Spectral Response (VNIR-SWIR) Associated with the Octahedral Sheet of Smectites †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. X-ray Diffraction
3.2. Chemical Analysis
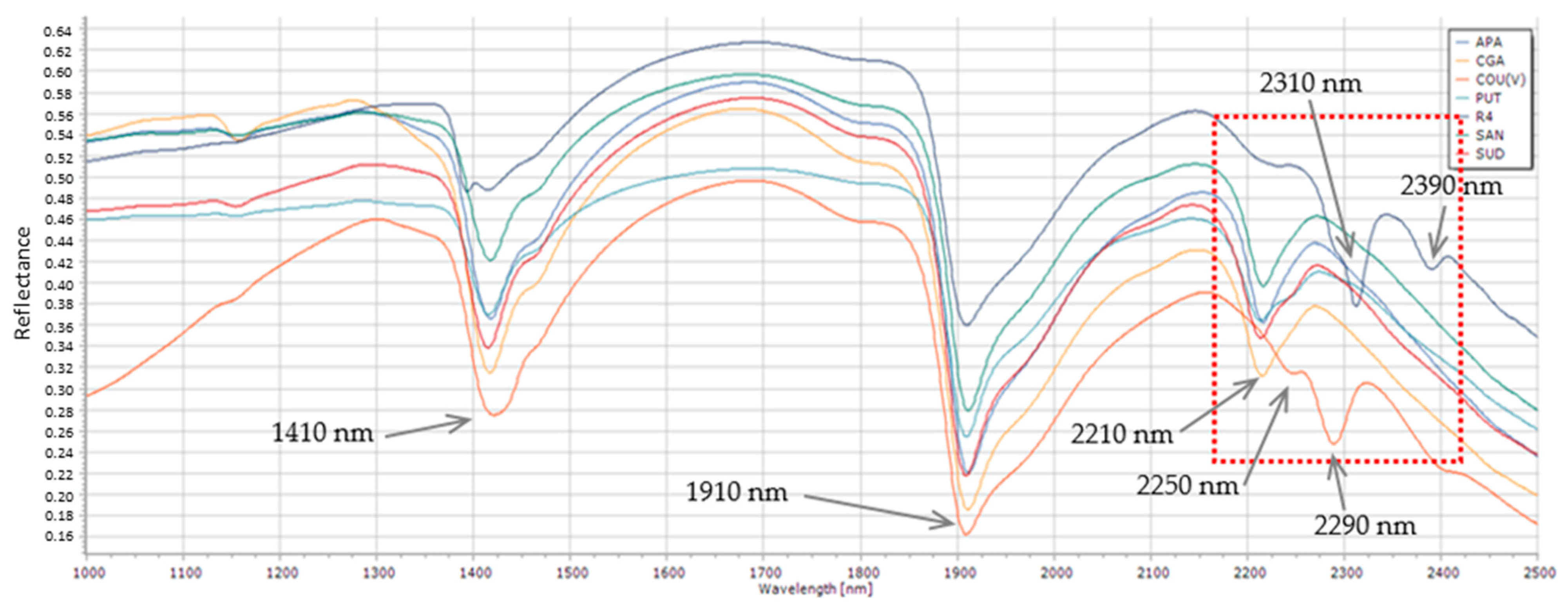
3.3. VNIR-SWIR Spectroscopy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergaya, F.; Jaber, M.; Lambert, J.-F. Clays and Clay Minerals as Layered Nanofillers for (Bio)Polymers. Green Energy Technol. 2012, 50, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.L.; Gates, W.P.; Makarewicz, H.D.; McKeown, N.K.; Hiroi, T. Reflectance spectroscopy of beidellites and their importance for mars. Clays Clay Miner. 2011, 59, 378–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Sobhi, N. Characterization of ASTER spectral bands for mapping of alteration zones of volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 88, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogena, Y.; Goldshlegerb, N.; Ben-Dorc, E. 3D spectral analysis in the VNIR–SWIR spectral region as a tool for soil classification. Geoderma 2017, 302, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaiti, M.; Benvenuti, M.; Costagliola, P.; Di Benedetto, F.; Moretti, S. Hyperspectral Sensors for the Characterization of Cultural Heritage Surfaces. In Sensing the Past: From Artifact to Historical Site; Masini, N., Soldovieri, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menges, F. Spectragryph-Optical Spectroscopy Software, Version 1.2.14. 2020. Available online: http://www.effemm2.de/spectragryph/ (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Christidis, G.E. Validity of the structural formula method for layer charge determination of smectites: A re-evaluation of published data. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Romero, E.; Manchado, E.; Suárez, M.; García-Rivas, J. Spanish Bentonites: A Review and New Data on Their Geology, Mineralogy, and Crystal Chemistry. Minerals 2019, 9, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G. Mineralogical Applications of Crystal Field Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.L.; Lane, M.D.; Dyar, M.D.; Brown, A.J. Reflectance and emission spectroscopy study of four groups of phyllosilicates: Smectites, kaolinite-serpentines, chlorites and micas. Clay Miner. 2008, 43, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.L.; Pieters, C.M.; Edwards, J.O. Infrared spectroscopic analyses on the nature of water in montmorillonite. Clays Clay Miner. 1994, 42, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J. Visible and Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy: Laboratory Spectra of Geologic Materials. In Remote Compositional Analysis: Techniques for Understanding Spectroscopy, Mineralogy, and Geochemistry of Planetary Surfaces; Bishop, J., Bell, J., III, Moersch, J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 68–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | Localization |
|---|---|
| APA | Arizona, USA (Clay Repository) |
| COU(V) | Washington, USA (Clay Repository) |
| PUT | Putifigari, Italy |
| R4 | Esquivias, Spain |
| SAN | Arizona, USA (Clay Repository) |
| SUD | Cabo de Gata, Spain |
| CGA | Cabo de Gata, Spain |
| Samples | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MgO | MnO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APA | 51.95 | 14.18 | 1.23 | 0.00 | 5.04 | 0.08 | 2.48 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 22.89 |
| COU(V) | 49.90 | 7.41 | 18.17 | 0.50 | 1.41 | 0.02 | 1.61 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 19.74 |
| PUT | 50.52 | 14.02 | 5.06 | 0.00 | 4.11 | 0.07 | 1.17 | 0.50 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 0.19 | 21.90 |
| R4 | 52.91 | 1.83 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 25.81 | 0.01 | 0.46 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 17.27 |
| SAN | 53.71 | 14.52 | 0.98 | 0.40 | 5.16 | 0.09 | 2.57 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 22.35 |
| SUD | 53.82 | 16.60 | 3.15 | 0.40 | 4.27 | 0.02 | 1.26 | 1.05 | 0.56 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 18.77 |
| CGA | 53.03 | 16.82 | 2.20 | 0.20 | 5.10 | 0.06 | 1.38 | 0.99 | 0.34 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 20.57 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorenzo, A.; García-Vicente, A.; Morales, J.; García-Romero, E.; Suárez, M. Spectral Response (VNIR-SWIR) Associated with the Octahedral Sheet of Smectites. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021, 6, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/iecms2021-09352
Lorenzo A, García-Vicente A, Morales J, García-Romero E, Suárez M. Spectral Response (VNIR-SWIR) Associated with the Octahedral Sheet of Smectites. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2021; 6(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/iecms2021-09352
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorenzo, Adrián, Andrea García-Vicente, Juan Morales, Emilia García-Romero, and Mercedes Suárez. 2021. "Spectral Response (VNIR-SWIR) Associated with the Octahedral Sheet of Smectites" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 6, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/iecms2021-09352
APA StyleLorenzo, A., García-Vicente, A., Morales, J., García-Romero, E., & Suárez, M. (2021). Spectral Response (VNIR-SWIR) Associated with the Octahedral Sheet of Smectites. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 6(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/iecms2021-09352






