A Comparative Assessment of XFEM and FEM for Stress Concentration at Circular Holes near Bi-Material Interfaces †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Methodology
2.1. Geometric Representation via the Level Set Method
2.2. XFEM Formulation for a Hole
2.3. Problem Setup
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishnamoorthy, C.S. Finite Element Analysis—Theory and Programming, 2nd ed.; Tata McGraw-Hill: New Delhi, India, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, D.B.P.; Belytschko, T. The extended finite element method for fracture in composite materials. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2009, 77, 214–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, N.; Chopp, D.L.; Moes, N.; Belytschko, T. Modeling holes and inclusions by level sets in the extended finite-element method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2001, 190, 6183–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belytschko, T.; Parimi, C.; Moes, N.; Sukumar, N.; Usui, S. Structured extended finite element method for solids defined by implicit surfaces. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2003, 56, 609–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daux, C.; Moes, N.; Dolbow, J.; Sukumar, N.; Belytschko, T. Arbitrary branched and intersecting cracks with the extended finite element method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2000, 48, 1741–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, N.; Moes, N.; Moran, B.; Belytschko, T. Extended finite element method for three-dimensional crack modeling. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2000, 48, 1549–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolbow, J.; Moes, N.; Belytschko, T. Modelling fracture in mindlin-reissner plates with the extended finite element method. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2000, 37, 7161–7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolbow, J. An Extended Finite Elment Method with Discontinuous Enrichment for Applied Mechanics. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Osher, S.; Sethian, J.A. Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: Algorithms based on hamilton-jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 1988, 79, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rietbergen, B.; Weinans, H.; Huiskes, R.; Odgaard, A. A new method to determine trabecular bone elastic properties and loading using micromechanical finite-elements models. J. Biomech. 1995, 28, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.-D.; Huang, S.-C. The Uniaxial Stress Strain Relationship of Hyperelastic Material Models of Rubber Cracks in the Platens of Papermaking Machines Based on Nonlinear Strain and Stress Measurements with the Finite Element Method. Materials 2021, 14, 7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Gao, C.; Chen, W. Stress concentration in a finite functionally graded material plate. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 2012, 55, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-D.; Huang, S.-C. Using the Extended Finite Element Method to Integrate the Level-Set Method to Simulate the Stress Concentration Factor at the Circular Holes Near the Material Boundary of a Functionally-Graded Material Plate. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 4658–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-D.; Huang, S.-C. Use of XTFEM based on the consecutive interpolation procedure of quadrilateral element to calculate J-integral and SIFs of an FGM plate. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2023, 127, 103985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-D.; Huang, S.C. Calculating Strain Energy Release Rate, Stress Intensity Factor and Crack Propagation of an FGM Plate by Finite Element Method Based on Energy Methods. Materials 2025, 18, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoirullah, A.T.; Sampurno, R.; Sailon, S.; Ramadhoni, T.; Rizal, S.; Yuliandi, R. Static Stress Analysis of Fork on Rubber Slab Lifting Aid using Finite Element Method. Int. J. Mech. Energy Eng. Appl. Sci. 2024, 2, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moës, N.; Dolbow, J.; Belytschko, T. A finite element method for crack growth without remeshing. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1999, 46, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belytschko, T.; Gracie, R.; Ventura, G. A review of extended/generalized finite element methods for material modeling. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 17, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkey, W.D.; Pilkey, D.F. Peterson’s Stress Concentration Factors; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]

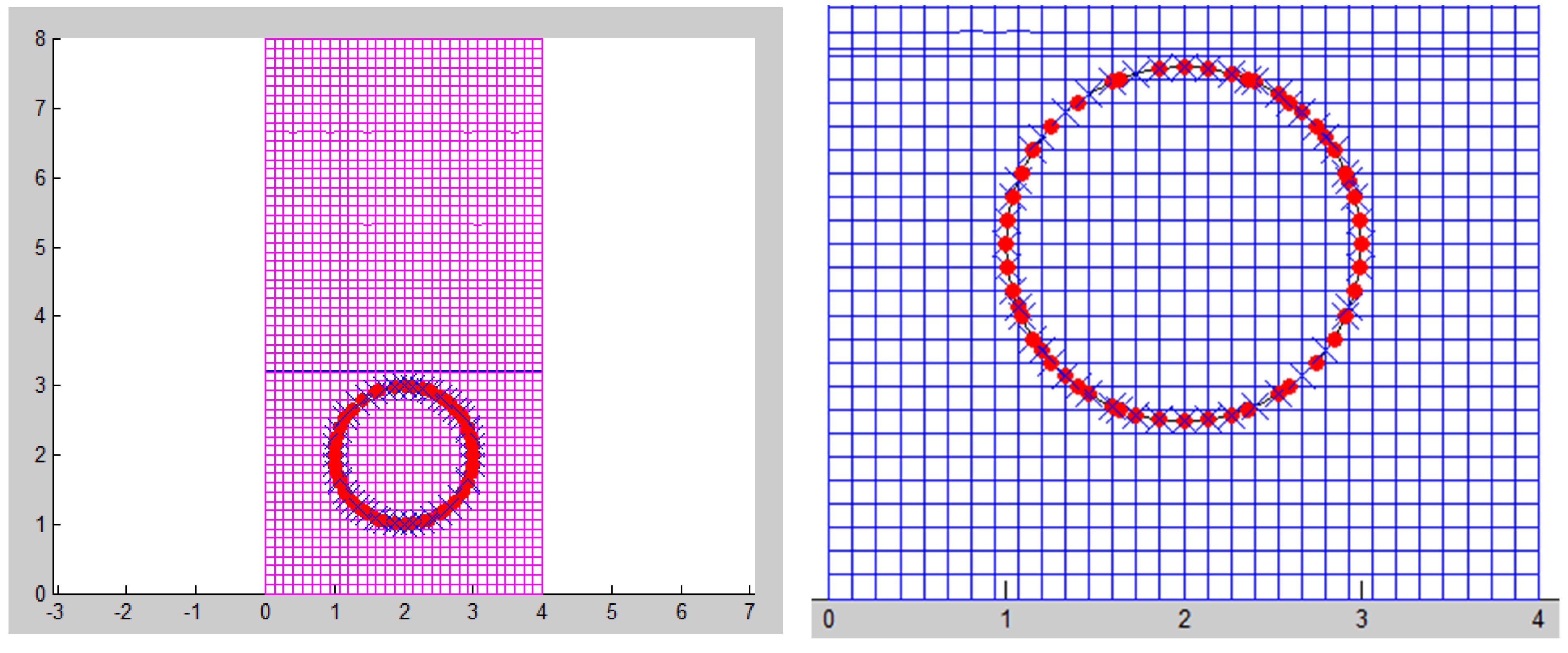


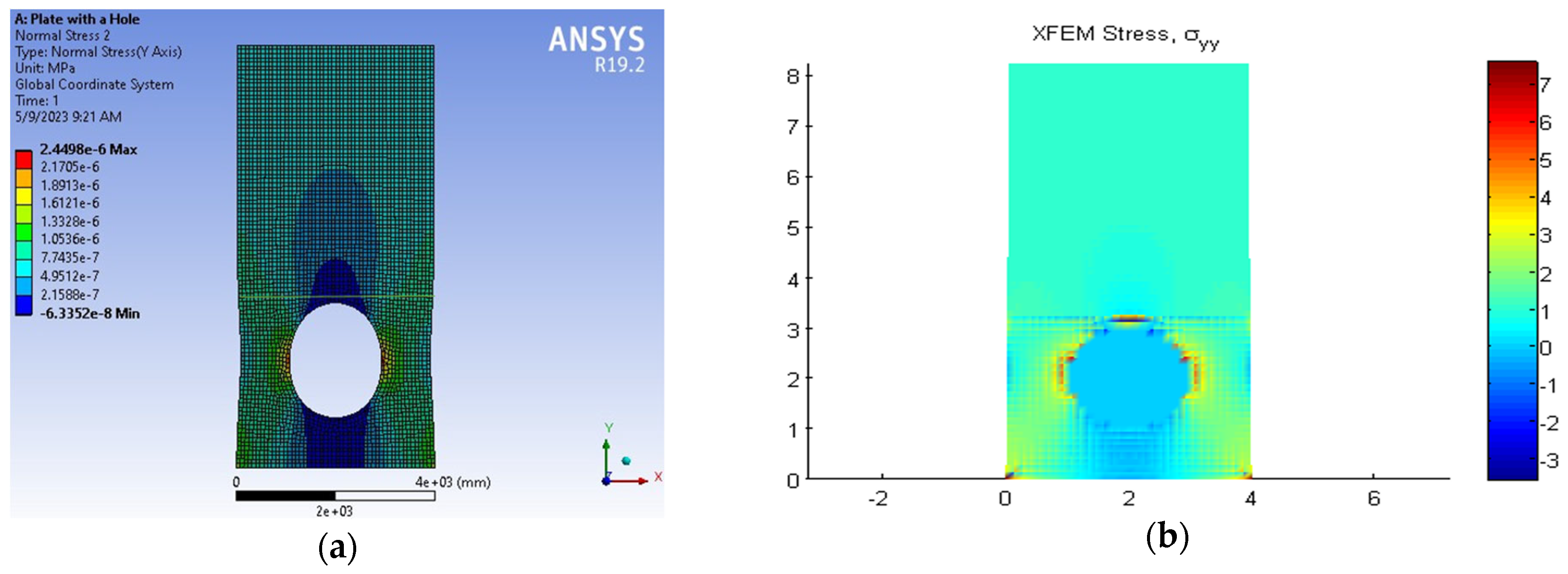
| Quantity | FEM | XFEM | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max () (mm) | 0.0719 | 0.0718 | 0.14 |
| Max () (MPa) | 3.18 | 3.15 | 0.94 |
| Max () (MPa) | 2.37 | 2.31 | 2.53 |
| SCF (=) | 2.37 | 2.31 | – |
| Error vs. analytical (%) | 14.11 | 4.19 | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.-D. A Comparative Assessment of XFEM and FEM for Stress Concentration at Circular Holes near Bi-Material Interfaces. Mater. Proc. 2025, 26, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025026003
Nguyen H-D. A Comparative Assessment of XFEM and FEM for Stress Concentration at Circular Holes near Bi-Material Interfaces. Materials Proceedings. 2025; 26(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025026003
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Huu-Dien. 2025. "A Comparative Assessment of XFEM and FEM for Stress Concentration at Circular Holes near Bi-Material Interfaces" Materials Proceedings 26, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025026003
APA StyleNguyen, H.-D. (2025). A Comparative Assessment of XFEM and FEM for Stress Concentration at Circular Holes near Bi-Material Interfaces. Materials Proceedings, 26(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025026003





