An Innovative Modelling Approach Based on Building Physics and Machine Learning for the Prediction of Indoor Thermal Comfort in an Office Building †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
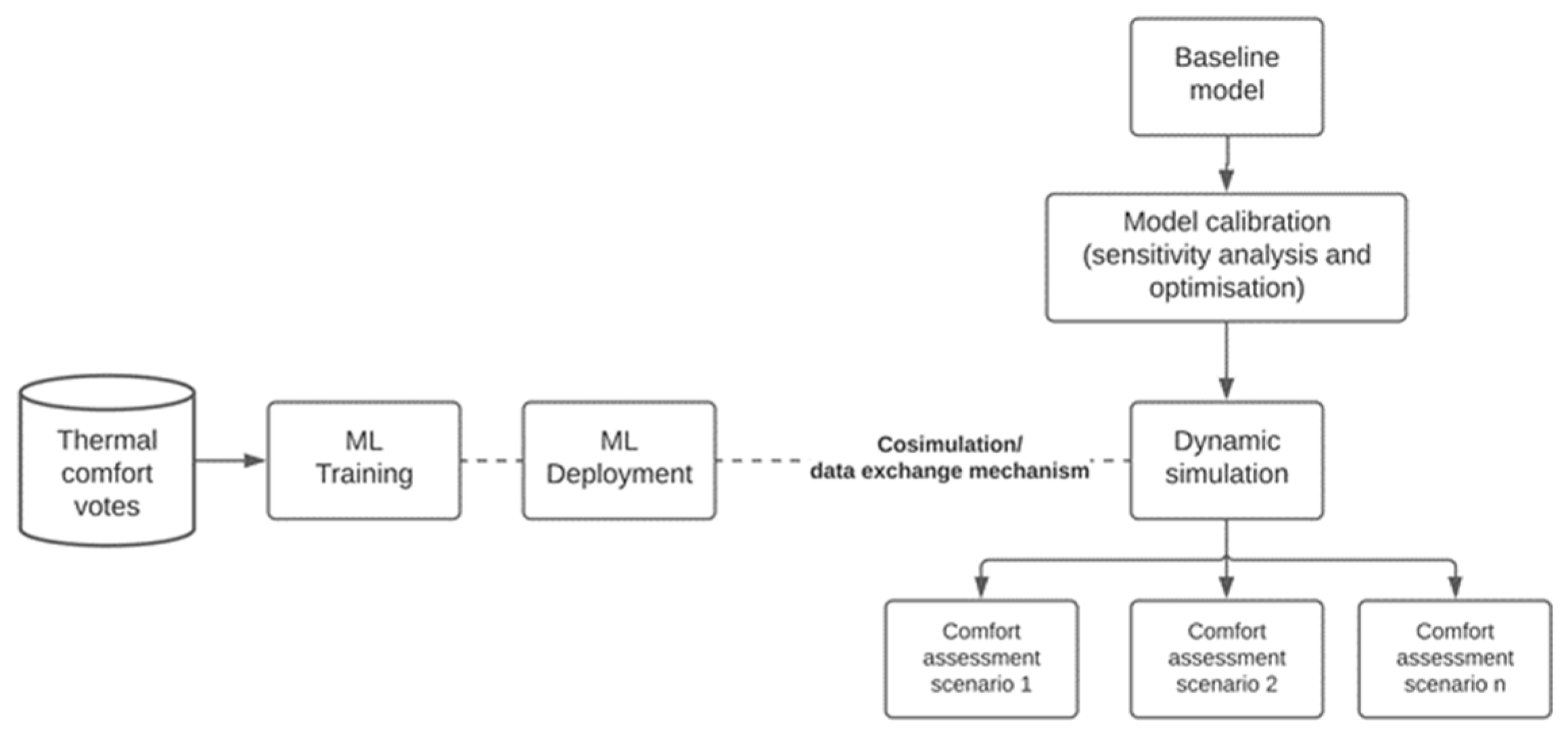
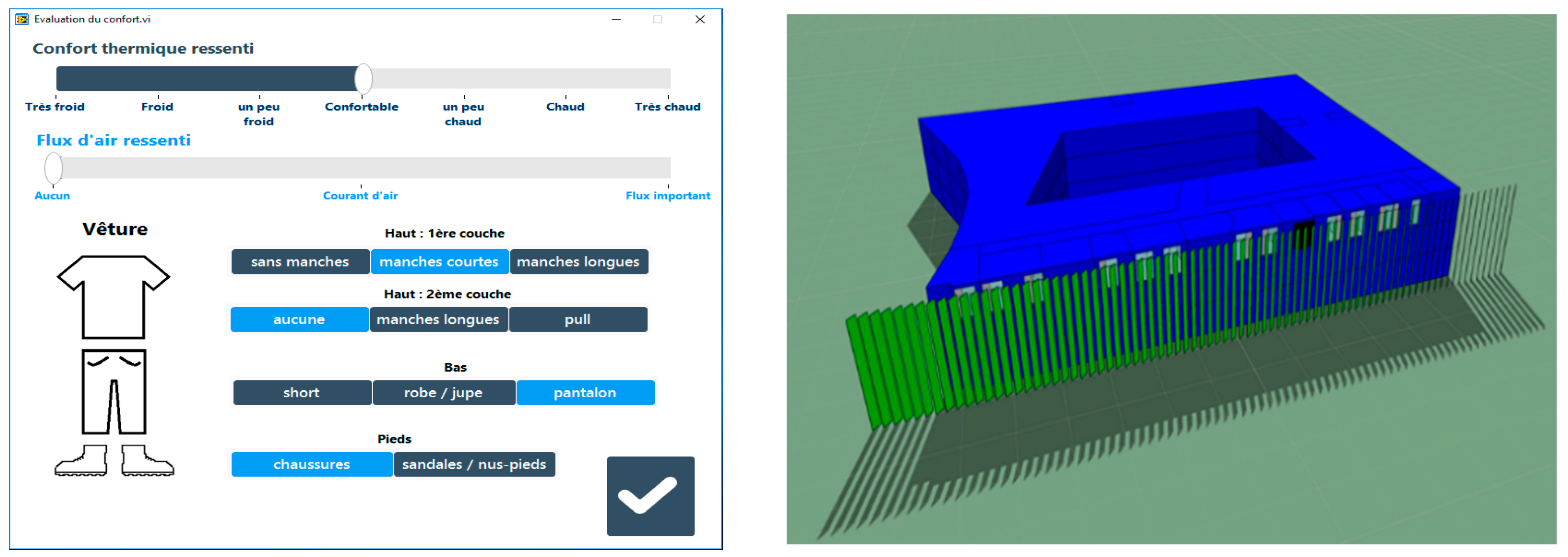
2. Materials and Methods
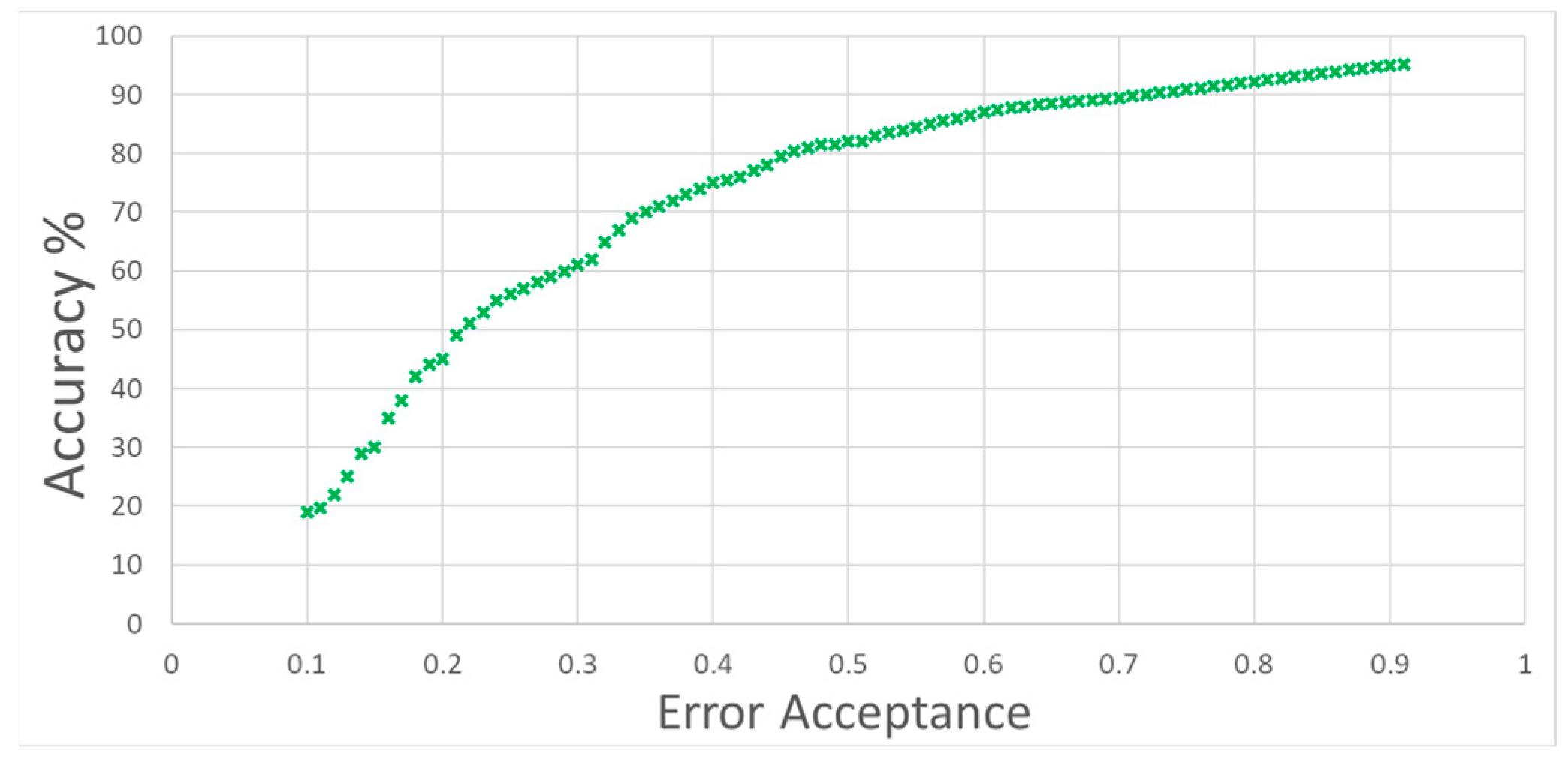
3. Results
4. Discussions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mallawaarachchi, H.; De Silva, L.; Rameezdeen, R. Modelling the relationship between green built environment and occupants’ productivity. Facilities 2017, 35, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.S.; Rohde, L.; Jønsson, K.T.; Rasmussen, B.; Jensen, R.L.; Knudsen, H.N.; Witterseh, T.; Bekö, G. IEQ-Compass—A tool for holistic evaluation of potential indoor environmental quality. Build. Environ. 2020, 172, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sehrawy, R.; Kumar, B. August. Digital twins in architecture, engineering, construction and operations. A brief review and analysis. In International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 924–939. [Google Scholar]
- Enescu, D. A review of thermal comfort models and indicators for indoor environments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 1353–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Xie, J.; Yan, Y.; Ke, Z.; Yu, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Comparing machine learning algorithms in predicting thermal sensation using ASHRAE Comfort Database II. Energy Build. 2020, 210, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aivaliotis, P.; Georgoulias, K.; Arkouli, Z.; Makris, S. Methodology for enabling digital twin using advanced physics-based modelling in predictive maintenance. Procedia CIRP 2019, 81, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinmoghadam, M.; Natephra, W.; Motamedi, A. BIM-and IoT-based virtual reality tool for real-time thermal comfort assessment in building enclosures. Build. Environ. 2021, 199, 107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tardioli, G.; Filho, R.; Bernaud, P.; Ntimos, D. An Innovative Modelling Approach Based on Building Physics and Machine Learning for the Prediction of Indoor Thermal Comfort in an Office Building. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021, 11, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2021011025
Tardioli G, Filho R, Bernaud P, Ntimos D. An Innovative Modelling Approach Based on Building Physics and Machine Learning for the Prediction of Indoor Thermal Comfort in an Office Building. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2021; 11(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2021011025
Chicago/Turabian StyleTardioli, Giovanni, Ricardo Filho, Pierre Bernaud, and Dimitrios Ntimos. 2021. "An Innovative Modelling Approach Based on Building Physics and Machine Learning for the Prediction of Indoor Thermal Comfort in an Office Building" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 11, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2021011025
APA StyleTardioli, G., Filho, R., Bernaud, P., & Ntimos, D. (2021). An Innovative Modelling Approach Based on Building Physics and Machine Learning for the Prediction of Indoor Thermal Comfort in an Office Building. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 11(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2021011025





