Analysis of the Status of Irrigation Management in North Carolina
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Results and Discussion
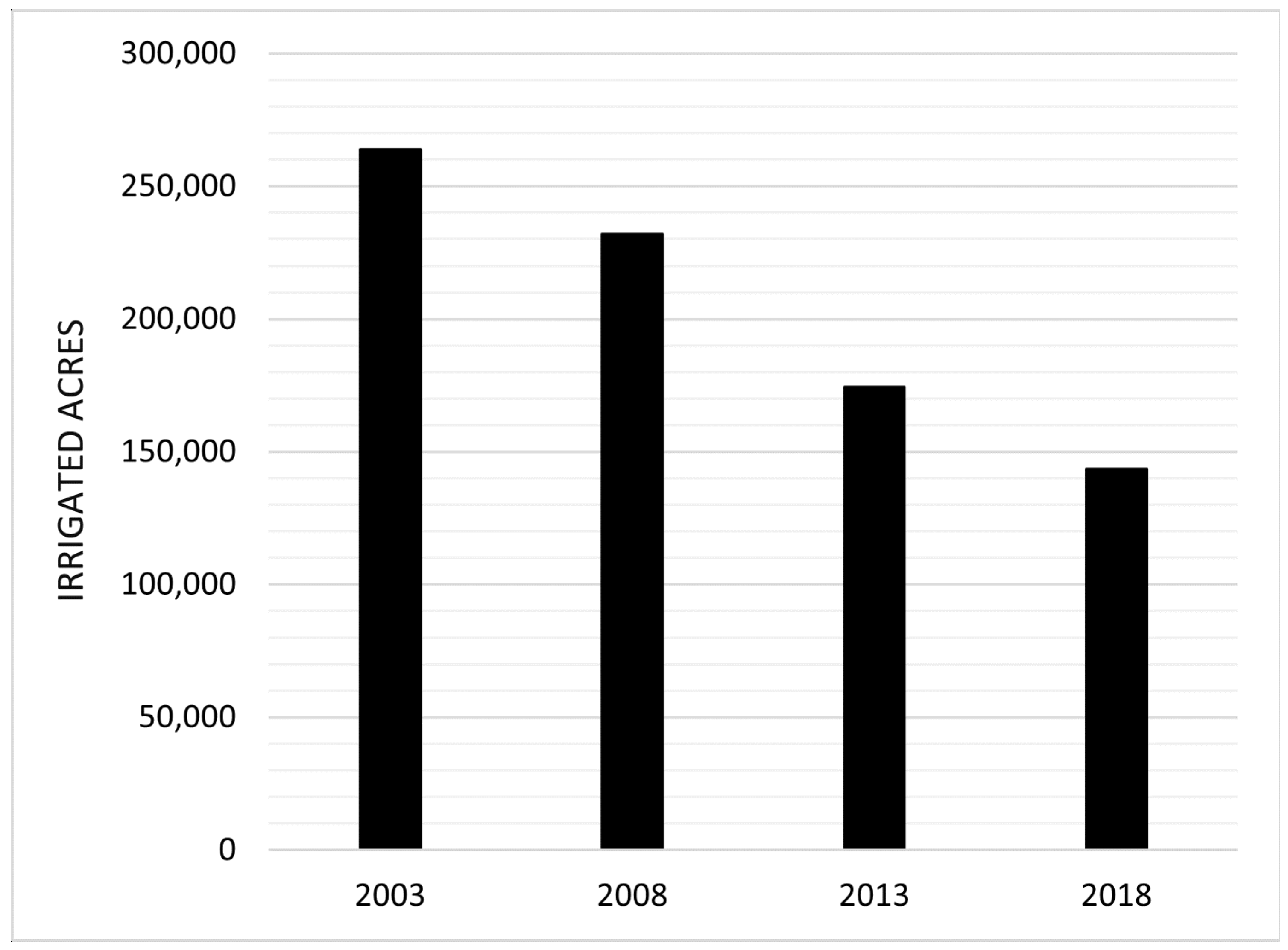
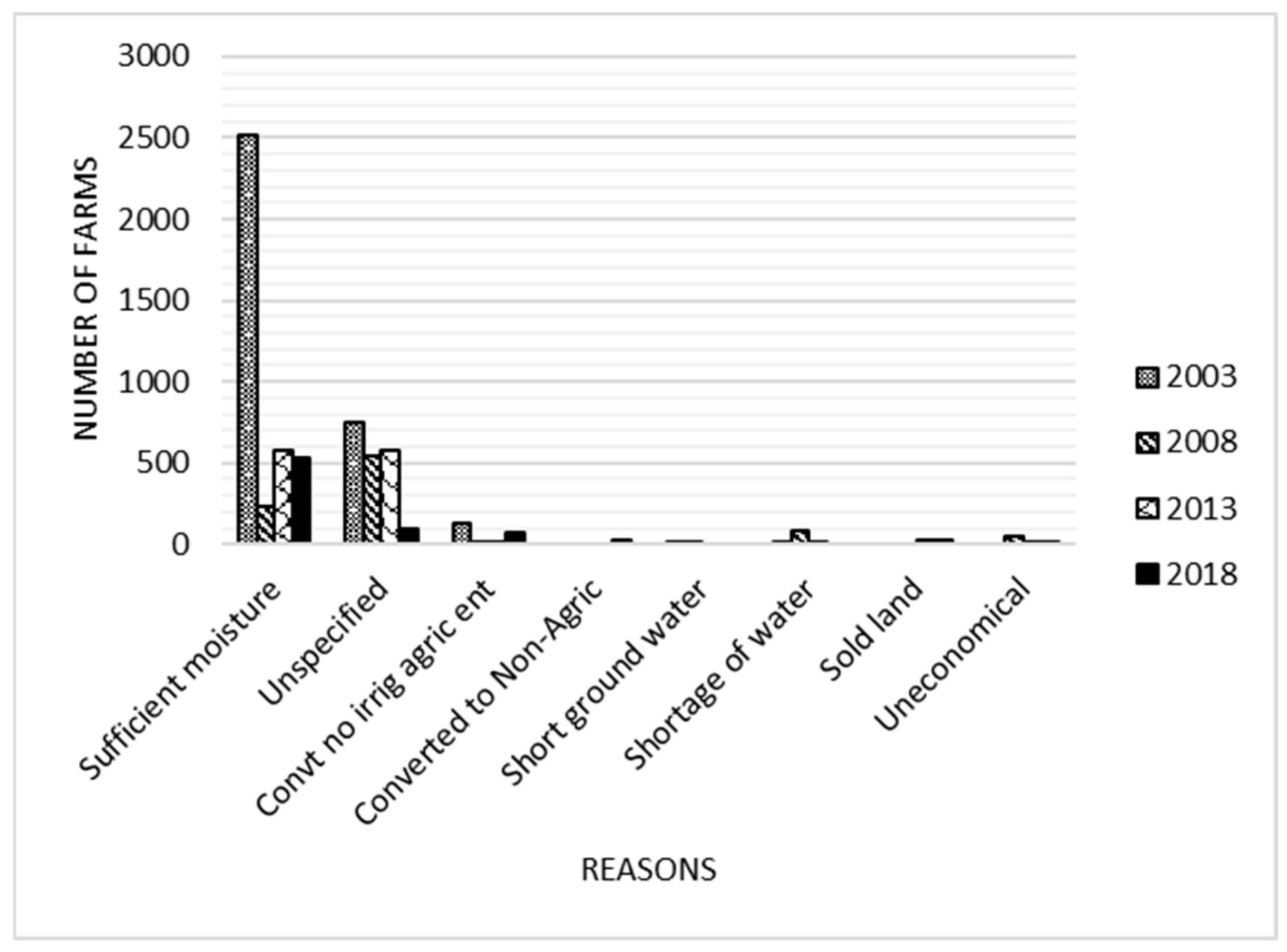
3.1. Irrigated Farms and Acres
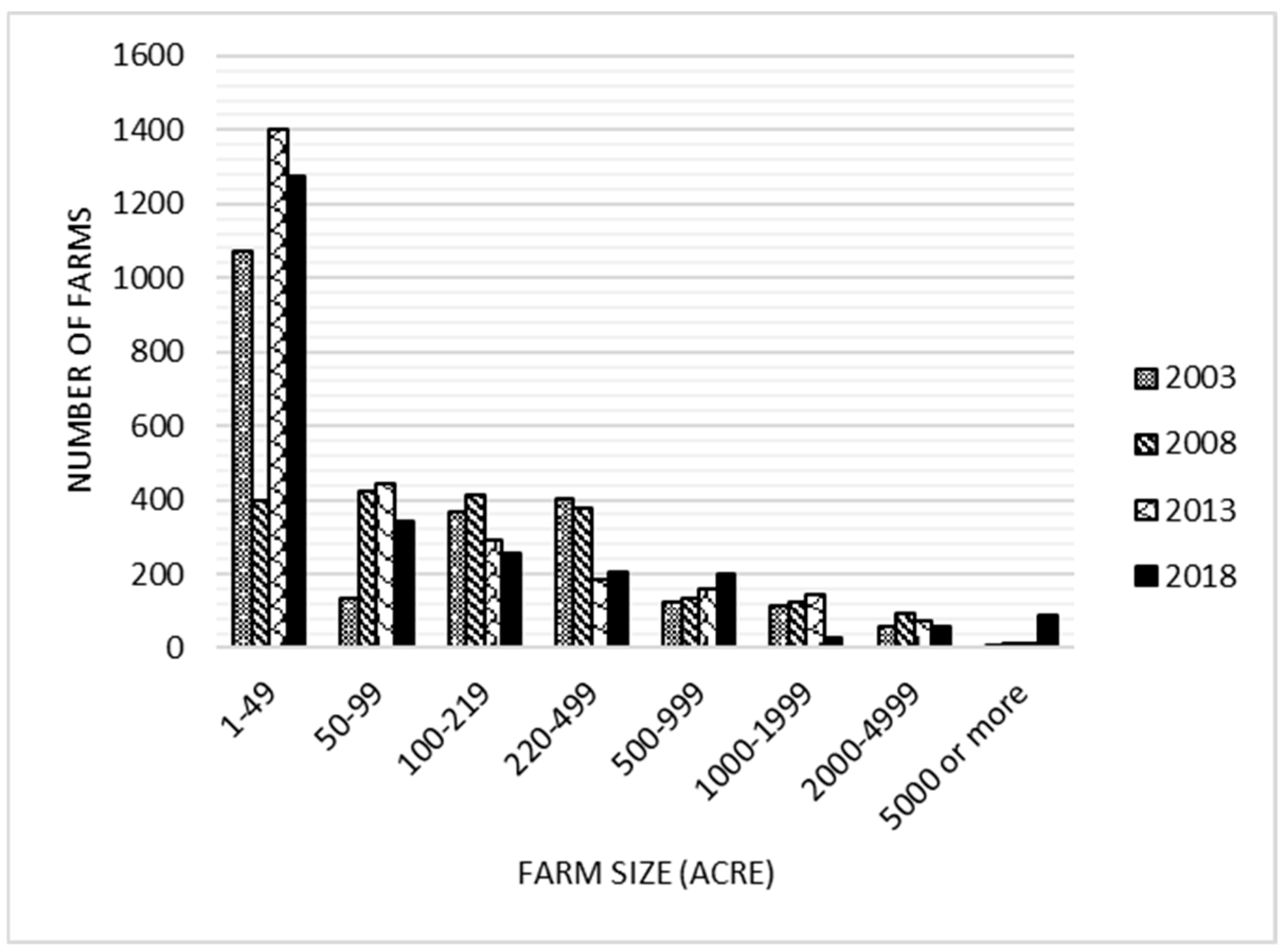
3.2. Irrigated Farm Acres by the Size of Farms
3.3. Irrigated Acres by Irrigation Methods
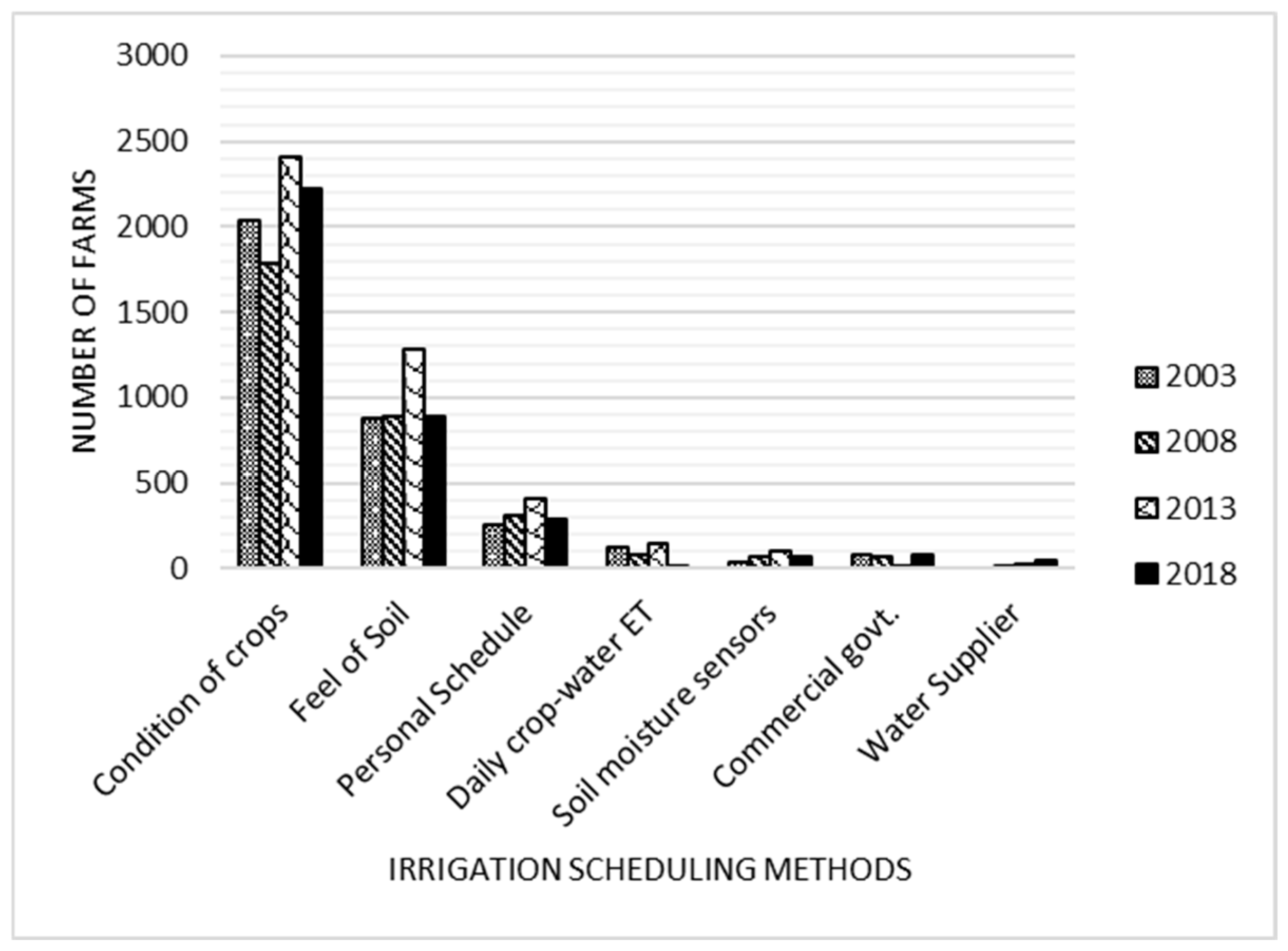
3.4. Irrigation Scheduling Methods
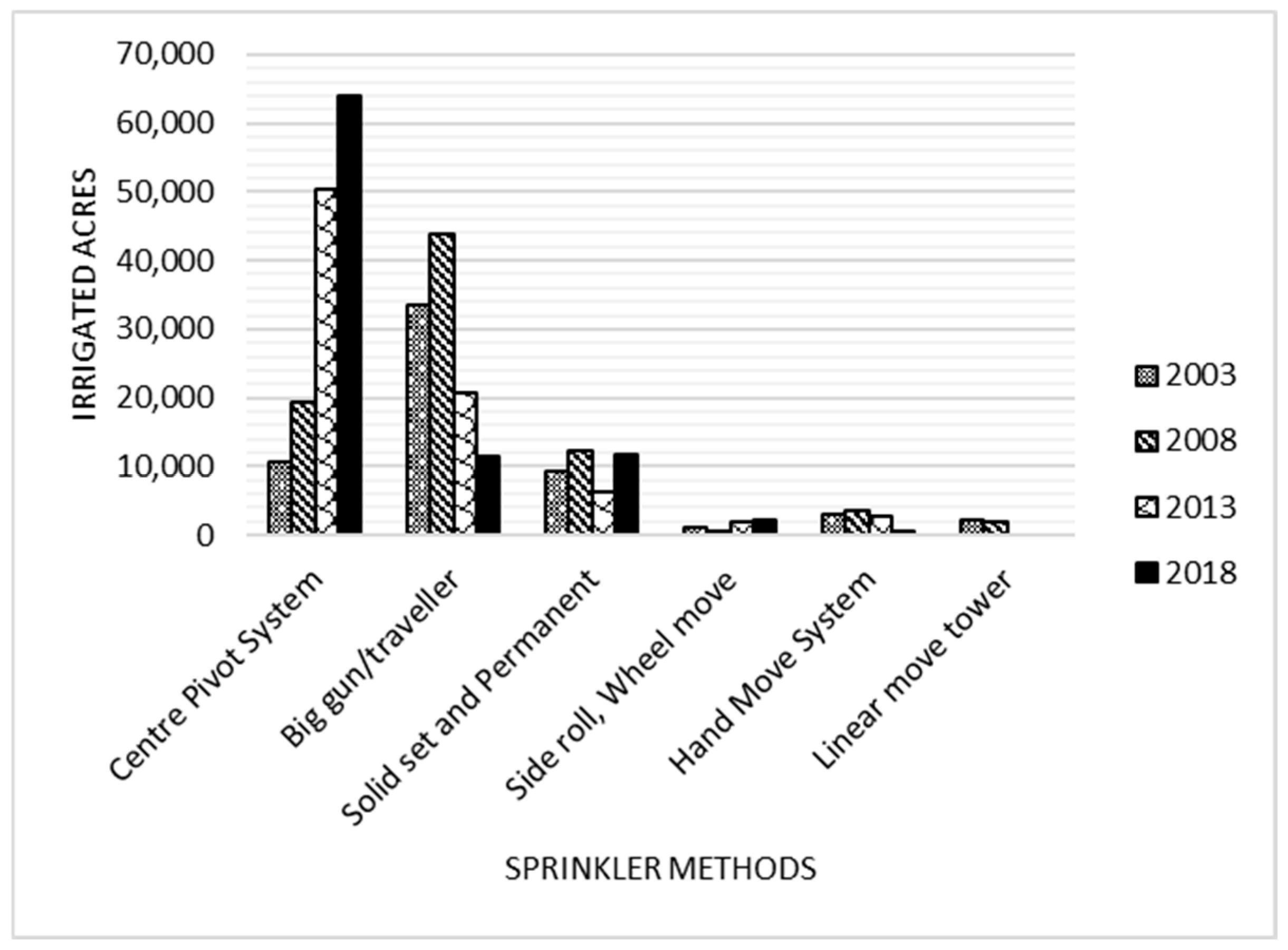
3.5. Irrigated Acres by Sprinkler Methods
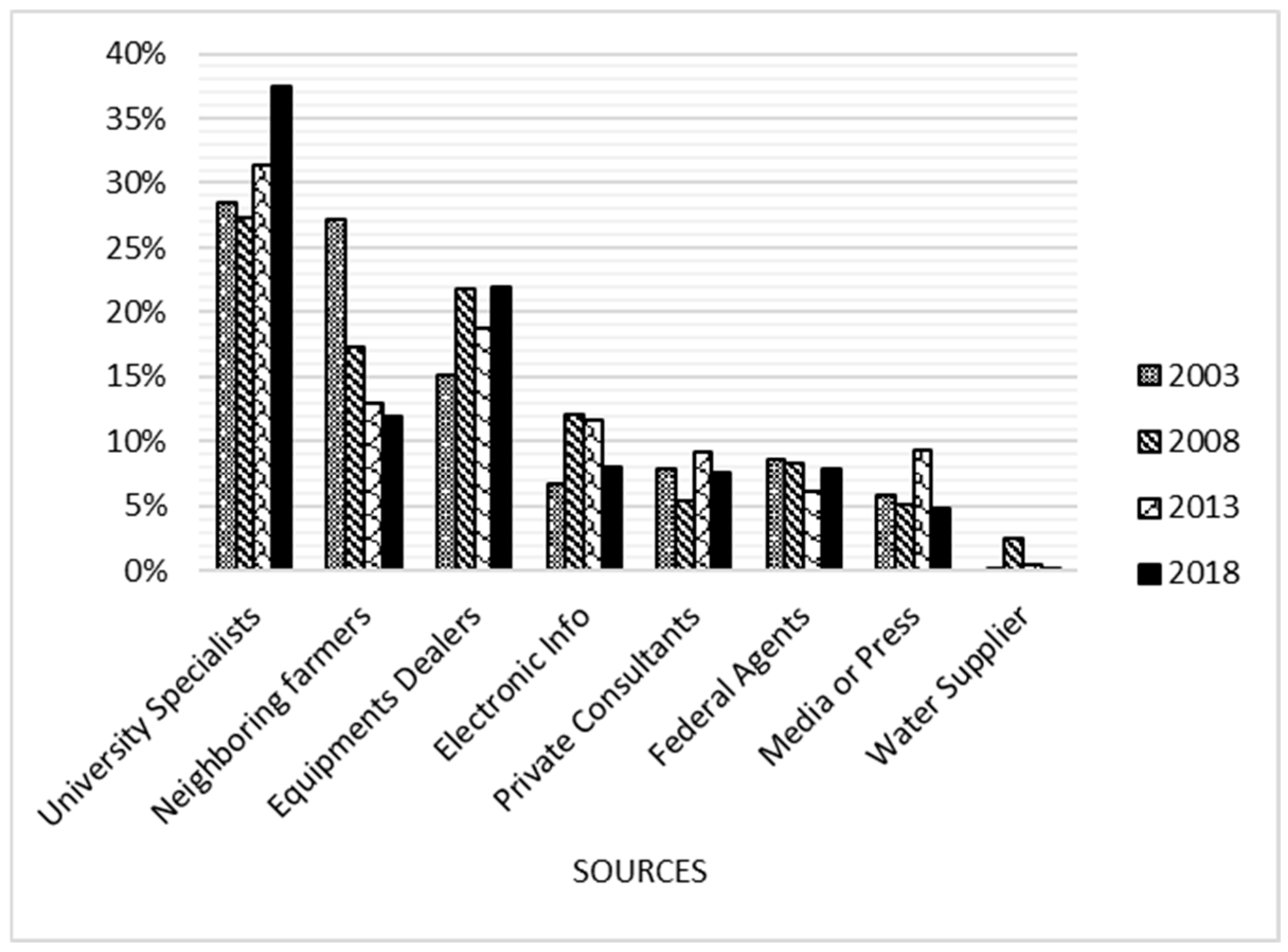
3.6. Sources of Irrigation Information Used by Farmers
3.7. Potential Innovative Irrigation Management and Outreach Programs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seager, R.; Tzanova, A.; Nakamura, J. Drought in the Southeastern United States: Causes, variability over the last millennium, and the potential for future hydroclimate change. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 5021–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, K.; Dow, K.; Carter, L.; Anderson, J. (Eds.) Climate of the Southeast United States: Variability, Change, Impacts, and Vulnerability; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 8–42. [Google Scholar]
- Knox, P.; Fuhrmann, C.M.; Konrad, C. Challenges and Opportunities for Southeast Agriculture in a Changing Climate: Perspectives from State Climatologists. Southeast. Geogr. 2014, 54, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North Carolina Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services. Small Farms. Available online: https://www.ncagr.gov/divisions/small-farms/small-farms-faqs (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Van Houtven, G.; Woollacott, J.; Bean, A. Climate Change and North Carolina: Near-Term Impacts on Society and Recommended Actions; Environmental Defense Fund: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- USDA NRCS. North Carolina Irrigation Guide; USDA NRCS: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 5–12. Available online: https://efotg.sc.egov.usda.gov/references/public/NC/NC_Irrigation_Guide_Apr_2010.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Wright Morton, L. The science of variable climate and agroecosystem management. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 69, 207A–212A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrini, B.; Basso, B. Drivers of within-field spatial and temporal variability of crop yield across the US Midwest. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodziewicz, D.; Dice, J. Drought Risk to the Agriculture Sector. Econ. Rev. 2020, 105, 01612387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North Carolina Department of Agriculture & Consumer Services. North Carolina Agricultural Statistics; North Carolina Department of Agriculture & Consumer Services: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2009.
- Salvati, L.; Venezian Scarascia, M.E.; Zitti, M.; Ferrara, A.; Urbano, V.; Sciortino, M.; Giupponi, C. The Integrated Assessment of Land Degradation. Ital. J. Agron. 2009, 4, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, G.; Neocleous, D.; Christou, A.; Kitta, E.; Katsoulas, N. Implementing Sustainable Irrigation in Water-Scarce Regions under the Impact of Climate Change. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Deryng, D.; Müller, C.; Frieler, K.; Konzmann, M.; Gerten, D.; Glotter, M.; Flörke, M.; Wada, Y.; Best, N.; et al. Constraints and potentials of future irrigation water availability on agricultural production under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3239–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaible, G.; Aillery, M. Water Conservation in Irrigated Agriculture: Trends and Challenges in the Face of Emerging Demands; USDA-ERS Economic Information Bulletin; USDA: Washinton, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 99. [CrossRef]
- USDA NRCS. Conservation Practices: Irrigation Water Management. 2020. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/main/national/programs/financial/eqip/ (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Carlesso, R.; Petry, M.T.; Trois, C. The use of a meteorological station network to provide crop water requirement information for irrigation management. In Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture II, Proceedings of the Second IFIP International Conference on Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture (CCTA2008), Beijing, China 18–20 October 2008; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Aulenbach, B.T.; Peters, N.E. Quantifying climate-related interactions in shallow and deep storage and evapotranspiration in a forested, seasonally water-limited watershed in the Southeastern United States. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 3037–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwambale, E.; Abagale, F.K.; Anornu, G.K. Data-driven modelling of soil moisture dynamics for smart irrigation scheduling. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, D.J.; Zhang, K.; Hilton, H.W.; Thompson, A.J. Opportunities for improving irrigation efficiency with quantitative models, soil water sensors and wireless technology. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 148, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkernagel, J.; Maestre-Valero, J.F.; Seresti, S.Y.; Intrigliolo, D.S. New technologies and practical approaches to improve irrigation management of open field vegetable crops. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 242, 106404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwambale, E.; Abagale, F.K.; Anornu, G.K. Smart irrigation monitoring and control strategies for improving water use efficiency in precision agriculture: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 260, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, R. Irrigation Scheduling Using Soil Moisture Sensors. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, F.R.; Stone, K.C.; Dukes, M.D.; Howell, T.A.; Robbins, J.W.D.; Mecham, B.Q. Emerging technologies for sustainable irrigation: Selected papers from the 2015 ASABE and IA irrigation symposium. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Sayemuzzaman, M.; Jha, M.K. Seasonal and annual precipitation time series trend analysis in North Carolina, United States. Atmos. Res. 2014, 137, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NC State Climate Office. Available online: https://products.climate.ncsu.edu/ (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Xie, Y.; Hunter, M.; Sorensen, A.; Nogeire-McRae, T.; Murphy, R.; Suraci, J.P.; Lischka, S.; Lark, T.J. US farmland under threat of urbanization: Future development scenarios to 2040. Land 2023, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Farmland Trust. Available online: https://farmland.org/no-farms-no-food/?gad_source=1&gclid=Cj0KCQjww5u2BhDeARIsALBuLnOFxKezMSCY5jlAQWTMxTEQiut154JhnYGY6_zZK53tCiYQ6BpLXk0aAl0uEALw_wcB (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Hoppe, R.A.; Banker, D.E. Structure and Finances of US Farms: Family Farm Report, 2010 ed.; EIB-66; US Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/webdocs/publications/44477/10951_eib66_1_.pdf?v=9576.5 (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Quaicoe, O.; Asiseh, F.; Baffoe-Bonnie, A.; Ng’ombe, J.N. Small Farms in North Carolina, United States: Analyzing Farm and Operator Characteristics in the Pursuit of Economic Resilience and Sustainability. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2024, 46, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, R.K.; Samani, Z. Farm size, irrigation practices, and on-farm irrigation efficiency. Irrig. Drain. J. Int. Comm. Irrig. Drain. 2005, 54, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, D.; Masasi, B.; Frazier, S.; Taghvaeian, S.; Warren, J.; Moriasi, D.N. Evaluating Uniformity of Center Pivot Irrigation Systems in Western Oklahoma. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2022, 38, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Irrigation efficiency and water withdrawal in US agriculture. Water Policy 2019, 21, 768–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA ERS. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/farm-practices-management/irrigation-water-use.aspx (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Frisvold, G.; Sanchez, C.; Gollehon, N.; Megdal, S.B.; Brown, P. Evaluating Gravity-Flow Irrigation with Lessons from Yuma, Arizona, USA. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masseroni, D.; Ricart, S.; De Cartagena, F.R.; Monserrat, J.; Gonçalves, J.M.; De Lima, I.; Facchi, A.; Sali, G.; Gandolfi, C. Prospects for improving gravity-fed surface irrigation systems in Mediterranean European contexts. Water 2017, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.G.; Sadler, E.J. Methods and technologies to improve efficiency of water use. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W00E04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, T.A. Irrigation efficiency. In Encyclopedia of Water Science; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 467–472. [Google Scholar]
- Clemmens, A.J.; Dedrick, A.R. Irrigation techniques and evaluations. In Management of Water Use in Agriculture; Tanji, K.K., Yaron, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 64–103. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Blanco, C.D.; Hrast-Essenfelder, A.; Perry, P. Irrigation Technology and Water Conservation: A Review of the Theory and Evidence. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 2020, 14, 216–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, D.E.; Martin, D.L.; Heeren, D.M.; Hoffman, G.J. Irrigation Scheduling. In Irrigation Systems Management; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2021; pp. 107–130. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, S.; Taghvaeian, S. Soil water sensors for irrigation scheduling in the United States: A systematic review of literature. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 278, 108148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levidow, L.; Zaccaria, D.; Maia, R.; Vivas, E.; Todorovic, M.; Scardigno, A. Improving water-efficient irrigation: Prospects and difficulties of innovative practices. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 146, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hendawy, S.E.; Schmidhalter, U. Optimal coupling combinations between irrigation frequency and rate for drip-irrigated maize grown on sandy soil. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussi, A.; Zero, E.; Sacile, R.; Trinchero, D.; Fossa, M. Smart Sensors and Smart Data for Precision Agriculture: A Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Minnesota Extension. Available online: https://extension.umn.edu/irrigation/soil-moisture-sensors-irrigation-scheduling (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Grieger, K.; Zarate, S.; Barnhill-Dilling, S.K.; Hunt, S.; Jones, D.; Kuzma, J. Fostering Responsible Innovation through Stakeholder Engagement: Case Study of North Carolina Sweetpotato Stakeholders. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvaeian, S.; Andales, A.A.; Allen, L.N.; Kisekka, I.; O’shaughnessy, S.A.; Porter, D.O.; Sui, R.; Irmak, S.; Fulton, A.; Aguilar, J. Irrigation scheduling for agriculture in the United States: The progress made and the path forward. Trans. ASABE 2020, 63, 1603–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Ashwell, N.; Gholson, D.M.; Krutz, L.J.; Henry, C.G.; Cooke, T. Adoption of Water-Conserving Irrigation Practices among Row-Crop Growers in Mississippi, USA. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwasegun Olamide, F.; Abidemi Olalekan, B.; Uthman Tobi, S.; Abdulwakiil Adeyemi, M.; Oladipupo Julius, J.; Kehinde Oluwaseyi, F. Fundamentals of Irrigation Methods and Their Impact on Crop Production; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, G.W.; Alwang, J. Changes in Agricultural Extension and Implications for Farmer Adoption of New Practices. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2020, 42, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shock, C.C.; Shock, C.B. Research, extension, and good farming practices improve water quality and productivity. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genius, M.; Koundouri, P.; Nauges, C.; Tzouvelekas, V. Information Transmission in Irrigation Technology Adoption and Diffusion: Social Learning, Extension Services, and Spatial Effects. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2014, 96, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, A.J.; Warner, L.A.; Martin, E.T.; White, S.A.; Fisher, P. Enhancing Extension Programs by Discussing Water Conservation Technology Adoption with Growers. J. Agric. Educ. 2017, 58, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, M.; Fuglie, K.; Ingram, C.; Jans, S.; Kascak, C. Adoption of Agricultural Production Practices: Lessons Learned from the U.S. Department of Agriculture Area Studies Project Resource Economics Division; Economic Research Service/USDA, AER-792; Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Rudnick, D.R.; Stockton, M.; Taghvaeian, S.; Warren, J.; Dukes, M.D.; Kremen, A.; Amosson, S.H. Innovative extension methods in the US to promote irrigation water management. Trans. ASABE 2020, 63, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šūmane, S.; Kunda, I.; Knickel, K.; Strauss, A.; Tisenkopfs, T.; Rios, I.D.I.; Rivera, M.; Chebach, T.; Ashkenazy, A. Local and farmers’ knowledge matters! How integrating informal and formal knowledge enhances sustainable and resilient agriculture. J. Rural. Stud. 2018, 59, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, K.; Franz, N. Cooperative Extension Program Development and the Community-University Engagement Movement: Perspectives from Two Lifelong Extension Professionals. J. Hum. Sci. Ext. 2015, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Misra, S.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Das, S.K. AgriSens: IoT-based dynamic irrigation scheduling system for water management of irrigated crops. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 5023–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Henriksen, A.; Edwards, G.T.; Pesonen, L.A.; Green, O.; Sørensen, C.A.G. Internet of Things in arable farming: Implementation, applications, challenges and potential. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 191, 60–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, M.A.; Sudduth, K.A.; Walthall, C.L.; Kitchen, N.R. Public–private collaboration toward research, education and innovation opportunities in precision agriculture. Precis. Agric. 2019, 20, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesapeake Bay Foundation. Available online: https://www.cbf.org/issues/agriculture/agricultural-cost-share-programs.html#:~:text=Agricultural%20cost%2Dshare%20programs%20provide,costs%20for%20installing%20conservation%20practices (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Hedley, C.B.; Yule, I.J. A method for spatial prediction of daily soil water status for precise irrigation scheduling. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1737–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adelabu, A.O.; Masasi, B.; Somefun, O.T. Analysis of the Status of Irrigation Management in North Carolina. Earth 2024, 5, 463-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth5030025
Adelabu AO, Masasi B, Somefun OT. Analysis of the Status of Irrigation Management in North Carolina. Earth. 2024; 5(3):463-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth5030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdelabu, Anuoluwapo Omolola, Blessing Masasi, and Olabisi Tolulope Somefun. 2024. "Analysis of the Status of Irrigation Management in North Carolina" Earth 5, no. 3: 463-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth5030025
APA StyleAdelabu, A. O., Masasi, B., & Somefun, O. T. (2024). Analysis of the Status of Irrigation Management in North Carolina. Earth, 5(3), 463-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth5030025





