Abstract
Under water insecurity conditions, electromagnetic saline water may be experienced in irrigation. This study examined the impact of electromagnetic saline water on three potato varieties (Spunta, Bellini and Alaska). The trial includes three treatments; ground water (T1: 2.2 ms cm−1 EC), saline water (T2: 8.5 ms cm−1 EC) and saline water having undergone electromagnetic treatment (T3: 8.5 ms cm−1 EC) with Aqua-4D. The results revealed an improvement in yield with T3 compared to T2. Spunta and Alaska were more responsive to T3 than Bellini. The approving response of Alaska was associated with effective adjustment with proline, while Spunta was more efficient in water use.
1. Introduction
Water scarcity is a worldwide problem for agricultural production. Tunisia is currently considered a food-deficit nation with an increasing trend in food imports due to lack of rainfall [1]. Additional brackish water supply can meet crops’ water needs [2]. In this way, the valuation of saline water is gaining increasing attention in many countries suffering from salinization [2]. Efforts are now intended at identifying inexpensive desalination techniques that respect the environment and ensure crop productivity. Physical treatment of saline water is a recommended option. However, most of the considered methods have some drawbacks regarding energy consumption, costs, long reaction time for the treatment etc. [3]. One advantaged strategy, adopted in agricultural irrigation, is electromagnetic treatment [4]. Magnetic treatment consists of passing water through an electromagnetic softener, where a Lorentz force is exerted on each ion which is in the opposite direction to each other. The redirection of the particles increases the collisions between ions and therefore precipitates formation. Additionally, magnetic fields decrease salt hydration and enhance salt solubility, coagulation and crystallization [5].
It was found that electromagnetic saline water improved plant growth, water and ions uptake [6]. In this context, an attempt was made to test whether electromagnetic saline water can alleviate salinity impacts on potatoes. We supposed that electromagnetic saline water may enhance plant-water relations, growth and yield. The applicability of this technique may be supportive in case of dry conditions of the Tunisian spring season.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Details
The present inestigation was carried out at the Regional Center of Agricultural Research of Sidi Bouzid (CRRA-Sidi Bouzid), Tunisia during March–June season of 2014–2015. The experimental layout had a factorial arrangement on the basis of a randomized complete block design with three replicates for each treatment. Potato varieties (Spunta, Bellini and Alaska) were irrigated with three irrigation treatments, T1 ground water (2.2 ms cm−1 electrical conductivity (EC)), T2 saline water (8.5 ms cm−1 EC) and T3 electromagnetic saline water (8.5 ms cm−1 EC). Electromagnetic treatment was done with an Aqua-4D® device which is composed of an electromagnet tube 60E (external diameter 65 mm, passage diameter 100 (DN 25) of 436 mm length and 60 L min−l maximum flow, designed for transmitting the electromagnetic signals into the water and coupled to an electromagnet box (Command 60E Pro) intended to generate electromagnetic signals. The experimental area had a semi-arid climate with 200 mm mean precipitation and 1200 mm mean evapotranspiration. Crop water requirement (ETc) was estimated as reference evapotranspiration (ET0) multiplied by the potato crop coefficient (Kc).
2.2. Agronomic Parameters
Plant height (cm), fresh weight (FW) (g plant−1) and dry weight (DW) (g plant−1) were measured at the tuber initiation stage. The tuber weight per plant was determined at harvest.
2.3. Plant Water Status and Proline Determination
Leaf-relative water content (RWC) was calculated as follows:
where FM is leaf fresh mass, DM is leaf dry mass determined after oven-drying at 75 °C for 24 h and TM is the turgid mass of the leaf, determined after the immersion of the fresh leaves in distilled water for 12 h. The leaf water potential (ψw) was determined before sunrise using a pressure chamber (Scholander model M-1000). Photosynthetic water use efficiency (PWUE) was calculated as the ratio between the amount of CO2 fixed by photosynthesis (Pn) to the transpiration rate (E): PWUE = (Pn/E).
Proline was extracted from the leaves using the sulphosalicylic acid method. A solution of the obtained extract, glacial acetic acid and ninhydrin (1:1:1) was incubated at 100 °C for 1h and the absorbance was determined at 546 nm.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed with SPSS 20 and the means were separated by the Duncan test (p ≤ 0.05). The means were subjected to a three-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
3. Results
3.1. Agronomic Traits
From Table 1, electromagnetic saline water (T3) increased the plant height (PH) of Spunta and Alaska by 34% and 41%, respectively. In addition, Alaska had the highest values of plant height. Hence, ANOVA results revealed that the PH was significantly affected by irrigation treatments and the variety factor. The T3 treatment enhanced the FW accumulation of Bellini and Alaska and the DW of Spunta and Alaska as compared to saline water (T2). The tuber yield varied significantly among the varieties and was increased with T3, but values do not exceed those obtained under ground water (T1).

Table 1.
Changes in plant height (PH), fresh weight (FW), dry weight (DW) and yield of potato varieties (Spunta, Bellini and Alaska), for each irrigation treatment.
3.2. Plant Water Status
The relative water content in potato leaves was in the order T1 > T3 > T2 (Table 2). The registered values of Ψw and PWUE increased with T3 in Spunta and Alaska. Alaska had the highest PWUE values, while Spunta had the highest RWC and Ψw. The RWC and Ψw were significantly influenced by water treatments.

Table 2.
Changes in relative water content (RWC), water potential (Ψw) and photosynthetic water use efficiency (PWUE) of potato varieties (Spunta, Bellini and Alaska), for each irrigation treatment.
3.3. Proline Content
The proline content in the Alaska leaves was set in the following decreasing trend T2 > T3 > T1 (Figure 1). However, there is no significant difference between T2 and T3 in Spunta and Bellini.
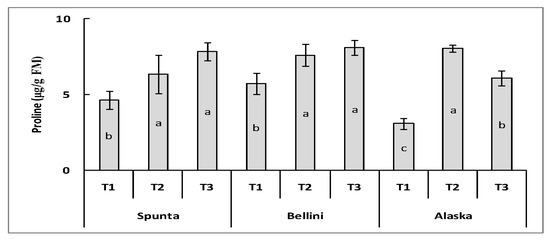
Figure 1.
Changes in proline content of potato varieties under each irrigation treatment. Different letters indicate significant difference between treatments according to Duncan test (p ≤ 0.05). T1: Ground water; T2: Saline water; T3: Electromagnetic saline water.
4. Discussion
Irrigation is an important determinant of potato development during the dry season of spring due to negligible rain. Moreover, the salinization of water resources makes the valuation of saline water very wanted. The present study showed that potato growth (plant height, FW and DW) and yield may be enhanced with electromagnetic saline water, depending on the assessed variety. These results agree with what [4,7]. The data of the present study may be due to the reduction of the soil sodium concentrations with electromagnetic water, by leaching it below the root zone [8]. Additionally, electromagnetic fields change the physical parameters of water (salt’s solubility and electrolytic potential), which improved water and nutrient uptake, and therefore plant growth [7]. Spunta and Alaska were more responsive to electromagnetic saline water while Bellini plant height and DW were not affected by T3. This may be caused by high transpiration rate of Bellini, as demonstrates the low PWUE values of this variety. This is indicative of more susceptible water relations in Bellini. In fact, the RWC, ΨW and PWUE of Spunta and Alaska were higher than Bellini and were enhanced by T3. This result point to a stronger photosynthetic activity of Spunta and Alaska compared to Bellini [7]. The data also shows that the effective adjustment with proline may be a key criterion in maintaining growth under saline conditions of Alaska. Instead, the highest values of the Ψw and RWC of Spunta under T1 and T3 suggest that it was more efficient in water use.
5. Conclusions
Electromagnetic water improved the RWC and Ψw of Spunta and Alaska. Thus, plant height and fresh and dry biomass accumulation were enhanced. The yield of the three studied varieties was increased with T3 compared to untreated saline water. However, further research is required to ensure the safe use of electromagnetic saline water and to identify the exact mechanisms that direct plant response.
Author Contributions
R.A.; methodology, original draft preparation, H.H. and M.M.; editing, M.D.; supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Regional Center of Agricultural Research of Tunisia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Planet Horizons Technologies SA Ecoparc de DavalA 9, 3960 Sierre, CH for supplying the Aqua-4D® 60E series device.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sadok, W.; Schoppach, R.; Ghanem, M.E.; Zucca, C.; Sinclair, T.R. Wheat drought-tolerance to enhance food security in Tunisia, birthplace of the Arab Spring. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 107, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Wu, H.; Wei, Q.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H. Growth performance, organ level ionic relations and organic osmoregulation of Elaeagnus angustifolia in response to salt Stress. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Raad, A.; Hanafiag, M.M.; Naje, A.S.; Ajeel, M.A.; Basheer, A.O.; Aljayashi, T.A.; Toriman, M.O. Treatment of Saline Water Using Electrocoagulation with Combined Electrical Connection of Electrodes. Processes 2019, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, J.A.T.; Dobránszki, J. Impact of magnetic water on plant growth. Environ. Exp. Biol. 2015, 12, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Abedinpour, M.; Rohani, E. Effects of magnetized water application on soil and maize growth indices under different amounts of salt in the water. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2017, 7, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilal, M.; Hilal, M. Application of magnetic technologies in desert agriculture. I-Seed germination and seedling emergence of some crops in a saline calcareous soil. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2000, 40, 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Akrimi, R.; Hajlaoui, H.; Rizzo, V.; Muratore, G.; Mhamdi, M. Agronomical traits, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in raw and cooked potato tubers growing under saline conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3719–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotopolski, V. Magnetic treatment reduces water usage in irrigation without negatively impacting yield, photosynthesis and nutrient uptake in lettuce. Int. J. Appl. Agric. Sci. 2017, 3, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).