The Use of Artificial Intelligence to Calculate the Estimate of a Public Procurement Act †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definitions
3. Problematic
4. Methodology of Research
5. Results
- -
- The efficiency of a public procurement act is directly related to the estimate of this procurement act, since the bids of competitors depend on the value of the estimate.
- -
- Artificial intelligence plays a key role in establishing an accurate estimate.
- -
- There are different artificial intelligence solutions that could be used to enhance efficiency in public procurement; machine learning, is one of these tools used to establish an accurate estimate.
- -
- There are different types of machine learning, and the ones that are mentioned in the table above are as follows: linear regression, random forest, and artificial neural networks (ANNs).
5.1. Machine Learning
5.1.1. Random Forest Algorithm
5.1.2. Linear Regression
5.1.3. Neutral Network
5.2. Comparison Between Random Forest, Linear Regression, and Neutral Networks Using a Case Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duncombe, W.; Searcy, C. Can the Use of Recommended Procurement Practices Save Money? Public Budg. Financ. 2007, 27, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A. The Role of Procurement. In The International Handbook of Public Financial Management; Allen, R., Hemming, R., Potter, B.H., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan UK: London, UK, 2013; pp. 312–335. ISBN 978-1-137-31530-4. [Google Scholar]
- Public Procurement Performance. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/2023/08/public-procurement-performance_0ebfe3e7.html (accessed on 5 October 2024).
- García Rodríguez, M.J.; Rodríguez Montequín, V.; Ortega Fernández, F.; Villanueva Balsera, J.M. Public Procurement Announcements in Spain: Regulations, Data Analysis, and Award Price Estimator Using Machine Learning. Complexity 2019, 2019, 2360610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, J.; Grandia, J. Public Procurement as a Policy Tool: Using Procurement to Reach Desired Outcomes in Society. Available online: https://pure.eur.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/47769624/REPUB_99935.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2017).
- Mrope, N.P.; Namusonge, G.S.; Iravo, M.A. Does compliance with rules ensure better performance? an assessment of the effect of compliance with procurement legal and regulatory framework on performance of public procurement in Tanzania. Eur. J. Logist. Purch. Supply Chain Manag. 2017, 5, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zaidane, A.; Arafi, H.E. La gouvernance de la commande publique au maroc: Vers une gestion axee sur la performance. Financ. Financ. Int. 2021, 1, 27350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckstrand, J.; Suurmond, R.; Van Raaij, E.; Chen, C. Purchasing process models: Inspiration for teaching purchasing and supply management. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2019, 25, 100577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, G.; Palombo, R.; Bauer, L.T.; Niehaves, B. Overcoming Inefficiency in Public Procurement: An OpenData Approach; Gesellschaft für Informatik e.V.: Bonn, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, P.; Lopane, N.; Lops, P.; Siciliani, L.; Taccardi, V.; Tamburrano, V. Artificial Intelligence Systems for Decision Support in Public Procurement. 2023. Available online: https://ricerca.uniba.it/handle/11586/454574# (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Nikitin, P.; Bakhtina, E.; Korchagin, S.; Korovin, D.; Gorokhova, R.; Dolgov, V. Evaluation of the execution of government contracts in the field of energy by means of artificial intelligence. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 402, 03041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søreide, T. Corruption in public procurement. In Causes, Consequences and Cures; Chr. Michelsen Intitute: Bergen, Norway, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Saussier, S.; Tirole, J. Renforcer l’efficacité de la commande publique. Notes Du Cons. D’analyse économique 2015, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, M.; Caniato, F.; Moretto, A.; Ronchi, S. The role of artificial intelligence in the procurement process: State of the art and research agenda. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2023, 29, 100823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coglianese, C. Chapter 18: Procurement and artificial intelligence. 2024. Available online: https://www.elgaronline.com/edcollchap/book/9781803922171/book-part-9781803922171-26.xm (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Lloyd, R.E. Public Procurement. In Encyclopedia of Public Administration and Public Policy; Routledge: London, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-429-27086-4. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N. What Is Public Procurement: Introduction. In Public Procurement Fundamentals; Emerald Publishing Limited: Leeds, UK, 2018; pp. 1–20. ISBN 978-1-78754-608-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hafsa, F.; Darnall, N.; Bretschneider, S. Estimating the True Size of Public Procurement to Assess Sustainability Impact. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroccan Decree N°2-22-431 of Public Procurement. Available online: https://www.tgr.gov.ma/wps/wcm/connect/f33f17af-1dc9-4768-bc88-72f58e3f698b/decret_des_marches_publics_version_francais+-3.pdf?MOD=AJPERES&CACHEID=f33f17af-1dc9-4768-bc88-72f58e3f698b (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- Artificial Intelligence—Artificial Intelligence: Definition, Trends, Techniques and Cases. Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS). Available online: https://www.eolss.net/Sample-Chapters/C15/E6-44.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2009).
- Borana, J. Applications of Artificial Intelligence & Associated Technologies. Science 2016, 5, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Balaeva, O.; Yakovlev, A. Estimation of costs in the Russian public procurement system. Int. J. Procure. Manag. 2017, 10, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Rodriguez, M.J.; Rodriguez Montequin, V.; Aranguren Ubierna, A.; Santana Hermida, R.; Sierra Araujo, B.; Zelaia Jauregi, A. Award Price Estimator for Public Procurement Auctions Using Machine Learning Algorithms: Case Study with Tenders from Spain. Stud. Inform. Control 2021, 30, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabuzin, K.; Modrušan, N. Prediction of Public Procurement Corruption Indices using Machine Learning Methods. In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management, Vienna, Austria, 17–19 September 2019; pp. 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests, Machine Learning. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What Is Machine Learning (ML)?|IBM. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/topics/machine-learning (accessed on 16 October 2024).
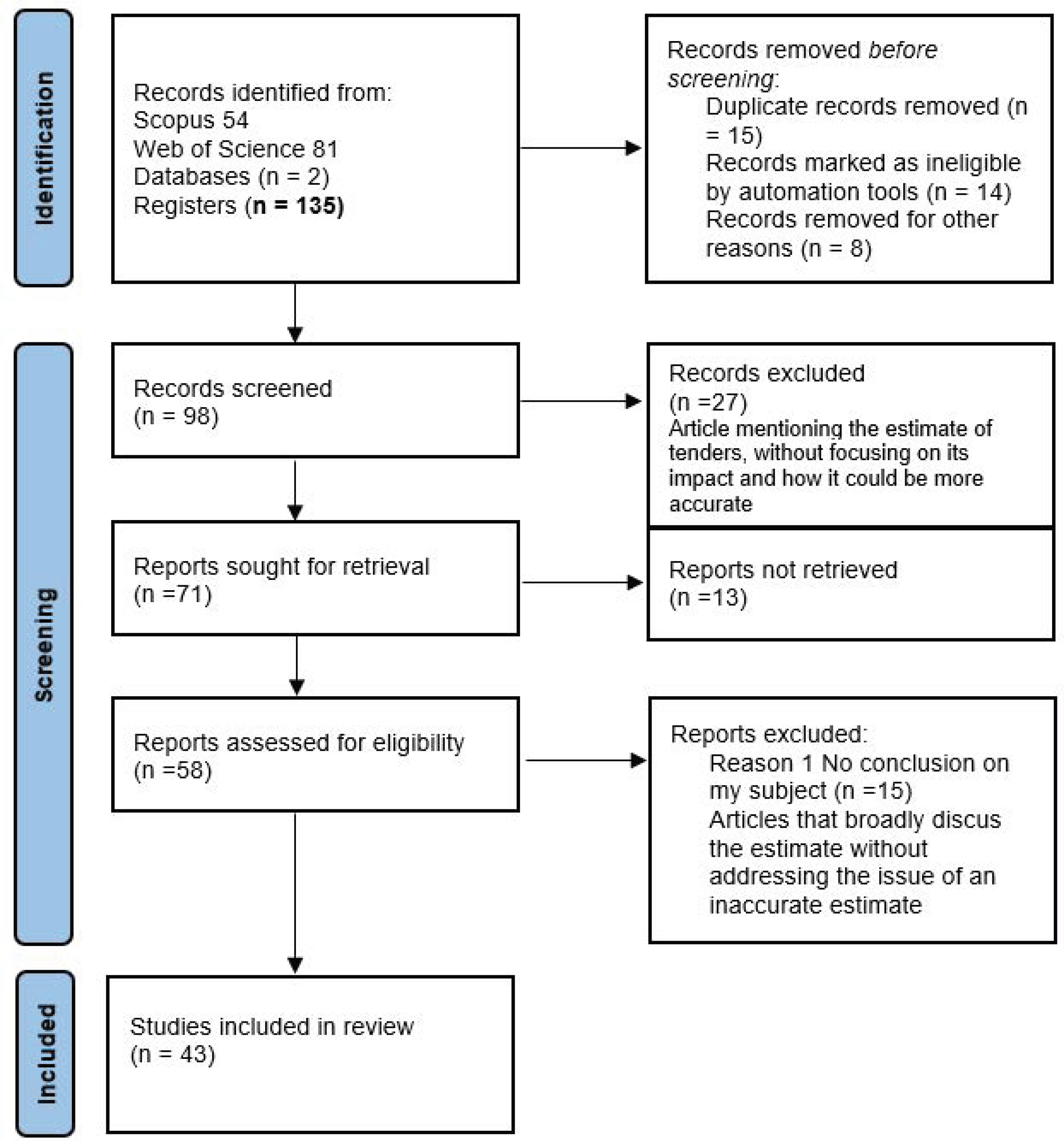
| Document Title/Year of Publication | Authors | Year Main Idea of the Article | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Award Price Estimator for Public Procurement Auctions Using Machine Learning Algorithms: Case Study with Tenders from Spain. 2023 | Rodriguez, MJG; | 2023 | |
| Montequin, VR, Ubierna, AA, Hermida, RS, Araujo, BS, Jauregi, AZ | Through a comparison between random forest and linear regression, with isotonic regression and popular artificial neural network models, the author explains the efficiency of each model and comes up with a model capable of delivering the awarding price with more accuracy. | ||
| Conceptual estimation of construction duration and cost of public highway projects. 2022 | Mohamed Basma, Moselhi, Osama | This study assesses a typical set of machine learning methods’ applicability to this task. The less studied paradigms, including isotonic regression and well-known artificial neural network models, are contrasted with the conventional regression techniques, like random forest and linear regression. Based on the Spanish public procurement announcement (tender) dataset, numerous tests are carried out using a variety of error measures and WEKA and Tensorflow 2 implementations. | |
| Budget-feasible Procurement Mechanisms in Two-sided Markets. 2018 | Wu, WW (Wu, Weiwei); Liu, X (Liu, Xiang); Li, MM (Li, Minming) | This study examines the mechanism design problem. Every seller is permitted to bid the price of their private commodity, if it has public worth. Buyers may present their own budgets, not always the accurate ones. The objective is to find financially feasible solutions that guarantee that sellers receive sufficient payment, and that purchasers’ budgets are not surpassed. The authors principally contribute a random method that ensures several required theoretical guarantees, including budget feasibility, simultaneous veracity on the part of sellers and buyers, and continuous approximation to the best possible overall procured value of purchasers. | |
| Predicting costs of local public bus transport services through machine learning methods | Amicosante, Andrea, Avenali Alessandro, D’Alfonso Tiziana, Giagnorio Mirko, Manno Andrea, Matteucci Giorgio | The study generates a model based on a machine learning system capable of predicting expenses for public bus transportation. To train the algorithms, a built-in dataset from 269 transportation providers offering urban services in the US between 2015 and 2019 was used. The model proposed could give various insights, such identifying the key factors of transportation cost, which lead to an improvement in service contract management. | |
| Model of Predicting Bidding Costs for Construction Projects in Nigeria using Public Procurement Act. 2007 | Mohammed Lawal Yahaya; Isma’il Umar; A. J Babalola; Mohammed Sani | The aim objective of this article is to create a model capable of predicting the cost of bids related to construction projects. The study concludes that, on average, contractors’ transaction costs when bidding on construction projects amount to 8.21% of the contract sum. This information will be useful to new companies entering the market as bidders because it will let them know what to expect in terms of entry costs for public projects. | |
| Reliable procurement cost estimation methodologies: A case study in complex environments. 2004 | Perluka, B.Y | The process of awarding the call for tenders is based on the price of the bid; therefore, knowing how to estimate the project is important for both suppliers to be competitive, and for public agencies to avoid a budget overrun. Establishing the estimate of a project is a complicated task regarding the multiple factors that are involved, such the appearance of new product development. In this article, the author aims to presents methodologies that could be useful for calculating the estimate and making it more reliable. | |
| Price Estimation Model Using Factor Analysis in Procurement. 2022 | Achmad Faizal, Zulkarnain Zulkarnain, Isti Surjandari, Authors Info and Claims | Managing procurement, which is essential for cost-saving, must involve bargaining with suppliers to acquire the best pricing when acquiring goods and services. A buyer’s price estimate is created as part of the negotiation process. Procurement professionals disagree on the aspects that go into pricing estimation. The goal of this study is to identify the key variables that influence price estimation in procurements and to develop a model based on those variables, particularly when it comes to leasing assets. | |
| The Accuracy of Independent Estimates of the Procurement Costs of Major Systems. 2005 | David L. McNicol, Project Leader Karen W, Tyson, John R. Hiller, Harely A, Could, Joshua A, Minix | The results of an evaluation of the reliability of the independent cost estimates for procurement that the Department of Defense employs for significant acquisition program milestone reviews are presented in this study. Initially, the IDA investigated sixty-three significant programs that were authorized to start Engineering and Manufacturing Development between 1985 and 1998. For just 25 of these programs could the information required to assess the precision of the independent procurement cost estimates be found. For eighteen of the twenty-five examples, the IDA determined that the independent cost estimate was fairly accurate. In the remaining cases, the independent estimate was sometimes much too high and sometimes substantially too low. | |
| Optimized artificial intelligence models for predicting project award price. 2015 | Chou, Jui-Sheng, Lin, Chih-Wei, Anh-Duc Pham, Shao, Ji-Yao. | This paper aims to estimate bid award amounts for bridge construction projects by using artificial intelligence algorithms such multiple regression analysis, artificial neural networks (ANNs), and case-based reasoning (OR). Information was gathered for public bridge building projects from the Taiwanese government’s e-procurement system. The study shows that the mathematical model for artificial neural networks (ANNs) offers more dependable simulations and has a better fit. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berraida, R.; Laila, E.A. The Use of Artificial Intelligence to Calculate the Estimate of a Public Procurement Act. Eng. Proc. 2025, 97, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025097007
Berraida R, Laila EA. The Use of Artificial Intelligence to Calculate the Estimate of a Public Procurement Act. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 97(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025097007
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerraida, Riyad, and EL Abbadi Laila. 2025. "The Use of Artificial Intelligence to Calculate the Estimate of a Public Procurement Act" Engineering Proceedings 97, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025097007
APA StyleBerraida, R., & Laila, E. A. (2025). The Use of Artificial Intelligence to Calculate the Estimate of a Public Procurement Act. Engineering Proceedings, 97(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025097007





