Overview of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Their Applications, Sources, and Potential Impacts on Human Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PFAS Applications/Uses
3. PFAS Analytical Techniques
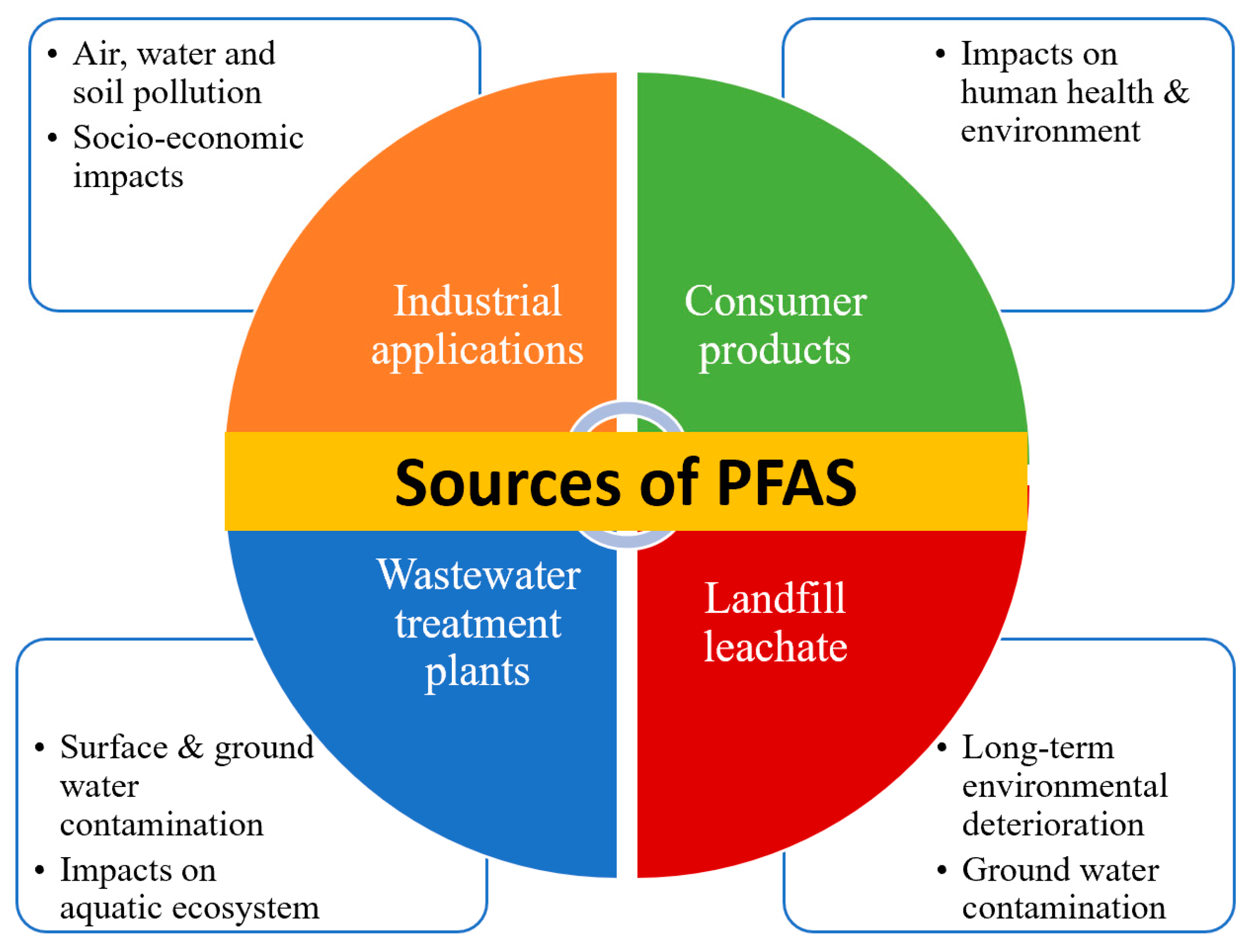
4. Sources and Their Dispersal into Environmental Sections
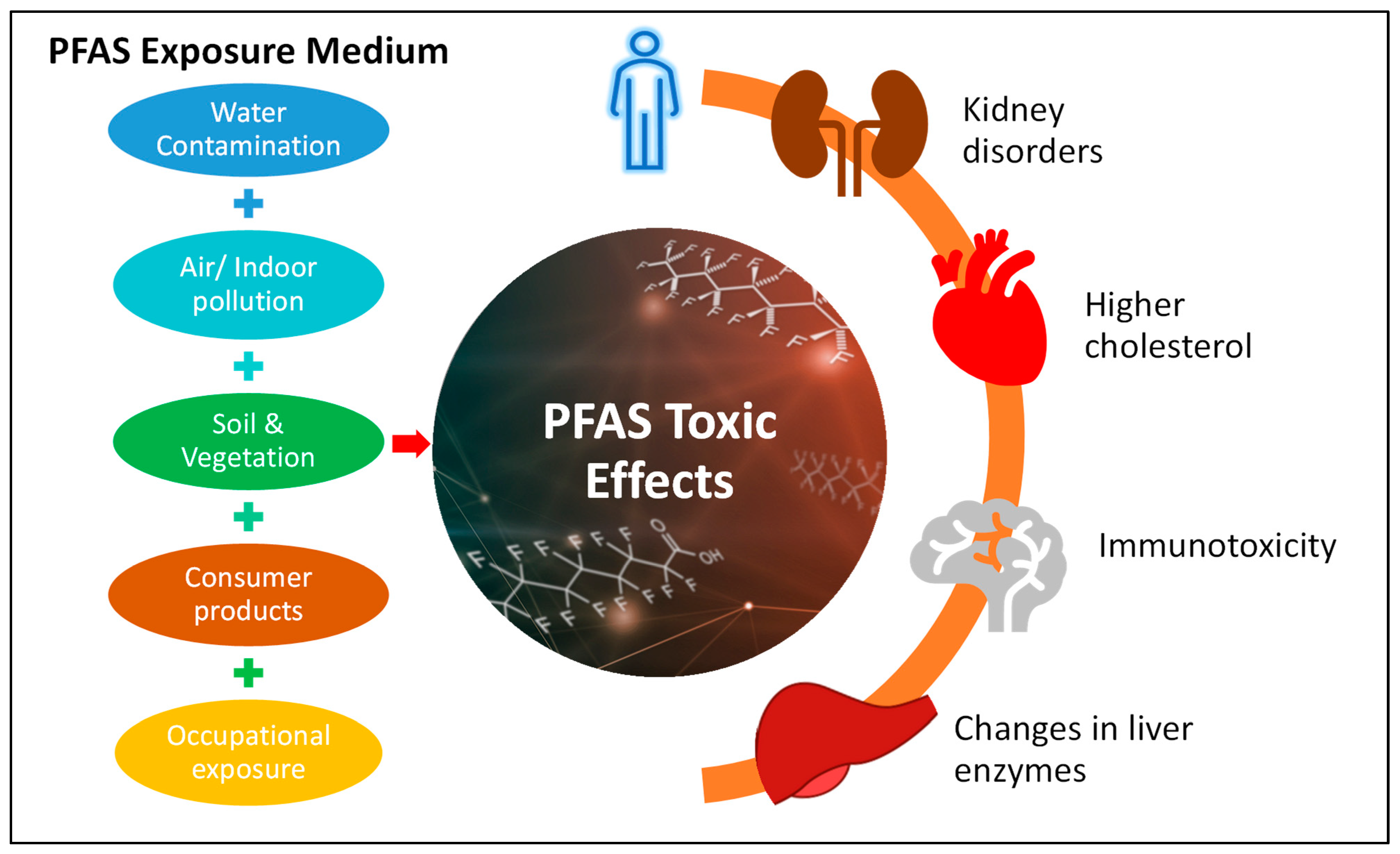
5. Exposure to Humans via Different Routes
5.1. Human Exposure to PFAS through Drinking Water
5.2. Human Exposure to PFAS through Soil and Vegetation
5.3. Human Exposure to PFAS during Occupational Activities
5.4. Human Exposure to PFAS through Consumer Products, Indoor Air, and Dust
6. PFAS Potential Effects on Human Health
6.1. Immunotoxicity
6.2. Carcinogenicity of Perfluoroalkyl Compounds
6.3. Endocrine Disruptors and Kidney Disorders
6.4. PFAS Exposure and Fetal Growth
7. Future Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
References
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; De Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojkumar, Y.; Pilli, S.; Rao, P.V.; Tyagi, R.D. Sources, occurrence and toxic effects of emerging per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2023, 97, 107174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Dane, J.; Kanel, S.R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Cawdrey, R.W.; Ambade, B.; Struckhoff, G.C.; Wilkin, R. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and wastewater: A critical review of their global occurrence and distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adu, O.; Ma, X.; Sharma, V.K. Bioavailability, Phytotoxicity and Plant Uptake of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Simcik, M.F.; Halbach, T.R.; Gulliver, J.S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in soils and groundwater of a US metropolitan area: Migration and implications for human exposure. Water Res. 2015, 72, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Du, P.; Luo, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, L. Impacts of daily intakes on the isomeric profiles of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in human serum. Environ. Int. 2016, 89, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bräunig, J.; Baduel, C.; Heffernan, A.; Rotander, A.; Donaldson, E.; Mueller, J.F. Fate and redistribution of perfluoroalkyl acids through AFFF-impacted groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poothong, S.; Thomsen, C.; Padilla-Sanchez, J.A.; Papadopoulou, E.; Haug, L.S. Distribution of novel and well-known poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in human serum, plasma, and whole blood. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13388–13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Health Statistics. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Baker, E.S.; Knappe, D.R. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)—Contaminants of emerging concern. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1187–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Yeung, L.W.; Wei, S.; Dai, J. Analysis of emerging per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Progress and current issues. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillette, T.; Jackson, T.W.; Guillette, M.; McCord, J.; Belcher, S.M. Blood concentrations of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances are associated with autoimmune-like effects in American alligators from Wilmington, North Carolina. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 1010185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riegel, M.; Haist-Gulde, B.; Sacher, F. Sorptive removal of short-chain perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) during drinking water treatment using activated carbon and anion exchanger. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Portal on per and Polyfluorinated Chemicals. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/portal-perfluorinated-chemicals/ (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Zhao, P.; Xia, X.; Dong, J.; Xia, N.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y. Short-and long-chain perfluoroalkyl substances in the water, suspended particulate matter, and surface sediment of a turbid river. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkle, A. Transfer von poly-und perfluorierten Chemikalien (PFC) von kontaminierten Agrarflächen in Nutzpflanzen Transition of poly-and perfluorinated chemicals from agricultural areas in foodstuffs. Tagungsbericht 2015, 2015, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Page, D.; Vanderzalm, J.; Kumar, A.; Cheng, K.Y.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Simpson, S. Risks of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) for sustainable water recycling via aquifers. Water 2019, 11, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Ibrar, I.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Singh, L.; Ganbat, N.; Kazwini, T.; Karbassiyazdi, E.; Samal, A.K.; Subbiah, S.; Altaee, A. Updated review on emerging technologies for PFAS contaminated water treatment. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 182, 667–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.N.P.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Nguyen, T.M.H.; Li, J.; Liang, H.; Deng, L.; Chen, Z.; Nguyen, T.A.H. Poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances in water and wastewater: A comprehensive review from sources to remediation. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101393. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.; Varma, R.S.; Nadagouda, M.N. Remediation and mineralization processes for per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentel, M.J.; Yu, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, Z.; Wong, B.M.; Men, Y.; Liu, J. Defluorination of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) with hydrated electrons: Structural dependence and implications to PFAS remediation and management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3718–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, C.T.; Wu, T. Recent progress in adsorptive removal of per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water/wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 90–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzyk, K.H.; Darlington, R.; Benotti, M.; Deeb, R.; Hawley, E. Novel treatment technologies for PFAS compounds: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevedouros, K.; Cousins, I.T.; Buck, R.C.; Korzeniowski, S.H. Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Boucher, J.M.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; Hungerbuhler, K. Toward a comprehensive global emission inventory of C4–C10 perfluoroalkanesulfonic acids (PFSAs) and related precursors: Focus on the life cycle of C8-based products and ongoing industrial transition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4482–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Veen, I.; Hanning, A.-C.; Stare, A.; Leonards, P.E.; de Boer, J.; Weiss, J.M. The effect of weathering on per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) from durable water repellent (DWR) clothing. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotthoff, M.; Müller, J.; Jürling, H.; Schlummer, M.; Fiedler, D. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in consumer products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14546–14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, Z.; Folk IV, E.E.; Roache, N.F. Determination of fluorotelomer alcohols in selected consumer products and preliminary investigation of their fate in the indoor environment. Chemosphere 2015, 129, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Krebs, K.A.; Roache, N.F. Perfluorocarboxylic Acid Content in 116 Articles of Commerce; US Environmental Protection Agency: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2009.
- Kissa, E. Fluorinated Surfactants and Repellents; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; Volume 97. [Google Scholar]
- Ebnesajjad, S. Introduction to Fluoropolymers: Materials, Technology, and Applications; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ober, C.K.; Käfer, F.; Deng, J. Review of essential use of fluorochemicals in lithographic patterning and semiconductor processing. J. Micro/Nanopatterning Mater. Metrol. 2022, 21, 010901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. UNEP Global PFC Group, Synthesis Paper on per-and Polyfluorinated Chemicals (PFCs); Environment, Health and Safety, Environment Directorate, OECD: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gaines, L.G. Historical and current usage of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A literature review. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2023, 66, 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.A.; Poulsen, P.B.; Bossi, R.; Miljøundersøgelser, D.; Technology, F. Survey and Environmental/Health Assessment of Fluorinated Substances in Impregnated Consumer Products and Impregnating Agents; Danish Environmental Protection Agency Copenhagen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; Volume 99.
- Fujii, Y.; Harada, K.H.; Koizumi, A. Occurrence of perfluorinated carboxylic acids (PFCAs) in personal care products and compounding agents. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinch, A.; Jensen, A.; Christensen, F. Risk Assessment of Fluorinated Substances in Cosmetic Products; The Danish Environmental Protection Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018; pp. 1–116.
- Whitehead, H.D.; Venier, M.; Wu, Y.; Eastman, E.; Urbanik, S.; Diamond, M.L.; Shalin, A.; Schwartz-Narbonne, H.; Bruton, T.A.; Blum, A. Fluorinated compounds in North American cosmetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dams, R.; Hintzer, K. Industrial Aspects of Fluorinated Oligomers and Polymers; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Putte, I.; Murín, M.; Van Velthoven, M.; Affourtit, F. Analysis of the Risks Arising from the Industrial Use of Perfuorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Ammonium Perfluorooctanoate (APFO) and from Their Use in Consumer Articles; RPS Advies: Delft, NL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tressaud, A.; Haufe, G. Fluorine and Health: Molecular Imaging, Biomedical Materials and Pharmaceuticals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.; Pang, J.; Li, W. Vitreous surgery for macular hole-related retinal detachment after phacoemulsification cataract extraction: 10-year retrospective review. Eye 2012, 26, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzhaf, S.; Filipovic, M.; Lewis, J.; Sparrenbom, C.J.; Barthel, R. A review of contamination of surface-, ground-, and drinking water in Sweden by perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Ambio 2017, 46, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Buck, R.C.; Hungerbühler, K. Global emission inventories for C4–C14 perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acid (PFCA) homologues from 1951 to 2030, Part I: Production and emissions from quantifiable sources. Environ. Int. 2014, 70, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caslavsky, V.B.; Gron, P. Method of Inhibiting the Formation of Plaque. US5100649A, 31 March 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquier, D.; Driancourt, A.; Audibert, A. Well Fluid Comprising a Fluorinated Liquid Phase. U.S. Patent 8,383,555, 26 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.U.; Crimi, M.; Andreescu, S. Current and Emerging Analytical Techniques for the Determination of PFAS in Environmental Samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 37, e00198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langton, C. Development of Quantitative Methods to Study PFAS Using Proton Induced Gamma-Ray Emission. 2022. Available online: https://digitalworks.union.edu/theses/2555/ (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Yandrasits, M.A.; Marimannikkuppam, S.; Lindell, M.J.; Kalstabakken, K.A.; Kurkowski, M.; Ha, P. Ion chromatography and combustion ion chromatography analysis of fuel cell effluent water during open circuit voltage. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 034526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, J.R.; Mabury, S.A. Identifying Unknown Fluorine-Containing Compounds in Environmental Samples Using 19F NMR and Spectral Database Matching. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8760–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camdzic, D.; Dickman, R.A.; Joyce, A.S.; Wallace, J.S.; Ferguson, P.L.; Aga, D.S. Quantitation of Total PFAS Including Trifluoroacetic Acid with Fluorine Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 5484–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camdzic, D.; Dickman, R.A.; Aga, D.S. Total and class-specific analysis of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in environmental samples using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2021, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreescu, S.; Vasilescu, A. Advances in electrochemical detection for probing protein aggregation. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 30, 100820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.D.; Lai, C.-Z.; Granda, L.P.; Fierke, M.A.; Mandal, D.; Stein, A.; Gladysz, J.A.; Bühlmann, P. Fluorous membrane ion-selective electrodes for perfluorinated surfactants: Trace-level detection and in situ monitoring of adsorption. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7471–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruyle, B.J.; Pickard, H.M.; LeBlanc, D.R.; Tokranov, A.K.; Thackray, C.P.; Hu, X.C.; Vecitis, C.D.; Sunderland, E.M. Isolating the AFFF signature in coastal watersheds using oxidizable PFAS precursors and unexplained organofluorine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3686–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brase, R.A.; Mullin, E.J.; Spink, D.C. Legacy and emerging per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Analytical techniques, environmental fate, and health effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesy, J.P.; Kannan, K. Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, E.; Mayack, D.T.; Roblee, K.; Yamashita, N.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of perfluoroalkyl surfactants in water, fish, and birds from New York State. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 50, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Q.; Sheng, N.; Yeung, L.W.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dai, J. First report on the occurrence and bioaccumulation of hexafluoropropylene oxide trimer acid: An emerging concern. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9553–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, N.-H.; Cho, C.-R.; Lee, J.-S.; Soh, H.-Y.; Lee, B.-C.; Lee, J.-A.; Tatarozako, N.; Sasaki, K.; Saito, N.; Iwabuchi, K. Perfluorinated alkyl substances in water, sediment, plankton and fish from Korean rivers and lakes: A nationwide survey. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 491, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisi, R.; Vamerali, T.; Manzetti, S. Accumulation of perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in agricultural plants: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrow, S.M.; Ruppel, B.; Lippincott, R.L.; Post, G.B.; Procopio, N.A. Investigation of levels of perfluoroalkyl substances in surface water, sediment and fish tissue in New Jersey, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Munir, U.; Huang, Q. Occurrence of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Soil: Sources, Fate, and Remediation. Soil Environ. Health 2023, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbo, N.; Stoiber, T.; Naidenko, O.V.; Andrews, D.Q. Locally caught freshwater fish across the United States are likely a significant source of exposure to PFOS and other perfluorinated compounds. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, M.N.; Riza, M.; Pervez, M.N.; Khyum, M.M.O.; Liang, Y.; Naddeo, V. Environmental and health impacts of PFAS: Sources, distribution and sustainable management in North Carolina (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance toxicity and human health review: Current state of knowledge and strategies for informing future research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, D.T.; Nickerson, A.; Kulkarni, P.R.; Higgins, C.P.; Popovic, J.; Field, J.; Rodowa, A.; Newell, C.; DeBlanc, P.; Kornuc, J.J. Mass-based, field-scale demonstration of PFAS retention within AFFF-associated source areas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15768–15777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtzwiler, G.W.; Silva, P.; Hall, A.; Ivey, A.; Vorst, K. Significance of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in food packaging. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, E.; Madden, C.; Szabo, D.; Coggan, T.L.; Clarke, B.; Currell, M. Contamination of groundwater with per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from legacy landfills in an urban re-development precinct. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panieri, E.; Baralic, K.; Djukic-Cosic, D.; Buha Djordjevic, A.; Saso, L. PFAS molecules: A major concern for the human health and the environment. Toxics 2022, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, S.; Weidemann, E.; Yeung, L.W.; Jansson, S. Occurrence of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and unidentified organofluorine in leachate from waste-to-energy stockpile—A case study. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahsavari, E.; Rouch, D.; Khudur, L.S.; Thomas, D.; Aburto-Medina, A.; Ball, A.S. Challenges and current status of the biological treatment of PFAS-contaminated soils. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 602040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, R.; Zhou, Y.; Nyberg, E.; Namazkar, S.; Yongning, W.; Xiao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Bergman, Å.; Benskin, J.P. Emerging per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in human milk from Sweden and China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, J.L.; Nadal, M. Human exposure to per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) through drinking water: A review of the recent scientific literature. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pétré, M.-A.; Genereux, D.P.; Koropeckyj-Cox, L.; Knappe, D.R.; Duboscq, S.; Gilmore, T.E.; Hopkins, Z.R. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) transport from groundwater to streams near a PFAS manufacturing facility in North Carolina, USA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5848–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitmeyer, S.E.; Williams, A.M.; Duris, J.W.; Eicholtz, L.W.; Shull, D.R.; Wertz, T.A.; Woodward, E.E. Per-and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in Pennsylvania surface waters: A statewide assessment, associated sources, and land-use relations. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenka, S.P.; Kah, M.; Padhye, L.P. Occurrence and fate of poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in urban waters of New Zealand. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Nielsen, C.; Li, Y.; Hammarstrand, S.; Andersson, E.M.; Li, H.; Olsson, D.S.; Engström, K.; Pineda, D.; Lindh, C.H. Serum perfluoroalkyl substances in residents following long-term drinking water contamination from firefighting foam in Ronneby, Sweden. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Jakobsson, K.; Harari, F.; Andersson, E.M.; Li, Y. Exposure to high levels of PFAS through drinking water is associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes—Findings from a register-based study in Ronneby, Sweden. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cserbik, D.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Farré, M.J.; Sanchís, J.; Bartolomé, A.; Paraian, A.; Herrera, E.M.; Caixach, J.; Villanueva, C.M.; Flores, C. Human exposure to per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and other emerging contaminants in drinking water. Npj Clean Water 2023, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.; Bolan, N.S.; Kumar, M.; Nitai, A.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Bolan, S.S.; Vithanage, M.; Rinklebe, J.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Srivastava, P. Distribution, transformation and remediation of poly-and per-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in wastewater sources. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 164, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, T.; Heyn, J.; Thiele, H.; Hüther, J.; Failing, K.; Georgii, S.; Brunn, H. Carryover of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) from soil to plants. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 57, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shan, X.-q.; Zhang, S. Bioavailability of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in biosolids-amended soils to earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 2015, 118, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krippner, J.; Falk, S.; Brunn, H.; Georgii, S.; Schubert, S.; Stahl, T. Accumulation potentials of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs) and perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids (PFSAs) in maize (Zea mays). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3646–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Hui, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, Y.; Shi, Y. Variations of the Level, Profile, and Distribution of PFAS around POSF Manufacturing Facilities in China: An Overlooked Source of PFCA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5264–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, B. PFAS use in electronic products and exposure risks during handling and processing of e-waste: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, H.; Chen, H.; Yao, Y.; Baqar, M.; Yu, H.; Qiao, B.; Sun, H. Electronic-waste-associated pollution of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Environmental occurrence and human exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S.; Kumar, P.; Mishra, V.; Guijt, R.; Singh, P.; Dumée, L.F.; Sharma, R.S. A review on the sources, occurrence and health risks of per-/poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) arising from the manufacture and disposal of electric and electronic products. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, K.; Gaines, L.G.; Paris-Davila, T.; Nylander-French, L.A. Occupational exposure and serum levels of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A review. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2023, 66, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, T.; Hsu, W.; Noonan, G.; Diachenko, G. Migration of fluorochemical paper additives from food-contact paper into foods and food simulants. Food Addit. Contam. 2008, 25, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tittlemier, S.A.; Pepper, K.; Seymour, C.; Moisey, J.; Bronson, R.; Cao, X.-L.; Dabeka, R.W. Dietary exposure of Canadians to perfluorinated carboxylates and perfluorooctane sulfonate via consumption of meat, fish, fast foods, and food items prepared in their packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 3203–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, V.; Dreyer, A.; Ebinghaus, R. Polyfluorinated compounds in residential and nonresidential indoor air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8075–8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beesoon, S.; Genuis, S.J.; Benskin, J.P.; Martin, J.W. Exceptionally high serum concentrations of perfluorohexanesulfonate in a Canadian family are linked to home carpet treatment applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12960–12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaider, L.A.; Balan, S.A.; Blum, A.; Andrews, D.Q.; Strynar, M.J.; Dickinson, M.E.; Lunderberg, D.M.; Lang, J.R.; Peaslee, G.F. Fluorinated compounds in US fast food packaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, K.; Monien, B.H. Transdermal absorption of 13C4-perfluorooctanoic acid (13C4-PFOA) from a sunscreen in a male volunteer–What could be the contribution of cosmetics to the internal exposure of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)? Environ. Int. 2022, 169, 107549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yi, S.; Ye, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, W.; Zhu, L. Insights into the Dermal Absorption, Deposition, and Elimination of Poly-and Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Rats: The Importance of Skin Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 16975–16984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, T.; Duboscq, S.; Genereux, D.; Pétré, M.; Solomon, D.; Knappe, D.; Hopkins, Z.; DeStefano, N. 3H/3He groundwater ages and discharge of PFAS from groundwater to a coastal plain stream in North Carolina. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting. 2020. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020AGUFMH096...01G/abstract (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- D’Ambro, E.L.; Pye, H.O.; Bash, J.O.; Bowyer, J.; Allen, C.; Efstathiou, C.; Gilliam, R.C.; Reynolds, L.; Talgo, K.; Murphy, B.N. Characterizing the air emissions, transport, and deposition of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances from a fluoropolymer manufacturing facility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassuncao, C.; Hu, X.C.; Zhang, X.; Bossi, R.; Dam, M.; Mikkelsen, B.; Sunderland, E.M. Temporal shifts in poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in North Atlantic pilot whales indicate large contribution of atmospheric precursors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4512–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassuncao, C.; Hu, X.C.; Nielsen, F.; Weihe, P.; Grandjean, P.; Sunderland, E.M. Shifting global exposures to poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) evident in longitudinal birth cohorts from a seafood-consuming population. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3738–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.M.; Braun, J.M. Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Outcomes Related to Metabolic Syndrome: A Review of the Literature and Current Recommendations for Clinicians. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, V.; Winquist, A.; Steenland, K. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) exposures and incident cancers among adults living near a chemical plant. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, C.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Tarone, R.E.; Olsen, J. Perfluorinated chemicals and fetal growth: A study within the Danish National Birth Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, U.N.; Bossi, R.; Leffers, H.; Jensen, A.A.; Skakkebæk, N.E.; Jørgensen, N. Do perfluoroalkyl compounds impair human semen quality? Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Espinosa, M.-J.; Mondal, D.; Armstrong, B.; Bloom, M.S.; Fletcher, T. Thyroid function and perfluoroalkyl acids in children living near a chemical plant. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.E.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Chang, S.-C.; Farrar, D.G.; Kennedy Jr, G.L.; Lau, C.; Olsen, G.W.; Seed, J.; Wallace, K.B. Perfluoroalkyl acids and related chemistries—Toxicokinetics and modes of action. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 102, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, M.B.; Thibodeaux, J.R.; Wood, C.R.; Zehr, R.D.; Schmid, J.E.; Lau, C. Gene expression profiling in the lung and liver of PFOA-exposed mouse fetuses. Toxicology 2007, 239, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, G.B.; Cohn, P.D.; Cooper, K.R. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), an emerging drinking water contaminant: A critical review of recent literature. Environ. Res. 2012, 116, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkov, A.; Wallace, K.B. Structural determinants of fluorochemical-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 66, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanden Heuvel, J.P.; Thompson, J.T.; Frame, S.R.; Gillies, P.J. Differential activation of nuclear receptors by perfluorinated fatty acid analogs and natural fatty acids: A comparison of human, mouse, and rat peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α,-β, and-γ, liver X receptor-β, and retinoid X receptor-α. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, P.; Andersen, E.W.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E.; Nielsen, F.; Mølbak, K.; Weihe, P.; Heilmann, C. Serum vaccine antibody concentrations in children exposed to perfluorinated compounds. JAMA 2012, 307, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, P.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E. Immunotoxicity of perfluorinated alkylates: Calculation of benchmark doses based on serum concentrations in children. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.I.; Ahmad, S.; Singh, R.; Fazal, Z.; Prins, G.S.; Madak Erdogan, Z.; Irudayaraj, J.; Spinella, M.J. Toward a mechanistic understanding of poly-and perfluoroalkylated substances and cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, A.M.; Hocevar, B.A.; Andrews, D.Q.; Naidenko, O.V.; Kamendulis, L.M. Application of the key characteristics of carcinogens to per and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Hsieh, C.Y.J. Exploring potential carcinogenic activity of per-and polyfluorinated alkyl substances utilizing high-throughput toxicity screening data. Int. J. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, U.; Mueller, J.F.; Toms, L.-M.L.; Hobson, P.; Kärrman, A. Temporal trends of PFSAs, PFCAs and selected precursors in Australian serum from 2002 to 2013. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Z. Human placental transfer of perfluoroalkyl acid precursors: Levels and profiles in paired maternal and cord serum. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihovic, S.; Kärrman, A.; Lind, L.; Lind, P.M.; Lindström, G.; van Bavel, B. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) including structural PFOS isomers in plasma from elderly men and women from Sweden: Results from the Prospective Investigation of the Vasculature in Uppsala Seniors (PIVUS). Environ. Int. 2015, 82, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, K.Y.; Raymond, M.; Thompson, B.A.; Anderson, H.A. Perfluoroalkyl substances in older male anglers in Wisconsin. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, M.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Skakkebæk, N.E.; Main, K.M. Environmental chemicals and thyroid function. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 154, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J.M.; Andersson, P.L.; Lamoree, M.H.; Leonards, P.E.; van Leeuwen, S.P.; Hamers, T. Competitive binding of poly-and perfluorinated compounds to the thyroid hormone transport protein transthyretin. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 109, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanifer, J.W.; Stapleton, H.M.; Souma, T.; Wittmer, A.; Zhao, X.; Boulware, L.E. Perfluorinated chemicals as emerging environmental threats to kidney health: A scoping review. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2018, 13, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, G.; Mohapatra, A. Interactions between thyroid disorders and kidney disease. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Teng, M.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhao, W.; Ruan, Y.; Leung, K.M.; Wu, F. Insight into the binding model of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances to proteins and membranes. Environ. Int. 2023, 175, 107951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, P.; Ganguly, A. The ligand-docking approach explores the binding affinity of PFOS and PFOA for major endogenous antioxidants: A potential mechanism to fuel oxidative stress. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2023, 4, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, L.; Du, E.; Fu, J. Binding Affinity and Mechanism of Six PFAS with Human Serum Albumin: Insights from Multi-Spectroscopy, DFT and Molecular Dynamics Approaches. Toxics 2024, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zong, W.; Liu, R. Interaction rule and mechanism of perfluoroalkyl sulfonates containing different carbon chains with human serum albumin. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24781–24788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamsen, L.S.; Jönsson, B.A.; Lindh, C.H.; Olesen, R.H.; Larsen, A.; Ernst, E.; Kelsey, T.W.; Andersen, C.Y. Concentration of perfluorinated compounds and cotinine in human foetal organs, placenta, and maternal plasma. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, C.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Cohort, S.B. Prenatal exposure to per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and child growth trajectories in the first two years. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 037006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashino, I.; Sasaki, S.; Okada, E.; Matsuura, H.; Goudarzi, H.; Miyashita, C.; Okada, E.; Ito, Y.M.; Araki, A.; Kishi, R. Prenatal exposure to 11 perfluoroalkyl substances and fetal growth: A large-scale, prospective birth cohort study. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spratlen, M.J.; Perera, F.P.; Lederman, S.A.; Robinson, M.; Kannan, K.; Trasande, L.; Herbstman, J. Cord blood perfluoroalkyl substances in mothers exposed to the World Trade Center disaster during pregnancy. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midasch, O.; Drexler, H.; Hart, N.; Beckmann, M.; Angerer, J. Transplacental exposure of neonates to perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoate: A pilot study. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2007, 80, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkens, K.; Vestergren, R.; Berger, U.; Cousins, I.T. Early life exposure to per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs): A critical review. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, R.; Feng, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. Perfluoroalkyl substances exposure in early pregnancy and preterm birth in singleton pregnancies: A prospective cohort study. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Applications | Purpose | Consumer Products | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paints, coatings, wax, and varnish | To reduce surface tension for dispersing agents, substrate wetting, penetration, and smoothing. To improve gloss, uniform surface treatment, and antistatic and antifouling properties. Oil and water repellent. | Agricultural glass and plastic covers (used as greenhouses) Automotive finishes Cellulose Cements Ceramics Chemical processing industry equipment (for example, reactors, ducts, pipes, tanks, and impellers) Transparent coats Cookware/bakeware Fishing rods Glass (i.e., mirrors, eyeglasses, windshields of automobiles and their headlights, etc.) Plastics Sport equipment strings Musical instrument strings Piano parts Resins and sealers Paints, polishes, and pigments Ink, varnish, and waxes | [31,32,33,34,35] |
| Cosmetics and personal care | PFAS are used in cosmetics as emulsifiers, lubricants, or oleophobic agents. A polyethylene wax containing PTFE called Clariant’s Ceridust 3920 F is used in cosmetic waxes for creams and powders. Aliphatic PFCAs are used in dental preparations, i.e., toothpastes, tooth powders, dental flosses, chewing gums, and tablets. | Acne treatment Blush/highlighter Dental floss and plaque removers Eye shadow Foundation Hair conditioner, creams, and shampoo Hand sanitizer and lotions Lip sticks/balm Mascara/lash products Nail polish Shaving cream Sunscreen | [36,37,38,39] |
| Electronics | PFAS are used because of their dielectric property, low flammability, chemical and heat resistance, and other mechanical properties. Electronics frequently make use of fluoropolymers. It is known that PFOA is utilized to create the fluoropolymers used in computer network cable and wire insulation. | Aerospace and automotive applications Cables and wires associated with communication and facilities Cell phones, Digital cameras Disk drives Electrical wiring insulation Zinc and lithium batteries Magnetic recording devices Optical fibers Printers Radar and satellite communication systems Scanners Solar collectors and coatings | [34,40,41] |
| Medical applications | Perfluoro-organic compound emulsions with gas-transporting characteristics are used for arterial administration in emergency situations of blood loss, as well as to treat numerous disorders accompanied by hypoxic or ischemic lesions. PFAS are renowned at increasing effective reattachment. | Bags Surfaces with blood contact Blood substitutes Containers Contact lenses Catheters Cannulae Drainage tubes Fistulas Fabric liners Grafts Gaskets Guide wires Hernia patches Inhaler propellant Joint repair and replacement Joint spacers Needles Oral capsules or tablets Ports Pericardial patches Seals shunts Space-filling or growth-increasing devices Surgical sheets Stylets Stent grafts and suppositories | [42,43] |
| Packaging material | PFAS are used to make paper products oil- and water-resistant for food, as well as nonfood usage. | Anti-corrosion liner Baking paper and wallpaper Coated raw paper and kraft paper, Food plates, bowls, containers, and wraps Folding cartons and pizza boxes Food bags for pets Paper food straws General liner, Paper combined with metal and raw paper for plaster board Wood-containing paper. | [35,44,45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habib, Z.; Song, M.; Ikram, S.; Zahra, Z. Overview of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Their Applications, Sources, and Potential Impacts on Human Health. Pollutants 2024, 4, 136-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4010009
Habib Z, Song M, Ikram S, Zahra Z. Overview of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Their Applications, Sources, and Potential Impacts on Human Health. Pollutants. 2024; 4(1):136-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabib, Zunaira, Minkyung Song, Sadaf Ikram, and Zahra Zahra. 2024. "Overview of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Their Applications, Sources, and Potential Impacts on Human Health" Pollutants 4, no. 1: 136-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4010009
APA StyleHabib, Z., Song, M., Ikram, S., & Zahra, Z. (2024). Overview of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Their Applications, Sources, and Potential Impacts on Human Health. Pollutants, 4(1), 136-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4010009





