Multi-Objective Optimization for Economic and Environmental Dispatch in DC Networks: A Convex Reformulation via a Conic Approximation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. General Context
1.2. Motivation
1.3. Literature Review
1.4. Contribution and Scope
- A novel convex reformulation of the economic–environmental dispatch (EED) problem in DC networks using second-order cone programming (SOCP), which transforms the original non-convex model into a tractable convex approximation with global optimality guarantees.
- A comparative and physical validation of the SOCP-based model against the original NLP formulation using two MT-HVDC test systems (6-node and 11-node) with photovoltaic generation, demonstrating significant improvements in computational efficiency and emission–cost trade-offs.
1.5. Document Structure
2. Problem Formulation for Economic–Environmental Dispatch
2.1. Objective Functions
2.2. Set of Constraints
3. Approximate Convex Reformulation
Conic Relaxation
4. Test Systems
4.1. Six-Node System
4.2. Eleven-Node System
5. Numerical Validation
5.1. Analysis 1: Comparison Between Convex and Non-Convex Models for the 6-Node System
- Scenario 1: , . Exclusively optimizing generation costs, constituting a single-objective problem.
- Scenario 2: , . Equal importance is given to operational costs and emissions, representing a balanced approach.
- Scenario 3: , . Solely prioritizing the minimization of emissions, ignoring operational costs.
5.1.1. Comparison Results Between DNLP and SOCP Models
5.1.2. Evaluation of the Physical Feasibility of the SOCP Solution
5.1.3. Comparative Analysis with and Without Thermal Current Constraint
5.2. Comparison Between Convex and Non-Convex Models with Photovoltaic Generation
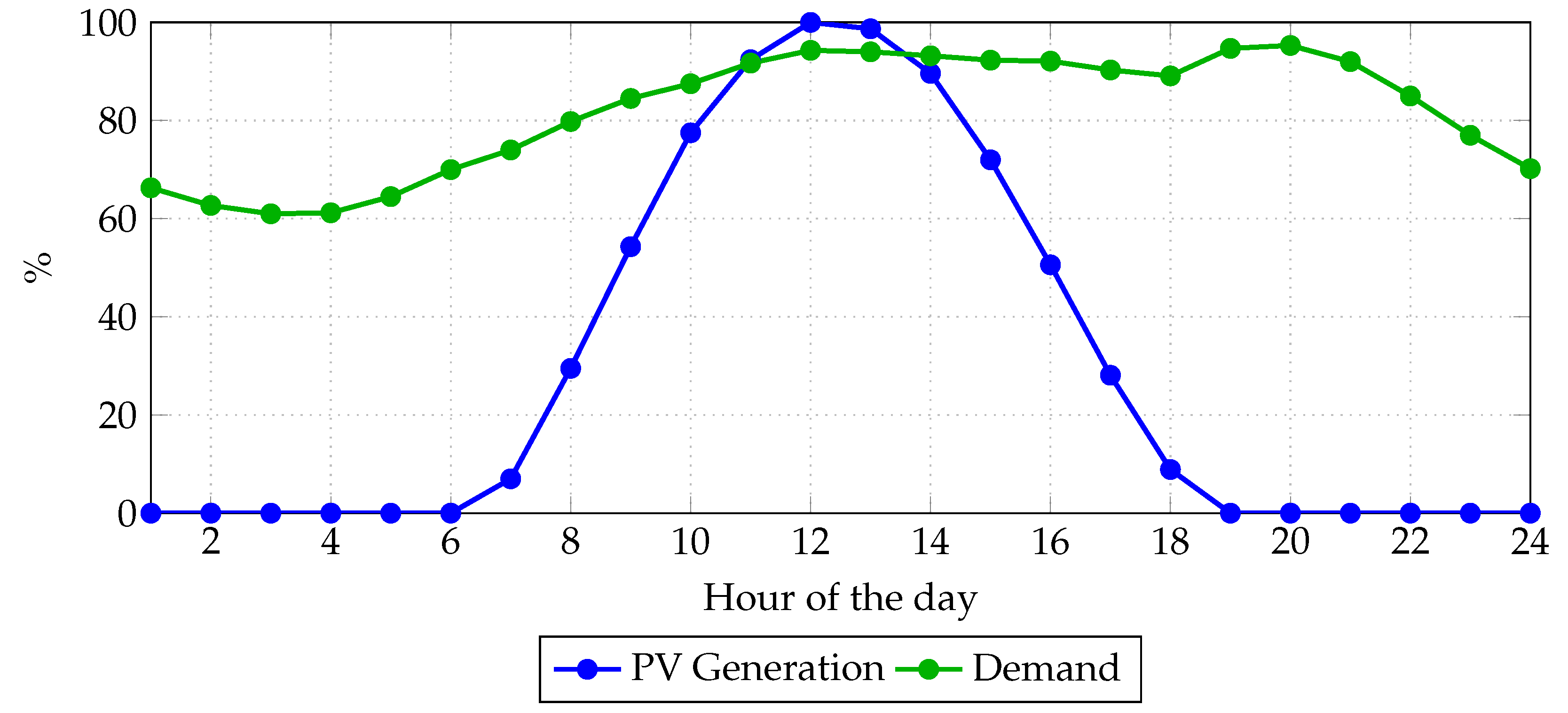
5.3. Analysis of the Impact of Photovoltaic Generation
6. Conclusions
- Relative errors between the SOCP and DNLP models remained below for both cost and emission objectives, confirming the accuracy of the convex approximation.
- The inclusion of thermal current constraints was successfully handled within the SOCP model, yielding operationally feasible and realistic dispatch solutions comparable to those of the non-convex formulation.
- The integration of photovoltaic generation led to a substantial reduction in operating costs and CO2 emissions. Specifically, costs decreased by approximately USD 2.54 million (24.34%) and emissions were reduced by 2.5 million kg of CO2 (27.27%) over a 24 h horizon.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nanda, G.; Yamgar, S.; Srivastava, S.C.; Singh, S.N.; Gupta, P.; Paul, D.; Shrestha, R.M. Implications of carbon tax on generation expansion plan & GHG emission: A case study on Indian power sector. Int. J. Emerg. Electr. Power Syst. 2005, 3, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahdi, S.; Lai, L.L.; Nankoo, D. Grid Integration of Wind-Solar Hybrid Renewables Using AC/DC Converters as DG Power Sources. In Proceedings of the 2011 World Congress on Sustainable Technologies (WCST), London, UK, 7–10 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- García Torres, D.A. Dynamics of Thermoelectric Generation in Colombia: Forecasting Through Long-Memory Time Series. Master’s Thesis, Universidad del Norte, Barranquilla, Colombia, 2014. (In Spanish). [Google Scholar]
- Bastidas, S.; Arcos, H. Despacho económico del sistema híbrido de las islas Santa Cruz y Baltra incorporando la aleatoriedad de potencia de los sistemas eólico y solar fotovoltaico. Rev. Téc. Energy 2019, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragičević, T.; Lu, X.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M. DC Microgrids–Part I: A Review of Control Strategies and Stabilization Techniques. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 4876–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Jeong, Y.W.; Shin, J.R.; Lee, K.Y. An improved particle swarm optimization for nonconvex economic dispatch problems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Shakeel, A.; Altalbe, A.; Alassafi, M.O.; Yasin, A.R. Impacts of MT-HVDC Systems on Enhancing the Power Transmission Capability. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavaei, J.; Low, S.H. Zero duality gap in optimal power flow problem. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrío Castro, K.J. Método de Solución para el Despacho Económico en Línea Considerando Restricciones y Reglas de un Mercado Eléctrico. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Medellín, Colombia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyakumar, D.; Jayabarathi, T.; Raghunathan, T. Particle swarm optimization for various types of economic dispatch problems. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2006, 28, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, O.D.; Gil-Gonzalez, W.; Garces, A. A Sequential Quadratic Programming Model for the Economic–Environmental Dispatch in MT-HVDC. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Workshop on Power Electronics and Power Quality Applications (PEPQA), Manizales, Colombia, 30–31 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Sepúlveda, W.; Montoya, O.D.; Gil-González, W. An economic-environmental energy management system design for MT-HVDC networks via a semi-definite programming approximation with robust analysis. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez Cervantes, J.D. Electric Power Distribution Systems (In Spanish); Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana, Unidad Azcapotzalco: Mexico City, Mexico, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, A.M.; Shaheen, A.M.; Alharthi, M.M.; Ghoneim, S.S.M.; El-Sehiemy, R.A. Adequate Operation of Hybrid AC/MT-HVDC Power Systems Using an Improved Multi-Objective Marine Predators Optimizer. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 51065–51087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa María, M.; von der Fehr, N.H.; Millán, J.; Benavides, J.; Gracia, O.; Schutt, E. The Electric Energy Market in Colombia: Characteristics, Evolution, and Impact on Other Sectors; Informe Técnico; Fedesarrollo: Bogotá, Colombia, 2009. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Gjorgiev, B.; Čepin, M. A multi-objective optimization based solution for the combined economic-environmental power dispatch problem. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtdar, M.; Flah, A.; Hosseinimoghadam, S.M.S.; Reddy, H.R.; Kotb, H.; AboRas, K.M.; Jasińska, E.; Jasiński, M. Solving the environmental/economic dispatch problem using the hybrid FA-GA multi-objective algorithm. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 13766–13779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, R.; Resch, G.; Panzer, C.; Busch, S.; Ragwitz, M.; Held, A. Efficiency and effectiveness of promotion systems for electricity generation from renewable energy sources - Lessons from EU countries. Energy 2011, 36, 2186–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.C. Optimization Methods for Electric Power Systems: An Overview. Int. J. Emerg. Electr. Power Syst. 2005, 2, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farivar, M.; Low, S.H. Branch Flow Model: Relaxations and Convexification. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Maui, HI, USA, 10–13 December 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhou, S. Environmental/economic power dispatch problem using multi-objective differential evolution algorithm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2010, 80, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawode, K.; Jubril, A.; Kehinde, L.; Ogunbona, P. Semidefinite programming solution of economic dispatch problem with non-smooth, non-convex cost functions. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 164, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozouri, M.A.; Abbaspour, A.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M.; Moeini-Aghtaie, M. On the Use of Pumped Storage for Wind Energy Maximization in Transmission-Constrained Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabr, R.A. Radial distribution load flow using conic programming. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 1458–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Low, S.H.; Topcu, U. Convex relaxations and linear approximation for optimal power flow in multiphase radial networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 Power Systems Computation Conference, Wroclaw, Poland, 18–22 August 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, H.Y.; Sağlam, Ü. Mixed-Integer Second-Order Cone Programming: A Survey. In INFORMS Tutorials in Operations Research; INFORMS: Catonsville, MD, USA, 2013; pp. 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Reference | Methodology | Limitations | Contribution of This Work |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nanda et al. (2005) [1] | Multi-objective optimization using classical programming methods | Limited to simplified systems; non-convexities not addressed; no renewable sources included | Incorporates renewable PV generation and addresses non-convexities via convex reformulation |
| Lahdi et al. (2011) [2] | Grid-based dispatch optimization with emissions consideration | Inflexible to renewable generation variability; focused on AC systems | Tailored to DC systems and includes dynamic PV profiles |
| Jeyakumar et al. (2006) [10] | Particle swarm optimization for EED | Heuristic nature yields suboptimal results; lacks guarantees of global optimality | Uses SOCP to guarantee global optimality with negligible error vs. exact NLP |
| Montoya et al. (2019) [11] | SQP for EED in AC systems | High computational burden; no conic relaxation; limited scalability | Reformulated as convex SOCP, reducing computational time and improving scalability |
| Farivar and Low (2012) [20] | Conic relaxation for optimal power flow in AC systems | AC-focused, no multi-objective formulation; lacks integration of emissions objective | Extends conic relaxation to multi-objective EED in DC networks with emissions modeling |
| Line Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Line #) | From | To | (Line #) | From | To | ||
| (Line 1) | 1 | 5 | 5.70 | (Line 5) | 3 | 6 | 4.75 |
| (Line 2) | 5 | 3 | 2.28 | (Line 6) | 1 | 2 | 1.90 |
| (Line 3) | 5 | 4 | 1.71 | (Line 7) | 2 | 6 | 1.90 |
| (Line 4) | 1 | 3 | 2.28 | – | – | – | – |
| Load Consumption | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node | P (MW) | Node | P (MW) | Node | P (MW) |
| 4 | 1500 | 5 | 1250 | 6 | 950 |
| Gen | c (USD) | b (USD/MW) | a (USD/MW2h) | (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 20 | 0.10 | 4.091 | |
| 100 | 15 | 0.12 | 2.543 | |
| 200 | 18 | 0.04 | 4.258 | |
| Gen | β (kg/MWh) | α (kg/MW2h) | pg,min (MW) | pg,max (MW) |
| −5.543 | 0.06490 | 50 | 1500 | |
| −6.047 | 0.05638 | 100 | 2000 | |
| −5.094 | 0.04586 | 140 | 1800 |
| Line # | From | To | (kA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 3.85 (3.50) |
| 2 | 1 | 4 | 4.22 (3.20) |
| 3 | 1 | 6 | 4.85 (3.10) |
| 4 | 2 | 6 | 2.37 (3.50) |
| 5 | 2 | 7 | 3.25 (3.10) |
| 6 | 3 | 7 | 2.95 (2.90) |
| 7 | 3 | 9 | 4.36 (3.20) |
| 8 | 4 | 6 | 4.02 (3.50) |
| 9 | 4 | 10 | 3.87 (3.60) |
| 10 | 5 | 9 | 3.34 (3.00) |
| 11 | 5 | 10 | 4.12 (2.80) |
| 12 | 5 | 11 | 3.78 (2.00) |
| 13 | 6 | 7 | 4.65 (3.00) |
| 14 | 6 | 11 | 5.25 (2.60) |
| 15 | 7 | 8 | 3.14 (3.00) |
| 16 | 8 | 9 | 4.55 (1.50) |
| 17 | 8 | 11 | 5.14 (1.60) |
| Load Consumption | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Node | P (MW) | Node | P (MW) |
| 6 | 850 | 7 | 750 |
| 8 | 950 | 9 | 800 |
| 10 | 650 | 11 | 700 |
| Gen. | c (USD) | b (USD/MWh) | a (USD/MW2h) | (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 14 | 0.10 | 3.002 | |
| 125 | 18 | 0.07 | 4.903 | |
| 180 | 22 | 0.05 | 5.236 | |
| 0 | 40 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| 0 | 42 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Gen. | β (kg/MWh) | α (kg/MW2h) | (MW) | (MW) |
| −4.268 | 0.075 | 150 | 1350 | |
| −5.324 | 0.087 | 300 | 1800 | |
| −6.576 | 0.060 | 250 | 2400 | |
| 32 | 0.000 | 0 | 2500 | |
| 29 | 0.000 | 0 | 2000 |
| Scenario | Model | [$] | [kg] | Error [%] | Error [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MATLAB (SOCP) | 420,988.63 | 253,833.13 | 0.00004 | 0.0124 |
| GAMS (DNLP) | 420,988.45 | 253,864.62 | – | – | |
| 2 | MATLAB (SOCP) | 421,639.60 | 252,204.00 | 0.000007 | 0.00001 |
| GAMS (DNLP) | 421,639.63 | 252,203.96 | – | – | |
| 3 | MATLAB (SOCP) | 456,269.90 | 245,303.81 | 0.319 | 0.0030 |
| GAMS (DNLP) | 454,819.58 | 245,311.09 | – | – |
| Generator | MATLAB (SOCP) | GAMS (DNLP) |
|---|---|---|
| 1039.60 | 1039.56 | |
| 981.70 | 981.72 | |
| 1800.00 | 1800.00 |
| Model | [$] | [kg] | PG1 [MW] | PG2 [MW] | PG3 [MW] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MATLAB (SOCP) | 570,814.38 | 277,442.58 | 1500.00 | 1426.50 | 913.50 |
| GAMS (DNLP) | 570,815.56 | 277,441.84 | 1500.00 | 1426.52 | 913.49 |
| Model | Constraint | [$] | [kg] | PG1 [MW] | PG2 [MW] | PG3 [MW] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MATLAB (SOCP) | Active | 570,814.38 | 277,442.58 | 1500.00 | 1426.50 | 913.50 |
| Inactive | 421,639.60 | 252,204.00 | 1039.60 | 981.70 | 1800.00 | |
| GAMS (DNLP) | Active | 570,815.56 | 277,441.84 | 1500.00 | 1426.52 | 913.49 |
| Inactive | 421,639.63 | 252,203.96 | 1039.56 | 981.72 | 1800.00 |
| Model | [$] | [kg CO2] |
|---|---|---|
| MATLAB (SOCP) | 7,906,357.61 | 6,643,278.60 |
| GAMS (DNLP) | 7,906,357.60 | 6,643,278.58 |
| Scenario | [$] | [kg CO2] |
|---|---|---|
| With photovoltaic generation | 7,906,357.60 | 6,643,278.58 |
| Without photovoltaic generation | 10,449,997.00 | 9,139,670.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernal-Carvajal, N.J.; Mora-Peña, C.A.; Montoya, O.D. Multi-Objective Optimization for Economic and Environmental Dispatch in DC Networks: A Convex Reformulation via a Conic Approximation. Electricity 2025, 6, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/electricity6030043
Bernal-Carvajal NJ, Mora-Peña CA, Montoya OD. Multi-Objective Optimization for Economic and Environmental Dispatch in DC Networks: A Convex Reformulation via a Conic Approximation. Electricity. 2025; 6(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/electricity6030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernal-Carvajal, Nestor Julian, Carlos Arturo Mora-Peña, and Oscar Danilo Montoya. 2025. "Multi-Objective Optimization for Economic and Environmental Dispatch in DC Networks: A Convex Reformulation via a Conic Approximation" Electricity 6, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/electricity6030043
APA StyleBernal-Carvajal, N. J., Mora-Peña, C. A., & Montoya, O. D. (2025). Multi-Objective Optimization for Economic and Environmental Dispatch in DC Networks: A Convex Reformulation via a Conic Approximation. Electricity, 6(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/electricity6030043










