Hierarchical Ag-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings on TiO2 Nanotubes Formed on Ti-407 Alloy: Antibacterial Evaluation Against Escherichia coli †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Processing of Ti-407 Alloy Samples
2.2. Surface Modification by Anodization
2.3. Electrodeposition of Functional Coatings
- Electrodeposition of metallic silver (Ag0): In the first group, silver was deposited by immersing the anodized samples for 5 min in 100 mL of 0.05 M AgNO3, prepared using 90 mL of ethylene glycol and 10 mL of distilled water. This 9:1 solvent ratio was selected because ethylene glycol-based systems have been shown to enhance electrolyte stability, including chemical, ionic, and thermal stability [19]. After deposition, the samples were dried with hot air, and excess solution was removed using compressed air for 30 s.
- Electrodeposition of bioactive ions: In the second group, anodized samples were treated for 20 min in 100 mL of an aqueous solution containing 0.2 M of K2HPO4, 0.1 M of MgCl2·6H2O, 0.2 M of CaCl2·2H2O, and 0.05 M of ZnCl2. After deposition, the same drying and air-blowing procedure was applied.
- Sequential electrodeposition of Ag and bioactive ions (hierarchical coating): In the third group, the anodized samples first underwent the silver deposition step described for the first group, followed immediately by immersion in the bioactive ion solution under the same conditions used for the second group. Both deposition stages were followed by drying and compressed air removal of excess solution.
2.4. Surface and Elemental Characterization
2.5. Antibacterial Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Morphology of Anodized and Functionalized Coatings
3.2. Chemical Composition and Mineral-Phase Assessment via EDS
- Ti anodization (NT formation): Ti(s) → Ti4+ + 4e− Ti4+ + 2O2− → TiO2(s) TiO2 + 6F− + 4H+ → [TiF6]2− + 2H2O;
- Silver electrodeposition: Ag+ + e− → Ag0(s);
- Mineral electrodeposition: 10Ca2+ + 6PO43− + 2OH− → Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2(s) with substitutions: Ca10-x-y(MgxZny)(PO4)6(OH)2;
- Final product (functionalized surface): Ti0 → TiO2 → Ag0 → Ca10-x-y(MgxZny)(PO4)6(OH)2.
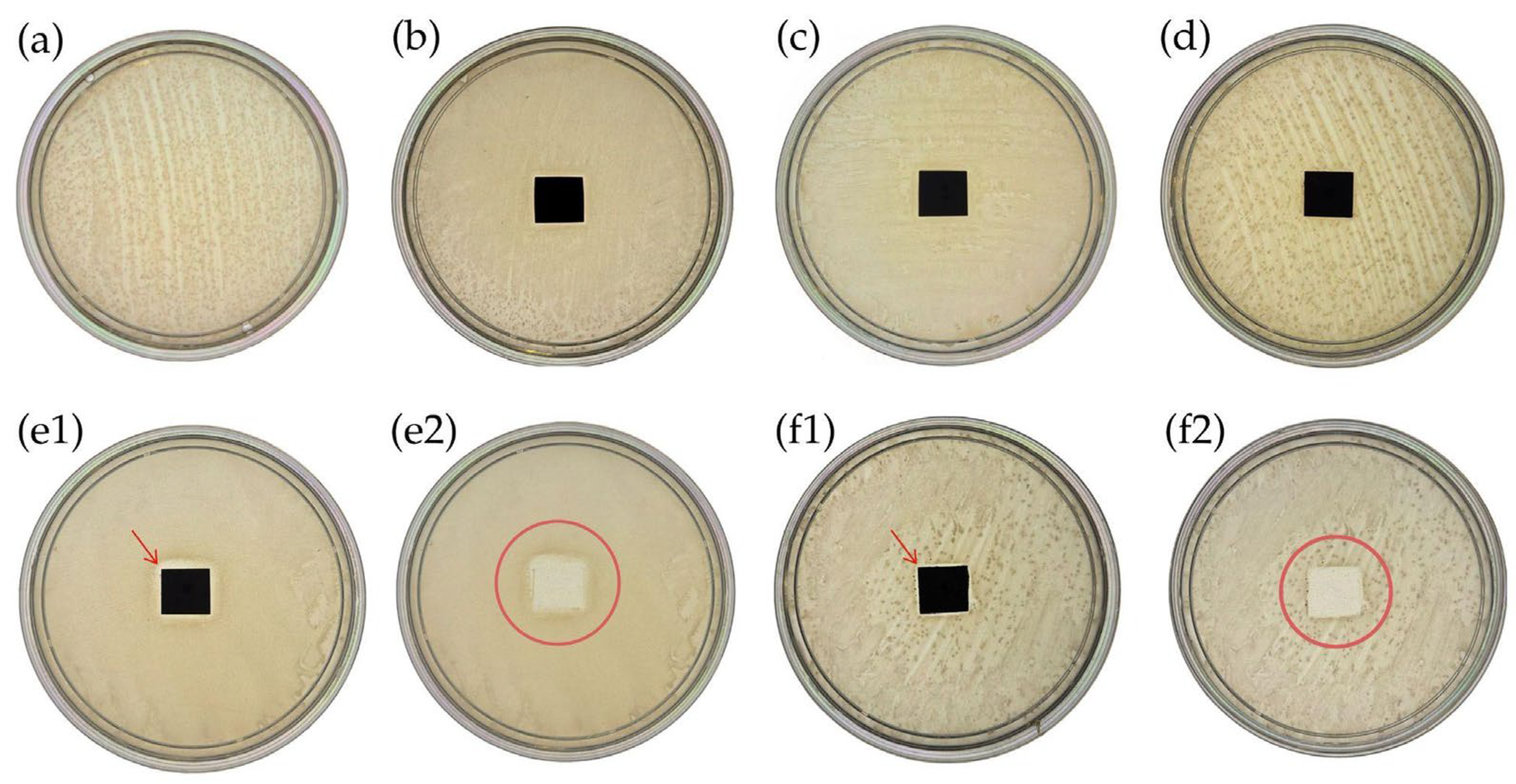
3.3. Antibacterial Activity Against Escherichia coli Assessed by Agar Diffusion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanner, M.C.; Fischer, C.; Schmidmaier, G.; Haubruck, P. Evidence-based uncertainty: Do implant-related properties of titanium reduce the susceptibility to perioperative infections in clinical fracture management? A systematic review. Infection 2021, 49, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xing, H.; Chang, Z.; Pan, J. Risk factors for deep surgical site infections following orthopedic trauma surgery: A meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonten, M.; Johnson, J.R.; van den Biggelaar, A.H.J.; Georgalis, L.; Geurtsen, J.; de Palacios, P.I.; Gravenstein, S.; Verstraeten, T.; Hermans, P.; Poolman, J.T. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli Bacteremia: A Systematic Literature Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katongole, P.; Nalubega, F.; Florence, N.C.; Asiimwe, B.; Andia, I. Biofilm formation, antimicrobial susceptibility and virulence genes of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from clinical isolates in Uganda. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, J.; Li, S.; Crean, S.J.; Barrak, F.N. Is titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V cytotoxic to gingival fibroblasts—A systematic review. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2021, 7, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneddon, S.; Xu, Y.; Dixon, M.; Rugg, D.; Li, P.; Mulvihill, D.M. Sensitivity of material failure to surface roughness: A study on titanium alloys Ti64 and Ti407. Mater. Des. 2021, 200, 109438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Tang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, X.; Xiang, L. Nanostructured titanium implant surfaces facilitating osseointegration from protein adsorption to osteogenesis: The example of TiO2 nanotube arrays. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Li, P.; Qin, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhu, X. Real role of fluoride ions in the growth of anodic TiO2 nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2024, 128, 5741–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassyouni, G.T.; Mouneir, S.M.; El-Shamy, A.M. Advances in surface modifications of titanium and its alloys: Implications for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2025, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Li, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Recent development and applications of electrodeposition biocoatings on medical titanium for bone repair. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 9863–9893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.; Offoiach, R.; Monteiro, C.; Morais, M.R.G.; Martins, M.C.L.; Pêgo, A.P.; Salatin, E.; Fedrizzi, L.; Lekka, M. Electrodeposition of Zn and Cu nanoparticles into TiO2 nanotubes on Ti6Al4V: Antimicrobial effect against S. epidermidis and cytotoxicity assessment. Micro 2024, 4, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Manga, Y.B.; Huang, W.-N.; Lin, C.-K.; Tseng, C.-L.; Huang, H.-M.; Wu, C.-Y.; Wu, C.-C. Effect of hydroxyapatite formation on titanium surface with bone morphogenetic protein-2 loading through electrochemical deposition on MG-63 cells. Materials 2018, 11, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, M.S.; Khalil-Allafi, J.; Restivo, E.; Ghalandarzadeh, A.; Hosseini, M.; Dacarro, G.; Malavasi, L.; Milella, A.; Listorti, A.; Visai, L. Enhanced in vitro immersion behavior and antibacterial activity of NiTi orthopedic biomaterial by HAp–Nb2O5 composite deposits. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. A review on the dissolution models of calcium apatites. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2002, 44, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirdar, M.R.; Izman, S.; Taheri, M.M.; Assadian, M.; Kadir, M.R.A. Effect of post-treatment techniques on corrosion and wettability of hydroxyapatite-coated Co–Cr–Mo alloy. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, S.; Ignjatović, N.L.; Lazarević, M.; Petrović, S.; Žekić, A.; Losic, D. Combined Effects of Dual-Scale Modified Surface with Micro- and Nanostructures on the Cellular Biocompatibility, Osteoinduction, and Antibacterial Properties of Titanium Implants. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwahr, C.; Helbig, R.; Werner, C.; Lasagni, A.F. Fabrication of multifunctional titanium surfaces by producing hierarchical surface patterns using laser-based ablation methods. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Lin, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Rong, M.; Guo, Z.; et al. The effects of hierarchical micro/nanosurfaces decorated with TiO2 nanotubes on the bioactivity of titanium implants in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6955–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoloni, C.; Legeai, S.; Michel, S.; Meux, E.; Lapicque, F. Electroleaching and electrodeposition of silver in ethaline 1:2 and propeline 1:3: Transport properties and electrode phenomena. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2024, 3, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez Anzures, F.E. Biocompatibilidad de Nanoestructuras Formadas por Anodizado en Aleaciones de Base Titanio para Aplicaciones Biomedicas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autonoma de Nuevo Leon, Monterrey, Mexico, 2023. Available online: http://eprints.uanl.mx/26463/1/1080312748.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- TIMET. TIMETAL® 407 Datasheet. Available online: https://www.timet.com/documents/datasheets/alpha-and-beta-alloys/timetal-407.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Bactericidal and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akshaya, S.; Rowlo, P.K.; Dukle, A.; Nathanael, A.J. Antibacterial coatings for titanium implants: Recent trends and future perspectives. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 22196:2011; Measurement of Antibacterial Activity on Plastics and Other Non-Porous Surfaces. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for in Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
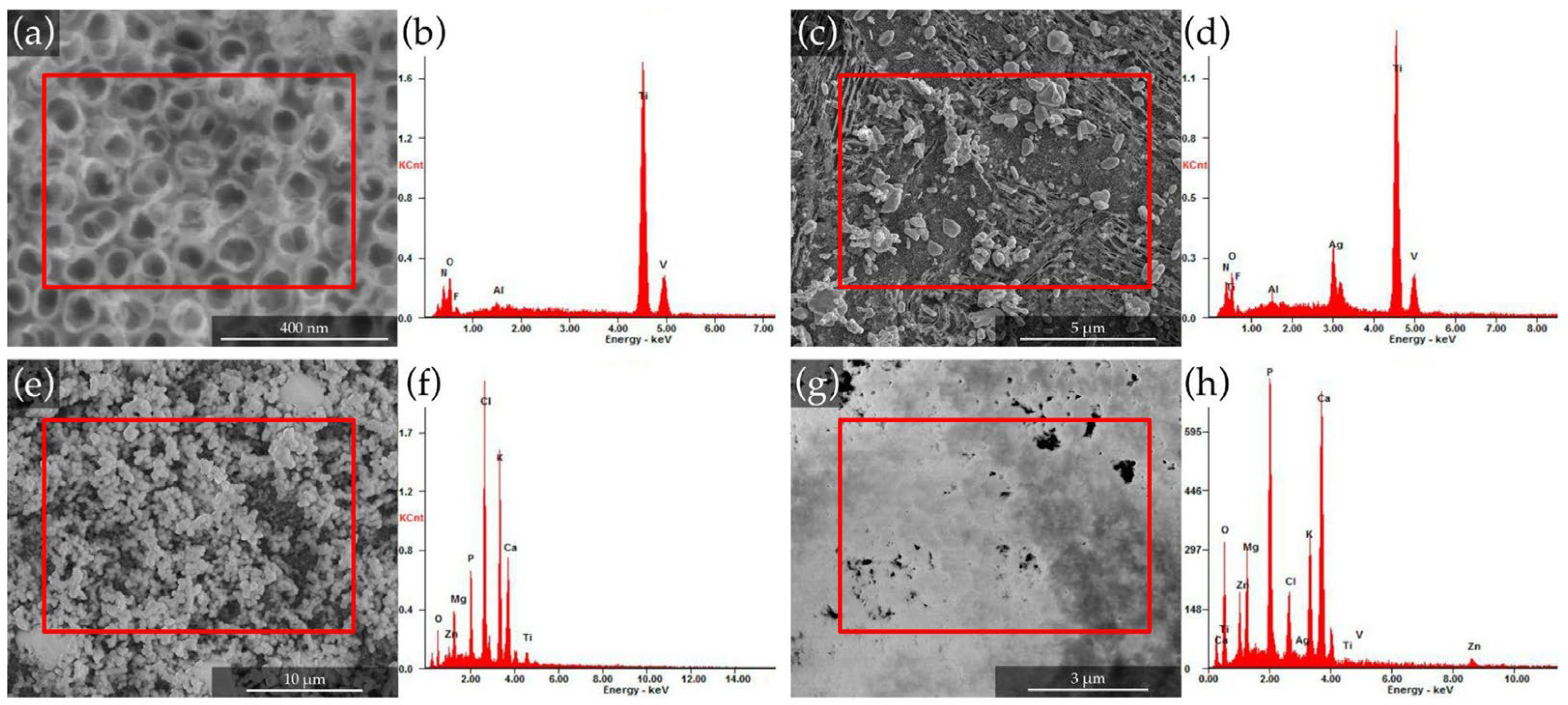
| Element | Control | Anodized | Anodized + Ag | Anodized + Zn-Mg-CaP | Anodized + Ag + Zn-Mg-CaP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | 94.58 ± 4.72 | 63.10 ± 3.79 | 57.34 ± 3.15 | 3.41 ± 0.22 | 0.94 ± 0.07 |
| V | 3.82 ± 0.23 | 2.36 ± 0.15 | 2.15 ± 0.13 | - | - |
| Al | 1.60 ± 0.11 | 0.91 ± 0.06 | 0.89 ± 0.06 | - | - |
| N | - | 6.52 ± 0.46 | 2.59 ± 0.18 | - | - |
| O | - | 23.57 ± 1.58 | 19.17 ± 1.23 | 14.13 ± 1.04 | 14.38 ± 1.72 |
| F | - | 3.54 ± 0.27 | 3.09 ± 0.21 | - | - |
| Ag | - | - | 14.78 ± 1.02 | - | 1.09 ± 0.08 |
| Zn | - | - | - | 3.17 ± 0.23 | 9.67 ± 0.08 |
| Mg | - | - | - | 4.63 ± 0.35 | 6.44 ± 0.47 |
| P | - | - | - | 7.71 ± 0.55 | 17.16 ± 1.08 |
| Cl | - | - | - | 21.21 ± 1.89 | 4.75 ± 0.36 |
| K | - | - | - | 24.97 ± 1.85 | 9.97 ± 0.69 |
| Ca | - | - | - | 20.95 ± 1.14 | 35.75 ± 1.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamayo-Jimenez, A.P.; Melendez-Anzures, F.E.; Barron-Gonzalez, M.P.; Lopez-Cuellar, E.M.; Quiñones-Gutierrez, Y.; Garza-Guajardo, J.A.; la Cruz, A.M.-D. Hierarchical Ag-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings on TiO2 Nanotubes Formed on Ti-407 Alloy: Antibacterial Evaluation Against Escherichia coli . Mater. Proc. 2025, 28, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025028004
Tamayo-Jimenez AP, Melendez-Anzures FE, Barron-Gonzalez MP, Lopez-Cuellar EM, Quiñones-Gutierrez Y, Garza-Guajardo JA, la Cruz AM-D. Hierarchical Ag-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings on TiO2 Nanotubes Formed on Ti-407 Alloy: Antibacterial Evaluation Against Escherichia coli . Materials Proceedings. 2025; 28(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025028004
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamayo-Jimenez, Angie P., Frank E. Melendez-Anzures, Maria P. Barron-Gonzalez, Enrique M. Lopez-Cuellar, Yadira Quiñones-Gutierrez, Javier A. Garza-Guajardo, and Azael Martinez-De la Cruz. 2025. "Hierarchical Ag-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings on TiO2 Nanotubes Formed on Ti-407 Alloy: Antibacterial Evaluation Against Escherichia coli " Materials Proceedings 28, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025028004
APA StyleTamayo-Jimenez, A. P., Melendez-Anzures, F. E., Barron-Gonzalez, M. P., Lopez-Cuellar, E. M., Quiñones-Gutierrez, Y., Garza-Guajardo, J. A., & la Cruz, A. M.-D. (2025). Hierarchical Ag-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings on TiO2 Nanotubes Formed on Ti-407 Alloy: Antibacterial Evaluation Against Escherichia coli . Materials Proceedings, 28(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025028004





