A Comparative Analysis of the Impact Behavior of Honeycomb Sandwich Composites †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Materials
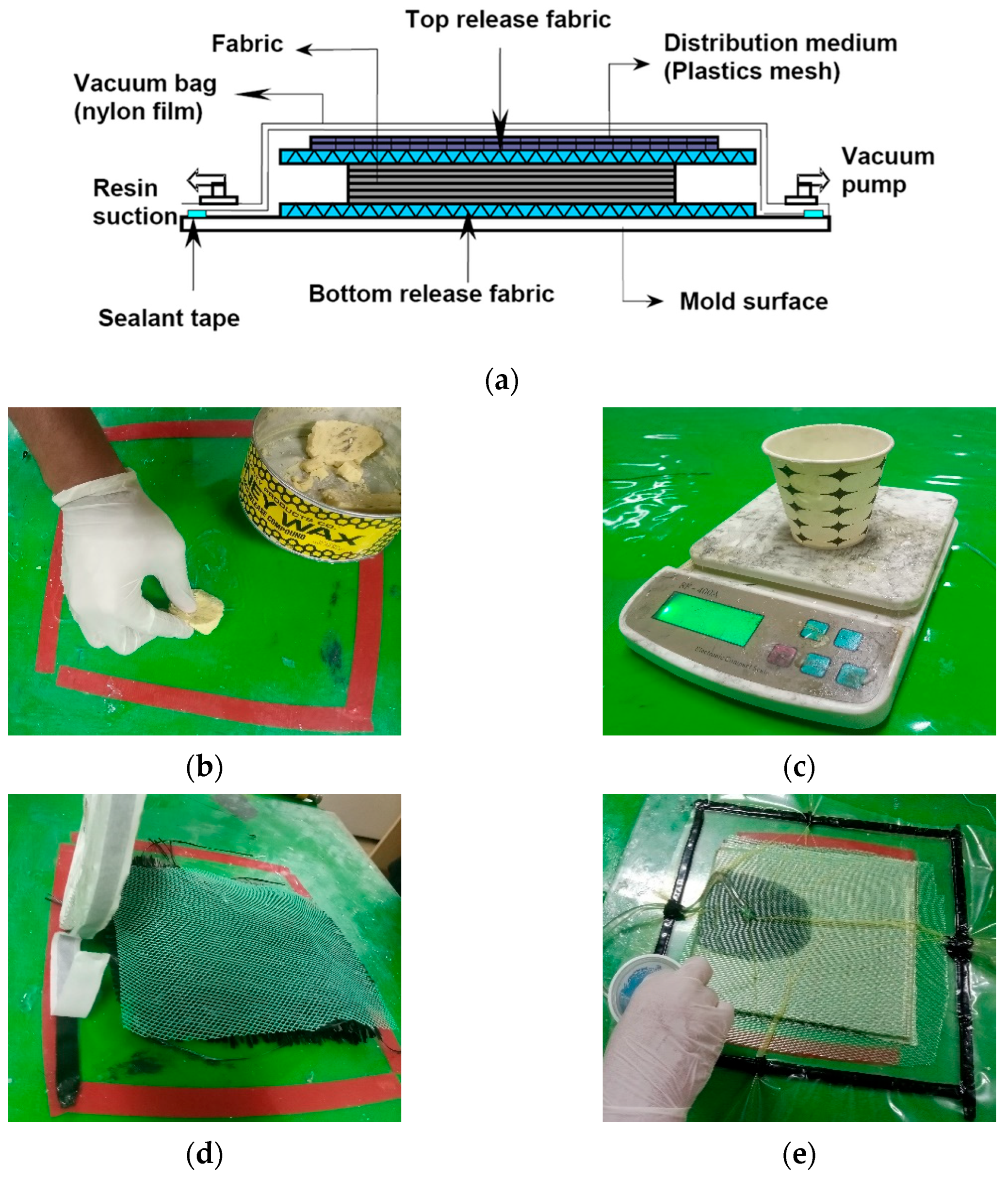
2.2. Fabrication Process
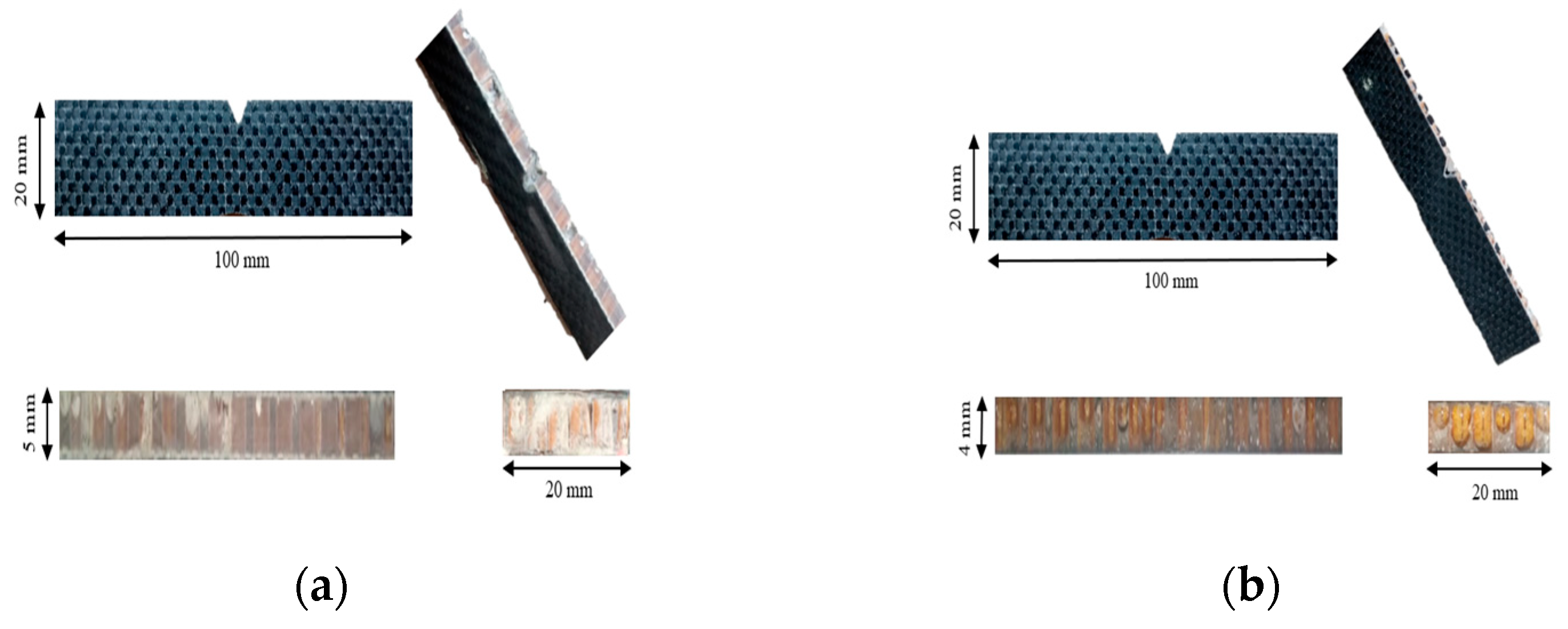
2.3. Design of Test Specimen
2.4. Charpy Impact Testing
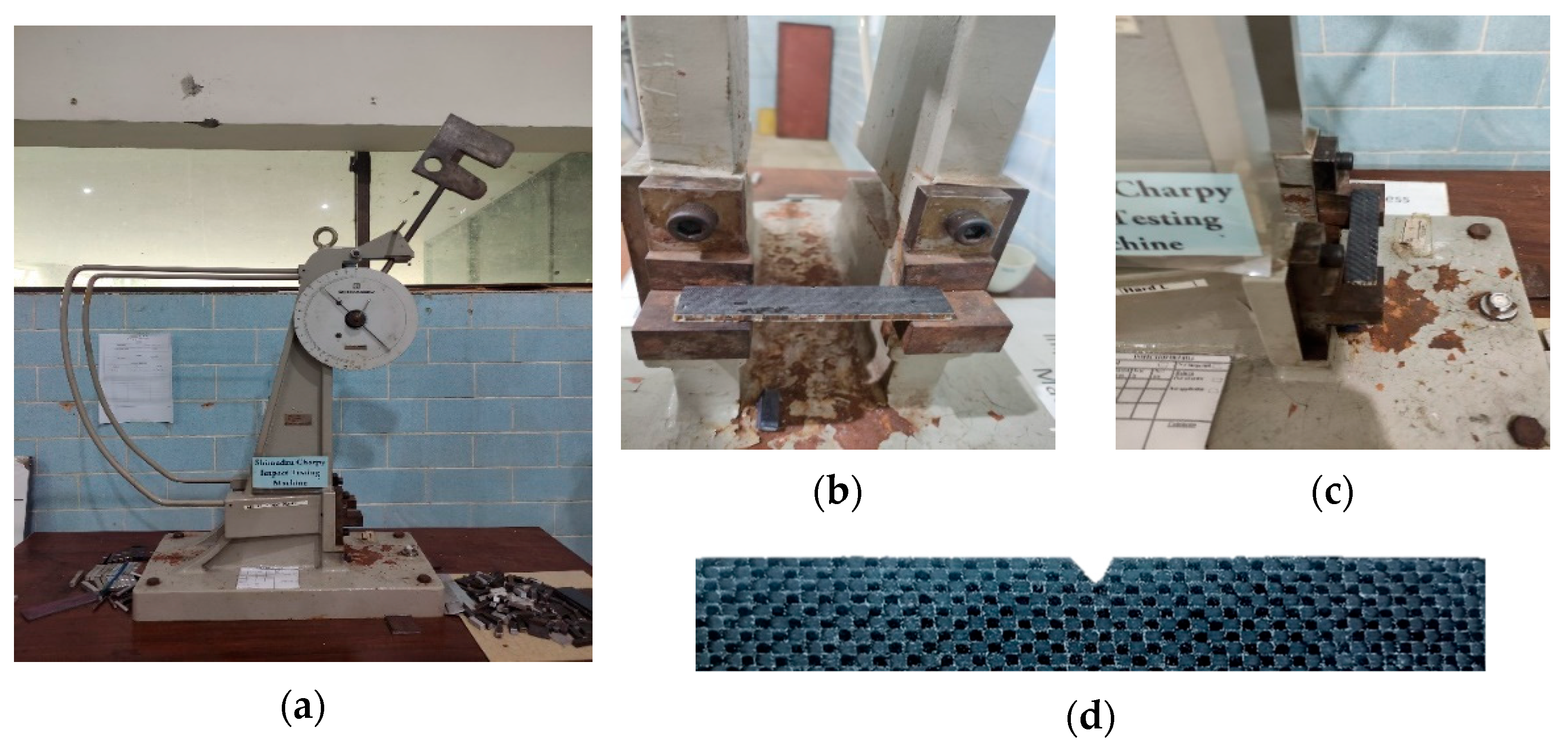
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- -
- Conduct SEM analysis to study the microstructure and failure modes of CKHKC composites.
- -
- Investigate the bending behavior of CKHKC structures under flexural loads.
- -
- Evaluate the long-term durability of CKHKC composites under cyclic or environmental conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C-H-C | Carbon Fiber–Honeycomb–Carbon Fiber |
| C-K-H-K-C | Carbon Fiber–Kevlar–Honeycomb–Kevlar–Carbon Fiber |
References
- Sun, G.; Chen, D.; Zhu, G.; Li, Q. Lightweight hybrid materials and structures for energy absorption: A state-of-the-art review and outlook. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 172, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Jing, K.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X. Mechanical properties of Nomex honeycomb sandwich panels under dynamic impact. Compos. Struct. 2020, 235, 111814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhu, K.; Chen, N.; Zheng, X.; Quaresimin, M. Energy-absorption characteristics of tube-reinforced absorbent honeycomb sandwich structure. Compos. Struct. 2021, 255, 112946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.K.; Sreekanth, P.S.R.; Reddy, S.V.K. A Brief Review on Advanced Sandwich Structures with Customized Design Core and Composite Face Sheet. Polymers 2022, 14, 4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, C.; Casavola, C.; De Cillis, F. Mechanical comparison of new composite materials for aerospace applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 162, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, J.E.; Cole, G.S. Metal-matrix composites in the automotive industry: Opportunities and challenges. JOM 1993, 45, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elachezhian, C.; Ramnath, V.B.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Raghavendra, K.N.S.; Muralidharan, M.; Kishore, V. Review on metal matrix composites for marine applications—ScienceDirect. Mater. Today 2018, 5, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siengchin, S. A review on lightweight materials for defence applications: Present and future developments. Def. Technol. 2023, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutis, C. Fibre reinforced composites in aircraft construction. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2005, 41, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djellab, A.; Chellil, A.; Lecheb, S.; Safi, B.; Mechakra, H.; Houari, A.; Kebir, H.; Madani, K. Experimental and numerical investigation of impact behavior in honeycomb sandwich composites. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2024, 238, 1342–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, Y.; Amin, F.; Iqbal, M.; Gerges, M.; Asif, M.; Majid, K.A.; Hussain, B. Radial compressive behavior of hand-laid GFRP pipes: An experimental and numerical study. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2025, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topkaya, T.; Solmaz, M.Y. Investigation of low velocity impact behaviors of honeycomb sandwich composites. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 3161–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H. Tensile and bending behavior for woven carbon-aramid/epoxy hybrid composites with various lamination structures by the VARTM method. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, A.; Prabhakar, P. Elucidating the Mechanisms of Damage in Foam Core Sandwich Composites under Impact Loading and Low Temperatures. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2022, 24, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvestani, A.N.; Tehrani, M. Investigation of Impact Energy Absorption and Damage in Woven Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite materials. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.07144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Chen, P.; Sun, W. Low-velocity impact response of sandwich composite panels with shear thickening gel filled honeycomb cores. Compos. Commun. 2022, 32, 101136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Huang, J.; Cao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zuo, X.; Yi, K.; Zhang, C. Thickness effect on ballistic impact behavior of hybrid carbon/Kevlar composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 254, 110692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Yan, L. Impact Response of Carbon/Kevlar Hybrid 3D Woven Composite Under High Velocity Impact: Experimental and Numerical Study. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2020, 27, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebaupin, Y.; Hoang, T.-Q.T.; Chauvin, M.; Touchard, F. Influence of the stacking sequence on the low-energy impact resistance of flax/PA11 composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 3187–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Hu, X. Dynamic response of composite honeycomb sandwich panels subjected to strong dynamic loading. Eng. Struct. 2025, 322, 119032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottapalli, P.K.; Balla, S.K.; Patel, H.V.; Dave, H.K. Study on Impact Properties of Hybrid Composites Fabricated by VARTM Process for Structural Applications. In Recent Advances in Manufacturing Processes and Systems; Dave, H.K., Dixit, U.S., Nedelcu, D., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, H. Hybrid effects and failure mechanisms of carbon/Kevlar fiber composite laminates under the bending-after-impact loading. Eng. Struct. 2024, 299, 117101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, Y.; Amin, F.; Asif, M.; Majid, K.A.; Ehsanullah, N. Investigating the Compressive Response of Hand-Laminated GFRP Pipes in the Hoop Direction through Experiment and FEM Modeling. Emir. J. Civ. Eng. Appl. 2024, 2, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Xiao, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Jia, P.; Wang, C. Experimental and Numerical Study on the Impact Response of Composite Sandwich Structures with Different Cores. Polymers 2024, 16, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkaoui, A.; Hassan, N.M.; Bahroun, Z.; Ibrahim, M. Low-velocity impact response of hybrid core sandwich panels with spring and strut cores filled with resin, silicone, and foam. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2024, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, G.; Gao, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, J.; Du, P.; Gao, M.; Chen, M. Study on impact properties of carbon/kevlar fiber hybrid composites. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 8665–8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghipour, P.; Schneider, J.; Bartsch, M.; Hausmann, J.; Voggenreiter, H. Fracture simulation of CFRP laminates in mixed mode bending. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2009, 76, 2821–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.U.; Nadeem, A.; Ashfaq, B.; Ullah, S.; Waseem, M.; Aslam, M.A.; Alam, Q.A. Optimizing Impact Toughness in 3D-Printed PLA Structures Using Hilbert Curve and Honeycomb Infill Patterns. Eng. Proc. 2024, 75, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

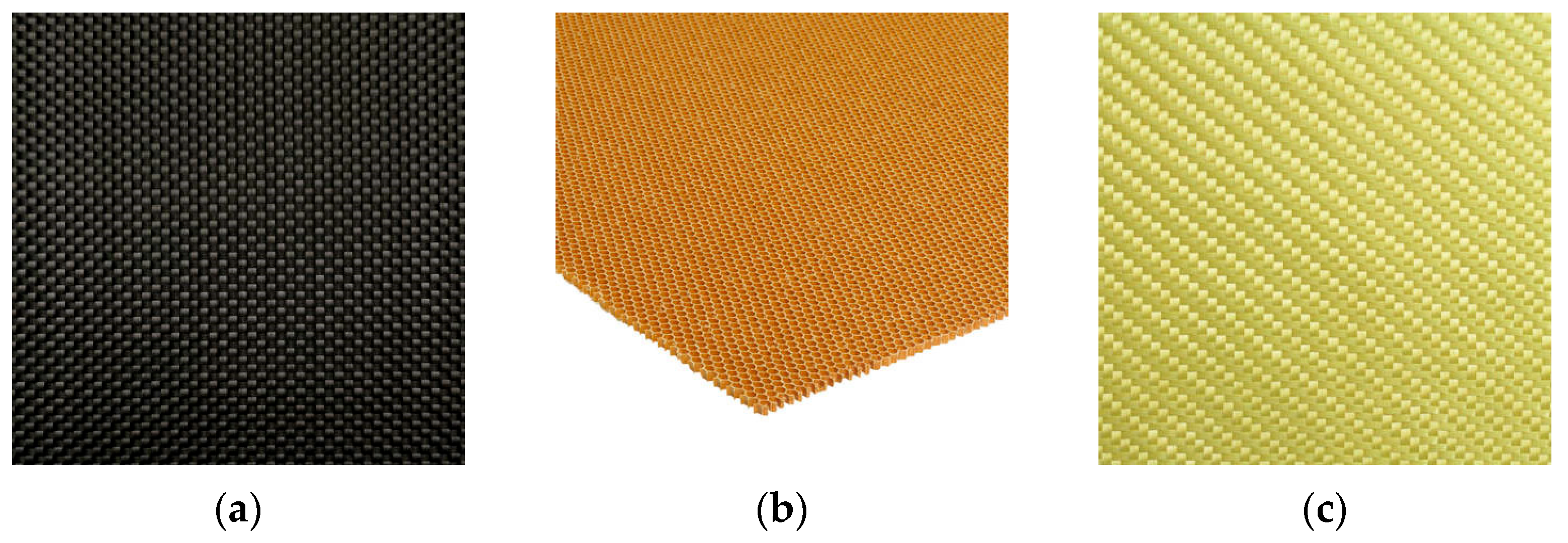
| Properties | Carbon Fiber | Nomex Honeycomb | Kevlar | Epoxy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.79 | 0.72 | 1.45 | 1.08–1.12 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 4120 | 2500 | 2900 | 70.0–80.0 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (MPa) | 234,000 | 5000 | 130,000 | 2500–3500 |
| Elongation (%) | 1.80 | 3–5 | 2.3 | 6.0–10.0 |
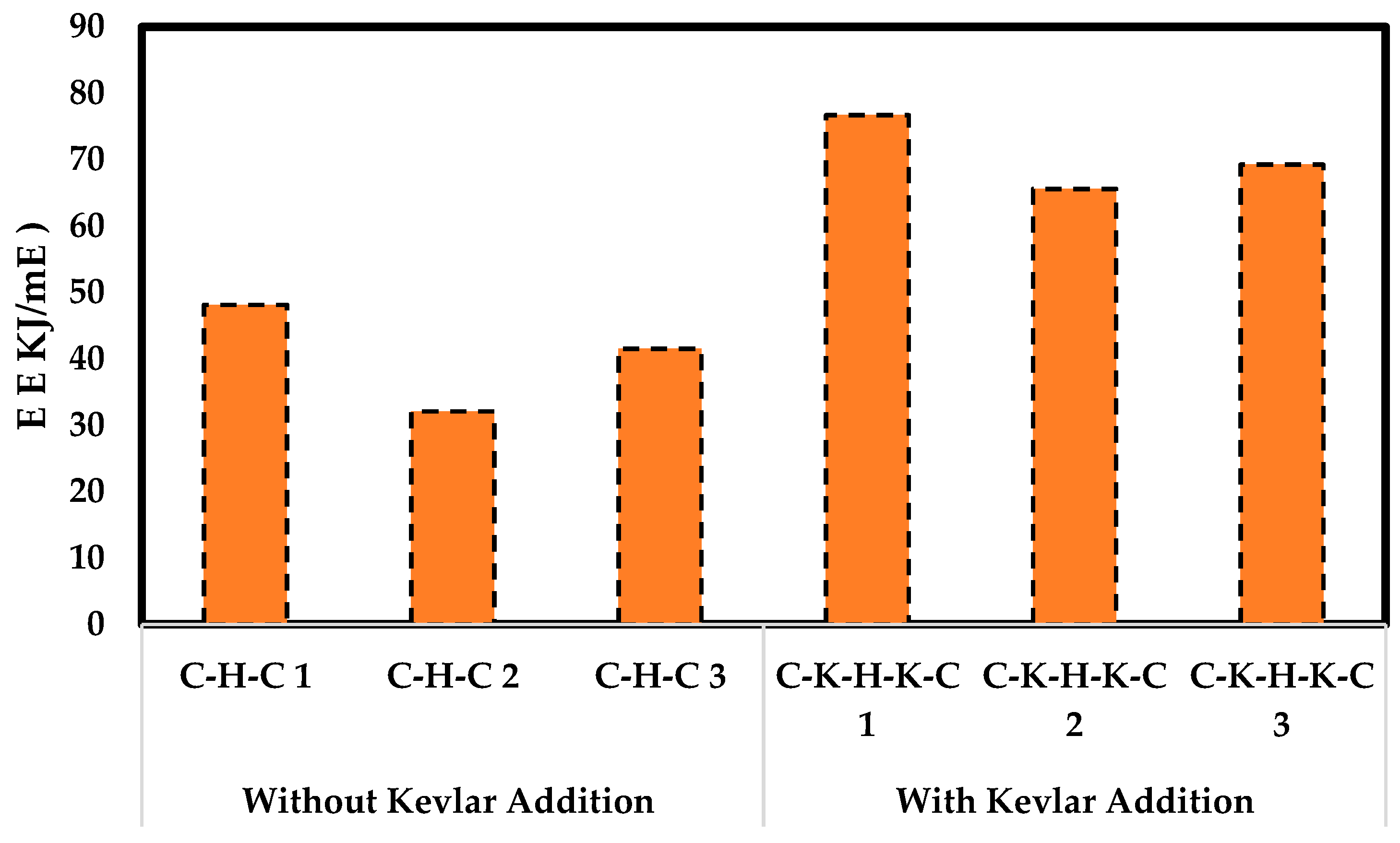
| Title 1 | β | α | Cos(β) − Cos(α) | E (J) | E (KJ/m2) | Average (KJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-H-C 1 | 134 | 151 | 0.17996 | 1.439 | 48.127 | 40.570 |
| C-H-C 2 | 139 | 151 | 0.11991 | 0.959 | 32.073 | |
| C-H-C 3 | 136 | 151 | 0.15528 | 1.241 | 41.505 | |
| C-K-H-K-C 1 | 126 | 151 | 0.28683 | 2.293 | 76.688 | 70.501 |
| C-K-H-K-C 2 | 129 | 151 | 0.24530 | 1.961 | 65.585 | |
| C-K-H-K-C 3 | 128 | 151 | 0.25896 | 2.070 | 69.230 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaman, Y.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, M.B.; Ashfaq, B.; Zafar, M.Q. A Comparative Analysis of the Impact Behavior of Honeycomb Sandwich Composites. Mater. Proc. 2025, 23, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025023003
Zaman Y, Ahmad S, Khan MB, Ashfaq B, Zafar MQ. A Comparative Analysis of the Impact Behavior of Honeycomb Sandwich Composites. Materials Proceedings. 2025; 23(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025023003
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaman, Yasir, Shahzad Ahmad, Muhammad Bilal Khan, Babar Ashfaq, and Muhammad Qasim Zafar. 2025. "A Comparative Analysis of the Impact Behavior of Honeycomb Sandwich Composites" Materials Proceedings 23, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025023003
APA StyleZaman, Y., Ahmad, S., Khan, M. B., Ashfaq, B., & Zafar, M. Q. (2025). A Comparative Analysis of the Impact Behavior of Honeycomb Sandwich Composites. Materials Proceedings, 23(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2025023003





