Industrial Applications, Environmental Fate, Human Exposure, and Health Effects of PFAS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature and Methodology
3. Industrial Applications of PFASs
3.1. Consumer and Personal Care Industries
3.2. Chemical and Material Processing Industries
3.3. Plastics, Resins, and Rubber
3.4. Recycling and Material Recovery
3.5. Pesticides and Fertilizers
3.6. High-Tech Industrial Applications
3.7. Medical Uses
3.8. Metal Coating and Surface Finishing
3.9. Mining Industry
3.10. Oil and Gas Industry
3.11. Safety and Defense Applications
3.12. Applications in Consumer Products and Surface Modifications
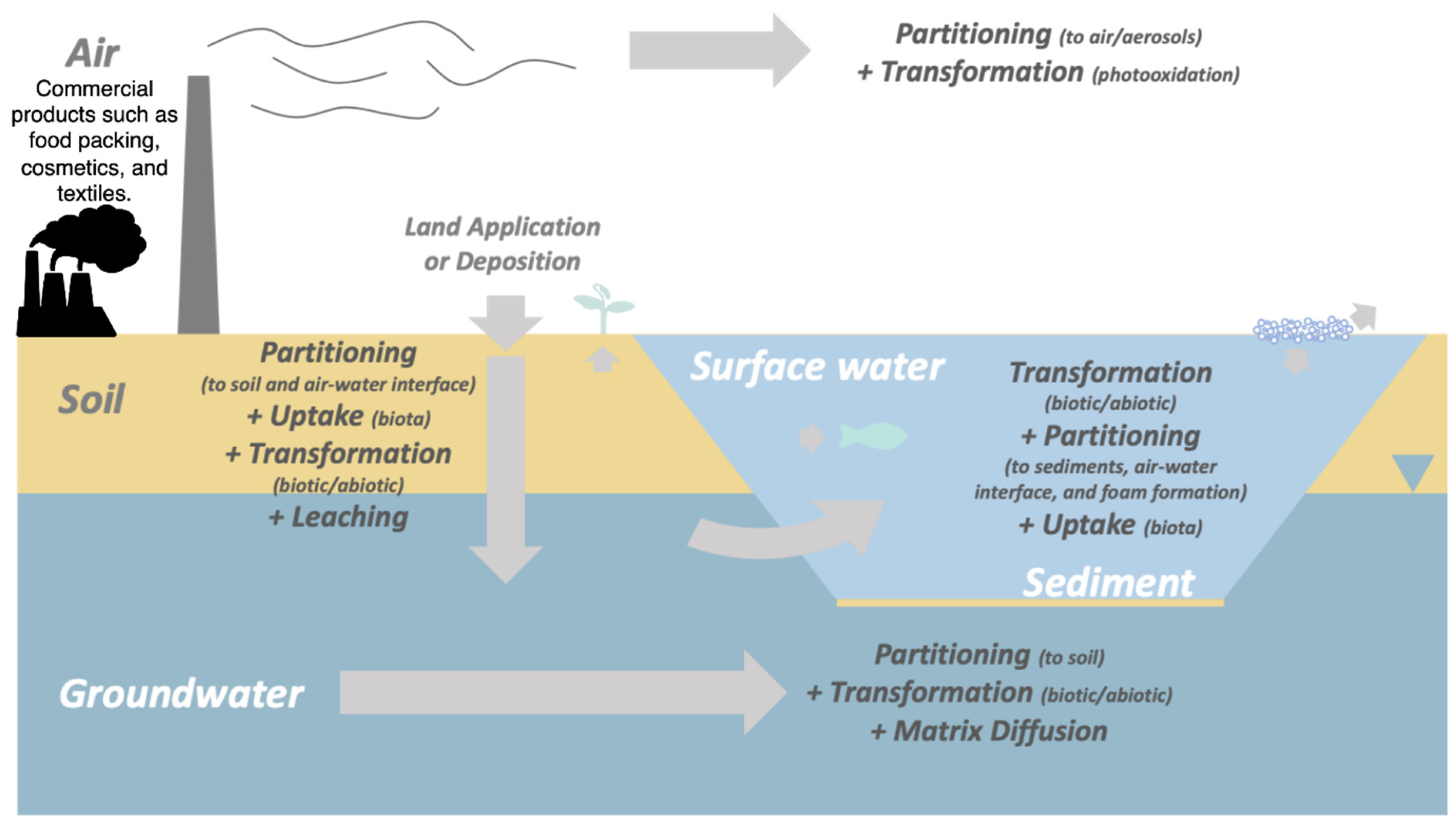
4. Environmental Fate and Transport of PFASs
4.1. Persistence and Mobility Characteristics
4.2. Atmospheric Transport and Deposition
4.3. Aquatic Ecosystems Contamination
4.4. Soil Contamination and Mobility
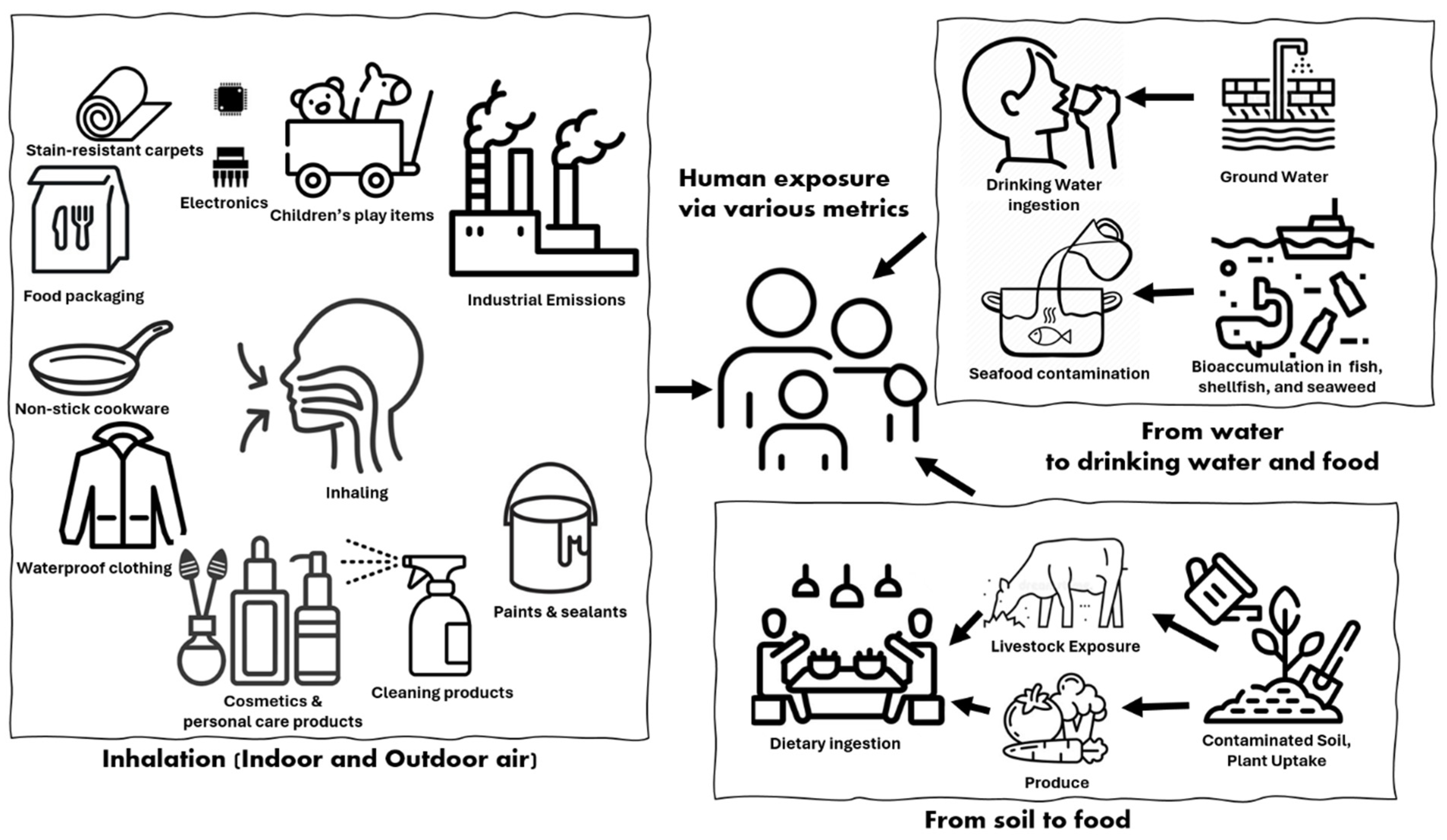
5. Human Exposure Pathways and Bioaccumulation
6. Health Effects of PFAS Exposure
7. Knowledge Gaps and Research Needs
7.1. PFAS Applications and Use Data
7.2. Exposure Assessment Gaps
7.3. Health Effects Uncertainties
7.4. Proportion of Studies Lacking Standardization
7.5. Recommendations for Future Research
8. Conclusions
8.1. Improving the Standardization of Detection
8.2. Empowering Through Information and Policy
8.3. Health Effects: Prioritizing Vulnerable Populations and Targeted Research
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, L.G.T. Historical and current usage of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A literature review. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2023, 66, 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, J. Fluoropolymers: Origin, Production, and Industrial and Commercial Applications. Aust. J. Chem. 2015, 68, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellenberger, S.; Hill, P.J.; Levenstam, O.; Gillgard, P.; Cousins, I.T.; Taylor, M.; Blackburn, R.S. Highly fluorinated chemicals in functional textiles can be replaced by re-evaluating liquid repellency and end-user requirements. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheringer, M.; Trier, X.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Fletcher, T.; Wang, Z.; Webster, T.F. Helsingør Statement on poly- and perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFASs). Chemosphere 2014, 114, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glüge, J.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Trier, X.; Wang, Z. An overview of the uses of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2345–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abunada, Z.; Alazaiza, M.Y.; Bashir, M.J. An overview of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the environment: Source, fate, risk and regulations. Water 2020, 12, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepper, T.P.E.; Lange, F.T. (Eds.) Polyfluorinated Chemicals and Transformation Products. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 17, No. 17. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Guidance on Alternatives to Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid and Its Derivatives. In Proceedings of the Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee on the Work of Its Sixth Meeting, Geneva, Switzerland, 15 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, A. Green Analytical Methods for the Determination of Perfluorocarboxylic Acids (PFCAs) and Fluorotelomer Alcohols (FTOHs) in Water. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Arevalo, E.; Strynar, M.; Lindstrom, A.; Richardson, M.; Kearns, B.; Pickett, A.; Smith, C.; Knappe, D.R.U. Legacy and Emerging Perfluoroalkyl Substances Are Important Drinking Water Contaminants in the Cape Fear River Watershed of North Carolina. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, P. A review of sources, multimedia distribution and health risks of novel fluorinated alternatives. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. FDA. Indirect Food Additives: Paper and Paperboard Components. In FDA, 21st ed.; CFR Part 176; Federal Register; U.S. FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2016; Volume 81, FR 5. [Google Scholar]
- Kissa, E. Fluorinated Surfactants and Repellents; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 3M. 3M Novec Contact Cleaner Safety Data Sheet. 3M Company. 2024. Available online: https://www.3m.com/3M/en_US/company-us/SDS-search/results/?gsaAction=msdsSRA&msdsLocale=en_US&co=ptn&q=novec (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- 3M. 3M Novec Flux Remover Safety Data Sheet. 3M Company. 2023. Available online: https://multimedia.3m.com/mws/mediawebserver?mwsId=SSSSSuUn_zu8l00xm8tBm8m9Pv70k17zHvu9lxtD7SSSSSS-- (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Dias, D.; Bons, J.; Kumar, A.; Kabir, M.H.; Liang, H. Forever chemicals, per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in lubrication. Lubricants 2024, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, A.; Yadav, S.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Properties, Uses, Sources, and Environmental Releases of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. PFAS Environ. Occur. Charact. Treat. Manag. 2025, 2, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Caslavsky, V.; Gron, P. Method of Inhibiting the Formation of Plaque. U.S. Patent 5,100,649, 31 March 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Cansell, F.; Aymonier, C.; Loppinet-Serani, A. Review on materials science and supercritical fluids. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2003, 7, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Ahamed, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Halim, M.E.; Uddin, K.M. Computational study of nickel complexes: Stability and electronic charge insights. Am. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohora, F.T.; Wasif, A.; Hussain, A.; Alam, M.J.; Debnath, T.; Halim, M.E. Synthesis, Characterization, and Computational Studies of Salophh2-Metal Complexes: Structural and Electronic Properties with Stability Insights. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5228206 (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Ebnesajjad, S. Introduction to Fluoropolymers: Materials, Technology, and Applications; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Synthesis Paper on Per- and Polyfluorinated Chemicals; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Compliance Guide for Surface Coatings Subject to the Long-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylate and Perfluoroalkyl Sulfonate Chemical Substances Significant New Use Rule; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2021-01/documents/final_lcpfac-snur_surface-coating-compliance-guide_0.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Plassmann, M.M.; Berger, U. Perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids with up to 22 carbon atoms in snow and soil samples from a ski area. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daikin. Fluoroelastomers. 2025. Available online: https://www.daikinchemicals.com/solutions/products/dai-el-fluoroelastomers.html (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Mansfield, C.; Hughes, J.; Gurevich, E.; Ux, B.; Quartapella, C. Fast Curing Fluoroelastomeric Compositions, Adhesive Fluoroelastomeric Compositions and Methods for Bonding Fluoroelastomeric Compositions. U.S. Patent 7,514,506 B2, 7 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Nesci, K. EPA’s Analytical Chemistry Branch PFAS Testing, Rinses from Selected Fluorinated and Non-Fluorinated HDPE Containers. 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2021-03/documents/results-of-rinsates-samples_03042021.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2025).
- Saito, S.; Ohno, O.; Igarashi, S.; Kato, T.; Yamaguchi, H. Separation and Recycling for Rare Earth Elements by Homogeneous Liquid-Liquid Extraction (HoLLE) Using a pH-Responsive Fluorine-Based Surfactant. Metals 2015, 5, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacanau, V.; Bonneté, F.; Wagner, P.; Schmitt, M.; Meyer, D.; Bihel, F.; Contino-Pépin, C.; Bourgeois, D. From Electronic Waste to Suzuki−Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction in Water: Direct Valuation of Recycled Palladium in Catalysis. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 5224–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Saito, S.; Oshite, S.; Igarashi, S. Powerful Concentration of Rhodium in Plating Wastewater Using Homogeneous Liquid–Liquid Extraction (HoLLE) and Study for Scale-up. Environ. Nat. Resour. Res. 2017, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leybros, A.; Segond, N.; Grandjean, A. Remediation of 137Cs-contaminated concrete rubble by supercritical CO2 extraction. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kim, T.; Park, J.; Yan, X.; Kim, H. Development of a carbamate-conjugated catechol ligand and its application to Cs extraction from contaminated soil by using supercritical CO2. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wai, C.M. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Lanthanides with Fluorinated beta. Diketones and Tributyl Phosphate. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, Y.; Wai, C.M. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Toxic Heavy Metals from Solid and Aqueous Matrices. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yan, B.; Fu, J.; Xiao, X. Absorption and recovery of n-hexane in aqueous solutions of fluorocarbon surfactants. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. CompTox Chemicals Dashboard. Retrieved 20 January 2025. Available online: https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Aoki, Y. Method for Producing Amide Derivative. U.S. Patent 9,890,110 B2, 13 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. EPA. Inert Ingredient; Revocation of the Tolerance Exemption for Mono- and Bis-(1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-perfluoroalkyl) Phosphates Where the Alkyl Group is Even Numbered and in the C6-C12 Range. In Federal Register, EPA US, ed.; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; 40 CFR Part 180; Volume EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0253, pp. 45408–45411. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, W.; Rowe, K.; Webber, A. Coated Particles, Methods of Making the Same, and Methods of Use. U.S. Patent 9,174,886 B2, 3 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, J. Fujitsu Liquid Immersion Not All Hot Air When It Comes to Cooling Data Centers; IEEE Spectrum: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ebnesajjad, S.; Snow, L.G. Fluorine-Containing Polymers, Poly(Vinyl Fluoride). In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchev, S.S.; Likhomanov, V.S.; Primachenko, O.N.; Khaikin, S.Y.; Barabanov, V.G.; Kornilov, V.V.; Odinokov, A.S.; Kulvelis, Y.V.; Lebedev, V.T.; Trunov, V.A. Scientific principles of a new process for manufacturing perfluorinated polymer electrolytes for fuel cells. Pet. Chem. 2012, 52, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.C.; Gollan, F. Survival of Mammals Breathing Organic Liquids Equilibrated with Oxygen at Atmospheric Pressure. Science 1966, 152, 1755–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, D.; Ferenz, K.B. Perfluorocarbons for the treatment of decompression illness: How to bridge the gap between theory and practice. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 2421–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, R.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F.; Yoneyama, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Yoshizawa, A.; Thompson, W.L.; Kannan, G.; Kobayashi, E.; Date, H.; et al. Mammalian enteral ventilation ameliorates respiratory failure. Med 2021, 2, 773–783.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, R.J.; Richard, T.J.; Stephens, R.A.; Goodin, T.H.; Allen, J.S.; Layton, T.E. Homogeneous Water-in-Perfluorochemical Stable Liquid Dispersion for Administration of a Drug to the Lung of an Animal. U.S. Patent 5,770,585, 23 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Maevsky, E.I.; Ivanitsky, G.R.; Makarov, K.N.; Kulakova, G.M.; Arkhipov, V.V.; Moroz, V.V.; Starovoitova, L.N.; Senina, R.Y.; Pushkin, S.J.; Ivashina, A.I. Emulsion of Perfluoroorganic Compounds for Medical Purposes, a Process for the Preparation Thereof and Methods for Treating and Preventing Diseases with the Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 6,562,872 B1, 13 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sabid, A.M.; Kamrul, H.M. Computational and Theoretical Analysis on the Single Proton Transfer Process in Adenine Base by Using DFT Theory and Thermodynamics. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2024, 17, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Garrelts, J.C. Fluosol: An Oxygen-Delivery Fluid for use in Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty. DICP 1990, 24, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, K.; Fu, C.; Peng, H.; Hawker, C.J.; Whittaker, A.K. Biological Utility of Fluorinated Compounds: From Materials Design to Molecular Imaging, Therapeutics and Environmental Remediation. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 167–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tressaud, A.; Haufe, G. (Eds.) Fluorine and Health: Molecular Imaging, Biomedical Materials and Pharmaceuticals; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer, H.; Weinmann, H.J.; Platzek, J. Perfluoroalkyl-Containing Complexes, Process for Their Production as Well as Their Use. U.S. Patent 2007/0020183 A1, 17 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.; Pang, J.; Li, W. Vitreous surgery for macular hole-related retinal detachment after phacoemulsification cataract extraction: 10-year retrospective review. Eye 2012, 26, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Reiner, E.J.; Bhavsar, S.P.; Helm, P.A.; Mabury, S.A.; Braekevelt, E.; Tittlemier, S.A. Determination of polyfluoroalkyl phosphoric acid diesters, perfluoroalkyl phosphonic acids, perfluoroalkyl phosphinic acids, perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids, and perfluoroalkane sulfonic acids in lake trout from the Great Lakes region. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 2699–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leland Stanford Junior University. BioPortal. Retrieved 10 February 2025. 2024. Available online: https://bioportal.bioontology.org/ (accessed on 21 June 2025).
- Liu, Y.; Huang, W. Stretchable Electrochemical Sensors for Cell and Tissue Detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2757–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, E.J.; Ellis, J.Y. Fluorine Containing Polymeric Compositions Useful in Contact Lenses. U.S. Patent 4,996,275, 11 August 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Olufayo, O.A.; Abou-El-Hossein, K.; Kadernani, M.M. Tribo-electric Charging in the Ultra-high Precision Machining of Contact Lens Polymers. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, K. Final Report for the Use of Wetting Agents/Fume Suppressants for Minimizing the Atmospheric Emissions from Hard Chromium Electroplating Baths 2004. TR-2243-ENV. 2004. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/tr/pdf/ADA423561.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- MI EGLE. Targeted and Nontargeted Analysis of PFAS in Fume Suppressant Products at Chrome Plating Facilities 2020. 2020. Available online: https://www.michigan.gov/documents/egle/wrd-ep-pfas-chrome-plating_693686_7.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Hepfer, I. Pre-Plating Conditioning Process. U.S. Patent No. 3,515,649, 2 June 1970. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US3515649A (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Murphy, P.M.; Hewat, T. Fluorosurfactants in Enhanced Oil Recovery. Open Pet. Eng. J. 2008, 1, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, E.-C. Metal-Fluorocarbon Based Energetic Materials; Wiley-VCH Verlag & Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Prevedouros, K.; Cousins, I.T.; Buck, R.C.; Korzeniowski, S.H. Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemguard Specialty Chemical Brochure. 2024. Available online: https://www.nationalfire.com/media/product_files/Chemguard_Brochure.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Kirsch, P. Modern Fluoroorganic Chemistry: Synthesis, Reactivity, Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Krafft, M.P. Fluorocarbons and fluorinated amphiphiles in drug delivery and biomedical research. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; Lide, D.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Politzer, P.; Jin, P.; Murray, J.S. Atomic polarizability, volume, and ionization energy. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 8197–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ömür-Özbek, P.; Dietrich, A.M. Determination of temperature-dependent Henry’s law constants of odorous contaminants and their application to human perception. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3957–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, M.W.; Robinson, B.H. The phytomanagement of PFAS-contaminated land. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, M.A.; Endo, S. Henry’s law constants of 15 per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances determined by static headspace analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100070. [Google Scholar]
- Evich, M.G.; Davis, M.J.; McCord, J.P.; Acrey, B.; Awkerman, J.A.; Knappe, D.R.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Speth, T.F.; Tebes-Stevens, C.; Strynar, M.J. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment. Science 2022, 375, eabg9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. EPA. Technical fact sheet—Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). In Office of Land and Emergency Management; Environmental Protection Agency, Ed.; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; EPA 505-F-17-001. [Google Scholar]
- Jahnke, A.; Ahrens, L.; Ebinghaus, R.; Temme, C. Urban versus remote air concentrations of fluorotelomer alcohols and other polyfluorinated alkyl substances in Germany. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.L.; Aucoin, M.D.; Larsen, B.S.; Kaiser, M.A.; Hartten, A.S. Transport of ammonium perfluorooctanoate in environmental media near a fluoropolymer manufacturing facility. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudinger, J.; Roberts, P.V. A critical compilation of Henry’s law constant temperature dependence relations for organic compounds in dilute aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusseau, M.L.; Van Glubt, S. The influence of surfactant and solution composition on PFAS adsorption at fluid-fluid interfaces. Water Res. 2019, 161, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Carvalho, P.J.; Queimada, A.J.; Marrucho, I.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Surface tension of liquid fluorocompounds. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1820–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Kancharla, S.; Hooper, J.; Tsianou, M.; Bedrov, D.; Alexandridis, P. Controlling the self-assembly of perfluorinated surfactants in aqueous environments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 10029–10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.A.; Hungerbühler, K. Bioconcentration of perfluorinated alkyl acids: How important is specific binding? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7214–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E.; Lefevre, G.H.; Timofee, A.E.; Hussain, F.A.; Sattely, E.S.; Luthy, R.G. Competing mechanisms for perfluoroalkyl acid accumulation in plants revealed using an Arabidopsis model system. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droge, S.T.J. Membrane-water partition coefficients to aid risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl anions and alkyl sulfates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vierke, L.; Berger, U.; Cousins, I.T. Estimation of the acid dissociation constant of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids through an experimental investigation of their water-to-air transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11032–11039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.H.; Bräunig, J.; Thompson, K.; Thompson, J.; Kabiri, S.; Navarro, D.A.; Kookana, R.S.; Grimson, C.; Barnes, C.M.; Higgins, C.P.; et al. Influences of chemical properties, soil properties, and solution pH on soil–water partitioning coefficients of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15883–15892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Kewalramani, J.A.; Li, B.; Marsh, R.W. A review of the applications, environmental release, and remediation technologies of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.R.; Allred, B.M.; Field, J.A.; Levis, J.W.; Barlaz, M.A. National Estimate of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Release to U.S. Municipal Landfill Leachate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Buck, R.C.; Hungerbühler, K. Global emission inventories for C4–C14 perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acid (PFCA) homologues from 1951 to 2030, Part I: Production and emissions from quantifiable sources. Environ. Int. 2014, 70, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Buck, R.C.; Hungerbühler, K. Global emission inventories for C4–C14 perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acid (PFCA) homologues from 1951 to 2030, part II: The remaining pieces of the puzzle. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunn, H.; Arnold, G.; Körner, W.; Rippen, G.; Steinhäuser, K.G.; Valentin, I. PFAS: Forever chemicals—Persistent, bioaccumulative and mobile. Reviewing the status and the need for their phase out and remediation of contaminated sites. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, H.G.; Nason, S.L.; Warren, J.L.; Prunas, O.; Deziel, N.C.; Saiers, J.E. Investigation of Sources of Fluorinated Compounds in Private Water Supplies in an Oil and Gas-Producing Region of Northern West Virginia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 17452–17464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.L.; Nazaroff, W.W. Particle Penetration Through Building Cracks. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, J.M.; MacLeod, M.; Cousins, I.T. Modeling the Global Fate and Transport of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFO) Emitted from Direct Sources Using a Multispecies Mass Balance Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thackray, C.P.; Selin, N.E.; Young, C.J. A global atmospheric chemistry model for the fate and transport of PFCAs and their precursors. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacInnis, J.J.; Lehnherr, I.; Muir, D.C.G.; St. Pierre, K.A.; St. Louis, V.L.; Spencer, C.; De Silva, A.O. Fate and Transport of Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Snowpacks into a Lake in the High Arctic of Canada. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10753–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, G.; Martínez-Varela, A.; Roscales, J.L.; Vila-Costa, M.; Dachs, J.; Jiménez, B. Enrichment of perfluoroalkyl substances in the sea-surface microlayer and sea-spray aerosols in the Southern Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, J.A. PFAS on atmospheric aerosol particles: A review. In Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts 2022; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2022; Volume 25, Issue 2; pp. 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.A.; Martin, J.W.; De Silva, A.O.; Mabury, S.A.; Hurley, M.D.; Sulbaek Andersen, M.P.; Wallington, T.J. Degradation of Fluorotelomer Alcohols: A Likely Atmospheric Source of Perfluorinated Carboxylic Acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3316–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yao, Y.; Chang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wu, F.; Sun, H. Occurrence and Phase Distribution of Neutral and Ionizable Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in the Atmosphere and Plant Leaves around Landfills: A Case Study in Tianjin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chang, S.; Sun, H.; Gan, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Neutral and ionic per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in atmospheric and dry deposition samples over a source region (Tianjin, China). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Allan, J.D.; Coe, H.; Ulbrich, I.; Alfarra, M.R.; Takami, A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Sun, Y.L.; et al. Ubiquity and dominance of oxygenated species in organic aerosols in anthropogenically-influenced Northern Hemisphere midlatitudes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemer, N.; Ault, A.P.; West, M.; Craig, R.L.; Curtis, J.H. Aerosol Mixing State: Measurements, Modeling, and Impacts. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 187–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Short-lived Climate Forcers. In Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 817–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The Earth’s Energy Budget, Climate Feedbacks and Climate Sensitivity. In Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 923–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwidetzky, R.; Sun, Y.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Kunert, A.T.; Bonn, M.; Meister, K. Ice Nucleation Activity of Perfluorinated Organic Acids. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 3431–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Karim, I.; Zaman, S.U. Seasonal dynamics and trends in air pollutants: A comprehensive analysis of PM2.5, NO2, CO, SO2 and O3 in Houston, USA. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2025, 18, 2625–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Rappenglueck, B.; Retama, A.H.; Rivera-Hernández, O. Investigating the Complexities of VOC Sources in Mexico City in the Years 2016–2022. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, I.; Rappenglück, B. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown regulations on PM2.5 and trace gases (NO2, SO2, CH4, HCHO, C2H2O2 and O3) over Lahore, Pakistan. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 303, 119746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Collins, D.B.; Arata, C.; Goldstein, A.H.; Mattila, J.M.; Farmer, D.K.; Ampollini, L.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Novoselac, A.; Vance, M.E.; et al. Surface reservoirs dominate dynamic gas-surface partitioning of many indoor air constituents. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.C.; Chung, S.M.; Kwak, S.G. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of stroke in adults: A meta-analysis. Rev. Environ. Health 2024, 39, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Harner, T.; Shoeib, M.; Koblizkova, M.; Reiner, E.J. Characterization of Two Passive Air Samplers for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14024–14033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, L.; Shoeib, M.; Harner, T.; Lee, S.C.; Guo, R.; Reiner, E.J. Wastewater Treatment Plant and Landfills as Sources of Polyfluoroalkyl Compounds to the Atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8098–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naile, J.E.; Khim, J.S.; Hong, S.; Park, J.; Kwon, B.-O.; Ryu, J.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Jones, P.D.; Giesy, J.P. Distributions and bioconcentration characteristics of perfluorinated compounds in environmental samples collected from the west coast of Korea. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naile, J.E.; Khim, J.S.; Wang, T.; Chen, C.; Luo, W.; Kwon, B.-O.; Park, J.; Koh, C.-H.; Jones, P.D.; Lu, Y. Perfluorinated compounds in water, sediment, soil and biota from estuarine and coastal areas of Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, X.; Cai, Y. Pilot investigation of perfluorinated compounds in river water, sediment, soil, and fish in Tianjin, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 87, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, D.P.; Kelly, J.E.; Huset, C.A.; Barry, K.M.; Hoffbeck, R.W.; Yingling, V.L.; Messing, R.B. Occurrence of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in garden produce at homes with a history of PFAS-contaminated drinking water. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Kannan, K. Distribution and partitioning of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids in surface soil, plants, and earthworms at a contaminated site. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorengard, M.; Kikuchi, J.; Wiberg, K.; Lutz, A. Spatial distribution and load of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in background soils in Sweden. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunig, J.; Baduel, C.; Heffernan, A.; Rotander, A.; Donaldson, E.; Mueller, J.F. Fate and redistribution of perfluoroalkyl acids through AFFF-impacted groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.G.; Jones, K.C.; Sweetman, A.J. A First Global Production, Emission, and Environmental Inventory for Perfluorooctane Sulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huset, C.A.; Chiaia, A.C.; Barofsky, D.F.; Jonkers, N.; Kohler, H.-P.E.; Ort, C.; Giger, W.; Field, J.A. Occurrence and Mass Flows of Fluorochemicals in the Glatt Valley Watershed, Switzerland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6369–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, A.; Ahrens, L.; Surm, R.; Westerveld, J.; van der Wielen, F.; Ebinghaus, R.; de Voogt, P. Distribution and sources of polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the River Rhine watershed. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3243–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.M.; Higgins, C.P.; Huset, C.A.; Luthy, R.G.; Barofsky, D.F.; Field, J.A. Fluorochemical Mass Flows in a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Facility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7350–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman Grunfeld, D.; Gilbert, D.; Hou, J.; Jones, A.M.; Lee, M.J.; Kibbey, T.C.; O’Carroll, D.M. Underestimated burden of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in global surface waters and groundwaters. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaafi, M.; Bafaqeer, A. Comprehensive Review of Global Perspectives on Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Compounds: Occurrence, Fate, and Remediation in Groundwater Systems. Water 2024, 16, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulini, G.; Nambi, I. Occurrence of forever chemicals in Chennai waters, India. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Dane, J.; Kanel, S.; Nadagouda, M.; Cawdrey, R.; Ambade, B.; Struckhoff, G.; Wilkin, R. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and wastewater: A critical review of their global occurrence and distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 809, 151003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulvado, J.G.; Blaine, A.C.; Hundal, L.S.; Higgins, C.P. Occurrence and Fate of Perfluorochemicals in Soil Following the Land Application of Municipal Biosolids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8106–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Q.; Sheng, N.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Y.; Dai, J. Worldwide Distribution of Novel Perfluoroether Carboxylic and Sulfonic Acids in Surface Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7621–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaboré, H.A.; Vo Duy, S.; Munoz, G.; Méité, L.; Desrosiers, M.; Liu, J.; Sory, T.K.; Sauvé, S. Worldwide drinking water occurrence and levels of newly-identified perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, L.W.Y.; Dassuncao, C.; Mabury, S.; Sunderland, E.M.; Zhang, X.; Lohmann, R. Vertical Profiles, Sources, and Transport of PFASs in the Arctic Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6735–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartell, S.M.; Calafat, A.M.; Lyu, C.; Kato, K.; Ryan, P.B.; Steenland, K. Rate of decline in serum PFOA concentrations after granular activated carbon filtration at two public water systems in Ohio and West Virginia. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisbee, S.J.; Brooks, A.P., Jr.; Maher, A.; Flensborg, P.; Arnold, S.; Fletcher, T.; Steenland, K.; Shankar, A.; Knox, S.S.; Pollard, C.; et al. The C8 health project: Design, methods, and participants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’eon, J.C.; Crozier, P.W.; Furdui, V.I.; Reiner, E.J.; Libelo, E.L.; Mabury, S.A. Perfluorinated phosphonic acids in Canadian surface waters and wastewater treatment plant effluent: Discovery of a new class of perfluorinated acids. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skutlarek, D.; Exner, M.; Färber, H. Perfluorinated surfactants in surface and drinking waters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2006, 13, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux, V.; Dauchy, X.; Rosin, C.; Munoz, J.F. National screening study on 10 perfluorinated compounds in raw and treated tap water in France. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 63, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.; Eaglesham, G.; Mueller, J. Concentrations of PFOS, PFOA and other perfluorinated alkyl acids in Australian drinking water. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Adachi, F.; Miyano, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Watanabe, I.; Tanabe, S.; Kannan, K. Fate of Perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoate in drinking water treatment processes. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3925–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, J.E. Assessment of individual-based perfluoroalkly substances exposure by multiple human exposure sources. J. Hazard Mater. 2019, 365, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.Y.; Lu, G.H.; Piao, H.T.; Chen, S.; Jiao, X.C.; Gai, N.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Pan, J.; Yang, Y.L. Current contamination status of perfluoroalkyl substances in tapwater from 17 cities in the Eastern China and their correlations with surface waters. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.M.; Bharat, G.K.; Tayal, S.; Larssen, T.; Bečanová, J.; Karásková, P.; Whitehead, P.G.; Futter, M.N.; Butterfield, D.; Nizzetto, L. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in river and ground/drinking water of the Ganges River basin: Emissions and implications for human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208 Pt B, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemat, H.; Wilhelm, M.; Völkel, W.; Mosch, C.; Fromme, H.; Wittsiepe, J. Low serum levels of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS) in children and adults from Afghanistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3493–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essumang, D.K.; Eshun, A.; Hogarh, J.N.; Bentum, J.K.; Adjei, J.K.; Negishi, J.; Nakamichi, S.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Masunaga, S. Perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in the Pra and Kakum River basins and associated tap water in Ghana. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamazaki, E.; Wei, S.; Wang, X.; Gai, N.; Kim, J.H.; Eun, H.; Lam, P.K.S.; Yamashita, N. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Air Particles of Asia: Levels, Seasonality, and Size-Dependent Distribution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14182–14191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.S.; Mott, R.; Potter, A.; Zhou, J.; Baumann, K.; Surratt, J.D.; Turpin, B.; Avery, G.B.; Harfmann, J.; Kieber, R.J.; et al. Atmospheric Deposition and Annual Flux of Legacy Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Replacement Perfluoroalkyl Ether Carboxylic Acids in Wilmington, NC, USA. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Munoz, G.; Sun, H. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in precipitation from mainland China: Contributions of unknown precursors and short-chain (C2 C3) perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids. Water Res. 2019, 153, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewurtz, S.B.; Bradley, L.E.; Backus, S.; Dove, A.; McGoldrick, D.; Hung, H.; Dryfhout-Clark, H. Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Great Lakes Precipitation and Surface Water (2006–2018) Indicate Response to Phase-outs, Regulatory Action, and Variability in Fate and Transport Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8543–8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, E.M.; Ellis, D.A. Understanding the atmospheric measurement and behavior of perfluorooctanoic acid. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2041–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.J.; Furdui, V.I.; Franklin, J.; Koerner, R.M.; Muir, D.C.G.; Mabury, S.A. Perfluorinated Acids in Arctic Snow: New Evidence for Atmospheric Formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3455–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S.A.; Mabury, S.A. Aqueous photolysis of 8:2 fluorotelomer alcohol. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthakur, A.; Leonard, J.; Koutnik, V.S.; Ravi, S.; Mohanty, S.K. Inhalation risks of wind-blown dust from biosolid-applied agricultural lands: Are they enriched with microplastics and PFAS? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 25, 100309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, D.T.; Kulkarni, P.R.; Nickerson, A.; Higgins, C.P.; Field, J.; Schwichtenberg, T.; Newell, C.; Kornuc, J.J. Characterization of relevant site-specific PFAS fate and transport processes at multiple AFFF sites. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffen, T.; Eens, M.; Bervoets, L. Do concentrations of perfluoroalkylated acids (PFAAs) in isopods reflect concentrations in soil and songbirds? A study using a distance gradient from a fluorochemical plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, I.L.; Brusseau, M.L.; Prevatt, F.J.; Escobar, B.A. Incidence of Pfas in soil following long-term application of class B biosolids. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.R. PFAS in soil and groundwater following historical land application of biosolids. Water Res. 2022, 211, 118035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loganathan, N.; Wilson, A.K. Adsorption, Structure, and Dynamics of Short- and Long-Chain PFAS Molecules in Kaolinite: Molecular-Level Insights. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 8043–8052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Yang, G.; Lehmann, A.; Riedel, S.; Rillig, M.C. Effects of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on soil structure and function. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2023, 5, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xie, S.; Huang, J.; Yu, L. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) influence the structure and function of soil bacterial community: Greenhouse experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesek, B.; Szymkiewicz, A.; Šimůnek, J.; Gumula-Kawecka, A.; Jaworska-Szulc, B. Numerical modeling of PFAS movement through the vadose zone: Influence of plant water uptake and soil organic carbon distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Sun, H.; Song, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Ying, G.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the soil-plant system: Sorption, root uptake, and translocation. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, H.; Liang, Y. Plant uptake and soil fractionation of five ether-PFAS in plant-soil systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Qiu, W.; Du, J.; Wan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, R.; Magnuson, J.; Zheng, C. Translocation, bioaccumulation, and distribution of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in plants. iScience 2022, 25, 104061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biek, S.; Khudur, L.; Rigby, L.; Singh, N.; Askeland, M.; Ball, A. Assessing the impact of immobilisation on the bioavailability of PFAS to plants in contaminated Australian soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 20330–20342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearon, S.; Orr, A.; Moyer, H.; Wang, M.; Tamamis, P.; Phillips, T. Montmorillonite clay-based sorbents decrease the bioavailability of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from soil and their translocation to plants. Environ. Res. 2021, 205, 112433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Navarro, D.; Du, J.; Ying, G.; Yang, B.; Mclaughlin, M.; Kookana, R. Increasing ionic strength and valency of cations enhance sorption through hydrophobic interactions of PFAS with soil surfaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarr, J.; Mbonimpa, E.; McAvoy, D.; Soltanian, M. Fate and Transport of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) at Aqueous Film Forming Foam (AFFF) Discharge Sites: A Review. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusseau, M.; Anderson, H.; Guo, B. PFAS concentrations in soils: Background levels versus contaminated sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panieri, E.; Baralić, K.; Djukic-Cosic, D.; Djordjevic, A.; Saso, L. PFAS Molecules: A Major Concern for the Human Health and the Environment. Toxics 2022, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemay, A.; Bourg, I. Interactions between Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) at the Water-Air Interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 2201–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Cao, H.; Pan, W.; Wang, C.; Liang, Y. The role of dissolved organic matter during Per- and Polyfluorinated Substance (PFAS) adsorption, degradation, and plant uptake: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weschler, C.J.; Nazaroff, W.W. Semivolatile organic compounds in indoor environments. Atmos Environ. 2008, 42, 9018–9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letcher, R.J.; Chu, S.G.; Smyth, S.A. Side-chain fluorinated polymer surfactants in biosolids from wastewater treatment plants. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 388, 122044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoeib, M.; Harner, T.; Wilford, B.H.; Jones, K.C.; Zhu, J. Perfluorinated sulfonamides in indoor and outdoor air and indoor dust: Occurrence, partitioning, and human exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6599–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowbridge, J.; Gerona, R.R.; Lin, T.; Rudel, R.A.; Bessonneau, V.; Buren, H.; Morello-Frosch, R. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances in a cohort of women firefighters and office workers in San Francisco. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3363–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, U.; Grandjean, P.; Nielsen, F.; Weihe, P.; Budtz-Jorgensen, E. Breastfeeding as an exposure pathway for perfluorinated alkylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10466–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poothong, S.; Papadopoulou, E.; Padilla-Sanchez, J.A.; Thomsen, C.; Haug, L.S. Multiple pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs): From external exposure to human blood. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.W.; Muir, D.C.G.; Moody, C.A.; Ellis, D.A.; Wai, C.K.; Solomon, K.R.; Mabury, S.A. Collection of airborne fluorinated organics and analysis by gas chromatography/chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, T.; Yao, B.; Song, W.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Cheng, T.; Li, X. Particle size distribution and respiratory deposition estimates of airborne perfluoroalkyl acids during the haze period in the megacity of Shanghai. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makey, C.M.; Webster, T.F.; Martin, J.W.; Shoeib, M.; Harner, T.; Dix-Cooper, L.; Webster, G.M. Airborne precursors predict maternal serum perfluoroalkyl acid concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7667–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goosey, E.; Harrad, S. Perfluoroalkyl substances in UK indoor and outdoor air: Spatial and seasonal variation, and implications for human exposure. Environ. Int. 2012, 45, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.M.; Boor, B.E.; Schreder, E.; Salamova, A. Indoor exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the childcare environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbersdorf, S.U.; Wieprecht, S. Biostabilization of cohesive sediments: Revisiting the role of abiotic conditions, physiology and diversity of microbes, polymeric secretion, and biofilm architecture. Geobiology 2015, 13, 68–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, G.; Fechner, L.C.; Geneste, E.; Pardon, P.; Budzinski, H.; Labadie, P. Spatiotemporal dynamics of per and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and transfer to periphytic biofilm in an urban river: Case-study on the River Seine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23574–23582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, N.J.M.; Wargenau, A.; Sorenson, C.; Pedersen, J.; Tufenkji, N.; Novak, P.J.; Simcik, M.F. Partitioning and accumulation of perfluoroalkyl substances in model lipid bilayers and bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10433–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, T.N.; Cope, W.G.; Kwak, T.J.; Strynar, M.J.; Grieshaber, C.A.; Heise, R.J.; Sessions, F.W. Trophodynamics of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the food web of a large Atlantic Slope River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6800–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, N.; Ng, J.; Kelly, B. Uptake and elimination kinetics of perfluoroalkyl substances in submerged and free-floating aquatic macrophytes: Results of mesocosm experiments with Echinodorus horemanii and Eichhornia crassipes. Water Res. 2017, 117, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Norström, K.; Viktor, T.; Cousins, A.P.; Josefsson, S. Stockholm Arlanda Airport as a source of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances to water, sediment and fish. Chemosphere 2015, 129, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, M.; Jin, X.; Liu, C.; Zheng, B.; Shen, J.; et al. High contamination, bioaccumulation and risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in multiple environmental media at the Baiyangdian Lake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Xia, X.; Hu, D.; Zhou, D.; Wang, H.; Zhai, Y.; Lin, H. Long-chain perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) affect the bioconcentration and tissue distribution of short-chain PFAAs in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12358–12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzotti, T.; Sirri, F.; Ghelli, E.; Zironi, E.; Zampiga, M.; Pagliuca, G. Perfluoroalkyl contaminants in eggs from backyard chickens reared in Italy. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (EFSA CONTAM Panel); Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.C.; et al. Risk to human health related to the presence of perfluoroalkyl substances in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.B.; Conder, J.M.; Arblaster, J.A.; Higgins, C.P. Assessing human health risks from per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS)-impacted vegetable consumption: A tiered modeling approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15202–15214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadia, M.; Yeung, L.W.; Fiedler, H. Trace level analyses of selected perfluoroalkyl acids in food: Method development and data generation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 113721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macheka, L.R.; Olowoyo, J.O.; Mugivhisa, L.L.; Abafe, O.A. Determination and assessment of human dietary intake of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in retail dairy milk and infant formula from South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, J.; Abraham, K.; Dietrich, S.; Fromme, H.; Voelkel, W.; Schwerdtle, T.; Weikert, C. Internal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in vegans and omnivores. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 237, 113808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, G.M.; Long, S.M.; Jones, O.A. What are the effects of PFAS exposure at environmentally relevant concentrations? Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- India-Aldana, S.; Yao, M.; Midya, V.; Colicino, E.; Chatzi, L.; Chu, J.; Gennings, C.; Jones, D.; Loos, R.; Setiawan, V.; et al. PFAS Exposures and the Human Metabolome: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2023, 9, 510–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, S.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.; Roberts, S. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Toxicity and Human Health Review: Current State of Knowledge and Strategies for Informing Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Lin, S.B.; Lv, J.Y.; Wu, Y.; Feng, W.R. Dissect the association between per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and kidney function from the perspective of lipid molecules. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Su, W.; Li, H.; Li, L.; An, Z.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Guo, H.; et al. Association of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances with hepatic steatosis and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease among patients with acute coronary syndrome. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Flaws, J.A.; Spinella, M.J.; Irudayaraj, J. The relationship between typical environmental endocrine disruptors and kidney disease. Toxics 2022, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.D.; Qian, Z.M.; Dharmage, S.C.; Perret, J.; Geiger, S.D.; Rigdon, S.E.; Howard, S.; Zeng, X.W.; Hu, L.W.; Yang, B.Y.; et al. Association of perfluoroalkyl substances exposure with impaired lung function in children. Environ. Res. 2017, 155, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvalem, H.E.; Nygaard, U.C.; Carlsen, K.L.; Carlsen, K.H.; Haug, L.S.; Granum, B. Perfluoroalkyl substances, airways infections, allergy and asthma related health outcomes–implications of gender, exposure period and study design. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Holst, H.; Nayak, P.; Dembek, Z.; Buehler, S.; Echeverria, D.; Fallacara, D.; John, L. Perfluoroalkyl substances exposure and immunity, allergic response, infection, and asthma in children: Review of epidemiologic studies. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, M.; Luo, K.; Luo, F.; Aimuzi, R.; Huo, X.; Chen, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J. Association between prenatal exposure to PFAS and fetal sex hormones: Are the short-chain PFAS safer? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8291–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Zhuang, T.; Liu, X.; Fu, J.; Zhang, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, A.; Liang, Y.; Song, M.; et al. Prenatal exposure to per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and association between the placental transfer efficiencies and dissociation constant of serum proteins–PFAS complexes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6529–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Walker, D.I.; Thomas, D.C.; Qiu, C.; Chatzi, L.; Alderete, T.L.; Kim, J.S.; Conti, D.V.; Breton, C.V.; et al. Dysregulated lipid and fatty acid metabolism link perfluoroalkyl substances exposure and impaired glucose metabolism in young adults. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Jin, M.; Huang, Y.; Aimuzi, R.; Zheng, T.; Nian, M.; Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; Luo, Z.; Shen, L.; et al. Environmental exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances in early pregnancy, maternal glucose homeostasis and the risk of gestational diabetes: A prospective cohort study. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldorsson, T.I.; Rytter, D.; Haug, L.S.; Bech, B.H.; Danielsen, I.; Becher, G.; Henriksen, T.B.; Olsen, S.F. Prenatal exposure to perfluorooctanoate and risk of overweight at 20 years of age: A prospective cohort study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, V.M.; Hoffman, K.; Shin, H.M.; Weinberg, J.M.; Webster, T.F.; Fletcher, T. Perfluorooctanoic acid exposure and cancer outcomes in a contaminated community: A geographic analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fletcher, T.; Mucs, D.; Scott, K.; Lindh, C.H.; Tallving, P.; Jakobsson, K. Half-lives of PFOS, PFHxS and PFOA after end of exposure to contaminated drinking water. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitter, G.; Da Re, F.; Canova, C.; Barbieri, G.; Zare Jeddi, M.; Daprà, F.; Manea, F.; Zolin, R.; Bettega, A.M.; Stopazzolo, G.; et al. Serum levels of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in adolescents and young adults exposed to contaminated drinking water in the Veneto region, Italy: A cross-sectional study based on a health surveillance program. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 027007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, J.; Gao, A. Contact to perfluoroalkyl substances and thyroid health effects: A meta-analysis directing on pregnancy. Chemosphere 2023, 315, 137748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fini, J.B.; Mughal, B.B.; Le Mével, S.; Leemans, M.; Lettmann, M.; Spirhanzlova, P.; Affaticati, P.; Jenett, A.; Demeneix, B.A. Human amniotic fluid contaminants alter thyroid hormone signalling and early brain development in Xenopus embryos. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisi, R.; Vamerali, T.; Manzetti, S. Accumulation of perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in agricultural plants: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzurro, D.M.; Seeley, M.; Kerper, L.E.; Beck, B.D. Interspecies differences in perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) toxicokinetics and application to health-based criteria. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 106, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiee, A.; Faridi, S.; Sly, P.D.; Stone, L.; Kennedy, L.; Mahabee-Gittens, E.M. Asthma and Decreased Lung Function in Children Exposed to Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): An Updated Meta-Analysis Unveiling Research Gaps. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiano, M.; Jouanneau, W.; Blévin, P.; Angelier, F.; Parenteau, C.; Gernigon, J.; Lemesle, J.C.; Robin, F.; Pardon, P.; Budzinski, H.; et al. High levels of fluoroalkyl substances and potential disruption of thyroid hormones in three gull species from South Western France. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvamme, S. Levels of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Trace Elements, and Steroid Hormones in Arctic Char (Salvelinus alpinus) from Lake Diesetvatnet, Svalbard. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dunder, L.; Salihovic, S.; Elmståhl, S.; Lind, P.M.; Lind, L. Associations between per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and diabetes in two population-based cohort studies from Sweden. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimbaugh, A.; Meyer, D.N.; Connell, M.L.; Blount-Pacheco, J.; Tolofari, D.; Gonzalez, G.; Banerjee, D.; Norton, J.; Miller, C.J.; Baker, T.R. Environmental Exposure to Per-and Polyfluorylalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Reproductive Outcomes in the General Population: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown-Leung, J.M.; Cannon, J.R. Neurotransmission targets of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance neurotoxicity: Mechanisms and potential implications for adverse neurological outcomes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 1312–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran Mahdavi, S.; Zamani, S.; Riahi, R.; Taheri, E.; Vahdatpour, B.; Sharifianjazi, F.; Kelishadi, R. Exposure to environmental chemicals and human bone health; A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expo. Health 2024, 16, 861–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Aris, I.M.; Fleisch, A.F.; Lin, P.I.; Nichols, A.R.; Oken, E.; Hivert, M.F. Associations of Prenatal Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Exposures with Offspring Adiposity and Body Composition at 16–20 Years of Age: Project Viva. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 127002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlezinger, J.J.; Gokce, N. Perfluoroalkyl/polyfluoroalkyl substances: Links to cardiovascular disease risk. Circ. Res. 2024, 134, 1136–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.N.; Badders, A.N.; Costacou, T.; Arthur, J.M.; Innes, K.E. Perfluoroalkyl substances and kidney function in chronic kidney disease, anemia, and diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.Y.; Eichler, C.M.A.; Amparo, D.E.; Zhou, J.; Baumann, K.; Cohen Hubal, E.A.; Surratt, J.D.; Morrison, G.C.; Turpin, B.J. Indoor air concentrations of PM2.5 quartz fiber filter-collected ionic PFAS and emissions to outdoor air: Findings from the IPA campaign. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2024, 27, 1603–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donat-Vargas, C.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Tornevi, A.; Wennberg, M.; Sommar, J.; Kiviranta, H.; Koponen, J.; Rolandsson, O.; Åkesson, A. Perfluoroalkyl substances and risk of type II diabetes: A prospective nested case-control study. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Peng, W.; Wang, X.; Jin, R.; Li, J. Triglycerides mediate the relationships of per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) exposure with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) risk in US participants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 289, 117436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Larebeke, N.; Koppen, G.; De Craemer, S.; Colles, A.; Bruckers, L.; Den Hond, E.; Govarts, E.; Morrens, B.; Schettgen, T.; Remy, S.; et al. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and immune system-related diseases: Results from the Flemish Environment and Health Study (FLEHS) 2008–2014. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesonen, M.; Vähäkangas, K. Involvement of per-and polyfluoroalkyl compounds in tumor development. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedsalehi, M.S.; Boffetta, P. Per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure and risk of kidney, liver, and testicular cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Lav. 2023, 114, e2023040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, L.K.; Ishikawa, T.; Dolinoy, D.C. Developmental toxicant exposures and sex-specific effects on epigenetic programming and cardiovascular health across generations. Environ. Epigenetics 2022, 8, dvac017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, A.; Armitage, J.; Bruton, T.; Dassuncao, C.; Heiger-Bernays, W.; Hu, X.; Kärrman, A.; Kelly, B.; Ng, C.; Robuck, A.; et al. PFAS Exposure Pathways for Humans and Wildlife: A Synthesis of Current Knowledge and Key Gaps in Understanding. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 40, 631–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendl, C.; Taylor, M.; Bräunig, J.; Ricolfi, L.; Ahmed, R.; Chin, M.; Gibson, M.; Hesselson, D.; Neely, G.; Lagisz, M.; et al. Profiling research on PFAS in wildlife: Systematic evidence map and bibliometric analysis. Ecol. Solut. Evid. 2024, 5, e12292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, N.M.; Minucci, J.M.; Mullikin, A.; Slover, R.; Hubal, E.A.C. Human exposure pathways to poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from indoor media: A systematic review. Environ. Int. 2022, 162, 107149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrega-Palau, J.; Vidal, M.; Rigol, A. Modelling the sorption behaviour of perfluoroalkyl carboxylates and perfluoroalkane sulfonates in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minovic, J.; Lacorte, S.; Vidal, M.; Rigol, A. Sorption behaviour of perfluoroalkyl substances in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podder, A.; Sadmani, A.A.; Reinhart, D.; Chang, N.-B.; Goel, R. Per and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) as a contaminant of emerging concern in surface water: A transboundary review of their occurrences and toxicity effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralba-Sanchez, T.L.; Di Toro, M.D.; Dmitrenko, O.; Murillo-gelvez, J.; Tratnyek, P.G. Modeling the Partitioning of Anionic Carboxylic and Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic and Sulfonic Acids to Octanol and Membrane Lipid. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 2317–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Industry Sector | Typical Product Types | Main Functional Roles | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Goods & Personal Care | Household cleaning agents, detergents, windshield washer fluids, fabric care products, cosmetics | Surface tension reduction, wetting, antifogging, stain and water resistance, lubricants | [14,17,56] |
| Textile Industry | Protective clothing, carpets, outdoor fabrics, food-contact packaging | Water, oil, and stain resistance, durability, cleanliness, grease resistance in packaging | [13,25] |
| Chemical & Material Processing | Ceramics, metal nanoparticles, coatings, inks | Surface tension, wetting, penetration, antifouling, antistatic properties, metal recovery, gloss enhancement | [20,23,25,67] |
| Plastics, Resins & Rubber | Fluoropolymers, medical devices, electrochemical applications | Chemical resistance, flame resistance, low permeability, high-temperature stability, processing aids | [24,27,43] |
| Recycling & Material Recovery | Metal extraction, solvent recovery | Metal recovery (e.g., palladium, platinum), extraction from contaminated soil, solvent regeneration | [30,31,33,34] |
| Pesticides & Fertilizers | Herbicides, insecticides, fungicides, fertilizers | Wetting agents, foam-breaking, stability, dust reduction | [38,39,40,41] |
| High-tech Industrial Applications | Electronic components, semiconductor manufacturing, cooling systems | Surface tension reduction, stability in electronic components, corrosion protection, improved processing | [14,25,42,44] |
| Medical Uses | Blood substitutes, drug delivery, imaging agents, medical devices | Oxygen-carrying properties, biocompatibility, stability, imaging, drug delivery, surface hydrophobicity | [45,51,53,58,59] |
| Metal Coating & Surface Finishing | Chrome plating, copper, nickel, tin electroplating, aluminum foil | Surface tension reduction, leveling, mist suppression, corrosion protection, wear resistance | [14,61,62] |
| Mining Industry | Metal extraction, flotation agents, electrowinning | Enhanced metal recovery, mist suppression, efficiency in leaching processes | [14,36,63] |
| Oil & Gas Industry | Drilling fluids, completion fluids, proppants, foam stabilization | Surface tension reduction, foam stabilization, improved oil extraction, oil spill containment | [9,14,64] |
| Safety & Defense Applications | Firefighting foams (AFFF), explosives, propellants, ammunition | Flame retardants, fire suppression, explosive binders, pyrotechnic applications | [23,65,66] |
| Consumer Products & Surface Modifications | Dry cleaning products, refrigeration, adhesives, coatings | Fabric protection, faster drying, low boiling points, enhanced adhesion and durability in coatings | [8,67] |
| Region | Country/Area | Investigated Sites | PFAS Concentration (ng/g) | Max. PFOA/ PFOS (ng/g) | Comments | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | South Korea | Estuarine/ coastal areas | 0.3–3.9 | 3.4/1.7 | Lower PFAS levels in coastal areas. | [116,117] |
| China (Tianjin, Wuhan) | Rivers/ Manufacturing plant | 0.2–5500 | 0.5/2.4 | Moderate to high contamination near industrial sites. | [118] | |
| North America | USA (Minnesota, Ohio) | Home gardens/ Fluoropolymer industry | 1.3–490 | 3.0/12 | PFASs detected in agriculture, linked to industrial activities. | [119,120] |
| Europe | Sweden, Germany, France | Forests/ Agricultural areas | 0.4–9250 | 0.6/8600 | Forests less impacted, agriculture at risk. | [121] |
| Oceania | Australia | Irrigated agriculture | 4.0–3067 | 1388/1692 | Irrigation with contaminated water spreads PFASs. | [122] |
| Region/ Country | Location | Sampling Type | PFOS (Unit) | PFOA (Unit) | Other Notable PFASs | Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Mid-Ohio Valley (West Virginia) | Drinking water from 6 water districts and private wells | 3.55 ng/mL | 1.5–7.2 ng/mL | - | [135,136] |
| Canada | Toronto, Ontario | Water samples from creeks and rivers | 80,000 pg/L | 19,000 pg/L | PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA | [137] |
| Germany | Rhine River, Moehne River, Ruhr catchment area | River and drinking water samples | 519 ng/L | - | PFHpA PFHxA | [138] |
| France | Various locations in France | Raw and treated water samples (331 raw, 110 treated) | 22 ng/L | 12 ng/L | PFBA, PFBS, PFHxA, PFPeA, PFHpA, PFNA, PFDA (detected in raw water) | [139] |
| Australia | 34 locations across Australia | Drinking water samples | 16 ng/L | 9.7 ng/L | PFHxS | [140] |
| Japan | Osaka | Water samples from water purification plants | 1.3–3.7 ng/L | 6.5–48 ng/L | - | [141] |
| South Korea (Seoul) | Seoul Metropolitan area | Drinking water, human serum, and food samples | 0.370–10.8 ng/L | <3.29 ng/L | PFNA, PFDA, PFCAs, PFSAs | [142] |
| China (Eastern China) | Eastern China (9 rivers, 9 lakes, 17 cities) | Tap water and surface water samples from rivers and lakes | 1.4–175 ng/L | 115–151 ng/L (Hangzhou exceeded USEPA standard) | PFHxS, PFHpA, others | [143] |
| India (Ganges River) | Along the Ganges River | Drinking water samples | 0.8–4.9 ng/L | 0.5–3.5 ng/L | PFHxA, PFHpA, PFPA | [144] |
| Afghanistan | Kabul and Ningarhar | Tap and well water samples | <0.03 ng/L | <0.015 ng/L | - | [145] |
| Ghana | Rivers of Kakum and Pra | Rivers and tap water samples | 197–398 ng/L | 197–200 ng/L | PFHxA, PFDA, PFPeA | [146] |
| Health Outcome | Evidence and Effects | Risk Level | Affected Group | Impact Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxicokinetics | Uptake Via water, soil, food; persists in organs. | High | Both | Long-term accumulation | [218,219] |
| Respiratory | Asthma, lung function decline in children. | Moderate | Children | Short-term respiratory issues | [220] |
| Endocrine Disruption | Affects thyroid, sex hormones, cortisol levels. | High | Both | Long-term hormonal imbalance | [221,222] |
| Metabolic Effects | Alters glucose, lipids, diabetes. | High | Both | Long-term metabolic disorders | [223] |
| Reproductive | Impaired fertility, miscarriage, developmental issues. | High | Pregnant women, children | Long-term fertility issues | [224] |
| Neurological | ADHD, cognitive decline, Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s. | High | Children, elderly | Long-term cognitive impairment | [225] |
| Bone Health | Osteoporosis risk, bone density loss. | Moderate | Elderly | Long-term bone weakness | [226] |
| Obesity | Increased obesity risk in offspring. | Moderate | Children | Long-term weight gain | [227] |
| Lipid Metabolism | Affects cholesterol, linked to cardiovascular disease. | High | Adults | Long-term cardiovascular effects | [228] |
| Kidney disease | Chronic kidney disease | Moderate | Adults | Long-term kidney damage | [229] |
| Cardiovascular Health | Linked to hypertension but not coronary heart disease. | Moderate | Adults | Long-term cardiovascular issues | [228] |
| Cerebrovascular | Links to stroke and cerebrovascular problems. | Moderate | Adults | Long-term stroke risk | [230] |
| Diabetes | Limited study about linking to Type 2 diabetes. | Low | Adults | Uncertain long-term impact | [231] |
| Liver Disease | Links to liver dysfunction, NAFLD, cirrhosis. | Moderate | Adults | Long-term liver complications | [232] |
| Immune System | Reduces immune function, increases autoimmune diseases. | High | Children | Long-term immune dysfunction | [233] |
| Cancer Risk | testicular, breast cancer. | High | Adults | Long-term cancer risk | [234,235] |
| Genetic Effects | Epigenetic changes passed to future generations. | High | Future Generations | Long-term generational effects | [236] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alam, M.J.; Habib, A.; Hasan, M.M.; Islam, S.; Halim, E. Industrial Applications, Environmental Fate, Human Exposure, and Health Effects of PFAS. Pollutants 2025, 5, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants5040043
Alam MJ, Habib A, Hasan MM, Islam S, Halim E. Industrial Applications, Environmental Fate, Human Exposure, and Health Effects of PFAS. Pollutants. 2025; 5(4):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants5040043
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlam, Mohammad Jahirul, Ahsan Habib, Mohammad Mehedi Hasan, Saiful Islam, and Ershad Halim. 2025. "Industrial Applications, Environmental Fate, Human Exposure, and Health Effects of PFAS" Pollutants 5, no. 4: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants5040043
APA StyleAlam, M. J., Habib, A., Hasan, M. M., Islam, S., & Halim, E. (2025). Industrial Applications, Environmental Fate, Human Exposure, and Health Effects of PFAS. Pollutants, 5(4), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants5040043









