, A.; Vinagre, J.; Sobrinho-Simoes, M.; Soares, P. TERT biology and function in cancer: Beyond immortalisation. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017, 58, R129–R146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, J.W.; Bacchetti, S. A survey of telomerase activity in human cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, S.; Figl, A.; Rachakonda, P.S.; Fischer, C.; Sucker, A.; Gast, A.; Kadel, S.; Moll, I.; Nagore, E.; Hemminki, K.; et al. TERT promoter mutations in familial and sporadic melanoma. Science 2013, 339, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.W.; Hodis, E.; Xu, M.J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Chin, L.; Garraway, L.A. Highly recurrent TERT promoter mutations in human melanoma. Science 2013, 339, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinagre, J.; Almeida, A.; Populo, H.; Batista, R.; Lyra, J.; Pinto, V.; Coelho, R.; Celestino, R.; Prazeres, H.; Lima, L.; et al. Frequency of TERT promoter mutations in human cancers. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melo, M.; Gaspar da Rocha, A.; Batista, R.; Vinagre, J.; Martins, M.J.; Costa, G.; Ribeiro, C.; Carrilho, F.; Leite, V.; Lobo, C.; et al. TERT, BRAF, and NRAS in Primary Thyroid Cancer and Metastatic Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.J.; Rube, H.T.; Kreig, A.; Mancini, A.; Fouse, S.D.; Nagarajan, R.P.; Choi, S.; Hong, C.; He, D.; Pekmezci, M.; et al. Cancer. The transcription factor GABP selectively binds and activates the mutant TERT promoter in cancer. Science 2015, 348, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulsson, J.O.; Backman, S.; Wang, N.; Stenman, A.; Crona, J.; Thutkawkorapin, J.; Ghaderi, M.; Tham, E.; Stalberg, P.; Zedenius, J.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of synchronous thyroid carcinomas identifies aberrant DNA repair in thyroid cancer dedifferentiation. J. Pathol. 2020, 250, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsson, J.O.; Rafati, N.; DiLorenzo, S.; Chen, Y.; Haglund, F.; Zedenius, J.; Juhlin, C.C. Whole-genome sequencing of follicular thyroid carcinomas reveal recurrent mutations in microRNA processing subunit DGCR8. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 3265–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, B.; Nadaf, J.; Fahiminiya, S.; Apellaniz-Ruiz, M.; Saskin, A.; Chong, A.S.; Sharma, S.; Wagener, R.; Revil, T.; Condello, V.; et al. DGCR8 microprocessor defect characterizes familial multinodular goiter with schwannomatosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poma, A.M.; Condello, V.; Denaro, M.; Torregrossa, L.; Elisei, R.; Vitti, P.; Basolo, F. DICER1 somatic mutations strongly impair miRNA processing even in benign thyroid lesions. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 1785–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canberk, S.; Correia, M.; Lima, A.R.; Bongiovanni, M.; Sobrinho-Simões, M.; Soares, P.; Máximo, V. The Multifaceted Profile of Thyroid Disease in the Background of DICER1 Germline and Somatic Mutations: Then, Now and Future Perspectives. J. Mol. Pathol. 2022, 3, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp3010001
Canberk S, Correia M, Lima AR, Bongiovanni M, Sobrinho-Simões M, Soares P, Máximo V. The Multifaceted Profile of Thyroid Disease in the Background of DICER1 Germline and Somatic Mutations: Then, Now and Future Perspectives. Journal of Molecular Pathology. 2022; 3(1):1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp3010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanberk, Sule, Marcelo Correia, Ana Rita Lima, Massimo Bongiovanni, Manuel Sobrinho-Simões, Paula Soares, and Valdemar Máximo. 2022. "The Multifaceted Profile of Thyroid Disease in the Background of DICER1 Germline and Somatic Mutations: Then, Now and Future Perspectives" Journal of Molecular Pathology 3, no. 1: 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp3010001
APA StyleCanberk, S., Correia, M., Lima, A. R., Bongiovanni, M., Sobrinho-Simões, M., Soares, P., & Máximo, V. (2022). The Multifaceted Profile of Thyroid Disease in the Background of DICER1 Germline and Somatic Mutations: Then, Now and Future Perspectives. Journal of Molecular Pathology, 3(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp3010001










