Abstract
The cognitive state of a person can be categorized using the Circumplex model of emotional states, a continuous model of two dimensions: arousal and valence. We exploit the Remote Collaborative and Affective Interactions (RECOLA) database, which includes audio, video, and physiological recordings of interactions between human participants to predict arousal and valance values using machine learning techniques. To allow learners to focus on the most relevant data, features are extracted from raw data. Such features can be predesigned or learned. Learned features are automatically learned and utilized by deep learning solutions. Predesigned features are calculated before machine learning and inputted into the learner. Our previous work on video recordings focused on learned features. In this paper, we expand our work onto predesigned visual features, extracted from video recordings. We process these features by applying time delay and sequencing, arousal/valence labelling, and shuffling and splitting. We then train and test regressors to predict arousal and valence values. Our results outperform those from the literature. We achieve a root mean squared error (RMSE), Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC), and concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) of 0.1033, 0.8498, and 0.8001 on arousal predictions; and 0.07016, 0.8473, and 0.8053 on valence predictions, using an optimizable ensemble, respectively.
1. Introduction
The cognitive state of a person can be categorized using the Circumplex model of emotional states [1], a continuous model of two dimensions: arousal and valence, where arousal measures the energy level and valence measures the positivity level of a person’s emotion. In this model, emotions are divided into four categories: happy, angry, sad, and relaxed. Each of these emotions is associated with a quadrant of the circumplex model. Happy emotions have high valence and high arousal, anger—low valence and high arousal, sad—low valence and low arousal, and relaxed—high valence and low arousal. The arousal and valence values can be estimated via machine learning regression.
We use the RECOLA database [2] which includes audio, video, and physiological recordings of online interactions between human participants to predict arousal and valance values using machine learning techniques. We previously predicted arousal and valence values using the physiological [3,4] and video [4,5] recordings of RECOLA. Features are attributes that describe the data. They can be predesigned or learned [6]. Learned features are attributes that are automatically extracted and utilized by deep machine learning solutions during the learning process. On the other hand, predesigned features are attributes that are calculated on the data before the learning process and provided as input to the machine learner. Our previous work on the video recordings of RECOLA focused on learned features from convolutional neural networks (CNNs), such as ResNet-18 and MobileNet-v2. MobileNet-v2 achieved a root mean squared error (RMSE), Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC), and concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) of 0.1220, 0.7838, and 0.7770 on arousal predictions; and 0.0823, 0.7789, and 0.7715 on valence predictions, respectively. In this paper, we expand our work to analyze and assess the predesigned visual features, extracted from the video recordings of RECOLA. We propose a novel combination of processing steps to prepare the visual features for regression. We leverage machine learning solutions such as regression trees, kernel regression, and ensemble regressors to predict the arousal and valence values of cognitive states. Our goal is to find the model(s) with the best prediction performance to later integrate into a virtual reality (VR) system that runs cognitive remediation exercises for users with mental health disorders (e.g., schizophrenia).
Solutions for the prediction of cognitive states ideally consist of two components: parametrization and recognition of facial expressions [6]. Parametrization is the process of specifying the visual features and coding schemes to describe the involved facial expressions. The visual features used for the prediction of cognitive states can be appearance or geometric features [7]. Geometric features represent the geometry of the face. Local Gabor Binary Patterns from Three Orthogonal Planes (LGBP-TOP) [8] is one method that is used in the extraction of appearance features, while facial landmarks [9] are usually used for geometric features. Examples of geometric features include the derivatives of the detected facial landmarks, the speed and direction of motion in facial expressions, the head pose, and the direction of the eye gaze. Appearance features represent the overall texture resulting from the deformation of the neutral facial expression. Appearance features depend on the intensity of an image, whereas geometrical features determine distances, deformations, curvatures, and other geometric properties [6]. Coding schemes can either be descriptive or judgmental [6]. Descriptive coding schemes depend on surface properties and what the face can do to describe facial expression. Judgmental coding schemes depend on the latent emotions or affects that produce them to parameterize facial expressions. The facial action coding system (FACS) [10] is one example of descriptive systems. FACS is a system that describes all visually evident facial movements [10,11]. It divides facial expressions into individual components of muscle movement, called Action Units (AUs). Coding schemes, such as facial AUs, as well as geometric and/or appearance features can then be treated as input parameters to machine learning regressors or classifiers for the prediction of cognitive states.
2. Literature Overview
RECOLA [2] is a multimodal database of natural emotions that is often used in studies on the prediction of cognitive states. It contains video, audio, and physiological recordings. It also provides predesigned features for these recordings. Arousal and valence annotations were provided by 6 raters every 40 ms of recording. The mean of the six ratings was used to label the data in our work. The database contains 5-min video recordings of 27 participants, where only data from 23 participants are publicly available. Since some of the data modalities in RECOLA contain records for 18 of the participants, we only used these 18 recordings from the RECOLA database to prove our concept.
The authors of the original RECOLA database [2] further extended their work in [11], where they performed experiments on the database for the prediction of arousal and valence values. They extracted 20 visual features on each video frame in the video recordings of RECOLA, along with their first order derivates. They then deployed a bidirectional long short-term memory recurrent neural network (BiLSTM RNN) to predict arousal and valence measures. They compared the prediction performance of the RNN between mean ratings (average of annotations from all 6 raters) and all six ratings, using both single-task and multi-task learning techniques. For arousal, they achieved a CCC of 0.427 using multi-task learning over all six ratings. For valence, they achieved a CCC of 0.431 using single-task learning over all six ratings. The authors of RECOLA [2,11] later introduced the Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge and Workshop (AVEC) in 2015 [12]. In AVEC 2018 [13], they experimented with the different types of visual features: appearance, geometric, 17 facial AUs, and bags-of-words. For arousal, they achieved a CCC of 0.312 via multi-task Lasso, while using appearance features. For valence, they achieved a CCC of 0.438 via a support vector machine (SVM), while using geometric features.
Other authors have also benefited from using the RECOLA database in their research. Han et al. [14] exploited the geometric visual features provided by AVEC to predict arousal and valence values through an RNN. They implemented an implicit fusion framework for joint audiovisual training. They achieved a CCC of 0.413 and 0.527 on arousal and valence predictions, respectively. Albadawy et al. [15] used the visual features provided by AVEC 2015, which included appearance (LGBP-TOP) and geometric (Euclidean distances between 49 facial landmarks) features. For arousal and valence predictions, they proposed a joint modelling strategy using a deep BiLSTM for ensemble and end-to-end models. Their ensemble BiLSTM model achieved a CCC of 0.699 and 0.617 for arousal and valence, respectively. In our work, we used and further processed the basic features extracted by the authors of RECOLA in [11] and experimented with a variety of regressors to predict the arousal and valence values of cognitive states.
3. Methods
We processed the visual features of RECOLA by applying time delay and sequencing, arousal and valence annotation labelling, and data shuffling and splitting. We then trained and tested regressors to predict the arousal and valence values. The following sections will discuss the details about our processing steps and regression methodology.
3.1. RECOLA’s Predesigned Visual Features
The video recordings of RECOLA were sampled at a sampling rate of 25 frames/s, where visual features were extracted for each video frame [11]. As predesigned visual features, RECOLA contains 20 attributes alongside their first order derivative, resulting in 40 features in total. These attributes/features include 15 facial AUs of emotional expressions, the head-pose in three dimensions (i.e., X, Y, Z), and the mean and standard deviation of the optical flow in the region around the head. The AUs are AU1 (Inner Brow Raiser), AU2 (Outer Brow Raiser), AU4 (Brow Lowerer), AU5 (Upper Lid Raiser), AU6 (Cheek Raiser), AU7 (Lid Tightener), AU9 (Nose Wrinkler), AU11 (Nasolabial Deepener), AU12 (Lip Corner Puller), AU15 (Lip Corner Depressor), AU17 (Chin Raiser), AU20 (Lip Stretcher), AU23 (Lip Tightener), AU24 (Lip Pressor), and AU25 (Lips Part) from FACS. For more information about these features and their extraction, please refer to [11]. We used these features in our work.
3.2. Time Delay and Sequencing
RECOLA’s video recordings were sampled at a rate of 25 frames/s. This means that one frame was captured every 0.04 s (40 ms). The visual features were calculated on each frame, meaning that they were provided every 40 ms as well. Since other data modalities of RECOLA only started being recorded after 2 s (2000 ms), we skipped any readings that occurred before that time. As a result, the first 50 frames (2 s × 25 frames/s) of the recordings were unused in our work.
3.3. Annotation Labelling
The data in RECOLA were labelled with respect to the arousal and valence emotional dimensions. The data samples were manually annotated using ANNEMO, an annotation tool, developed by Ringeval et al. [2]. Each recording was annotated by six raters. The mean of these six ratings was used to label the data in our work. The mean arousal and valence values were also sampled every 40 ms. As we proceeded in Section 3.2, the first 50 annotations were discarded. The remaining annotations were accordingly used to label the corresponding vectors of visual features. All labelling and fusion of data samples and features were completed according to the timing of the video frames.
3.4. Data Shuffling and Splitting
Data shuffling ensures the randomization and diversity of the data. The data were shuffled and split, where 80% went towards training and validation, and 20% went towards testing. Our training and validation dataset was 106,201 frames × 40 features in size, while the testing dataset was 26,550 frames × 40 features in size.
3.5. Regression
For the prediction of arousal and valence values, we used an optimizable ensemble regressor. We also experimented with other regression models for comparison purposes: tree regressors, regression kernels, and ensemble regression. We trained and validated four tree regressors (fine, medium, coarse, and optimizable tree), two regression kernels (SVM and least squares regression kernel), and two ensembled regressors (boosted and bagged trees). A fine regression tree is small with a leaf size of 4 [16]. A medium regression tree has 12 leaves. A coarse regression tree is large and has a leaf size of 36. An optimizable regression tree optimizes the minimum leaf size through a Bayesian optimizer. Regression kernels are Gaussian regression models for nonlinear regression over large datasets. An SVM kernel maps the features into a high-dimensional space and fits a linear SVM model to the transformed features. A least squares regression kernel maps the features into a high-dimensional space and fits a least squares linear regression model to the transformed features. The boosted trees model ensembles regression trees using the LSBoost algorithm. The bagged trees model ensembles regression trees by bootstrap-aggregation. An optimizable regression ensemble optimizes training hyperparameters (ensemble method, number of learners, learning rate, minimum leaf size, and number of predictors to sample) via Bayesian optimization. We implemented 5-fold cross-validation during training to avoid overfitting.
4. Discussion of Results
After training the aforementioned models, we tested them by predicting the arousal and valence values on the testing set to evaluate the performance when presented with new data. Table 1 summarizes the validation and testing performances in terms of the RMSE, PCC, and CCC performance measures. A smaller RMSE value signifies better performance, whereas greater PCC and CCC values signify better performance. We have achieved a testing RMSE, PCC, and CCC of 0.1033, 0.8498, and 0.8001 on arousal predictions, respectively. We have achieved a testing RMSE, PCC, and CCC of 0.07016, 0.8473, and 0.8053 on valence predictions, respectively. These performances were obtained using an optimizable ensemble regressor. Our performances are better than those from the literature [11,12,13,14,15] (see Section 2), who performed more complex processing and feature extraction. In Table 1, the validation performances were evaluated by performing 5-fold cross validation across the training data. The testing performances were computed by using the trained model for predicting the arousal and valence values of the testing set. The rows corresponding to the best prediction performances are displayed in bold font in Table 1. Figure 1 displays a plot of the predicted arousal and valence values against the actual values, as per the best model (i.e., optimizable ensemble). In the plot of a perfect regression model, the predicted values would be the same as the actual values, resulting in a diagonal line of points [16]. Models where the points are scattered near the diagonal line represent good models, with less errors. Table 1 and Figure 1 also compare the performances of our models for learned [4] and predesigned features. Using predesigned features showed an improvement in our prediction performance.

Table 1.
Summary of Prediction Performances.
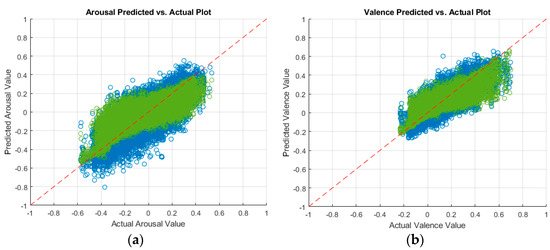
Figure 1.
Predicted versus actual plots of (a) arousal, and (b) valence predictions by an optimizable ensemble trained on visual features (green), and MobileNet-v2 trained on video frames (blue). The diagonal, red-dashed line represents a perfect regression model.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we performed arousal and valence predictions by exploiting the predesigned visual features of the RECOLA database. The feature vectors were processed and accordingly labelled with their corresponding arousal or valence annotations. We trained, validated, and tested an optimizable ensemble as well as other regressors to predict arousal and valence values. The optimizable ensemble achieved a RMSE, PCC, and CCC of 0.1033, 0.8498, and 0.8001 on arousal predictions, and 0.07016, 0.8473, and 0.8053 on valence predictions, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, our prediction performances on arousal and valence predictions are the best in comparison to the literature. Going forward, we will carry out our project with the optimizable ensemble as the prediction mechanism for predesigned visual features. Since we achieved good prediction performance using physiological [3,4] and visual data, we can work on acoustic data and start combining our solutions for the different data modalities. In the future, we will apply our findings to real data, obtained from a VR system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.O.J., A.-M.C. and S.B.; methodology, I.O.J.; software, I.O.J.; validation, I.O.J.; formal analysis, I.O.J.; investigation, I.O.J.; resources, A.-M.C. and S.B.; data curation, I.O.J.; writing—original draft preparation, I.O.J.; writing—review and editing, I.O.J., A.-M.C. and S.B.; visualization, I.O.J.; supervision, A.-M.C. and S.B.; project administration, A.-M.C. and S.B.; funding acquisition, A.-M.C. and S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC)’s Discovery grant, number RGPIN-2023-03415.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created. Data was obtained from the RECOLA team and are available, upon request at https://diuf.unifr.ch/main/diva/recola/download.html.
Acknowledgments
A special thank you to the providers of the RECOLA database, F. Ringeval, A. Sonderegger, J. Sauer, and D. Lalanne.
Conflicts of Interest
Stéphane Bouchard is the President of, and owns equity in, In Virtuo Clinics and Development, a spin-off company from the university that distributes virtual environments designed for the treatment of mental disorders. The terms of these arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the University of Québec in Outaouais in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. Stéphane Bouchard has received honoraria for presenting research and providing workshops. He also receives royalties from books.
References
- Russell, J. Affective Space Is Bipolar; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Ringeval, F.; Sonderegger, A.; Sauer, J.; Lalanne, D. Introducing the RECOLA multimodal corpus of remote collaborative and affective interactions. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Shanghai, China, 22–26 April 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Joudeh, I.O.; Cretu, A.; Guimond, S.; Bouchard, S. Prediction of Emotional Measures via Electrodermal Activity (EDA) and Electrocardiogram (ECG). Eng. Proc. 2022, 27, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Joudeh, I.O.; Cretu, A.-M.; Bouchard, S.; Guimond, S. Prediction of Continuous Emotional Measures through Physiological and Visual Data. Sensors 2023, 23, 5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joudeh, I.O.; Cretu, A.-M.; Bouchard, S.; Guimond, S. Prediction of Emotional States from Partial Facial Features for Virtual Reality Applications. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual CyberPsychology, CyberTherapy and Social Networking Conference (CYPSY26), Paris, France, 11–13 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Corneanu, C.A.; Simon, M.O.; Cohn, J.F.; Guerrero, S.E. Survey on RGB, 3D, Thermal, and Multimodal Approaches for Facial Expression Recognition: History, Trends, and Affect-Related Applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 1548–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Osman, H.; Falk, T.H. Multimodal affect recognition: Current approaches and challenges. Emot. Atten. Recognit. Based Biol. Signals Images 2017, 8, 59–86. [Google Scholar]
- Almaev, T.R.; Valstar, M.F. Local Gabor Binary Patterns from Three Orthogonal Planes for Automatic Facial Expressions Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 Humaine Association Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, Geneva, Switzerland, 2–5 September 2013; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA; pp. 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; De la Torre, F. Supervised descent method and its applications to face alignment. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 532–539. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Facial Action Coding System: A Technique for the Measurement of Facial Movement; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Ringeval, F.; Eyben, F.; Kroupi, E.; Yuce, A.; Thiran, J.P.; Ebrahimi, T.; Lalanne, D.; Schuller, B. Prediction of Asynchronous Dimensional Emotion Ratings from Audiovisual and Physiological Data. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2015, 66, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringeval, F.; Schuller, B.; Valstar, M.; Jaiswal, S.; Marchi, E.; Lalanne, D.; Cowie, R.; Pantic, M. AV+EC 2015—The First Affect Recognition Challenge Bridging Across Audio, Video, and Physiological Data. In Proceedings of the AVEC’15, Brisbane, Australia, 26–27 October 2015; ACM: New York, NY, USA; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ringeval, F.; Schuller, B.; Valstar, M.; Cowie, R.; Kaya, H.; Schmitt, M.; Amiriparian, S.; Cummins, N.; Lalanne, D.; Michaud, A.; et al. AVEC 2018 Workshop and Challenge: Bipolar Disorder and Cross-Cultural Affect Recognition. In Proceedings of the AVEC’18, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22 October 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Schuller, B. Implicit Fusion by Joint Audiovisual Training for Emotion Recognition in Mono Modality. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 5861–5865. [Google Scholar]
- Albadawy, E.; Kim, Y. Joint Discrete and Continuous Emotion Prediction Using Ensemble and End-to-End Approaches. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction (ICMI ‘18), Boulder, CO, USA, 16–20 October 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA; pp. 366–375. [Google Scholar]
- Help Center. Help Center for MATLAB, Simulink, and Other MathWorks Products. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/ (accessed on 2 September 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).