Mercury in Temperate Forest Soils and Suspended Sediments in the Connecticut River, Merrimack River, and Thames River Watersheds, USA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
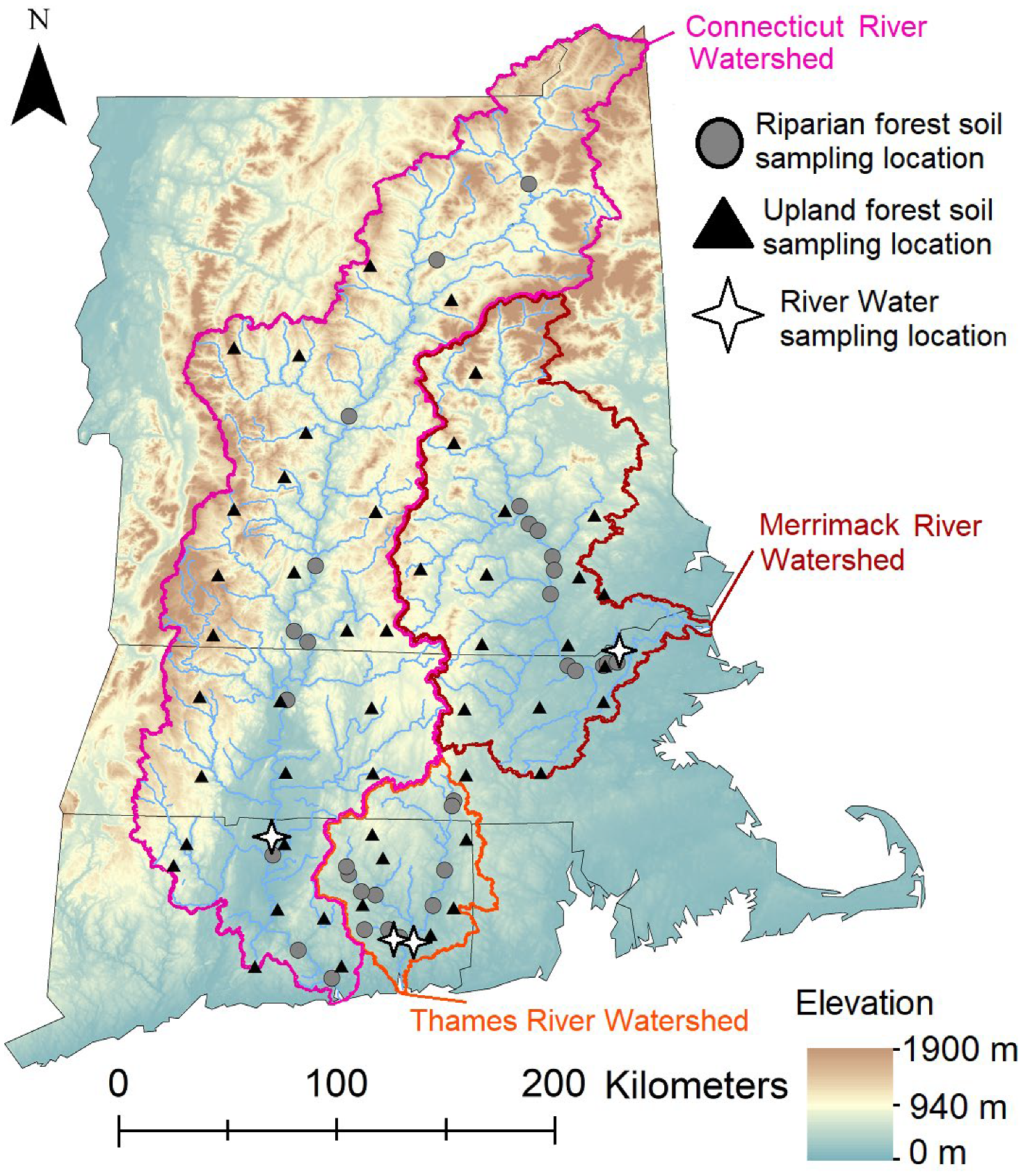
2.1. Watersheds
2.2. General Geology and Soils
2.3. Site Characterization, Soil Sampling, and Soil Processing
2.4. River Water and Suspended Sediment Sampling
2.5. Soil, Suspended Sediment, and Water Elemental Analyses
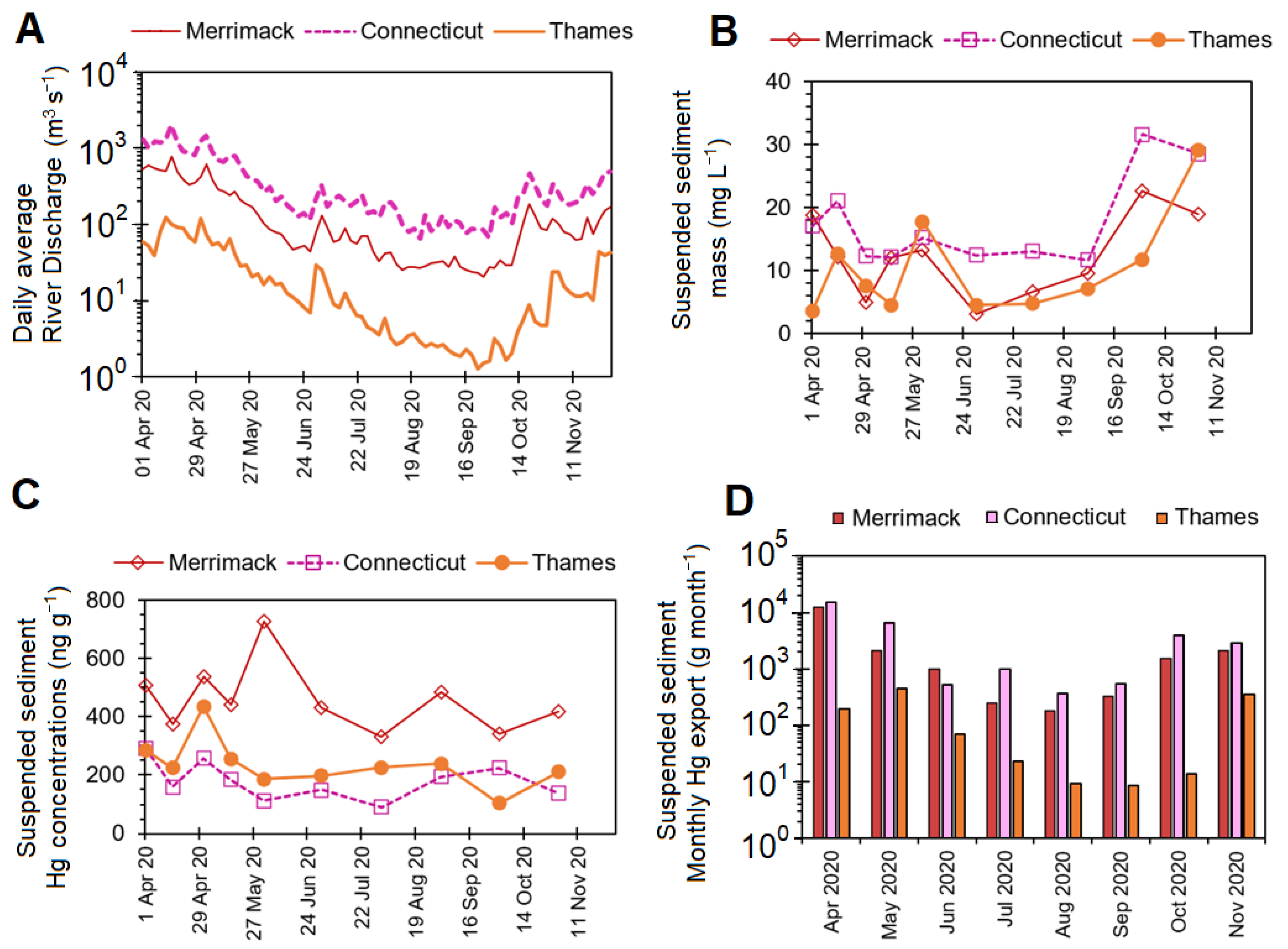
2.6. Suspended Sediment Hg Export Estimation
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Upland and Riparian Forest Soil Hg among the Watersheds
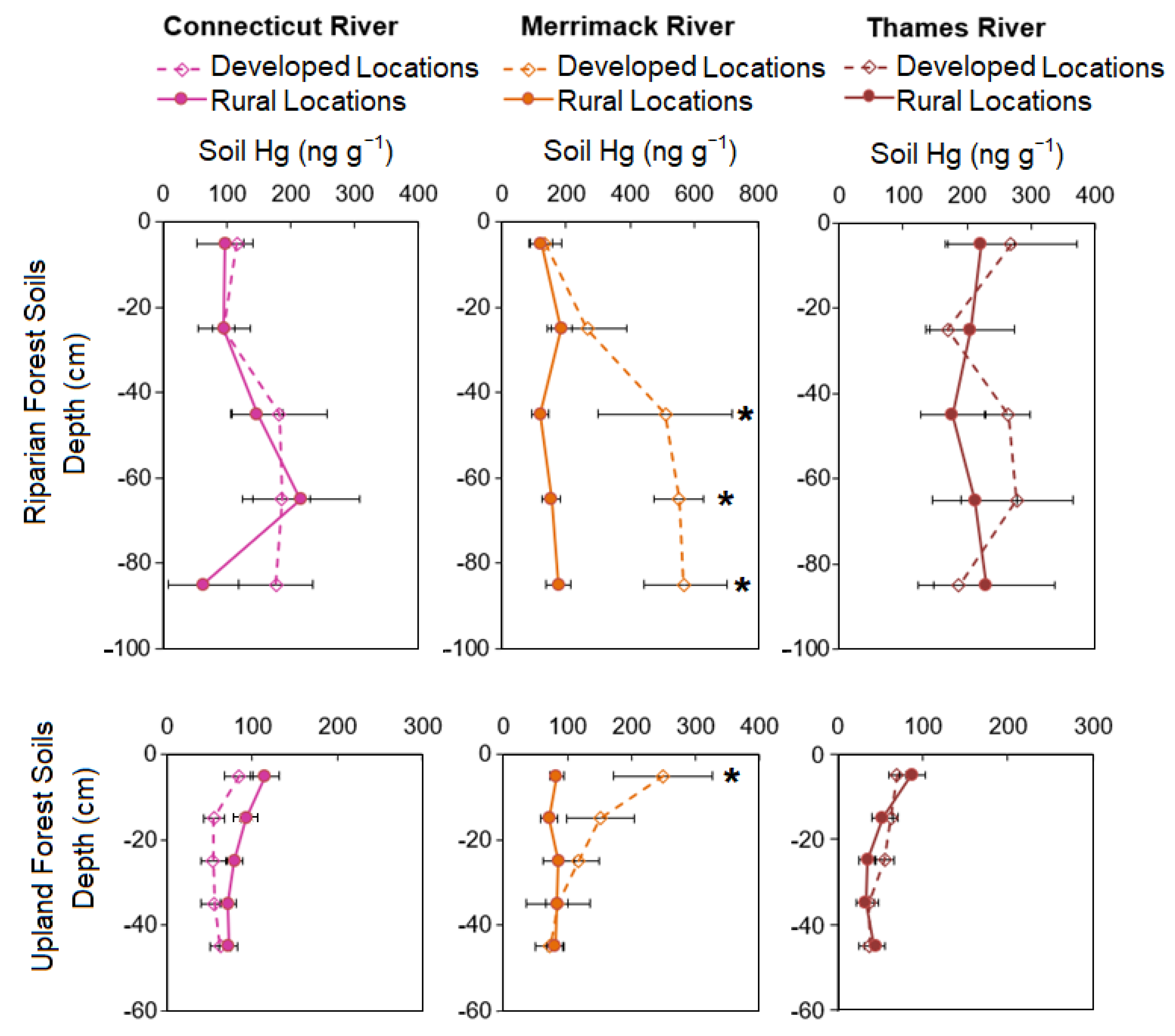
3.2. Upland and Riparian Forest Soil Hg between Rural and Developed Locations
3.3. Suspended Sediment Hg Concentrations
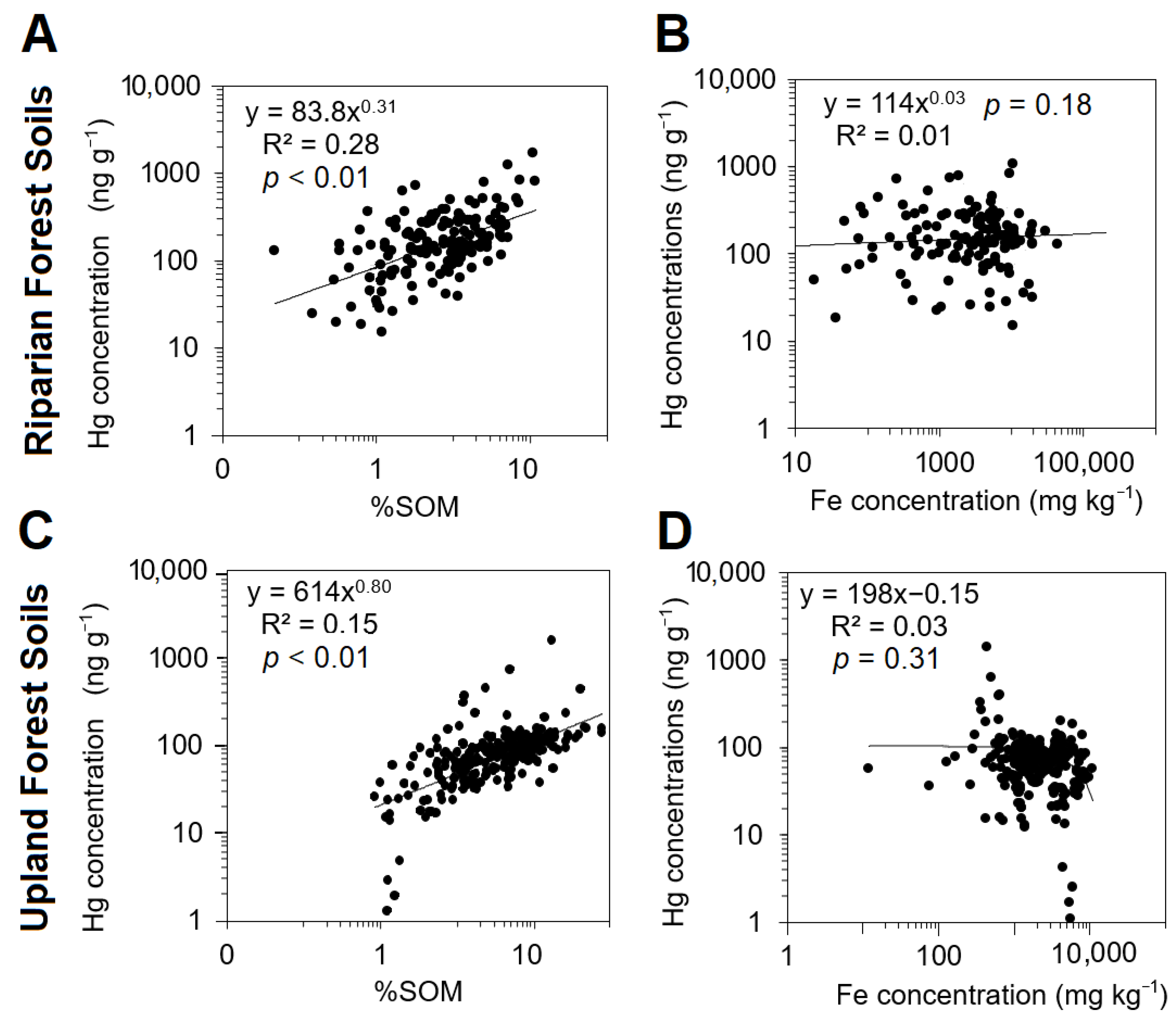
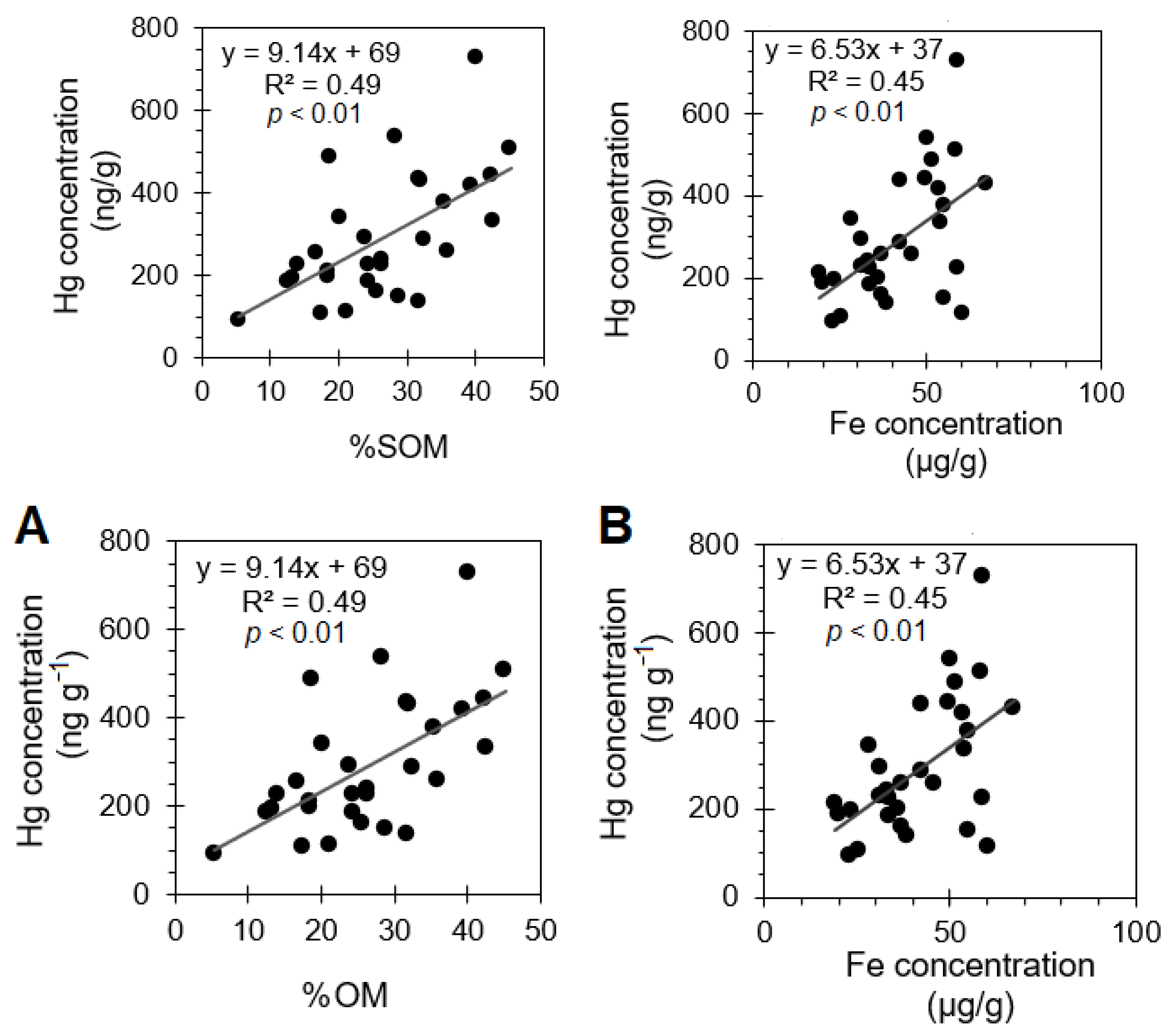
3.4. Linkages between Upland and Riparian Soils with Suspended Sediments
4. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Streets, D.G.; Horowitz, H.M.; Lu, Z.; Levin, L.; Thackray, C.P.; Sunderland, E.M. Global and regional trends in mercury emissions and concentrations, 2010–2015. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Selin, N.E.; Soerensen, A.L.; Angot, H.; Artz, R.; Brooks, S.; Brunke, E.G.; Conley, G.; Dommergue, A.; Ebinghaus, R.; et al. Top-down constraints on atmospheric mercury emissions and implications for global biogeochemical cycling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7103–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raihan, S.M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.; Bai, S.C. Evaluation of dietary organic and inorganic mercury threshold levels on induced mercury toxicity in a marine fish model. Animals 2020, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, J.B.; Friedland, A.J.; Engerbretson, T.R.; Kaste, J.M.; Jackson, B.P. Spatial and vertical distribution of mercury in upland forest soils across the northeastern United States. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Wang, R.Q.; Xue, T.; Ge, X.L.; Liu, J. Effects of soil properties and flooding on the mobility and transformation of mercury in a temperate Riparian wetland. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2015, 24, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.B.; Moore, L. A tale of three cities: Mercury in urban deciduous foliage and soils across land-uses in Poughkeepsie NY, Hartford CT, and Springfield MA USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, J.D.; Yavitt, J.B.; Driscoll, C.T.; Montesdeoca, M.R. Legacy mercury and stoichiometry with C, N, and S in soil, pore water, and stream water across the upland-wetland interface: The influence of hydrogeologic setting. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista-Salazar, C.; Richard, J.H.; Horf, M.; Rejc, M.; Gosar, M.; Biester, H. Grain-size dependence of mercury speciation in river suspended matter, sediments and soils in a mercury mining area at varying hydrological conditions. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 81, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, O.; Cenci, R.; Beone, G.M.; Dantas, M.; Lodigiani, P. Trace element concentrations in freshwater mussels and macrophytes as related to those in their environment. J. Limnol. 2003, 62, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regnell, O.; Watras, C.J. Microbial mercury methylation in aquatic environments: A critical review of published field and laboratory studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jović, M.D.; Stanković, S. Determination of marine pollution by comparative analysis of metal pollution indices. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2014, 66, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Tian, L.; Braaten, H.F.V.; Wu, Q.; Luo, J.; Cai, L.M.; Meng, J.H.; Lin, Y. Mercury–organic matter interactions in soils and sediments: Angel or devil? Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Maavara, T.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Raymond, P.A. Rivers as the largest source of mercury to coastal oceans worldwide. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcom, P.H.; Fitzgerald, W.F.; Vandal, G.M.; Lamborg, C.H.; Rolfhus, K.R.; Langer, C.S.; Hammerschmidt, C.R. Mercury sources and cycling in the Connecticut River and Long Island Sound. Mar. Chem. 2004, 90, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, T. Methylmercury Exposure through Fish Ingestion and Trends in Human Health Risk in the Merrimack River Watershed. Master’s Thesis, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA, August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection [CT DEEP]. Long Island Sound Blue Plant. 2019. Available online: https://portal.ct.gov/DEEP/Coastal-Resources/LIS-Blue-Plan/Blue-Plan-Basic-Background (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Lindbo, D.L.; Veneman, P.L.M. Morphological and physical properties of selected fragipan soils in Massachusetts. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.B. Comparing Trace Elements (As, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn) in Soils and Surface Waters among Montane, Upland Watersheds and Lowland, Urban Watersheds in New England, USA. Water 2021, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellen, B.; Woodruff, J.D.; Kratz, L.N.; Mabee, S.B.; Morrison, J.; Martini, A.M. Source, conveyance and fate of suspended sediments following Hurricane Irene. New England, USA. Geomorphology 2014, 226, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.M.; Snyder, N.P.; Castle, S.; Hopkins, A.J.; Waltner, M.; Merritts, D.J.; Walter, R.C. Legacy sediment storage in New England river valleys: Anthropogenic processes in a postglacial landscape. Geomorphology 2019, 327, 417–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, K.J.; Tiner, R.W. Wetlands of Connecticut. State Geological and Natural History Survey of Connecticut; Department of Environmental Protection: Hartford, CT, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lindbo, D.L.; Brigham-Grette, J.; Veneman, P.L. Depositional and Post-Depositional Features in the Late Illinoian and Late Wisconsinan Tills of Massachusetts. Whole Regolith Pedol. 1994, 34, 75–95. [Google Scholar]
- Friesz, P.J. Geohydrology of Stratified Drift and Streamflow in the Deerfield River Basin, Northwestern Massachusetts; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Marlborough, MA, USA, 1996; Volume 96. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, J.; Stehman, S.V.; Sorenson, D.G.; Gass, L.; Dewitz, J.A. Thematic accuracy assessment of the NLCD 2016 land cover for the conterminous United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 257, 112357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackowiak, T.J.; Mischenko, I.C.; Butler, M.J.; Richardson, J.B. Trace metals and metalloids in peri-urban soil and foliage across geologic materials, ecosystems, and development intensities in Southern California. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1713–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). Collection of Water Samples (ver. 2.0): U.S. Geological Survey Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations, Book 9, Chap. A4. September 2006. Available online: http://pubs.water.usgs.gov/twri9A4/ (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Kasper, D.; Amaral, J.H.F.; Forsberg, B.R. The effect of filter type and porosity on total suspended sediment determinations. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5532–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayvantash, D.; Cojan, I.; Kissel, C.; Franke, C. Magnetic fingerprint of the sediment load in a meander bend section of the Seine River (France). Geomorphology 2017, 286, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patault, E.; Alary, C.; Franke, C.; Abriak, N.E. Quantification of tributaries contributions using a confluence-based sediment fingerprinting approach in the Canche river watershed (France). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hintelmann, H.; Dimock, B. Chromatographic pre-concentration of Hg from dilute aqueous solutions for isotopic measurement by MC-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2010, 25, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Driscoll, C.T.; Warby, R.A.; Montesdeoca, M.; Johnson, C.E. Soil mercury and its response to atmospheric mercury deposition across the northeastern United States. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, J.B.; Friedland, A.J. Mercury in coniferous and deciduous upland forests in northern New England, USA: Implications of climate change. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 6737–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, W.F.; Engstrom, D.R.; Hammerschmidt, C.R.; Lamborg, C.H.; Balcom, P.H.; Lima-Braun, A.L.; Bothner, M.H.; Reddy, C.M. Global and local sources of mercury deposition in coastal New England reconstructed from a multiproxy, high-resolution, estuarine sediment record. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7614–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studer, M.M. The Chemistry and Geochemistry of Selected Metals in the Merrimack River of New England and Regulatory Considerations of Water Quality. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Massachusetts-Boston, Boston, MA, USA, September 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, L.A. Mercury in the Thames estuary. Environ. Technol. 1981, 2, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.J. Mobilization of Mercury-Contaminated Sediment in a Regulated River, Androscoggin River, Nrthern New Hampshire. Master’s Thesis, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH, USA, 19 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Navrátil, T.; Shanley, J.; Rohovec, J.; Hojdová, M.; Penížek, V.; Buchtová, J. Distribution and pools of mercury in Czech forest soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruba, P.; Socha, J.; Pietrzykowski, M.; Pasichnyk, D. Tree species affects the concentration of total mercury (Hg) in forest soils: Evidence from a forest soil inventory in Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, D.H.; Liang, C.H.; Wang, S.F.; Jia, Y.F. Concentration and speciation distribution of mercury in forest soils on northern slope of Changbai Mountain. Chin. J. Ecol. 2011, 30, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X.; Zhu, W.; Rothenberg, S.; Yao, H.; Zhang, H. Elevated atmospheric deposition and dynamics of mercury in a remote upland forest of southwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2324–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tang, L.; Qiu, G.; Liu, C. Total mercury and methylmercury in the soil and vegetation of a riparian zone along a mercury-impacted reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, S.J.; Blum, J.D.; Kurz, A.Y.; Pizzuto, J.E. Spatial and temporal variation in the isotopic composition of mercury in the South River, VA. Chem. Geol. 2018, 494, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamby, R.L.; Hammerschmidt, C.R.; Costello, D.M.; Lamborg, C.H.; Runkle, J.R. Deforestation and cultivation mobilize mercury from topsoil. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.B.; Petrenko, C.L.; Friedland, A.J. Organic horizon and mineral soil mercury along three clear-cut forest chronosequences across the northeastern USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27994–28005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, J.D.; Magilligan, F.J.; Renshaw, C.E. Predicting the type, location and magnitude of geomorphic responses to dam removal: Role of hydrologic and geomorphic constraints. Geomorphology 2015, 251, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, S.; Snyder, N.P.; Ouimet, W.B.; Martini, A.M.; Yellen, B.; Woodruff, J.D.; Newton, R.M.; Merritts, D.J.; Walter, R.C. Estimating the timescale of fluvial response to anthropogenic disturbance using two generations of dams on the South River, Massachusetts, USA. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2020, 45, 2380–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guédron, S.; Amouroux, D.; Tessier, E.; Grimaldi, C.; Barre, J.; Berail, S.; Perrot, V.; Grimaldi, M. Mercury isotopic fractionation during pedogenesis in a tropical forest soil catena (French Guiana): Deciphering the impact of historical gold mining. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11573–11582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.O.; Baulig, Y.; Fischer, H.; Blöthe, J. Scale breaks of suspended sediment rating in large rivers in Germany induced by organic matter. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2020, 8, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Obrist, D. Inorganic and methylated mercury dynamics in estuarine water of a salt marsh estuary in Massachusetts, USA. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 294, 118657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evers, D.C.; Han, Y.J.; Driscoll, C.T.; Kamman, N.C.; Goodale, M.W.; Lambert, K.F.; Holsen, T.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Clair, T.A.; Butler, T. Biological mercury hotspots in the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. BioScience 2007, 57, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoton, F.E.; Bennett, S.J. Soil and sediment properties affecting the accumulation of mercury in a flood control reservoir. Catena 2009, 79, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzuto, J.E. Long-term storage and transport length scale of fine sediment: Analysis of a mercury release into a river. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5875–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Watershed | Watershed Area | Urban Area | Forested Area | Wetland Area | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | km2 | % | km2 | % | km2 | % | |
| Connecticut | 29,200 | 2813 | 10 | 21,562 | 74 | 1721 | 6 |
| Merrimack | 12,975 | 2142 | 17 | 8243 | 64 | 1076 | 8 |
| Thames | 3817 | 433 | 11 | 2512 | 66 | 12 | 12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Richardson, J.B.; Mischenko, I.C.; Butler, M.J. Mercury in Temperate Forest Soils and Suspended Sediments in the Connecticut River, Merrimack River, and Thames River Watersheds, USA. Pollutants 2022, 2, 252-268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants2020017
Richardson JB, Mischenko IC, Butler MJ. Mercury in Temperate Forest Soils and Suspended Sediments in the Connecticut River, Merrimack River, and Thames River Watersheds, USA. Pollutants. 2022; 2(2):252-268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants2020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleRichardson, Justin B., Ivan C. Mischenko, and Mark J. Butler. 2022. "Mercury in Temperate Forest Soils and Suspended Sediments in the Connecticut River, Merrimack River, and Thames River Watersheds, USA" Pollutants 2, no. 2: 252-268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants2020017
APA StyleRichardson, J. B., Mischenko, I. C., & Butler, M. J. (2022). Mercury in Temperate Forest Soils and Suspended Sediments in the Connecticut River, Merrimack River, and Thames River Watersheds, USA. Pollutants, 2(2), 252-268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants2020017






