Abstract
In the recent consumer market, eyewear has gone beyond the improvement of visual function and is used for the individual style and the symbolization of social standing. Consequently, the aesthetic design of eyewear influences consumer purchasing decisions. Thus, it is necessary to investigate how eyewear design incorporating elements with aesthetic appeal can enhance the sensory experiences of consumers, thereby intensifying their preference for products and fostering their intent to purchase. Utilizing the Evaluation Grid Method (EGM), the design characteristics of eyewear products in the market were explored to assess how these characteristics affect consumer selections. A quantitative analysis of the key quality attributes in eyewear design was conducted using the Kano Model. The results demonstrated a nonlinear relationship between design attributes and consumer satisfaction, confirming the relevance of the Kano Model’s classification. By providing a multi-dimensional quality, the Kano Model elucidated variations in consumer quality requirements for eyewear design, allowing designers and manufacturers to strategically enhance key product design elements, thus creating items with greater market appeal. The results provide recommendations for the improvement of product design aesthetics to increase visual allure for consumers and strengthen market competitiveness.
1. Introduction
In the consumer-driven market, practitioners must understand and assess the integral role of the quality attributes of eyewear design in cultivating and sustaining brand competitiveness. The complexity of product design quality demands that companies satisfy the consumers’ fundamental functional requirements and identify and leverage the latent elements of allure for consumer satisfaction. Kansei Engineering and the Kano Model furnish a research framework to decode the nonlinear dynamics of consumer satisfaction and appraise the contributions of various quality attributes. This study, through its empirical application, aims to investigate the particular quality facets of eyewear design that significantly influence consumer satisfaction. The findings can be used to direct the orientation for design innovation and encourage focused product enhancements for consumer experience and product market viability.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research in Eyeglass Design
In the consumer-oriented market, stakeholders must recognize and evaluate the quality attributes of eyeglass design to establish and maintain brand competitiveness. The multifaceted nature of product design quality demands that companies fulfill the fundamental functional requirements of consumers and grasp implicit and charming elements capable of eliciting profound customer satisfaction. Ergonomic charm and the Kano Model provide a framework for understanding the nonlinear characteristics of consumer satisfaction, as well as the differential contributions of various quality attributes to satisfaction. Therefore, it is necessary to unveil which elements in eyeglass style design have a decisive impact on consumer satisfaction and guide the strategic positioning of design. The result promotes targeted product improvements for optimizing consumer experience and enhancing market performance.
Contemporary eyeglass design has been studied to assess aesthetic and functional elements and their impact on consumer preferences. The evolution of professional image and personalized demands propels design innovation. Research on eyeglass frames for different professions emphasized the significance of professional image in choosing frames, suggesting positive attributes such as expertise and youthful appearance [1]. This guides optometrists to broaden the spectrum of choices in the retail industry.
As a fashion accessory, eyeglasses serve a crucial function in the dynamic between design and fashion trends in the 21st century. Design trends shift with cultural and popular changes, where the synergy of color and image assumes critical importance in fashion design [2]. Furthermore, eyewear research has expanded to consider the bifunctional role of eyeglasses in both fashion and health, with [3] offering a fresh perspective on how design practices can satisfy both contemporary fashion trends and health needs, proposing the creation of eyewear that conforms to health standards while retaining a fashionable allure. In the exploration of eyeglass design for fit, Peng [4] identified the challenges faced when Taiwanese design data depend on foreign standards, advocating for the application of scientific data to enhance eyeglass design for improved wearing comfort and ocular health. Additionally, the commercial design and evaluation of eyeglasses, through computer-aided design and product flaw analysis, have increased the development efficiency from conceptualization to mass production, enriching the consumer experience with glasses utilizing 3D display technologies [5]. Within the scope of individualized eyeglass design, consumer preference-based design approaches have introduced interactive design interfaces that promote consumer involvement in the design process, facilitating personalized adjustments to eyeglasses [6]. In the research on eyeglass design, it is necessary to integrate style and functionality, the personal needs of consumers, professional imagery, and product comfort. The results provide a basis for the development of eyeglass design, thereby crafting fashionable and functional products.
2.2. Kano Model
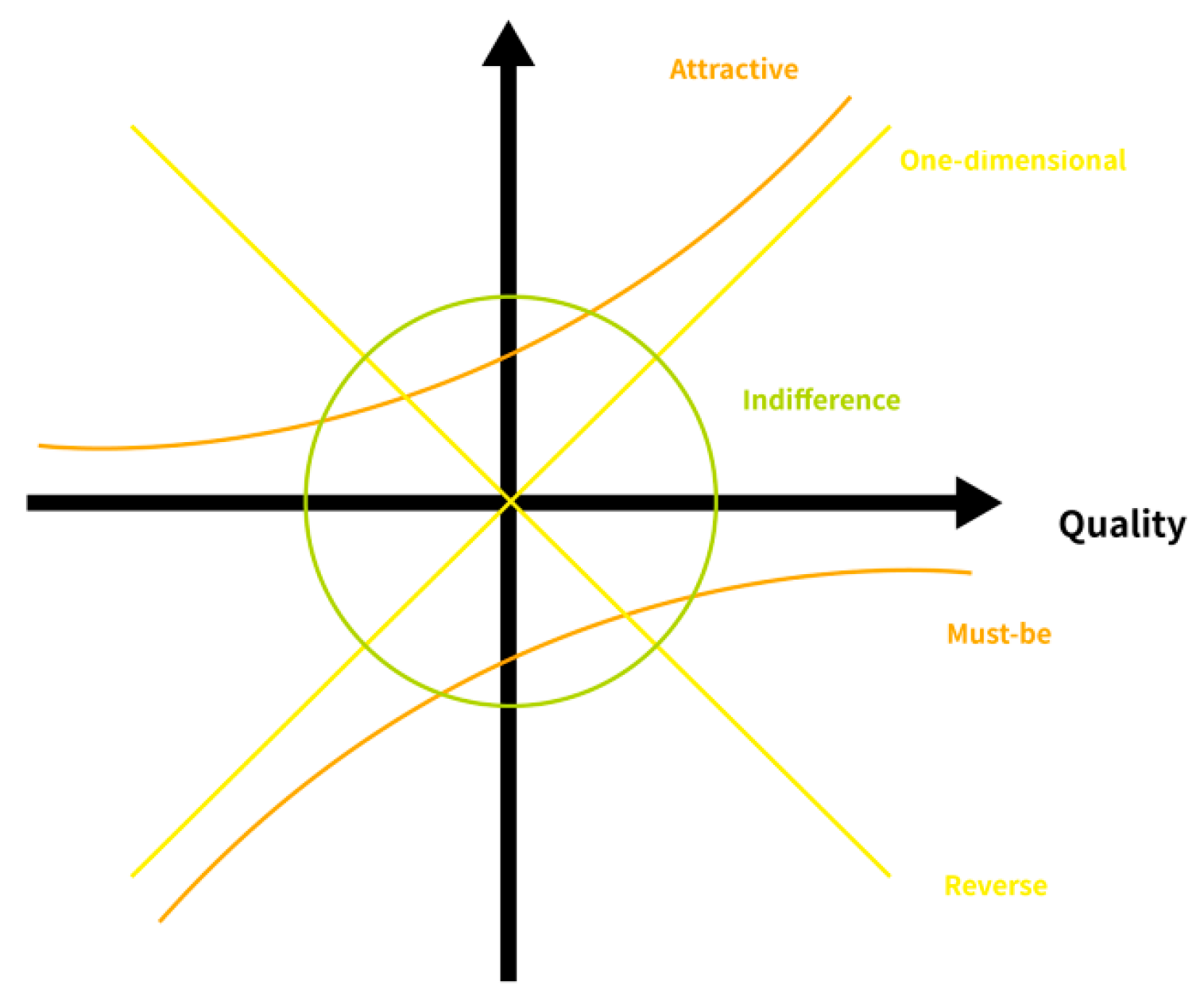
Amidst the swift shifts within the global marketplace, companies must comprehend the needs of consumers and probe how these needs influence customer satisfaction [7]. The Kano Model has been widely implemented in recent years [8]. Stemming from the research of Kano et al. [9], this model amends the perceptions of quality management [10]. The ‘unidimensional’ notion of quality introduces a nuanced classification of quality [11]. The Kano Model delineates quality into five principal categories, suggesting that each category affects consumer satisfaction distinctly [12]. The Kano model of customer satisfaction categorizes product attributes into five distinct categories, providing insights into how different attributes impact customer satisfaction (Figure 1).
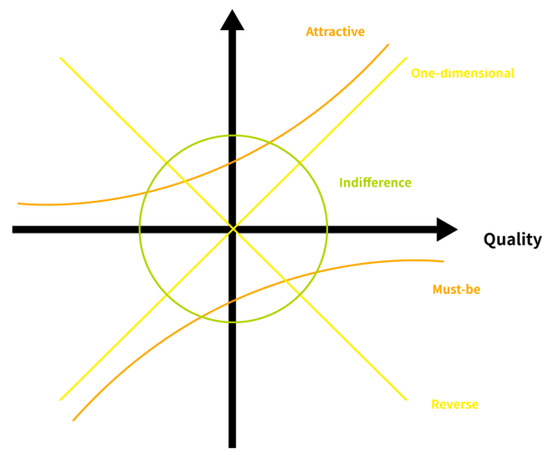
Figure 1.
Kano model of customer satisfaction.
- The Must-be Quality constitutes the essential requirements anticipated by consumers [13]. A failure to meet the quality results in dissatisfaction, whereas satisfaction does not increase proportionally once these requirements are adequately met [14].
- The One-dimensional Quality is related to the demands that consumers have for the product [15]. The relationship between meeting the one-dimensional quality and consumer satisfaction is linear, indicating that as these demands are more effectively satisfied, consumer satisfaction also increases accordingly [16].
- The Attractive Quality includes the needs not indicated by consumers but which, if met, enhance their satisfaction [10].
The Kano Model enables companies to ascertain important consumer needs and distinguish and innovate their offerings to secure differentiation from their competitors [17]. This model equips companies with an encompassing instrument to understand consumer needs, thereby promoting heightened customer satisfaction [18].
3. Methodology
In this research, the attributes of eyeglass design and their impact on consumer satisfaction were explored. The Expressed Goal Method (EGM) was utilized for in-depth interviews, coupled with the Kano model for a dual-structured questionnaire. After the EGM interviews, the features of the eyeglass design were decoded. Seven respondents with rich experience in eyeglass design and diverse backgrounds (four males and three females from product design, fashion analytics, and marketing strategy sectors) were interviewed to construct an attractiveness factor diagram. Subsequently, a bidirectional questionnaire using the Kano model was employed to understand respondents’ perceptions and requirements for eyewear design. A total of 127 valid responses were gathered from young respondents. The questionnaire items included the following.
- Positive dimension: what are your feelings when the eyeglasses you intend to purchase feature modern design elements?
- Negative dimension: what are your feelings when the eyeglasses you intend to purchase do not incorporate modern design elements?
To verify the survey’s reliability, Cronbach’s Alpha analysis was performed. The Cronbach’s Alpha for the survey was 0.930, with the positive dimension scoring 0.923 and the negative dimension scoring 0.973. These high coefficients indicated a high degree of reliability in assessing respondents’ reactions to eyeglass design attributes.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of EGM Interviews
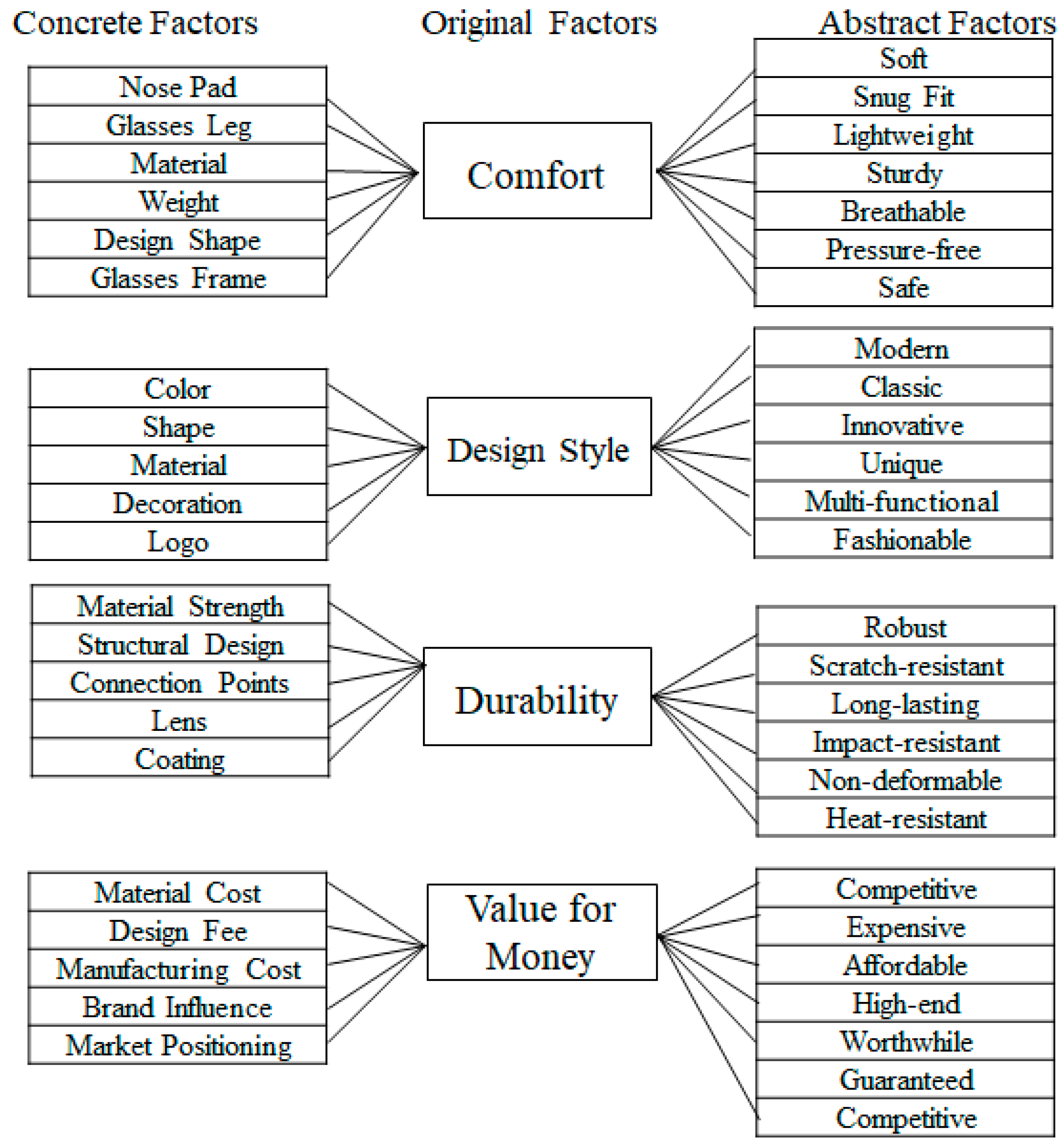
Figure 2 summarizes the results of the interview. The design attributes of eyewear were presented into Concrete, Original, and Abstract Factors. Original Factors were identified as Comfort, Design Style, Durability, and Value for Money, with each category further explicating related characteristics. Concrete Factors for Comfort included nose pads, temple arms, materials, weight, design shape, and the frame. These attributes are directly experienced by the customer and influence product satisfaction. Abstract Factors, in contrast, are perceptions derived from customer experience, encompassing qualities such as softness, fit, lightness, sturdiness, breathability, a pressure-free experience, and security, which customers typically come to appreciate and evaluate over time.
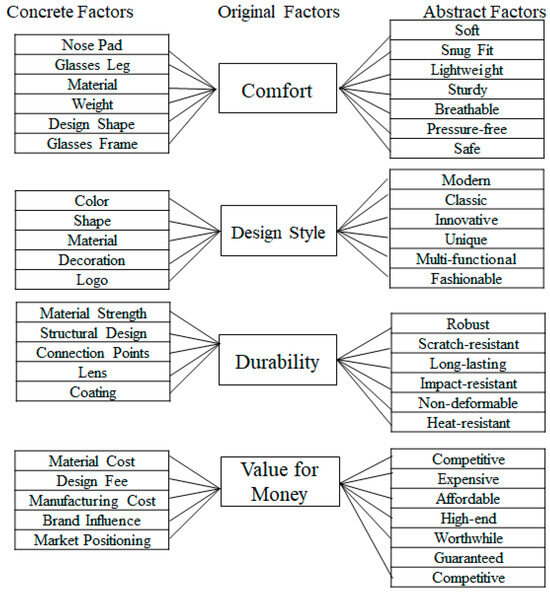
Figure 2.
Analysis framework of EGM Interviews.
In Design Style, Concrete Factors comprised visually distinguishable attributes such as color, shape, texture, decorations, and branding. Conversely, Abstract Factors such as modernity, classic appeal, innovation, uniqueness, multifunctionality, and fashion sense were subjective evaluations shaped by individual preferences and cultural contexts.
Durability’s Concrete Factors pertain to measurable and testable attributes, including material strength, structural design, joints, lenses, and coatings. Abstract Factors such as robustness, scratch resistance, longevity, impact resistance, resistance to deformation, and thermal tolerance reflect customers’ expectations and perceptions regarding product longevity. The Concrete Factors are related to Value for Money, including material costs, design fees, manufacturing expenditures, brand influence, and market positioning. Companies must consider these critical tangible attributes for pricing and market strategies. At the abstract level, Value for Money includes subjective evaluations by customers, such as competitive pricing, perception of luxury, affordability, premium quality, perceived worth, assurance, and market competitiveness.
The attractive attributes of eyewear design consist of an analytical framework for assessing eyewear design quality and addressing the tangible technical requirements of product design and production and the emotive needs and anticipations of consumers. Using this model, designers and manufacturers can enhance their comprehension of, and alignment with, market needs and product offerings, thus creating products that not only satisfy practical use requirements but also meet the expectations of consumers.
4.2. Analysis of Kano Model Results
4.2.1. Classification of Quality Attributes
Using the bidirectional questionnaire of the Kano Model, the quality attributes were identified by the respondents using the predominant quality attribute. Table 1 shows the four Attractive Quality factors, six Must-be Quality factors, one One-dimensional Quality factor, and one Indifferent Quality factor. In contemporary consumer culture, eyeglasses serve as emblems of fashion trends and personal style beyond the function of vision correction. The Kano Model dissects multi-faceted quality characteristics and delineates consumer expectations and predilections for various design quality features and their impact on consumer satisfaction. As shown in Table 1, Must-be Quality (M) attributes such as innovation and multifunctionality were epitomized by innovative designs, versatile functionality, unprecedented characteristics, and novel materials. Such attributes are anticipated by consumers, and their absence causes marked dissatisfaction. Therefore, companies need to pursue technological innovation and multifunctional solutions to satisfy the requirements of consumers’ usage. Additionally, design elements need to be identified as Attractive Quality (A) attributes of modern aesthetics, distinctiveness, and alignment with prevailing trends. These traits elevate consumer satisfaction, whereas their absence does not engender dissatisfaction. Designers MUST exploit these elements to engender a ‘wow’ factor, enhancing the allure of the product.

Table 1.
Factors of Kano Model.
Designs being characterized as timeless and incorporating fashion elements and are considered as One-dimensional Quality (O) attributes, which suggests a direct relationship between these features and consumer satisfaction. The explicit portrayal of branding and minimalist design (I) affect satisfaction levels, as they attract niche customers. With these qualities, eyewear must be designed to satisfy functional requirements while also catering to consumer desires for aesthetic appeal and individualistic expression. In a competitive environment, this approach allows for design strategies that augment the consumer experience with additional value while preserving essential functionality.
The Kano Model was used to explore the relationship between eyewear design quality attributes and consumer satisfaction, and provide user-centric data for strategic design and marketing decisions. Understanding the influence of these attributes on consumer perceptions, companies need to craft eyewear designs to fulfill fundamental requirements and add value.
4.2.2. Kano Weighting Method
The Kano Weighting Method operates to increase satisfaction and mitigate dissatisfaction gain in determining consumer satisfaction. By comparing the “Customer Satisfaction (CS) Increase Coefficient” and the “Customer Dissatisfaction (CD) Reduction Coefficient”, the method is used to identify the attribute with the greatest impact (the coefficient with the larger absolute value) (Equation (1)). Initially, qualities lacking differentiation are omitted from consideration and determined by using Equation (2).
Table 2 presents the relative weights within the Kano model and a discernible pattern in consumer satisfaction and dissatisfaction with a product or design. The weights derived from the Kano analysis present consumer anticipations towards brands and products and show trends within the contemporary marketplace. A weight associated with the attribute of “brand or logo” underscores the salience of brand identity. A brand transcends its emblematic logo or nomenclature and embodies a testament to quality, dependability, and societal identity. Consumers’ purchasing decisions extend beyond the product’s functional or aesthetic attributes, encompassing an alignment with the ethos and values emblematic of the brand. Similarly, the considerable weight of “innovative special materials” suggests a consumer inclination towards novel and distinctive experiences. The weight was used to distinguish cutting-edge technologies for enhanced performance. Such products have advantages over the competing ones. The weights of “fashion trends” and “fashion elements” underscore consumer predilections for functional utility or efficacy. Emotional aspiration exists to identify the personal and sartorial acumen of the eyewear. The weights attributed to “classic design” and “simplicity” suggest that in the vanguard of innovation and style, traditional or simple designs may not align with the preferences of the consumer.

Table 2.
Discrimination of quality attributes and weights of satisfaction coefficients.
The data derived from the Kano model’s weighting system offer information on consumer predilections and trends in the market. For brand designers, this underscores imperative innovation with the emotional rapport with consumers, as a strategy to obtain differentiation in a competitive market.
5. Conclusions
Using the EGM interview method and the Kano Model, the consumer quality attributes were determined to elucidate the relationship between the attractive factors of eyewear design and consumer satisfaction. The Kano Model’s results indicated that innovative materials, multifunctionality, and fashionable elements were the determinants of consumer satisfaction in the ‘Must-be Quality’ and ‘One-dimensional Quality’ categories. The existence or improvement of these attributes increased consumer satisfaction. Herein, innovation and multifunctionality were identified as basic requirements and essential elements to enhance consumer satisfaction in eyewear design. Contemporary aesthetics, personalized elements, and alignment with fashion trends forged strong brand associations with the consumer, thereby bolstering their intent to purchase. The result of the interview validated charm factors such as distinctive ornamentation or details and the incorporation of innovative materials, which affected consumer evaluation. In designing new eyeglass models, designers pay particular attention to the incorporation of these elements. Although a logo or brand is not an important factor, differentiated brand presentation is imperative to raise recognition in the marketplace. Such results can be used to transform consumer needs and preferences into tangible design references. It is necessary to integrate innovative materials and technologies to craft products with enhanced functionality to satisfy the fundamental needs of consumers. It is also necessary to use the results of the Kano Model for products to meet the demands of various consumers and prioritize functionality or unique designs.
Funding
This research did not receive external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not involve humans or animals, and therefore, ethical review and approval were not required.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable, as the study did not involve humans.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huarng, K.; Lin, Y.-C. A Study on Filling a Prescription According to Different Professional Images and Face Shapes. J. Bus. Des. 2020, 24, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.-H. A Study on the Conditions of 21st Century Eyewear Design and Total Fashion Trends—Focused on Clothing, Hair, and Makeup. J. Korean Ophthalmic Opt. Soc. 2005, 10, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- DeLong, M.; Daly, C. Eyewear, Fashion, Design, and Health. Fash. Pract. J. Des. Creat. Process Fash. Ind. 2015, 5, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.-Y. Human Facial Measurement Survey for Eyewear Design. J. Des. 2009, 6, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, I.-M. Study on the Design of Shutter Glasses. Master’s Thesis, Precision and Automation Engineering Program, College of Engineering, National Chiao Tung University, Taipei City, Taiwan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-X.; Li, Y.-R. Generative Product Design by Form Preferences with Kansei Evaluations—A Case Study of Eyeglasses Design. J. Kansei 2017, 5, 60–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.K.; Chen, I.S. Kano’s Model and Customer Satisfaction. Int. J. Commer. Strategy 2010, 2, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Matzler, K.; Hinterhuber, H.H. How to Make Product Development Projects More Successful by Integrating Kano’s Model of Customer Satisfaction into Quality Function Deployment. Technovation 1998, 18, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, N.; Seraku, N.; Takahashi, F.; Tsuji, S. Attractive Quality and Must-Be Quality. J. Jpn. Soc. Qual. Control 1984, 14, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, C.; Blauth, R.; Boger, D. Kano’s Methods for Understanding Customer-Defined Quality. Cent. Qual. Manag. J. 1993, 2, 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.C.; Shen, X.X. Integrating Kano’s Model into Internal/External Customer Satisfaction. Total Qual. Manag. 2000, 11, 813–819. [Google Scholar]
- Sireli, Y.; Kauffmann, P.; Ozan, E. Integrated Application of Kano’s Model and AHP to R&D Projects. J. Eng. Des. 2007, 18, 167–183. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, E.W.; Sullivan, M.W. The Antecedents and Consequences of Customer Satisfaction for Firms. Mark. Sci. 1993, 12, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L. Satisfaction: A Behavioral Perspective on the Consumer; Irwin/McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kotler, P.; Armstrong, G. Principles of Marketing; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shahin, A. Integration of Fuzzy Logic and Kano’s Model in Quality Function Deployment. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2004, 21, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.C.; Pawitra, T.A. Integrating SERVQUAL and Kano’s Model into QFD for Service Excellence Development. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2001, 11, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittink, D.R.; Bayer, L.R. Measuring Product Perceptions: A Structural Analysis of the Relationship Between Attribute Judgments and Overall Evaluations. J. Consum. Mark. 1994, 6, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).