Assessment of Heavy Metals (Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn) Bioaccumulation and Translocation by Erigeron canadensis L. in Polluted Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil
3.2. Plant
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kushwaha, A.; Rani, R.; Kumar, S.; Gautam, A. Heavy metal detoxification and tolerance mechanisms in plants: Its implications for Phytoremediation. Environ. Rev. 2015, 24, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, J.; Uhlik, O.; Viktorova, J.; Macek, T. Phytoextraction of heavy metals: A promising tool for clean-up of polluted environment? Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, S.; Ali, Q.; Zahir, Z.; Ashraf, S.; Asghar, H. Phytoremediation: Environmentally sustainable way for reclamation of heavy metal polluted soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, V.; Bajpai, O. Chapter 1—Phytoremediation: From Theory Toward Practice, Phytomanagement of Polluted Sites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–49. ISBN 9780128139127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D. Water Quality Assessments: A Guide to the Use of Biota, Sediments and Water in Environmental Monitoring, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall Ltd.: London, UK, 1996; p. 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, S.; Baskar, A.; Geevarghese, D.; Ali, M.; Bahubali, P.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.; Senatov, F.; Koppala, S.; et al. Bioaccumulation of lead (Pb) and its effects in plants: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; ITPS. Status of the World’s Soil Resources (SWSR)—Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pourrut, B.; Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Winterton, P.; Pinelli, E. Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 213, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B. Heavy metals in soils. In Trace Elements and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Environmental Pollution; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 22, pp. 11–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrat, A.; Ezzat, K.; Ikram, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.; Yedjou, C.; Patlolla, A.; Sutton, D. Heavy Metals Toxicity and the Environment. Mol. Clin. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadaa, W.; Mohammed, H. Heavy Metals—Definition, Natural and Anthropogenic Sourcesof Releasing into Ecosystems, Toxicity, and Removal Methods—An Overview Study. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritsan, N.; Babiy, A. Hazardous materials in the environment of Dnepropetrovsk region (Ukraine). J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 76, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharytonov, M.; Benselhoub, A.; Shupranova, L.; Kryvakovska, R.; Khlopova, V. Environmental assessment of atmospheric pollution in Dnipropetrovsk province (Ukraine). In Studia Universitatis “Vasile Goldis” Arad. Seria Stiintele Vietii (Life Sciences Series); Vasyl Goldis Western University: Arad, Romania, 2015; Volume 25, p. 125. [Google Scholar]
- Shparyk, Y.S.; Parpan, V.I. Heavy metal pollution and forest health in the Ukrainian Carpathians. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 130, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytar, O.; Taran, N. Effect of heavy metals on soil and crop pollution in Ukraine—A review. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2022, 23, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, C.; Charveron, M.; Tarroux, R.; Gall, Y. Environmental pollutants and skin cancer. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2002, 18, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, S. Soil quality in relation to agricultural uses. Integrated soil and sediment research: A basic for proper protection; Kluwer Publishers: London, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Clemens, S. Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menshov, O.; Kruglov, O. Agricultural Soil Degradation in Ukraine. In Impact of Agriculture on Soil Degradation II. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Pereira, P., Muñoz-Rojas, M., Bogunovic, I., Zhao, W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Ma, K. Spatial and Temporal Distribution and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of Ningxia, Northwest of China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nriagu, J.; Pacyna, J. Quantiative assessment of worldwide contmiantion of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature 1988, 333, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, V.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Kumar Maiti, S. Potential and prospects of weed plants in phytoremediation and eco-restoration of heavy metals polluted sites. In Phytoremediation Technology for the Removal of Heavy Metals and Other Contaminants from Soil and Water; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Zhang, J.; Hussain, A.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X. Accumulation and translocation of food chain in soil-mulberry (Morus alba L.)-silkworm (Bombyx mori) under single and combined stress of lead and cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, M.; Surendran, U.; Raja, P.; Kumar, A.; Senapathi, V. A review of heavy metals accumulation pathways, sources and management in soils. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon-Smits, E. Phytoremediation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2005, 56, 1545–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Al-Tabbaa, A.; O’Connor, D.; Hu, Q.; Wang, L.; Kirkwood, N.; Ok, Y.; Tsang, D.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J. Sustainable remediation and redevelopment of brownfield sites. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, W.; Cunningham, S. Phytostabilization of metals. In Phytoremediation of Toxic Metals: Using Plants to Clean-Up the Environment; Raskin, I., Ensley, B.D., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 71–88. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, A.; Rangel, A.; Castro, P. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils: Phytoremediation as a potentially promising clean-up technology. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 622–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mench, M.; Lepp, N.; Bert, V.; Schwitzguébel, J.-P.; Gawronski, S.; Schröder, P.; Vangronsveld, J. Successes and limitations of phytotechnologies at field scale: Outcomes, assessment and outlook from COST Action 859. J. Soil Sediments 2010, 10, 1039–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.; Okieimen, F. Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2011, 2011, 402647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, D.; Blaylock, M.; Kumar, N.; Dushenkov, V.; Ensley, B.; Chet, I.; Raskin, I. Phytoremediation: A novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 1995, 13, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Sajad, M. Phytoremediation of heavy metals-concepts and applications. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, N.; Imran, M.; Shaheen, M.; Ishaque, W.; Kamran, M.; Matloob, A.; Rehim, A.; Hussain, S. Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: Modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Oh, K. Advancements in Phytoremediation Research for Soil and Water Resources: Harnessing Plant Power for Environmental Cleanup. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Wang, Y.; Tan, S.; Mohd Yusof, M.; Ghosh, S.; Chen, Z. Phytoremediation: A Promising Approach for Revegetation of Heavy Metal-Polluted Land. Front Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jing, F.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Guo, B. Heavy metals status, transport mechanisms, sources, and factors affecting their mobility in Chinese agricultural soils. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabovskyi, O. Accumulation of heavy metals by soil and plant objects under anthropogenic load. Uzhhorod State Univ. Sci. Bull. Ser. Biol.-Uzhhorod 2000, 8, 158–160. [Google Scholar]
- Myslyva, T.M. Heavy metals in the soils of agricultural landscapes of Zhytomyr Polissia. Agroecol. J. 2009, 4, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhenko, N.; El Amrani, A.; Giltrap, M.; Furong, T.; Laptiev, V. Bioaccumulation of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn in Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. in the polluted area by enterprise for the production and processing of batteries. Ann. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 26–030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laptiev, V.; Apori, S.; Giltrap, M.; Tian, F.; Ryzhenko, N. Bioaccumulation of Cr, Zn, Pb and Cu in Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. and Erigeron canadensis L. Resources 2024, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondar, O.; Ryzhenko, N.; Laptiev, V.; Makhniuk, V. Bioaccumulation of Hg, Cr, Zn, As, Cd, Pb, Cu in the “soil-plant” system in the rea of influenceof enterprises for the production and processing of batteries. Ecologicalscience 2022, 1, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko, V.; Khvorost, O.; Serbin, A.; Makarevych, I. The current state of pharmacognostic study of plants of the genus Erigeron L. Physiol. Act. Subst. 1999, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Mobli, A.; Oliveira, M.; Butts, L.; Proctor, C.; Lawrence, N.; Werle, R. Emergence pattern of horseweed (Erigeron canadensis L.) accessions across Nebraska. Weed Technol. 2022, 36, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, L.; Doll, J.; Holm, E.; Pancho, J.; Herberger, J. World Weeds: Natural Histories and Distribution; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1997; pp. 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Strzelecka, H.; Glinkowska, G. Studies on the chemistry of Erigeron canadensis. Part 1. Herba Pol. 1981, 27, 201. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlaczyk, I.; Czerchawski, L.; Kuliczkowski, W.; Karolko, B.; Pilecki, W.; Witkiewicz, W.; Gancarz, R. Anticoagulant and anti-platelet activity of polyphenolic-polysaccharide preparation isolated from the medicinal plant Erigeron canadensis L. Thromb. Res. 2011, 127, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Feng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhu, C.; Qu, Y.; Wang, H. Predicting the potential distribution of an invasive species, Erigeron canadensis L., in China with a maximum entropy model. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, V.; Trifkovic, J.; Krgovic, R.; Milojković-Opsenica, D.; Markovic, M.; Ramadan, N.; Mutic, J. Uptake of metals and metalloids by Conyza canadensis L. from a thermoelectric power plant landfill. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2016, 68, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krgović, R.; Trifković, J.; Milojković-Opsenica, D.; Manojlović, D.; Marković, M.; Mutić, J. Phytoextraction of metals by Erigeron canadensis L. from fly ash landfill of power plant “Kolubara”. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10506–10515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaman, A. Assessment of the Use of Artemisia dracunculus L. and Erigeron canadensis in The Remediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils and Their Ability to Phytoextraction and Biomass Yield. Turk. J. Nat. Sci. 2022, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajad, M.; Khan, M.; Ali, H. Lead phytoremediation potential of sixty-one plant species: An open field survey. Pure Appl. Biol. (PAB) 2019, 8, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, J.; Wei, X.; Xue-Gang, L.; Shah, S.; Buzdar, M.; Ahmed, I.; Abdullah, S.; Babar, A.; Jakhar, A.; Azam, T. Garlic (Allium sativum) based interplanting alters the heavy metals absorption and bacterial diversity in neighboring plants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Wu, X.; Xia, P.; Lin, T.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and screening of accumulating plants around the Wanshan mercury mine in Northeast Guizhou Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48837–48850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocaman, A. Determination of Phytoextraction and Hyperaccumulating Capacity of Artemisa dracunculus L and Erigeron canadensis Plants of the Asteraceae Family. 2021; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Passport of the City of Dnipro; Department of Transport and Environmental Protection of the Dnipro City Council: Dnipro, Ukraine, 2016; p. 64.
- DSTU 4287:2004; Soil Quality. Sampling of Samples. 2005. Available online: https://environmentallab.com.ua/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/dstu-4287-2004-yakist-gruntu.-vidbirannya-prob.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2024).
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 13th ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- Varun, M.; D’Souza, R.; Favas, P.; Pratas, J.; Paul, M. Utilization and Supplementation of Phytoextraction Potential of Some Terrestrial Plants in Metal-Contaminated Soils. In Phytoremediation: Management of Environmental Contaminants; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouei, A.; Cherati, A.; Naghipour, D. Heavy Metals Contamination and Risk Assessment of Surface Soils of Babol in Northern Iran. Health Scope 2018, 7, e62423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massas, I.; Kalivas, D.; Ehaliotis, C.; Gasparatos, D. Total and available heavy metal concentrations in soils of the Thriassio plain (Greece) and assessment of soil pollution indexes. Environ. Monit. Ass. 2013, 185, 6751–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violante, A.; Cozzolino, V.; Perelomov, L.; Caporale, A.G.; Pigna, M. Mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 10, 268–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calace, N.; Petronio, B.M. The role of organic matter on metal toxicity and bio-availability. Ann. Chim. J. Anal. Environ. Cult. Herit. Chem. 2004, 94, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health of Ukraine. Order, Regulation of 14.07.2020 № 1595 “On Approval of the Hygienic Regulations for the Permissible Content of Chemicals in Soil”; Ministry of Health of Ukraine: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2020.
- Köljonen, T. The geochemical atlas of Finland. Geol Survey of Finland, Espoo. J. Environ. Qual. 1992, 32, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, J. Concentrations of 61 Trace Elements in Sewage Sludge, Farmyard Manure, Mineral Fertilizers, Precipitation and in Oil and Crops; Swedish EPA Rep 5159; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2001.
- Alloway, B. Heavy Metals in Soils, 2nd ed.; Blackie Acad: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Håkanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control—A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.; Norvell, W. Mechanisms of cadmium uptake, translocation and deposition in plants. In Cadmium in Soils and Plants; McLaughlin, M.J., Singh, B.R., Eds.; Kluwer Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 85, pp. 125–150. [Google Scholar]
- Wakeel, A.; Xu, M. Chromium Morpho-Phytotoxicity. Plants 2020, 9, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, D.; Tiwari, M.; Dutta, P.; Singh, P.; Chawda, K.; Kumari, M.; Chakrabarty, D. Chromium stress in plants: Toxicity, tolerance, and phytoremediation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H. Chromium as an Environmental Pollutant: Insights on Induced Plant Toxicity. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 375843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djingova, R.; Kuleff, I. Seasonal Variations in the Metal Concentration of Taraxacum officinale, Plantago major and Plantago lanceolata. Chem. Ecol. 1999, 16, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farraji, H.; Aziz, H.; Tajuddin, R.; Mojiri, A. Optimization of Phytoremediation of Lead-contaminated Soil by Spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Int. J. Sci. Res. Knowl. 2014, 2, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, M. Plant uptake of soil and atmospheric lead in Southern California. Chemosphere 1972, 1, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelsen, B.O.; Olsen, R.A.; Steinnes, E. Ectomycorrhizal heavy metal accumulation as a contributing factor to heavy metal levels in organic surface soils. Sci. Total Environ. 1995, 170, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomašević, M.; Aničić, M.; Jovanović, L.; Perić-Grujić, A.; Ristić, M. Deciduous tree leaves in trace elements biomonitoring: A contribution to methodology. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Schreck, E.; Xiong, T.; Niazi, N.K. Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: A comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Mukherjee, A. Trace Elements from Soil to Human; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, A.; Bhalerao, S. Response of Plants towards Heavy Metal Toxicity: An overview of Avoidance, Tolerance and Uptake Mechanism. Ann. Plant Sci. 2013, 2, 362–368. [Google Scholar]
- Lasat, M.M. The Use of Plants for the Removal of Toxic Metals from Contaminated Soil; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Zunic, J.; Mihajlovic, D.; Kelecevic, B.; Kovačević, Z. Determination of potentially toxic elements in some wild edible and medicinal plants. AГPOЗHAЊE 2022, 23, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Néel, C.; Soubrand-Colin, M.; Piquet-Pissaloux, A.; Bril, H. Mobility and bioavailability of Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in a basaltic grassland: Comparison of selective extractions with quantitative approaches at different scales. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.; McGrath, S.; Reeves, R.; Smith, J. Metal hyperaccumulator plants: A review of the ecology and physiology of a biological resource for phytoremediation of metal-polluted soils. In Phytoremediation of Contaminated Soils; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 85–107. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, S.; Zhao, F.-J. Phytoextraction of metals and metalloids from contaminated soils. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.; Brooks, R. Terrestrial Higher Plants which Hyperaccumulate Metallic Elements. A Review of Their Distribution, Ecology and Phytochemistry. Biorecovery 1989, 1, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Archana, H.S.; Jaitly, A.K. Bioremediation: Environmental Biotechnology for Heavy Metal Decontamination of Soil and Water. Biochem. Cell. Arch. 2014, 14, 259–281. [Google Scholar]
- Purakayastha, T.; Chhonkar, P. Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils. In Soil Heavy Metals; Soil Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimou, S.G.; Barbayiannis, Ν.; Golia, E.E. Preliminary investigation of the use of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. as a Cd accumulator in contaminated Mediterranean soils: The relationships among cadmium (Cd) soil fractions and plant Cd content. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2024, 9, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porębska, G.; Ostrowska, A. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Wild Plants: Implications for Phytoremediation. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 1999, 8, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
| Location | pHsalt | OM, % | CEC, mmol 10−2 g−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N 48°49′48.32″ E 35°13′67.86″ | P1 (1 km) | 6.58 ± 0.12 b | 4.11 ± 0.15 a | 42.6 ± 1.95 b |
| N 48°46′50.60″ E 35°18′99.85″ | P2 (5.5 km) | 6.2 ± 0.15 c | 4.60 ± 0.08 b | 38.63 ± 1.60 c |
| N 48°58′64.79″ E 35°21′81.27″ | P3 (12.02 km) | 6.70 ± 0.02 a | 4.40 ± 0.12 c | 45.0 ± 1.40 a |
| Indicator | Plots | Cr | Cu | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
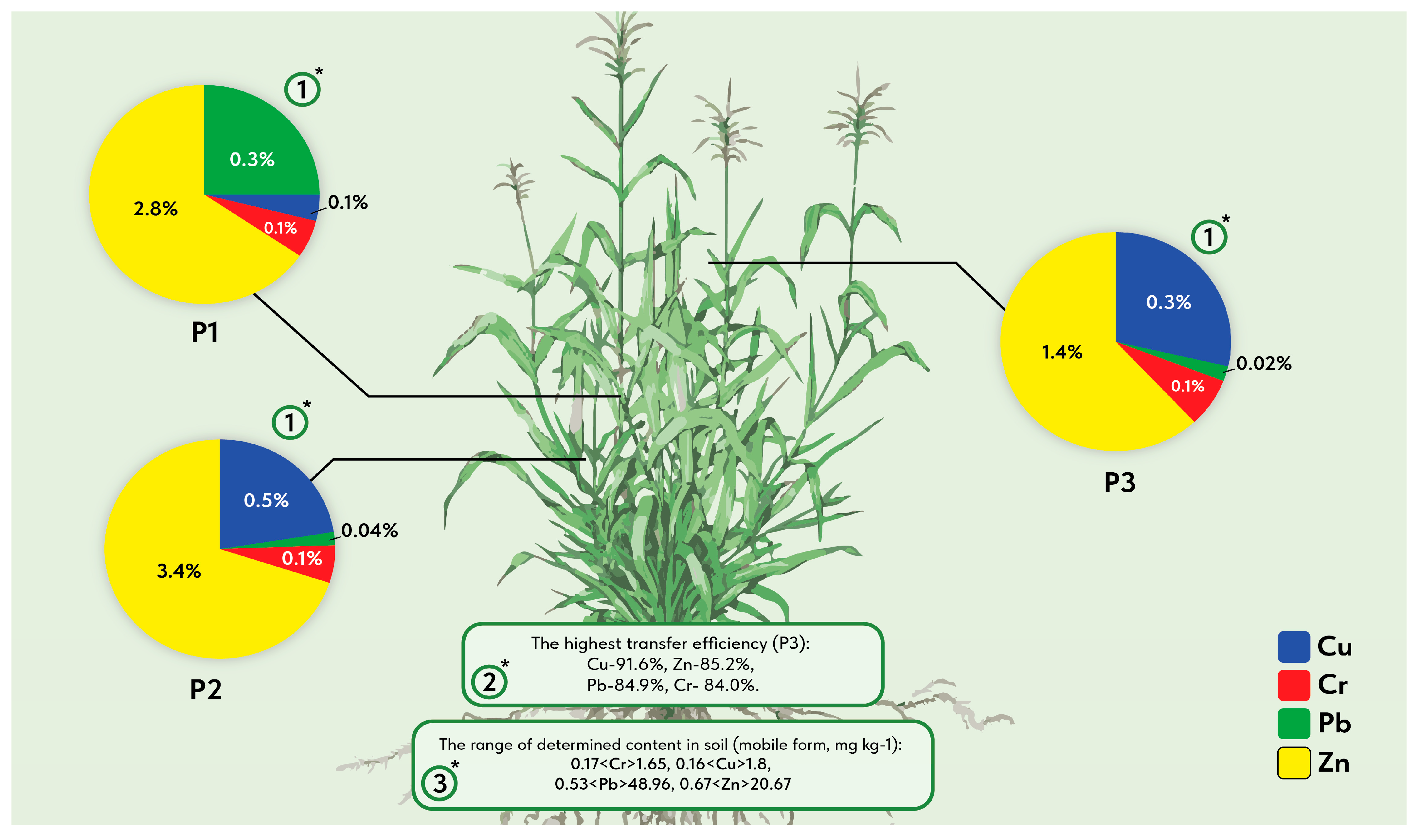
| CMF, mg kg−1 | P1 | 1.65 ± 0.24 a | 1.80 ± 0.19 ab | 48.96 ± 4.12 bc | 20.67 ± 1.88 a |
| P2 | 0.17 ± 0.02 bc | 0.16 ± 0.01 ab | 0.53 ± 0.05 bc | 0.67 ± 0.06 b | |
| P3 | 0.89 ± 0.17 bc | 0.28 ± 0.05 c | 2.72 ± 0.52 a | 4.73 ± 0.91 c | |
| MPCMF *, mg kg−1 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 23.0 | |
| CTF, mg kg−1 | P1 | 2219.0 ± 39.40 bc | 1039.0 ± 72.75 ab | 7830.0 ± 29.77 a | 1918.0 ± 61.90 a |
| P2 | 36.51 ± 2.92 bc | 15.42 ± 1.17 ab | 4.53 ± 0.47 bc | 14.29 ± 0.52 bc | |
| P3 | 21.21 ± 1.91 a | 5.66 ± 0.40 c | 10.03 ± 0.90 bc | 15.11 ± 0.77 bc | |
| Target value of soil **, mg kg−1 | 100.0 | 36.0 | 85.0 | 50.0 | |
| AR, % | P1 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.63 | 1.08 |
| P2 | 0.47 | 1.04 | 11.7 | 4.69 | |
| P3 | 4.2 | 4.95 | 27.12 | 31.3 | |
| The contamination factor, CF | P1 | 22.19 | 28.86 | 92.12 | 38.36 |
| P2 | 0.37 | 0.43 | 0.05 | 0.29 | |
| P3 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.3 | |
| The degree of contamination, Cdeg | P1 | 181.53 | |||
| P2 | 1.14 | ||||
| P3 | 0.79 | ||||
| Plots | A Series of Heavy Metals in Order of Decreasing Concentrations in Erigeron canadensis L. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflorescence | Leaves | Stem | Roots | |
| P1 (1 km) | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb | Zn > Cu > Pb > Cr > Cd | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb > Cd | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb > As |
| P2 (5.5 km) | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb > Cd | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb > As |
| P3 (12.02 km) | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb | Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb > As |
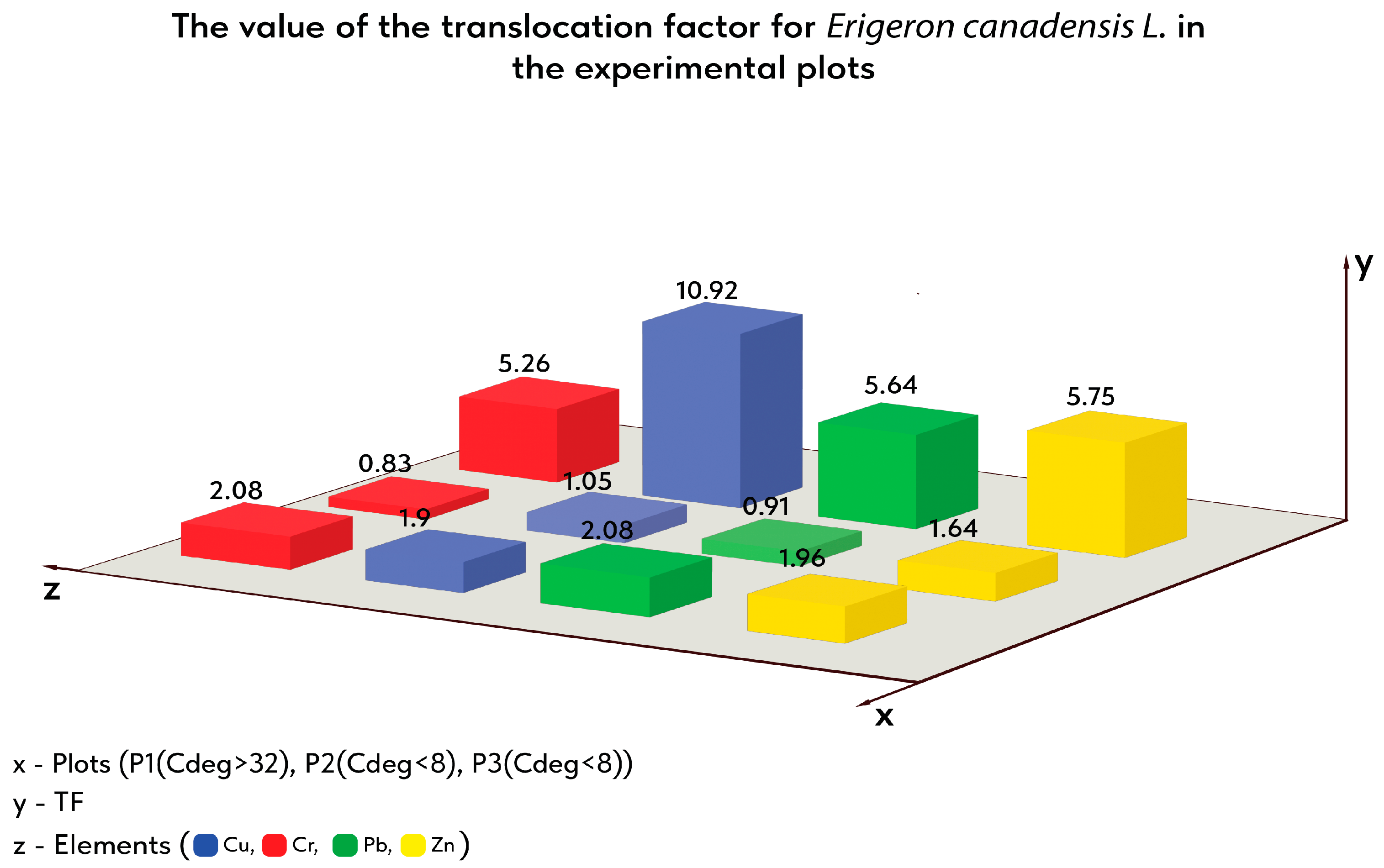
| PUI | BAC | BCF | TF Shoot/Root | TF Inflorescence/Root | TF Leaf/Root | TF Stem/Root | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 4.18 | 2.82 | 1.36 | 2.08 | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.63 |
| P2 | 65.18 | 29.47 | 35.71 | 0.83 | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0.19 |
| P3 | 8.3 | 6.98 | 1.33 | 5.26 | 0.64 | 2.74 | 1.88 |
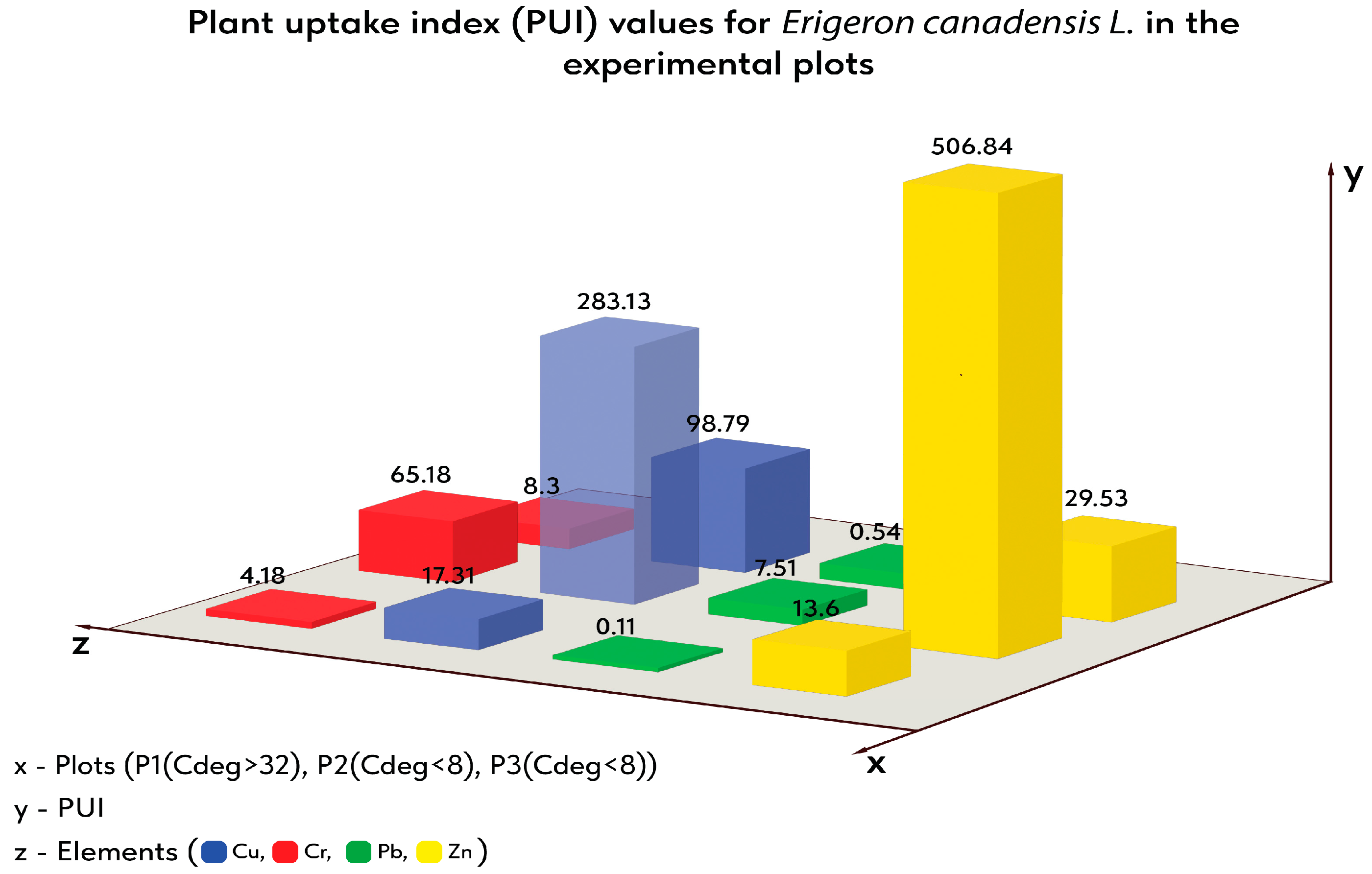
| PUI | BAC | BCF | TF Shoot/Root | TF Inflorescence/Root | TF Leaf/Root | TF Stem/Root | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 17.31 | 11.34 | 5.97 | 1.9 | 0.86 | 0.51 | 0.53 |
| P2 | 283.13 | 145.31 | 137.81 | 1.05 | 0.47 | 0.37 | 0.21 |
| P3 | 98.79 | 90.5 | 8.29 | 10.92 | 1.16 | 6.93 | 2.84 |
| PUI | BAC | BCF | TF Shoot/Root | TF Inflorescence/Root | TF Leaf/Root | TF Stem/Root | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 2.08 | 0.35 | 1.37 | 0.36 |
| P2 | 7.51 | 3.59 | 3.92 | 0.91 | 0.26 | 0.54 | 0.11 |
| P3 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.08 | 5.64 | 0.41 | 2.23 | 3 |
| PUI | BAC | BCF | TF Shoot/Root | TF Inflorescence/Root | TF Leaf/Root | TF Stem/Root | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 13.6 | 9.01 | 4.59 | 1.96 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.55 |
| P2 | 506.84 | 314.9 | 191.94 | 1.64 | 0.54 | 0.75 | 0.35 |
| P3 | 29.53 | 25.16 | 4.37 | 5.75 | 1.83 | 1.48 | 2.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laptiev, V.; Giltrap, M.; Tian, F.; Ryzhenko, N. Assessment of Heavy Metals (Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn) Bioaccumulation and Translocation by Erigeron canadensis L. in Polluted Soil. Pollutants 2024, 4, 434-451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4030029
Laptiev V, Giltrap M, Tian F, Ryzhenko N. Assessment of Heavy Metals (Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn) Bioaccumulation and Translocation by Erigeron canadensis L. in Polluted Soil. Pollutants. 2024; 4(3):434-451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaptiev, Volodymyr, Michelle Giltrap, Furong Tian, and Nataliia Ryzhenko. 2024. "Assessment of Heavy Metals (Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn) Bioaccumulation and Translocation by Erigeron canadensis L. in Polluted Soil" Pollutants 4, no. 3: 434-451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4030029
APA StyleLaptiev, V., Giltrap, M., Tian, F., & Ryzhenko, N. (2024). Assessment of Heavy Metals (Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn) Bioaccumulation and Translocation by Erigeron canadensis L. in Polluted Soil. Pollutants, 4(3), 434-451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4030029








