High-Performance Solid-Phase Extraction Chromatography for Recycling of NdFeB Magnet Waste †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Experimental Procedure
- Cleaning: 14 column volumes (CVs) of absolute ethanol (0.1 to 1 mL/min).
- Conditioning: 20 CVs of 65 vol.% ethanol (1 mL/min).
- Impregnation: 15 CVs of 0.75 mol D2EHPA in 65 vol.% ethanol (0.6 to 1 mL/min).
- Flushing: 20 CVs MilliQ-grade water (0.2 to 2 mL/min).
2.4. Analytical Method
3. Results and Discussion
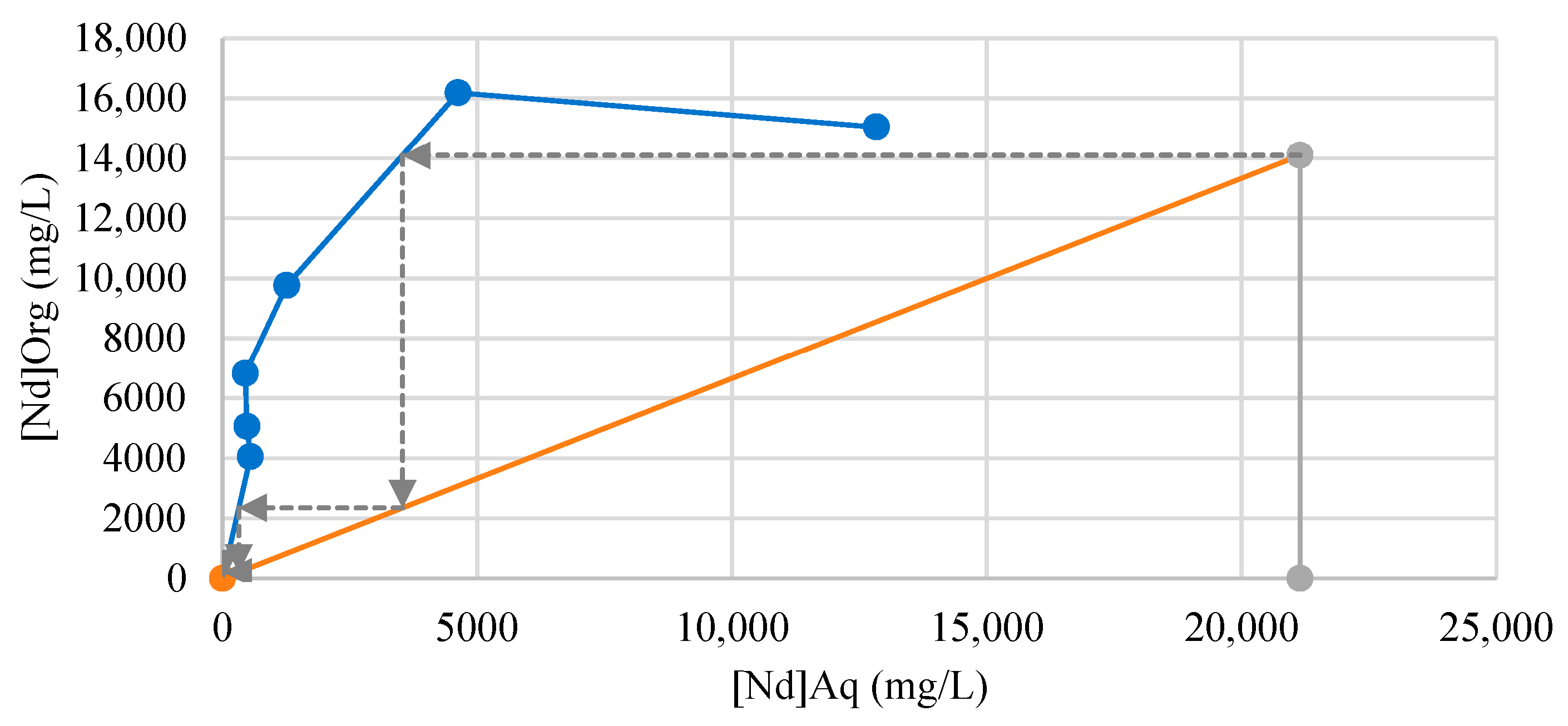
3.1. REE Solvent Extraction
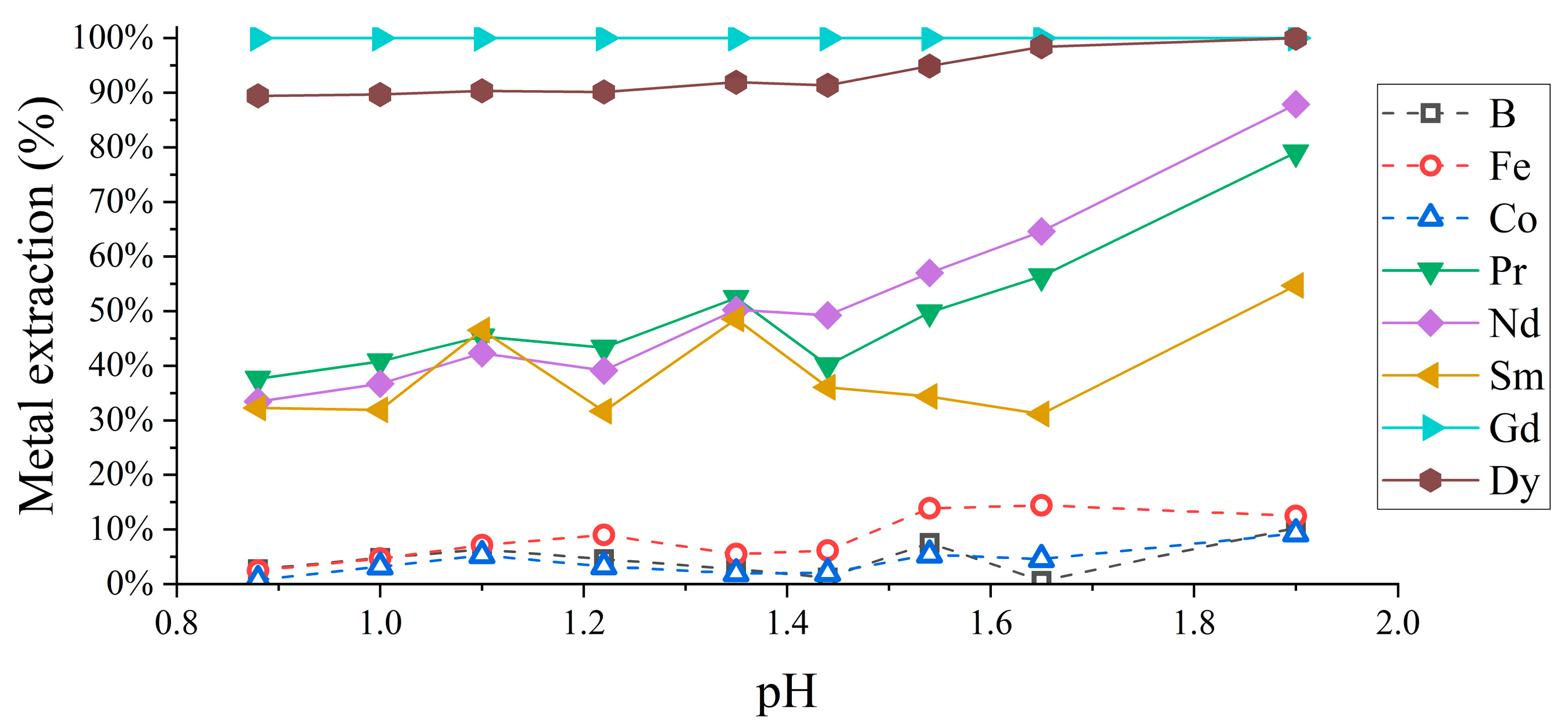
3.1.1. REE Extraction pH Dependence
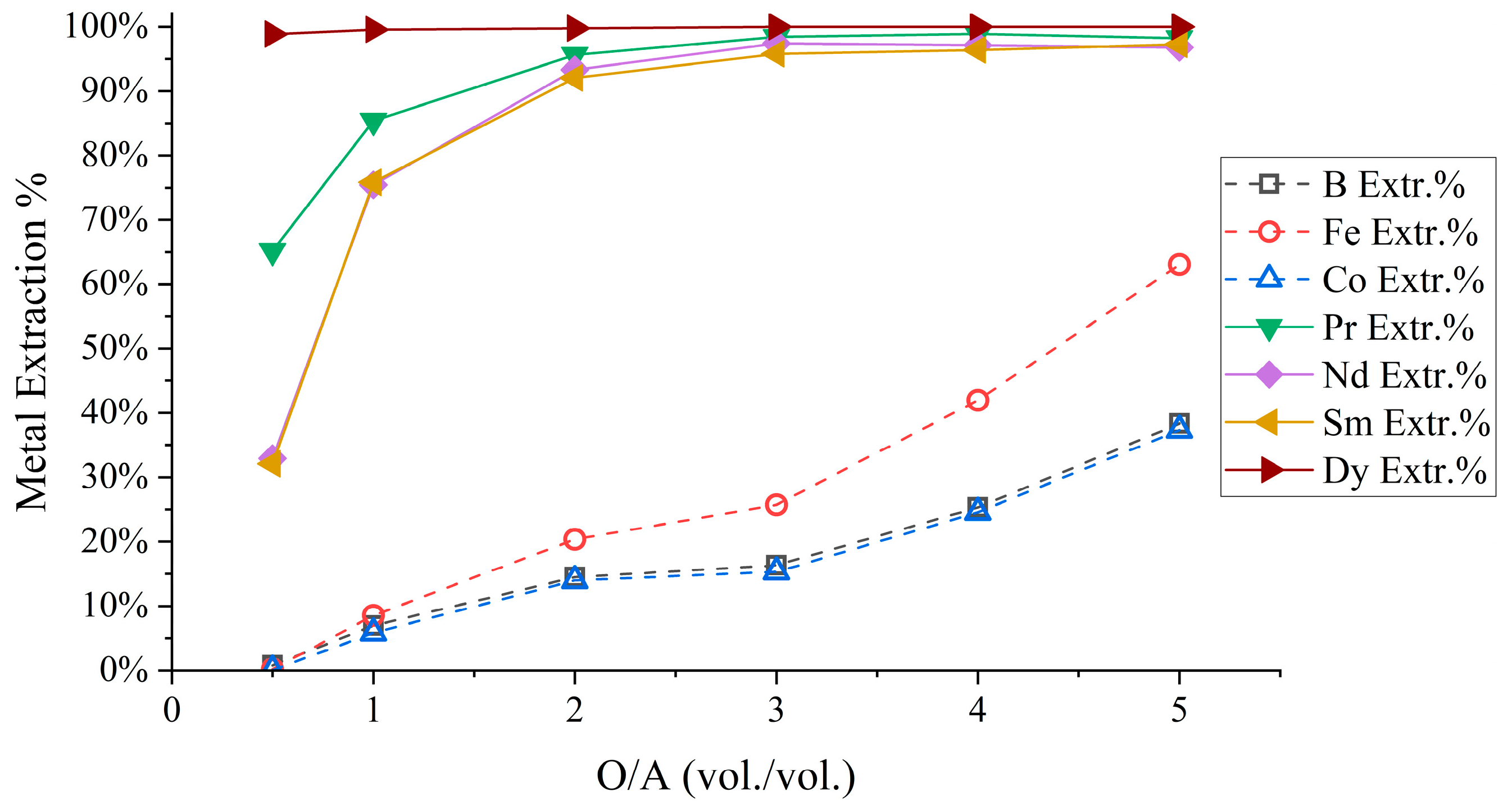
3.1.2. REE Separation Optimization
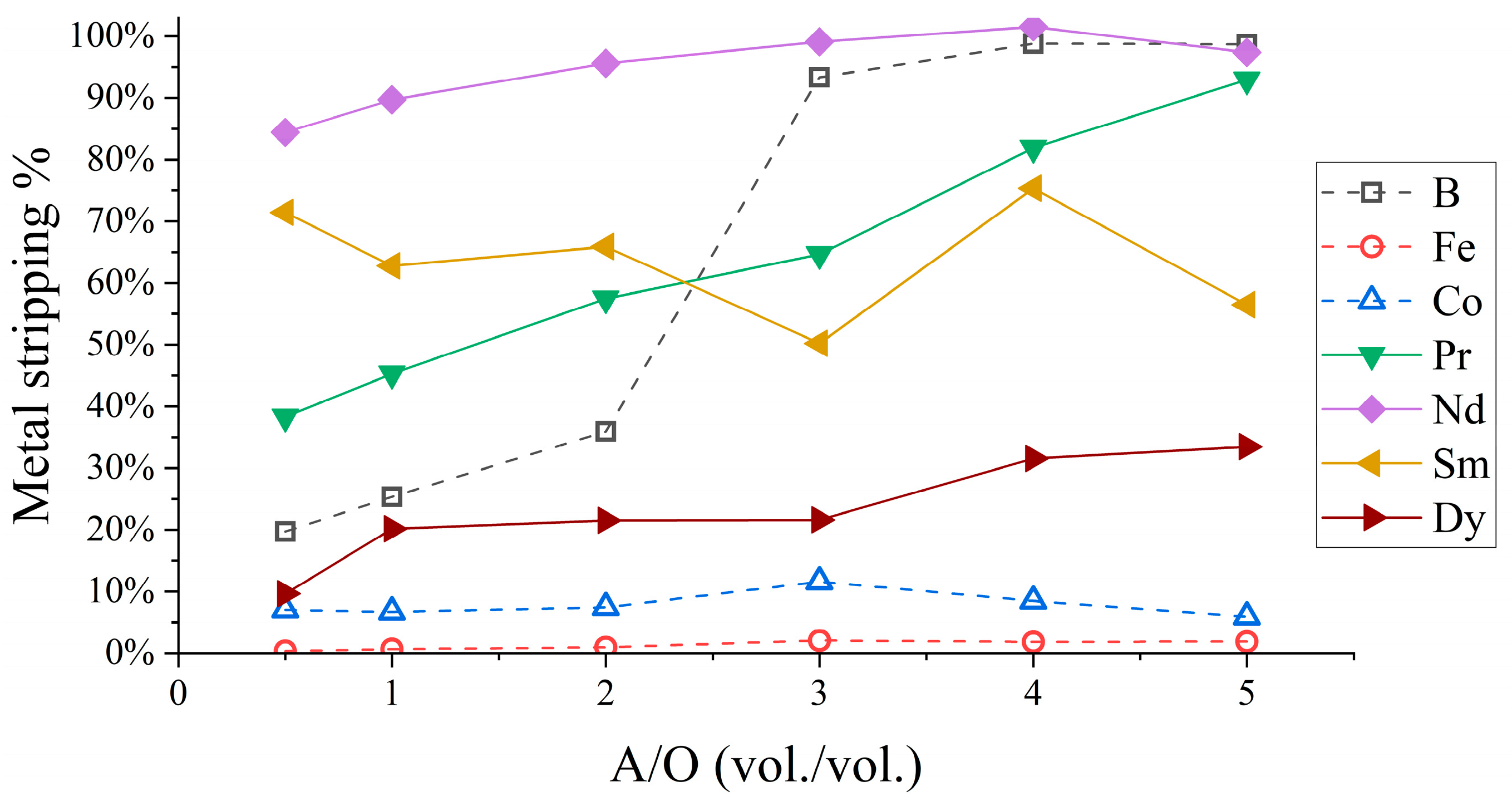
3.1.3. Organic Stripping and Scrubbing
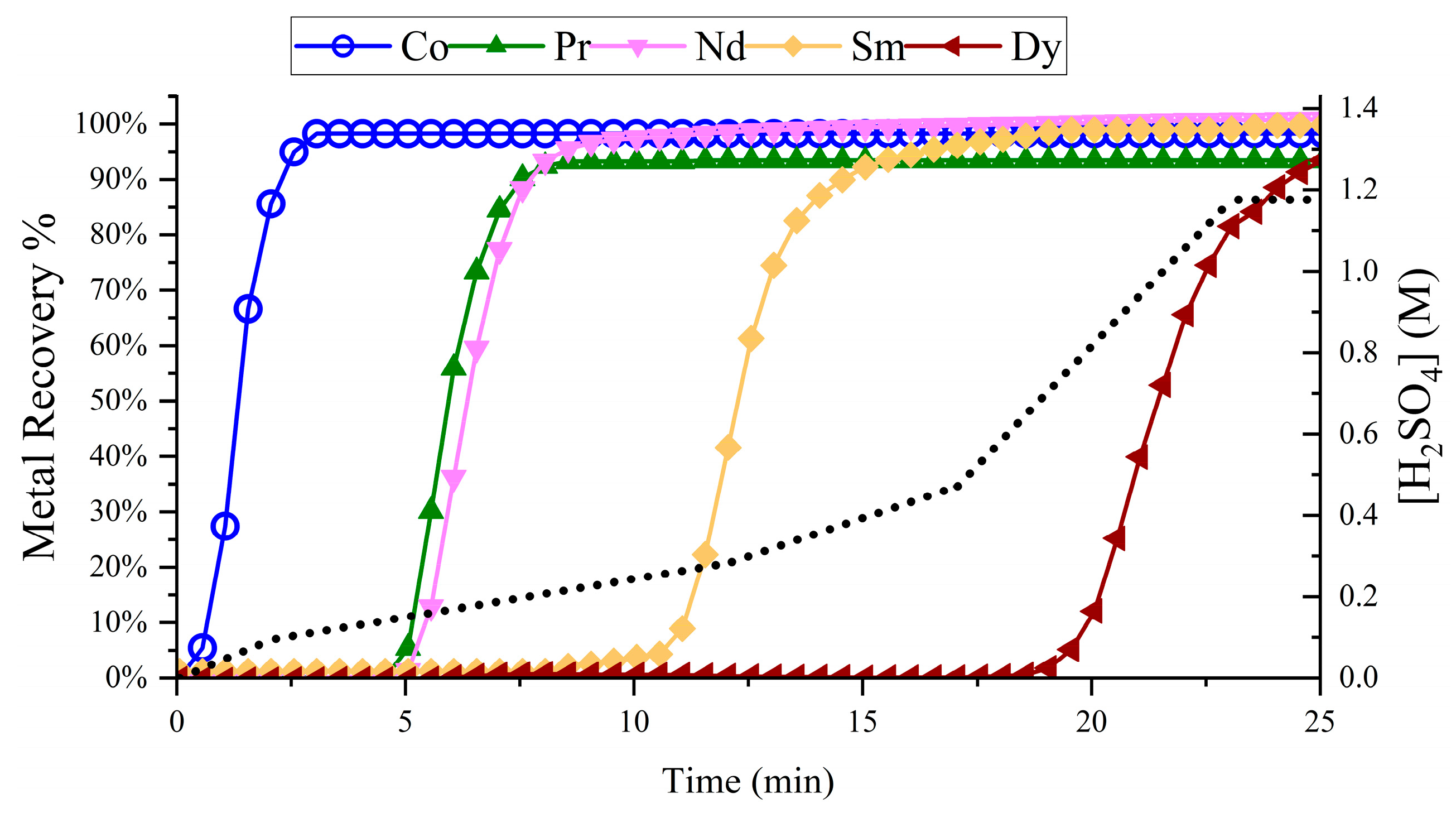
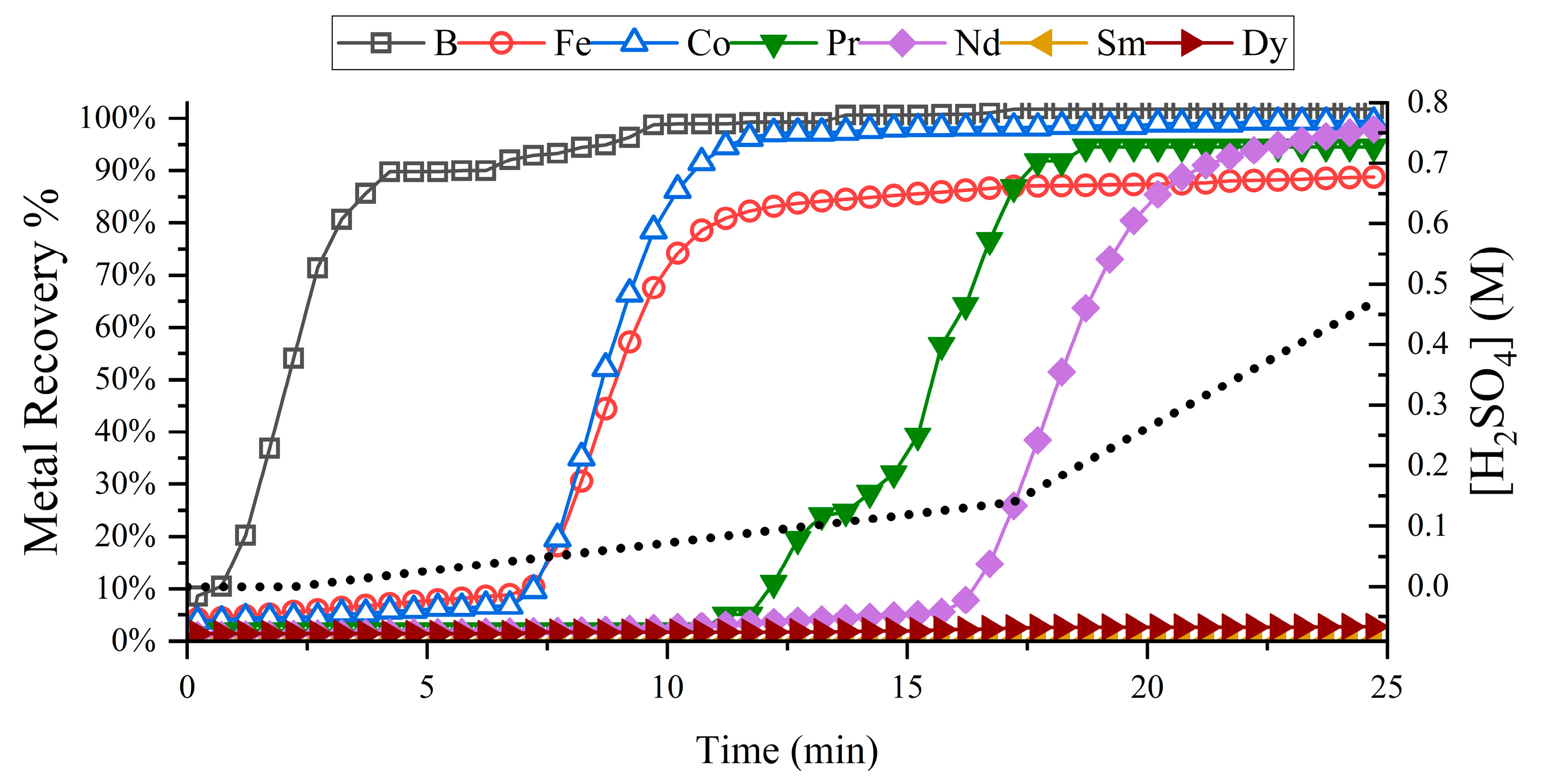
3.2. REE Chromatographic Separation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. Perspectives for the Recovery of Rare Earths from End-of-Life Fluorescent Lamps. J. Rare Earths 2014, 32, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Binnemans, K. From NdFeB Magnets towards the Rare-Earth Oxides: A Recycling Process Consuming Only Oxalic Acid. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 64099–64111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petranikova, M.; Herdzik-Koniecko, I.; Steenari, B.-M.; Ekberg, C. Hydrometallurgical Processes for Recovery of Valuable and Critical Metals from Spent Car NiMH Batteries Optimized in a Pilot Plant Scale. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 171, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Kumari, A.; Panda, R.; Rajesh Kumar, J.; Yoo, K.; Lee, J.Y. Review on Hydrometallurgical Recovery of Rare Earth Metals. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 161, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission, Directorate-General for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs; Grohol, M.; Veeh, C. Study on the Critical Raw Materials for the EU 2023: Final Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiró, L.T.; Méndez, G.V.; Ayres, R.U. Material Flow Analysis of Scarce Metals: Sources, Functions, End-Uses and Aspects for Future Supply. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2939–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, A.; Senin, H.B.; Idris, N.H. Effects of Zr Substitution in NdFeB Permanent Magnets. AIP Conf. Proc. 2007, 909, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sole, K.C. Solvent Extraction in the Hydrometallurgical Processing and Purification of Metals: Process Design and Selected Applications. In Solvent Extraction and Liquid Membranes: Fundamentals and Applications in New Materials; Aguilar, M., Cortina, J.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 141–200. ISBN 9780824740153. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, C.K. Extractive Metallurgy of Rare Earths; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-415-33340-7alk. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, M.; Forsberg, K.; Kloo, L.; Martinez De La Cruz, J.; Rasmuson, Å. Separation of ND(III), DY(III) and Y(III) by Solvent Extraction Using D2EHPA and EHEHPA. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 156, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, G.-S. Solvent Extraction of Neodymium Ions from Hydrochloric Acid Solution Using PC88A and Saponified PC88A. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 46, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.; Bailey, P.J.; Tasker, P.A.; Turkington, J.R.; Grant, R.A.; Love, J.B. Solvent Extraction: The Coordination Chemistry behind Extractive Metallurgy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Liu, Y.; Jeon, H.S. Solvent Extraction of Pr and Nd from Chloride Solution by Mixtures of Acidic Extractants and LIX 63. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2016, 54, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul, M.; Topkaya, Y.; Karakaya, İ. Rare Earth Double Sulfates from Pre-Concentrated Bastnasite. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 93, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, D.; Deblonde, G.J.-P.; Bélair, S.; Weigel, V. Recovery of Yttrium and Lanthanides from Sulfate Solutions with High Concentration of Iron and Low Rare Earth Content. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 157, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of Rare Earths: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kifle, D.; Wibetoe, G.; Frøseth, M.; Bigelius, J. Impregnation and Characterization of High Performance Extraction Columns for Separation of Metal Ions. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2013, 31, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Kifle, D.; Wibetoe, G. A Rapid Impregnation Method for Loading Desired Amounts of Extractant on Prepacked Reversed-Phase Columns for High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Separation of Metal Ions. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1500, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanku, M.G.; Forsberg, K.; Svärd, M. Impregnation of Preparative High-performance Solid Phase Extraction Chromatography Columns by Organophosphorus Acid Compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1676, 463278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Zhang, T.A.; Dreisinger, D.; Doyle, F. A Critical Review on Solvent Extraction of Rare Earths from Aqueous Solutions. Miner. Eng. 2014, 56, 10–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, C.; Dittrich, L.; Dunn, G.M. Method of Dissolution and Separation of Critical Raw Materials (CRM) 2020. EP Patents 3702479 A1, 2 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, A.R.; Pickering, R.W. Improved Leaching Technologies in the Electrolytic Zinc Industry. Metall. Trans. B 1975, 6, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, P.T.; Scott, T.R. Removal of Iron from Leach Liquors by the “Goethite” Process. Hydrometallurgy 1976, 2, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, R.; Dorfling, C.; Bradshaw, S.M. Characterization of Precipitate Formed during the Removal of Iron and Precious Metals from Sulphate Leach Solutions. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2017, 117, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, H.-K.; Max-Hansen, M.; Jönsson, C.; Borg, N.; Nilsson, B. Experimental Productivity Rate Optimization of Rare Earth Element Separation through Preparative Solid Phase Extraction Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1348, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramzan, M.; Kifle, D.; Wibetoe, G. Comparative Study of Stationary Phases Impregnated with Acidic Organophosphorus Extractants for HPLC Separation of Rare Earth Elements. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemettinen, A.; Adamski, Z.; Chojnacka, I.; Leśniewicz, A.; Rycerz, L. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from the Leaching Solutions of Spent NdFeB Permanent Magnets by Selective Precipitation of Rare Earth Oxalates. Minerals 2023, 13, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilatovskaia, M.; Lonski, O.; Löffler, M.; Blenau, L.; Charitos, A.; Fabrichnaya, O. Phase Relations in the CaO-Nd2O3-Al2O3 System in Application for Rare Earth Recycling. JOM 2023, 75, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Metal | NdFeB Material wt.% (kg/kg) | Pregnant Leach Solution Composition (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| B | 0.973% ± 0.017% | 787.7 ± 23.4 |
| Fe | 65.0% ± 0.7% | 62,860 ± 649 |
| Co | 3.20% ± 0.02% | 2723 ± 47 |
| Cu | 0.148% ± 0.023% | 11.64 ± 10.32 |
| Pr | 0.965% ± 0.003% | 1522 ± 166 |
| Nd | 22.9% ± 0.1% | 20,493 ± 276 |
| Sm | 0.911% ± 0.004% | 594.9 ± 136.3 |
| Gd | 0.144% ± 0.006% | 51.49 ± 8.92 |
| Dy | 6.57% ± 0.02% | 6368 ± 275 |
| Total | 100.9% ± 0.9% | 95,412 ± 1592 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Punt, T.; Forsberg, K.; Svärd, M. High-Performance Solid-Phase Extraction Chromatography for Recycling of NdFeB Magnet Waste. Mater. Proc. 2023, 15, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015067
Punt T, Forsberg K, Svärd M. High-Performance Solid-Phase Extraction Chromatography for Recycling of NdFeB Magnet Waste. Materials Proceedings. 2023; 15(1):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015067
Chicago/Turabian StylePunt, Tiaan, Kerstin Forsberg, and Michael Svärd. 2023. "High-Performance Solid-Phase Extraction Chromatography for Recycling of NdFeB Magnet Waste" Materials Proceedings 15, no. 1: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015067
APA StylePunt, T., Forsberg, K., & Svärd, M. (2023). High-Performance Solid-Phase Extraction Chromatography for Recycling of NdFeB Magnet Waste. Materials Proceedings, 15(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015067








