Examination of Nanochannels in Diluted Magnetic Doped CoTiSb Semiconductor †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Calculation Method
3. Results and Discussion
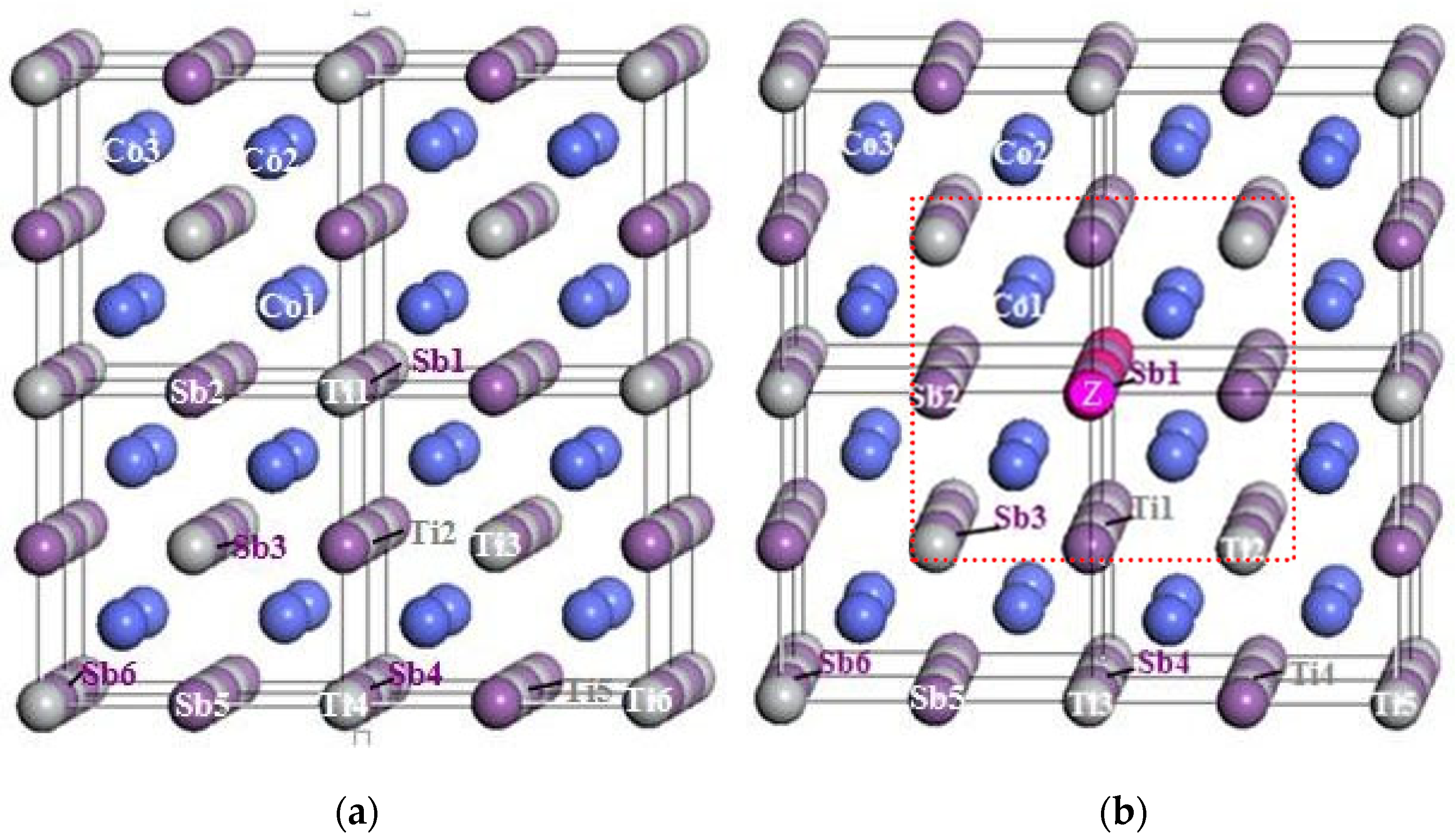
3.1. Crystal Structure
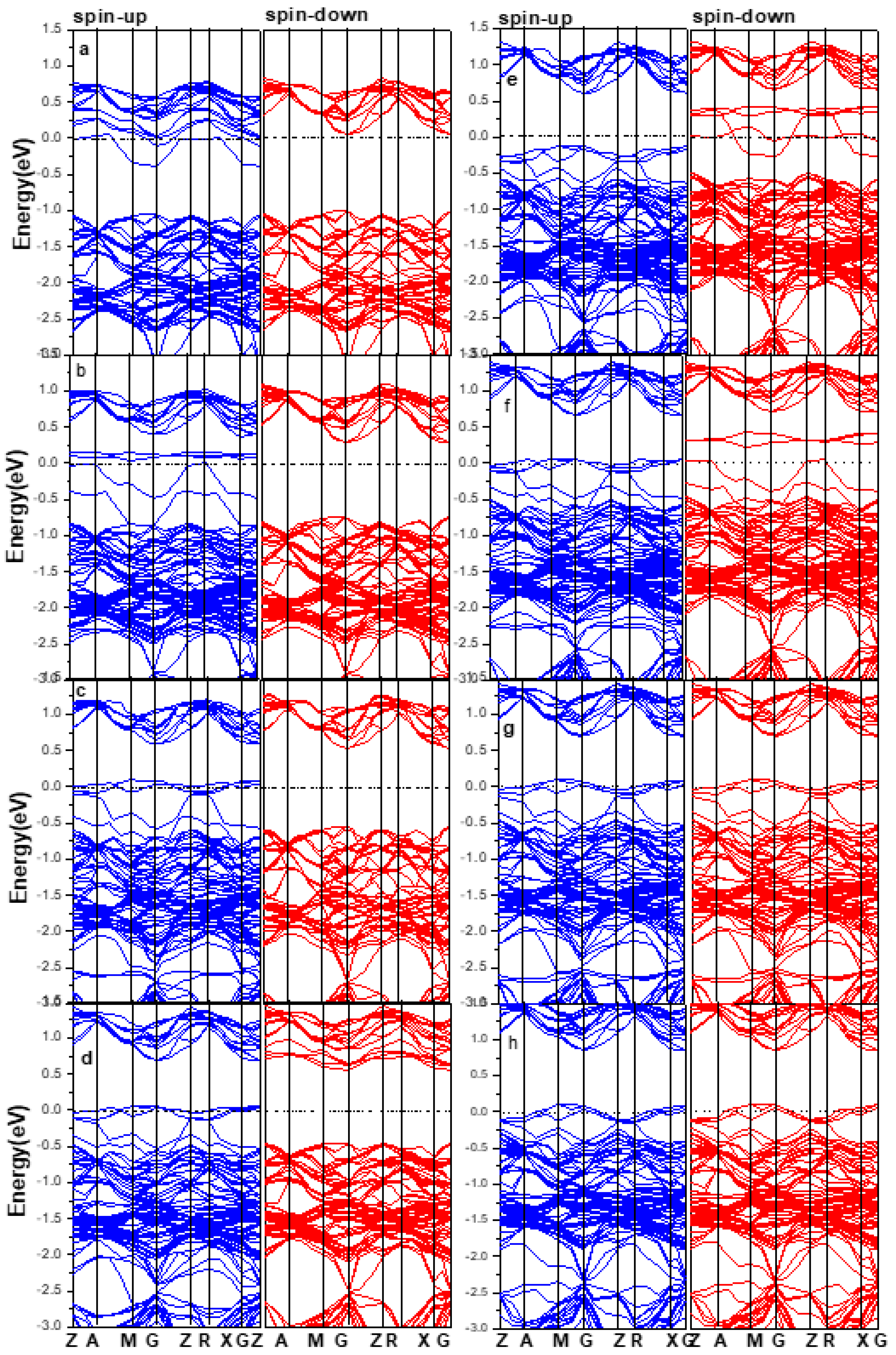
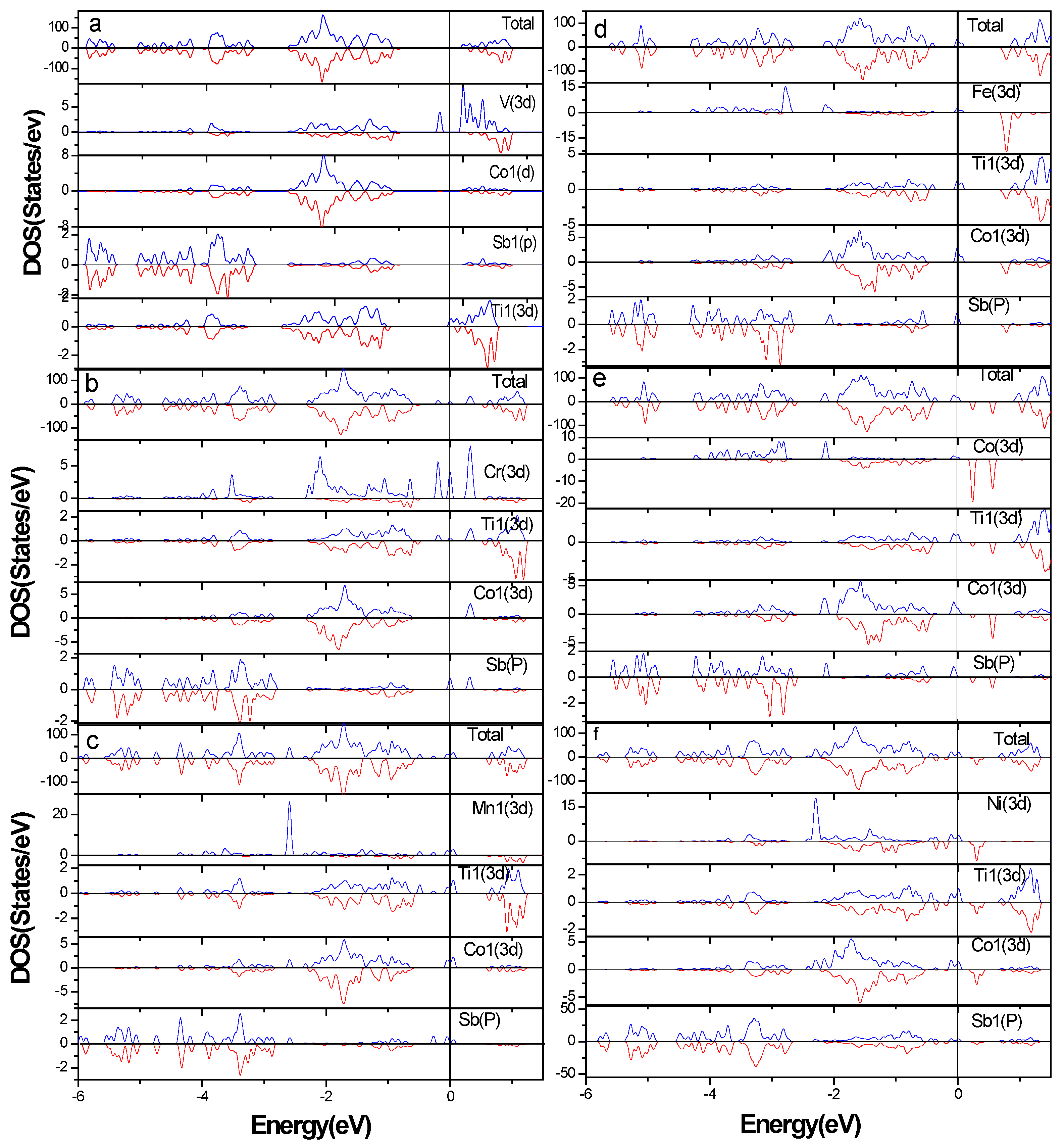
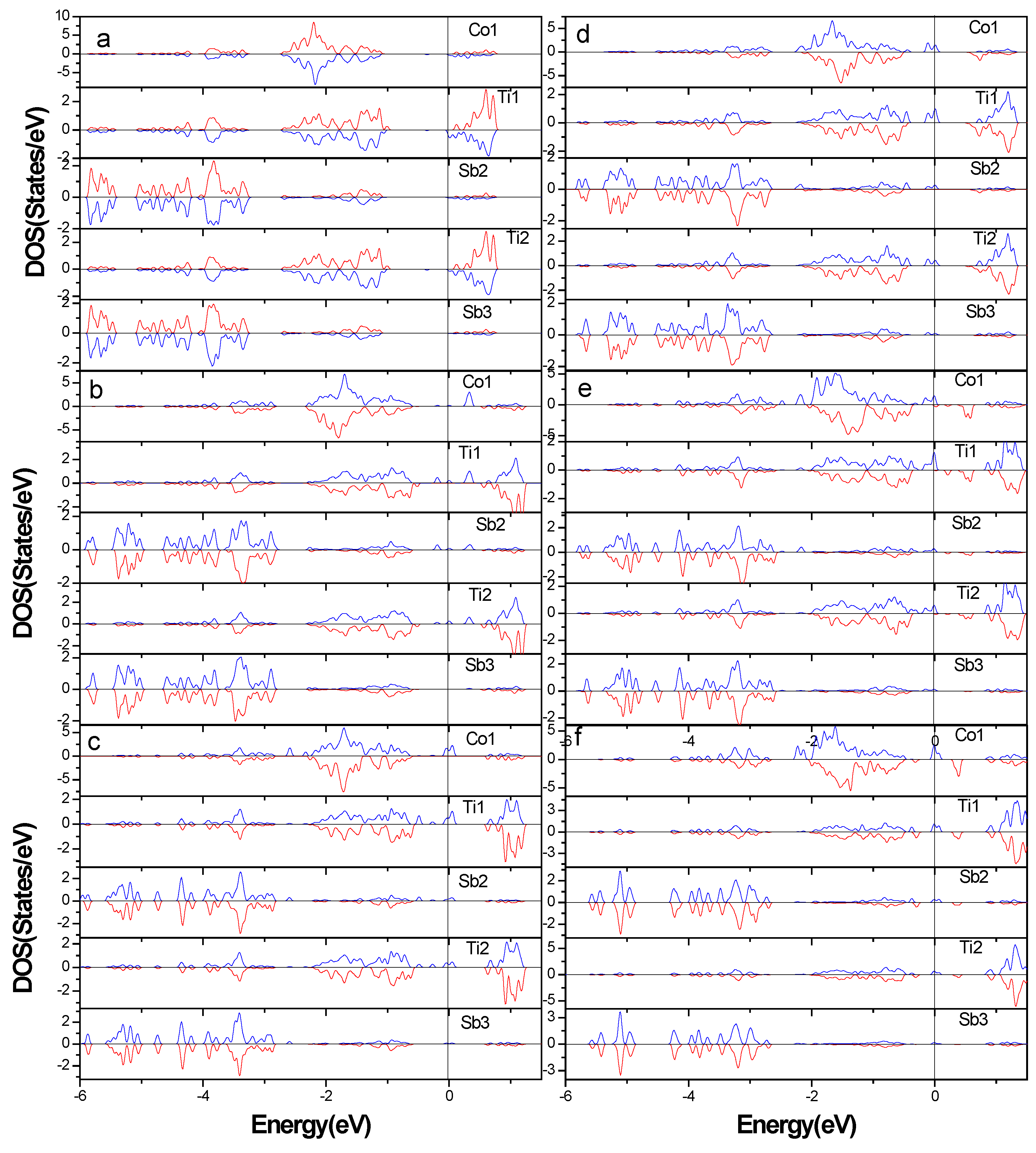
3.2. Electronic Structure of Supercells
3.3. Bandgap Width of Alloy
3.4. Total Magnetic Moment of Supercells
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Groot, R.A.; Mueller, F.M.; Van Engen, P.G.; Buschow, K.H.J. New class of materials: Half-metallic ferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 2024–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Z. Current-driven magnetic switching in manganite trilayer junctions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 202, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katine, J.A.; Albert, F.J.; Buhrman, R.A. Current-induced realignment of magnetic domains in nanostructured Cu/Co multilayer pillars. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, L. Emission of spin waves by a magnetic multilayer traversed by a current. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 9353–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazaliy, Y.B.; Jones, B.A.; Zhang, S.C. Modification of the Landau-Lifshitz equation in the presence of a spin-polarized current in colossal-and giant-magnetoresistive materials. Phys. Rev. B. 1998, 57, R3213–R3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintal, X.; Myers, E.B.; Brouwer, P.W.; Ralph, D.C. Role of spin-dependent interface scattering in generating current-induced torques in magnetic multilayers. Phys. Rev. B. 2000, 62, 12317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Dai, X.F.; Wang, X.T.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.M.; Cui, Y.T.; Liu, G.D. Highly-spin-polarized interface in CoTiSb/Fe(Mn)/CoTiSb superlattice. Superlattices Microstruct. 2015, 86, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, M.D.; Lindan, P.J.D.; Probert, M.J.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Clark, S.J.; Payne, M.C. First-principles simulation: Ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2002, 14, 2717–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanakis, I.; Dederichs, P.H. Half-Metallic Heusler Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Prinz, G.A. Magnetoelectronics. Science 1998, 282, 1660–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planes, A.; Manosa, L.; Saxena, A. Magnetism and Structure in Functional Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 58–112. [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuken, H.; De Groot, R.A. Half-metallic antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickett, W.E. Spin-density-functional-based search for half-metallic antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, 10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akai, H.; Ogura, M. Half-metallic diluted antiferromagnetic semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 026401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanakis, I.; Dederichs, P.H.; Papanikolaou, N.J.P.R.B. Origin and properties of the gap in the half-ferromagnetic Heusler alloys. Phys. Rev. B. 2002, 66, 134428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Venkatesan, M.; Bari, M.A. Half-Metallic Ferromagnets. In High Magnetic Fields; Berthier, C., Levy, L., Martinez, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 595, pp. 377–396. [Google Scholar]
- Felser, C.; Fecher, G.H.; Balke, B. Spintronics: A challenge for materials science and solid-state chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 668–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kübler, J. First principle theory of metallic magnetism. Physica B+C 1984, 127, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, J.; Skolozdra, R.V.; Gorelenko, Y.K.; Kouacou, M. From nonmagnetic semiconductor to itinerant ferromagnet in the TiNiSn-TiCoSn series. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1994, 134, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobola, J.; Pierre, J.; Kaprzyk, S.; Skolozdra, R.V.; Kouacou, M.A. Crossover from semiconductor to magnetic metal in semi-Heusler phases as a function of valence electron concentration. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 1998, 10, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balke, B.; Fecher, G.H.; Gloskovskii, A.; Barth, J.; Kroth, K.; Felser, C.; Robert, R.; Weidenkaff, A. Doped semiconductors as half-metallic materials: Experiments and first-principles calculations of CoTi1−xMxSb (M = Sc, V, Cr, Mn, Fe). Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 045209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Dai, X.F.; Wang, X.T.; Li, P.P.; Xia, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.T.; Liu, G.D. Single spin channels in Fe-doped CoTiSb semiconductor. Superlattices Microstruct. 2015, 83, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Supercell | Bandgap/eV |
|---|---|
| V-Sb | 1.1 |
| Cr-Sb | 1.0 |
| Mn-Sb | 1.0 |
| Fe-Sb | 1.0 |
| Co-Sb | 0.75 |
| Ni-Sb | 0.25 |
| Cu-Sb | - |
| Zn-Sb | - |
| Supercell | Bandgap/eV |
|---|---|
| V-Sb | 1.0 |
| Cr-Sb | 2.0 |
| Mn-Sb | 3.0 |
| Fe-Sb | 4.0 |
| Co-Sb | 5.0 |
| Ni-Sb | 2.0 |
| Cu-Sb | 0.8 × 10−2 |
| Zn-Sb | 1.0 × 10−1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y. Examination of Nanochannels in Diluted Magnetic Doped CoTiSb Semiconductor. Eng. Proc. 2025, 98, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025098036
Chang Y. Examination of Nanochannels in Diluted Magnetic Doped CoTiSb Semiconductor. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 98(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025098036
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Yuehua. 2025. "Examination of Nanochannels in Diluted Magnetic Doped CoTiSb Semiconductor" Engineering Proceedings 98, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025098036
APA StyleChang, Y. (2025). Examination of Nanochannels in Diluted Magnetic Doped CoTiSb Semiconductor. Engineering Proceedings, 98(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025098036





