Impact of Climate Variability on Maize Yield Under Different Climate Change Scenarios in Southern India: A Panel Data Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
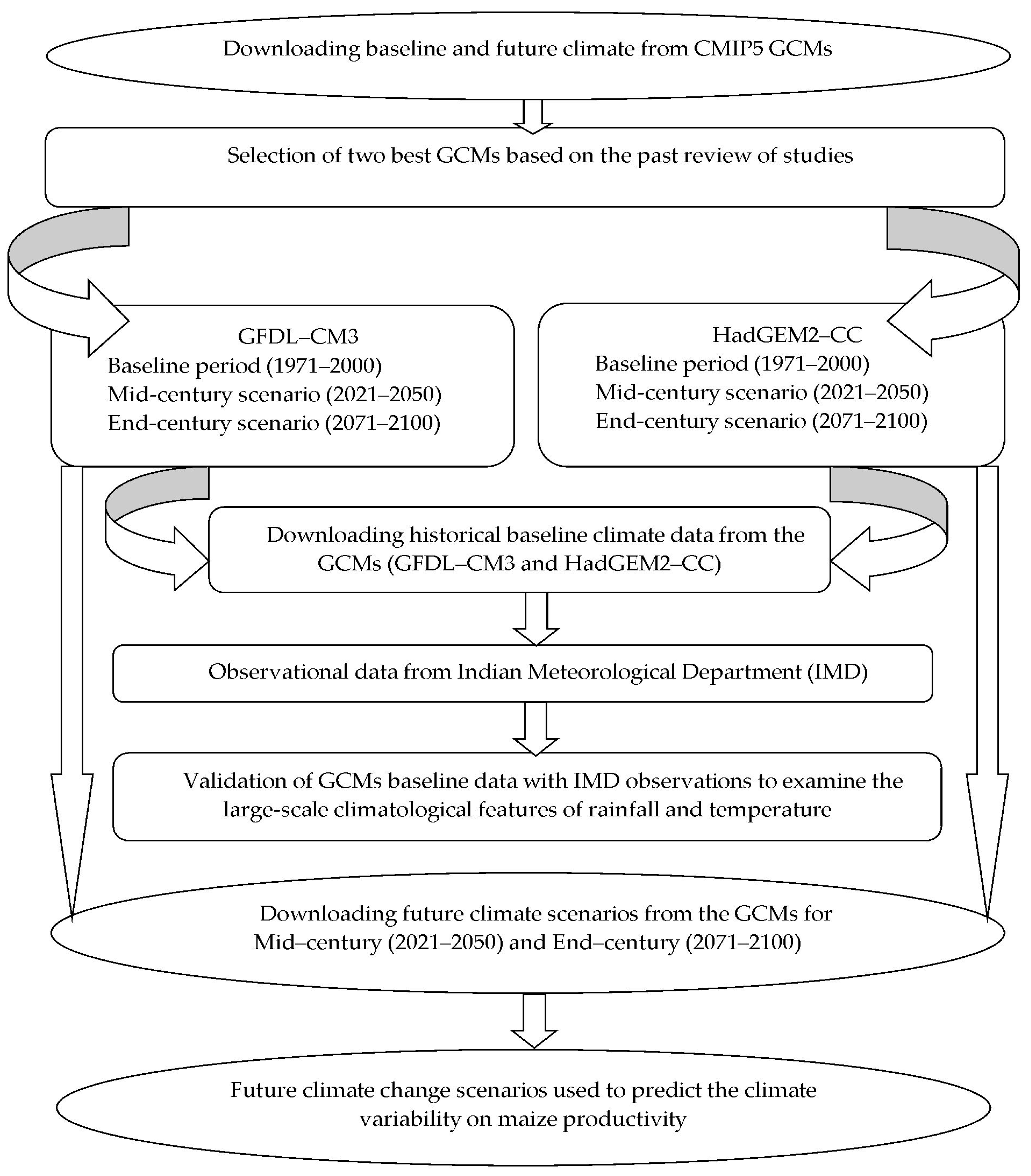
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. Global Climate Models: Historical Data
2.3. CMIP5 Future Climate Change Scenarios
2.4. Panel Data Regression Models
- = maize yield for the zone i and at time t;
- = rainfall (mm) in zone i and year t;
- = temperature (°C) in zone i and year t;
- = regression coefficients;
- = trend variable to capture technological change and adaptation measures;
- = agro-climatic zone level fixed effect, which equals 1 for observations, from zone i and 0 otherwise;
- = error term.
3. Results and Discussion
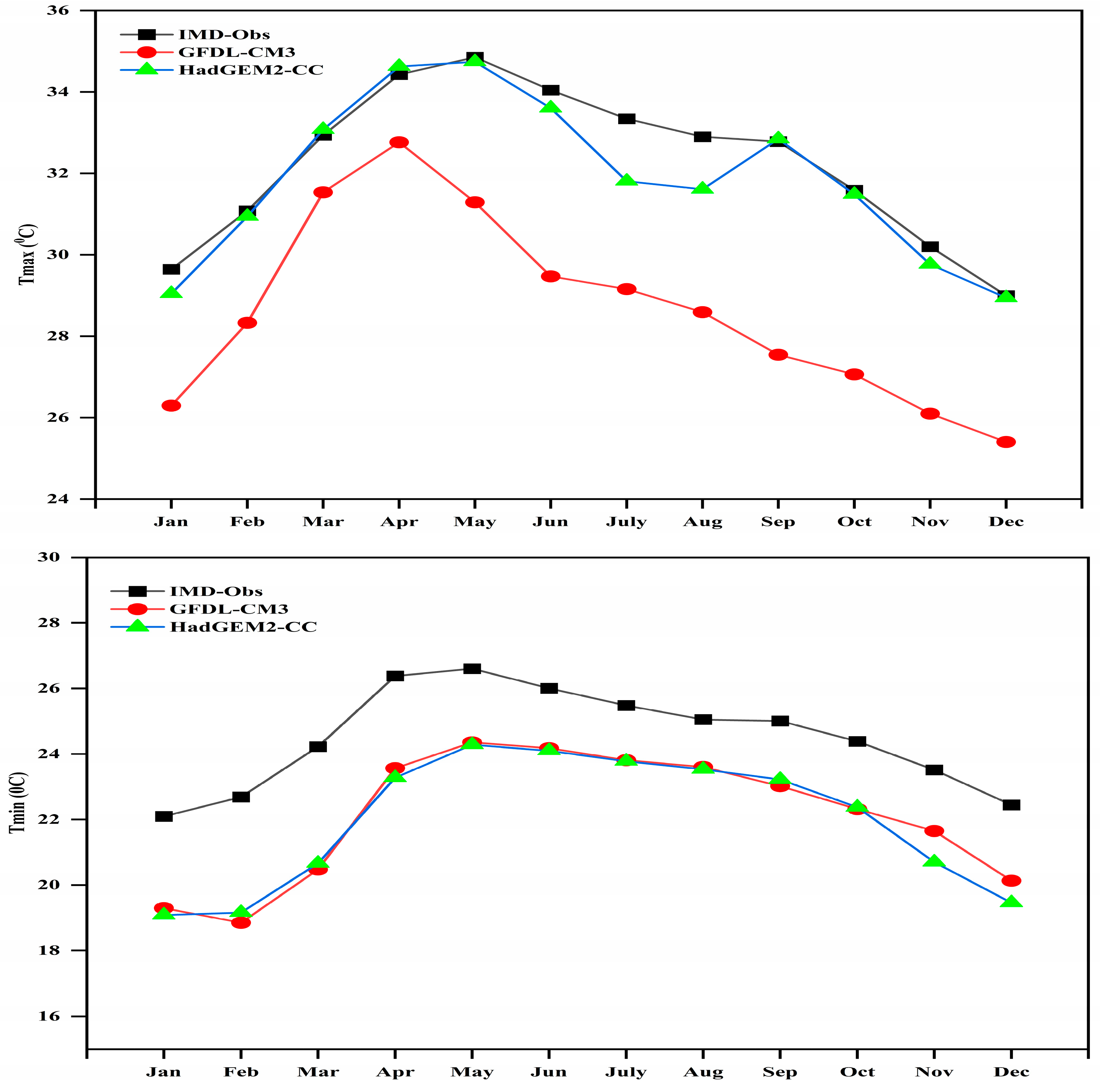
3.1. Seasonal Cycle Evaluation of GCM Baseline Climate with Observations
3.2. Seasonal Cycle of HadGEM2 Model Projections
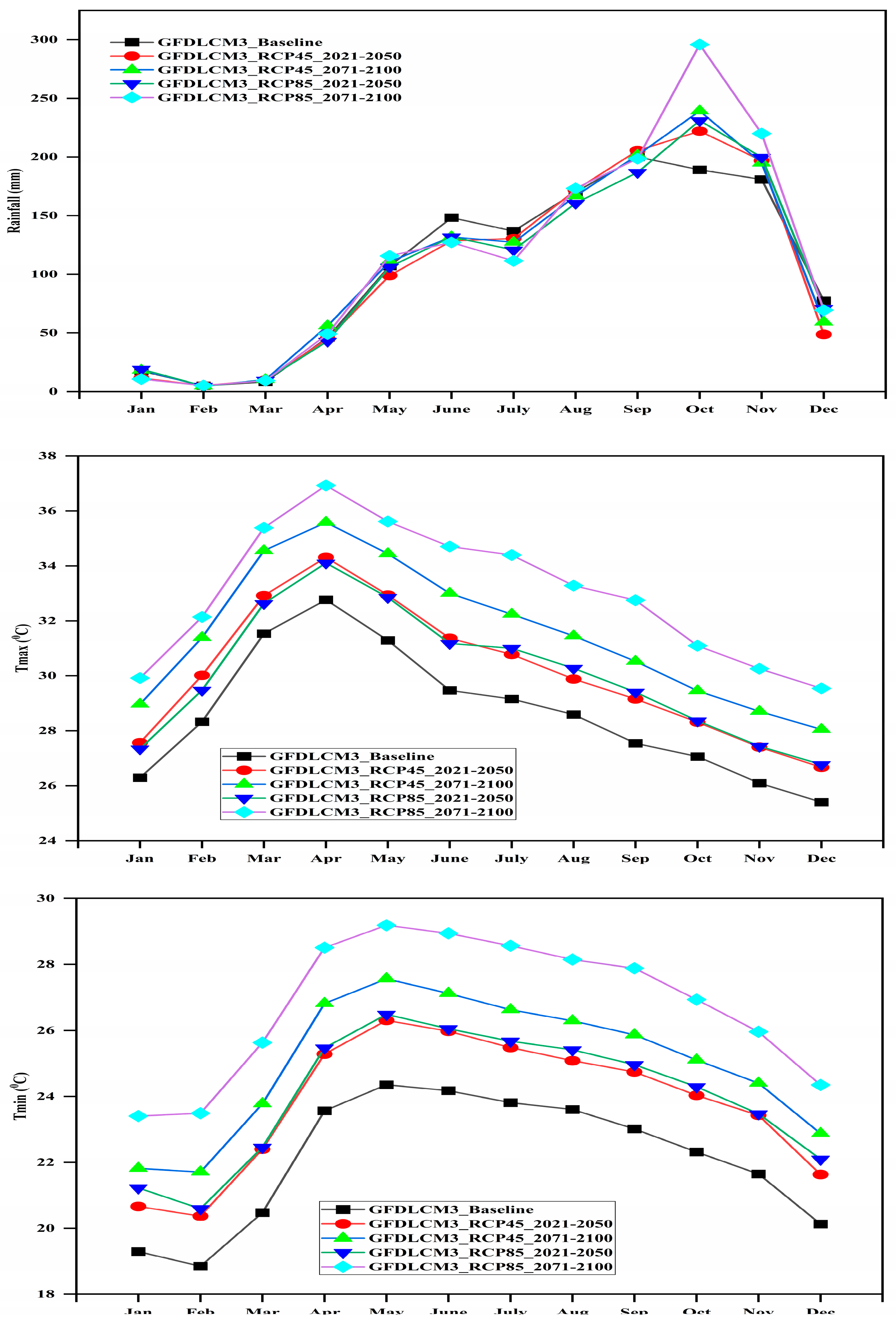
3.3. Seasonal Cycle Projections of the GFDL_CM3 Model
3.4. Impact of Tempearature and Rainfall on Extreme Weather Events and Pests and Diseases on Maize Yield
3.5. Estimation of Panel Data Regression: Impact of Climate Variables on Maize Yield
3.6. Marginal Productivity and Elasticity of Climate Variables
3.7. Prediction of Maize Yield Under Future Climate Change Scenarios
4. Conclusions and Future Strategies
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. World Food and Agriculture—Statistical Yearbook 2020; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FAOSTAT. Data. FAO. 2023. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 19 May 2024).
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, Government of India (GOI). Agriculture Statistics at a Glance: 2024; Directorate of Economics and Statistics: New Delhi, India, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. In The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; p. 976. [Google Scholar]
- Auffhammer, M.; Ramanathan, V.; Vincent, J.R. Integrated model shows that atmospheric brown clouds and greenhouse gases have reduced rice harvests in India. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19668–19672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.R.; Dube, O.P.; Solecki, W.; Aragón-Durand, F.; Cramer, W.; Humphreys, S.; Kainuma, M.; Kala, J.; Mahowald, N.; Mulugetta, Y.; et al. Framing and Context. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C Above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D., Skea, J., Shukla, P.R., Pirani, A., Moufouma-Okia, W., Péan, C., Pidcock, R., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 49–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.; Knutti, R.; Arblaster, J.; Dufresne, J.-L.; Fichefet, T.; Friedlingstein, P.; Gao, X.; Gutowski, W.J.; Johns, T.; Krinner, G.; et al. Long-term Climate Change: Projections, Commitments and Irreversibility. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lonergan, S. Climate warming and India. In Measuring the Impact of Climate Change on Indian Agriculture; World Bank Technical Paper 402; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Special Event on Impact of Climate Change, Pests and Diseases on Food Security and Poverty Reduction; 31st Session of the Committee on World Food Security; FAO: Italy, Rome, 2005; pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment and Forests. Agenda 21: An Assessment New Delhi: Ministry of Environment and Forests; Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Isik, M.; Devadoss, S. An analysis of the impact of climate change on crop yields and yield variability. Appl. Econ. 2006, 38, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, W. Response of crop yields to climate trends since 1980 in China. Clim. Res. 2012, 54, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchena, P.; Iglesias, A. Vulnerability of maize yields to climate change in different farming sectors in Zimbabwe. In Climate Change and Agriculture: Analysis of Potential International Impacts; American Society of Agronomy; Crop Science Society of America; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1995; Volume 59, pp. 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Takahashi, T.; Suzuki, N.; Kaiser, H.M. The impact of climate change on maize yields in the United States and China. Agric. Syst. 2011, 104, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Li, J. The effects of projected climate change and extreme climate on maize and rice in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 282, 107867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Sheehy, J.E.; Laza, R.C.; Visperas, R.M.; Zhong, X.; Cassman, K.G. Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9971–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperber, K.R.; Annamalai, H.; Kang, I.-S.; Kitoh, A.; Moise, A.; Turner, A.; Wang, B.; Zhou, T. The Asian summer monsoon: An intercomparison of CMIP5 vs. CMIP3 simulations of the late 20th century. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 41, 2711–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, H.; Hafner, J.; Sooraj, K.P.; Pillai, P. Global warming shifts the monsoon circulation, drying South Asia. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2701–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherchi, A.; Annamalai, H.; Masina, S.; Navarra, A. South Asian summer monsoon and the eastern Mediterranean climate: The monsoon-desert mechanism in CMIP5 simulations. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 6877–6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.; Edmonds, J.; Hibbard, K.; Manning, M.R.; Rose, S.K.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Carter, T.R.; Emori, S.; Kainuma, M.; Kram, T.; et al. The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment. Nature 2010, 463, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, G.Y.; Uehara, G.; Balas, S. (Eds.) Decision Support System for Agrotechnology Transfer (DSSAT) Version 3; University of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Allen, L.H., Jr.; Jones, J.W.; Tsuji, G.Y.; Hildebrand, P. (Eds.) Climate Change and Agriculture: Analysis of Potential International Impacts (ASA Special Publication No. 59); American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1995; p. 382. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R.; Jones, C.A.; Dyke, P.T. A Modeling Approach to Determining the Relationships Between Erosion and Soil Productivity; Transactions of the ASAE 27, 129/144; ASABE: St. Joseph, MI, USA,, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Keating, B.A.; Carberry, P.S.; Hammer, G.L.; Probert, M.E.; Robertson, M.J.; Holzworth, D.; Huth, N.I.; Hargreaves, J.N.G.; Meinke, H.; Hochman, Z.; et al. An overview of APSIM, a model designed for farming systems simulation. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 18, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Parry, M.L. Impacts of climate change on world food supply. Nature 1994, 367, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, M.L.; Rosenzweig, C.; Iglesias, A.; Livermore, M.; Fischer, G. Effects of climate change on global food production under SRES emissions and socio-economic scenarios. Global Environ. Change 2004, 14, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, G.; van Velthuizen, H.; Shah, M.; Nachtergaele, F.O. Global Agro-Ecological Assessment for Agriculture in the 21st Century: Methodology and Results IIASA RR-02-02; IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn, R.; Nordhaus, W.D.; Shaw, D. The Impact of Global Warming on Agriculture: A Ricardian Analysis. Am. Econ. Rev. 1994, 84, 753–771. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn, R. The Market Impacts of Climate Change Across Nations: A Comparison of Effects in the United States, Brazil, and India. In Proceedings of the Environmetrics Conference, Sao Paulo, Brazil; 22–26 July 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cline, W. The impact of global warming on agriculture: Comment. Am. Econ. Rev. 1996, 86, 1309–1311. [Google Scholar]
- Schlenker, W.; Roberts, M.J. Nonlinear effects of weather on corn yields. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2006, 28, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilnathan, S.; Annamalai, H.; Prasanna, V.; Hafner, J.; Balaji, N. Impact of regional climate model projected changes on rice yield over southern India. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2838–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, V.; Lohano, H.D.; Balasubramanian, R. A district-level analysis for measuring the effects of climate change on production of rice: Evidence from Southern India. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 150, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwary, M.; Samiappan, S.; Khan, G.D.; Moahid, M. Climate Change and Cereal Crops Productivity in Afghanistan: Evidence Based on Panel Regression Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, J.R.; Vincent, J.R.; Auffhammer, M.; Moya, P.F.; Dobermann, A.; Dawe, D. Rice yields in tropical/subtropical Asia exhibit large but opposing sensitivities to minimum and maximum temperatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14562–14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-z.; Zhang, J.; Ge, X.-m.; Xing, L.-w.; Han, S.-q.; Chen, S.; Kong, F.-t. Impact of climate change on maize yield in China from 1979 to 2016. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschênes, O.; Greenstone, M. The economic impacts of climate change: Evidence from agricultural output and random fluctuations in weather. Am. Econ. Rev. 2007, 97, 354–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenker, W.; Roberts, M.J. Nonlinear temperature effects indicate severe damages to US crop yields under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15594–15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiteras, R. The Impact of Climate Change on Indian Agriculture (Working Paper); Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT): Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, N.; Siddique, K.; Ahmed, M.S.; Hakimi, S. Climate-smart agriculture strategies for South Asia to address the challenges of climate change: Identification of climate-resilient agriculture practices for India, Bangladesh, and Afghanistan. APN Sci. Bull. 2023, 13, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, D.S.; Wise, K.A.; Sisson, A.J.; Allen, T.W.; Bergstrom, G.C.; Bissonnette, K.M.; Bradley, C.A.; Byamukama, E.; Chilvers, M.I.; Collins, A.A.; et al. Corn yield loss estimates due to diseases in the United States and Ontario, Canada, from 2016 to 2019. Plant Health Prog. 2020, 21, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, M.; De Groote, H.; Munyua, B.; Makumbi, D.; Owino, F.; Crossa, J.; Beyene, Y.; Mugo, S.; Jumbo, M.; Asea, G.; et al. On-farm performance and farmers’ participatory assessment of new stress-tolerant maize hybrids in Eastern Africa. Field Crops Res. 2020, 246, 107693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, J.E.; Sonder, K.; Zaidi, P.H.; Verhulst, N.; Mahuku, G.; Babu, R.; Nair, S.K.; Das, B.; Govaerts, B.; Vinayan, M.T.; et al. Maize production in a changing climate: Impacts, adaptation, and mitigation strategies. Adv. Agron. 2012, 114, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-H.; Lee, B.-M. Effects of climate change and drought tolerance on maize growth. Plants 2023, 12, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryanto, S.; Wang, L.; Jacinthe, P.-A. Global synthesis of drought effects on maize and wheat production. PloS ONE 2016, 11, e0156362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.L. Drought and heat stress effects on corn pollination. J. Agron. 2002, 196, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Longmei, N.; Gill, G.K.; Kumar, R.; Zaidi, P.H. Selection indices for identifying heat tolerant of maize (Zea mays). Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 93, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, G.V.; Rajalakshmi, D.; Bhuvaneswari, K.; Srinivasan, R.; Sridhar, G.; Sekhar, N.U.; Annamalai, H. Climate change adaptation strategies in the Bhavani basin using the SWAT Model. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2011, 27, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshaya, S.; Kokilavani, S.; Pazhanivelan, S.; Dheebakaran, G.; Boomiraj, K.; Kumar, S.M. Assessment of Climate Change Impact and Adaptation Strategies for Rainfed Maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanya, P.; Geethalakshmi, V.; Ramanathan, S.; Senthilraja, K.; Sreeraj, P.; Pradipa, C.; Bhuvaneshwari, K.; Vengateswari, M.; Dheebakaran, G.; Kokilavani, S.; et al. Impacts and Climate Change Adaptation of Agrometeorological Services among the Maize Farmers of West Tamil Nadu. AgriEngineering 2022, 4, 1030–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Panda, R.K.; Chakraborty, A. Assessment of climate change impact on maize yield and yield attributes under different climate change scenarios in eastern India. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesh, B.; Reddy, K.S.; Polisgowdar, B.S.; Maruthi, V.; Satishkumar, U.; Ayyanagoudar, M.S.; Rao, S.; Veeresh, H. Assessment of climate change impact on maize (Zea mays L.) through aquacrop model in semi-arid alfisol of southern Telangana. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, P.J.; Johnson, S.N.; Newton, A.C.; Ingram, J.S.I. Integrating pests and pathogens into the climate change/food security debate. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 2827–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, H.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Singh, S.D. Climate Change Impact, Adaptation and Mitigation in Agriculture: Methodology for Assessment and Applications; Indian Agricultural Research Institute: New Delhi, India, 2012; Volume 302, p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan, C.R. Vulnerability and resilience of social-ecological systems. In Working Paper on Social-Ecological Resilience Series No. 2009-008; Research Institute for Humanity and Nature: Kyoto, Japan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Chen, F.; Yue, L.; Ding, Y.; Xu, H.; Rasmann, S.; Xiao, Z. Nanosilicon enhances maize resistance against oriental armyworm (Mythimna separata) by activating the biosynthesis of chemical defenses. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethalakshmi, V.; Gowtham, R.; Gopinath, R.; Priyanka, S.; Rajavel, M.; Senthilraja, K.; Dhasarathan, M.; Rengalakshmi, R.; Bhuvaneswari, K. Potential Impacts of Future Climate Changes on Crop Productivity of Cereals and Legumes in Tamil Nadu, India: A Mid-Century Time Slice Approach. Adv. Meteorol. 2022, 2023, 4540454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermid, S.; Gowtham, R.; Bhuvaneswari, K.; Geethalakshmi, V. The impacts of climate change on Tamil Nadu rainfed maize production: A multi-model approach to identify sensitivities and uncertainties. Curr. Sci. 2016, 110, 1257–1271. [Google Scholar]



| Variables | Coefficient | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Constant | 4259.176 | 0.949 |
| Trend | 24.058 ** | 0.022 |
| Rainfall | 5.344 | 0.479 |
| Temperature | −378.972 | 0.941 |
| Rainfall square | −0.002 * | 0.089 |
| Temperature square | 9.400 | 0.924 |
| RF*Temperature | −0.102 | 0.709 |
| Northwestern zone | 83.141 | 0.871 |
| Western zone | −136.945 | 0.873 |
| Cauvery delta zone | 505.130 *** | 0.008 |
| Southern zone | 207.099 | 0.267 |
| F-test | 2.58 *** | 0.0086 |
| R2 | 0.23 | |
| Climate Variables | Marginal Productivity | Elasticity |
|---|---|---|
| Rainfall | 0.162 | 0.047 |
| Temperature | 51.199 | 0.736 |
| Climate Change Scenario | Period | GFDL_CM3 | HadGEM2_CC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change in Maize Yield (kg/ha) | Percentage Increase | Change in Maize Yield (kg/ha) | Percentage Increase | ||
| RCP45 | 2021–2050 | 86.19 | 4.82 | 53.66 | 3.00 |
| 2071–2100 | 154.44 | 8.63 | 129.73 | 7.25 | |
| RCP85 | 2021–2050 | 97.88 | 5.47 | 65.84 | 3.68 |
| 2071–2100 | 259.90 | 14.53 | 253.99 | 14.20 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senthilnathan, S.; Benson, D.; Prasanna, V.; Mallick, T.; Thiyagarajan, A.; Ramasamy, M.; Sundaram, S. Impact of Climate Variability on Maize Yield Under Different Climate Change Scenarios in Southern India: A Panel Data Approach. Earth 2025, 6, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6010016
Senthilnathan S, Benson D, Prasanna V, Mallick T, Thiyagarajan A, Ramasamy M, Sundaram S. Impact of Climate Variability on Maize Yield Under Different Climate Change Scenarios in Southern India: A Panel Data Approach. Earth. 2025; 6(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenthilnathan, Samiappan, David Benson, Venkatraman Prasanna, Tapas Mallick, Anitha Thiyagarajan, Mahendiran Ramasamy, and Senthilarasu Sundaram. 2025. "Impact of Climate Variability on Maize Yield Under Different Climate Change Scenarios in Southern India: A Panel Data Approach" Earth 6, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6010016
APA StyleSenthilnathan, S., Benson, D., Prasanna, V., Mallick, T., Thiyagarajan, A., Ramasamy, M., & Sundaram, S. (2025). Impact of Climate Variability on Maize Yield Under Different Climate Change Scenarios in Southern India: A Panel Data Approach. Earth, 6(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6010016









