Abstract
Green roofs performance is strongly impacted by climatic conditions, design parameters and aging. In particular, the evolution in time of physical and chemical properties may lead to substantial changes in their retention and detention capacity. The growth of the roots, above all, seems to affect the interpretation of the soil water content, a key parameter for GRs retention performance. Generally, Frequency Domain Reflectometry sensors are used in the assessment of the volumetric water content of the soil but they require a calibration procedure in order to obtain reliable measurements. In this study, changes in Frequency Domain Reflectometry sensors calibration caused by the presence of root system were investigated. For this purpose, two substrate soil samples have been collected from an experimental Green Roofs located within the University of Salerno: the first, mainly consisting of peat, during the construction phase and the second, consisting of peat with a developed root system, two years later. Frequency Domain Reflectometry sensor measurements were plotted against observed volumetric water content to obtain calibration curves. Results show that the sensors seem not to be able to predict the water adsorbed by the root system, confirming the hypothesis that Green Roofs evolution can have an important impact on substrate volumetric water content observation.
1. Introduction
In the last decades, strategies involving the use of green infrastructures became necessary to mitigate environmental problems and hydrogeological risks associated with invasive urbanization dynamics [1,2]. Green Roofs (GRs) are considered, in this context, a promising solution able to help traditional drainage systems to manage urban runoff in a sustainable and effective manner retaining stormwater and reducing the peak flow [3]. GRs retention capacity depends on numerous variables such as climatic conditions, design parameters and substrate ageing [4,5,6,7,8,9]. In particular, the evolution of physical and chemical properties of the substrate and vegetation layers of a green roofs may lead to substantial changes in their hydraulic parameters and in the overall hydrological behavior. The growth of the roots in the substrate layer, above all, seems to affect the interpretation of the soil moisture content [10,11]. The latter, especially in Mediterranean regions, characterized by long periods of drought and heavy rainfall, is considered one of the key parameters in the definition of GRs retention performance [12,13]. Generally, Frequency Domain Reflectometry (FDR) sensors are widely used in the assessment of the volumetric water content (VWC) of the soil for their durability and reliability but a calibration procedure of these tools is essential to get accurate assessments.
This research investigated changes in FDR sensors calibration caused by the presence of root system in an experimental GR. In order to assess how the presence of root system affect FDR sensor calibration and therefore also soil moisture content observations, two substrate soil samples were collected from an experimental GR located within the campus of the University of Salerno, in Southern Italy [14]. The samples differ in the presence of root system since the first one was collected during the construction phase in 2017 while a second one was collected two years later. FDR measurements from the two samples were plotted against actual volumetric water content to obtain calibration curves.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The University of Salerno Experimental Site
The experimental GR (Figure 1a), set up in January 2017 at the Laboratory of Environmental and Maritime Hydraulic, Department of Civil Engineering of the University of Salerno UNISA (40.770425, 14.789427, altitude 282 m.a.s.l.), includes three layers: a vegetation layer made up of succulent plants called Mesembryanthemum, a 10 cm deep support substrate and a 5 cm deep drainage layer made up of expanded clay. The roof is placed on bench of stainless steel with a surface of 2.5 m2 (1 × 2.5 m) and a double pitch slope of 1%.

Figure 1.
(a) Green Roof test bed within the University of Salerno Campus; (b) FDR sensor installed at the experimental site.
The experimental site is continuously monitored (5 min time step) by a weather station, Watchdog 2000 Series (Model 2550), which includes: Tipping bucket rain gauge, hygrometer for air humidity measurement, pyranometer with silicon sensor (spectral field 300–1100 nm, range 1–1250 W/m2) for solar radiation measurements, and an anemometer for wind speed and direction measurements. Runoff from the experimental sites is collected in circular-shaped tanks located above digital calibrated scales for stormwater measurement at 5 min time steps).
Volumetric water content within the substrate layer is monitored with the use of the commercial moisture FDR sensor SM 100 (Figure 1b). It is shaped as a thin plate with a sharp tip at the bottom. The sensor has a thickness of 3 mm, a height of 60 mm, and a width of 20 mm, and has been installed vertically. The sensor is made up of two electrodes that act as a capacitor, with the surrounding soil serving as the dielectric. An 80 MHz oscillator drives the capacitor and a signal proportional to the soil’s dielectric properties.
2.2. GR Substrate Soil Sampling
A first substrate soil sample (S2017) was collected in 2017 (Figure 2a), at the moment of the GR installation. It consists of a mix of blond peat, baltic brown peat, zeolites and simple non-composted vegetable primer (coconut fibers), completed with the addition of a mineral fertilizer (biostimulant algae). More information about physical and hydraulic properties are reported in [13].

Figure 2.
(a) GRs soil sampling in 2019; (b) Sample with roots.
A second sample (S2019) was then collected two years later, in 2019 (Figure 2b), and in this case a well developed root system was detected within the previously mentioned soil mix. The sample was took making sure to preserve vegetation and GR functionality.
2.3. FDR Calibration Curves
The FDR calibration curve was obtained by plotting each value of the soil moisture content provided by the FDR sensor against the corresponding volumetric water content (VWC) of the sample. In total, 18 FDR measurements were collected for S2017 and 20 for S2019. For each reading the VWC has been derived as:
where BD is the bulk density of the soil (g cm−3) calculated as the ratio between Dry Weight and Volume of the Sample, and GWC is the gravimetric water content given by:
VWC % = GWC (%) ∙ BD
GWC (%) = (Wet Weight − Dry Weight)/(Dry Weight) ∙ 100
In the previous equation, “Dry Weight” is the weight of the dried sample while “Wet Weight” is the actual weight of the sample during the single measurement. The calibration of FDR sensors was made within the range of 0–40% VWC, above the substrate soil water holding capacity of about 30%.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 3 shows calibration curves obtained by soil moisture content measurement of sample S2017, green dots, and sample S2019, blue dots.
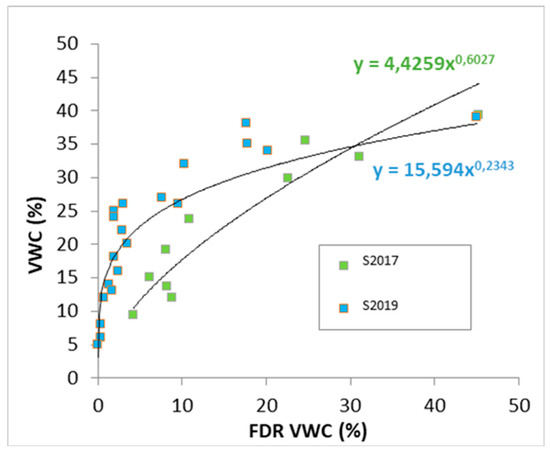
Figure 3.
FDR calibration curves.
From the observation of Figure 3, it results that the same reading provided by the FDR sensor could return, for the sample with root system, a VWC at most 90% larger than for the sample without the root system. The closer the VWC is to the water holding capacity of the soil, the lower is the difference between actual VWC of S2017 and S2019. On the other side, the same value of actual VWC returns a lower FDR reading for the sample with root system. This finding would suggest that, likely, a part of the water inside S2019 is adsorbed by the root system but FDR sensor is not able to measure this amount of water. The overall findings are:
- from the analysis of the two samples (with and without root system), the GR hydraulic and physical characteristics could change in a small time period (within 2 years);
- the use of an unique relationship between FDR measurements and actual VWC, calibrated during the GR installation phase would have led to an underestimation in time of the observed values of VWC with associated consequences;
- The monitoring of the VWC should be carried out by considering the GR ageing effects.
4. Conclusions
Green roofs performance strongly depend on a number of factors including the ageing. Indeed, in time, the GR substrate is interested by the growth of a root system which could affect the interpretation of the soil moisture content. In light of this, the FDR sensors, widely used in the assessment of VWC of the soil, require a calibration procedure in order to return accurate measurements. The aim of the present work was to investigate changes in FDR sensor calibration curves caused by the presence of root system. Two samples were collected in different years, from an experimental GR located in the campus of university of Salerno. The two samples differ in the presence of the root system. For each sample, a calibration curve was built by plotting the FDR measurements against the corresponding VWC values. The result showed that the growth of the roots within the GR substrate impacts the VWC observation indeed, the calibration curves significantly differ for the two samples. The use of the wrong calibration curve could imply incorrect estimates of the GR performances, especially for low VWC. In conclusion, a careful interpretation is needed when monitoring substrate moisture content in presence of a growing root system through FDR soil moisture sensors. Further studies are needed to deepen this aspect, for example studying the ageing effect of a different green roof substrate and technology or monitoring the same substrate over a longer time interval.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L.; methodology, R.D., A.L. and M.M.; software, R.D., M.M.; formal analysis, R.D., M.M.; investigation, R.D., A.L. and M.M.; resources, R.D., A.L., M.M.; data curation, R.D., M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, R.D., M.M.; writing—review and editing, R.D., A.L., M.M.; visualization, R.D., M.M.; supervision, A.L.; project administration, A.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Versini, P.-A.; Kotelnikova, N.; Poulhes, A.; Tchiguirinskaia, I.; Schertzer, D.; Leurent, F. A distributed modelling approach to assess the use of Blue and Green Infrastructures to fulfil stormwater management requirements. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 173, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozos, E.; Makropoulos, C.; Maksimović, Č. Rethinking urban areas: An example of an integrated blue-green approach. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2013, 13, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, T.L.; Rasmussen, T.C. Hydrologic behavior of vegetated roofs. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 42, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.K.; Jim, C. Quantitative hydrologic performance of extensive green roof under humid-tropical rainfall regime. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.; Nigro, G.; Garofalo, G.; Piro, P. Experimental Testing for Evaluating the Influence of Substrate Thickness on the Sub-Surface Runoff of a Green Roof. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 737, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, X. The influence of dual-substrate-layer extensive green roofs on rainwater runoff quantity and quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akther, M.; He, J.; Chu, A.; Huang, J.; Van Duin, B. A Review of Green Roof Applications for Managing Urban Stormwater in Different Climatic Zones. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, I.; Sailor, D.J.; Starry, O. Effects of substrate depth and precipitation characteristics on stormwater retention by two green roofs in Portland OR. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 18, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzouidja, R.; Rousseau, G.; Galzin, V.; Claverie, R.; Lacroix, D.; Séré, G. Green roof ageing or Isolatic Technosol’s pedogenesis? J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kizito, F.; Campbell, C.S.; Cobos, D.R.; Teare, B.L.; Carter, B.; Hopmans, J.W. Frequency, electrical conductivity and temperature analysis of a low-cost capacitance soil moisture sensor. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; van Iersel, M.; Kim, J. Plant root growth affects FDR soil moisture sensor calibration. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 252, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenot, J.; Gaget, E.; Moinardeau, C.; Jaunatre, R.; Buisson, E.; Dutoit, T. Substrate Composition and Depth Affect Soil Moisture Behavior and Plant-Soil Relationship on Mediterranean Extensive Green Roofs. Water 2017, 9, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longobardi, A.; D’Ambrosio, R.; Mobilia, M. Predicting Stormwater Retention Capacity of Green Roofs: An Experimental Study of the Roles of Climate, Substrate Soil Moisture, and Drainage Layer Properties. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mobilia, M.; Longobardi, A. Impact of rainfall properties on the performance of hydrological models for green roofs simulation. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).