Enhancing Microfluidic Systems’ Mixing Efficiency Using Design Models with Convergent–Divergent Sinusoidal Microchannel Walls: Experimental Investigations Based on Entropy Minimization Flow Structures †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
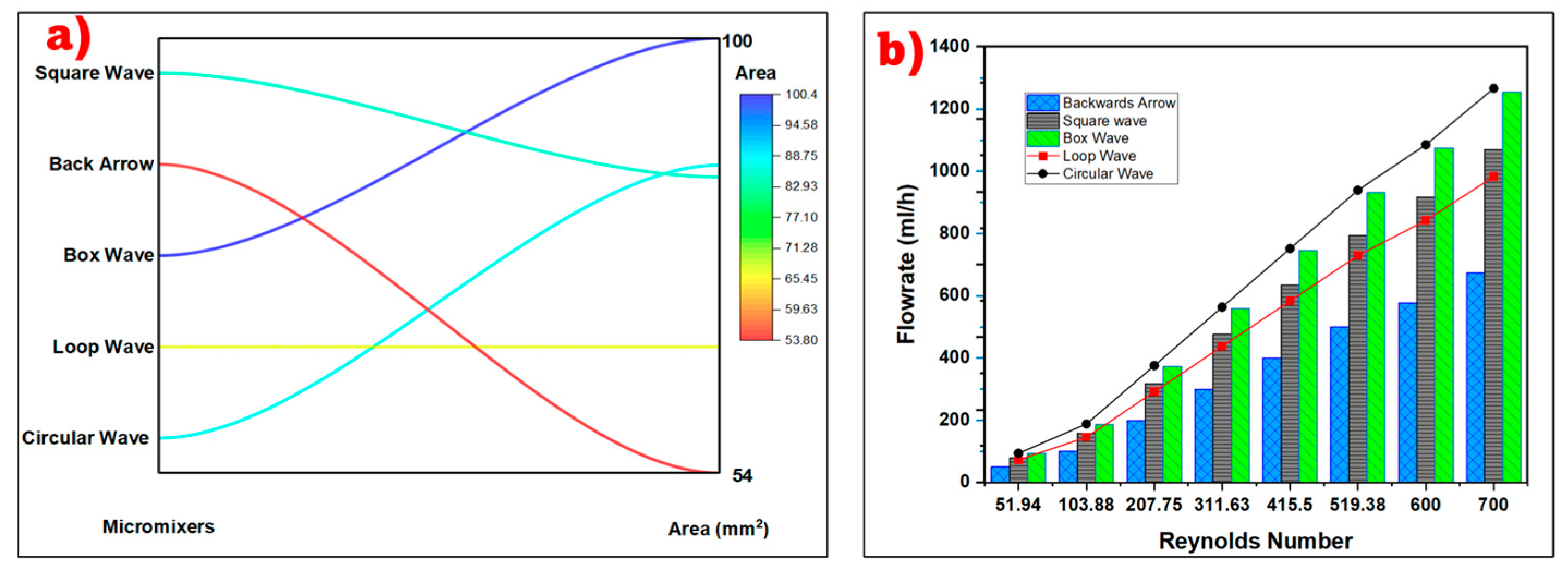
3.1. Micromixer Design and Effect of Reynolds Number on Flow Rate in Each Micromixer
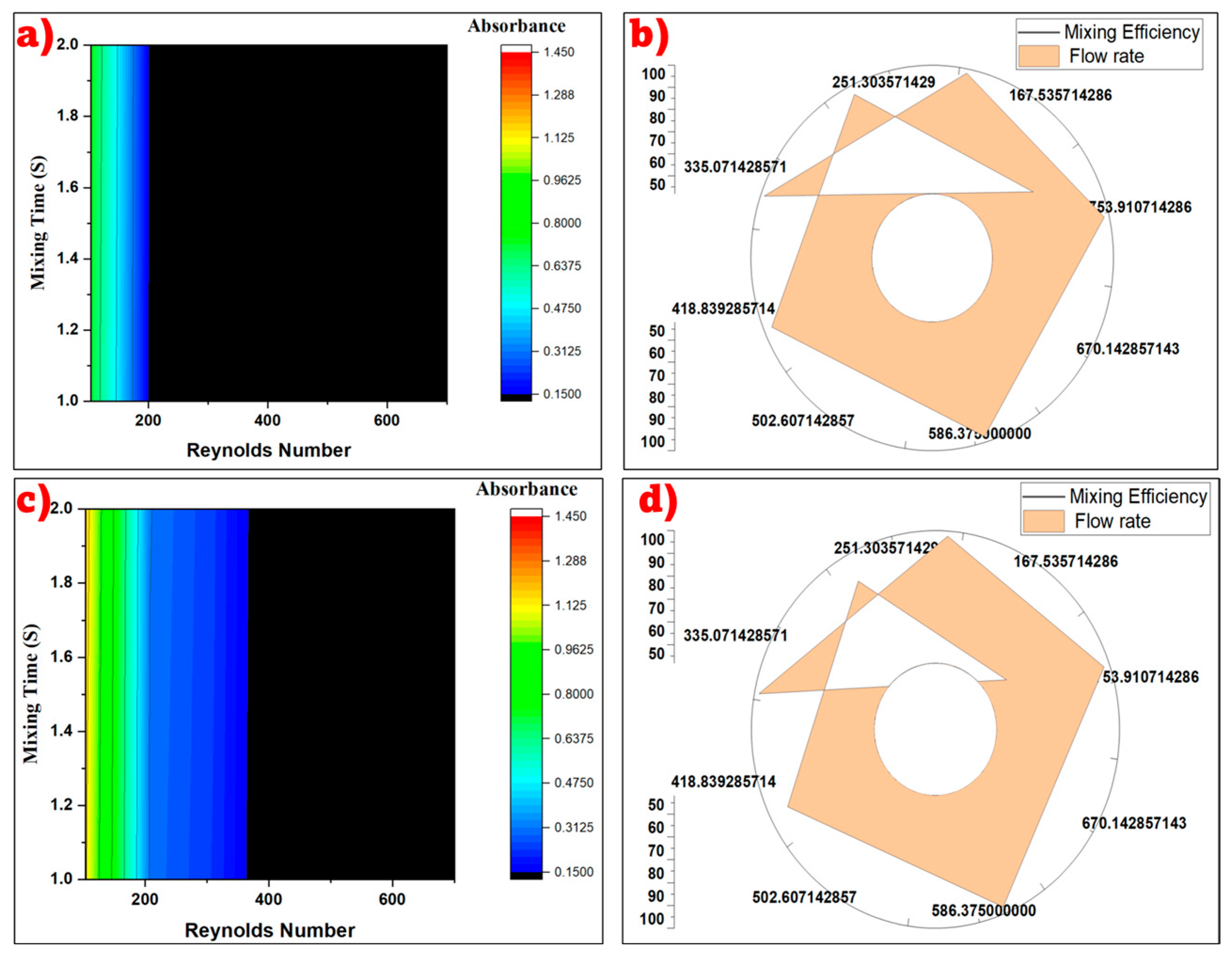
3.2. Evaluating Mixing Efficiency for Backward Arrow and Loop-Wave Micromixers
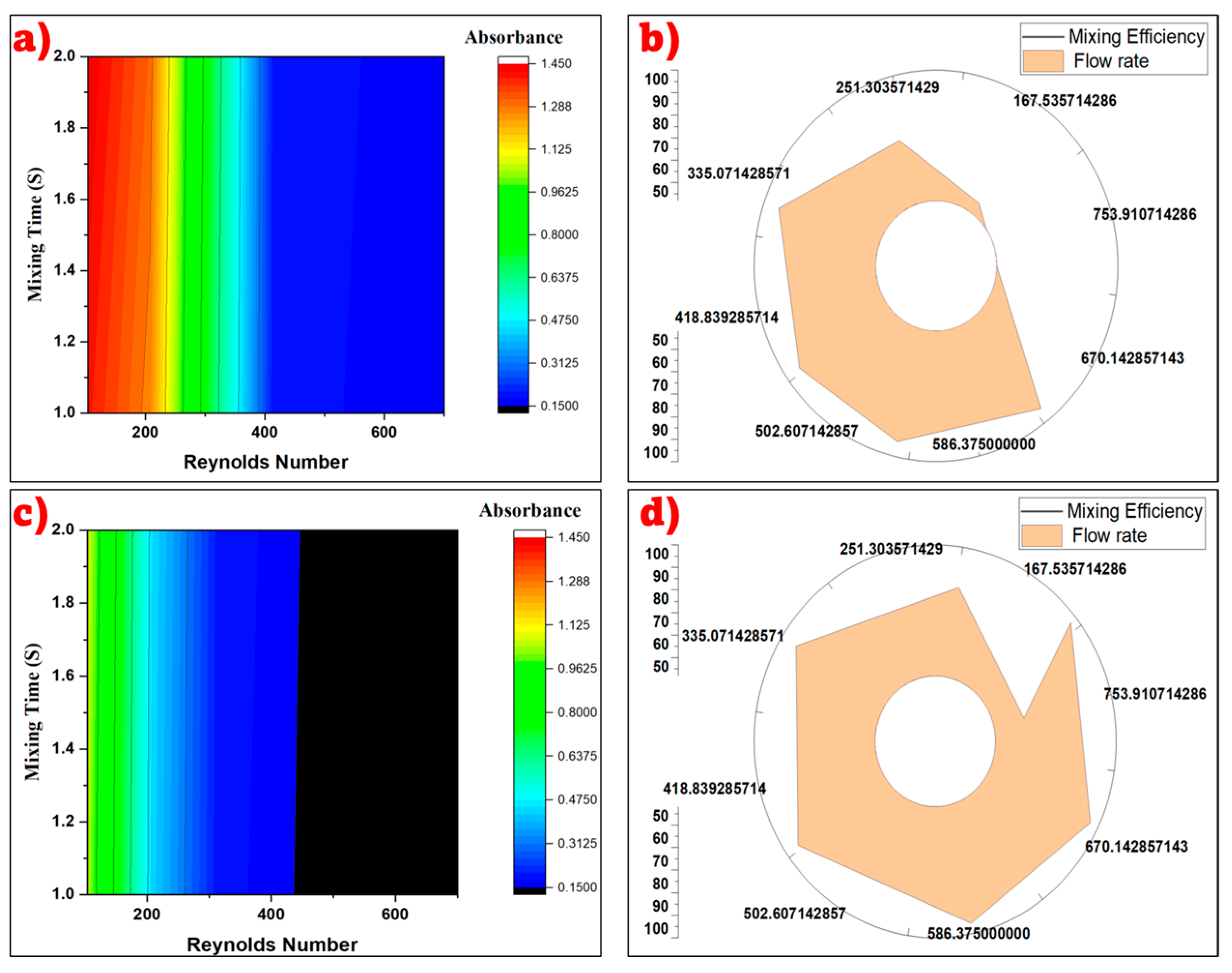
3.3. Evaluating Mixing Efficiency for Square-Wave and Circular-Wave Micromixers
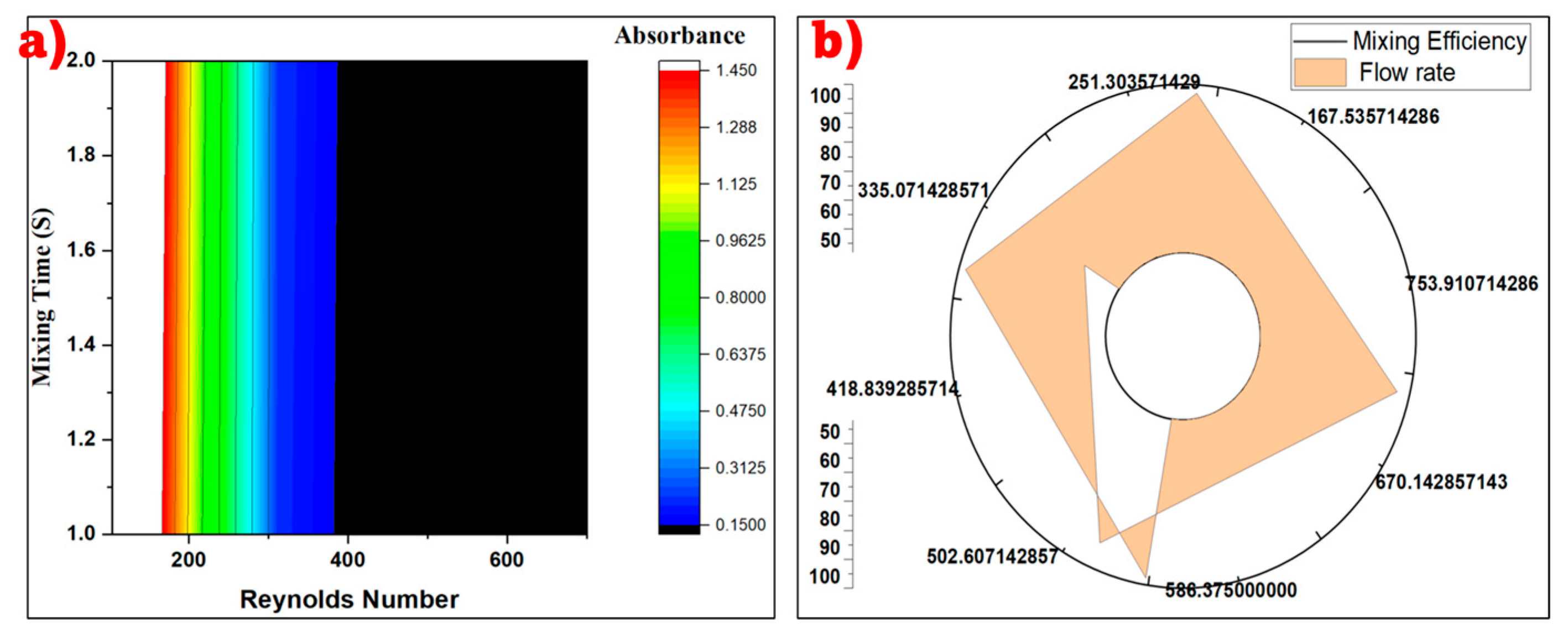
3.4. Evaluating Mixing Efficiency for Box-Wave Micromixer
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dartoomi, H.; Khatibi, M.; Ashrafizadeh, S.N. Importance of nanochannels shape on blue energy generation in soft nanochannels. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 431, 141175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, K.; Datta, A.; Biswas, N.; Das, S.; Das, P. Designing of microsink to maximize the thermal performance and minimize the Entropy generation with the role of flow structures. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 176, 121421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayen, B.; Manna, N.K.; Biswas, N. Enhanced mixing quality of ring-type electroosmotic micromixer using baffles. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2023, 189, 109381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Mao, X.; Shi, J.; Juluri, B.K.; Huang, T.J. A millisecond micromixer via single-bubble-based acoustic streaming. Lab Chip. 2009, 9, 2738–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayareh, M.; Ashani, M.N.; Usefian, A. Active and passive micromixers: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2019, 147, 107771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibi, M.; Mehta, S.K.; Ashrafizadeh, S.N.; Mondal, P.K. Surface charge-dependent slip length modulates electroosmotic mixing in a wavy micromixer. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 073105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safo, K. Investigations of the mixing e ffi ciency of fi ve novel micromixer designs with backward arrow inlet using the Villermaux Dushman protocol. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2024, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.; Lin, J. A review on micromixers. Micromachines 2017, 8, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zschieschang, E.; Pfeifer, P.; Schebek, L. Environmentally optimized microreactor design through Life Cycle Assessment. Green Process. Synth. 2012, 1, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, P.; Wiles, C. Recent advances in synthetic micro reaction technology. Chem. Commun. 2007, 5, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commenge, J.M.; Falk, L. Villermaux-Dushman protocol for experimental characterization of micromixers. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2011, 50, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwundu, O.S.; Fuseini, M.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Elkady, M.F. Comparison of mixing performances of T, Y and arrow-shaped micromixers using Villermaux–Dushman protocol at low Reynolds number. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2020, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gande, V.V.; Podupu, P.K.R.; Berry, B.; Nere, N.K.; Pushpavanam, S.; Singh, M.R. Engineering advancements in microfluidic systems for enhanced mixing at low Reynolds numbers. Biomicrofluidics 2024, 18, 011502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Manna, N.K.; Sarkar, S.; Biswas, N. Enhancing mixing efficiency of a circular electroosmotic micromixer with cross-reciprocal electrodes. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 083626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodies, S. Numerical Study on the Hydraulic and Mixing Performance of Fluid Flow within a Channel with Different Numbers of Sector Bodies. Water 2024, 16, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
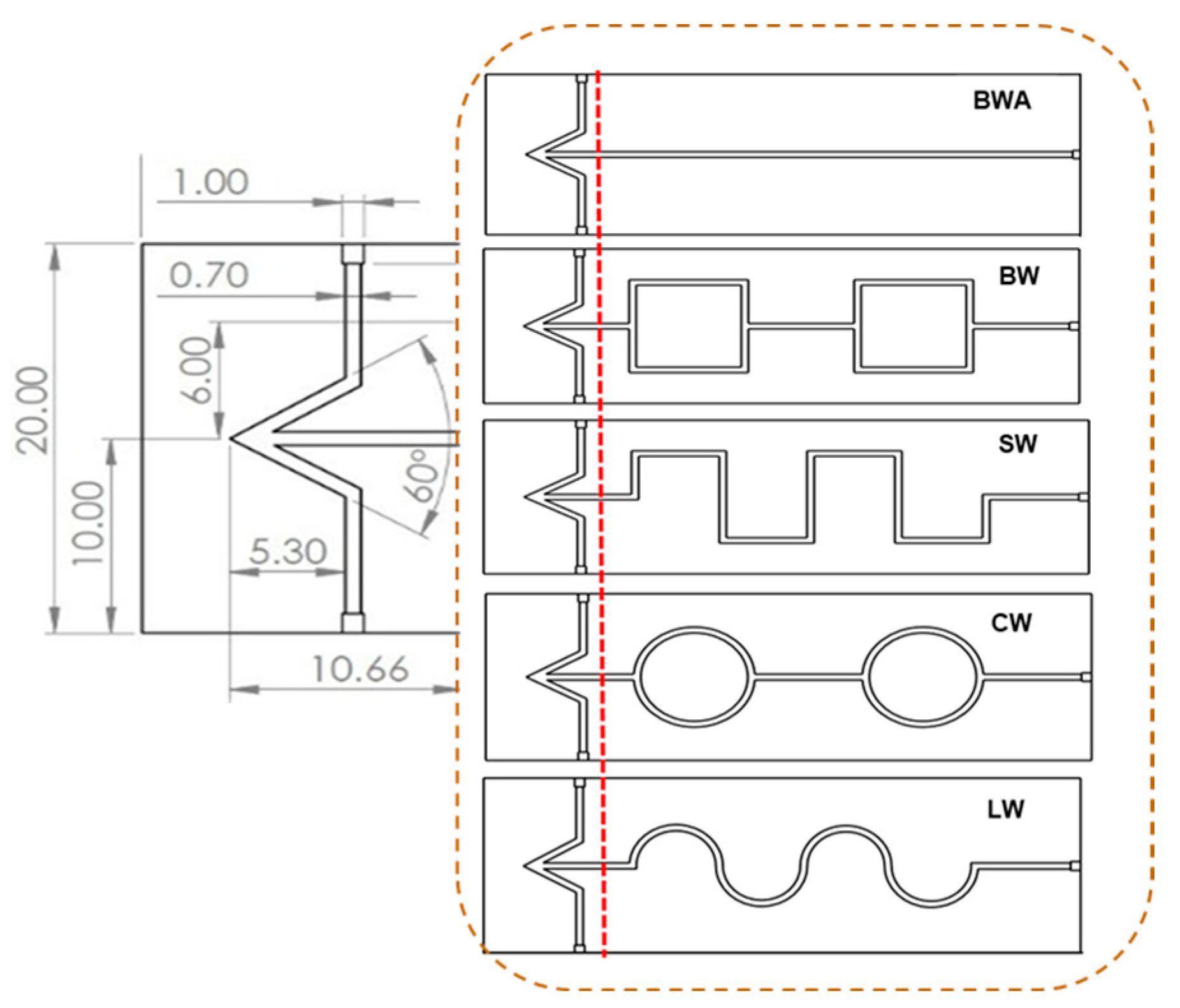
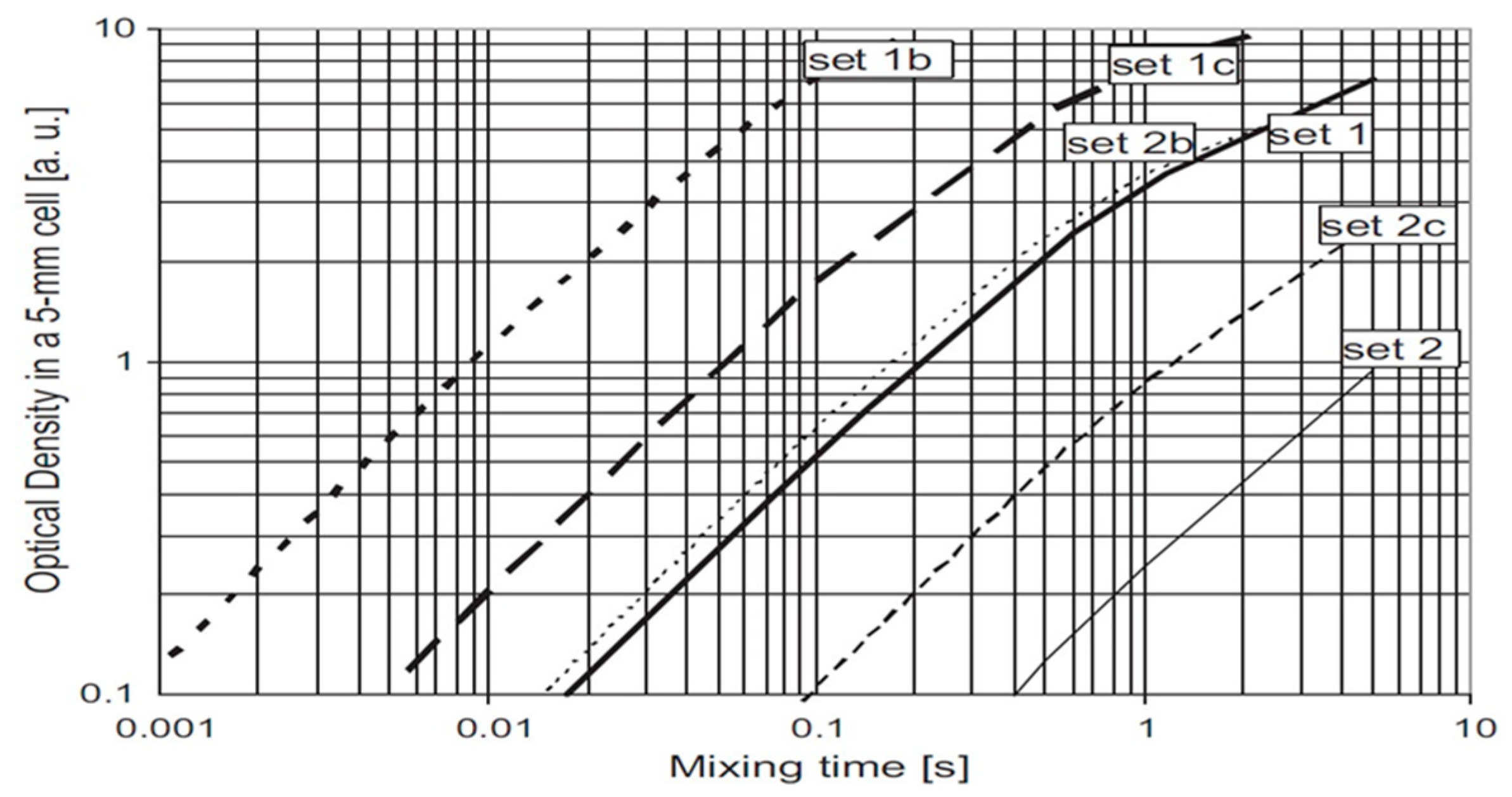
| C [mol/L] | 1 | 1b | 1c | 2 | 2b | 2c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [H+] | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.015 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| [KI] | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.016 |
| [KIO3] | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| [NaOH] | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.045 |
| [H3BO3] | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.045 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Safo, K.; Anani, J.; El-Shazly, A.H. Enhancing Microfluidic Systems’ Mixing Efficiency Using Design Models with Convergent–Divergent Sinusoidal Microchannel Walls: Experimental Investigations Based on Entropy Minimization Flow Structures. Eng. Proc. 2024, 67, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024067054
Safo K, Anani J, El-Shazly AH. Enhancing Microfluidic Systems’ Mixing Efficiency Using Design Models with Convergent–Divergent Sinusoidal Microchannel Walls: Experimental Investigations Based on Entropy Minimization Flow Structures. Engineering Proceedings. 2024; 67(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024067054
Chicago/Turabian StyleSafo, Kingsley, Joshua Anani, and Ahmed H. El-Shazly. 2024. "Enhancing Microfluidic Systems’ Mixing Efficiency Using Design Models with Convergent–Divergent Sinusoidal Microchannel Walls: Experimental Investigations Based on Entropy Minimization Flow Structures" Engineering Proceedings 67, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024067054
APA StyleSafo, K., Anani, J., & El-Shazly, A. H. (2024). Enhancing Microfluidic Systems’ Mixing Efficiency Using Design Models with Convergent–Divergent Sinusoidal Microchannel Walls: Experimental Investigations Based on Entropy Minimization Flow Structures. Engineering Proceedings, 67(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024067054









