Abstract
The concepts of sustainability and waste utilization have received urgent attention in the European construction industries. Material selection plays a vital role in the manufacturing process of sustainable building construction. The general objective of this study is the transformation of waste diabase mud into a value-added product. The diabase mud was characterized, and different parameters were selected for the cement, as well as the metakaolin in the mixture. This paper includes analytical research results of a geopolymer paste embedded with diabase mud waste material as its precursor, and a combination of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and sodium silicate (Na2SiO3) as its alkaline activators to form a geopolymeric system. The compressive strength of the optimum mix sample was recorded as 14.0 MPa at 72 h. The embedding of a diabase mud into a geopolymer resulted in a viable composite for use in the construction industry.
1. Introduction
Globally, the ever-increasing exigency for Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), owing to the wide-ranging application of concrete by the construction and infrastructure industries, has given rise to numerous concerns with regards to sustainability and the environment. Presently, concrete is the highest consumable material next to water in the world. Conversely, OPC production contributes to around 10% of the total global CO2 emissions and consumes approximately 15% of the entire industrial energy produced, leading to a significant burden on the environment and also on sustainability objectives [1,2,3,4,5,6]. In the preceding couple of years, concrete researchers have increasingly endeavored to develop sustainable and eco-benevolent solutions to manufacture an extensive quantity of concrete for the worldwide construction industry.
In the preceding decades, alkali-activated materials (AAMs) or ‘geopolymers’, have been steadily accepted by both concrete technologists and industries as a family of efficient and promising alternatives to Portland cement-based materials (PCMs). Geopolymers can be manufactured through the exothermic process of “geopolymerization”, i.e., the activation of a reactive solid alumino-silicate precursor such as blast furnace slag, fly ash (Class-F fly ash in this paper unless otherwise stated), metakaolin, etc., with alkaline activators, typically concentrated aqueous solution of alkali hydroxide, silicate or carbonate at room temperatures. Accurately designed AAMs demonstrate a denser microstructure than that of normal PCMs, with superior engineering performance, particularly in severe environmental conditions [7,8,9]. An optimum mix design is highly essential because the application of sodium silicate leads to higher CO2 emissions and surface water acidification, reducing the environmental advantages. The across-the-board engineering application of AAMs has advanced slowly yet steadily. Irrespective of the regulation hindrances, there seem to be several technical challenges, such as shrinkage risk [10], the quality of raw materials and of the alkali activators to be utilized [8], workability issues, etc. Additionally, the majority of commercial chemical admixtures for PCMs are found to be incompatible with developing AAMs [10]. Consequently, the impact of their composition on the rheological properties of AAMs must be fully understood in order to control their workability.
The accumulation of diabase mud as a residue from the regular production operations of a concrete manufacturing company is a pressing issue that should be addressed efficiently. The aggregates and ready-mix concrete production of the industry generates waste in form of a residue, i.e., diabase mud. More specifically, this residue of diabase mud is generated by the crushing process and the washing of aggregates. The washing creates mud with a solid fraction, smaller than 0.063 mm in size. Besides the lower fraction, the mud possesses a humidity content of approximately 30%, rendering it as an “unsuitable raw material” for the construction industry since it necessitates dry materials for feedstock. LATOMIA PHARAMAKAS PLC is one of the main quarries in Cyprus (EU) and produces of diabase mud waste of nearly 25,000 tonnes per annum. Unfortunately, the large quantity of diabase mud is dumped in a landfill within the production facilities of the company. In accordance with EU legislation, the industrial waste of diabase mud should be recycled instead of being disposed of in landfills. Until 2012, this type of Industrial Waste (IW) had not even been registered in the Cyprus National Report. So far, there are no existing national regulations or targets for IW disposal management in Cyprus since the state has not hitherto dealt with the waste crisis and waste is continuously being accumulated. In addition, the company has limited open lands where it can store, either temporarily or permanently, this generated waste. The same is the case with some analogous industries facing similar challenges.
This present study describes the research approach of diabase mud-based geopolymer formulation and evaluates its properties. Hence, efforts are made towards systematic parametric studies such as that of the effect of the diabase content, the effect of NaOH concentration, and the addition of sodium silicate in the sodium hydroxide ratio on the compressive strength of geopolymer paste produced using diabase mud as a precursor. In this study, diabase mud (DM), metakaolin and cement are employed as pozzolanic precursor materials along with alkaline solutions of sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate, both of which are essential for geopolymerization reaction kinetics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
A commercial metakaolin was employed as a key alumino-silicate precursor. A few other materials, namely, diabase mud, metakaolin and cement were utilized. It is evident that diabase mud in its current form is more suitable to be used as a filler in metakaoline-based geopolymers rather than as a geopolymeric precursor. The chemical composition of diabase mud is exhibited in Table 1. The alkali activators were prepared through the dissolution of NaOH-pellets in water, and a Na2SiO3 solution to obtain the preferred molar ratios. Diabase mud, as a precursor, was obtained from Latomia Pharmakas Plc, Cyprus (EU) for use. Table 1 represents the chemical analysis of diabase mud.

Table 1.
Chemical analysis of diabase mud.
As presented in Table 1, diabase mud is a type of siliceous material, which is also rich in Fe-oxides and Al. Additionally, it encloses high quantities of oxides such as Mg, Ca, and Na. The mineralogical analysis of DM, determined through X-ray diffraction technique (Siemens D 5000 Diffractometer), is depicted in Figure 1. It was observed that DM is mainly constituted of a crystalline silicate or alumino-silicate phase. The diabase mud was used in the geopolymeric materials after drying. The humidity of the diabase mud is around 19–25%. There are three factors associated with the compressive strength such as the content of DM, concentration (M) of NaOH, and the ratio of Na2SiO3 to NaOH, which were all examined (Table 2 and Table 3). Table 2 and Table 3 present the mixture proportions of diabase mud-based geopolymer paste. This investigation consisted of two phases: The S/L ratio and D.M. content were maintained consistent in phase 1, whereas in phase 2 the S/L ratio and DM content were kept variable.
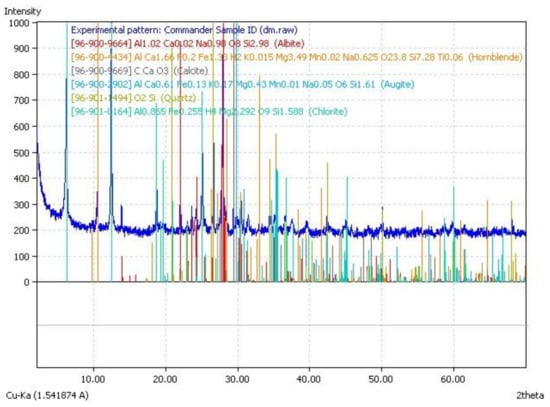
Figure 1.
XRD analysis of diabase mud.

Table 2.
Mix proportions for Phase 1.

Table 3.
Mix proportions for Phase 2.
2.2. Compressive Strength Test
To determine the compressive strength of the investigated formulations, cubes of 50 mm × 50 mm × 50 mm in size were cast and tested in accordance with ASTM C109. Following the casting, the samples were examined on a 2000 kN electro-hydraulic mechanical testing machine. The average of the three cubic specimens was used for each measurement of compressive strength.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of NaOH Concentration
The effect of the NaOH-concentration on the diabase mud-based geopolymer paste specimens was analyzed for all the developed mixes and the outcomes of testing are shown in Figure 2. It was observed that a higher concentration of the NaOH solution contributed to improved compressive strength, while the solid to liquid and alkaline activator ratio was maintained as constant.
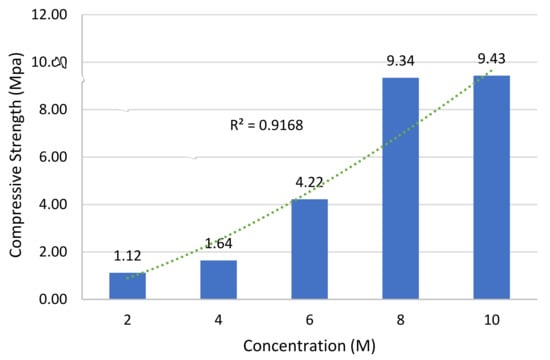
Figure 2.
Effect of NaOH concentration on average 72 h compressive strength.
On the whole, the compressive strength of geopolymer specimens increased with an increase in the Sodium Hydroxide concentration, from 2 to 10 M (Molarity). The strength of the geopolymer paste is found to rely on the NaOH-concentration, since it influences the dissolution of Si+4 and Al+3 ions in source materials [11]. An increase in the strength at a 10 M concentration of Sodium Hydroxide solution owes to its OH-concentration, which is high enough to accelerate the hydrolysis process and the dissolution rate [11].
Furthermore, it was observed that q low NaOH concentration led to an inferior strength in the context of geopolymer mixes. A surplus OH-concentration was found, resulting in aluminosilicate gel precipitation at the initial phases [11]. In the current study, the optimum concentration of Sodium Hydroxide is considered to be 10M. The concentration of the NaOH solution was found to be lower than in the study of Patankar et al. [12] whereby the recorded optimum concentration was 12 M. The ratio of Si: Al is a chief factor that can influence the mechanical, physical and microstructural characteristics of geopolymers.
3.2. Effect of Na2SiO3 to NaOH Ratio
The effect of the solution of Na2SiO3 on the NaOH solution ratio was investigated, taking into consideration all the mixtures developed in the present experimental study. The outcomes are graphically represented in Figure 3. When the value of Na2SiO3 decreased, the compressive strength of diabase mud-based geopolymer paste was also found to decrease. The decline in the compressive strength of the specimens largely relies upon the chemical process controlling the geopolymerization [13]. A few mixtures representing a diminished compressive strength since their geopolymerisation rate was lower, hence, the compressive strength of the batches is low. Furthermore, the utilization of Na2SiO3 assisted in improving the geopolymerisation by speeding up the dissolution rate of the source material [7]. The compressive strength tends to reduce, probably due to surplus alkali quantity which slowed down the geopolymerisation. This occurs while the Al-Si phase precipitation stops the interaction between the reacting material and activator, thus decreasing the concentration of the activator [14].
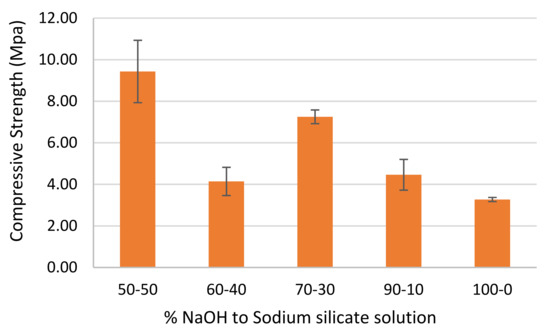
Figure 3.
Effect of alkaline solution ratio on average 72 h compressive strength.
3.3. Effect of Diabase Mud on Compressive Strength
The effect of diabase mud on the compressive strength of a geopolymer paste is determined as shown in Figure 4. It was found that the quantity of diabase mud increases the compressive strength of geopolymer paste. Moreover, according to Figure 4, the compressive strength is not proportional to the DM content. It is similar to the DM content from 70 to 115 g and then, it decreases sharply with a increase of DM to 125 g and remains almost constant for any further increase in the DM content.
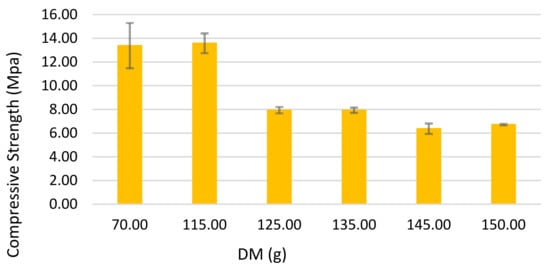
Figure 4.
Effect of diabase mud on average 72 h compressive strength.
4. Conclusions
The following conclusions were made, based on the present research work:
- The ratio of Na2SiO3 to NaOH by a mass equivalent of 50:50 led to an increase in the compressive strength of the relevant formulation, compared to the other ratios investigated.
- The compressive strength is not proportional to an increase in the NaOH concentration for values higher than 8 M.
From the above points, it may be concluded that a wider variety of parameters impact the geopolymer’s compressive strength.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L.; methodology, S.L.; validation, S.L. and M.S.; formal analysis, S.L. and P.S.; investigation, M.S.; resources, P.S., S.I., M.F.P., D.N. and I.L.; data curation, P.S., S.I., M.F.P., D.N. and I.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L., I.L.; writing—review and editing, S.I. and D.N.; supervision, P.S., D.N. and M.F.P.; project administration, P.S.; funding acquisition, P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Project ENTERPRISES/0618/0041 is co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund and the Republic of Cyprus through the Cyprus Research & Innovation Foundation (RIF).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to Cyprus, the Cyprus Research & Innovation Foundation (RIF) and the European Regional Development Fund, for funding the research project entitled “Valorization of diabase mud for the development of innovative building materials” (Contract Number: ENTERPRISES/0618/0041).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Luhar, S.; Nicolaides, D.; Luhar, I. Fire Resistance Behaviour of Geopolymer Concrete: An Overview. Buildings 2021, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, S.; Luhar, I.; Nicolaides, D.; Gupta, R. Durability Performance Evaluation of Rubberized Geopolymer Concrete. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, I.; Luhar, S.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Nabiałek, M.; Sandu, A.V.; Szmidla, J.; Jurczyńska, A.; Razak, R.A.; Aziz, I.H.A.; Jamil, N.H.; et al. Assessment of the Suitability of Ceramic Waste in Geopolymer Composites: An Appraisal. Materials 2021, 14, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tingley, D.D.; Zhang, Y. Life cycle sustainability assessment of fly ash concrete structures. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, S.; Suntharalingam, T.; Navaratnam, S.; Luhar, I.; Thamboo, J.; Poologanathan, K.; Gatheeshgar, P. Sustainable and Renewable Bio-Based Natural Fibres and Its Application for 3D Printed Concrete: A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, S.; Luhar, I.; Shaikh, F.U.A. Review on Performance Evaluation of Autonomous Healing of Geopolymer Composites. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, T.; Juenger, M.C.G. The role of activating solution concentration on alkali–silica reaction in alkali-activated fly ash concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 83, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglas, E.; Bilodeau, A.; Malhotra, V.M. Properties and durability of alkali activated slag concrete. Mater. J. 1992, 89, 509–516. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.M.; Jiang, W.; Silsbee, M.R. Chloride diffusion in ordinary, blended, and alkali-activated cement pastes and its relation to other properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Jang, J.G.; Lee, H.K. Shrinkage characteristics of alkali-activated fly ash/slag paste and mortar at early ages. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 53, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupaei, R.H.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z. The effect of different parameters on the development of compressive strength of oil palm shell geopolymer concrete. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 898536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patankar, S.V.; Ghugal, Y.M.; Jamkar, S.S. Effect of concentration of sodium hydroxide and degree of heat curing on fly ash-based geopolymer mortar. Indian J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 2014, 938789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, Z.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Hussin, K.; Ismail, K.N.; Razak, R.A.; Sandu, A.V. Effect of solids-to-liquids, Na2SiO3-to-NaOH and curing temperature on the palm oil boiler ash (Si + Ca) geopolymerisation system. Materials 2015, 8, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Hussin, K.; Abdullah, M.M.; Yahya, Z.; Sochacki, W.; Razak, R.A.; Błoch, K.; Fansuri, H. The Effects of Various Concentrations of NaOH on the Inter-Particle Gelation of a Fly Ash Geopolymer Aggregate. Materials 2021, 14, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).