Innovative Roadmap for Smart Water Cities: A Global Perspective †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Issues in Urban Cities
2.1. Urbanization
2.2. Water Infrastructure That Is Undervalued
2.3. Living Condition
2.4. Strengthening of Institutional Capability
2.5. Technical Advancement
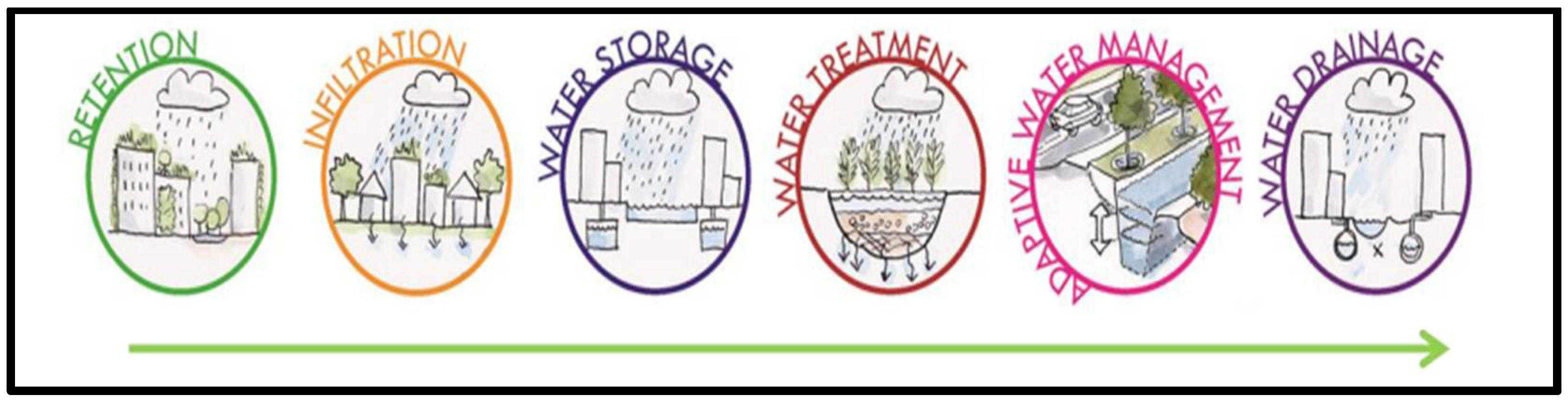
2.6. Water Logging
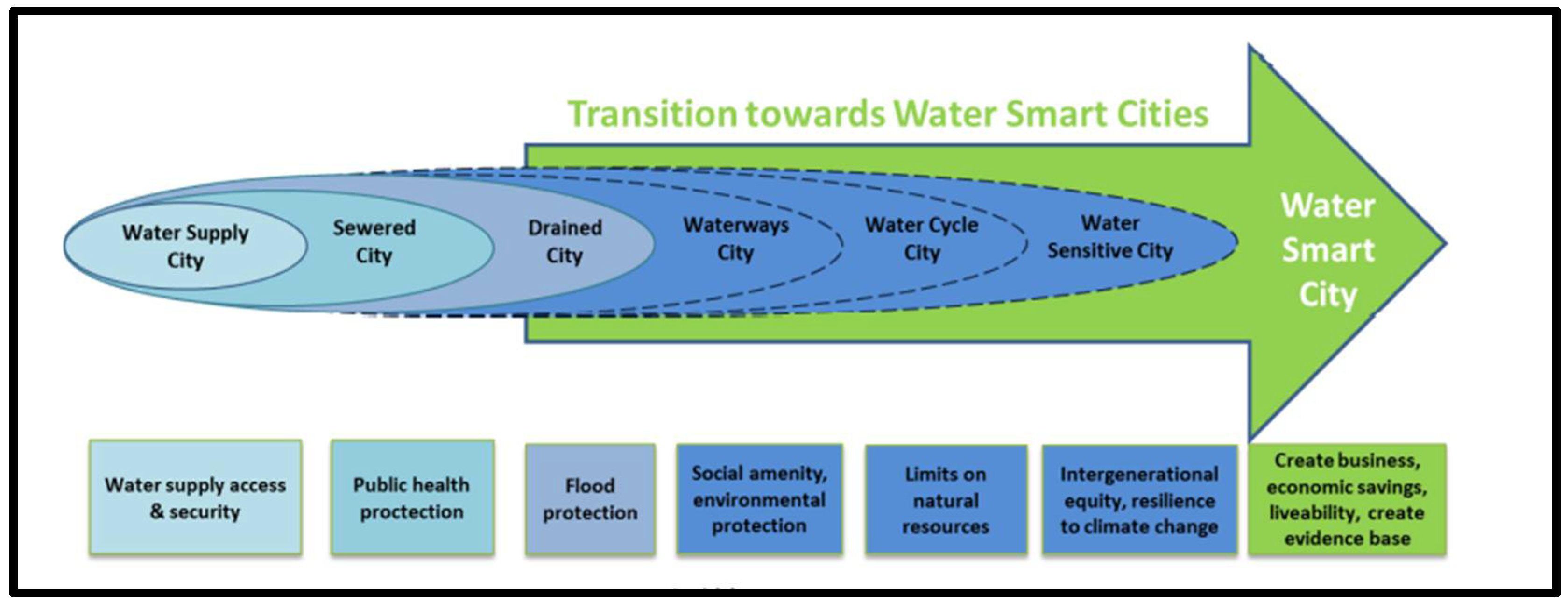
2.7. Water Smart City Approach
Water-Smart City Benefits
- Integrating water and green spaces into urban areas to create places where people want to live, work, or play is the first step in creating beautiful locations where people want to live, work, and play.
- Increase in the value of properties near open water and green space.
- The goal is to reduce the danger of flooding and to safeguard and enhance the quality of ground and surface water.
- Reduce the urban heat island effect and noise, and enhance air quality, to create a healthy city.
- Restoring reduced groundwater levels and improving soil moisture.
- Promoting and enhancing local biodiversity and natural environments.
- Give the community a much-needed water supply.
- Raise public awareness of and enhance knowledge of the management and utilization of runoff from their development.
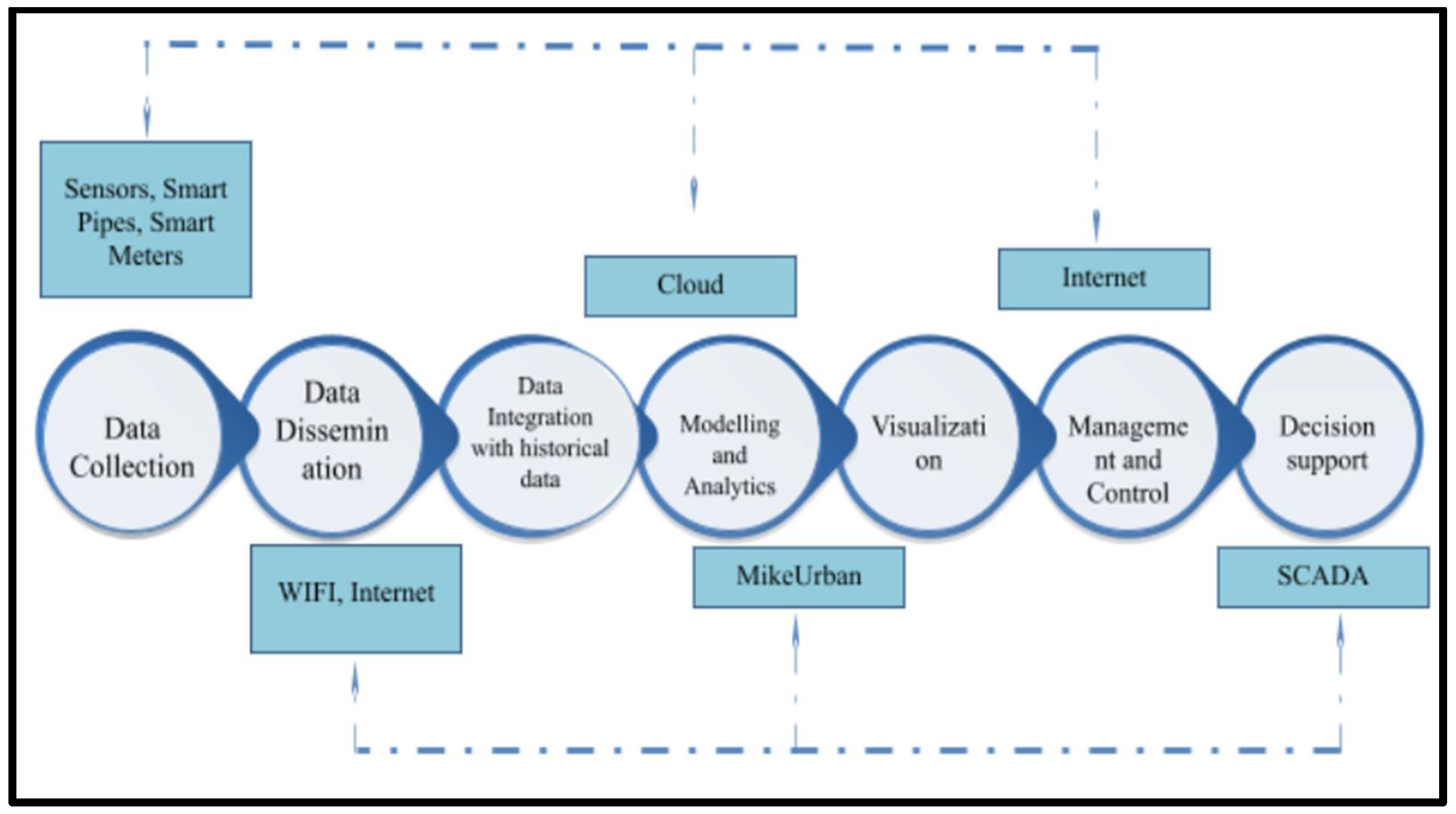
3. Methodology for Smart Water City
- Acquisition and integration of data is the first step (e.g., sensor networks, smart pipes, and smart meters).
- Radio transmitters, wireless fidelity (WiFi), and the Internet are examples of data delivery methods.
- Geospatial modelling and analytics (either via the use of GIS, Mike Urban, Aquacycle, AISUWRS, or urban groundwater sustainability) is the third part of this section (UGROW).
- This section deals with the actual processing and archiving of data.
- Visualizing and making decisions (e.g., web-based communication and information systems tools).
- Data and information return to cities’ technological services and end users (e.g., tools for sharing information on water and on services).
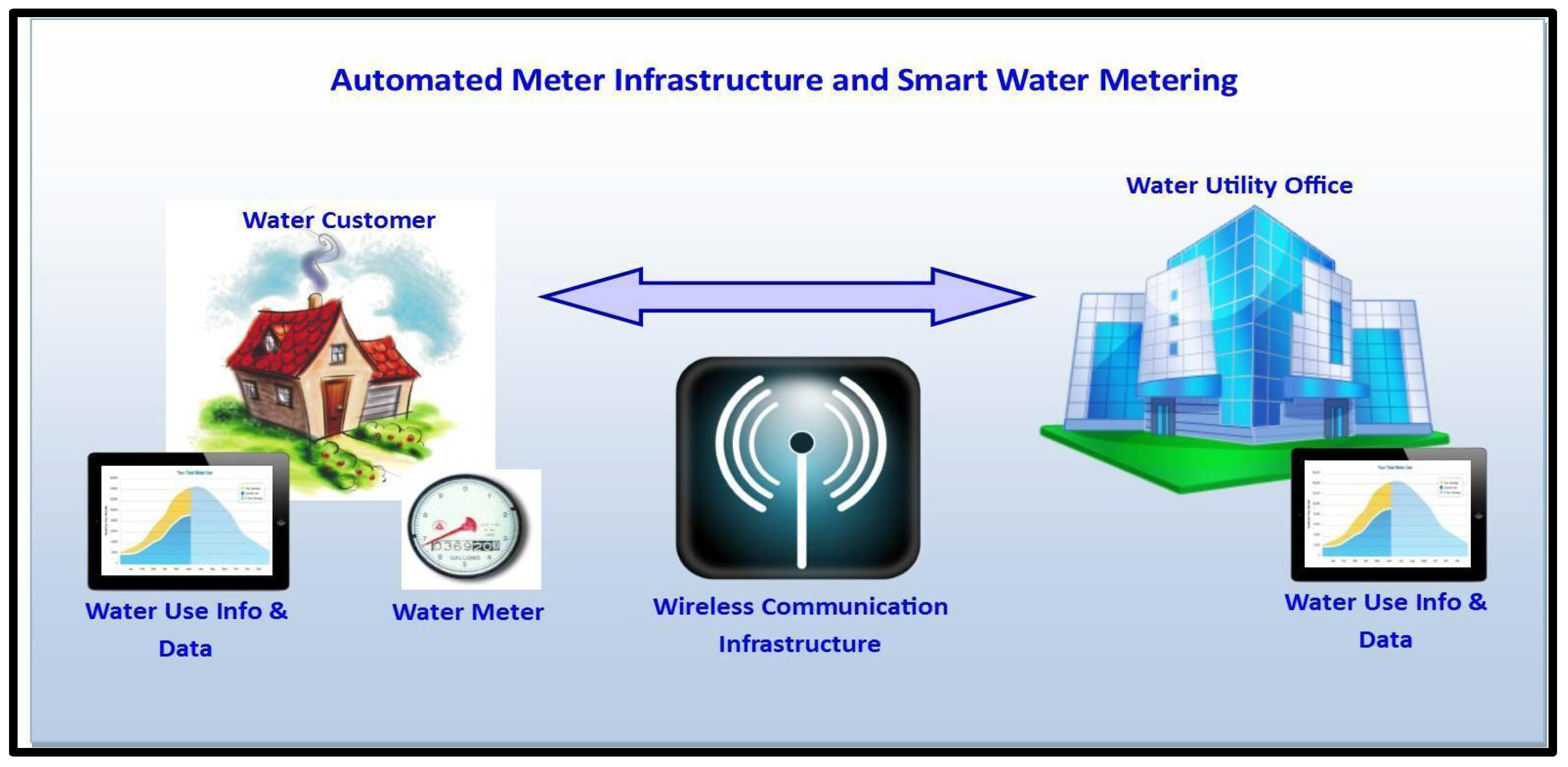
3.1. Smart Meters
3.2. Communication Modems
3.3. Information Systems Based on Geographic Data (GIS)
3.4. Computing in the Cloud
- Data gathering and monitoring (SCADA)
- Integrating SWM: Improving Water Management in Cities
4. Results and Discussion—Global Case Study
4.1. The Netherlands—Amsterdam
Wet-Proofed City of Amsterdam
4.2. Denmark—Copenhagen
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asadi, S.; Heshmati, M.; Dia, H.; Ghaderi, H.; Pettit, C. Blockchain: The operating system of smart cities. Cities 2021, 112, 103104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertone, E.; Sahin, O.; Stewart, R.A.; Zou, P.; Alam, M.; Blair, E. Gulf Organisation for Research and Development State-of-the-art review revealing a roadmap for public building water and energy efficiency retrofit projects. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2016, 5, 526–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caird, S. City approaches to smart city evaluation and reporting: Case studies in the United Kingdom. Urban Res. Pract. 2017, 11, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caird, S.P.; Hallett, S.H. Towards evaluation design for smart city development. J. Urban Des. 2018, 24, 188–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, T. Smart Water Solutions for Smart Cities. In Smart Cities; McClellan, S., Jimenez, J., Koutitas, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchina, L.; Calabrese, A.; Inzerilli, G.; Scatto, E.; Brutti, G. Thinking green: The role of smart technologies in transforming cities’ waste and supply Chain’s flow. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 2, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourbesville, P. Key Challenges for Smart Water. Procedia Eng. 2016, 154, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; El-zaart, A.; Adams, C. Smart Sustainable Cities Roadmap: Readiness for Transformation towards Urban Sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 37, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jnr, B.A.; Petersen, S.A.; Ahlers, D.; Krogstie, J. API deployment for big data management towards sustainable energy prosumption in smart cities-a layered architecture perspective. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2019, 39, 263–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, M.; Juhola, S.; Klein, J. The role of scale in integrating climate change adaptation and mitigation in cities. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2018, 62, 741–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.; Chen, C.; Yu, H. Technology roadmap for building a smart city: An exploring study on methodology. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzimakwe, T.I. Urbanisation and Future Smart Cities: Challenges of Water and Sanitation Services. In Reflections on African Cities in Transition; Reddy, P.S., Wissink, H., Eds.; Advances in African Economic, Social and Political Development; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Patel, A. Low cost model for desalination of water using solar energy to overcome water scarcity in India. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Zala, K.; Solanki, K. Ground Water Potential Zone Mapping Using Remote Sensing and GIS in Saurashtra Region of Gujarat, India. In Proceedings of the F-EIR Conference on Environment Concerns and Its Remediation, Chandigarh, India, 18–22 October 2021; Ashish, D.K., de Brito, J., Eds.; Environmental Restoration. F-EIR 2021. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Panchal, U.; Keriwala, N. A Novel Plan for Gujarat to Mitigate the Effect of Flood, Drought and Salinity Using Interlinking of Canal and Rivers. In Proceedings of the F-EIR Conference on Environment Concerns and Its Remediation, Chandigarh, India, 18–22 October 2021; Ashish, D.K., de Brito, J., Eds.; Environmental Restoration. F-EIR 2021. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Shah, A. Sustainable solution for lake water purification in rural and urban areas. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 32, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahanas, K.M.; Sivakumar, P.B. Framework for a smart water management system in the context of smart city initiatives in India. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 92, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharifi, A. A typology of smart city assessment tools and indicator sets. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.; Veselitskaya, N.; Carabias, V.; Yildirim, O. Technological Forecasting & Social Change Scenario-based identification of key factors for smart cities development policies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 148, 119729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Tao, W. Geo-spatial Information Science Interdisciplinary urban GIS for smart cities: Advancements and opportunities. Geo-Spatial Inf. Sci. 2013, 16, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taji, S.G.; Saraf, V.R.; Regulwar, D.G. Smart Rain Water Harvesting for Smart Cities. In Security and Privacy Applications for Smart City Development; Tamane, S.C., Dey, N., Hassanien, A.E., Eds.; Studies in Systems, Decision and Control; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachokostas, C. Smart buildings need smart consumers: The meet- in-the middle approach towards sustainable management of energy sources approach towards sustainable management of energy sources. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2020, 39, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keriwala, N.; Patel, A. Innovative Roadmap for Smart Water Cities: A Global Perspective. Mater. Proc. 2022, 10, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2022010001
Keriwala N, Patel A. Innovative Roadmap for Smart Water Cities: A Global Perspective. Materials Proceedings. 2022; 10(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2022010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeriwala, Neha, and Anant Patel. 2022. "Innovative Roadmap for Smart Water Cities: A Global Perspective" Materials Proceedings 10, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2022010001
APA StyleKeriwala, N., & Patel, A. (2022). Innovative Roadmap for Smart Water Cities: A Global Perspective. Materials Proceedings, 10(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2022010001





