Evaluation of Geogenic Enrichment Using Satellite, Geochemical, and Aeromagnetic Data in the Central Anti-Atlas (Morocco): Implications for Soil Enrichment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ▪
- To map hydrothermally altered zones (argillic, phyllic, and propylitic) using ASTER data.
- ▪
- To study the geochemical characteristics of alluvial soils and the level of base metal concentrations in the soil.
- ▪
- To interpret aeromagnetic geophysical data to understand the origins of this enrichment problem in the region.
- ▪
- Assess the occurrence of hydrothermal risk zones through field studies and develop a map showing naturally affected areas to provide in-depth knowledge for identifying potential risks to eco-environmental systems and better preventing the effects of geogenic enrichment.
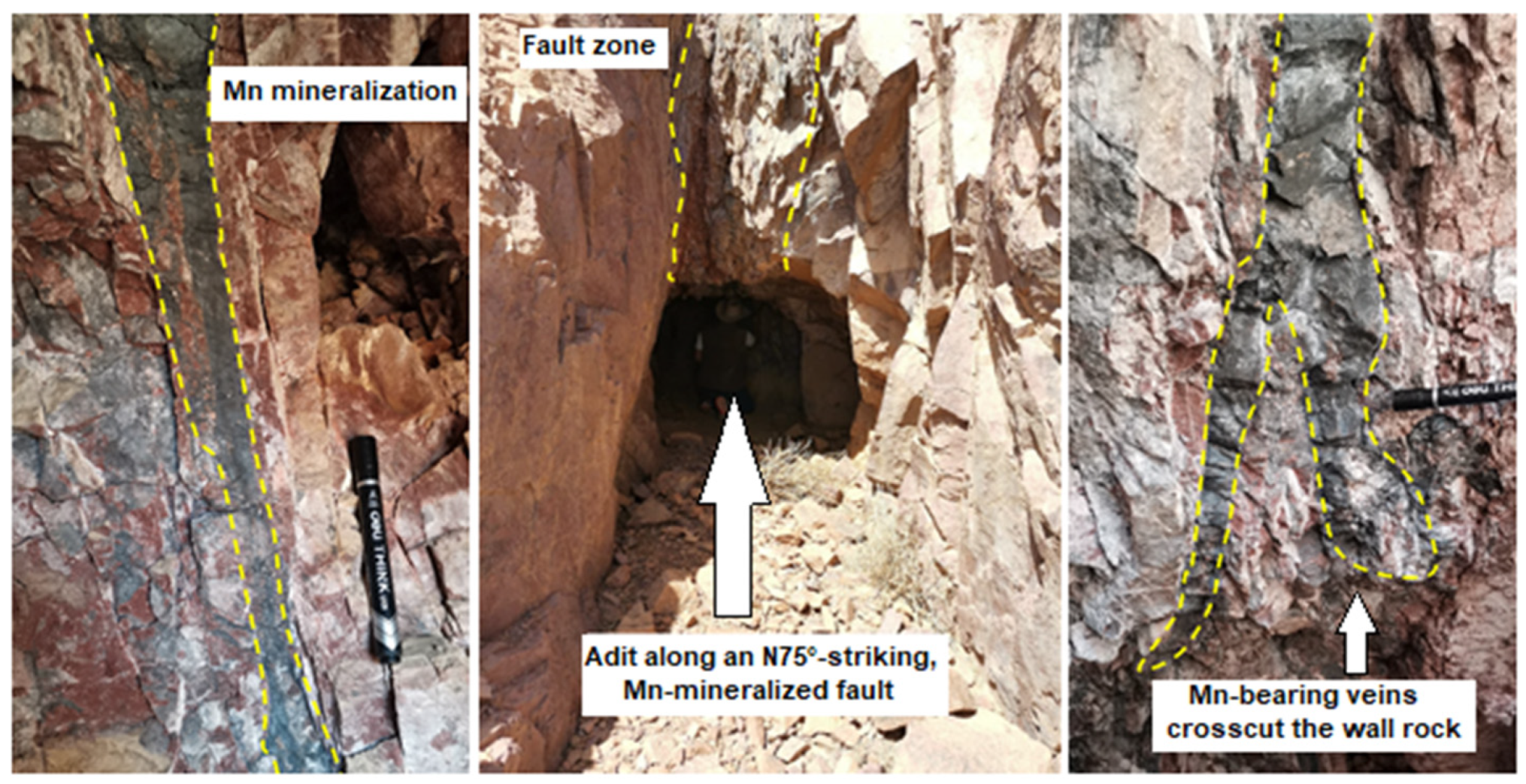
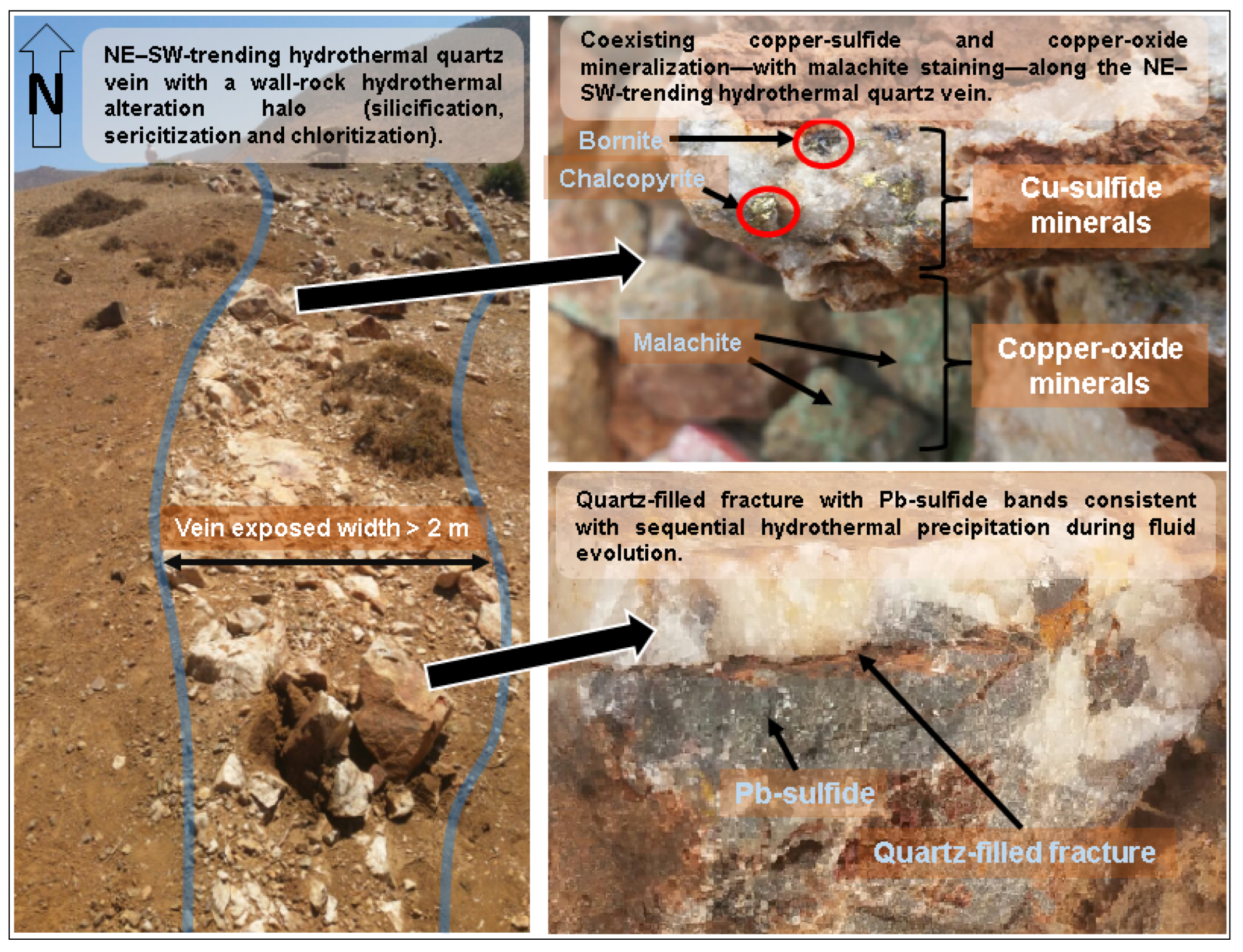
2. Geology of the Oued Iriri Watershed
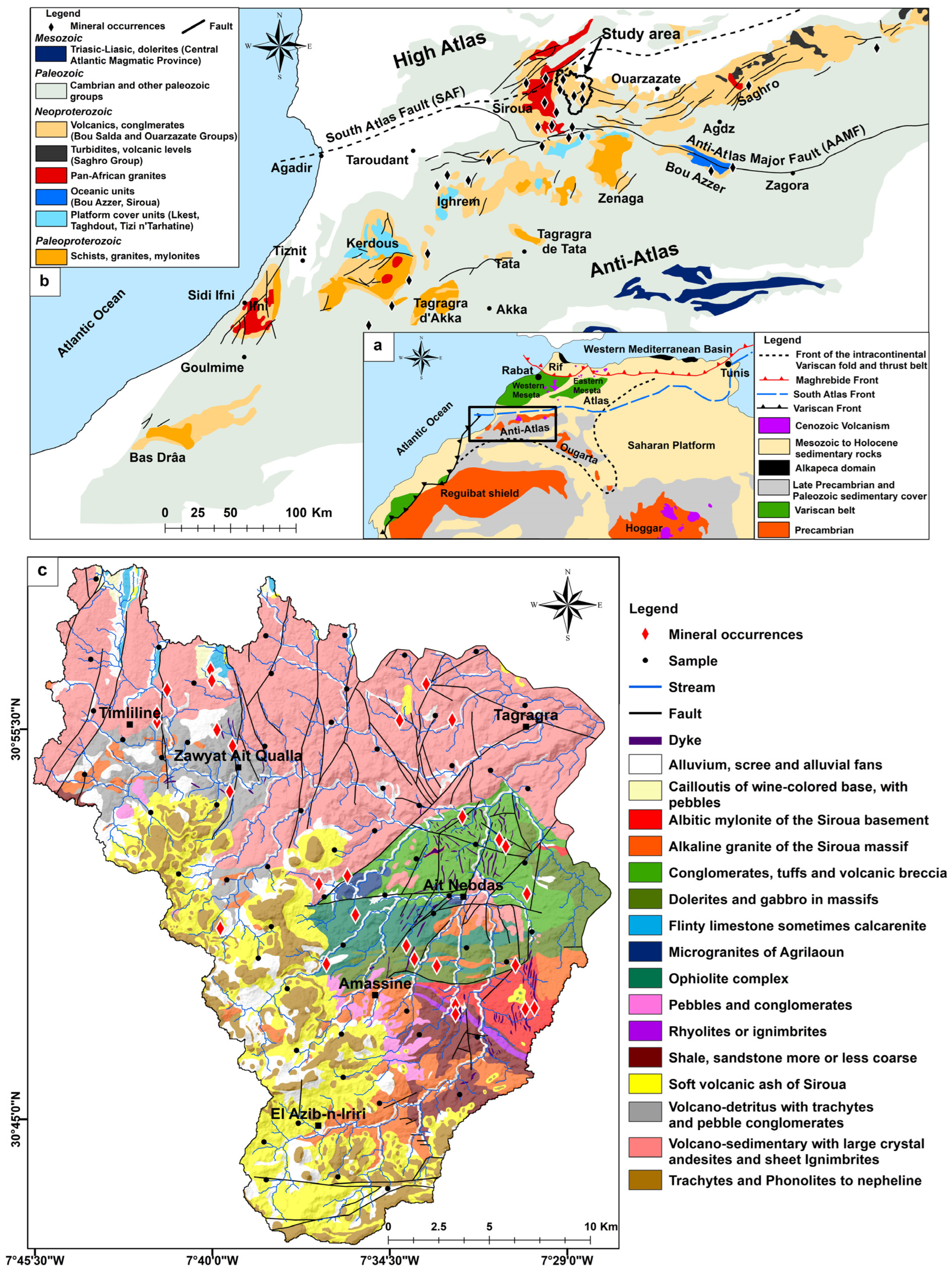
3. Methodology
3.1. Data and Image Processing Methods
3.2. Geochemical Data and Analysis
3.2.1. Sample Collection and Analysis
3.2.2. Data Analysis
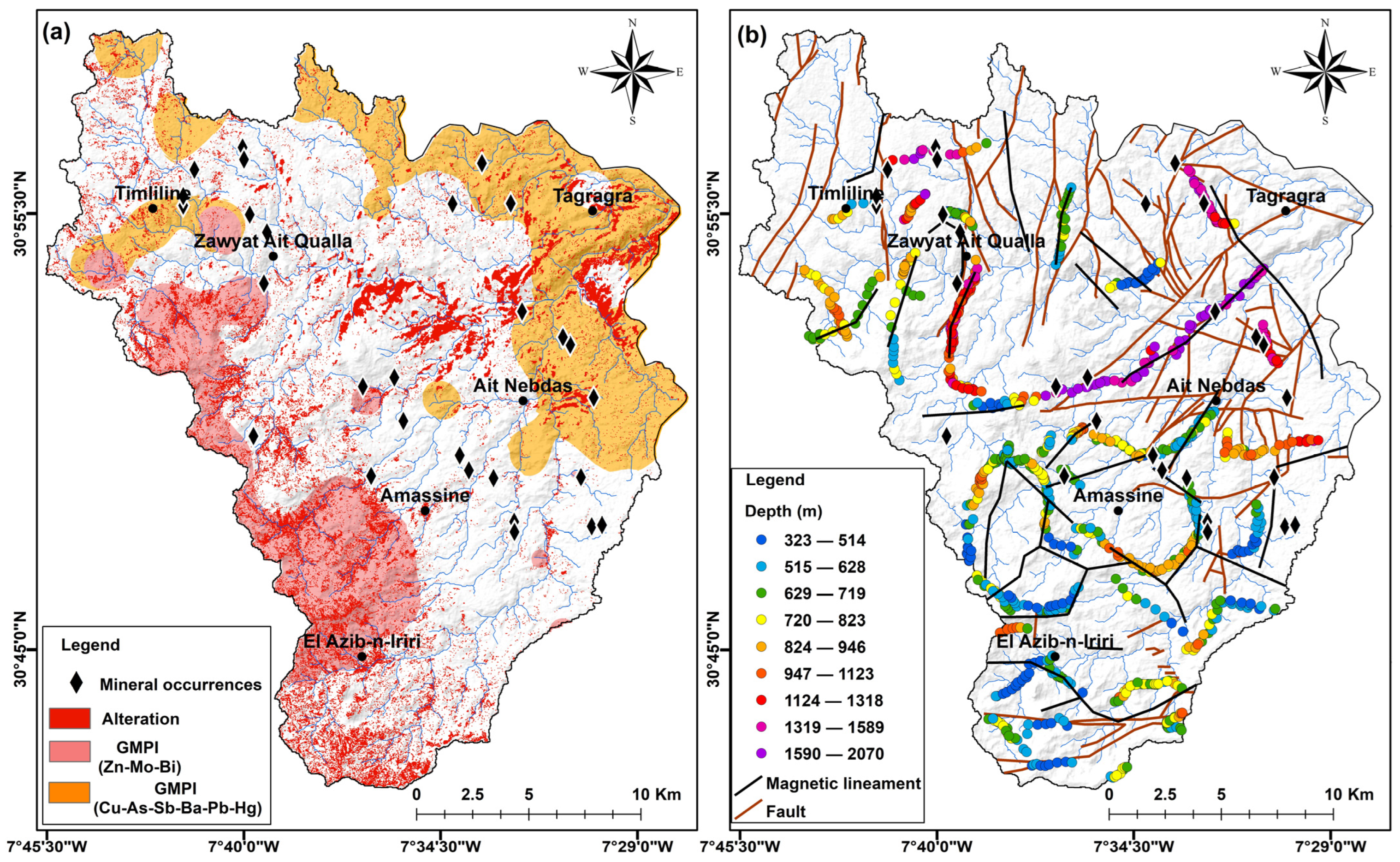
Determination of the Geochemical Mineralization Probability Index (GMPI)
Study of Fractal Discretization of Geochemical Signatures
Evaluation of Geochemical Signatures Using Prediction-Area (P-A) Plots
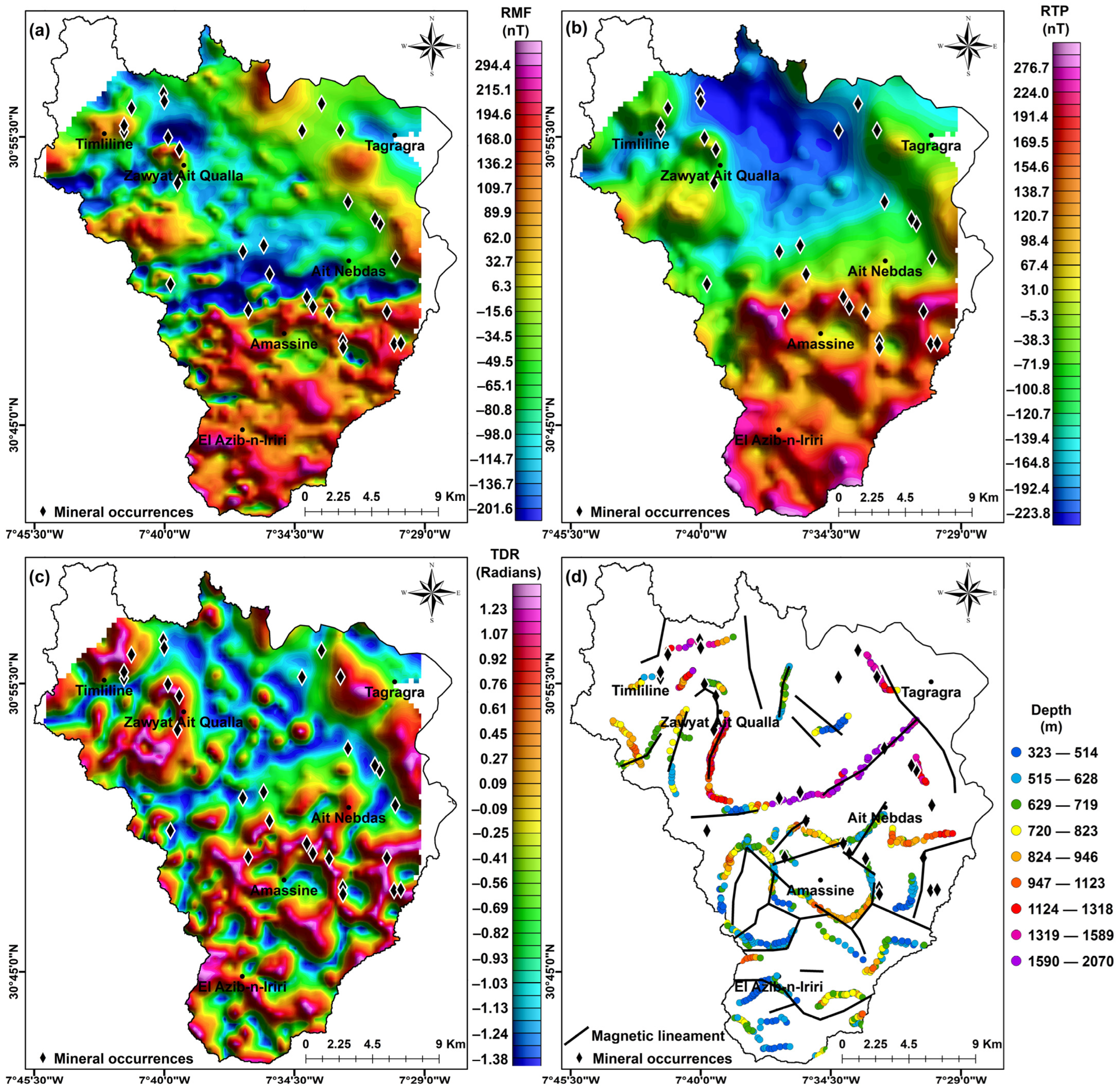
3.3. Aeromagnetic Data and Processing
3.3.1. Aeromagnetic Data
3.3.2. Data Processing
Reduction to the Pole (RTP)
Tilt Derivative Application (TDR)
Depth Estimation via Euler Deconvolution
4. Results
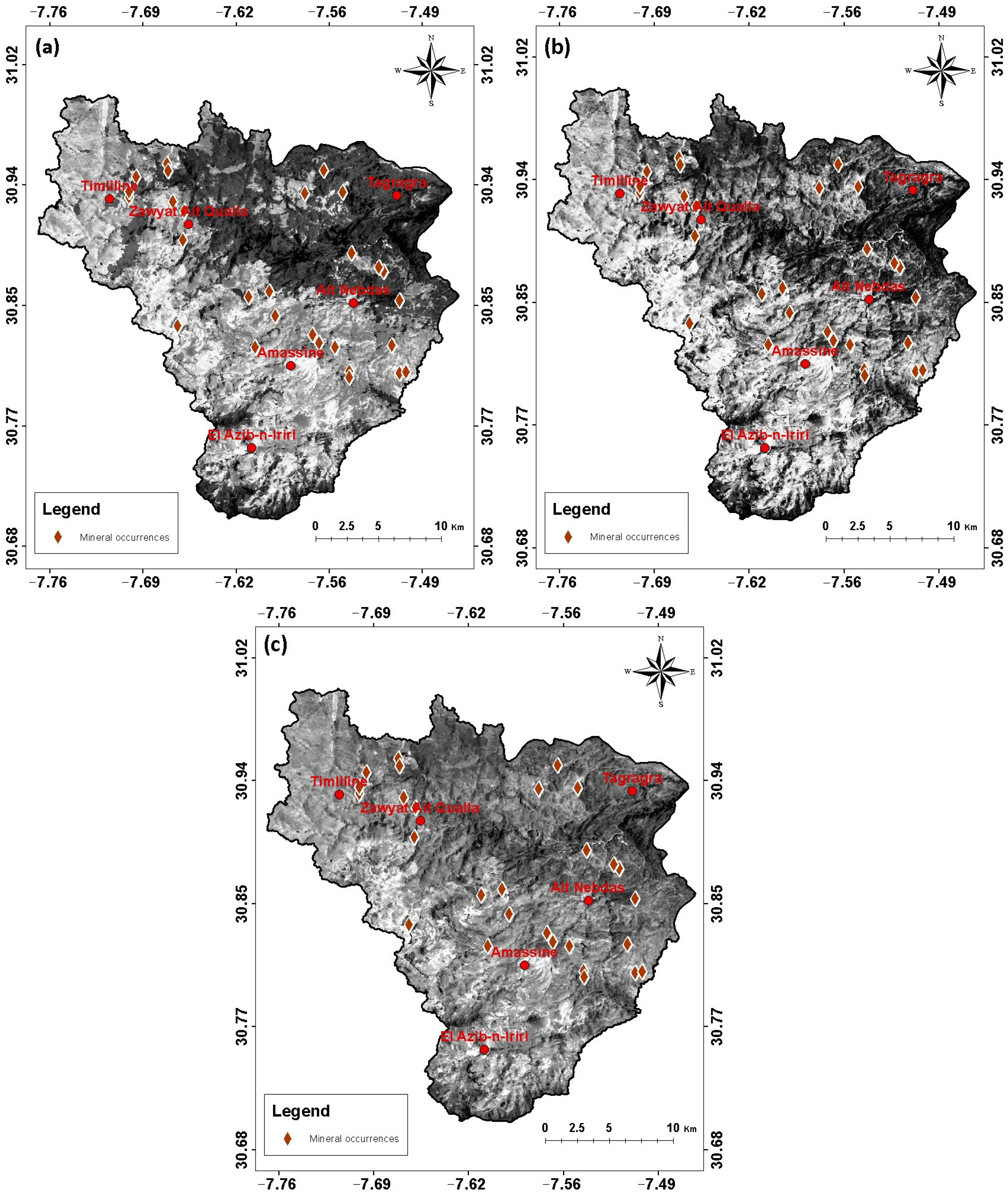
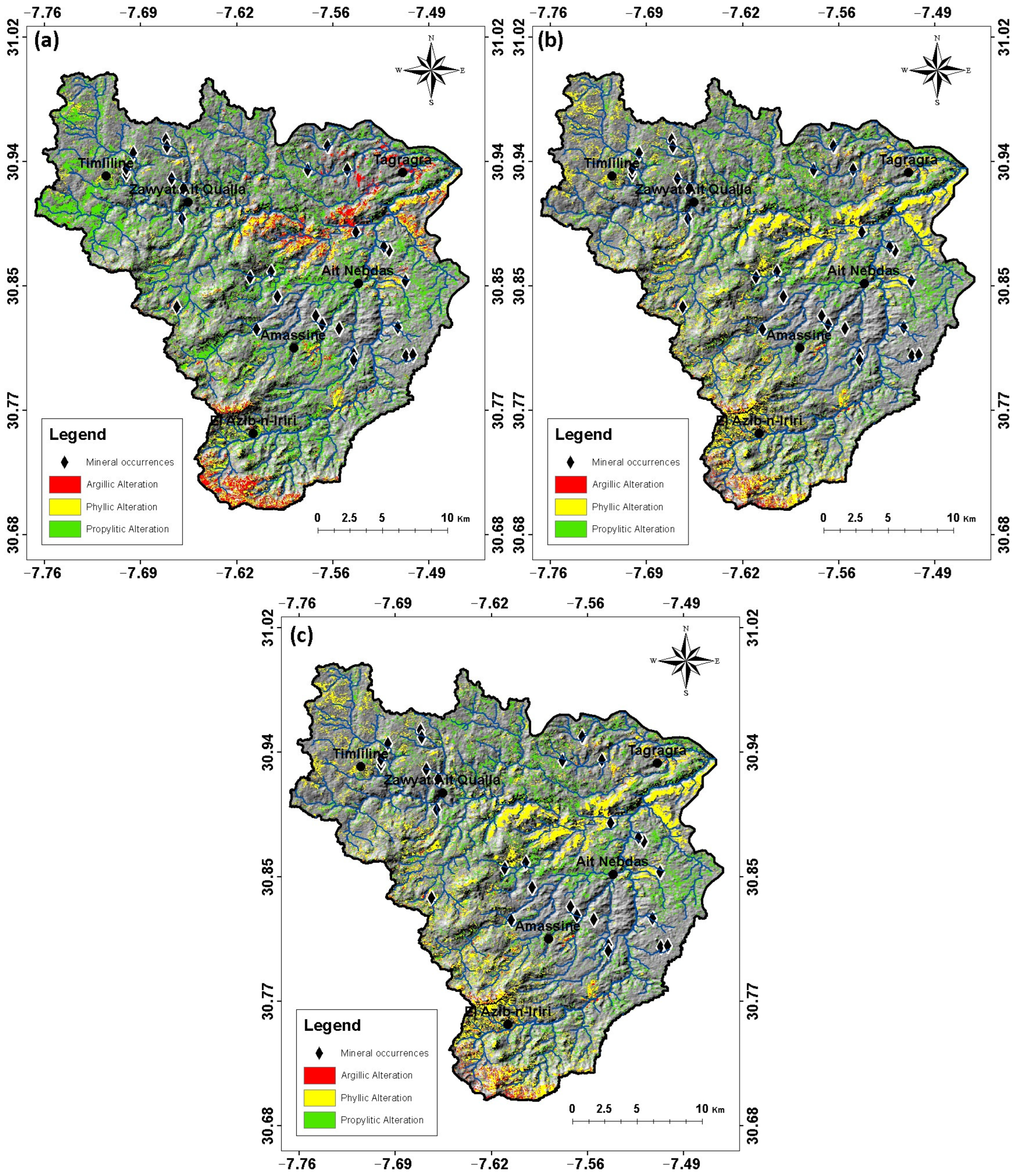
4.1. Mapping of Hydrothermal Alteration Zones and Altered Minerals
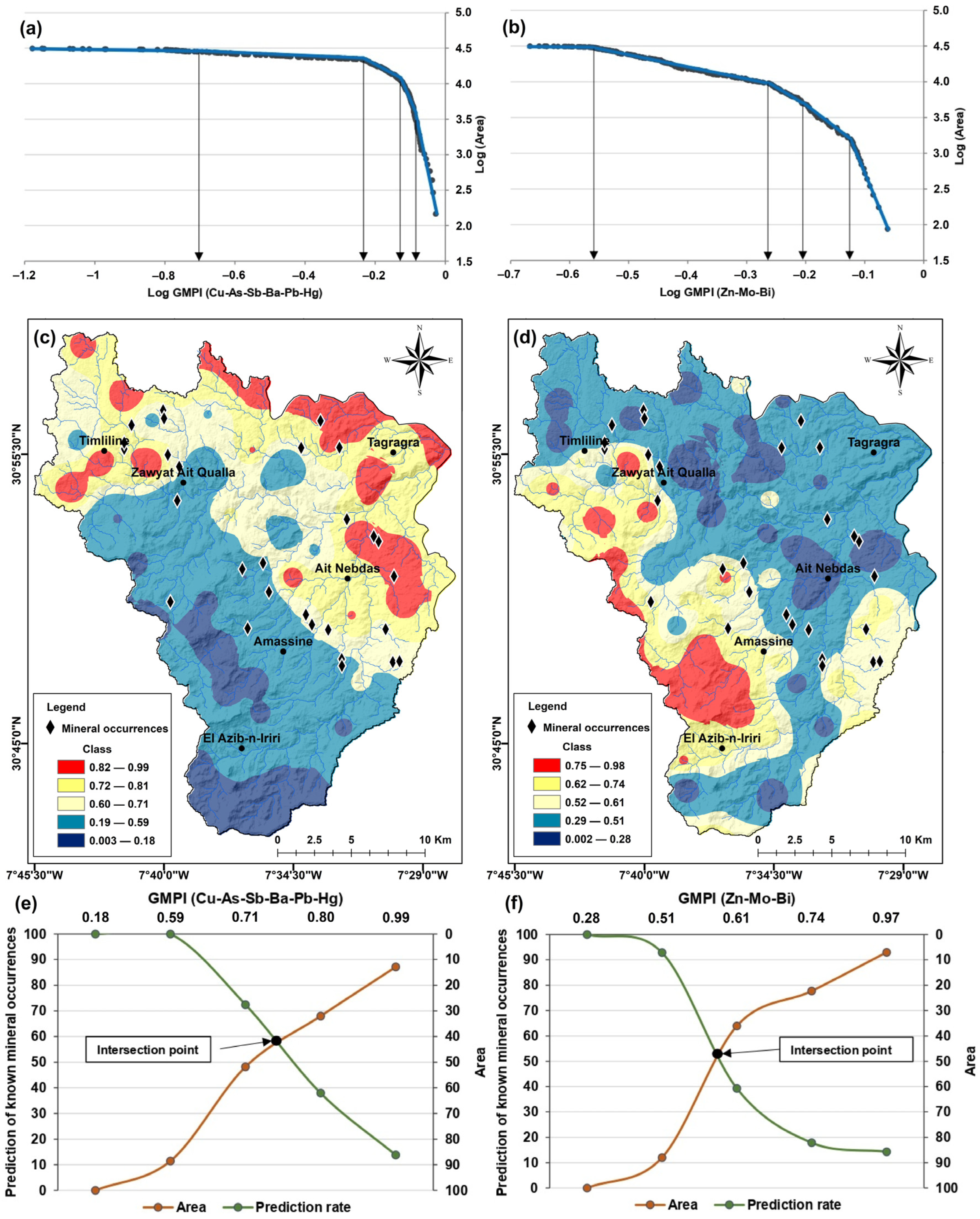
4.2. Geochemical Signature
4.2.1. Element Distribution
4.2.2. Fractal Model for Anomaly Separation
4.3. Analysis of Geophysical Data
5. Discussion
- ▪
- There is a good correlation between residual anomalies, mining indicators, and high enrichment zones, especially for faults with deep rooting. Exceptions to this correlation are found in the indicators located east of the village of Amassine, which show structural rooting at depths less than 500 m.
- ▪
- Although geogenic enrichment indicators and most sulfide minerals exhibit low or antiferromagnetic magnetic susceptibility values, magnetic data effectively detect these high enrichment zones.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramón, F.; Lull, C. Legal measures to prevent and manage soil contamination and to increase food safety for consumer health: The case of Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, L.; Li, H.; Ning, Z. Geogenic pollution, fractionation and potential risks of Cd and Zn in soils from a mountainous region underlain by black shale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiao, W.H.; Chen, L.H.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Song, X.Y.; Wang, H.J. Contributions of climate change and anthropogenic activities to runoff change in the Hongshui River, Southwest China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 191, 012143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.; Mao, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Jin, M.; Zhao, T.; Hoffman, F.M.; Ricciuto, D.M.; Wullschleger, S.D. Human-caused long-term changes in global aridity. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qin, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Jin, G.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhan, Y. The hydrological regime of Taihu Lake under the influence of anthropogenic activities. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 50, 101568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izah, S.C.; Chakrabarty, N.; Srivastav, A.L. A review on heavy metal concentration in potable water sources in Nigeria: Human health effects and mitigating measures. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, E.; Appiah-Adjei, E.K.; Adjei, K.A. Potential heavy metal pollution of soil and water resources from artisanal mining in Kokoteasua, Ghana. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Hameed, A.; Aslam, S.; Ullah, R.; Kashif, A. Phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soils and water in Pakistan: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisabokhae, J.; Alimi, S.; Adeoye, M.; Oresajo, B. Geological structure and hydrothermal alteration mapping for mineral deposit prospectivity using airborne geomagnetic and multispectral data in Zuru Province, northwestern Nigeria. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2023, 26, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olomo, K.O.; Olayanju, G.M.; Bayode, S.; Alagbe, O.A.; Olaleye, O.K. Electrical and electromagnetic geophysical signature associated with geological frame of polymineralic deposit within hydrothermal alteration zones. J. Appl. Geophys. 2024, 222, 105315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Tao, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Su, C.; Yang, W.; Liao, S.; Wang, N. Geology context, vent morphology, and sulfide paragenesis of the Longqi-1 modern seafloor hydrothermal system on the ultraslow-spreading Southwest Indian ridge. Deep-Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2023, 194, 103962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Gao, F.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Z. Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic sludge biochar for tetracycline and ciprofloxacin adsorptive removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.J.; Chevallier, L.P.; Gresse, P.G.; Harmer, R.E.; Eglington, B.M.; Armstrong, R.A.; de Beer, C.H.; Martini, J.E.J.; de Kock, G.S.; Macey, P.H.; et al. Precambrian evolution of the Sirwa window, Anti-Atlas orogen, Morocco. Precambrian Res. 2002, 118, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, S. Spatial distribution, source identification and affecting factors of heavy metals contamination in urban–suburban soils of Lishui city, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chang, Q.; Liu, J.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Kooistra, L. Identification of soil heavy metal sources and improvement in spatial mapping based on soil spectral information: A case study in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Krishan, G.; MacDonald, A.M.; Rao, M.S. Groundwater quality in the alluvial aquifer system of northwest India: New evidence of the extent of anthropogenic and geogenic contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Christakos, G.; Xiao, R.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lv, X. Improved heavy metal mapping and pollution source apportionment in Shanghai City soils using auxiliary information. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpana, L.; Brindha, K.; Elango, L. FIMAR: A new Fluoride Index to Mitigate Geogenic Contamination by Managed Aquifer Recharge. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliqi, E.; Jusufi, K.; Singh, S.K. Assessment and spatial mapping of groundwater quality parameters using metal pollution indices, graphical methods and geoinformatics. Anal. Chem. Lett. 2020, 10, 152–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligate, F.; Ijumulana, J.; Ahmad, A.; Kimambo, V.; Irunde, R.; Mtamba, J.O.; Mtalo, F.; Bhattacharya, P. Groundwater resources in the East African Rift Valley: Understanding the geogenic contamination and water quality challenges in Tanzania. Sci. Afr. 2021, 13, e00831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petermann, E.; Bossew, P. Mapping indoor radon hazard in Germany: The geogenic component. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Song, Z.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, S.; Zhan, Z.W.; He, D. Heavy metal dynamics in riverine mangrove systems: A case study on content, migration, and enrichment in surface sediments, pore water, and plants in Zhanjiang, China. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 203, 106832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcoux, E.; Wadjinny, A. The Ag-Hg Zgounder ore deposit (Jebel Siroua, Anti-Atlas, Morocco): A Neoproterozoic epithermal mineralization of the Imiter type. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2005, 337, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkacim, S.; Ikenne, M.; Souhassou, M.; Elbasbas, A.; Toummite, A. The Cu-Mo ± Au mineralizations associated to the high-K calc-alkaline granitoids from Tifnoute valley (Siroua massif, Anti-Atlas, Morocco): An arc-type porphyry in the Late Neoproterozoic series. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 4, 90–106. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.C.; Flight, D.M.A.; Lister, T.R.; Strutt, M.H. Le Rapport Final Pour les Travaux de Recherches Géologique Pour la Réalisation de Cinq Cartes Géochimiques au 1/100 000 dans le Domaine de l’Anti-Atlas (Maroc); Geological Survey Confidential Internal Report Prepared for the Moroccan Ministry of Mines and Energy; Commissioned Report Series; No. CR/01/031; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2001.
- Ouchchen, M.; Abia, E.H.; Soulaimani, A.; Abioui, M.; Lutz, B.; Benssaou, M.; Abdelrahman, K.; Abu-Alam, T.; Echogdali, F.Z.; Boutaleb, S. The Missing Link in the Genesis of the Lower Paleozoic Copper Deposits of the Anti-Atlas (Morocco): The Late Triassic Central Atlantic Magmatic Province Event. Minerals 2023, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hamzaoui, E.H.; El Baghdadi, M.; Oumenskou, H.; Aadraoui, M.; Hilali, A. Spatial repartition and contamination assessment of heavy metal in agricultural soils of Beni-Moussa, Tadla plain (Morocco). Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 1387–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khalil, H.; El Hamiani, O.; Bitton, G.; Ouazzani, N.; Boularbah, A. Heavy metal contamination from mining sites in South Morocco: Monitoring metal content and toxicity of soil runoff and groundwater. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimouni, Y.; Chafi, A.; Bouabdli, A.; Baghdad, B.; Deliege, J.F. Assessment of Multiple Trace Metal Fluxes in a Semi-Arid Watershed Containing Mine Tailing, Using a Multiple Tool Approach (Zaida Mine, Upper Moulouya Watershed, Morocco). Hydrology 2024, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aouad, N.; Admou, H.; Wafik, A.; Ahmid, H.; Kharis, A.A.; Atif, Y.; Daafi, Y.; Chaib, L. Geology, geochemistry, and geodynamic implications of Ediacaran magmatic rocks of the Zgounder inlier, Siroua window, Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbey, P.; Oberli, F.; Burg, J.P.; Nachit, H.; Pons, J.; Meier, M. The Palaeoproterozoic in western Anti-Atlas (Morocco): A clarification. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 39, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuduri, J. Processus de Formation et Relations Spatio-Temporelles des Minéralisations à or et Argent en Contexte Volcanique Précambrien (Jbel Saghro, Anti-Atlas, Maroc): Implications sur Les Relations Déformation-Magmatisme-Volcanisme-Hydrothermalisme. Doctoral Dissertation, Orléans University, Orléans, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chatir, A.; Berger, J.; Ennih, N.; Triantafyllou, A.; de Parseval, P.; Errami, E.; Boutaleb, M. Formation of the Nkob talc deposit by contact metamorphism and fluid infiltration into siliceous dolostones (Moroccan Anti-Atlas). Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 140, 104629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beer, C.H.; Chevallier, L.P.; De Kock, G.S.; Gresse, P.G.; Thomas, R.J. Notice Explicatif Pour Carte Géologique du Maroc au 1/50 000 Feuille Sirwa; Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique; Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 2000; No. 395. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.J.; Fekkak, A.; Ennih, N.; Errami, E.; Loughlin, S.C.; Gresse, P.G.; Chevallier, L.P.; Liégeois, J.P. A new lithostratigraphic framework for the Anti-Atlas Orogen, Morocco. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 39, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulaimani, A.; Ouanaimi, H.; Saddiqi, O.; Baidder, L.; Michard, A. The Anti-Atlas pan-african belt (Morocco): Overview and pending questions. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2018, 350, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubert, G. Note sur le Précambrien marocain. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. 1945, 221, 249–251. [Google Scholar]
- Choubert, G. L’accident majeur de l’Anti-Atlas. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. 1947, 234, 1172–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Choubert, G. Histoire Géologique de l’Anti-Atlas; Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique du Maroc; Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 1963; 162p. [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc, M.; Lancelot, J.R. Interprétation géodynamique du domaine pan-africain (Précambrien terminal) de l’Anti-Atlas (Maroc) à partir des données géologiques et géochronologiques. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1980, 17, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toummite, A.; Liégeois, J.P.; Gasquet, D.; Bruguier, O.; Beraaouz, E.H.; Ikenne, M. Field, geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotopes of the PanAfrican granitoids from the Tifnoute Valley (Sirwa, Anti-Atlas, Morocco): A post-collisional event in a metacratonic setting. Miner. Petrol. 2012, 107, 739–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouyaté, D.; Söderlund, U.; Youbi, N.; Ernst, R.; Hafid, A.; Ikenne, M.; Soulaimani, A.; Bertrand, H.; El Janati, M.; R’kha Chaham, K. U–Pb baddeleyite and zircon ages of 2040 Ma, 1650 Ma and 885 Ma on dolerites in the West African Craton (Anti-Atlas inliers): Possible links to break-up of Precambrian supercontinents. Lithos 2013, 174, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michard, A.; Frizon de Lamotte, D.; Liégeois, J.P.; Saddiqi, O.; Chalouan, A.; Roure, F. Conclusion: Continental evolution in Western Maghreb. In Continental Evolution: The Geology of Morocco; Michard, A., Saddiqi, O., Chalouan, A., Frizon de Lamotte, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasquet, D.; Ennih, N.; Liégeois, J.P.; Soulaimani, A.; Michard, A. The Pan-African belt. In Continental Evolution: The Geology of Morocco; Michard, A., Saddiqi, O., Chalouan, A., Frizon Lamotte, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 33–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, Y. Étude du Potentiel des Données Satellitaires Pour la Cartographie Géologique; Bibliothèque et Archives Canada: Ottawa, QC, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, M. The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER): Data products for the high spatial resolution imager on NASA’s Terra platform. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, Y. A stabilized vegetation index and several mineralogic indices defined for ASTER VNIR and SWIR data. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2003 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS’03), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1552–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Mars, J.C.; Rowan, L.C. Regional mapping of phyllic-and argillic-altered rocks in the Zagros magmatic arc, Iran, using Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) data and logical operator algorithms. Geosphere 2006, 2, 161–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tommaso, I.; Rubinstein, N. Hydrothermal alteration mapping using ASTER data in the Infiernillo porphyry deposit, Argentina. Ore Geol. Rev. 2007, 32, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, J.C.; Rowan, L.C. ASTER spectral analysis and lithologic mapping of the Khanneshin carbonatite volcano, Afghanistan. Geosphere 2011, 7, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, H. Application of spectral analysis in mapping hydrothermal alteration of the Northwestern Part of the Kerman Cenozoic Magmatic Arc, Iran. J. Sci. Islam. Repub. Iran 2011, 22, 221–238. [Google Scholar]
- Shahriari, H.; Honarmand, M.; Ranjbar, H. Comparison of multi-temporal ASTER images for hydrothermal alteration mapping using a fractal-aided SAM method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 1271–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, H.; Ranjbar, H.; Honarmand, M. Image segmentation for hydrothermal alteration mapping using PCA and concentration–area fractal model. Nat. Resour. Res. 2013, 22, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.J.; Ranjbar, H.; Alirezaei, S.; Dargahi, S.; Lentz, D.R. Comparison of hydrothermal alteration patterns associated with porphyry Cu deposits hosted by granitoids and intermediate-mafic volcanic rocks, Kerman Magmatic Arc, Iran: Application of geological, mineralogical and remote sensing data. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 142, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Lian, C.; Huntington, J.F.; Peng, Q.; Wang, Q. Infrared spectral reflectance characterization of the hydrothermal alteration at the Tuwu Cu–Au deposit, Xinjiang, China. Miner. Depos. 2005, 40, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beygi, S.; Talovina, I.V.; Tadayon, M.; Pour, A.B. Alteration and structural features mapping in Kacho-Mesqal zone, Central Iran using ASTER remote sensing data for porphyry copper exploration. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2021, 12, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.R. Spectral signatures of particulate minerals in the visible and near infrared. Geophysics 1977, 42, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.R.; Ashley, R.P. Spectra of altered rocks in the visible and near infrared. Econ. Geol. 1979, 74, 1613–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, M.H.; Tangestani, M.H.; Roldan, F.V.; Yusta, I. Spectral characteristics of minerals in alteration zones associated with porphyry copper deposits in the middle part of Kerman copper belt, SE Iran. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 62, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Nasir, S. Characterization of ASTER spectral bands for mapping of alteration zones of volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 88, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, A.; Guisseau, D.; Patrier Mas, P.; Beaufort, D.; Genter, A.; Sanjuan, B.; Girard, J.P. Clay minerals related to the hydrothermal activity of the Bouillante geothermal field (Guadeloupe). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2016, 158, 380–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molan, Y.E.; Refahi, D.; Tarashti, A.H. Mineral mapping in the Maherabad area, eastern Iran, using the HyMap remote sensing data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 27, 17–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, L.C.; Wilkinson, J.J.; Mason, P.J.; Chang, Z. Spectral characteristics of propylitic alteration minerals as a vectoring tool for porphyry copper deposits. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.J.; Hook, S.; Abrams, M.C. Imaging Spectrometry in the Thermal Infrared. In Imaging Spectrometry; Meer, F.D.V., Jong, S.M.D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2002; pp. 283–306. [Google Scholar]
- Rowan, L.C.; Hook, S.J.; Abrams, M.J.; Mars, J.C. Mapping hydrothermally altered rocks at Cuprite, Nevada, using the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER), a new satellite-imaging system. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, L.C.; Mars, J.C. Lithologic mapping in the Mountain Pass, California area using Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.; Hook, S.J. Simulated ASTER data for geologic studies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusky, T.M.; Ramadan, T.M. Structural controls on Neoproterozoic mineralization in the South Eastern Desert, Egypt: An integrated field, Landsat TM, and SIR-C/X SAR approach. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2002, 35, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, S.; Ghulam, A.; Kusky, T. Detecting areas of high-potential gold mineralization using ASTER data. Ore Geol. Rev. 2010, 38, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Mathew, G. Lithological discrimination of the Phenaimata felsic–mafic complex, Gujarat, India, using the advanced Spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer (ASTER). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 198–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdikhani, B.; Imamalipour, A. ASTER-based remote sensing image analysis for prospection criteria of podiform chromite at the Khoy ophiolite (NW Iran). Minerals 2021, 11, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughlin, W.P. Principal component analysis for alteration mapping. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1991, 57, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Pour, A.B.; Hashim, M. Identification of hydrothermal alteration minerals for exploring of porphyry copper deposit using ASTER data, SE Iran. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 42, 1309–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, K. Identification of hydrothermal alteration zones of the Baogutu porphyry copper deposits in northwest China using ASTER data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 015016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A.; Lefkoff, A.B.; Boardman, J.W.; Heidebrecht, K.B.; Shapiro, A.T.; Barloon, P.J.; Goetz, A.F.H. The spectral image processing system (SIPS)—Interactive visualization and analysis of imaging spectrometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 44, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, J.A.; Gomez, R. Mapping impervious surface type and sub-pixel abundance using hyperion hyperspectral imagery. Geocarto Int. 2005, 20, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinjani, M.; Tangestani, M.H. Mapping alteration minerals using sub-pixel unmixing of ASTER data in the Sarduiyeh area, SE Kerman, Iran. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2011, 4, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzied, S.M.; Ibrahim, S.K.; Kaiser, M.F.; Seleem, T.A. Application of remote sensing and spatial data integrations for mapping porphyry copper zones in Nuweiba area, Egypt. Int. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2016, 4, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magendran, T.; Sanjeevi, S. Hyperion image analysis and linear spectral unmixing to evaluate the grades of iron ores in parts of Noamundi, Eastern India. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, H.; Rostami Paydar, G.; Feizizadeh, B.; Blaschke, T.; Pour, A.B.; Valizadeh Kamran, K.; Hossain, M.S. Fusion of ASTER satellite imagery, geochemical and geology data for gold prospecting in the Astaneh granite intrusive, West Central Iran. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2021, 13, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarpour, A.; Paydar, G.R.; Mehregan, F.; Hejazi, S.J.; Jafari, M.A. Application of geographically weighted regression (GWR) and singularity analysis to identify stream sediment geochemical anomalies, case study, Takab Area, NW Iran. J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 235, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, P.; Mirzaei, M.; Yousefi, M.; Adib, A.; Khalajmasoumi, M.; Zarifi, A.Z.; Foster, P.; Yasrebi, A.B. Delineation of geochemical anomalies based on stream sediment data utilizing fractal modeling and staged factor analysis. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 119, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P. Normal and lognormal data distribution in geochemistry: Death of a myth. Consequences of geochemical and environmental data. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza, E.J.M. Analysis and mapping of geochemical anomalies using logratio transformed stream sediment data with censored values. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 110, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filzmoser, P.; Hron, K.; Reimann, C. Univariate statistical analysis of environmental (compositional) data: Problems and possibilities. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 6100–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Agterberg, F.P.; Ballantyne, S.B. The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods. J. Geochem. Explor. 1994, 51, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filzmoser, P.; Hron, K.; Reimann, C. Principal components analysis for compositional data with outliers. Environmetrics 2009, 20, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. The varimax criteria for analytical rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika 1958, 23, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Kamkar-Rouhani, A.; Carranza, E.J.M. Geochemical mineralization probability index (GMPI): A new approach to generate enhanced stream sediment geochemical evidential map for increasing probability of success in mineral potential mapping. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 115, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Kamkar-Rouhani, A.; Carranza, E.J.M. Application of staged factor analysis and logistic function to create a fuzzy stream sediment geochemical evidence layer for mineral prospectivity mapping. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2014, 14, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borojerdnia, A.; Rozbahani, M.M.; Nazarpour, A.; Ghanavati, N.; Payandeh, K. Application of exploratory and Spatial Data Analysis (SDA), singularity matrix analysis, and fractal models to delineate background of potentially toxic elements: A case study of Ahvaz, SW Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, M.; Maghsoudi, A.; Yousefi, M.; Sadeghi, M. Prospectivity modeling of porphyry-Cu deposits by identification and integration of efficient mono-elemental geochemical signatures. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 114, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Xu, Y.; Grunsky, E. Integrated spatial and spectral analysis for geochemical anomaly separation. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Conference of the International Association for Mathematical Geology, Trondheim, Norway, 6–11 August 1999; pp. 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Agterberg, F.P. Multifractal modeling of the sizes and grades of giant and supergiant deposits. Int. Geol. Rev. 1995, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, T.; Shi, J. Application of a fractal method relating concentrations and distances for separation of geochemical anomalies from background. J. Geochem. Explor. 2003, 77, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agterberg, F.P.; Bonham-Carter, G.F. Measuring the performance of mineral-potential maps. Nat. Resour. Res. 2005, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porwal, A.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Hale, M. A hybrid d fuzzy weights-of-evidence model for mineral potential mapping. Nat. Resour. Res. 2006, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Carranza, E.J.M. Prediction–area (P–A) plot and C–A fractal analysis to classify and evaluate evidential maps for mineral prospectivity modeling. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 79, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalasky, M.J.; Bonham-Carter, G.F. Lithodiversity and its spatial association with metallic mineral sites, Great Basin of Nevada. Nat. Resour. Res. 2001, 10, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, V. A new method for interpretation of aeromagnetic maps: Pseudo-gravimetric anomalies. Geophysics 1957, 22, 359–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissie, Z.; Mickus, K.; Bridges, D.; Abdelsalam, M.G.; Atekwana, E. Upper lithospheric structure of the Dobi graben, Afar Depression from magnetics and gravity data. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 147, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.; Williams, S.; Fairhead, J.D.; Ravat, D.; Smith, R. Tilt-depth method: A simple depth estimation method using first-order magnetic derivatives. Lead. Edge 2007, 26, 1502–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.T. EULDPH: A new technique for making computer-assisted depth estimates from magnetic data. Geophysics 1982, 47, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.B.; Allsop, J.M.; Granser, H.; Millett, A.J.; Somerton, I.W. Magnetic interpretation in three dimensions using Euler deconvolution. Geophysics 1990, 55, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siljestrom, P.; Moreno, A.; Vikgren, K.; Cáceres Puro, L. The application of selective principal components analysis (SPCA) to a Thematic Mapper (TM) image for the recognition of geomorphologic configuration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 3843–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, M.G.; Stern, R.J.; Berhane, W.G. Mapping gossan in arid regions with Landsat TM and SIR-C images, the Beddaho Alteration Zone in northern Eritrea. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2000, 30, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, L.C.; Robert, G.S.; John, C. Distribution of hydrothermally altered rocks in the Peko Diq, Pakistan mineralized area based on spectral analysis of ASTER data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, L.; Pour, A.; Askari, G.; Taghipour, N.; Pradhan, B.; Lee, C.W.; Honarmand, M. Comparison of different algorithms to map hydrothermal alteration zones using ASTER remote sensing data for polymetallic vein-type ore exploration: Toroud–Chahshirin Magmatic Belt (TCMB), North Iran. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Nasir, S.; Kusky, T.M.; Ghulam, A.; Gabr, S.; El-Ghali, M.A. Detection of hydrothermal mineralized zones associated with listwaenites in Central Oman using ASTER data. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 53, 470–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Nasir, S. Hydrothermal altered serpentinized zone and a study of Ni-magnesioferrite–magnetite–awaruite occurrences in Wadi Hibi, Northern Oman Mountain: Discrimination through ASTER mapping. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 62, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Nasir, S. Mapping of high pressure metamorphics in the As Sifah region, NE Oman using ASTER data. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 1134–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Vinod Kumar, K. Comparative analysis on utilisation of linear spectral unmixing and band ratio methods for processing ASTER data to delineate bauxite over a part of Chotonagpur plateau, Jharkhand, India. Geocarto Int. 2016, 31, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helvoort, P.J.; Filzmoser, P.; Gaans, P.F.M. Sequential Factor Analysis as a new approach to multivariate analysis of heterogeneous geochemical datasets: An application to a bulk chemical characterization of fluvial deposits (Rhine–Meuse delta, The Netherlands). Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 2233–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezelbash, R.; Maghsoudi, A.; Carranza, E.J.M. An improved data-driven multiple criteria decision making procedure for spatial modeling of mineral prospectivity: Adaption of prediction–area plot and logistic functions. Nat. Resour. Res. 2019, 28, 1299–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.; Williams, S.; Fairhead, D.; Smith, R.; Ravat, D. Interpretation of magnetic data using tilt-angle derivatives. Geophysics 2008, 73, L1–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.T.; Eldosouky, A.M.; Abdelrahman, K.; Fnais, M.S.; Gomez-Ortiz, D.; Khedr, F. Application of the improved parabola-based method in delineating lineaments of subsurface structures: A case study. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.T.; Oksum, E.; Vu, M.D.; Vo, Q.T.; Du Le-Viet, K.; Eldosouky, A.M. An improved approach for detecting ridge locations to interpret the potential field data for more accurate structural mapping: A case study from Vredefort dome area (South Africa). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 175, 104099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, J.R.; Blenkinsop, T.G. The Cloncurry Lineament: Geophysical and geological evidence for a deep crustal structure in the Eastern Succession of the Mount Isa Inlier. Precambrian Res. 2008, 163, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, J.R.; Blenkinsop, T.G. Local to regional scale structural controls on mineralisation and the importance of a major lineament in the eastern Mount Isa Inlier, Australia: Review and analysis with autocorrelation and weights of evidence. Ore Geol. Rev. 2009, 35, 298–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, P.A.; Blewett, R.S.; Roy, I.G.; Miller, J.M.; Czarnota, K. 4D architecture and tectonic evolution of the Laverton region, eastern Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Precambrian Res. 2010, 183, 338–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Hashim, M. Identifying areas of high economic-potential copper mineralization using ASTER data in the Urumieh–Dokhtar Volcanic Belt, Iran. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, L. Quantifying hydrothermal alteration: A review of methods. Geosciences 2018, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, A.; Nazarpour, A.; Ghanavati, N.; Babainejad, T.; Watts, M.J. An integrated approach for spatial distribution of potentially toxic elements (Cu, Pb and Zn) in topsoil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golabkesh, F.; Ghanavati, N.; Nazarpour, A.; Nejad, T.B. Monitoring Soil Salinity Changes, Comparison of Different Maps and Indices Extracted from Landsat Satellite Images (Case Study: Atabieh, Khuzestan). Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 1139–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Shi, H.; Miao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, X.; Li, Z.; Pan, M.; Feng, W.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Duarte, I.M. Evolution of chemical characteristics and irrigation suitability of groundwater in arid and semi-arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 311, 109361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dong, P.; Yan, J.; Gong, R.; Meng, Q.; Yao, J.; Xie, R. Analytical study on heavy metal output fluxes and source apportionment of a non-ferrous smelter in southwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 331, 121867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essarraj, S.; Boiron, M.C.; Cathelineau, M.; Banks, D.A.; El Boukhari, A.; Chouhaidi, M.Y. Brines related to Ag deposition in the Zgounder silver deposit (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Eur. J. Mineral. 1998, 10, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, L.A. Geophysical Characteristics of Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits; Report 2010–5070–C; U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; 16p.





| a | SPC1 | SPC2 | SPC3 |
| Band 4 | −0.13655 | −0.12307 | −0.06399 |
| Band 5 | 0.58030 | −0.07095 | 0.01265 |
| Band 6 | −0.41620 | 0.70393 | −0.04989 |
| b | SPC1 | SPC2 | SPC3 |
| Band 4 | −0.13655 | −0.06399 | 0.94242 |
| Band 6 | −0.41620 | −0.04989 | 0.04350 |
| Band 7 | 0.38082 | 0.02632 | 0.09839 |
| c | SPC1 | SPC2 | SPC3 |
| Band 7 | 0.09839 | 0.00657 | −0.00194 |
| Band 8 | 0.19268 | 0.02541 | 0.00147 |
| Band 9 | 0.07720 | 0.01386 | 0.00256 |
| Cu | Ba | As | Hg | Sb | Mo | Pb | Bi | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Max | 143.6 | 52,630 | 652.8 | 373 | 37.9 | 44.9 | 24,600 | 126.6 | 1451 |
| Average | 38.09322 | 2339.166 | 70.33136 | 43.03333 | 7.373833 | 13.92167 | 523.9155 | 6.157167 | 411.6483 |
| Median | 29.1 | 532.7 | 46 | 18.5 | 2.35 | 10.1 | 33.75 | 3.17 | 190.95 |
| Elements | F1 | F2 | F3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0.760 | 0.152 | −0.202 |
| Zn | −0.118 | 0.887 | 0.049 |
| As | 0.919 | −0.177 | 0.070 |
| Mo | 0.068 | 0.912 | 0.011 |
| Sb | 0.665 | −0.235 | 0.632 |
| Ba | 0.742 | 0.066 | −0.536 |
| Pb | 0.821 | 0.245 | −0.033 |
| Bi | 0.104 | 0.826 | 0.235 |
| Hg | 0.728 | −0.121 | 0.103 |
| Eigenvalues | 3.650 | 2.490 | 0.802 |
| Variance (%) | 40.551 | 27.670 | 8.916 |
| Cumulative variance (%) | 40.551 | 68.221 | 77.138 |
| Model | Prediction Rate (Pr) (%) | Occupied Area (Oa) (%) | Normalized Density (Nd) | Weight (We) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMPI (Cu-As-Sb-Ba-Pb-Hg) | 59 | 41 | 1.44 | 0.36 |
| GMPI (Zn-Mo-Bi) | 53 | 47 | 1.13 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Id-Belqas, M.; Boutaleb, S.; Echogdali, F.Z.; Ikirri, M.; El Ayady, H.; Abioui, M. Evaluation of Geogenic Enrichment Using Satellite, Geochemical, and Aeromagnetic Data in the Central Anti-Atlas (Morocco): Implications for Soil Enrichment. Earth 2025, 6, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040113
Id-Belqas M, Boutaleb S, Echogdali FZ, Ikirri M, El Ayady H, Abioui M. Evaluation of Geogenic Enrichment Using Satellite, Geochemical, and Aeromagnetic Data in the Central Anti-Atlas (Morocco): Implications for Soil Enrichment. Earth. 2025; 6(4):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040113
Chicago/Turabian StyleId-Belqas, Mouna, Said Boutaleb, Fatima Zahra Echogdali, Mustapha Ikirri, Hasna El Ayady, and Mohamed Abioui. 2025. "Evaluation of Geogenic Enrichment Using Satellite, Geochemical, and Aeromagnetic Data in the Central Anti-Atlas (Morocco): Implications for Soil Enrichment" Earth 6, no. 4: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040113
APA StyleId-Belqas, M., Boutaleb, S., Echogdali, F. Z., Ikirri, M., El Ayady, H., & Abioui, M. (2025). Evaluation of Geogenic Enrichment Using Satellite, Geochemical, and Aeromagnetic Data in the Central Anti-Atlas (Morocco): Implications for Soil Enrichment. Earth, 6(4), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040113







