Optimization of Fe, Al, and Na Recovery from H2-Reduced Bauxite Residue (“Red Mud”) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
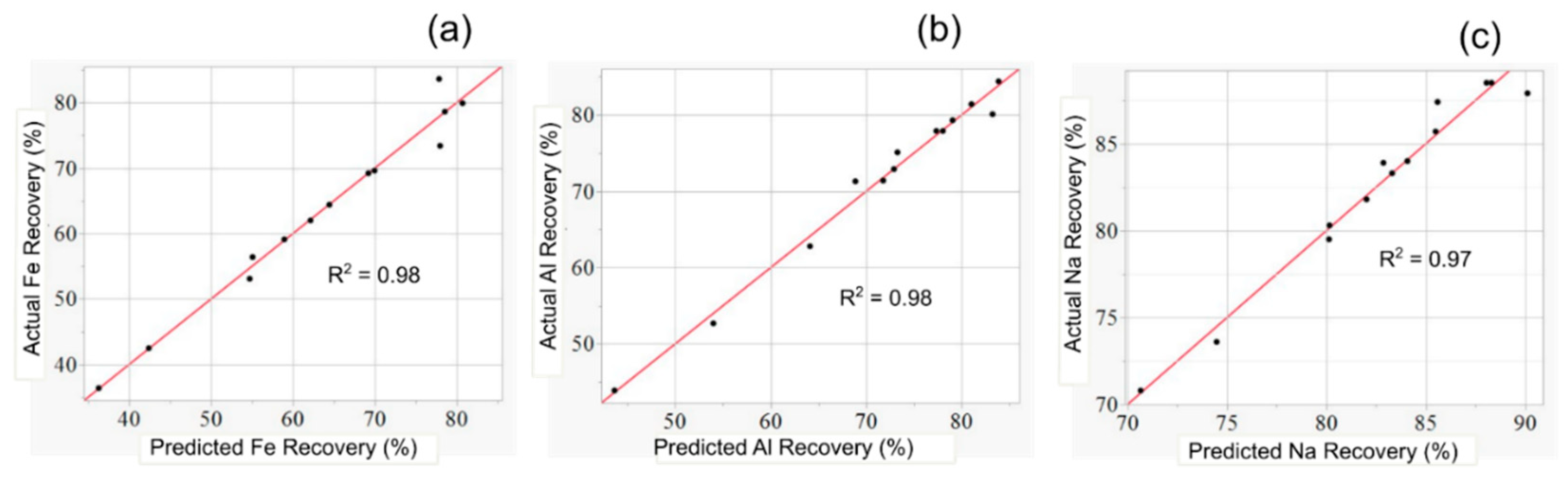
3.1. Evaluating Model Fit
3.2. ANOVA Analysis
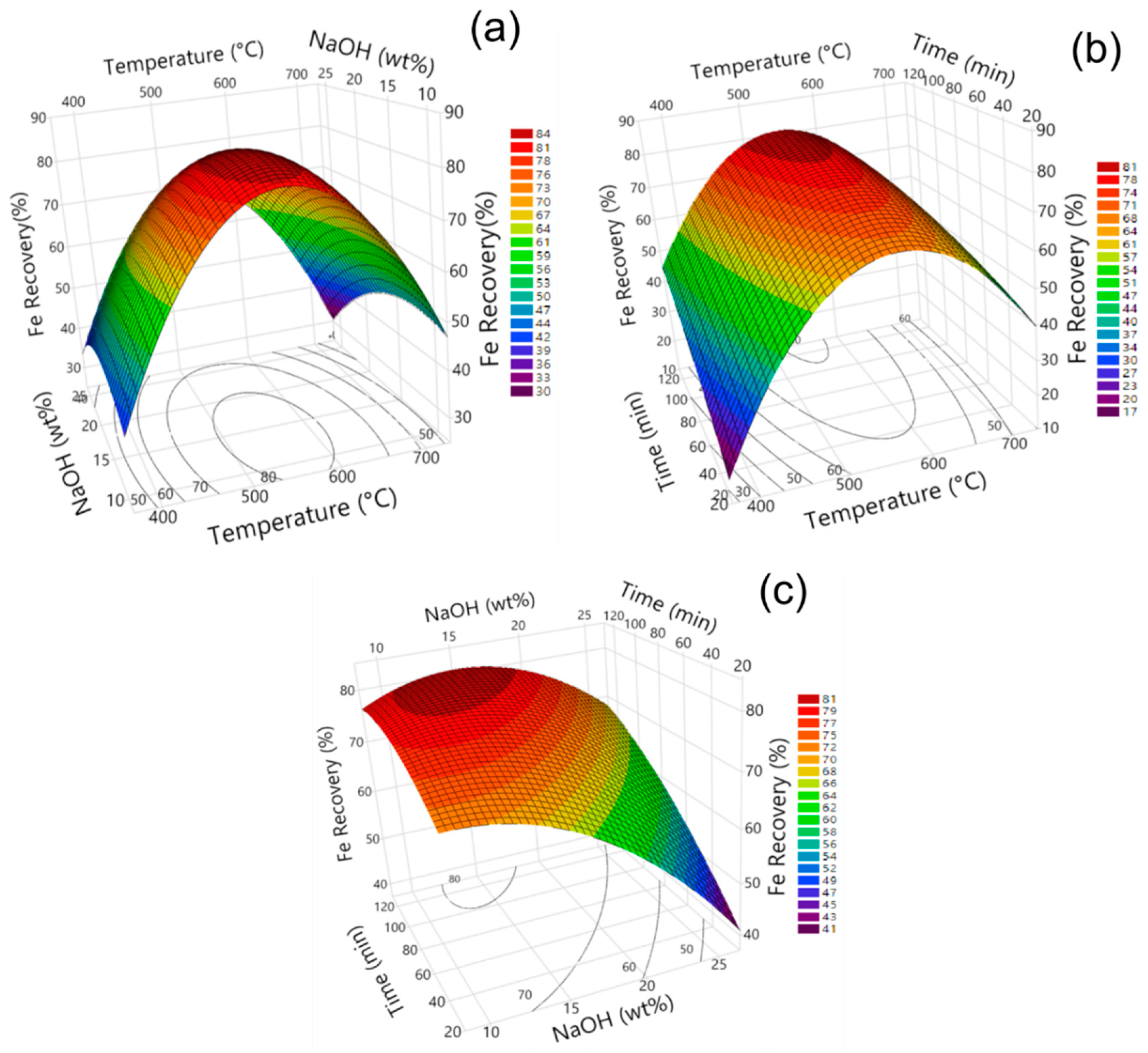
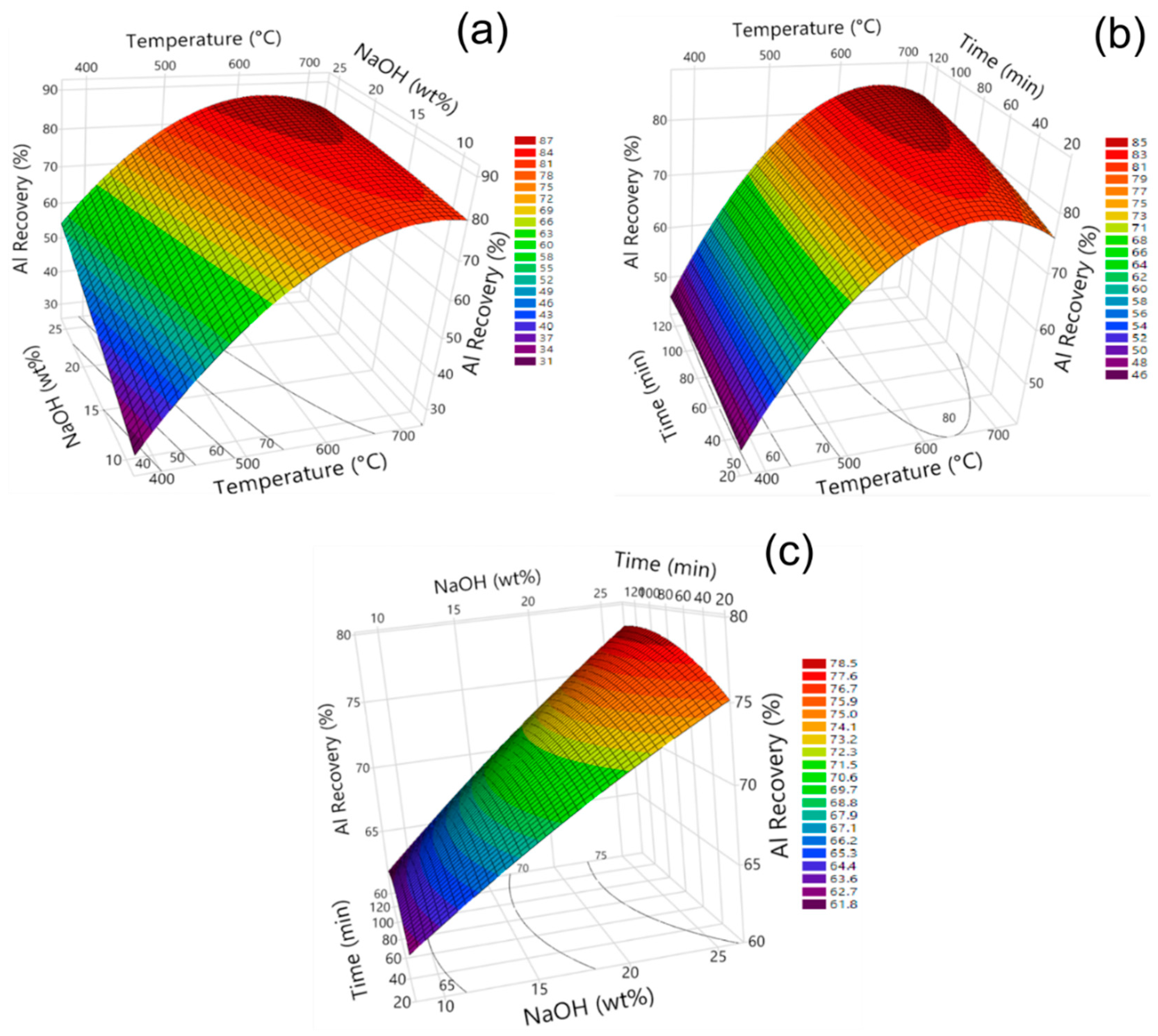
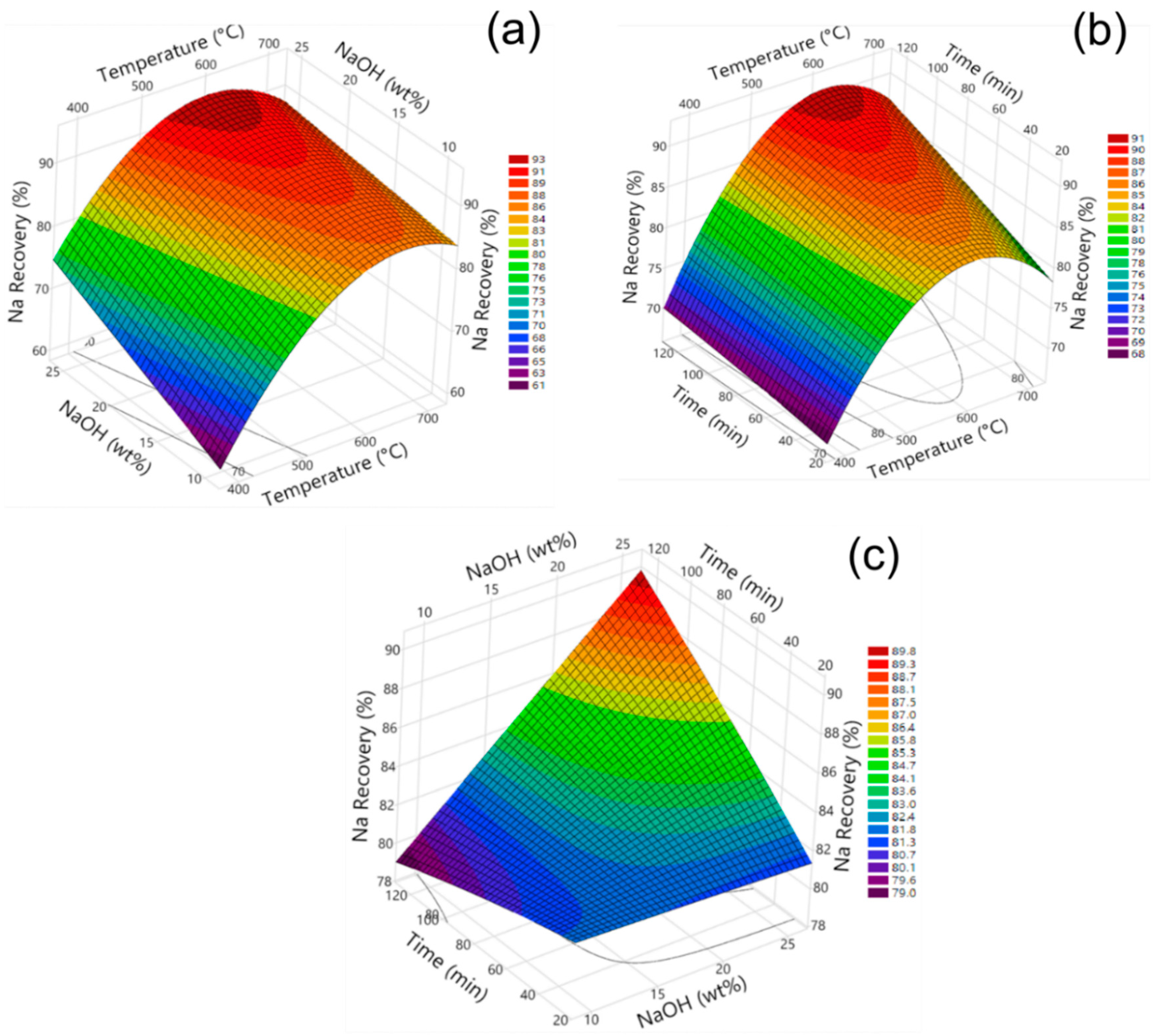
3.3. Influence of Model Parameters on Fe, Al, and Na Recovery
3.4. Process Optimization and Validation
4. Conclusions and Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, K. The History, Challenges, and New Developments in the Management and Use of Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Met. 2016, 2, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Han, Y.; He, F.; Gao, P.; Yuan, S. Characteristic, hazard, and iron recovery technology of red mud—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, A.; Pilla, G.; Kar, M.K.; Kowalczuk, P.B. An Invitation on Characterization of H2-Reduced Bauxite Residue and Recovering Iron through Wet Magnetic Separation Processes. Minerals 2023, 13, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelari, S.; Gamaletsos, P.N.; Pilla, G.; Pontikes, Y.; Blanpain, B. Developing a Low-Temperature, Carbon-Lean Hybrid Valorisation Process for Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) Towards Metallic Fe and Al Recovery. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 9, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, C.R.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Recovery of Rare Earths and Major Metals from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) by Alkali Roasting, Smelting, and Leaching. J. Sustain. Met. 2016, 3, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenia, C.; Balomenos, E.; Panias, D. Iron Recovery from Bauxite Residue through Reductive Roasting and Wet Magnetic Separation. J. Sustain. Met. 2018, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samouhos, M.; Taxiarchou, M.; Pilatos, G.; Tsakiridis, P.; Devlin, E.; Pissas, M. Controlled reduction of red mud by H2 followed by magnetic separation. Miner. Eng. 2017, 105, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, G.; Kapelari, S.V.; Hertel, T.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y. Hydrogen reduction of bauxite residue and selective metal recovery. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 57, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, G.; Hertel, T.; Kapelari, S.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y. Reactions and phase transformations during the low-temperature reduction of bauxite residue by H2 in the presence of NaOH, and recovery rates downstream. In Proceedings of the 40th International ICSOBA Conference, Athens, Greece, 10–14 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Anawati, J.; Azimi, G. Integrated carbothermic smelting–Acid baking–Water leaching process for extraction of scandium, aluminum, and iron from bauxite residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Chu, M.; Wang, H.-T.; Zhao, W.; Gao, L.-H. Modeling assessment of recovering iron from red mud by direct reduction: Magnetic separation based on response surface methodology. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2018, 25, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, A.; Pilla, G.; Hertel, T.; Pontikes, Y.; Kowalczuk, P.B. H2-reduction of bauxite residue and iron recovery through magnetic separation. In Proceedings of the 17th International Mineral Processing Symposium, İstanbul, Turkey, 15 December 2022; Turkish Mining Development Foundation: İstanbul, Turkey; pp. 233–243. [Google Scholar]
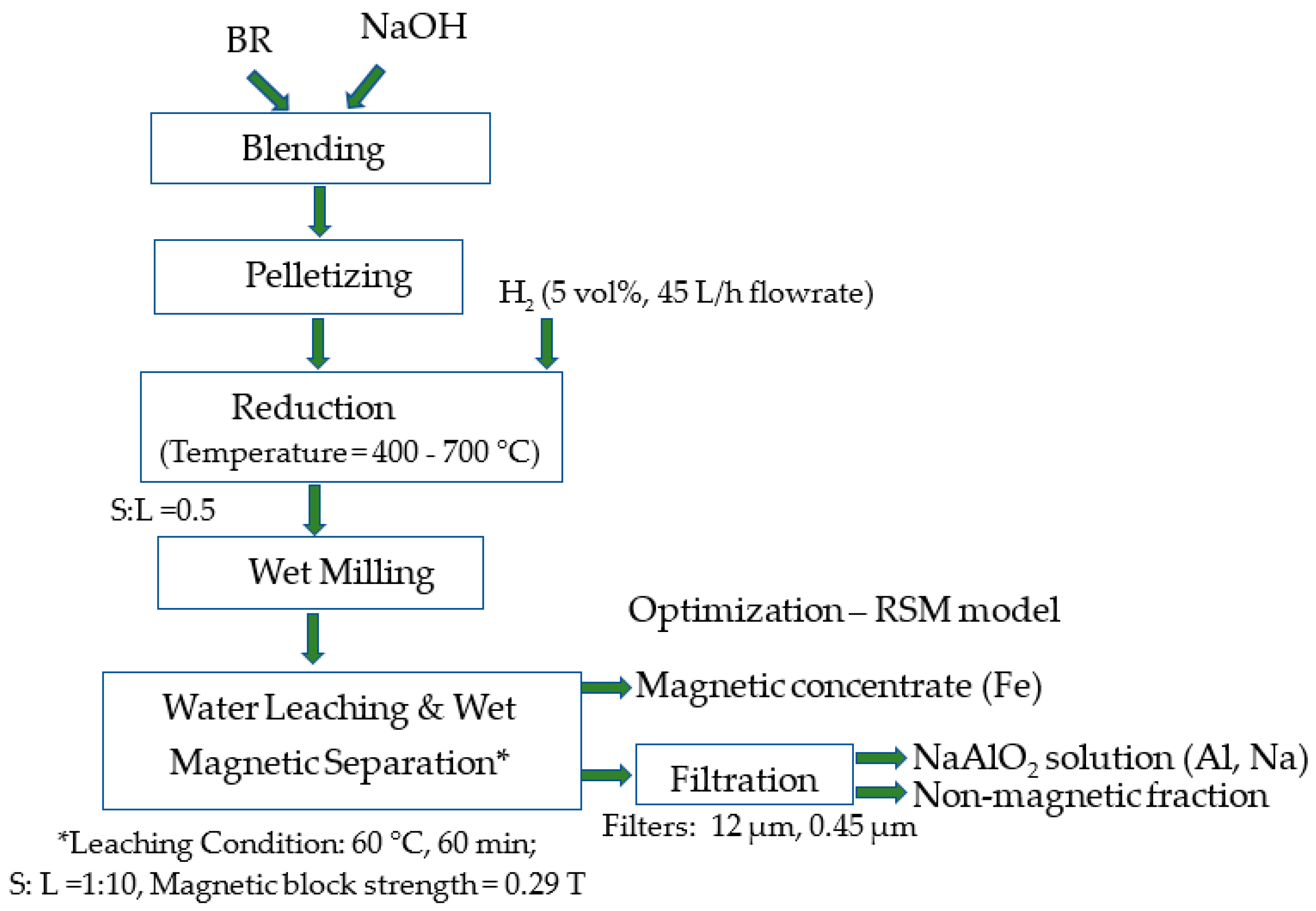
| Experiment Run | Variables | Response (Experimental Data of Recovery,%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduction Temperature (°C)–x1 | Reduction Time (min)–x2 | NaOH Concentration (wt%)–x3 | Fe | Al | Na | |
| 1 | 500 | 120 | 10 | 78 | 62 | 79 |
| 2 | 500 | 120 | 15 | 79 | 71 | 83 |
| 3 | 500 | 120 | 20 | 83 | 75 | 87 |
| 4 | 500 | 120 | 25 | 69 | 77 | 88 |
| 5 | 500 | 30 | 20 | 62 | 71 | 81 |
| 6 | 500 | 60 | 20 | 69 | 72 | 83 |
| 7 | 400 | 120 | 20 | 53 | 52 | 73 |
| 8 | 600 | 120 | 20 | 73 | 80 | 87 |
| 9 | 700 | 120 | 20 | 56 | 84 | 88 |
| 10 | 700 | 120 | 10 | 59 | 81 | 85 |
| 11 | 700 | 30 | 10 | 64 | 77 | 84 |
| 12 | 700 | 30 | 25 | 36 | 79 | 80 |
| 13 | 400 | 30 | 10 | 42 | 43 | 70 |
| Source | Variable | R2 | Adj. R2 | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quadratic | Fe recovery | 0.98 | 0.90 | 4.4 |
| Al recovery | 0.98 | 0.94 | 2.8 | |
| Na recovery | 0.97 | 0.88 | 1.9 |
| Item | Fe Recovery (%) | Range in Fe Recovery (%) | Al Recovery (%) | Range in Al Recovery (%) | Na Recovery (%) | Range in Na Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted | 75.8 | 67–84 | 84 | 78–89 | 90 | 96–94 |
| Actual | 73.4 | -- | 80.1 | -- | 87.9 | -- |
| Deviation | −2.4 | -- | −3.9 | -- | −2.1 | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pilla, G.; Hertel, T.; Pontikes, Y. Optimization of Fe, Al, and Na Recovery from H2-Reduced Bauxite Residue (“Red Mud”) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Mater. Proc. 2023, 15, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015085
Pilla G, Hertel T, Pontikes Y. Optimization of Fe, Al, and Na Recovery from H2-Reduced Bauxite Residue (“Red Mud”) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Materials Proceedings. 2023; 15(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015085
Chicago/Turabian StylePilla, Ganesh, Tobias Hertel, and Yiannis Pontikes. 2023. "Optimization of Fe, Al, and Na Recovery from H2-Reduced Bauxite Residue (“Red Mud”) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM)" Materials Proceedings 15, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015085
APA StylePilla, G., Hertel, T., & Pontikes, Y. (2023). Optimization of Fe, Al, and Na Recovery from H2-Reduced Bauxite Residue (“Red Mud”) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Materials Proceedings, 15(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015085







