Figure 1.
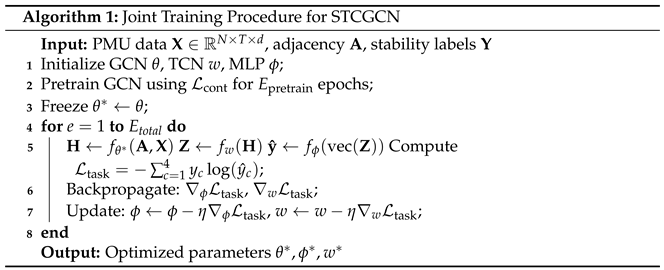
The framework of the joint STCGCN stability prediction.
Figure 1.
The framework of the joint STCGCN stability prediction.
Figure 2.
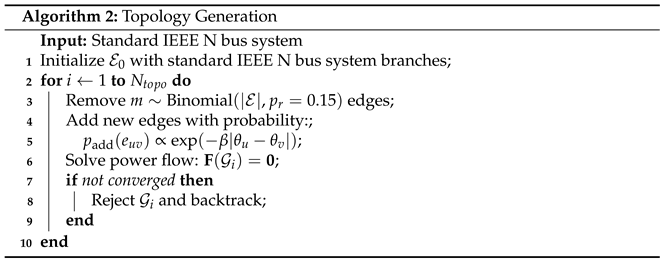
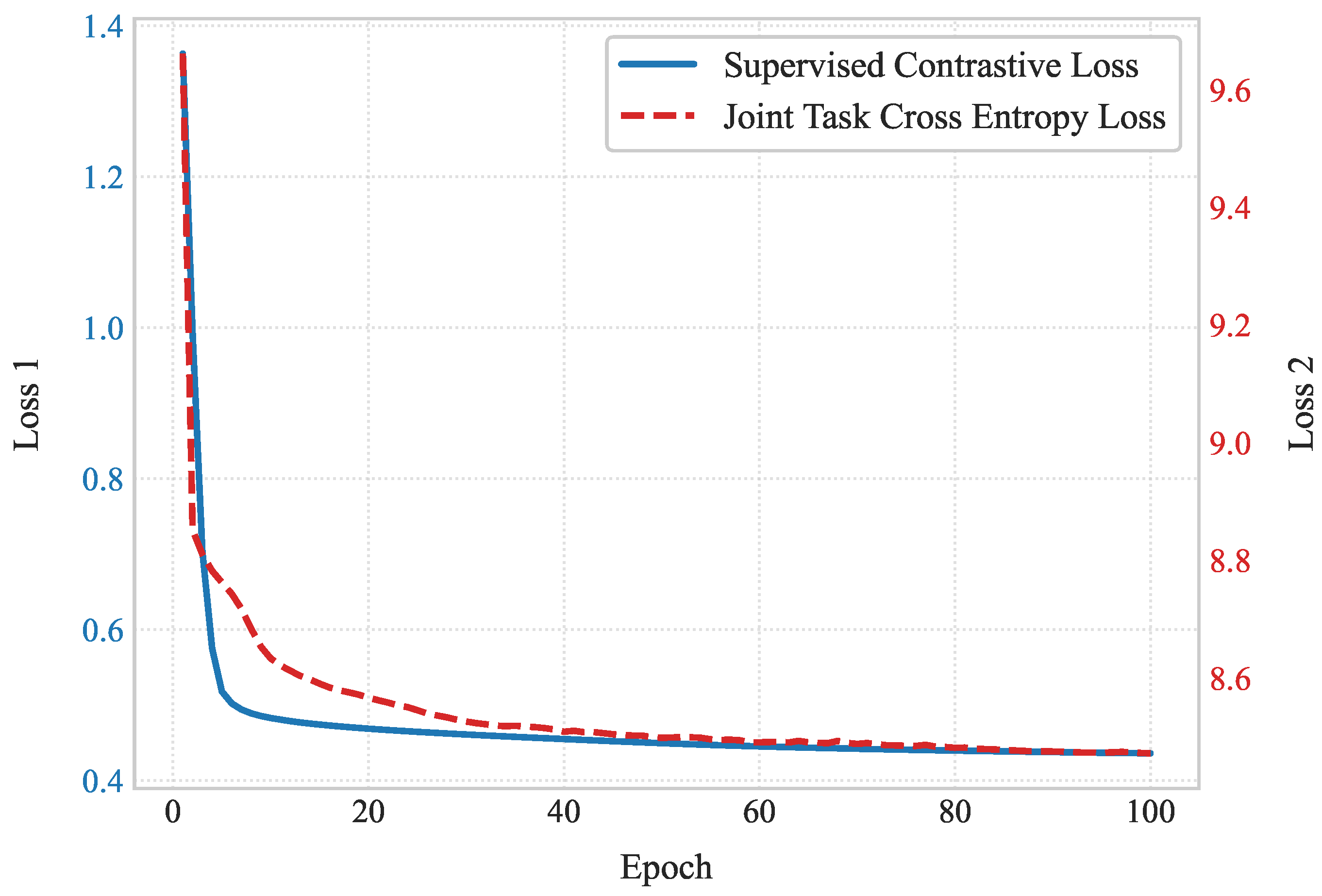
Training loss curves for the joint prediction model.
Figure 2.
Training loss curves for the joint prediction model.
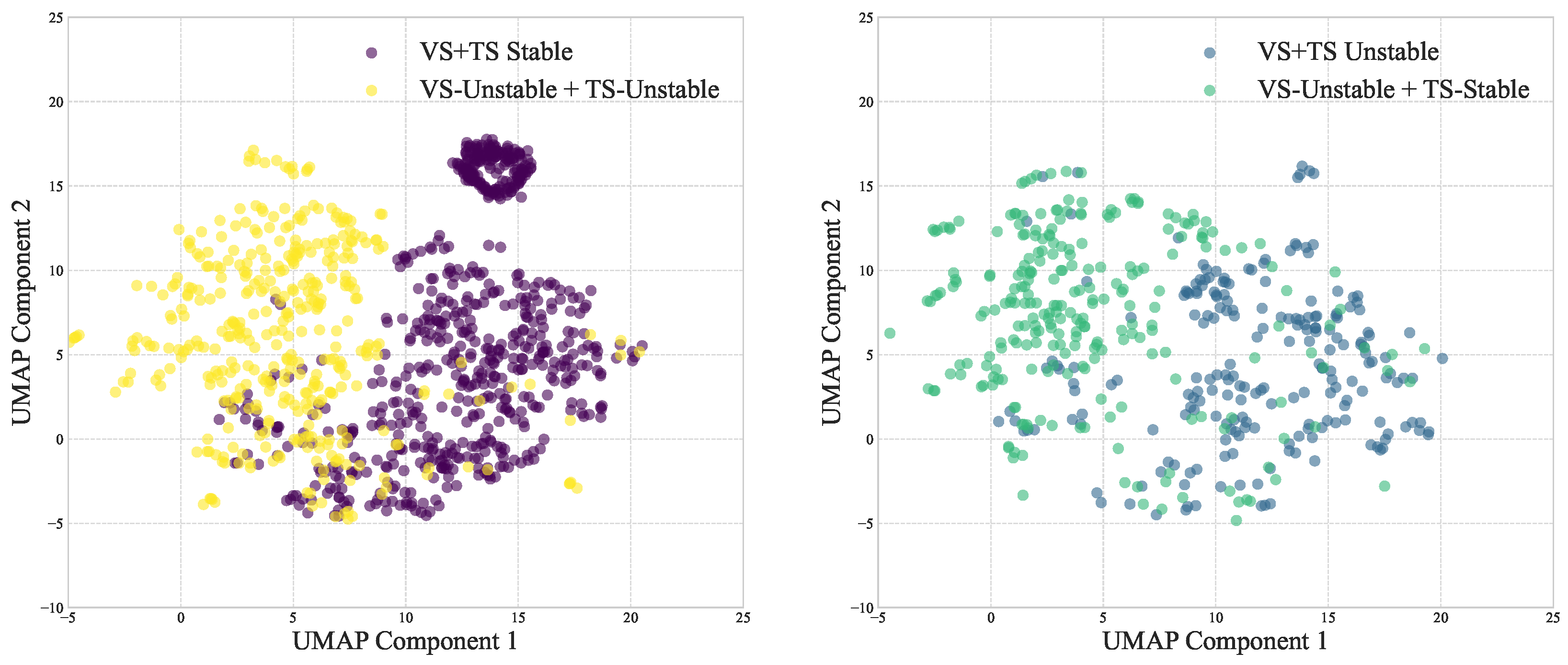
Figure 3.
In-sample dataset GCN encoder representation quality. Two-dimensional UMAP projection of supervised contrastive GCN features showing clear cluster separation among stable, unstable, voltage-unstable, and transient-unstable feature labels.
Figure 3.
In-sample dataset GCN encoder representation quality. Two-dimensional UMAP projection of supervised contrastive GCN features showing clear cluster separation among stable, unstable, voltage-unstable, and transient-unstable feature labels.
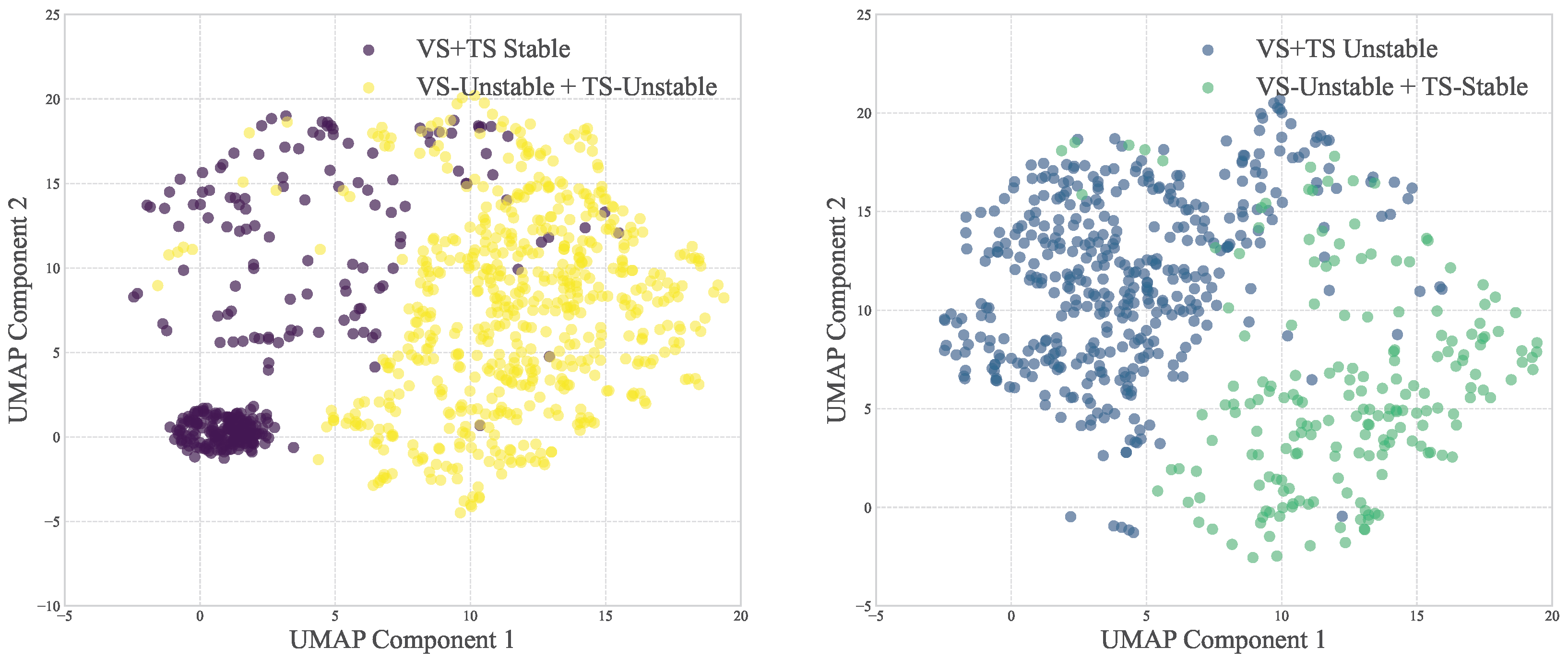
Figure 4.
Out-of-sample dataset GCN encoder representation quality. Two-dimensional UMAP projection of supervised contrastive GCN features obtained with the out-of-sample with unseen topologies, showing clear cluster separation and demonstrating cross-topology robustness.
Figure 4.
Out-of-sample dataset GCN encoder representation quality. Two-dimensional UMAP projection of supervised contrastive GCN features obtained with the out-of-sample with unseen topologies, showing clear cluster separation and demonstrating cross-topology robustness.
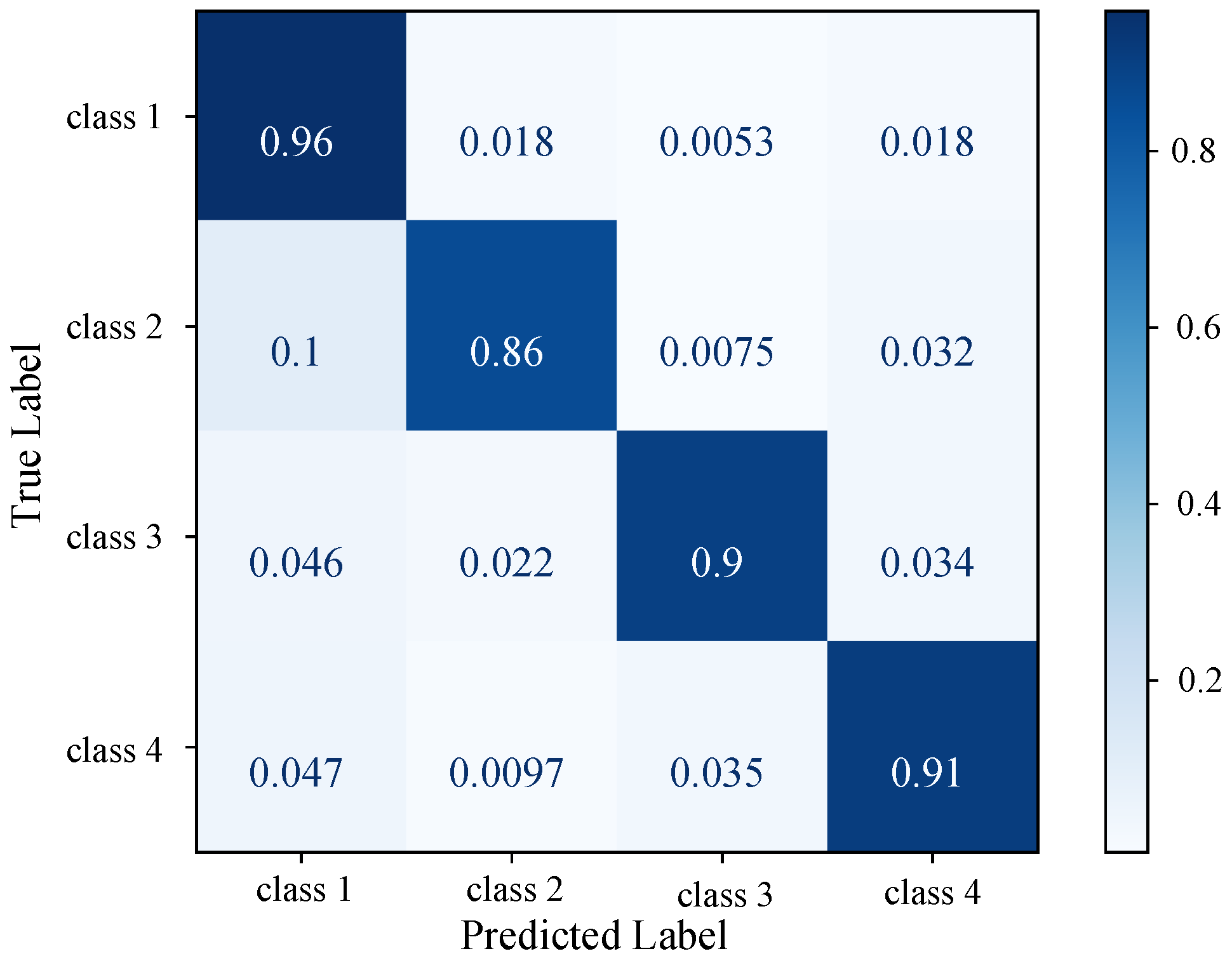
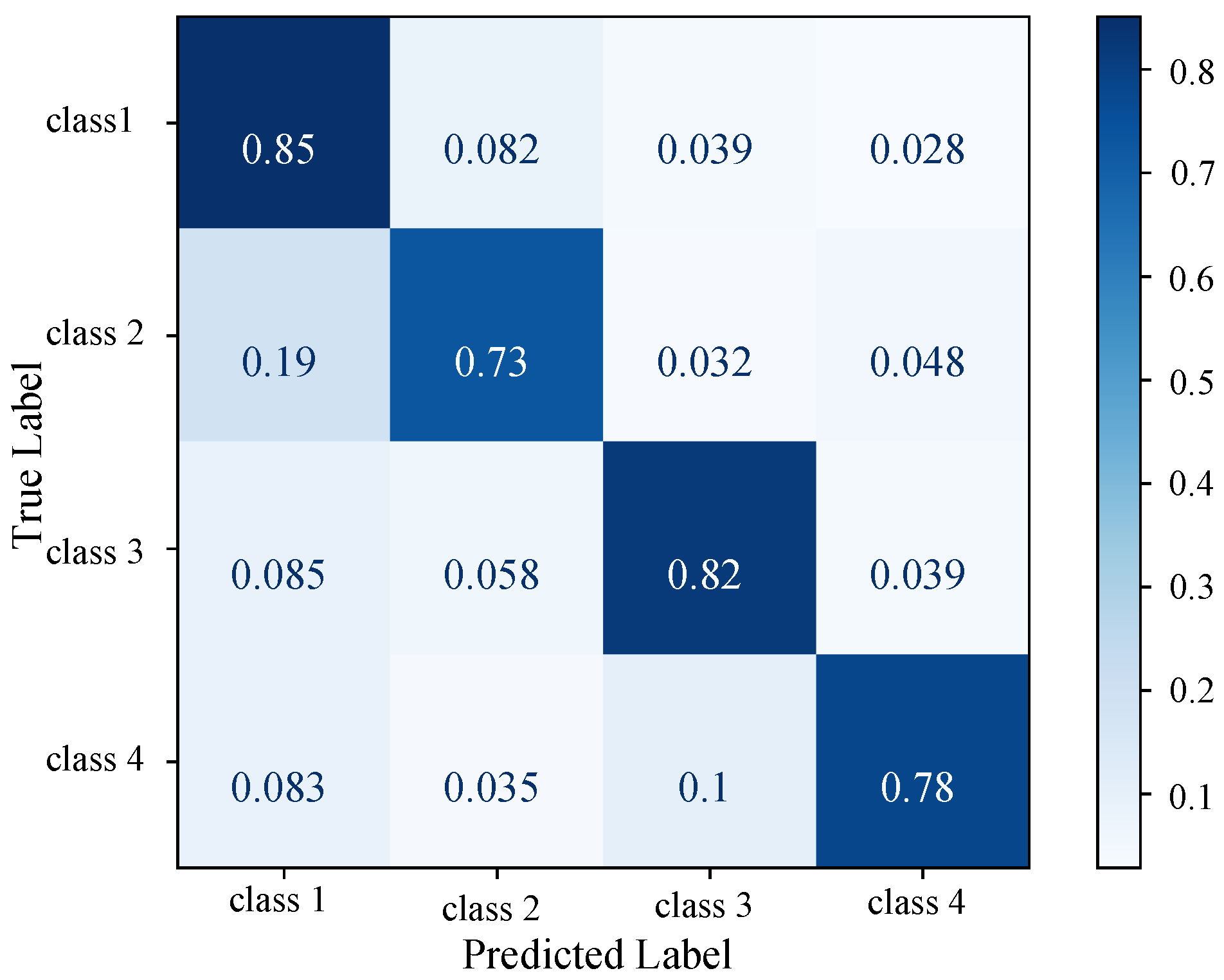
Figure 5.
STCGCN confusion matrix on the in-sample dataset. Four classes (class 1, class 2, class 3, and class 4) correspond to one-hot labels , , , and , respectively.
Figure 5.
STCGCN confusion matrix on the in-sample dataset. Four classes (class 1, class 2, class 3, and class 4) correspond to one-hot labels , , , and , respectively.
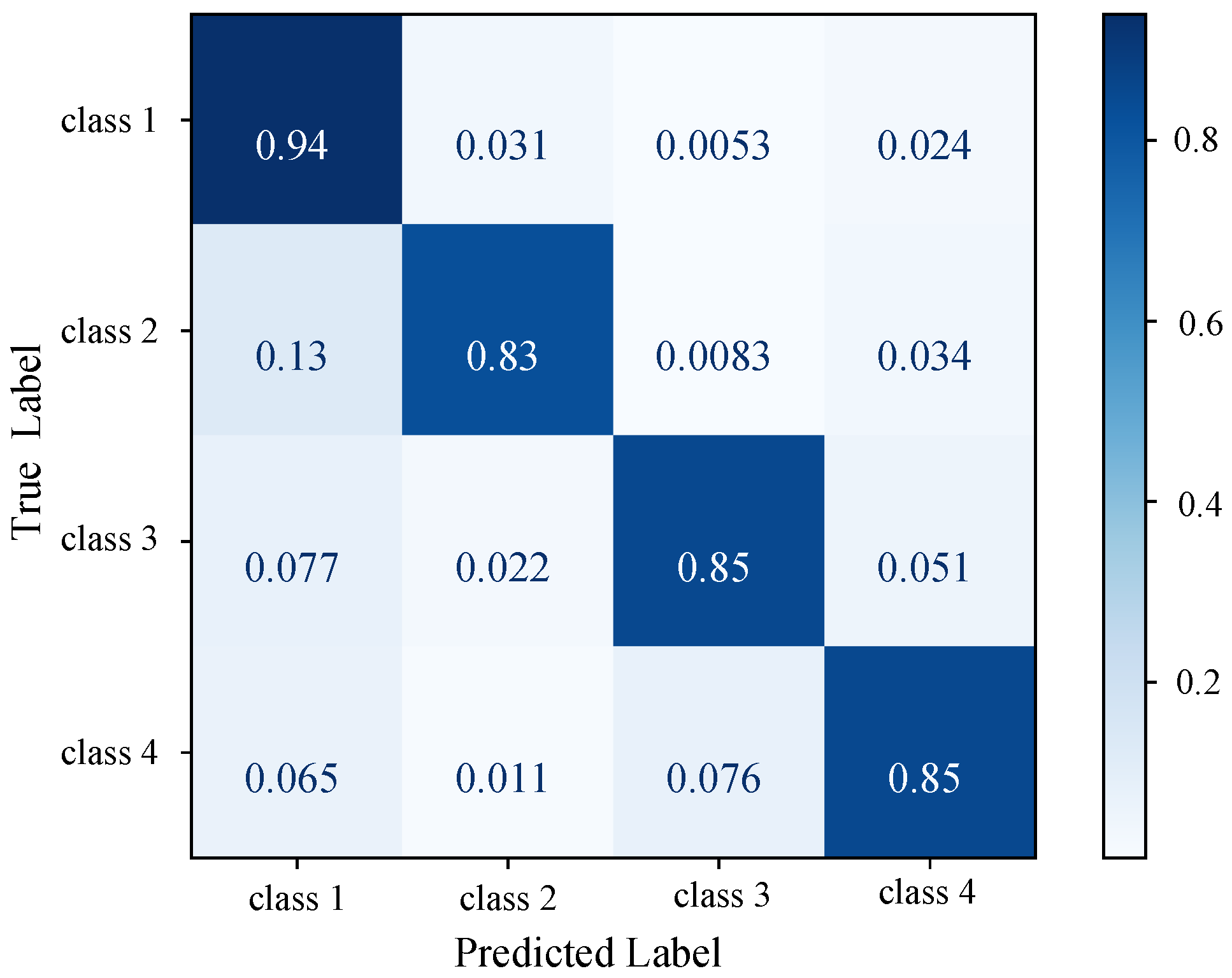
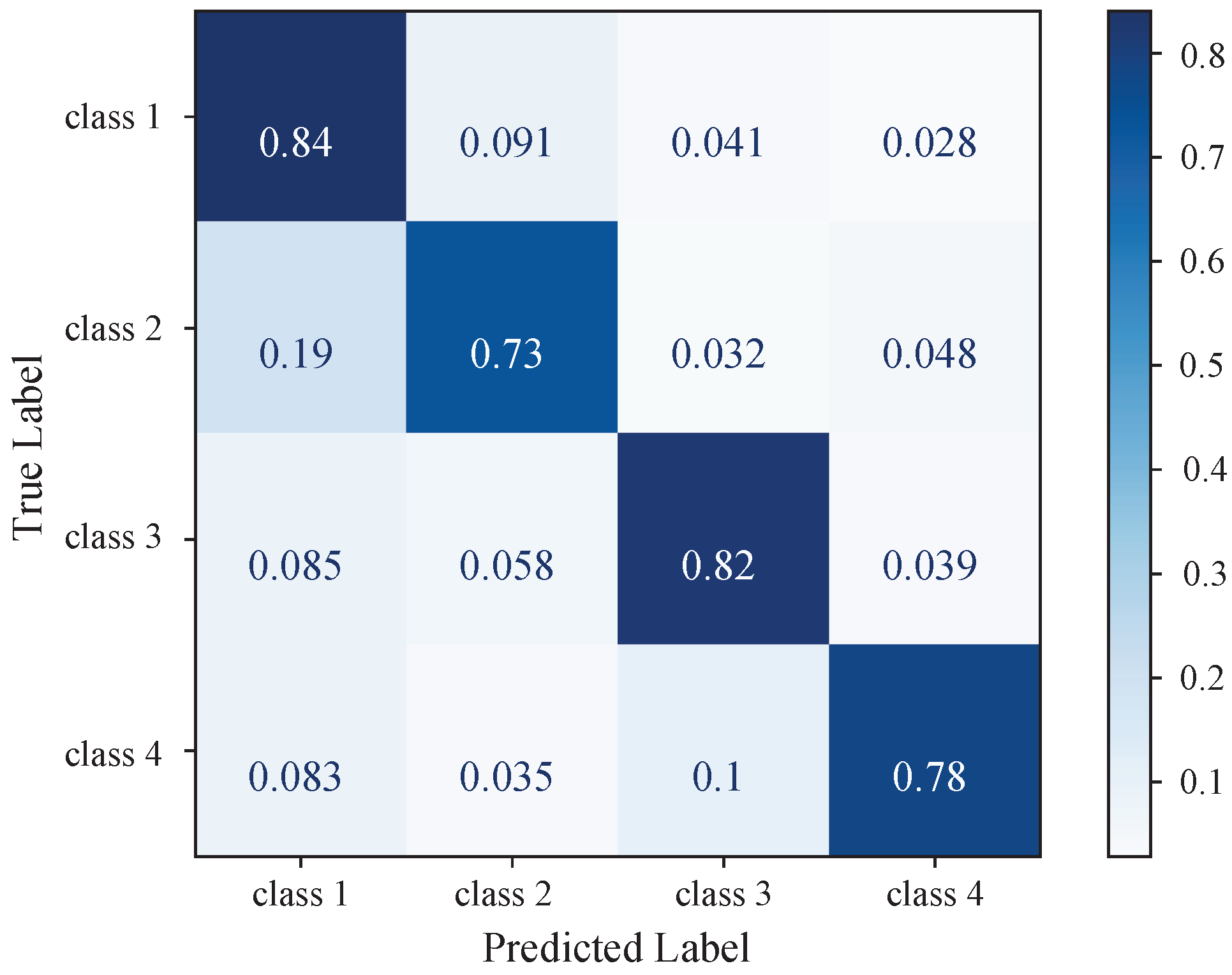
Figure 6.
STCGCN confusion matrix on the out-of-sample dataset. Four classes (class 1, class 2, class 3, and class 4) correspond to one-hot labels , , , and , respectively.
Figure 6.
STCGCN confusion matrix on the out-of-sample dataset. Four classes (class 1, class 2, class 3, and class 4) correspond to one-hot labels , , , and , respectively.
Figure 7.
STEGNN confusion matrix on the in-sample test dataset with unseen topologies. Four classes (class 1, class 2, class 3, and class 4) correspond to one-hot labels , , , and .
Figure 7.
STEGNN confusion matrix on the in-sample test dataset with unseen topologies. Four classes (class 1, class 2, class 3, and class 4) correspond to one-hot labels , , , and .
Figure 8.
STEGNN Confusion matrix on the out-of-sample test dataset with unseen topologies. Four classes (class 1, class 2, class 3, and class 4) correspond to one-hot labels , , , and .
Figure 8.
STEGNN Confusion matrix on the out-of-sample test dataset with unseen topologies. Four classes (class 1, class 2, class 3, and class 4) correspond to one-hot labels , , , and .
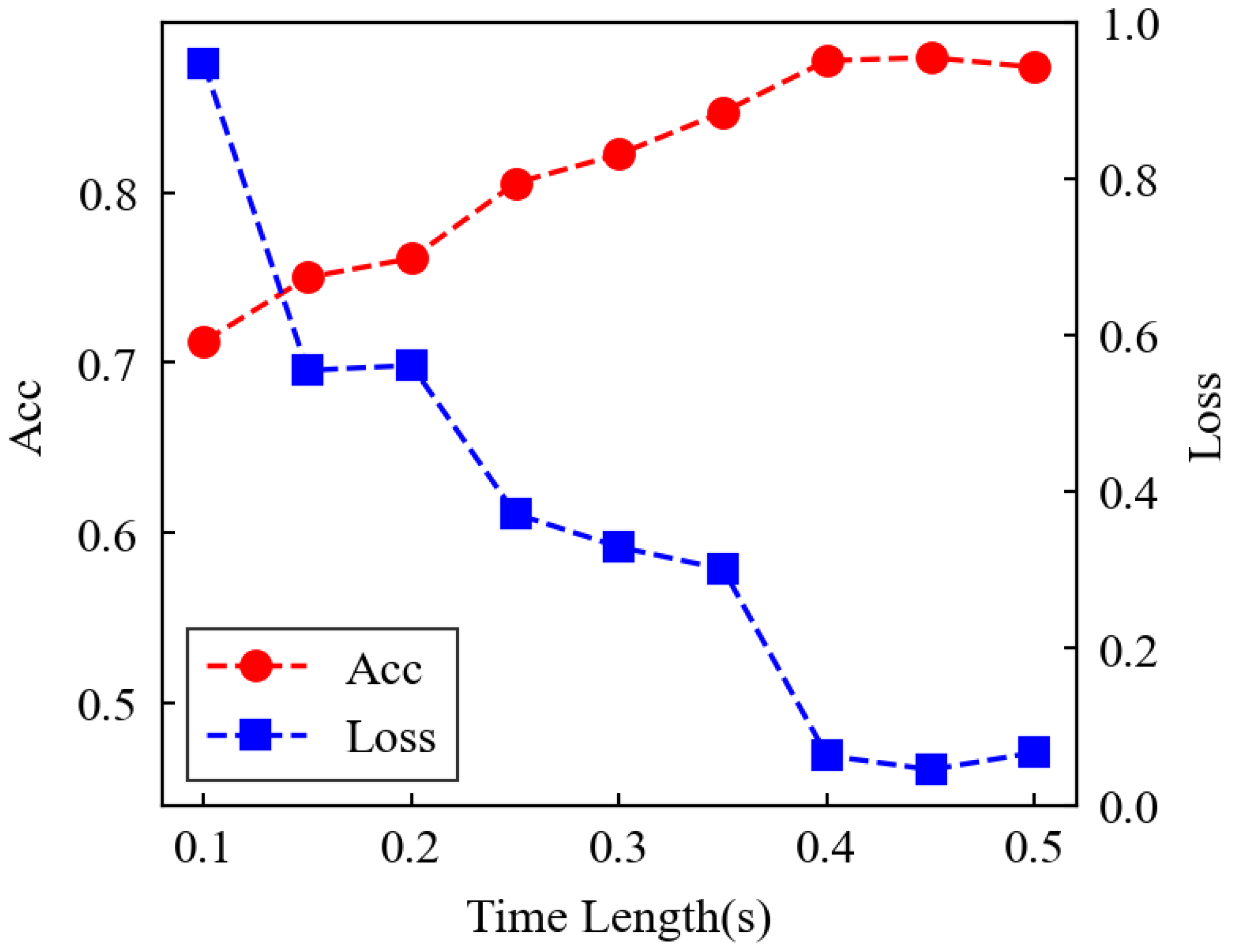
Figure 9.
Effect of post-fault PMU window length on the joint STCGCN prediction accuracy in the IEEE 39-bus system.
Figure 9.
Effect of post-fault PMU window length on the joint STCGCN prediction accuracy in the IEEE 39-bus system.
Table 1.
Description as table header, please confirm. of label and as one-hot form for transient stability and voltage stability.
Table 1.
Description as table header, please confirm. of label and as one-hot form for transient stability and voltage stability.
| Label y | = 1 | = 0 |
|---|
| = 1 | [1, 0, 0, 0] | [0, 1, 0, 0] |
| = 0 | [0, 0, 1, 0] | [0, 0, 0, 1] |
Table 2.
Hyperparameter settings and selection rationale for the STCGCN model.
Table 2.
Hyperparameter settings and selection rationale for the STCGCN model.
| Category | Hyperparameter | Value | Selection Criteria |
|---|
| Architecture | GCN Layers | 3 | Balances spatial feature extraction depth and computational cost. Fewer layers led to underfitting, while more caused overfitting. |
| GCN Hidden Dimension | 256 | Provides sufficient model capacity. Determined via grid search over {128, 256, 512}. |
| TCN Kernel Size | 3 | Effective for capturing local temporal patterns. |
| TCN Dilation Rates | {1, 2, 4} | Designed to capture multi-scale electromechanical dynamics within the 0.4 s window. |
| Dropout Rate | 0.2 | Mitigates overfitting; validated on the out-of-sample topology test set. |
| MLP Hidden Units | 512 | Offers ample nonlinear transformation capability for the final joint classification. |
| Training | Batch Size | 64 | Maximizes GPU memory utilization while maintaining stable gradient descent. |
| Initial Learning Rate | | Used with the Adam optimizer for stable and efficient convergence. |
| SCL | Temperature () | 0.1 | Scales the cosine similarity in the contrastive loss function. |
| Projection Head Dim | 128 | Projects GCN embeddings into the space where contrastive loss is applied. |
| Positive Pair Margin | 0.5 | Defines the similarity threshold for constructing positive pairs in SCL. |
| Data | Observation Window | 0.40 s | Selected as the optimal trade-off between prediction accuracy and real-time latency, as analyzed in Section 4.5. |
Table 3.
Per-class performance metrics of STCGCN on in-sample dataset.
Table 3.
Per-class performance metrics of STCGCN on in-sample dataset.
| Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support |
|---|
| Class 1 | 0.889 | 0.959 | 0.923 | 1690 |
| Class 2 | 0.948 | 0.858 | 0.901 | 1203 |
| Class 3 | 0.934 | 0.899 | 0.916 | 785 |
| Class 4 | 0.896 | 0.908 | 0.902 | 925 |
Table 4.
Per-class performance metrics of STCGCN on the out-of-sample dataset.
Table 4.
Per-class performance metrics of STCGCN on the out-of-sample dataset.
| Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support |
|---|
| Class 1 | 0.853 | 0.941 | 0.871 | 1690 |
| Class 2 | 0.942 | 0.842 | 0.865 | 1178 |
| Class 3 | 0.874 | 0.861 | 0.868 | 782 |
| Class 4 | 0.869 | 0.847 | 0.856 | 945 |
Table 5.
Performance of STCGCN vs. STEGNN in the out-of-sample dataset with unseen power grid topologies.
Table 5.
Performance of STCGCN vs. STEGNN in the out-of-sample dataset with unseen power grid topologies.
| Method | Correct | Missing | Accuracy (%) |
|---|
| STCGCN | 4036 | 564 | 87.73 |
| STEGNN | 3746 | 854 | 81.43 |
Table 6.
Performance of STCGCN vs. STEGNN in the in-sample dataset with unseen power grid topologies.
Table 6.
Performance of STCGCN vs. STEGNN in the in-sample dataset with unseen power grid topologies.
| Method | Correct | Missing | Accuracy (%) |
|---|
| STCGCN | 4124 | 476 | 89.66 |
| STEGNN | 3634 | 966 | 79.00 |
Table 7.
Performance and result reliability.
Table 7.
Performance and result reliability.
| Model | In-Sample Dataset (%) | Out-of-Sample Dataset (%) |
|---|
| STCGCN (Run 1) | 89.51 | 87.62 |
| STCGCN (Run 2) | 90.12 | 88.05 |
| STCGCN (Run 3) | 89.08 | 86.91 |
| STCGCN (Mean ± SD) | | |
Table 8.
Transient stability prediction (TSP): single-task vs. joint-task for the IEEE 39-bus system.
Table 8.
Transient stability prediction (TSP): single-task vs. joint-task for the IEEE 39-bus system.
| Method | Correct | Missing | Accuracy (%) |
|---|
| Single-task TSP | 3984 | 616 | 86.60 |
| Joint-task TSP | 4156 | 444 | 90.34 |
Table 9.
Voltage stability prediction (VSP): single-task vs. joint-task for the IEEE 39-bus system.
Table 9.
Voltage stability prediction (VSP): single-task vs. joint-task for the IEEE 39-bus system.
| Method | Correct | Missing | Accuracy (%) |
|---|
| Single-task VSP | 3798 | 802 | 82.56 |
| Joint-task VSP | 4353 | 247 | 94.63 |
Table 10.
Performance comparison across different window sizes.
Table 10.
Performance comparison across different window sizes.
| | Window (s) |
|---|
| | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.50 |
| Joint-task in four classes | | | | | | | | | |
| ACC (%) | 71.24 | 75.01 | 76.12 | 80.54 | 82.24 | 84.71 | 87.73 | 87.91 | 87.34 |
| Joint-task TSP | | | | | | | | | |
| ACC (%) | 74.32 | 77.85 | 79.08 | 83.67 | 85.42 | 88.13 | 90.34 | 90.28 | 89.97 |
| FPR (%) | 10.87 | 9.42 | 8.65 | 7.34 | 6.73 | 6.28 | 6.06 | 6.11 | 6.09 |
| FNR (%) | 24.25 | 21.50 | 19.15 | 16.84 | 14.92 | 14.08 | 13.82 | 13.91 | 13.87 |
| Joint-task VSP | | | | | | | | | |
| ACC (%) | 78.95 | 82.43 | 84.17 | 88.92 | 90.86 | 92.98 | 94.63 | 94.57 | 94.21 |
| FPR (%) | 6.15 | 5.48 | 4.87 | 4.13 | 3.78 | 3.52 | 3.45 | 3.48 | 3.46 |
| FNR (%) | 15.43 | 13.62 | 11.95 | 9.84 | 8.92 | 8.67 | 8.61 | 8.65 | 8.69 |
Table 11.
Inference time for STCGCN on the IEEE 39-bus system.
Table 11.
Inference time for STCGCN on the IEEE 39-bus system.
| Batch Size | Avg. Time (ms) | Throughput (Samples/s) |
|---|
| 1 | 18.5 | 54.1 |
| 8 | 12.3 | 650.4 |
| 32 | 9.8 | 3265.3 |
Table 12.
Joint-task STCGCN performance under different PMU SNR levels in the IEEE 39-bus system.
Table 12.
Joint-task STCGCN performance under different PMU SNR levels in the IEEE 39-bus system.
| Task | SNR (dB) | Metrics |
|---|
| ACC (%) | FNR (%) | FPR (%) |
|---|
| Joint-task TSP | None | 90.34 | 13.82 | 6.06 |
| 60 | 89.97 | 14.25 | 6.38 |
| 50 | 89.23 | 14.88 | 6.92 |
| 40 | 87.85 | 16.24 | 7.81 |
| 30 | 84.06 | 19.83 | 10.52 |
| 20 | 80.37 | 23.14 | 13.75 |
| Joint-task VSP | None | 94.63 | 8.61 | 3.45 |
| 60 | 94.25 | 8.92 | 3.78 |
| 50 | 93.68 | 9.47 | 4.25 |
| 40 | 92.31 | 10.85 | 5.14 |
| 30 | 88.92 | 14.24 | 8.03 |
| 20 | 85.43 | 17.86 | 11.32 |