Classification of Urban Environments Using State-of-the-Art Machine Learning: A Path to Sustainability †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
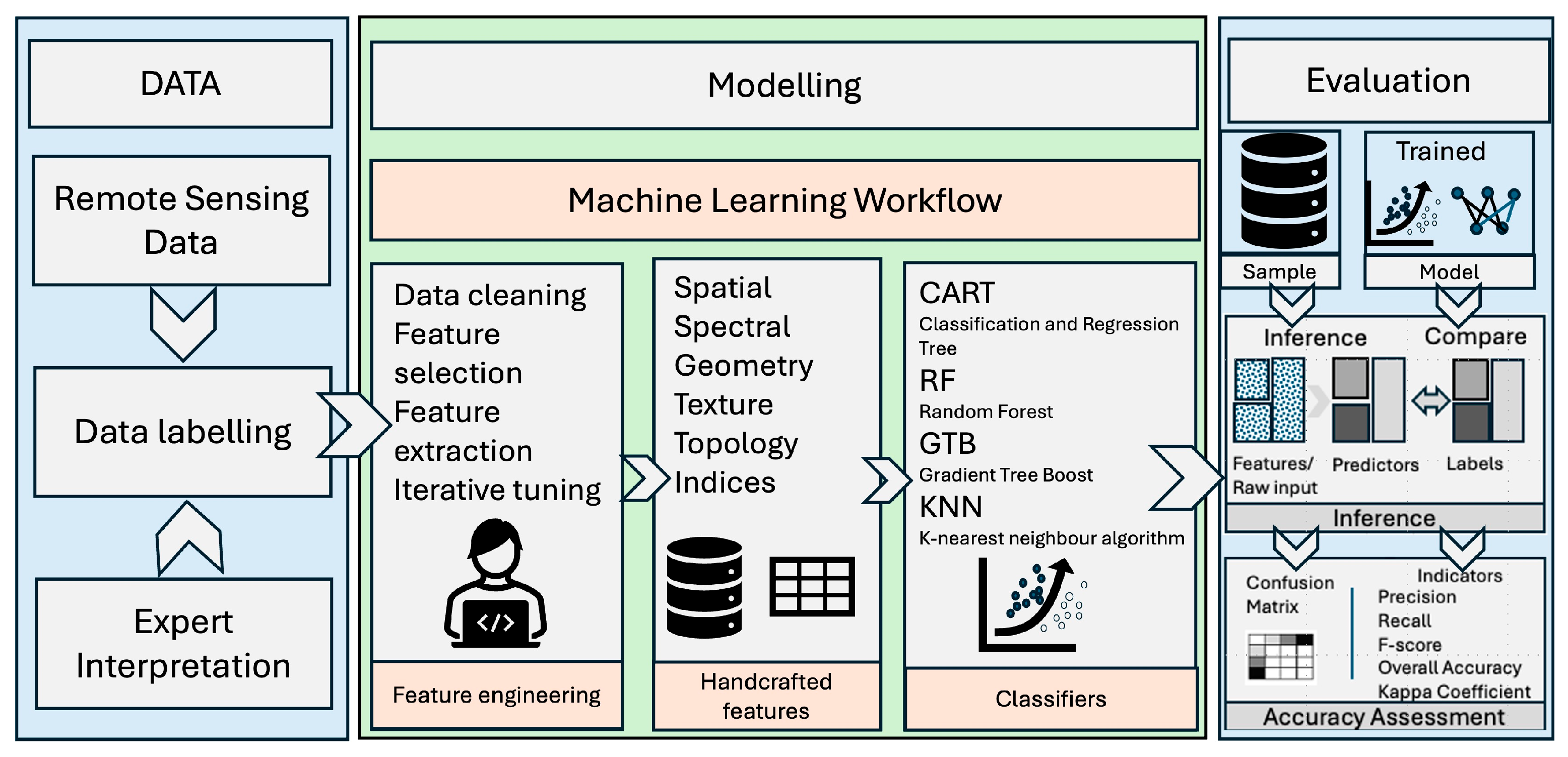
2.1. Data
2.2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions and Future Developments
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Population Division D of E and SA. World Urbanisation Prospects: The 2018 Revision. United Nations. 2019. Available online: https://population.un.org/wup/ (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Parker, J.; Zingoni de Baro, M.E. Green Infrastructure in the Urban Environment: A Systematic Quantitative Review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.; Tzoulas, K.; Adams, M.D.; Barber, A.; Box, J.; Breuste, J.; Elmqvist, T.; Frith, M.; Gordon, C.; Greening, K.; et al. Towards an integrated understanding of green space in the European built environment. Urban For. Urban Green. 2009, 8, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, D.E.; Buyung-Ali, L.; Knight, T.M.; Pullin, A.S. Urban greening to cool towns and cities: A systematic review of the empirical evidence. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Crane, D.E.; Stevens, J.C. Air pollution removal by urban trees and shrubs in the United States. Urban For. Urban Green. 2006, 4, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.; Matos, P.; Mexia, T.; Silva, P.; Lopes, N.; Freitas, C.; Correia, O.; Santos-Reis, M.; Branquinho, C.; Pinho, P. Green spaces are not all the same for the provision of air purification and climate regulation services: The case of urban parks. Environ. Res. 2018, 160, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.R.; Teodoro, A.C.; Gonçalves, A. Study of the Urban Heat Island (UHI) Using Remote Sensing Data/Techniques: A Systematic Review. Environments 2021, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezzo, L.V.; Coltri, P.P.; Dubreuil, V. Microscale models and urban heat island studies: A systematic review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.M.; Altamura, P.; Giampaoletti, M.; Hemeida, F.A.; Mohamed, A.F.A. Optimizing human thermal comfort and mitigating the urban heat island effect on public open spaces in Rome, Italy through sustainable design strategies. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, L.P.; January-Bevers, D.J.; Caton, E.K.; Campos, L.A. A simple tree planting framework to improve climate, air pollution, health, and urban heat in vulnerable locations using non-traditional partners. Plants People Planet 2022, 4, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichowicz, R.; Bochenek, A.D. Assessing the effects of urban heat islands and air pollution on human quality of life. Anthropocene 2024, 46, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, Z.; van Dijk, J.; Lan, T.; Longley, P.A.; Treleaven, P.; Batty, M.; Penn, A. Data-driven urban management: Mapping the landscape. J. Urban Manag. 2020, 9, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, C.W.; Lee, X.; Smith, R.B. Remotely sensing the cooling effects of city scale efforts to reduce urban heat island. Build. Environ. 2012, 49, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkoç, E. City-wide assessment of urban tree cover and land-cover changes in Edirne using web-based tools. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, R.; Rambhia, M.; Naber, E.; Schultmann, F. Urban Resource Assessment, Management, and Planning Tools for Land, Ecosystems, Urban Climate, Water, and Materials—A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennersten, R.; Qie, S. United Nations Sustainable Development Goals for 2030 and Resource Use. In Handbook of Sustainability Science and Research; Leal Filho, W., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, J.; Yan, L. Defining and measuring urban sustainability: A review of indicators. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1175–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Raghubanshi, A. Urban sustainability indicators: Challenges and opportunities. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Mora, S.; Preisler, Y.; Duarte, F.; Prasad, V.; Ratti, C. Tools and methods for monitoring the health of the urban greenery. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Zeng, L.; Li, S.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wan, B. Spatial context-aware method for urban land use classification using street view images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 192, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, J.; Kuenzer, C.; Wehrmann, T.; Gebhardt, S.; Tuan, V.Q.; Dech, S. Land Cover and Land Use Classification with TWOPAC: Towards Automated Processing for Pixel- and Object-Based Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2530–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X. A review of regional and Global scale Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) mapping products generated from satellite remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 206, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, F.; Sy, O.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; Fernandez, V.; Colin, O.; Hoersch, B.; Meygret, A. Overview of Sentinel-2. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 1707–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martimort, P.; Arino, O.; Berger, M.; Biasutti, R.; Carnicero, B.; Del Bello, U.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Greco, B.; Silvestrin, P.; et al. Sentinel-2 optical high resolution mission for GMES operational services. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 2677–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Le Saint, T.; Nabucet, J.; Hubert-Moy, L.; Adeline, K. Estimation of Urban Tree Chlorophyll Content and Leaf Area Index Using Sentinel-2 Images and 3D Radiative Transfer Model Inversion. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisenheimer, L.; Wellmann, T.; Jänicke, C.; Haase, D. Monitoring drought impacts on street trees using remote sensing—Disentangling temporal and species-specific response patterns with Sentinel-2 imagery. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, A.; Sannier, C.; Corpetti, T. Monitoring Urban Areas with Sentinel-2A Data: Application to the Update of the Copernicus High Resolution Layer Imperviousness Degree. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, D.; Simwanda, M.; Salekin, S.; Nyirenda, V.R.; Murayama, Y.; Ranagalage, M. Sentinel-2 Data for Land Cover/Use Mapping: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Altman, N. Classification and regression trees. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.; Bunn, A.; Powell, S.; Zambon, M. Classification of remotely sensed imagery using stochastic gradient boosting as a refinement of classification tree analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okfalisa; Gazalba, I.; Mustakim, M.; Reza, N.G.I. Comparative analysis of k-nearest neighbor and modified k-nearest neighbor algorithm for data classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conferences on Information Technology, Information Systems and Electrical Engineering (ICITISEE), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 1–2 November 2017; pp. 294–298. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsina, S.; Aryal, J.; Kirkpatrick, J.B. Mapping Urban Tree Cover Changes Using Object-Based Convolution Neural Network (OB-CNN). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, M. Swin-CFNet: An Attempt at Fine-Grained Urban Green Space Classification Using Swin Transformer and Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 2503405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Hanan, A.; Kenzhebay, M.; Gazzea, M.; Arghandeh, R. Transformer-based land use and land cover classification with explainability using satellite imagery. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, S.; Arfvidsson, H.; Simon, D. Governance for sustainable urban development: The double function of SDG indicators. Area Dev. Policy 2019, 4, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, F.; Krellenberg, K. How to Contextualize SDG 11? Looking at Indicators for Sustainable Urban Development in Germany. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, S. Defining a Global Urban Development Agenda. World Dev. 2016, 78, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Jia, Y.; Gui, G. Deep Learning-Based Classification Methods for Remote Sensing Images in Urban Built-Up Areas. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36274–36284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Islam, F.; Waseem, L.A.; Tariq, A.; Nawaz, M.; Islam, I.U.; Bibi, T.; Rehman, N.U.; Ahmad, W.; Aslam, R.W.; et al. Comparison of Three Machine Learning Algorithms Using Google Earth Engine for Land Use Land Cover Classification. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 92, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, B.S.; Biju, V.G.; Prashanth, C.M. Kappa and accuracy evaluations of machine learning classifiers. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd IEEE International Conference on Recent Trends in Electronics, Information & Communication Technology (RTEICT), Bangalore, India, 19–20 May 2017; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar]


| Model | Accuracy | Macro F1-Score | Weighted F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| CART | 0.83 | 0.823 | 0.830 |
| GTB | 0.86 | 0.839 | 0.857 |
| RF | 0.90 | 0.892 | 0.901 |
| KNN | 0.87 | 0.847 | 0.868 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tessema, T.; Azarmehr, N.; Saadati, P.; Mortimer, D.; Tosti, F. Classification of Urban Environments Using State-of-the-Art Machine Learning: A Path to Sustainability. Eng. Proc. 2025, 94, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025094014
Tessema T, Azarmehr N, Saadati P, Mortimer D, Tosti F. Classification of Urban Environments Using State-of-the-Art Machine Learning: A Path to Sustainability. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 94(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025094014
Chicago/Turabian StyleTessema, Tesfaye, Neda Azarmehr, Parisa Saadati, Dale Mortimer, and Fabio Tosti. 2025. "Classification of Urban Environments Using State-of-the-Art Machine Learning: A Path to Sustainability" Engineering Proceedings 94, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025094014
APA StyleTessema, T., Azarmehr, N., Saadati, P., Mortimer, D., & Tosti, F. (2025). Classification of Urban Environments Using State-of-the-Art Machine Learning: A Path to Sustainability. Engineering Proceedings, 94(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025094014







