Artificial Intelligence in Journalism: A Ten-Year Retrospective of Scientific Articles (2014–2023)
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The 4 Waves of AI
1.2. The Impact of AI on Journalism
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
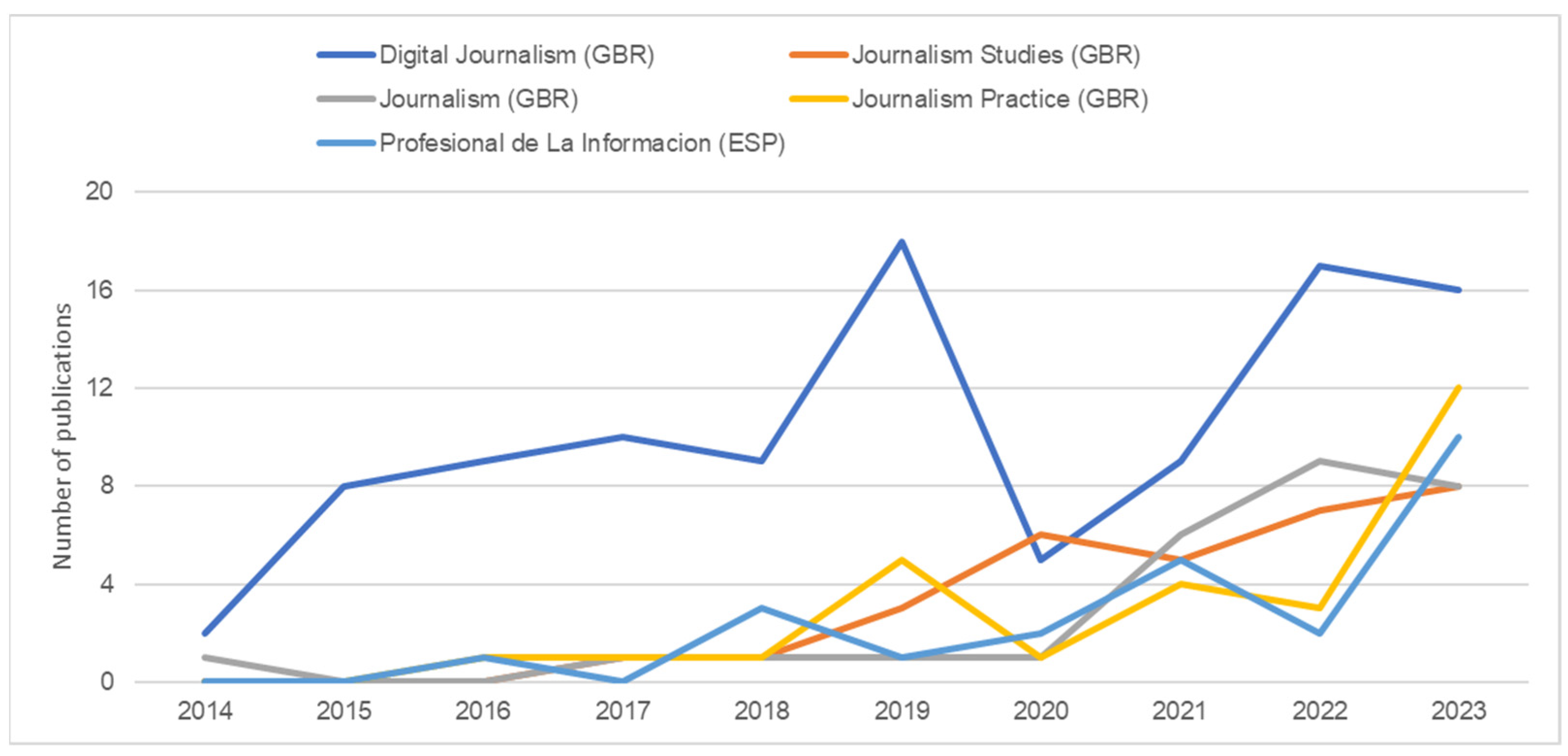
3.1. Journalism and AI Research in Numbers
3.2. Themes, Approaches, and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | The Transformer architecture is a type of machine learning model used for tasks involving natural language processing (NLP). |
| 2 | Database cleansing is performed in Microsoft Excel using duplicate filter functions. |
| 3 | We created the ND (not defined) category for articles that do not mention the collection technique in the abstract and at the same time are not available in the full version for consultation. |
| 4 | From January 2024, Profesional de La Información is being published by Oxbridge, UK. |
| 5 | Affiliation includes universities, research institutes and centres, companies and non-governmental organisations. |
| 6 | Dictionaries provide static definitions of terms. Machine learning is a dynamic technique that allows computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. |
References
- Bakir, Vian, and Andrew McStay. 2018. Fake news and the economy of emotions: Problems, causes, solutions. Digital Journalism 6: 154–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, Iara, and Gerson Battisti. 2008. Métodos estatísticos. Rio Grande do Sul: Unijuí. [Google Scholar]
- Bäck, Asta, Nicholas Diakopoulos, Mark Granroth-Wilding, Lauri Haapanen, Leo Leppänen, Magnus Melin, Tom Moring, Myriam Munezero, Stefanie Sirén-Heikel, Caj Södergård, and et al. 2019. News Automation: The Rewards, Risks and Realities of ‘Machine Journalism’. WAN-IFRA Report. Edited by Carl-Gustav Lindén and Hanna Tuulonen. Amsterdam: Elsevier B.V. [Google Scholar]
- Beckett, Charles. 2019. New Powers, New Responsibilities: A Global Survey of Journalism and Artificial Intelligence. The London School of Economics and Political Science, Polis Journalism and Society, & Google News Initiative. Available online: https://bit.ly/3P4tf4G/ (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Beckett, Charles, and Mira Yaseen. 2023. Generating Change: A global survey of what news organizations are doing with AI. JournalismAI, Polis, Department of Media and Communications, The London School of Economics and Political Science. Available online: https://www.journalismai.info/research/2023-generating-change (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Berendt, Bettina, Peter Burger, Rafael Hautekiet, Jan Jagers, Alexander Pleijter, and Peter Van Aelst. 2021. FactRank: Developing automated claim detection for Dutch-language fact-checkers. Online Social Networks and Media 22: 100–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankespoor, Elizabeth, Ed deHaan, and Christina Zhu. 2018. Capital market effects of media synthesis and dissemination: Evidence from robo-journalism. Review of Accounting Studies 23: 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomberg. 2023. Introducing BloombergGPT, Bloomberg’s 50-Billion Parameter Large Language Model, Purpose-Built from Scratch for Finance. Available online: https://www.bloomberg.com/company/press/bloomberggpt-50-billion-parameter-llm-tuned-finance/ (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Boczkowski, Pablo, Eugenia Mitchelstein, and Mora Matassi. 2018. “News comes across when I’m in a moment of leisure”: Understanding the practices of incidental news consumption on social media. New Media & Society 20: 3523–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Rubio, Luis-Mauricio, and María-José Ufarte-Ruiz. 2021. Artificial intelligence and journalism: Systematic review of scientific production in Web of Science and Scopus (2008–2019). Communication & Society 34: 159–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavilhas, João. 2021. Epistemology of mobile journalism. A review. Profesional de la información 30: 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavilhas, João. 2023. Produção automática de texto jornalístico com IA: Contributo para uma história. Textual & Visual Media 17: 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, Gustavo, Vania Baldi, Paulo Couraceiro, and Miguel Paisana. 2021. Algoritmos e notícias: A oportunidade da inteligência artificial no jornalismo. Available online: https://ciencia.iscte-iul.pt/publications/algoritmos-e-noticias--a-oportunidade-da-inteligencia-artificial-no-jornalismo/83821 (accessed on 16 January 2024).
- Carlson, Matt. 2014. The Robotic Reporter. Automated journalism and the redefinition of labor, compositional forms, and journalistic authority. Digital Journalism 3: 416–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, Matt. 2018. Automating judgment? Algorithmic judgment, news knowledge, and journalistic professionalism. New Media & Society 20: 1755–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, David, and Konstantin Dörr. 2017. Automated Journalism 2.0: Event-driven narratives: From simple descriptions to real stories. Journalism Practice 12: 477–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Sujin. 2019. An exploratory approach to the computational quantification of journalistic values. Online Information Review 43: 133–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuze, Mark, and Charlie Beckett. 2022. Imagination, Algorithms and News: Developing AI Literacy for Journalism. Digital Journalism 10: 1913–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakopoulos, Nicholas. 2019. Automating the News: How Algorithms Are Rewriting the Media. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Diakopoulos, Nicholas, and Michael Koliska. 2017. Algorithmic transparency in the news media. Digital Journalism 5: 809–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, Konstantin. 2016. Mapping the field of algorithmic journalism. Digital Journalism 4: 700–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, Konstantin, and Katharina Hollnbuchner. 2017. Ethical challenges of algorithmic journalism. Digital Journalism 5: 404–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entman, Robert, and Nikki Usher. 2018. Framing in a fractured democracy: Impacts of digital technology on ideology, power and cascading network activation. Journal of Communication 68: 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franganillo, Jorge. 2023. La inteligencia artificial generativa y su impacto en la creación de contenidos mediáticos. Methaodos.Revista de Ciencias Sociales 11: 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Orosa, Berta, João Canavilhas, and Jorge Herrero. 2023. Algoritmos y comunicación: Revisión sistematizada de la literatura. Comunicar: Revista Científica Iberoamericana de Comunicación y Educación 74: 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, Adriana, Luísa Torre, and Paulo Victor Melo. 2024. Inteligência Artificial e Algoritmos: Desafios e Oportunidades para os media. Covilhã: LabCom. [Google Scholar]
- Graefe, Andreas. 2016. Guide to Automated Journalism. New York: Columbia University. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graefe, Andreas, Mario Haim, Bastian Haarmann, and Hans-Bernd Brosius. 2018. Readers’ perception of computer-generated news: Credibility, expertise, and readability. Journalism 19: 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helberger, Natali. 2019. On the democratic role of news recommenders. In Algorithms, Automation, and News. London: Routledge, pp. 14–33. Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/oa-edit/10.4324/9781003099260-2/democratic-role-news-recommenders-natali-helberger (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Hermida, Alfred, and Mary Lynn Young. 2017. Finding the data unicorn: A hierarchy of hybridity in data and computational journalism. Digital Journalism 5: 159–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioscote. 2021. Jornalismo e inteligência artificial: Tendências nas pesquisas brasileiras entre 2010 e 2020. Available online: https://www.revistas.usp.br/novosolhares/article/view/188912 (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Jukes, Stephen. 2013. A perfect storm. In Journalism: New Challenges. pp. 1–18. Available online: https://eprints.bournemouth.ac.uk/20937/1/2013-Journalism-New_Challenges-Fowler-Watt_and_Allan-v1-02.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Jung, Jaemin, Haeyeop Song, Youngju Kim, Hyunsuk Im, and Sewook Oh. 2017. Intrusion of software robots into journalism: The public’s and journalists’ perceptions of news written by algorithms and human journalists. Computers in Human Behavior 71: 291–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Kai-Fu. 2019. Inteligência artificial: Como os robôs estão mudando o mundo, a forma como amamos, nos relacionados, trabalhamos e vivemos, Tradução: Marcelo Barbão—1ª ed. Rio de Janeiro: Globo Livros. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, Seth C., and Oscar Westlund. 2015. Big data and journalism: Epistemology, expertise, economics, and ethics. Digital Journalism 3: 447–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, Seth C., Andrea L. Guzman, and Thomas R. Schmidt. 2019. Automation, journalism, and human–machine communication: Rethinking roles and relationships of humans and machines in news. Digital Journalism 7: 409–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindén, Carl-Gustav. 2017. Algorithms for journalism: The future of news work. The Journal of Media Innovations 4: 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, Francesco. 2020. Newsmakers: Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Journalism. New York: Columbia University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Maslej, Nestor, Loredana Fattorini, Erik Brynjolfsson, John Etchemendy, Katrina Ligett, Terah Lyons, James Manyika, Helen Ngo, Juan Carlos Niebles, Vanessa Parli, and et al. 2023. Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2023. New York: Cornell University. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljević, Marko, and Igor Vobič. 2019. ‘Our task is to demystify fears’: Analysing newsroom management of automation in journalism. Journalism: Theory, Practice & Criticism 22: 2203–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, Dang, H. Xiang Wang, Y. Fen Li, and Tan N. Nguyen. 2022. Explainable artificial intelligence: A comprehensive review. Artificial Intelligence Review 55: 3503–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montal, Tal, and Zvi Reich. 2017. I, robot. You, journalist. Who is the author? Authorship, bylines and full disclosure in automated journalism. Digital Journalism 5: 829–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia Verdú, Francisco José, Rubén Ramos Antón, and Luis Mauricio Calvo Rubio. 2022. Análisis comparado de la calidad de crónicas deportivas elaboradas por inteligencia artificial y periodistas. Revista Latina de Comunicación Social 80: 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechushtai, Efrat, and Seth C. Lewis. 2019. What kind of news gatekeepers do we want machines to be? Filter bubbles, fragmentation, and the normative dimensions of algorithmic recommendations. Computers in Human Behavior 90: 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, Jacob. 2020. The Persistence of the Popular in Mobile News Consumption. Digital Journalism 8: 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, Nic, Richard Fletcher, Kirsten Eddy, Craig T. Robertson, and Rasmus Kleis Nielsen. 2023. Digital News Report 2023. Available online: https://policycommons.net/artifacts/4164711/digital_news_report_2023/4973510/ (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Parasie, Sylvain. 2015. Data-driven revelation? Epistemological tensions in investigative journalism in the age of “big data”. Digital Journalism 3: 364–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parratt-Fernández, Sonia, Javier Mayoral-Sánchez, and Monste Mera-Fernández. 2021. The application of artificial intelligence to journalism: An analysis of academic production. Profesional de la Información 30: e300317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlik, John. 2023. Collaborating with ChatGPT: Considering the implications of generative artificial intelligence for journalism and media education. Journalism & Mass Communication Educator 78: 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Fernández, Simón, Koldobika Meso-Ayerdi, Ainara Larrondo-Ureta, and Javier Díaz-Noci. 2023. Without journalists, there is no journalism: The social dimension of generative artificial intelligence in the media. Profesional de la información 32: e320227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Seijo, Sara, and Paulo Nuno Vicente. 2022. After the hype: How hi-tech is reshaping journalism. In Total Journalism: Models, Techniques and Challenges. Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, Moisés Costa, and Suzana Oliveira Barbosa. 2024. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Brazilian Digital Journalism: Historical Context and Innovative Processes. Journalism and Media 5: 325–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poell, Thomas, David Nieborg, and José van Dijck. 2020. Plataformização. Fronteiras 22: 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, Elia. 2017. My news feed is filtered? Awareness of news personalization among college students. Digital Journalism 5: 1315–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primo, Alex, and Gabriela Zago. 2015. Who and what do journalism? An actor-network perspective. Digital Journalism 3: 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo-Silva, Filipe, Eduardo Biagi de Almeida Santos, Marcelo Moll Brandão, and Leonardo Vils. 2016. Estudo bibliométrico: Orientações sobre sua aplicação. Revista Brasileira de Marketing 15: 246–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, Richard. 2017. Foundations of digital methods. Query Design. In The Datafied Society: Studying Culture through Data. Edited by Mirko Schaefer and Karin van Es. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press, pp. 77–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio, Rafael, and Diógenes Lycarião. 2018. Eu quero acreditar! Da importância, formas de uso e limites dos testes de confiabilidade na Análise de Conteúdo. Revista De Sociologia E Política 26: 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, Rafael, and Diógenes Lycarião. 2021. Análise de conteúdo categorial: Manual de aplicação. Brasília: Enap. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval-Martín, Teresa, and Leonardo La-Rosa Barrolleta. 2023. Research on the quality of automated news in international scientific production: Methodologies and results. Cuadernos.Info 55: 114–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, Anurag, K. Murali Krishna, Moti Lal Rinawa, Mukesh Soni, Gowtham Ramkumar, and Sushma Jaiswal. 2023. Inclusion of IoT, ML, and Blockchain Technologies in Next Generation Industry 4.0 Environment. Materials Today: Proceedings 80: 3471–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, Felix. 2022. Uneasy bedfellows: AI in the news, platform companies and the issue of journalistic autonomy. Digital Journalism 10: 1832–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, Felix. 2024. Artificial Intelligence in the News How AI Retools, Rationalizes, and Reshapes Journalism and the Public Arena. Available online: https://www.cjr.org/tow_center_reports/artificial-intelligence-in-the-news.php (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Sirén-Heikel, Stefanie, Leo Leppänen, Carl-Gustav Lindén, and Asta Bäck. 2019. Unboxing news automation. Nordic Journal of Media Studies 1: 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavelin, Eirik. 2013. Computational Journalism: When Journalism Meets Programming. Doctoral thesis, (PHD Philosophiae)—Department of Information Science and Media Studies, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway. Available online: https://stavelin.com/uib/ComputationalJournalism_EirikStavelin.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Thormundsson, Bergur. 2023. Change in Artificial Intelligence (AI) Investments Worldwide in the Fiscal Year 2023. Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1368382/expected-ai-investment-in-the-next-fiscal-year/ (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Thurman, Neil, Konstantin Dörr, and Jessica Kunert. 2017. When reporters get hands-on with robo-writing: Professionals consider automated journalism’s capabilities and consequences. Digital Journalism 5: 1240–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, Neil, Seth C. Lewis, and Jessica Kunert. 2019. Algorithms, automation, and news. Digital Journalism 7: 980–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, Ashish, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N. Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. 2017. Attention is all you need. Paper presented at the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, December 4–9, vol. 31, pp. 1–11. Available online: https://bit.ly/483iwy7 (accessed on 16 January 2024).
- Waddell, T. Franklin. 2018. A robot wrote this? How perceived machine authorship affects news credibility. Digital Journalism 6: 236–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Julian. 2018. Modelling contemporary gatekeeping: The rise of individuals, algorithms and platforms in digital news dissemination. Digital Journalism 6: 274–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlund, Oscar. 2013. Mobile news: A review and model of journalism in an age of mobile media. Digital journalism 1: 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölker, Anja, and Thomas E. Powell. 2021. Algorithms in the newsroom? News readers’ perceived credibility and selection of automated journalism. Journalism 22: 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Keywords | Number of Articles | |
|---|---|---|
| Scopus | WoS | |
| Journalism AND Artificial Intelligence | 212 | 166 |
| Journalism AND Algorithm OR Algorithmic | 344 | 344 |
| Journalism AND Automated OR Automation | 348 | 325 |
| Journalism AND Robot OR Robotic | 75 | 73 |
| Total on each base | 979 | 908 |
| Coincidences | 396 | 652 |
| Total number of coincidences in each base | 583 | 256 |
| Total articles | 839 | |
| Coincidences in each base | 140 | |
| Total | 699 | |
| Variable | Category |
|---|---|
| (A) Phase of the journalistic process | 1—Gathering 2—Production 3—Distribution ND (not defined/does not fit)3 |
| (B) Themes | 1—Disinformation 2—Ethics and regulation 3—GenAI 4—Journalist’s work 5—Tools/framework 6—Public sphere, democracy and political communication 7—Business models, startups and organisation management 8—Fact-checking 9—Audience 10—Journalism research and education 11—Platforms 12—Others |
| (C) Focus | 1—Theoretical 2—Empirical/experimental |
| (D) Approach | 1—Quantitative 2—Qualitative 3—Mixed |
| (E) Collection techniques | 1—Interview 2—Ethnographic method 3—Questionnaire 4—Digital methods 5—Focus group 6—Framing 7—Others 8—ND (not defined) |
| Authorship | Number of Articles | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (author) | 223 | 31.9% |
| 2 (authors) | 192 | 27.5% |
| 3 (authors) | 162 | 23.2% |
| 4 (authors) | 61 | 8.7% |
| 5 (authors or more) | 61 | 8.7% |
| Total | 699 | 100.0% |
| # | Affiliation | Country | Authorships | Authors | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | University of Amsterdam | NED | 59 | 35 | 33 |
| 2 | University of Santiago de Compostela | ESP | 51 | 16 | 24 |
| 3 | University of Zurich | SUI | 40 | 20 | 18 |
| 4 | Lomonosov Moscow State University | RUS | 23 | 16 | 10 |
| 5 | University of Vienna | AUT | 22 | 17 | 11 |
| 6 | University of Castilla-La Mancha | ESP | 21 | 5 | 10 |
| 7 | University of Ljubljana | SLO | 21 | 8 | 11 |
| 8 | Ludwig Maximilians University Munich | GER | 20 | 11 | 14 |
| 9 | Nanyang Technological University | SGP | 20 | 10 | 9 |
| 10 | University of Münster | GER | 20 | 11 | 8 |
| 11 | Others | 1.408 | 1.149 | 551 | |
| Total | 69 | 1.705 | 1.298 | 699 | |
| Themes | Quantify | % |
|---|---|---|
| 1—Disinformation | 3 | 5.1% |
| 2—Ethics and regulation | 3 | 5.1% |
| 3—GenAI | 5 | 8.5% |
| 4—Journalist’s work | 10 | 16.9% |
| 5—Tools/framework | 10 | 16.9% |
| 6—Public sphere, democracy and political communication | 3 | 5.1% |
| 7—Business models, startups and organisation management | 2 | 3.4% |
| 8—Fact-checking | 2 | 3.4% |
| 9—Audience | 8 | 13.6% |
| 10—Journalism research and education | 1 | 1.7% |
| 11—Platforms | 5 | 8.5% |
| 12—Others | 7 | 11.9% |
| Total | 59 | 100.0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ioscote, F.; Gonçalves, A.; Quadros, C. Artificial Intelligence in Journalism: A Ten-Year Retrospective of Scientific Articles (2014–2023). Journal. Media 2024, 5, 873-891. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia5030056
Ioscote F, Gonçalves A, Quadros C. Artificial Intelligence in Journalism: A Ten-Year Retrospective of Scientific Articles (2014–2023). Journalism and Media. 2024; 5(3):873-891. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia5030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleIoscote, Fabia, Adriana Gonçalves, and Claudia Quadros. 2024. "Artificial Intelligence in Journalism: A Ten-Year Retrospective of Scientific Articles (2014–2023)" Journalism and Media 5, no. 3: 873-891. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia5030056
APA StyleIoscote, F., Gonçalves, A., & Quadros, C. (2024). Artificial Intelligence in Journalism: A Ten-Year Retrospective of Scientific Articles (2014–2023). Journalism and Media, 5(3), 873-891. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia5030056








