Mucoadhesive Pentoxifylline Microsphere for Non-Invasive Nasal Drug Delivery †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Preparation of Pentoxifylline–Sodium Alginate Microspheres
2.2. Experimental Design
3. Result and Discussion
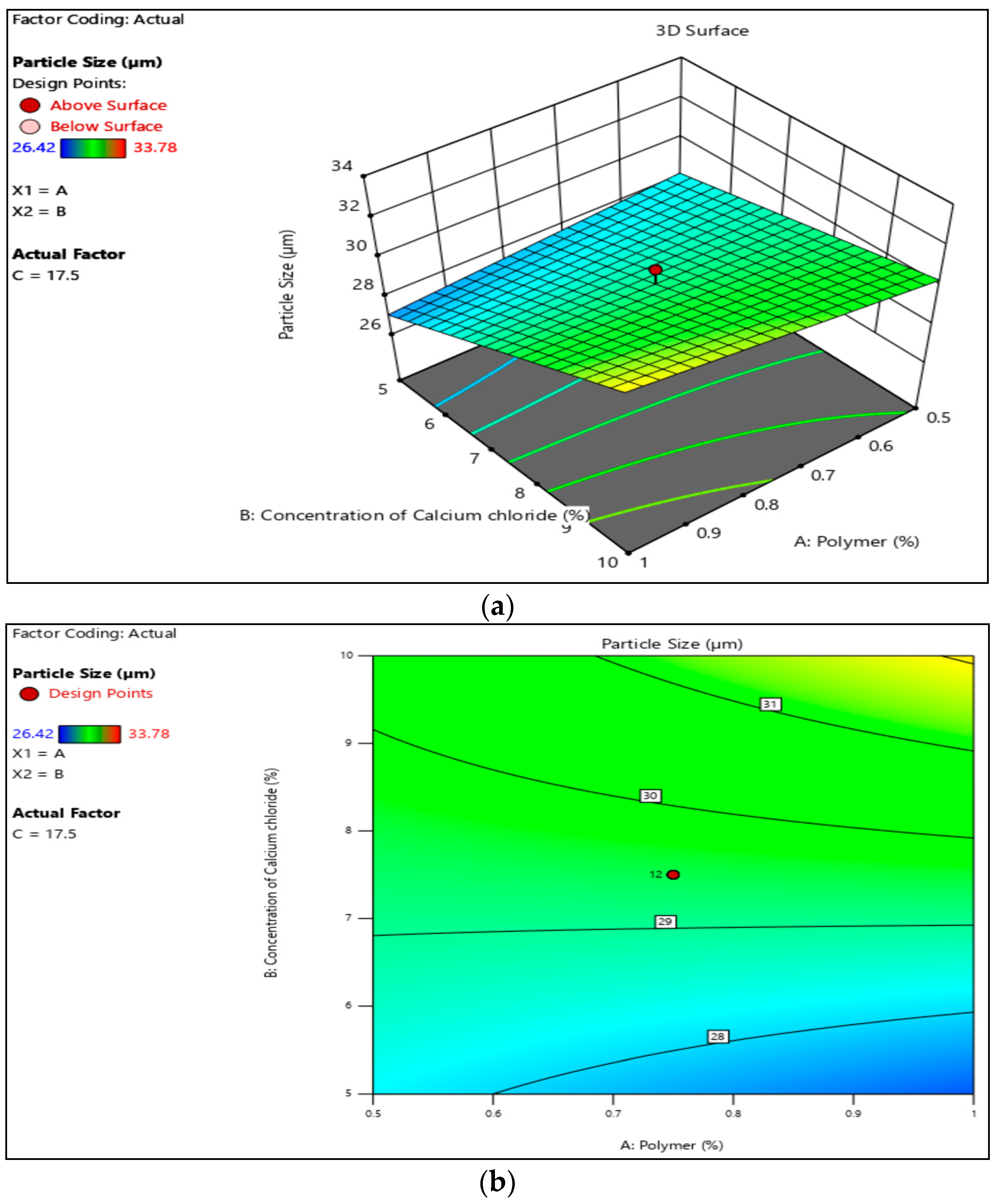
3.1. Particle Size
3.2. Surface Morphology
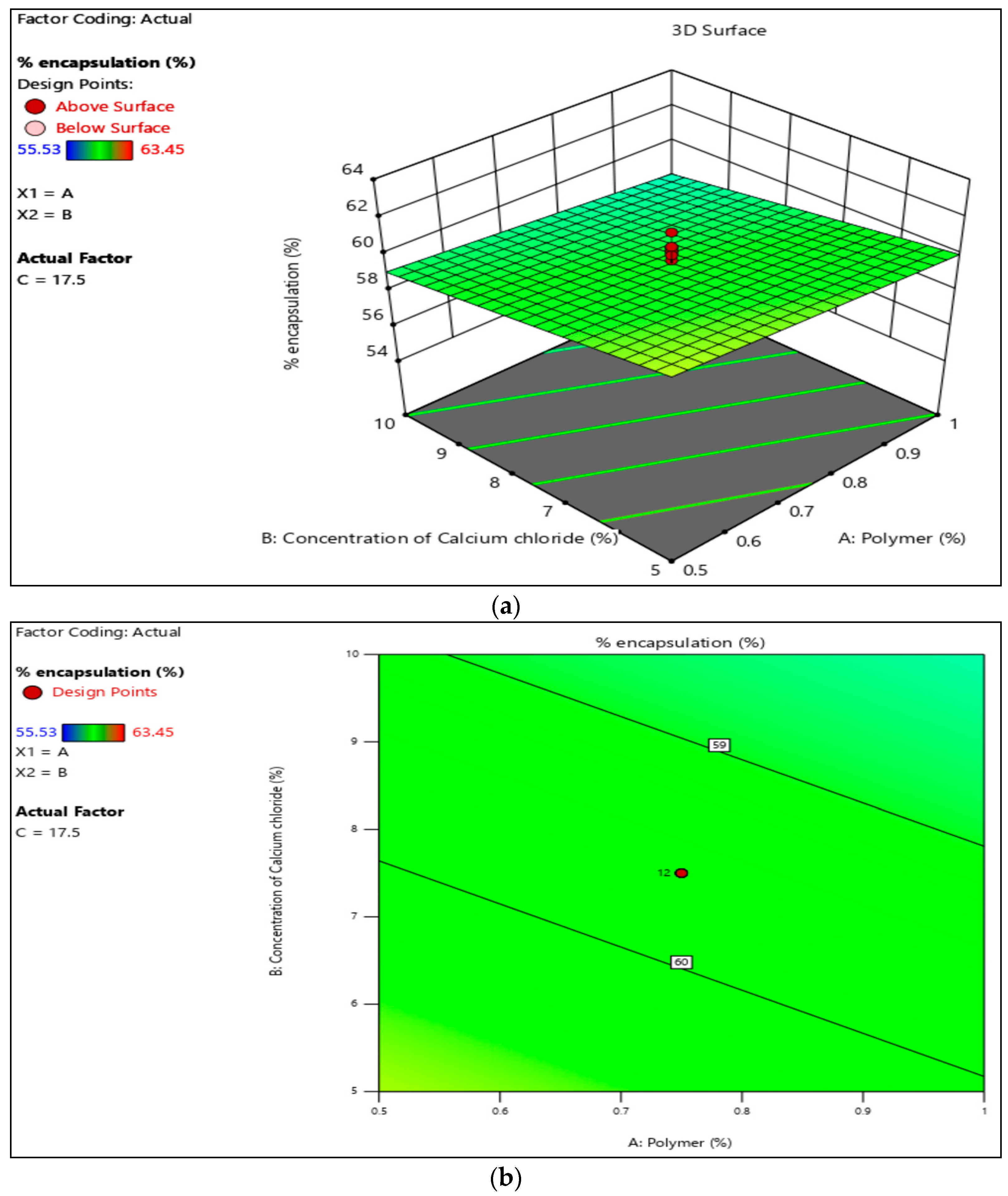
3.3. Encapsulation Efficacy
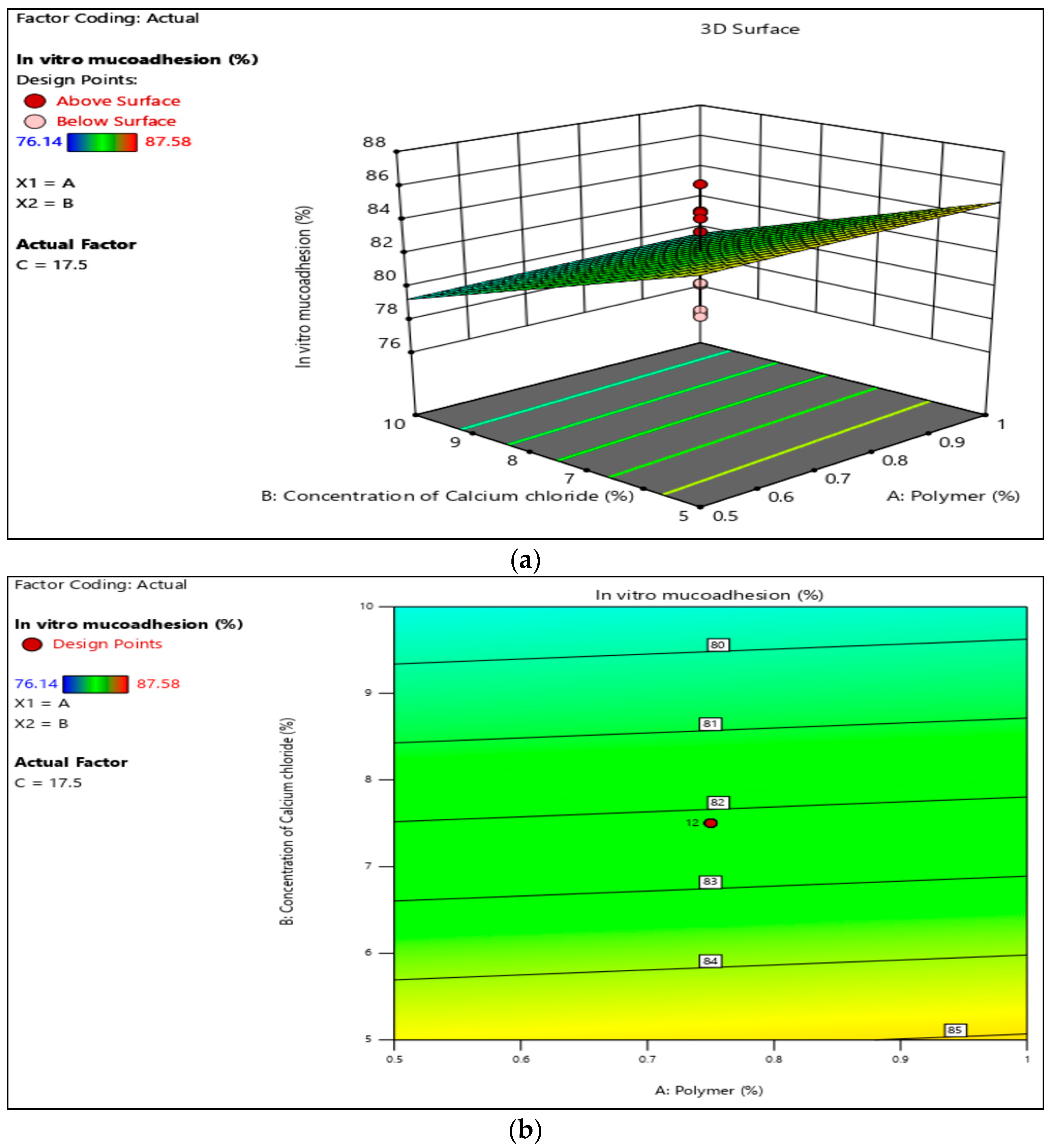
3.4. In-Vitro Mucoadhesion
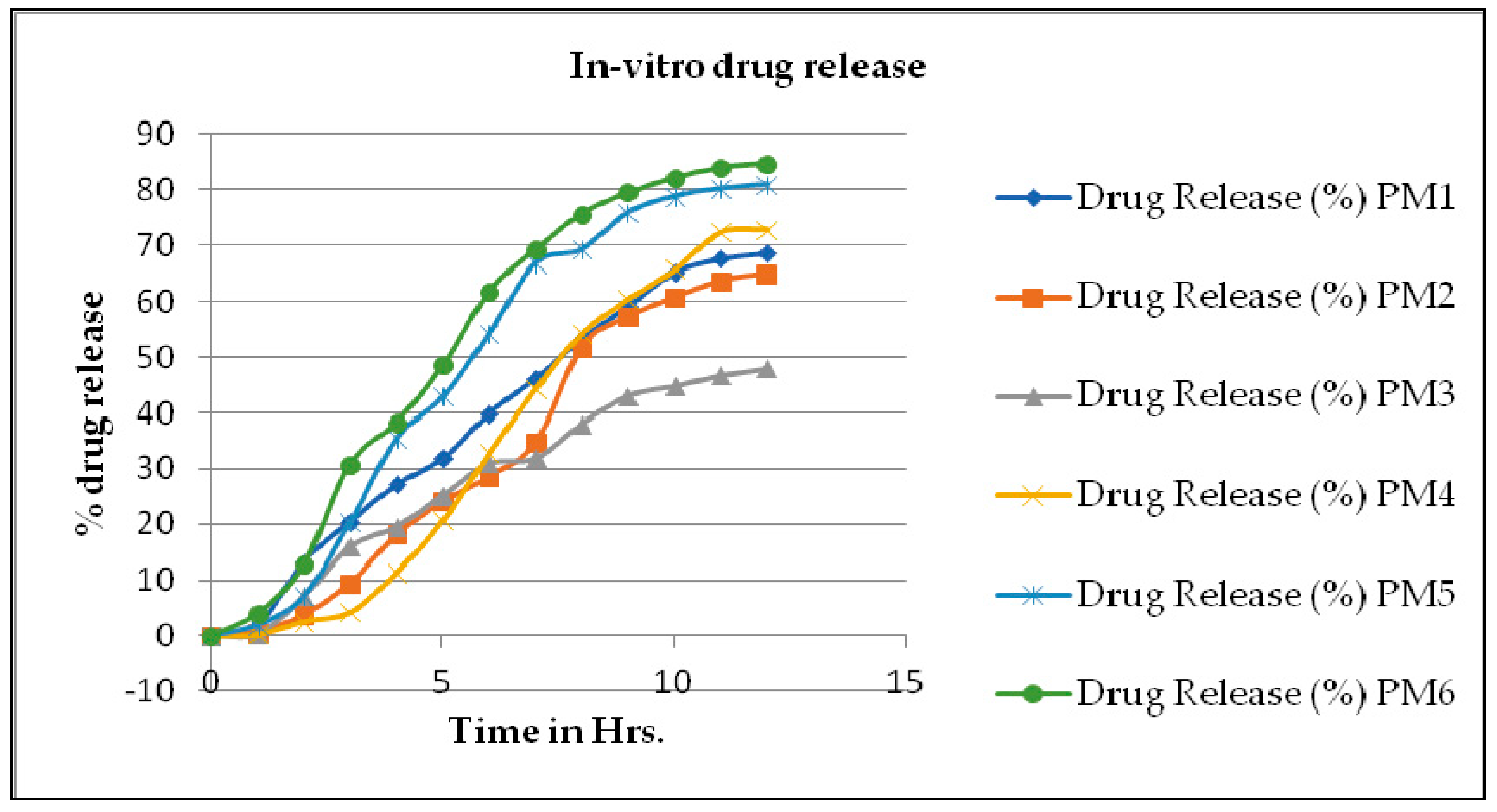
3.5. In-Vitro Diffusion Study
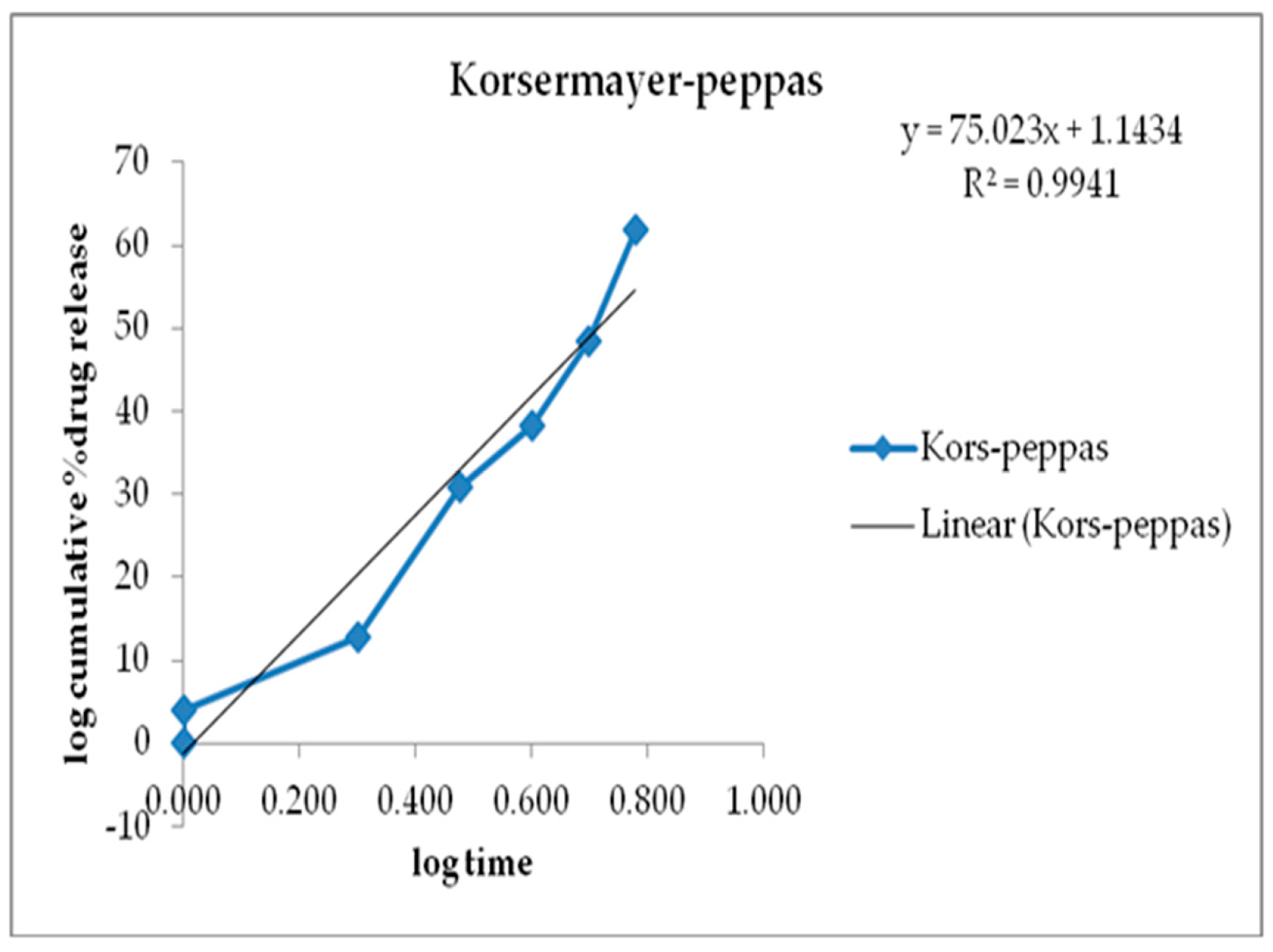
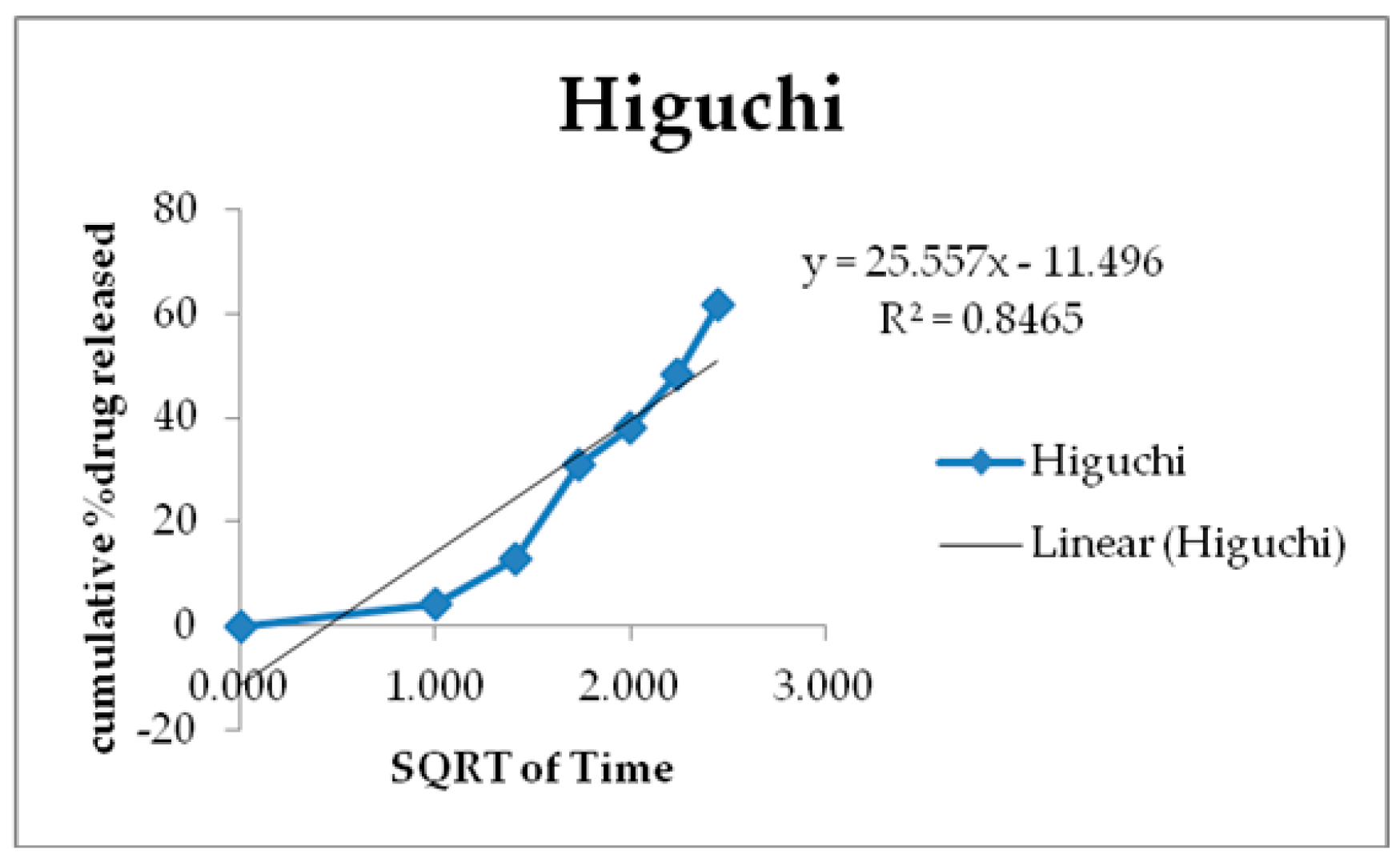
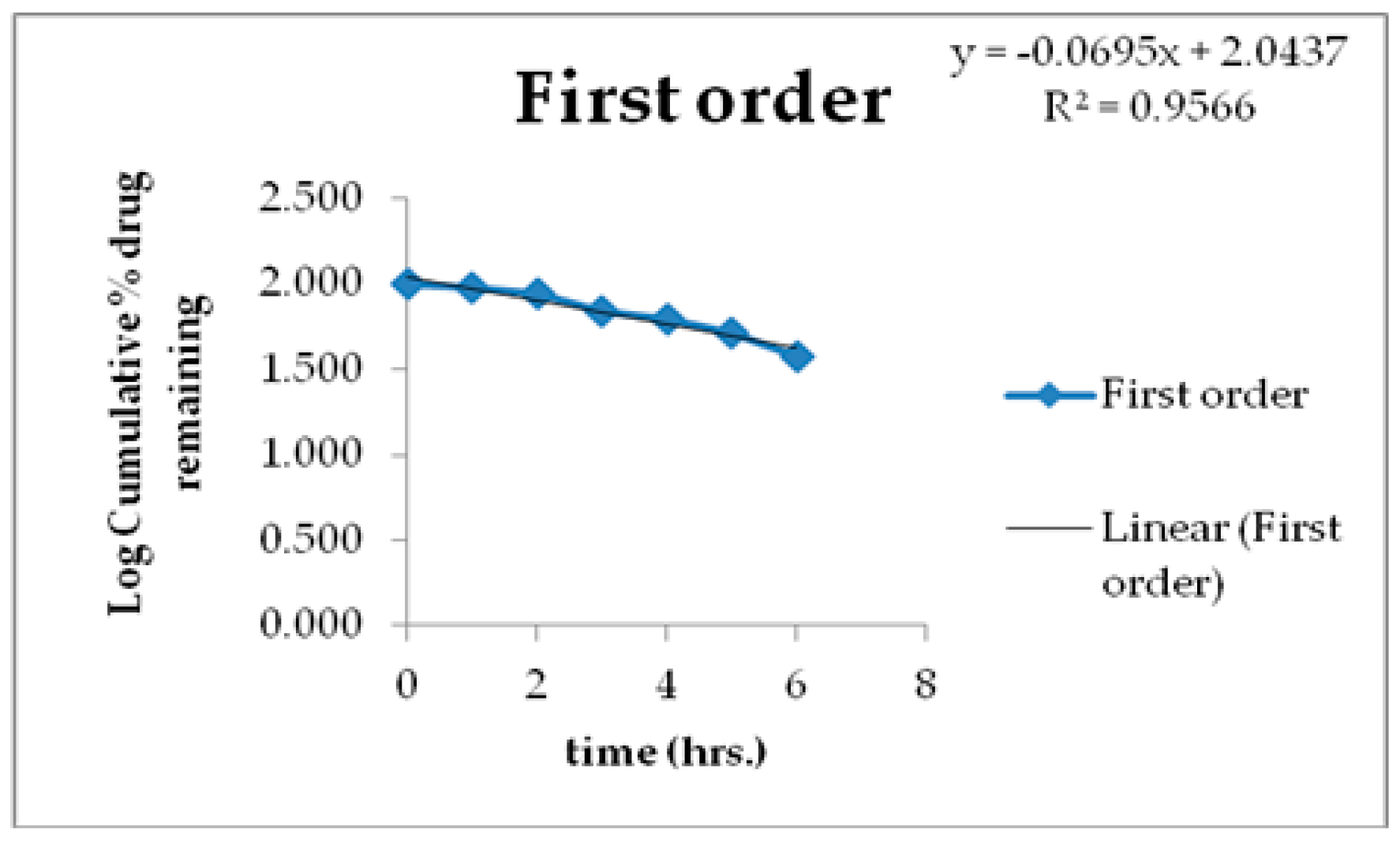
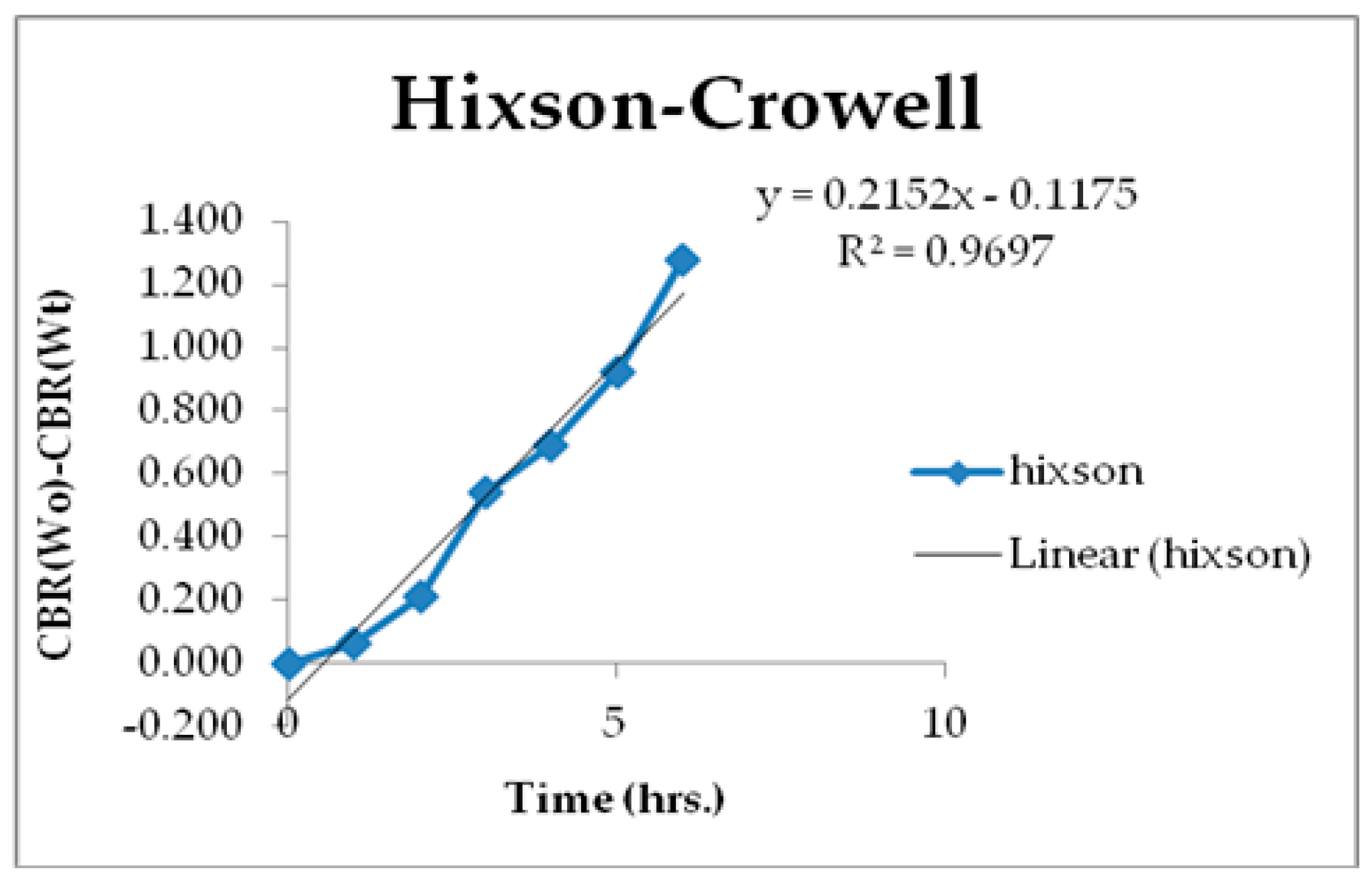
3.6. Kinetics of Drug Release
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Annamaraju, P.; Baradhi, K.M. Pentoxifylline. Pentoxifylline—[Updated 19 September 2022]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gudziol, V.; Hummel, T. Effects of Pentoxifylline on Olfactory Sensitivity: A Postmarketing Surveillance Study. Arch. Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2009, 135, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Belgamwar, V.S.; Patel, H.S.; Joshi, A.S.; Agrawal, A.; Surana, S.J.; Tekade, A.R. Design and Development of Nasal Mucoadhesive Microspheres Containing Tramadol HCl for CNS Targeting. Drug Deliv. 2011, 18, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Tang, L.; Ma, J. The Application of Mucoadhesive Polymers in Nasal Drug Delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Phar. 2010, 36, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, H.C.; Chaudhari, L.Y.; Chaudhari, P.A.; Bhavsar, S.P.; Tadavi, S.A. Formulation and Evaluation of Microsphere Containing Telmisartan Drug by Ionotropic Gelation Method. Int. J. Res. Trends Innov. 2022, 7, 1489–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, N.N. Formulations and Evaluations of Metformin Microspheres by Ionotropic Gelation Technique. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 6, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.B.; Sawant, K.K. Development, Optimization and in Vitro Evaluation of Alginate Mucoadhesive Microspheres of Carvedilol for Nasal Delivery. J. Microencapsul. 2009, 26, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.; Babbar, A.; Mathur, R.; Mishra, A.; Sawant, K. Mucoadhesive Chitosan Microspheres of Carvedilol for Nasal Administration. J. Drug Target. 2010, 18, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnanadh, M.; Kumar, D.S.; Shirwaikar, A.; Kumar Ravi Sampath Kumar, D.; Prasad, R.S. Preparation of Mucoadhesive Micrspheres for Nasal Delivery by Spray Drying. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 69, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamizharasi, S.; Rathi, J.C.; Rathi, V. Formulation, and Evaluation of Pentoxifylline-Loaded Poly(?-Caprolactone) Microspheres. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 70, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, N.; Mishra, A.; Pathak, A.K. Preparation and Evaluation of Mucoadhasive Microspheres of Propranolol HCl for Nasal Delivery. Int. J. Adv. Pharm. 2015, 4, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Arefin, P.; Hasan, I.; Islam, M.S.; Reza, M.S. Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation of Eudragit RL 100 Loaded Fexofenadine HCl Microspheres. Bangladesh Pharm. J. 2016, 19, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jain, S.; Jain, N.; Gupta, Y.; Jain, A.; Jain, D.; Chaurasia, M. Mucoadhesive Chitosan Microspheres for Non-Invasive and Improved Nasal Delivery of Insulin. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 69, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavini, E.; Rassu, G.; Sanna, V.; Cossu, M.; Giunchedi, P. Mucoadhesive Microspheres for Nasal Administration of an Antiemetic Drug, Metoclopramide: In-Vitro/Ex-Vivo Studies. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 57, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taksande, J.B.; Umekar, M.J. Preparation of Intranasal Pregabalin Microspheres: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Evaluation. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 12, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Sonje, A.G.; Mahajan, H.S. Nasal inserts containing ondansetron hydrochloride based on Chitosan-gellan gum polyelectrolyte complex: In vitro–in vivo studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 64, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Name | Units | Low | High | –Alpha | +Alpha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium Alginate | Gm | 1.95 | 2.05 | 1.92929 | 2.07071 |
| Carbopol | Mg | 450 | 550 | 429.289 | 570.711 |
| Formulation Code | Particle Size, µm |
|---|---|
| PM1 | 27.01 ± 0.08 |
| PM2 | 30.48 ± 0.02 |
| PM3 | 29.11 ± 0.05 |
| PM4 | 33.78 ± 0.03 |
| PM5 | 32.74 ± 0.07 |
| PM6 | 31.45 ± 0.03 |
| Formulation Code | % Drug Encapsulation |
|---|---|
| PM1 | 58.63 ± 0.10 |
| PM2 | 56.24 ± 0.04 |
| PM3 | 59.75 ± 0.08 |
| PM4 | 63.45 ± 0.06 |
| PM5 | 59.27 ± 0.07 |
| PM6 | 60.45 ± 0.02 |
| Formulation Code | % In-Vitro Mucoadhesion |
|---|---|
| PM1 | 78.15 ± 0.07 |
| PM2 | 76.14 ± 0.08 |
| PM3 | 80.85 ± 0.04 |
| PM4 | 87.58 ± 0.06 |
| PM5 | 85.63 ± 0.07 |
| PM6 | 84.12 ± 0.01 |
| Drug Release (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time in Hrs. | PM1 | PM2 | PM3 | PM4 | PM5 | PM6 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1.89 ± 0.05 | 0.71 ± 0.04 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.07 | 1.89 ± 0.05 | 4.02 ± 0.023 |
| 2 | 13.27 ± 0.09 | 3.79 ± 0.03 | 7.1 ± 0.05 | 2.6 ± 0.05 | 7.11 ± 0.07 | 12.81 ± 0.05 |
| 3 | 20.44 ± 0.08 | 9.49 ± 0.07 | 15.9 ± 0.04 | 4.27 ± 0.06 | 20.4 ± 0.05 | 30.86 ± 0.09 |
| 4 | 27.11 ± 0.04 | 18.05 ± 0.05 | 19.5 ± 0.01 | 11.39 ± 0.05 | 35.4 ± 0.07 | 38.3 ± 0.08 |
| 5 | 31.88 ± 0.03 | 24.02 ± 0.08 | 25.21 ± 0.05 | 20.66 ± 0.03 | 42.82 ± 0.05 | 48.53 ± 0.02 |
| 6 | 39.96 ± 0.05 | 28.55 ± 0.09 | 30.92 ± 0.05 | 32.79 ± 0.05 | 54.23 ± 0.08 | 61.84 ± 0.07 |
| 7 | 46.16 ± 0.07 | 34.73 ± 0.05 | 31.9 ± 0.04 | 44.23 ± 0.05 | 66.85 ± 0.07 | 69.26 ± 0.06 |
| 8 | 53.3 ± 0.08 | 51.82 ± 0.07 | 38.07 ± 0.03 | 54.24 ± 0.04 | 69.29 ± 0.04 | 75.69 ± 0.04 |
| 9 | 59.26 ± 0.03 | 57.36 ± 0.05 | 43.07 ± 0.02 | 60.45 ± 0.05 | 75.93 ± 0.06 | 79.53 ± 0.03 |
| 10 | 65.22 ± 0.02 | 60.71 ± 0.04 | 44.76 ± 0.05 | 65.7 ± 0.07 | 78.81 ± 0.04 | 82.15 ± 0.05 |
| 11 | 67.62 ± 0.07 | 63.8 ± 0.05 | 46.66 ± 0.04 | 72.36 ± 0.06 | 80.25 ± 0.07 | 84.05 ± 0.03 |
| 12 | 68.58 ± 0.02 | 65.01 ± 0.07 | 47.86 ± 0.07 | 72.87 ± 0.05 | 80.96 ± 0.08 | 84.78 ± 0.01 |
| Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer-Peppas | Hixson-Crowell | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.7925 | 0.9566 | 0.8465 | 0.952 | 0.9697 |
| K | 61.156 | 2.044 | 25.55 | 71.536 | - |
| N | - | - | - | - | 0.2152 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tadavi, S.; Pawar, S. Mucoadhesive Pentoxifylline Microsphere for Non-Invasive Nasal Drug Delivery. Eng. Proc. 2023, 56, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-15957
Tadavi S, Pawar S. Mucoadhesive Pentoxifylline Microsphere for Non-Invasive Nasal Drug Delivery. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 56(1):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-15957
Chicago/Turabian StyleTadavi, Sandip, and Sunil Pawar. 2023. "Mucoadhesive Pentoxifylline Microsphere for Non-Invasive Nasal Drug Delivery" Engineering Proceedings 56, no. 1: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-15957
APA StyleTadavi, S., & Pawar, S. (2023). Mucoadhesive Pentoxifylline Microsphere for Non-Invasive Nasal Drug Delivery. Engineering Proceedings, 56(1), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-15957






