Changes in Timing and Precipitation of the East Asian Summer Monsoon over China Between 1960 and 2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
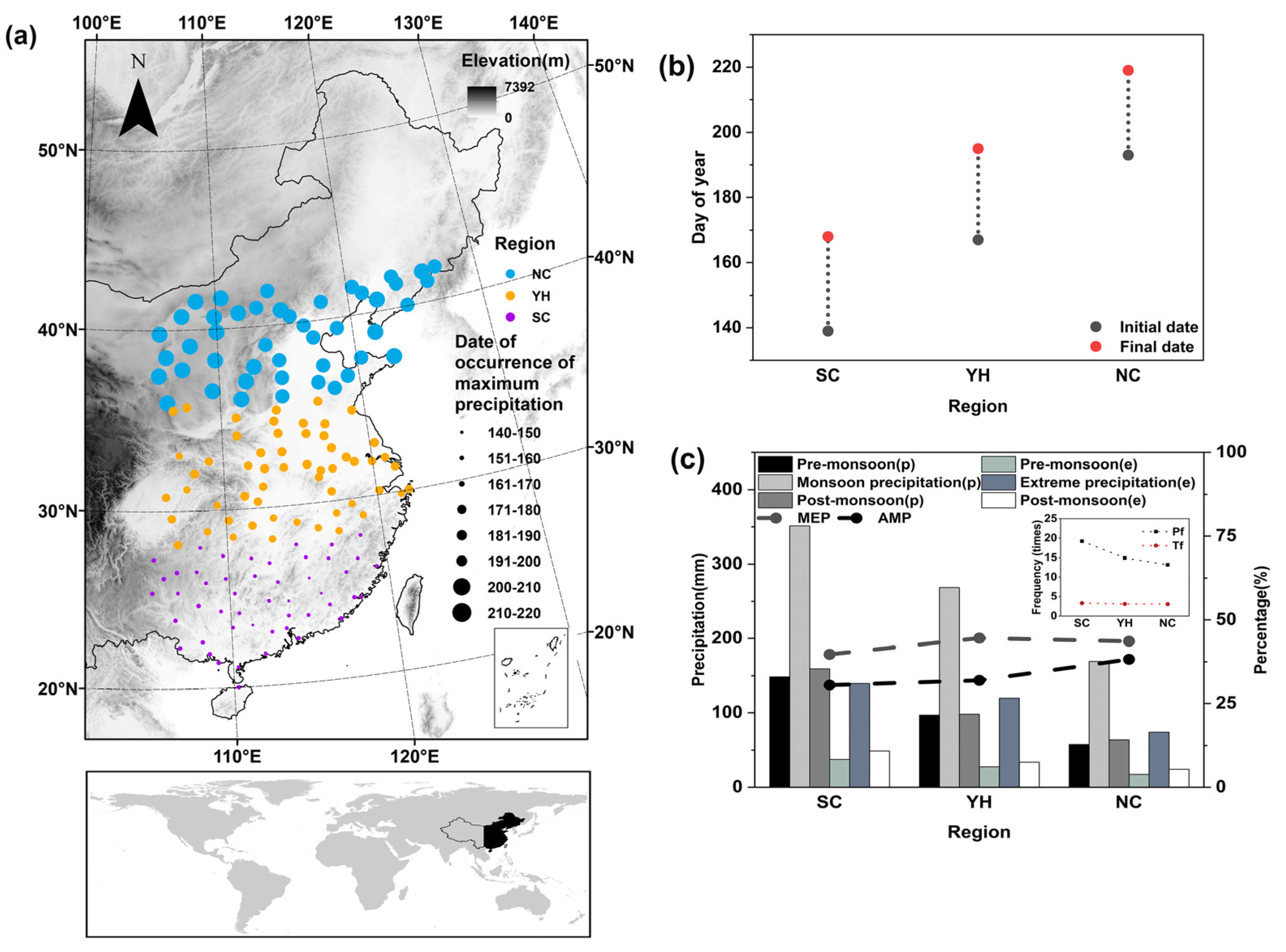
2.2. Definition of the Monsoon Rainband and Regionalization
2.3. Methods of Analyzing Precipitation Characteristics
3. Results
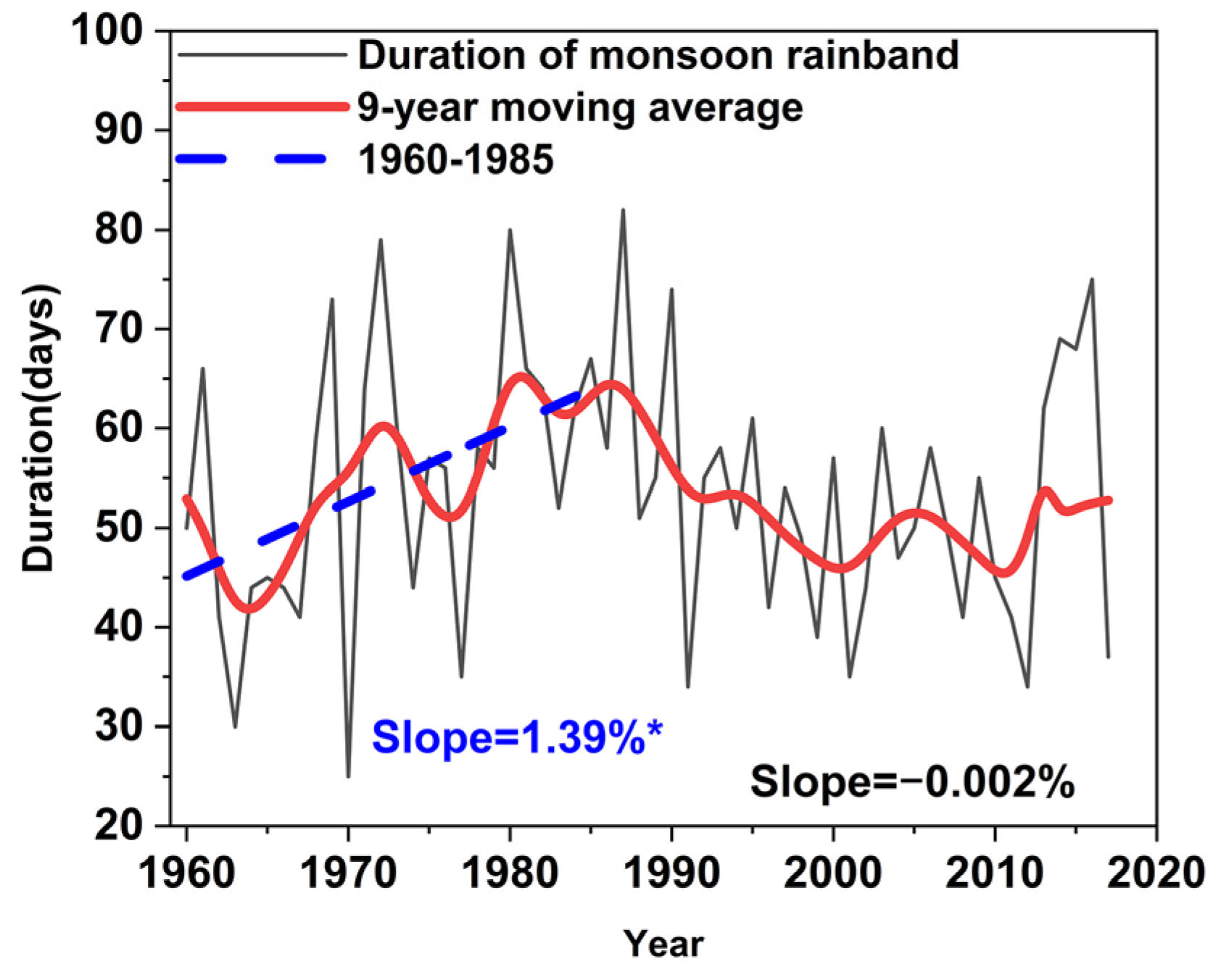
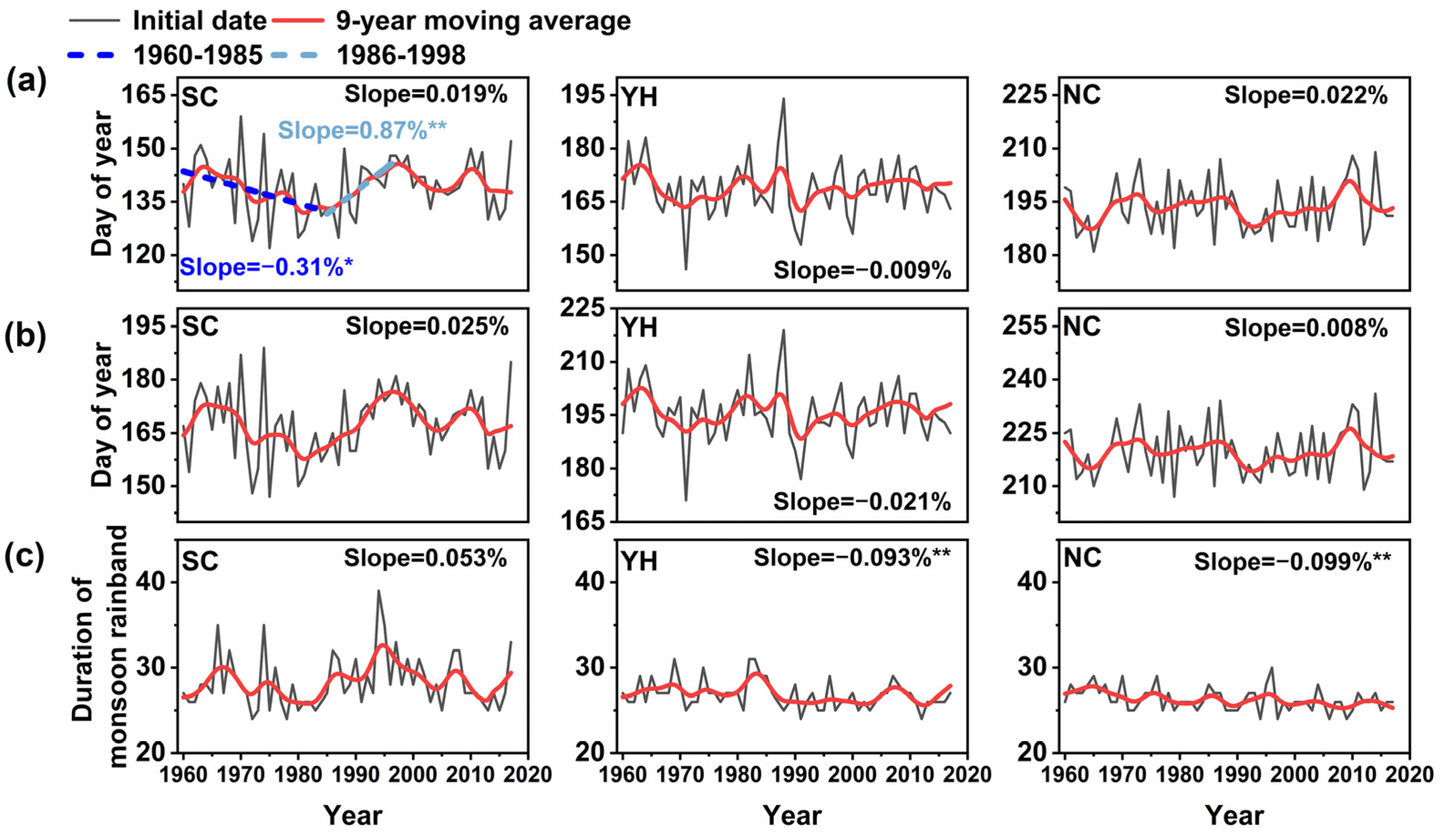
3.1. Variation in the Monsoon Rainband Configuration
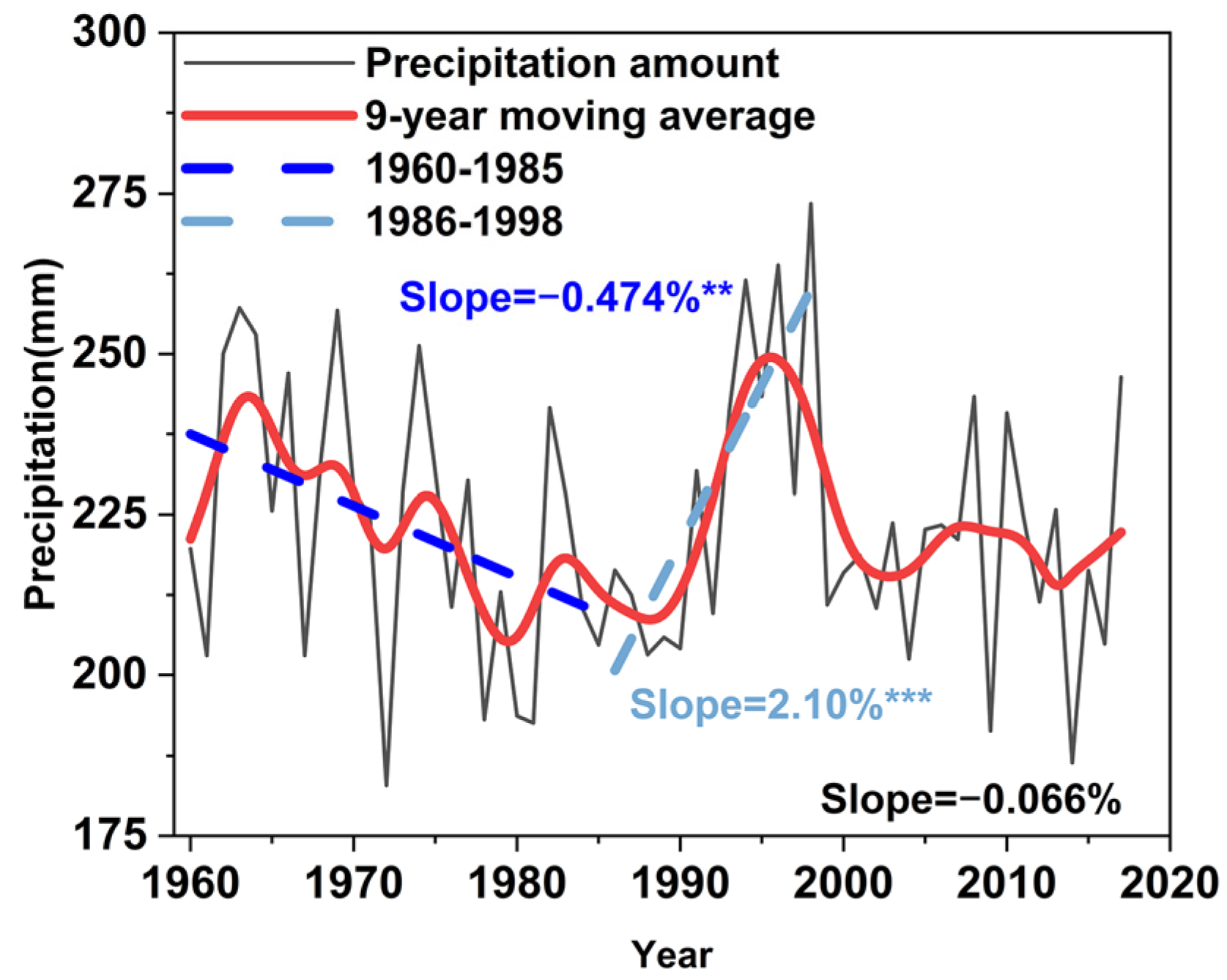
3.2. Variation in the Monsoon Rainband Precipitation
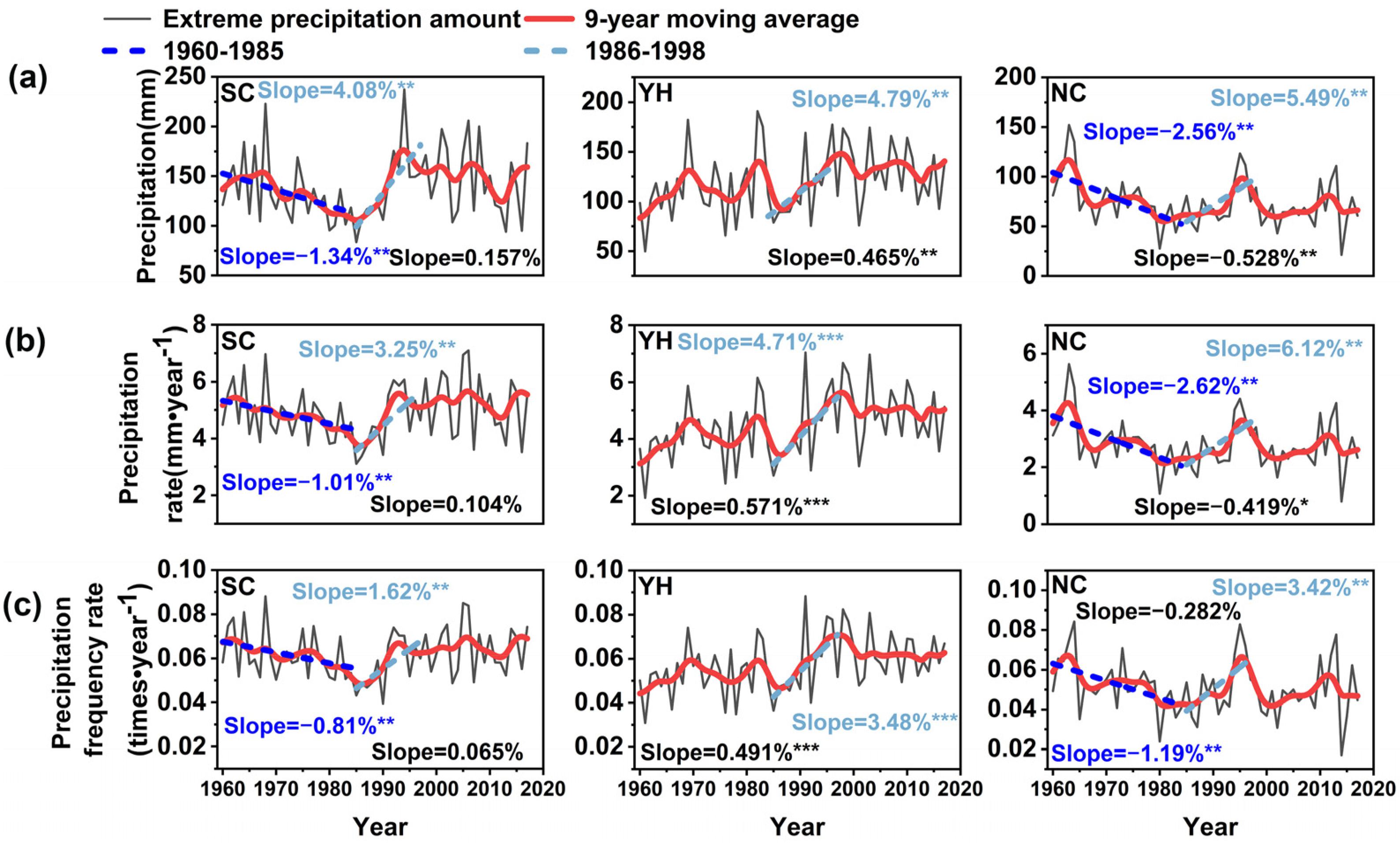
3.3. Variation in the Monsoon Rainband Extreme Precipitation
3.4. Asymmetrical Regional Changes in Precipitation Amount
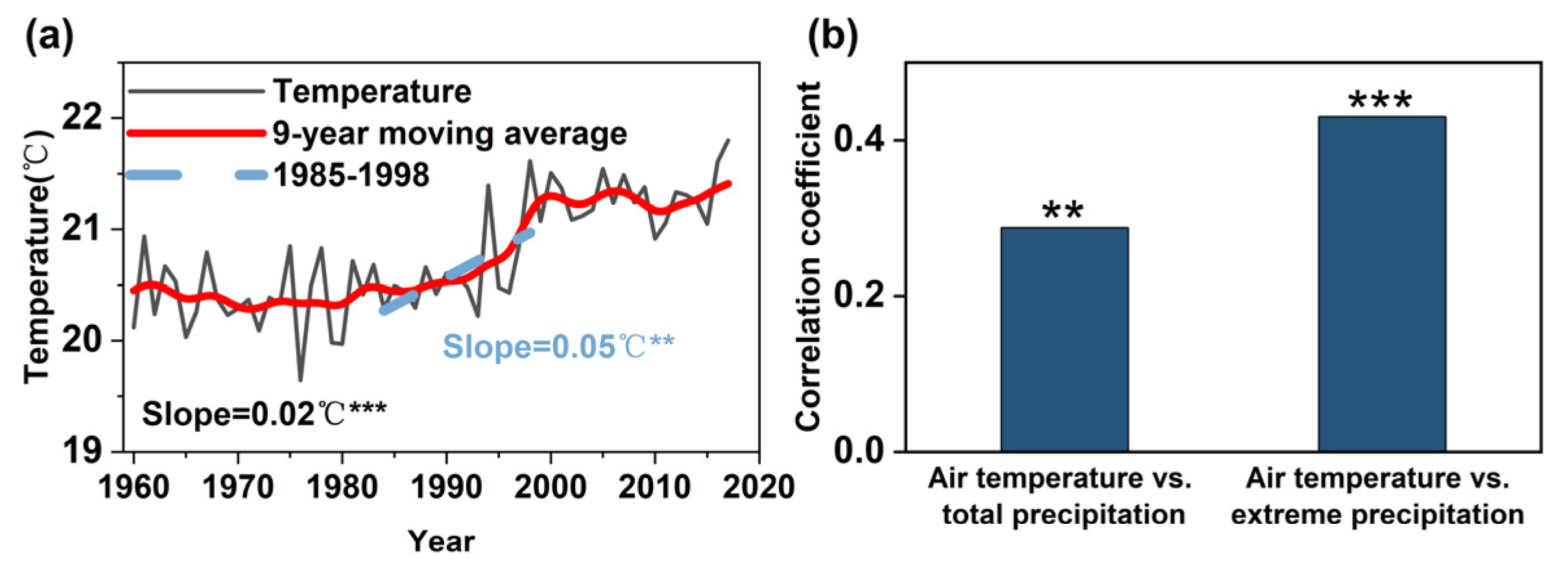
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Monsoon rainband precipitation in eastern China decreased from 1960 to the mid-1980s (−0.47% per year), then increased to around 1998 (2.10% per year). This reflects the weakening and then strengthening of the monsoon. During the monsoon weakening period, the monsoon arrived earlier on the Chinese mainland (−0.31% per year), with a longer transition period from SC to YH and a longer duration of the monsoon rainband’s march from South to North China (1.39% per year). The opposite pattern characterized the strengthening period.
- The monsoon rainband precipitation rate decreased significantly in NC (−1.09% per year) but showed no significant change in the other regions during the weakening monsoon period; all three regions showed significant increases in the strengthening monsoon period, with the greatest increases in the south (SC: 2.33% per year, YH: 2.10% per year, and NC: 1.87% per year).
- The extreme precipitation rate decreased significantly in NC (−1.01% per year) and SC (−2.62% per year) but showed no significant change in YH during the weakening monsoon period, then increased significantly in all three regions during the strengthening monsoon period, again with the greatest increases in the north (SC: 3.25% per year, YH: 4.71% per year, NC: 6.12% per year). Changes in extreme precipitation (95th percentile) contributed to most of the change in monsoon rainband precipitation, especially during the warming period.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EASM | East Asian Summer Monsoon |
| SC | South China |
| YH | the lower Yangtze and Huaihe river basins of East-Central China |
| NC | North China |
References
- Xu, M.; Chang, C.-P.; Fu, C.; Qi, Y.; Robock, A.; Robinson, D.; Zhang, H.-m. Steady decline of east Asian monsoon winds, 1969–2000: Evidence from direct ground measurements of wind speed. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2006, 111, 24111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.G.; Annamalai, H. Climate change and the South Asian summer monsoon. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.; Birks, H.J.B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Jin, L.; An, C.; Telford, R.J.; Cao, X.; et al. East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtadi, M.; Prange, M.; Steinke, S. Palaeoclimatic insights into forcing and response of monsoon rainfall. Nature 2016, 533, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ding, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Huang, X. Warming-induced northwestward migration of the East Asian monsoon rain belt from the Last Glacial Maximum to the mid-Holocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13178–13183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lau, W.K.M.; Ramanathan, V.; Wu, G.; Ding, Y.; Manoj, M.G.; Liu, J.; Qian, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.; et al. Aerosol and monsoon climate interactions over Asia. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 866–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Distinct effects of anthropogenic aerosols on the East Asian summermonsoon between multidecadal strong and weakmonsoon stages. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2016, 121, 7026–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. Seasonal rain changes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.-M.; Li, M.-T. The monsoon of East Asia and its global associations—A survey. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1984, 65, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T’u, C.-W.; Hwang, S.-S. The advance and retreat of the summer monsoon in China. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1945, 26, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fung, I.Y.; Chiang, J.C.H. East Asian Rainbands and Associated Circulation over the Tibetan Plateau Region. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 3211–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samel, A.N.; Wang, W.-C.; Liang, X.-Z. The monsoon rainband over China and relationships with the Eurasian circulation. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yi, S.; Liu, Z.; Mason, J.A.; Jiang, D.; Cheng, J.; Stevens, T.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, E.; Jin, L.; et al. Variation of East Asian monsoon precipitation during the past 21 k.y. and potential CO2 forcing. Geology 2013, 41, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhai, M.-Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhu, F.; Shen, H.-M.; Qiu, K.; Gao, B.-Y.; Reynolds, D.R.; Chapman, J.W.; et al. Changing patterns of the East Asian monsoon drive shifts in migration and abundance of a globally important rice pest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2023, 29, 2655–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, W.; Wang, Y.; Tan, D. The Response of the Aerosol Distribution to Monsoon Intensity Over the Summer Monsoon Transition Zone. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 7, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-P. East Asian Monsoon; World Scientific: Singapore, 2004; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.-C. Climatic pulsations during historic time in China. Geogr. Rev. 1926, 16, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, C. Variation of rainfall over south China through the wet season. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1952, 33, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, Z.; Xiang, K. A preliminary study on the causes of the two major floods of the Yangtze River in 1954 and 1998 and their prevention and control measures. J. Catastrophol. 1999, 14, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tao, S. Structure and Formation of Mei-Yu Front in 1998. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2002, 13, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, A.; Zhou, T.; Lu, J. Responses of East Asian summer monsoon to historical SST and atmospheric forcing during 1950–2000. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 34, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.C.H.; Swenson, L.M.; Kong, W. Role of seasonal transitions and the westerlies in the interannual variability of the East Asian summer monsoon precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 3788–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific SSTs. Part I Roles Subtrop. Ridge. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 4310–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; He, J. Can Global Warming Strengthen the East Asian Summer Monsoon? J. Clim. 2010, 23, 6696–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, I.M.; Soden, B.J. Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5686–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, R. Global change—Monsoon linkages. Nature 2003, 421, 324–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, P.-L.; Jiang, J.H.; Su, H.; Rasch, P.J. Toward reconciling the influence of atmospheric aerosols and greenhouse gases on light precipitation changes in Eastern China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2016, 121, 5878–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, C.W.; Hall, A.; Norris, J.; Chen, D. Constraining the increased frequency of global precipitation extremes under warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E. Changes in precipitation with climate change. Clim. Res. 2011, 47, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.-Z.; Samel, A.N.; Wang, W.-C. Observed and GCM simulated decadal variability of monsoon rainfall in east China. Clim. Dyn. 1995, 11, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Henderson, M.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y. Observed changes in precipitation on the wettest days of the year in China, 1960–2000. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, M.; Henderson, M. Where have all the showers gone? Regional declines in light precipitation events in China, 1960–2000. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Ho, C.-H.; Kim, J.; Gong, D.-Y.; Park, R.J. The impact of aerosols on the summer rainfall frequency in China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Giorgi, F.; Washington, W.M. Simulation of summer monsoon climate over East Asia with an NCAR regional climate model. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122, 2331–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, T.; Hu, Z.-Z. Summer climate variability in China and its association with 500 hPa height and tropical convection. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 1996, 74, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wu, Z.; Zong, S.; Meng, X.; Wang, L. Assessing the characteristics of extreme precipitation over northeast China using the multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 6165–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, H.; Zhu, Z. Quantitative Analysis of Changes of Summer Extremes Temperature and Precipitation Days over China with Respect to the Mean Temperature Increase. Plateau Meteorol. 2020, 39, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The changing character of precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ding, Y. Climatic Characteristics of Rainy Seasons in China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erxu, Z.; Gang, Z.; Jianhua, J.U.; Shuhui, Z. Impacts of activity of tropical monsoon air mass on the rainy season of Yunnan. J. Yunnan Univ. Nat. Sci. 2011, 33, 428–433,438. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, M.; Matsunaka, T.; Wang, J.; Matoba, S.; Tsushima, A.; Zhu, L.; Izutsu, Y. Sources and behavior of monsoon air masses in the lowest-latitude region on the Tibetan Plateau, and their paleoclimatic implications. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 554, 109750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Xu, M.; Henderson, M.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.Q. Taking China’s temperature: Daily range, warming trends, and regional variations, 1955–2000. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 4453–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Horton, B.; Jones, P.D.; Peterson, T.C.; Karl, T.R.; Parker, D.E.; Salinger, M.J.; Razuvayev, V.; Plummer, N.; Jamason, P. Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe. Science 1997, 277, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.L.; Jones, P.; Parker, D.; Zhou, L.; Feng, Y.; Gao, Y. China experiencing the recent warming hiatus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, P.D.; Guedes, J.d.A. Monsoon Rains, Great Rivers and the Development of Farming Civilisations in Asia; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Simpkins, G. Shorter monsoon season. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Chang, C.-P.; Ding, Y.; Wu, G. How to measure the strength of the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 4449–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon Part II: Possible causes. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1926–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Griffiths, M.L.; Chiang, J.C.H.; Kong, W.; Wu, S.; Atwood, A.; Huang, J.; Cheng, H.; Ning, Y.; Xie, S. East Asian hydroclimate modulated by the position of the westerlies during Termination I. Science 2018, 362, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, H.; Wang, C.; Zhu, X. Higher Sensitivity of Northern Hemisphere Monsoon to Anthropogenic Aerosol Than Greenhouse Gases. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I Obs. Evid. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 1139–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Biasutti, M.; Byrne, M.P.; Castro, C.; Chang, C.-P.; Cook, K.; Fu, R.; Grimm, A.M.; Ha, K.-J.; Hendon, H.; et al. Monsoons Climate Change Assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 102, E1–E19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; Fowler, H.J. Understanding rainfall extremes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, R.; Hiraga, Y.; Kazama, S. Climate change effects on the localized heavy rainfall event in northern Japan in 2022: Uncertainties in a pseudo-global warming approach. Atmos. Res. 2025, 314, 107780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraga, Y.; Tahara, R.; Meza, J. A methodology to estimate Probable Maximum Precipitation (PMP) under climate change using a numerical weather model. J. Hydrol. 2025, 652, 132659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakakita, E. An influence of atmospheric stabilization and water vapor invasion on characteristics of guerrilla-heavy rainfall under climate change. Kyoto Univ. Disaster Prev. Res. Inst. Annu. Rep. 2020, 63, 241. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dou, Z.; Liu, B.; Henderson, M.; Zhou, W.; Ma, R.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Z. Changes in Timing and Precipitation of the East Asian Summer Monsoon over China Between 1960 and 2017. Earth 2025, 6, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020024
Dou Z, Liu B, Henderson M, Zhou W, Ma R, Chen M, Zhang Z. Changes in Timing and Precipitation of the East Asian Summer Monsoon over China Between 1960 and 2017. Earth. 2025; 6(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020024
Chicago/Turabian StyleDou, Zeyu, Binhui Liu, Mark Henderson, Wanying Zhou, Rong Ma, Mingyang Chen, and Zhi Zhang. 2025. "Changes in Timing and Precipitation of the East Asian Summer Monsoon over China Between 1960 and 2017" Earth 6, no. 2: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020024
APA StyleDou, Z., Liu, B., Henderson, M., Zhou, W., Ma, R., Chen, M., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Changes in Timing and Precipitation of the East Asian Summer Monsoon over China Between 1960 and 2017. Earth, 6(2), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020024







