Impact of Lockdown on Column and Surface Aerosol Content over Ahmedabad and a Comparison with the Indo-Gangetic Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Utilized
3. Results and Discussion
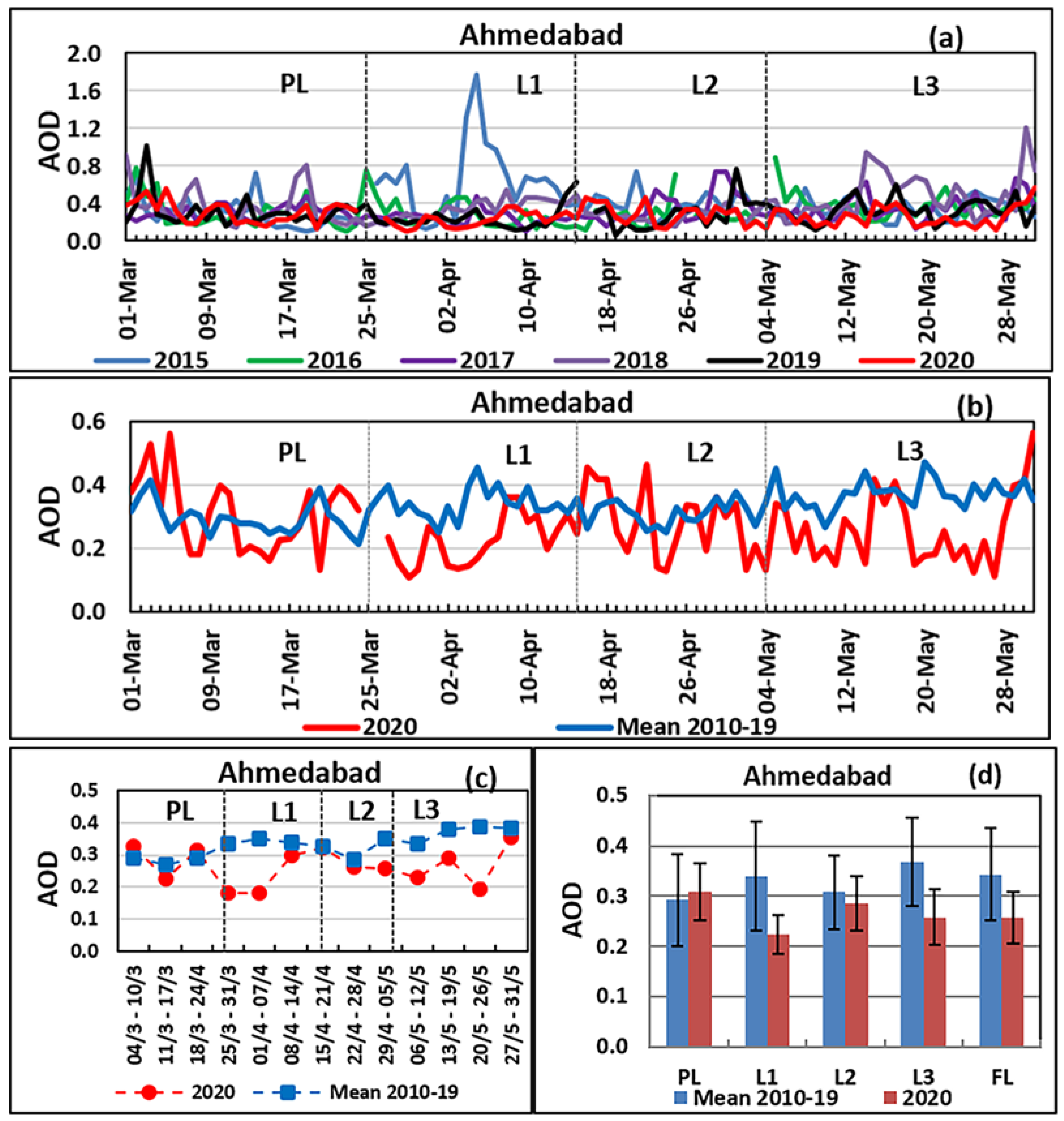
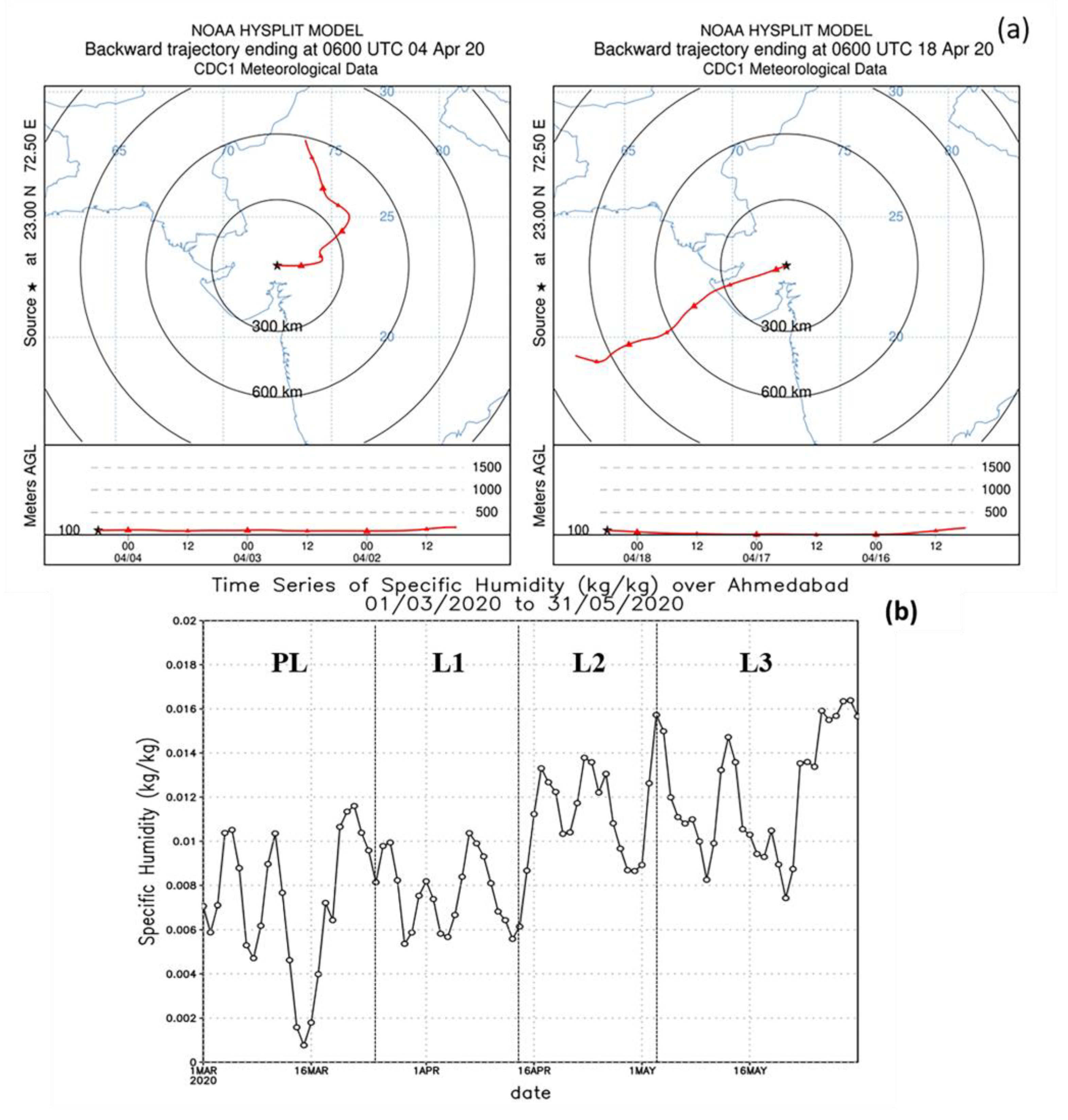
3.1. Variation in AOD over Ahmedabad
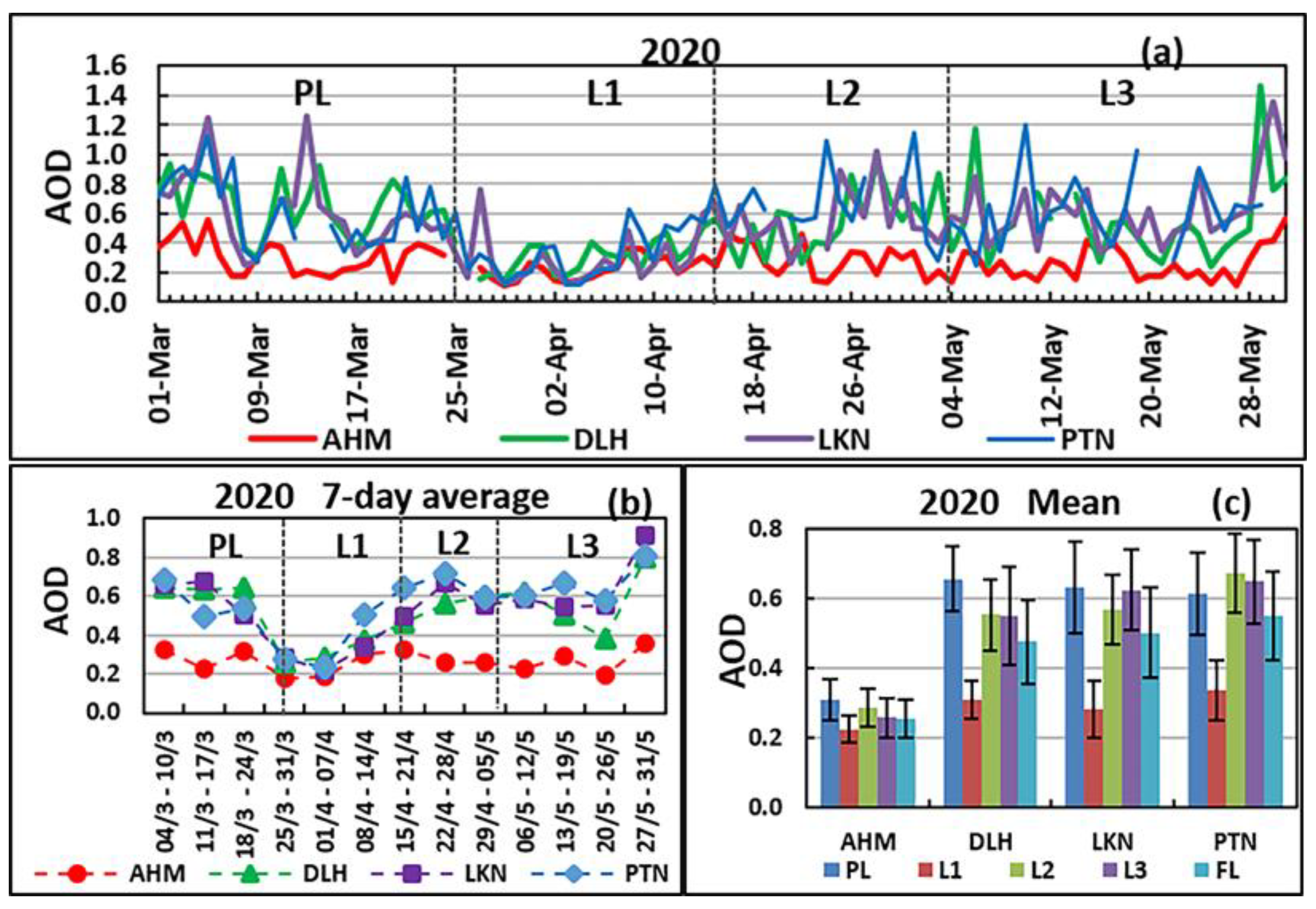
3.2. Comparison between AOD over Ahmedabad and the Indo-Gangetic Plain
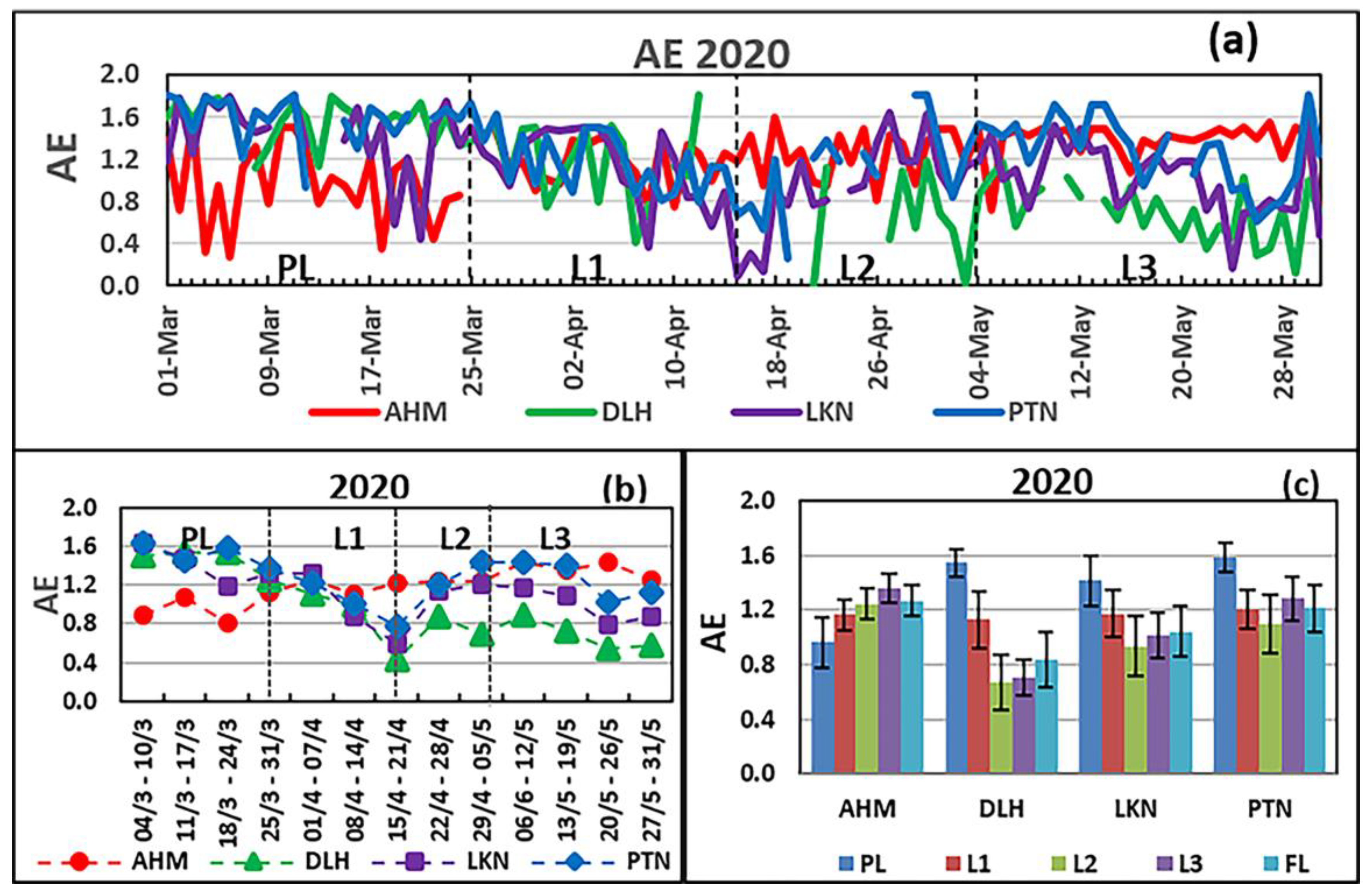
3.3. Variation in the Angstrom Exponent
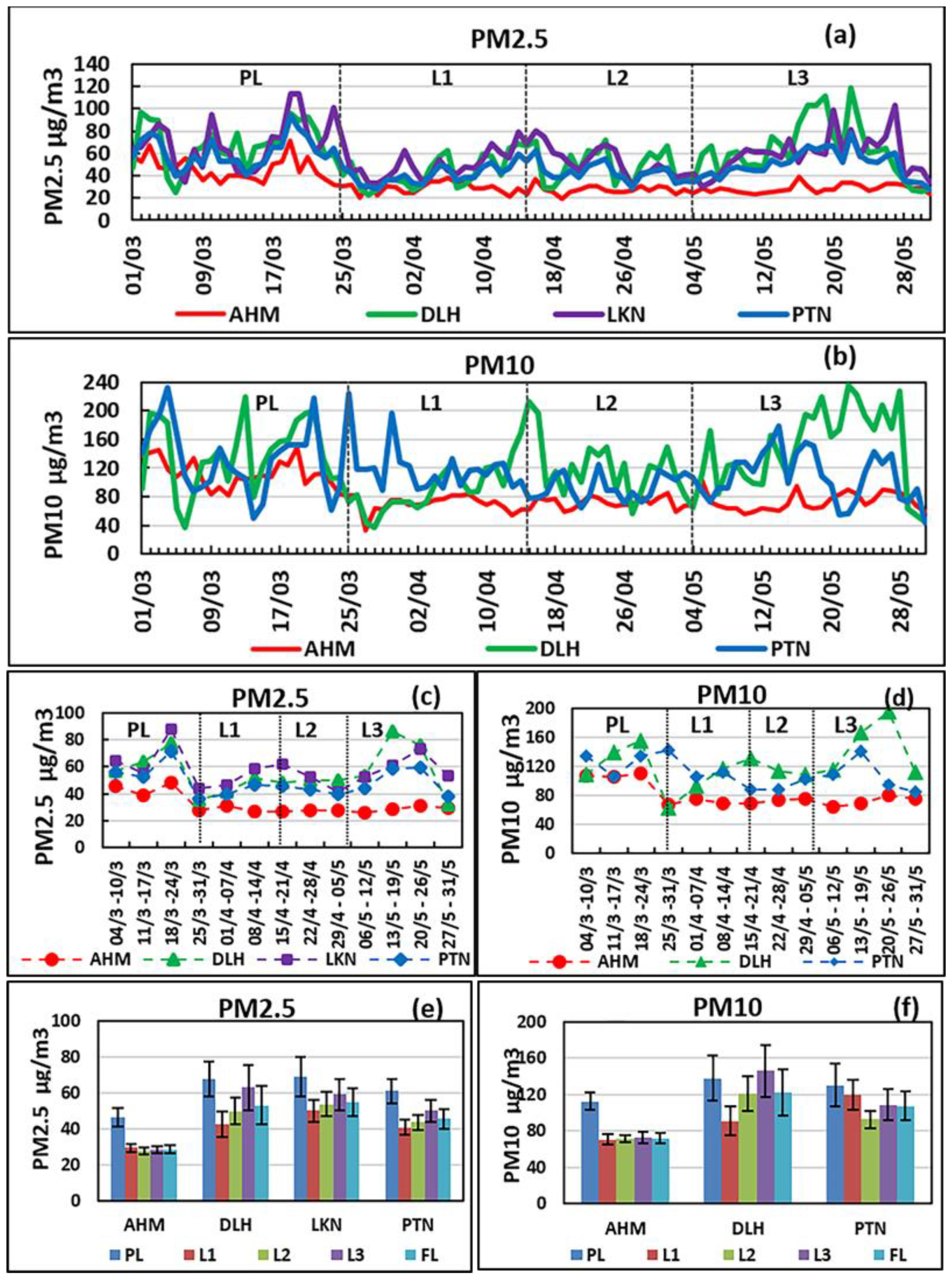
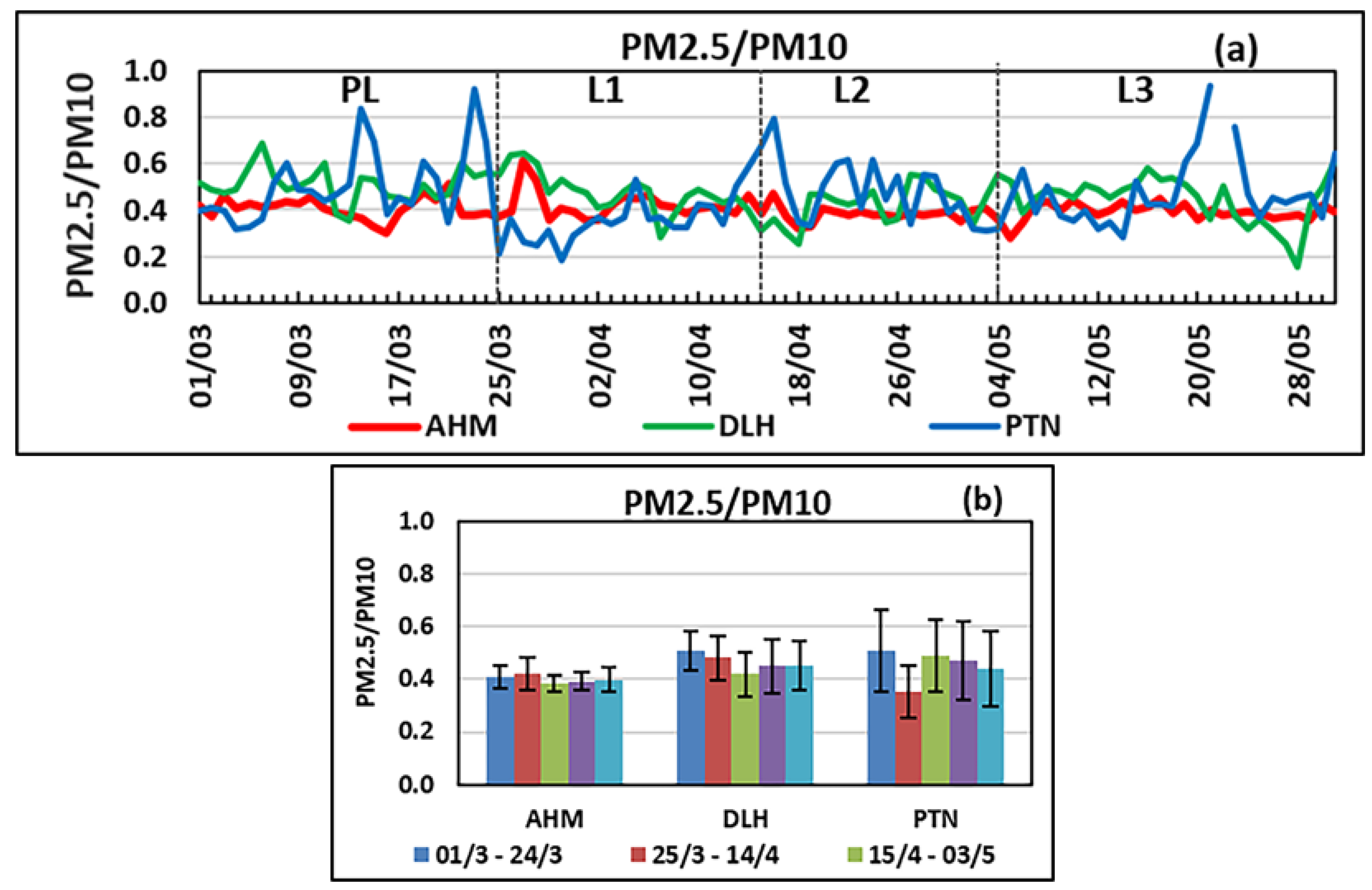
3.4. Variation in PM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, R.P.; Samuel, C.; Rekha, S.R.; Gautam, S. Air pollution in five Indian megacities during the Christmas and New Year celebration amidst COVID-19 pandemic. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 3653–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.P.; Perumpully, S.J.; Samuel, C.; Gautam, S. Exposure and health: A progress update by evaluation and scientometric analysis. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 37, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, S.; Niwalkar, A.; Gupta, A.; Gautam, S.; Anshul, A.; Bherwani, H.; Biniwale, R.; Kumar, R. Is safe distance enough to prevent COVID-19? Dispersion and tracking of aerosols in various artificial ventilation conditions using OpenFOAM. Gondwana Res. 2022, 114, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, H.R.; Mutreja, G.; Shakeel, A.; Singh, K.; Abbas, K.; Fatma, D.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Gautam, A.S.; Gautam, S.; et al. Wildfire-induced pollution and its short-term impact on COVID-19 cases and mortality in California. Gondwana Res. 2022, 114, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, S.; Gollakota, A.R.K. Introduction to the special issue “Environmental impacts of COVID-19 pandemic”. Gondwana Res. 2022, 114, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelani, A.; Gautam, S. Lockdown during COVID-19 pandemic: A case study from Indian cities shows insignificant effects on urban air quality. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelani, A.; Gautam, S. The influence of meteorological variables and lockdowns on COVID-19 cases in urban agglomerations of Indian cities. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 2949–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Sammuel, C.; Gautam, A.S.; Kumar, S. Strong link between coronavirus count and bad air: A case study of India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 16632–16645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bherwani, H.; Gautam, S.; Gupta, A. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Impact of COVID-19 on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in Indian Subcontinent with a Focus on Air Quality. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, C. Estimation of ground-level PM2.5 concentration using MODIS AOD and corrected regression model over Beijing, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Ichoku, C.; Remer, L.A.; Tanre, D.; Holben, B.N. Validation of MODIS aerosol optical depth retrieval over land. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, MOD2-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A.; Wang, J.; Gehrig, R.; Lee, Y.C.; Kumar, N. Satellite remote sensing of particulate matter and air quality assessment over global cities. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5880–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Chu, A.; Foster, A. An empirical relationship between PM2.5 and aerosol optical depth in Delhi Metropolitan. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4492–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Zhang, X.; Holt, J.B.; Liu, Y. Spatio-Temporal variations in the associations between hourly PM2.5 and AOD from MODIS Sensors on Terra and Aqua. Health 2013, 5, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bherwani, H.; Kumar, S.; Musugu, K.; Nair, M.; Gautam, S.; Gupta, A.; Ho, C.H.; Anshul, A.; Kumar, R. Assessment and valuation of health impacts of fine particulate matter during COVID-19 lockdown: A comprehensive study of tropical and subtropical countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 28, 44522–44537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, J.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Prakash, S.; Patni, B.; Gautam, S.; Gautam, A.S. Addressing the relevance of COVID–19 pandemic in nature and human socio-economic fate. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 3239–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Blessy, A.; Kumar, R.P. A methodological approach to identify communities at risk: Trajectory dispersion models to trace air pollutants during colour festival. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2022, 4, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambade, B.; Sankar, T.K.; Kumar, A.; Gautam, A.S.; Gautam, S. COVID-19 lockdowns reduce the Black carbon and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of the Asian atmosphere: Source apportionment and health hazard evaluation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 12252–12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Hens, L. SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in India: What might we expect? Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 3867–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Sankar, T.K.; Kumar, A.; Ambade, B.; Gautam, S.; Gautam, A.S.; Biswas, J.K.; Salam, M.A. Emissions of black carbon and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Potential implications of cultural practices during the COVID-19 pandemic. Gondwana Res. 2022, 114, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Tiwari, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, R.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Lal, D.M.; Singh, A.K.; Mall, R.K.; Srivastava, M.K. Radiative impact of fireworks at a tropical Indian location: A case study. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014, 197072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Sagnik, D.; Holben, B. Aerosol behavior in Kanpur during Diwali festival. Curr. Sci. 2003, 84, 1302–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Vaghmaria, N.; Mevada, N.; Maliakal, J. Impact of Diwali festival on aerosol optical properties over an urban city, Ahmedabad (India). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, B.M.; Saraswat, V. Studies of atmospheric aerosol’s parameters during pre-Diwali to post–Diwali festival period over Indian Semi-arid station i.e., Udaipur. Appl. Phys. Res. 2012, 4, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, G.; John, I.B.P.; Mary, T.; Packiavathy, S.V.; Gautam, S. Internet of Things (IoT) based automated sanitizer dispenser and COVID-19 statistics reporter in a post-pandemic world. Health Technol. 2023, 13, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvadass, S.; Paul, J.J.; Marry, T.B.; Packiavathy, I.S.V.; Gautam, S. IoT-Enabled smart mask to detect COVID-19 outbreak. Health Technol. 2022, 12, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, N.; Cao, Y.; Alwalid, O.; Gu, J.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, C. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2020. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Kanniah, K.D.; Zaman Kamarul, N.A.F.; Kaskaoutis, G.D.; Latif, M.T. COVID-19’s impact on the atmospheric environment in the Southeast Asia region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Huang, Y.; Huang, J.; Dong, L.; Guan, X.; Ge, J.; Hu, Z. Using Lidar and Historical Similar Meteorological Fields to Evaluate the Impact of Anthropogenic Control on Dust Weather During COVID-19. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, V.; Stefan, S.; Nemuc, A. Changes in the aerosol properties during pandemic restrictions in Romania. Rom. J. Phys. 2022, 67, 809. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, B.; Jin, S.; Shen, A.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Q. Aerosol Characteristics during the COVID-19 Lockdown in China: Optical Properties, Vertical Distribution, and Potential Source. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, S.; Sabin, T.P.; Rap, A.; Müller, R.; Kubin, A.; Heinold, B. The Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown Measures on the Indian Summer Monsoon. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 074054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Hooda, W.; Chauhan, P. A satellite view of the changes in summer-time aerosol vertical distribution before and during COVID-19 lockdown conditions in India. Curr. Sci. 2021, 120, 1818–1819. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan, A.K.; Patra, A.K.; Gorai, A.K. Effect of lockdown due to SARS COVID-19 on AOD over urban and mining regions in India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, N.; Sharma, G.; Baruah, P.; Shukla, V.K.; Gargava, P. Impact of shutdown due to COVID-19 pandemic on aerosol characteristics in Kanpur, India. J. Health Pollut. 2020, 10, 201201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.A.; Sen, A.; Menon, H.B. Effect of SARS-CoV-2 pandemic induced lockdown on the aerosol loading over the coastal state. Goa. Curr. Sci. 2021, 120, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resmi, C.T.; Nishanth, T.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Manoj, M.G.; Balachandramohan, M.; Valsaraj, K.T. Air quality improvement during triple-lockdown in the coastal city of Kannur, Kerala to combat COVID-19 transmission. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Vinoj, V. Surprising Changes in Aerosol Loading over India amid COVID-19 Lockdown. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnam, V.; Prasad, P.; Raj, S.A.; Ibrahim, H. Effect of Lockdown due to COVID-19 on the Aerosol and Trace Gases Spatial Distribution over India and Adjoining Regions. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.O.R.; Gugamsetty, B.; Tandule, C.R.; Kotalo, R.G.; Thotli, L.R.; Rajuru, R.R.; Palle, S.N.R. Impact of aerosols on surface ozone during COVID-19 pandemic in southern India: A multi-instrumental approach from ground and satellite observations, and model simulations. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2021, 212, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shang, H.; Cui, Z.; Dai, Z.; Ma, Z. COVID-19 as a Factor Influencing Air Quality? A City Study in China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 210080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobías, A.; Carnerero, C.; Reche, C.; Massagué, J.; Via, M.; Minguillón, M.C.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. Changes in air quality during the lockdown in Barcelona (Spain) one month into the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristina, M.; Abbà, A.; Bertanza, G.; Pedrazzani, R.; Ricciardi, P.; Carnevale, M. Lockdown for COVID-19 in Milan: What are the effects on air quality? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139280. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas, G.; Siciliano, B.; França, B.B.; da Silva, C.M.; Arbilla, G. The impact of COVID-19 partial lockdown on the air quality of the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, B.; Carvalho, G.; da Silva, C.M.; Arbilla, G. The impact of COVID-19 partial lockdown on primary pollutant concentrations in the atmosphere of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo megacities (Brazil). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerimray, A.; Baimatova, N.; Ibragimova, O.P.; Bukenov, B.; Kenessov, B.; Plotitsyn, P.; Karaca, F. Assessing air quality changes in large cities during COVID-19 lockdowns: The impacts of traffic-free urban conditions in Almaty, Kazakhstan. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otmani, A.; Benchrif, A.; Tahri, M.; Bounakhla, M.; Chakir, E.M.; El Bouch, M.; Krombi, M. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on PM10, SO2 and NO2 concentrations in Salé City (Morocco). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Kumar, K.R.; Zhao, T. The Impact of Lockdown on Air Quality in Pakistan during the COVID-19 Pandemic Inferred from the Multi-sensor Remote Sensed Data. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Bherwani, H.; Gautam, S.; Anjum, S.; Musugu, K.; Kumar, N.; Anshul, A.; Kumar, R. Air pollution aggravating COVID-19 lethality? Exploration in Asian cities using statistical models. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 6408–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bherwani, H.; Nair, M.; Musugu, K.; Gautam, S.; Gupta, A.; Kapley, A.; Kumar, R. Valuation of air pollution externalities: Comparative assessment of economic damage and emission reduction under COVID-19 lockdown. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.; Kumar, S.; Singh, T.; Dogra, S.; Pandey, V.; Ravindra, K. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on air quality in Chandigarh, India: Understanding the emission sources during controlled anthropogenic activities. Chemosphere 2020, 263, 127978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, A.; Singh, T.; Singh, V.; Ravindra, K.; Mor, S. COVID-19 lockdown and its impact on tropospheric NO2 concentrations over India using satellite-based data. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Cui, K.; Young, L.; Hsieh, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wan, S. Impact of the COVID-19 event on air quality in Central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, T.A.; Ramachandran, S. Assessment of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic imposed lockdown and unlock effects on black carbon aerosol, its source apportionment, and aerosol radiative forcing over an urban city in India. Atmos. Res. 2021, 267, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, S. The influence of COVID-19 on air quality in India: A boon or inutile. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, S. COVID-19: Air pollution remains low as people stay at home. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jethva, H.; Satheesh, S.K.; Srinivasan, J. Seasonal variability of aerosols over the Indo-Gangetic basin. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Tripathi, S.N.; Singh, R.P.; Holben, B.N. Influence of dust storms on the aerosol optical properties over the Indo-Gangetic plains. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D20211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambade, B.; Sankar, T.K.; Gupta, M.; Sahu, L.K.; Gautam, S. A comparative study in black carbon concentration and its emission sources in tribal area. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Dey, S.; Tripathi, S.N. Aerosol characteristics over the Indo-Gangetic Basin: Implications to regional climate. In Atmospheric Aerosols-Regional Characteristics-Chemistry and Physics; Abdul-Razzak, H., Ed.; Texas A&M University: Kingsville, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Singh, R.P.; Gautam, R.; Sharma, M.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Tripathi, S.N. Variability and trends of aerosol properties over Kanpur, northern India using AERONET data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Kaufman, Y.J. Algorithm for remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol over dark targets from MODIS: Collection 005 and 051: Revision 2. In MODIS Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document; GSFC/NASA: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2009; Volume 20771, p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Hama, S.M.L.; Kumar, P.; Harrison, R.M.; Bloss, W.J.; Khare, M.; Mishra, S.; Sharma, C. Four-year assessment of ambient particulate matter and trace gases in the Delhi-NCR region of India. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, Y.; Mitra, D.; Chauhan, P. Space-based observations on the impact of COVID-19-induced lockdown on aerosols over India. Curr. Sci. 2020, 119, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Regions | AOD Data | PM Data | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | Longitude | ||
| Ahmedabad | 22–24° N | 72–73° E | Maninagar, Gandhinagar, Vatva. |
| Delhi | 28–29° N | 76–78° E | Ashok Vihar, CRRI Mathura Road, Aya Nagar, Bawana, Alipur |
| Lucknow | 26–27° N | 80–82° E | Gomti Nagar, Central School; Lalbaugh, Talkatora |
| Patna | 25–26° N | 84–86° E | Muradpur, Rajhansi Nagar |
| AOD | AE | PM2.5 | PM10 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | PL | L1 | FL | PL | L1 | FL | PL | L1 | FL | PL | L1 | FL |
| Ahmedabad | 0.31 | 0.22 (−29) | 0.26 (−16) | 0.96 | 1.16 (21) | 1.27 (32) | 46.1 | 29.3 (−36) | 28.4 (−38) | 112.5 | 70.4 (−37) | 71.8 (−36) |
| Delhi | 0.66 | 0.31 (−53) | 0.48 (−27) | 1.54 | 1.13 (−27) | 0.83 (−46) | 67.5 | 42.6 (−37) | 52.9 (−22) | 138.1 | 91.1 (−34) | 122.2 (−12) |
| Lucknow | 0.63 | 0.28 (−56) | 0.50 (−21) | 1.41 | 1.17 (−17) | 1.04 (−26) | 68.9 | 49.9 (−28) | 54.6 (−21) | |||
| Patna | 0.61 | 0.34 (−44) | 0.55 (−10) | 1.58 | 1.20 (−24) | 1.21 (−23) | 60.8 | 40.7 (−33) | 45.3 (−26) | 130.4 | 120.2 (−8) | 107.7 (−17) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaghmaria, N.; ME, J.; Gautam, A.S.; Gautam, S. Impact of Lockdown on Column and Surface Aerosol Content over Ahmedabad and a Comparison with the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Earth 2023, 4, 278-295. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth4020015
Vaghmaria N, ME J, Gautam AS, Gautam S. Impact of Lockdown on Column and Surface Aerosol Content over Ahmedabad and a Comparison with the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Earth. 2023; 4(2):278-295. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth4020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaghmaria, Nisha, James ME, Alok Sagar Gautam, and Sneha Gautam. 2023. "Impact of Lockdown on Column and Surface Aerosol Content over Ahmedabad and a Comparison with the Indo-Gangetic Plain" Earth 4, no. 2: 278-295. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth4020015
APA StyleVaghmaria, N., ME, J., Gautam, A. S., & Gautam, S. (2023). Impact of Lockdown on Column and Surface Aerosol Content over Ahmedabad and a Comparison with the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Earth, 4(2), 278-295. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth4020015







