Abstract
Forms of gold and arsenic, as one of the main pathfinders, were researched in the podzolic, illuvial, and parent material horizons of podzol soil at the Novye Peski gold deposit. Forms of gold and arsenic were studied with the sequential extraction method. The results of this study showed that the main forms of gold are water-soluble, bound to organic matter, and “insoluble”; for arsenic: bound to Fe and Mn-(oxy)hydroxides and bound to organic matter. The form bound to organic matter was considered in detail and gold and arsenic were analyzed in humic and fulvic acids solutions extracted from podzol soil. It was determined that gold is mainly bound to humic acid (HA), and arsenic to fulvic acid. Due to the prevalence of the form of gold bound to humic acid, the modelling process of different gold and arsenic (III) contents sorption on solid humic acid were observed and data on quantity of adsorbed ions per unit mass of HA and recovery ratio were obtained. More than 90% gold recovery rate was observed for concentrations less than 10 µg/cm3 and for arsenic it was in a range of 8–15%.
1. Introduction
The problems faced in the 20th century while prospecting for deposits covered by surface sediments contributed to the development of ideas about the migration and concentration of chemical elements and their forms in the supergene zone [1]. The theory of “jet-like” migration of chemical elements therefore appeared [2]. All of this contributed to the development of geochemical methods for prospecting for deposits by secondary dispersion halos, in particular, gold deposits (mobile metal ions; NAnoscale Metals in EarthGas; mobile forms of MEtals in Overburden, etc.). However, information on the migration and concentration of gold in loose sediments is still insufficient.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geology of the Study Area
Gold and arsenic forms were studied in loose sediments in the Novye Peski gold deposit area (Karelia Republic, Russia). The gold-sulfo-arsenide deposit Novye Peski is located within the Segozero–Vedlozero Archean greenstone belt and is attributed to the category of a small deposit with indicated reserves of 0.97 t (2.7 g/t Au), inferred reserves of 4.18 t (2.9 g/t Au), and approved speculative resources of 10.8 t [3]. The main types of host rocks within the deposit are metamorphosed basalts, basaltic andesites and their tuffs, amphibolites over gabbro or gabbro-amphibolites, including garnet and epidote with magnetite and ilmenite. Metasomatic alterations are presented by biotitized rocks (biotitites over andesites), epidosites over basalts, and skarnoids over gabbro-amphibolites. Ore mineralization is confined to the North-trending shear zone in metamorphosed and altered gabbroids.
The amount of sulfoarsenides and sulfides in the deposit is about 20–25%. The ore zone is distinguished by anomalous concentrations of As, Au, and slightly increased W content. The mineral association of disseminated-vein gold-sulfoarsenide ores includes arsenopyrite (5–25%), lellingite (1–3%), pyrite (5–10%), pyrrhotite (1–3%), chalcopyrite (up to 1–3%), sphalerite (up to 1%), glaucodot (0.5%), galena (less than 0.3%), scheelite, gold, sporadic bismuth, and maldonite Au2Bi inclusions [4].
Gold and arsenic forms were studied in soil horizons E (sampling depth 0.1–0.15 m), B (sampling depth 0.3–0.4 m), and C (depth 0.1 m above the bedrock), which were collected from three vertical soil profiles above the ore zone (soil profile No. 1), circum-ore zone (soil profile No. 2), and outside those zones (soil profile No. 3); thus, the material for the research was presented as nine soil samples. The samples were air-dried and passed through a 1 mm sieve.
2.2. Sampling, Mineralogical, and Chemical Characteristic of Surface Sediment Horizons
The main chemical and mineralogical characteristics of the samples are presented in Table 1. The extraction of humus acids and humic and fulvic acids was carried out by the pyrophosphate express method of Kononova and Belchikova [5], modified by V.V. Ponomareva and T.A. Plotnikova. The method of I.V. Tyurin modified by V.N. Simakova was used to determine the amount of humic acid carbon (CHA) and fulvic acid carbon (CFA) and total humus content [6]. Soil pH was measured in water extract [7]. Mineral phases were identified with X-ray powder diffraction and clay mineral content with full-profile Ritveld quantitative XRD analysis.

Table 1.
Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of the surface sediments.
According to the National Atlas of Soils of the Russian Federation [8], the podzol soil in the Novye Peski is attributed to the illuvial-iron (illuvial-low-humus) subtype. Illuvial-iron podzols have the following profile: O-E-BF-C; these soils are characterized by a low, not exceeding 2%, humus content in the illuvial horizon and 0.5–1.0% in the eluvial; the humus composition is fulvate [9]. The humus content in the soil of the Novye Peski area presented in Table 1 is similar to the characteristics of iron-illuvial podzols, therefore, they can be attributed to this subunit.
2.3. Methods
Determination of gold and arsenic forms in soil were conducted with the sequential extraction method (Table 2) with a further ICP–MS analysis of the extracts. The obtained extracts of HA and FA from soil by the pyrophosphate express method were also analyzed with ICP–MS. The sample in the sequential extraction experiment was 1 g and for HA and FA extraction −5 g.

Table 2.
Sequential extraction scheme.
In the experiment of gold and arsenic sorption by solid humic acid, standard solutions of gold (GSO 8429-2003) and arsenic (III) (GSO 7976-2001) with a background of 2.0 M and 0.1 M HCl, respectively were used. HA was extracted from an air-dry soil sample by double extraction with a 0.1 mol/dm3 NaOH solution (soil solution ratio 1:10). Then, a saturated Na2SO4 solution (20% of the extract volume) was added to the alkaline extract to coagulate colloidal particles and centrifuged for 1 h at 12,000 rpm. HA was precipitated in the purified extract by the gradual addition of a 10% H2SO4 solution, bringing the pH of the solution to 2. The HA was purified by dialysis, then transferred into porcelain dishes, dried in an oven at 40 °C, and pulverized and sieved through 0.25 mm sieve.
To study the sorption of ions on HA, solutions containing gold and arsenic ions with concentrations of 5, 10, 25, 35, 50, 75, and 100 μg/cm3 were prepared separately by diluting the standards solutions with 1 mmol/dm3 HCl. The pH of the prepared solutions was in the range 3.0–3.1. An amount of 50 mg of air-dry HA was placed in a flask, and 25 cm3 of gold ions solutions was added with a concentration from 5 to 100 μg/cm3, thus, there were 7 flasks with solutions, each containing the same amount of HA, but different gold content. The solutions were mixed for 1 hour using a shaker. After the adsorption equilibrium was established, suspended particles were separated from the solution by filtration through a membrane filter with a pore diameter of 0.22 μm. Similar operations were made for solutions of arsenic ions. The determination of filtrates was carried out by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sequential Extraction Experiment
The main forms of gold are water-soluble, bound to organic matter, and “insoluble”. This element was also detected in the form bound to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides, but its percentage is insignificant (Figure 1, Appendix A Table A1 and Table A2). The main forms for arsenic are bound to organic matter and to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides. The percentage of each form varies in soil horizons, thus, the highest water-soluble gold content is in the E horizon, which is characterized by the less content of absorbing complex and where the percentage of bound to organic matter gold is less; however, this form becomes predominant in the bottom horizon, which is characterized by a low humus content. Arsenic is bound preferably to organic matter in the E horizon, and the percentage of that form is less in the bottom horizon where the form bound to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides predominates. The highest “insoluble” form percentage for gold is in the illuvial horizon, whereas for arsenic it is less; for this element, the highest percentage of that form is in the C horizon.
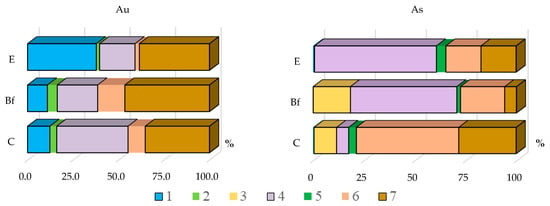
Figure 1.
Forms of gold and arsenic in loose sediment (mean percentage): 1–water-soluble; 2 –loosely adsorbed; 3–strongly adsorbed; 4–bound to organic matter; 5–bound to carbonates; 6–bound to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides; 7–residue (“insoluble”).
The figures below show the distribution of gold and arsenic in different forms and in different soil profiles: over the mineralization zone (profile No. 1), over the circum-ore zone (profile No. 2) and outside those zones (profile No. 3) (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4).
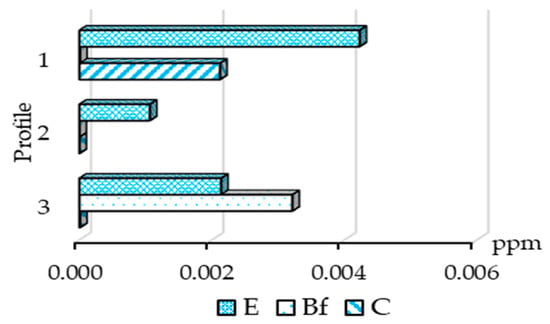
Figure 2.
Distribution of water-soluble gold in soil horizons.
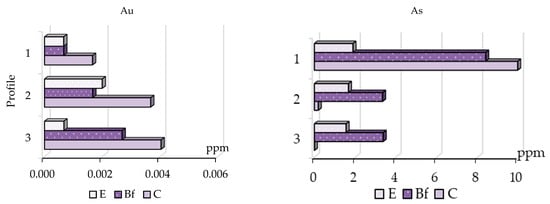
Figure 3.
Distribution of gold and arsenic bound to organic matter in soil horizons.
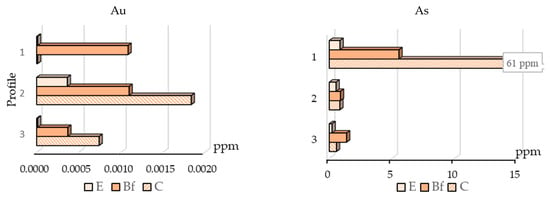
Figure 4.
Distribution of gold and arsenic bound to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides in soil horizons.
The water-soluble gold was detected in samples of the E horizon, but the highest content of the element is above the mineralized zone. In the BF horizon, water-soluble gold was detected only in the profile over barren rocks.
The distribution of gold and arsenic bound to organic matter has different tendencies (Figure 3); gold concentrates mostly in the C horizon and its content increases from profile No. 1 to profile No. 3, which does not point to the mineralized zone; arsenic preferably concentrates in the BF horizon and its content increases from profile No. 3 to No. 1 and the highest arsenic content is in C horizon over the mineralized zone. Thus, this makes it possible to conclude that gold bound to organic matter does not point to the mineralized zone, despite it being one of the main forms of this element in the soil in the Novye Peski area.
The distribution of gold and arsenic bound to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides is presented in Figure 4. For gold, this form is not the main one, but we consider it for comparison with arsenic distribution. Gold concentrates mainly in the C horizon and its highest content is in this horizon of profile No. 2. Thus, analyzing the gold bound to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides in C horizon does not point to the mineralized zone, but there is some increase of this element content in the BF horizon in profiles No. 1 and No. 2 against No. 3 profile over barren rock. Arsenic concentrates in horizon BF, where the iron and manganese oxides and hydroxides accumulate in the highest degree within the podzol soil profiles. The highest arsenic contents are in BF and C horizons of profile No. 1, over the mineralized zone.
As was shown above, gold has a higher concentration in soil samples in profile No. 1 (over the mineralized zone), then in other profiles, only in water-soluble form in E horizon, but this form is not common for arsenic. Gold bound to organic matter does not have the highest concentration in surface sediment over the mineralized zone, but opposite–over the barren rock, which is opposite to arsenic distribution in this form. Perhaps, this is a consequence of interaction with various types of organic matter: humic (HA) and fulvic acids (FA), which contribute differently to gold migration and concentration [10,11,12,13].
3.2. Interaction of Gold and Arsenic with Humic and Fulvic Acids
The distribution of gold and arsenic analyzed in HA and FA extracts is shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6. In surface sediments at Novye Peski, gold was bound to both humic and fulvic acids, but to HA in a higher degree. The distribution of gold analyzed in HA extracts is different to gold bound to organic matter, and as shown in Figure 5, gold content increases in the BF horizon from profile No. 3 to No. 1. However, gold bound to FA has the highest content in profile No. 3, as gold bound to organic matter, but in the BF horizon. As the gold bound to HA has the highest concentration in profile No. 1 in horizon BF, it points to the mineralized zone.
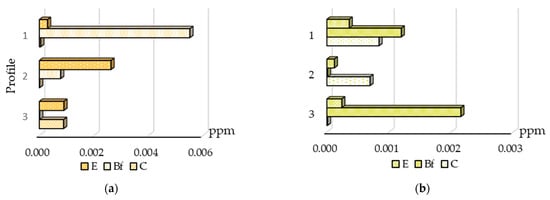
Figure 5.
Distribution of gold bound to humic acid (a) and fulvic acid (b) in soil horizons.
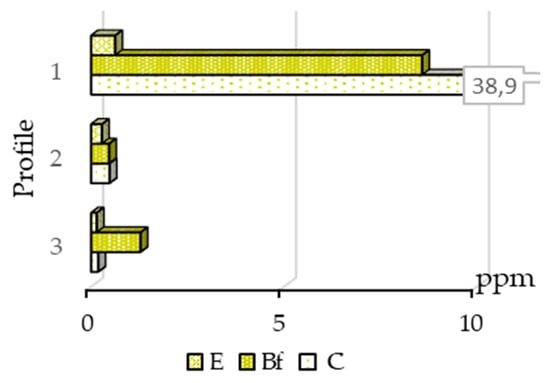
Figure 6.
Distribution of arsenic bound to fulvic acid in soil horizons.
Arsenic was not detected in HA extracts; thus, this element was bound only to FA in surface sediments at Novye Peski (Figure 6). In profile No. 1, arsenic bound to HA had the same distribution pattern as that bound to organic matter and to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides with the highest content in the C horizon. Gold and arsenic bound to FA have different distribution patterns.
Despite the fact that arsenic is not sorbed by humic acid in loose sediments at Novye Peski, the experiment of sorption by solid humic acid was curried out for both elements. Based on the obtained results (Appendix A Table A3), the specific excess Gibbs adsorption and amounts of adsorbed gold and arsenic ions per 1 g of HA were calculated (Appendix A Table A4 and Table A5).
The sorption isotherm of As ions does not reach a plateau, which indicates an insufficient concentration of ions (up to 100 μg/cm3) for limiting sorption (Figure 7).
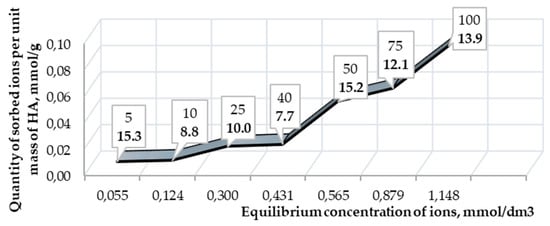
Figure 7.
Isotherm of arsenic ions sorption on HA. The footnotes indicate the initial concentrations of the element in solutions and recovery rate (in bold type).
In contrast to arsenic, gold interacts more actively with HA, which is indicated by the high values of recovery degree from the solution. The highest gold recovery degree from the solution within 1 hour of interaction occurs at concentrations of 5 and 10 μg/cm3 (Figure 8). However, with an increase in the concentration of gold, the recovery degree decreases, while for arsenic, it remains within the range of 8–15% at any concentration level.
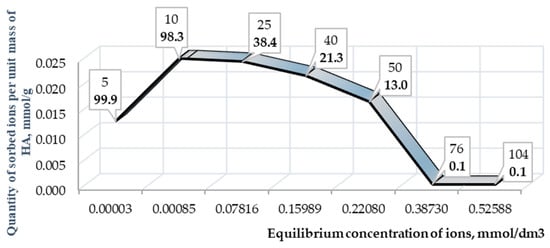
Figure 8.
Isotherm of gold ions sorption on HA. The footnotes indicate the initial concentrations of the element in solutions and recovery rate (in bold type).
It can be assumed that the sorption decrease of high concentrations of gold by solid humic acid can be caused either by a change in the form of the element or by the change in the balance of its forms, where the concentration that shows worse sorption prevails. Gold and HA interaction time needs to be extended for sorption of this form, but more detailed research is needed to identify the reason for the same.
4. Conclusions
The study of gold and arsenic forms in surface sediments showed that water-soluble gold and bound to HA can point to a mineralized zone at Novye Peski, while for arsenic, those forms are bound to organic matter, to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides, and to FA; thus, these two elements have different concentration media. Solid humic acid is quite an active concentrator of low gold concentrations in hydrochloric solution and recovery degree can exceed 90%, which is opposite to that of arsenic, for which recovery degree does not exceed 15%.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.K.; methodology, V.K. and M.C.; investigation, V.K.; writing—original draft preparation, V.K.; writing—review and editing, V.K. and M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to S.N. Chukov for the solid humic acid used in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Table A1. Concentration of gold in extracts obtained by the sequential extraction method. Table A2. Concentration of arsenic in extracts obtained by the sequential extraction method. Table A3. Concentration of elements in solutions after interaction with solid humic acid. Table A4. Data on the sorption of gold ions by solid humic acid. Table A5. Data on the sorption of arsenic ions by solid humic acid.

Table A1.
Concentration of gold in extracts obtained by the sequential extraction method. water-soluble; 2—loosely adsorbed; 3—strongly adsorbed; 4—bound to organic matter; 5—bound to carbonates; 6—bound to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides; 7—«insoluble» residue (ppm).
Table A1.
Concentration of gold in extracts obtained by the sequential extraction method. water-soluble; 2—loosely adsorbed; 3—strongly adsorbed; 4—bound to organic matter; 5—bound to carbonates; 6—bound to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides; 7—«insoluble» residue (ppm).
| Profile | Horizon | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | E | 0.0042 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | 0.0007 | <0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0026 |
| Bf | <0.0001 | 0.0003 | <0.0001 | 0.0007 | <0.0001 | 0.0011 | 0.0022 | |
| C | 0.0021 | 0.0003 | <0.0001 | 0.0017 | <0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0017 | |
| 2 | E | 0.0011 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | 0.0020 | <0.0001 | 0.0004 | 0.0017 |
| Bf | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0017 | <0.0001 | 0.0011 | 0.0041 | |
| C | <0.0001 | 0.0003 | <0.0001 | 0.0037 | <0.0001 | 0.0018 | 0.0041 | |
| 3 | E | 0.0021 | 0.0000 | <0.0001 | 0.0007 | <0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0028 |
| Bf | 0.0032 | 0.0008 | <0.0001 | 0.0027 | <0.0001 | 0.0004 | 0.0028 | |
| C | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | 0.0040 | <0.0001 | 0.0007 | 0.0028 |

Table A2.
Concentration of arsenic in extracts obtained by the sequential extraction method. water-soluble; 2—loosely adsorbed; 3—strongly adsorbed; 4—bound to organic matter; 5—bound to carbonates; 6—bound to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides; 7—«insoluble» residue (ppm).
Table A2.
Concentration of arsenic in extracts obtained by the sequential extraction method. water-soluble; 2—loosely adsorbed; 3—strongly adsorbed; 4—bound to organic matter; 5—bound to carbonates; 6—bound to Fe-Mn (hydr-)oxides; 7—«insoluble» residue (ppm).
| Profile | Horizon | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | E | 0.073 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 1.888 | 0.134 | 0.852 | 0.828 |
| Bf | 0.061 | <0.003 | 6.187 | 8.398 | 0.330 | 5.554 | 1.079 | |
| C | 0.151 | 0.007 | 24.641 | 9.966 | 4.963 | 60.783 | 2.095 | |
| 2 | E | <0.003 | 0.003 | <0.003 | 1.667 | 0.101 | 0.538 | 0.398 |
| Bf | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.950 | 3.344 | 0.057 | 0.886 | 0.323 | |
| C | 0.021 | 0.006 | 0.126 | 0.188 | 0.094 | 0.838 | 1.046 | |
| 3 | E | <0.003 | 0.006 | <0.003 | 1.552 | 0.152 | 0.216 | 0.346 |
| Bf | <0.003 | 0.004 | 0.532 | 3.373 | 0.164 | 1.376 | 0.381 | |
| C | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.038 | <0.003 | 0.025 | 0.572 | 0.387 |

Table A3.
Concentration of elements in solutions after the interaction with solid humic acid.
Table A3.
Concentration of elements in solutions after the interaction with solid humic acid.
| Initial Concentration of Gold in Solution, mg/dm3 | Au, mg/dm3 (after Interaction) | Initial Concentration of As in Solution, mg/dm3 | As, mg/dm3 (after Interaction) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.0 | 0.005 | 4.9 | 4.15 |
| 10.0 | 0.168 | 10.2 | 9.3 |
| 25.0 | 15.398 | 25.0 | 22.5 |
| 40.0 | 31.498 | 35.0 | 32.3 |
| 50.0 | 43.498 | 50.0 | 42.4 |
| 76.4 | 76.298 | 75.0 | 65.9 |
| 103.7 | 103.598 | 100.0 | 86.1 |

Table A4.
Data on the sorption of gold ions by solid humic acid.
Table A4.
Data on the sorption of gold ions by solid humic acid.
| Initial Concentration of Gold in Solution, μg/cm3 | Equilibrium Concentration of Ions, mmol/dm3 | Quantity of Adsorbed Ions Per Unit Mass of HA, mmol/g | Au Recovery Rate from Solution, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.00003 | 0.0127 | 99.9 |
| 10 | 0.00085 | 0.0250 | 98.3 |
| 25 | 0.07816 | 0.0244 | 38.4 |
| 40 | 0.15989 | 0.0216 | 21.3 |
| 50 | 0.22080 | 0.0165 | 13.0 |
| 76 | 0.38730 | 0.0003 | 0.1 |
| 104 | 0.52588 | 0.0003 | 0.1 |

Table A5.
Data on the sorption of arsenic ions by solid humic acid; the values of the total concentration of As ions are given, the forms of which, depending on the experimental conditions, can be different: H2AsO4-, H3AsO3, H3AsO4 и etc.
Table A5.
Data on the sorption of arsenic ions by solid humic acid; the values of the total concentration of As ions are given, the forms of which, depending on the experimental conditions, can be different: H2AsO4-, H3AsO3, H3AsO4 и etc.
| Initial Concentration of Gold in Solution, μg/cm3 | Equilibrium Concentration of Ions, mmol/dm3 | Quantity of Adsorbed Ions Per Unit Mass of HA, mmol/g | As Recovery Rate from Solution, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.055 | 0.005 | 15.3 |
| 10 | 0.124 | 0.006 | 8.8 |
| 25 | 0.300 | 0.017 | 10.0 |
| 40 | 0.431 | 0.018 | 7.7 |
| 50 | 0.565 | 0.051 | 15.2 |
| 75 | 0.879 | 0.061 | 12.1 |
| 100 | 1.148 | 0.093 | 13.9 |
References
- Antropova, L.V. Formy Nakhozhdeniya Elementov v Oreolakh Rasseyaniya Rudnykh Mestorozhdeniy; Nedra: Leningrad, Russia, 1975; p. 144. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ryss, Y.S.; Goldberg, I.S.; Alekseev, S.G.; Dukhanin, A.S. Struynaya migratsiya veshchestva v obrazovanii vtorichnykh oreolov rasseyaniya. DAS USSR 1987, 297, 956–958. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivaschenko, V.I.; Bushmin, S.A.; Ruchev, A.M.; Kornakov, A.S.; Bogomolov, E.S.; Savva, E.V.; Ivanov, M.V.; Tytyk, V.M.; Frolov, P.V. First Evidence of the Archean Age of Orogenic Gold of the Russian Part of the Karelian Craton (Fennoscandian Shield): Sm–Nd Mineral Isochron for Gold-Bearing Metasomatites of the Novye Peski Deposit. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2018, 480, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshevich, L.V.; Tytyk, V.M. Metamorfogenno-metasomaticheskiye preobrazovaniya i Au-S-As mineralizatsiya na mestorozhdenii Novye Peski. Geol. Miner. Karelia 2014, 17, 59–73. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kononova, M.M.; Belchikova, N.P. Uskorennyye metody opredeleniya sostava gumusa mineral'nykh pochv. Pedology 1961, 10, 75–85. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Novitsky, M.V.; Donskikh, I.N.; Chernov, D.V.; Nazarova, A.V.; Melnikov, S.P.; Baeva, N.N.; Lavrischev, A.V. Laboratorno-Prakticheskiye Zanyatiya Po Pochvovedeniyu: Training Guide; Prospect Nauki: Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 2009; p. 320. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Garkusha, I.F. Pochvovedenie s Osnovami Geologii; Sel'hozizdat: Leningrad, USSR, 1963; p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Collective of authors. Natsional'nyy Atlas Pochv Rossiyskoy Federatsii; Astrel: Moscow, Russia, 2011; p. 632. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shishov, L.L.; Tonkonogov, V.D.; Lebedeva, I.I.; Gerasimova, M.I. Klassifikatsiya i Diagnostika Pochv Rossii; Oykumena: Smolensk, Russia, 2004; p. 342. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Y.; Fu, J.; Rate, A.W.; Gilkes, R.J. Adsorption of Au(I, III) complexes on Fe, Mn oxides and humic acid. Chem. Geol. 2002, 185, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.J.; Lintern, M.J.; Longman, G.D. Chemistry of Gold-Humic Interaction CSIRO Division of Exploration, 2nd ed.; CRC LEME: Wembley, Australia, 1990; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Varshal, G.M.; Velykhanova, T.K.; Baranova, N.N. Vzaimodeistvie zolota s guminovymi veschestvami. Geokhimia 1990, 3, 316–327. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Baker, W.E. The role of humic acid in the transport of gold. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1978, 41, 645–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).