Abstract
Artificial neural networks with different structures are used for identification of complex dynamic plant with distributed parameters. The plant is a high-temperature plasma in the spherical Globus-M2 tokamak. Experimental data from it were processed by plasma reconstruction code based on Picard iterations, namely, the Flux-Current Distribution Identification (FCDI) code. This represents smart technology employed to obtain distributed plasma parameters by minimizing the difference between measured and reconstructed signals. An artificial neural network was then applied to identify the data obtained by the FCDI code on the hardware as a real-time testbed realized on a Speedgoat computer. The aim of this repeated identification is to increase the operational response speed in real time in the closed-loop control system of the plasma shape.
1. Introduction
An artificial neural network is a powerful and universal algorithm of identification and approximation. It can be used to predict parameters of a complex dynamical plants under control. The advantages of neural network models include low computational complexity and wide possibilies of hardware implementation. From this perspective, it is especially beneficial to employ neural networks with a small number of neurons.
In tokamak experiments, plasma parameters cannot be directly measured because of the high temperature plasma that is able to disable diagnostics. The simplest and most widely used method to detect the boundary and integral parameters of the plasma is the use of magnetic sensors which measure the changes in magnetic field and flux outside the plasma, but within the region of the magnetic field produced by the plasma. The plasma shape is to be identified from the signals of the tokamak diagnostic system. This inverse problem is known as the plasma equilibrium reconstruction problem [1,2]. The FCDI algorithm was developed for plasma equilibrium reconstruction in the Globus-M2 tokamak and uses the Picard iteration approach [3]. The FCDI code is able to obtain the plasma shape offline after cessation of experiment and cannot be used online because of high computational complexity and high task execution time. For real-time use, it is necessary to achieve identification of the FCDI code via a fast model.
There are different approximation methods of a plasma reconstruction algorithm [4]. Neural networks were used for plasma reconstruction in COMPASS tokamak (UK) [5], ASDEX-Upgrade (Germany) [6], D-IIID (USA) [7], and models of ITER [8]. The EFIT reconstruction code was approximated through neural networks by researchers in [9]. In these works, fully connected neural networks with different layer numbers, activation functions, layers sizes were employed.
An artificial neural network was used for identification of a reconstruction algorithm for Globus-M2 in [4,10]. In [10], a neural network was used for identification of moving filaments of the plasma reconstruction approach. In [4], several methods of FCDI algorithm identification were considered including artificial neural networks. The present work offers further development in the use of artificial neural networks for plasma shape prediction in the Globus-M2 tokamak. Neural network structure, optimization of hyperparameters and real-time hardware implementation are considered.
A real-time imitation platform was constructed for working out algorithms of tokamaks plasma control [11]. It is composed of two Speedgoat Performance computers including digital-to-analog and analog-to-digital converters connected by analog feedback. The first computer models the controller with a plasma reconstruction algorithm; the second computer models the tokamak with plasma and actuators. Such an approach provides several opportunities for digital control systems development. In particular, the imitation platform allows us to measure the working time required of the plasma reconstruction algorithm for plasma shape calculation. Calculation of TET of the Globus-M2 plasma shape control system with a plasma reconstruction algorithm on a Speedgaot computer gives less than 100 s. Consequently, the time for plasma shape calculation should be about 10 s.
2. Experimental Signals
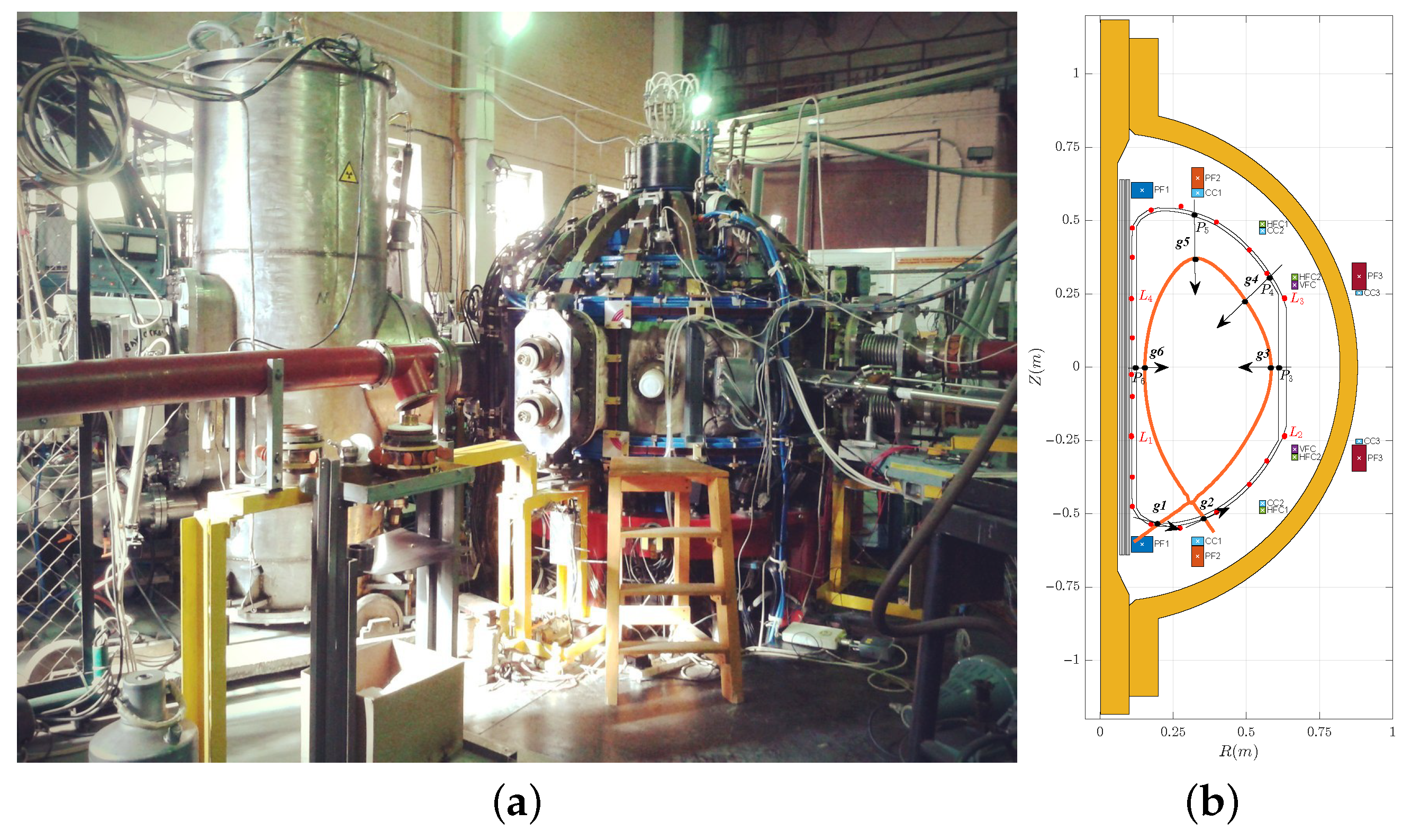
This paper deals with the spherical Globus-M2 tokamak (Ioffe Institute, Saint-Petersburg, Russia) [12]. The basic parameters of this device are as follows: major radius R = 0.36 m, minor radius a = 0.24 m, aspect ratio R/a = 1.5, toroidal magnetic field, B t max = 1 T, plasma current 0.5 MA, impulse duration less than 0.7 s. Plasma confinement and control are provided by 8 poloidal field coils: horizontal field coil, vertical field coil, central solenoid, 4 poloidal field coils and a correcting coil. Plasma diagnostics consists of measurements of plasma current and 24 magnetic fluxes loops.
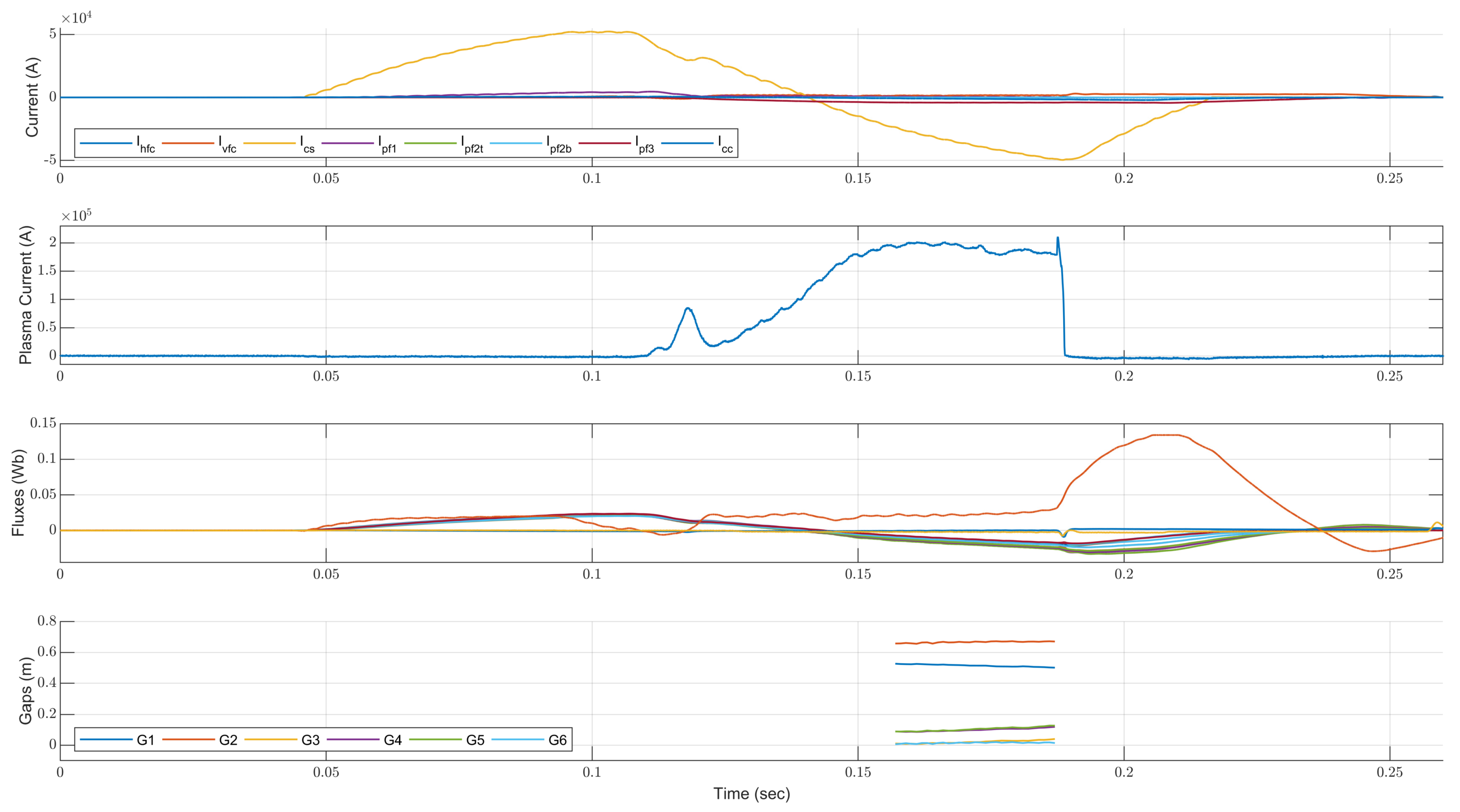
A plasma discharge consists of several phases. The phase when plasma is present inside the vacuum vessel and is not in contact with the inner walls is known as the diverter phase. In the Globus-M2 tokamak, a duration of the diverter phase is about 30 ms. For improving plasma confinement and control, it is necessary to use feedback control of the plasma shape. The plasma shape is determined at 6 points on a separatrix. The separatrix is the largest closed equal line of magnetic flux in Figure 1. In this paper, time series from 51 Globus-M2 discharges were processed. The FCDI algorithm was used to obtain the plasma shape in these discharges on the diverter phase. An example from the experimental data can be seen in Figure 2. The time step of the experimental data is 1 ms.
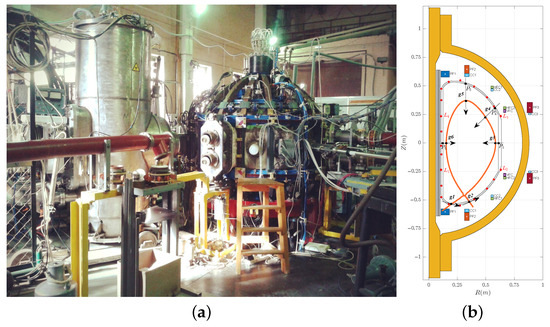
Figure 1.
(a) Globus-M2 tokamak (b) Vertical cross-section with poloidal system, diagnostic probes (red dots) and points on separatrix (g1–g6).
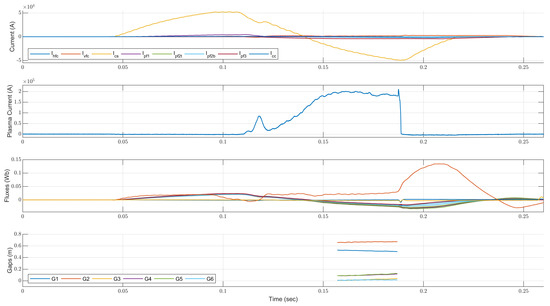
Figure 2.
Experimental signals from shot #37255 and Gaps reconstructed by the FCDI algorithm at a divertor phase of the plasma discharge.
3. Artificial Neural Networks
The simplest type of artificial neural network is a single layer perceptron [13]. The signal from inputs multiplied by weights, summarized with bias, and converted by a nonlinear activation function is written as follows:
3.1. Fully Connected Feedforward Neural Networks
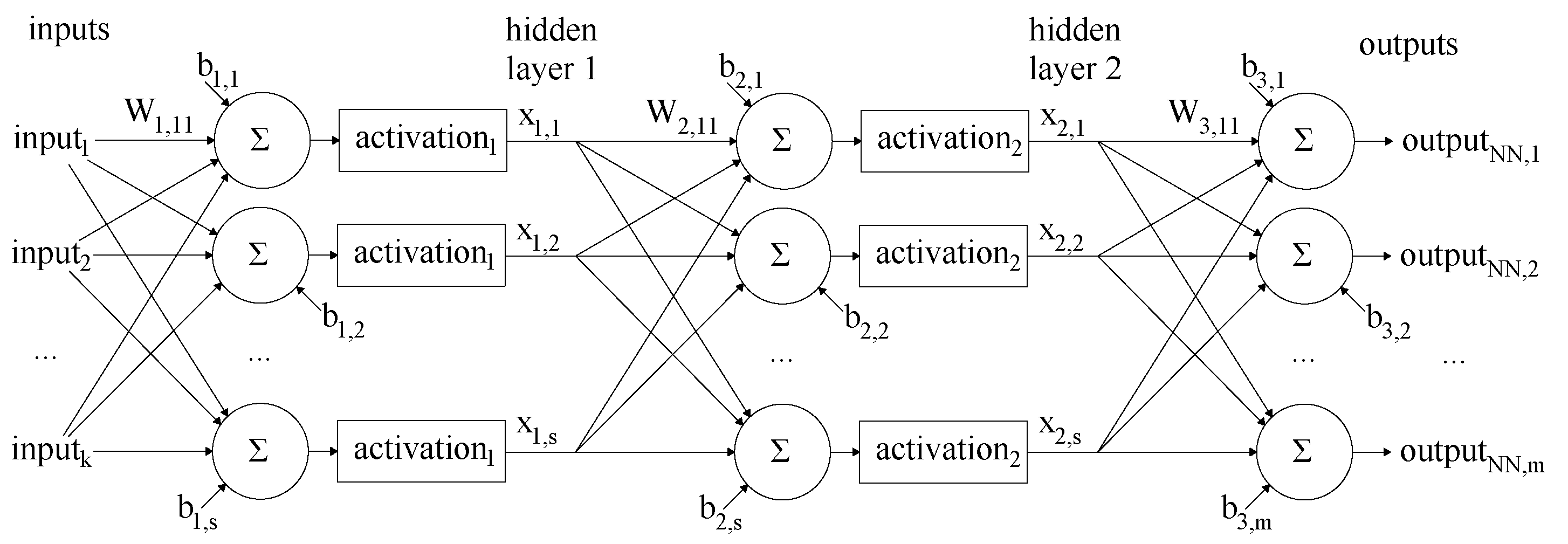
An artificial neural network consisting of a set of fully connected layers is called a fully connected feedforward neural network [14]. In these neural networks, the layers are connected consequentially without loops (Figure 3). Values of are referred to as hidden layers.
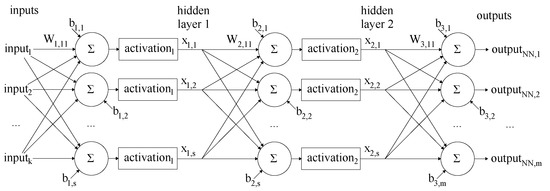
Figure 3.
Structure of the fully connected feedforward neural network containing two hidden layers at a size of s. Input size is k, output size is m.
Regarding the identification of the FCDI algorithm, the neural network has 33 input signals (8 coil currents, plasma current and 24 magnetic fluxes) and 6 output signals (2 strike point coordinates and 4 gaps between the plasma separatrix and the vacuum vessel). In general cases, the sizes the of hidden layers differ, and in the case of the FCDI code identification neural networks with hidden layers of the same size s were considered
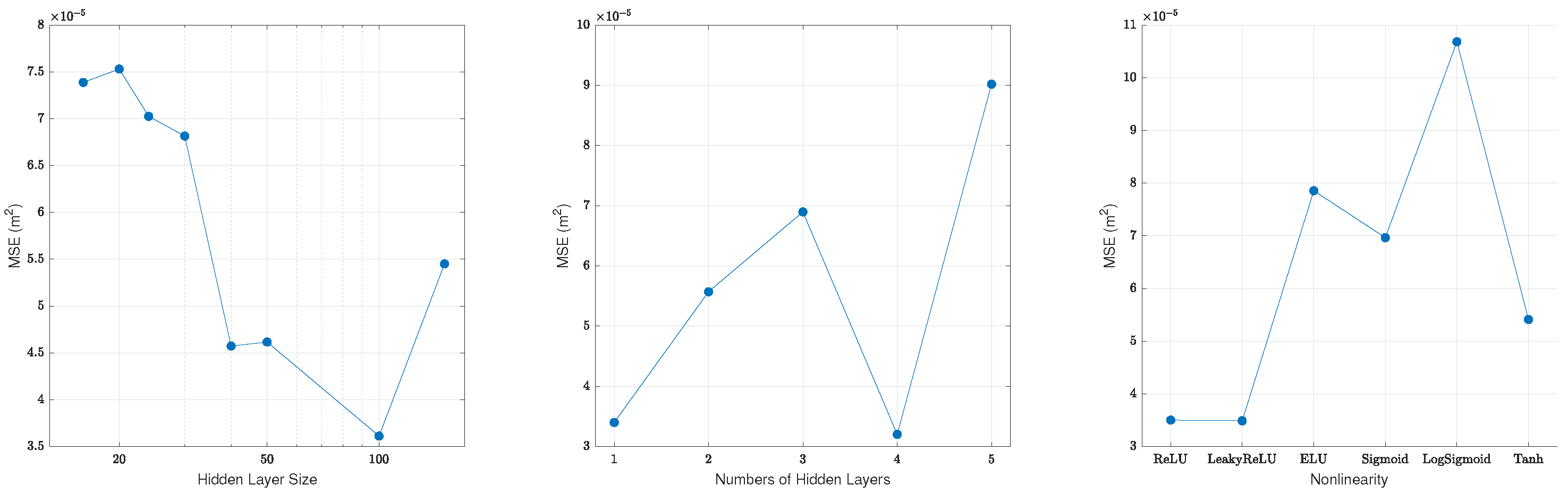
An activation function is a nonlinear function that is needed for separating different hidden layers. In general, activation functions in various layers can differ. In the case of FCDI identification, a neural network with different activation functions but the same in all layers was considered. These are ReLU, LeakyReLU, ELU, Sigmoid, LogSigmoid, Tanh. Values of n and s and type of the activation function are called hyperparameters of the neural network (Figure 4). It is necessary to obtain optimal values of hyperparameters.
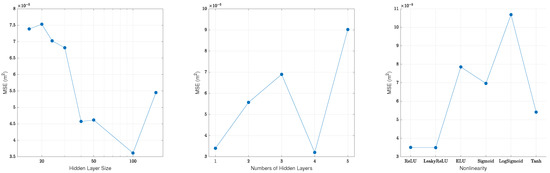
Figure 4.
Dependency of accuracy on hyperparameter values of the fully connected feedforward neural network. Accuracy is measured on test data.
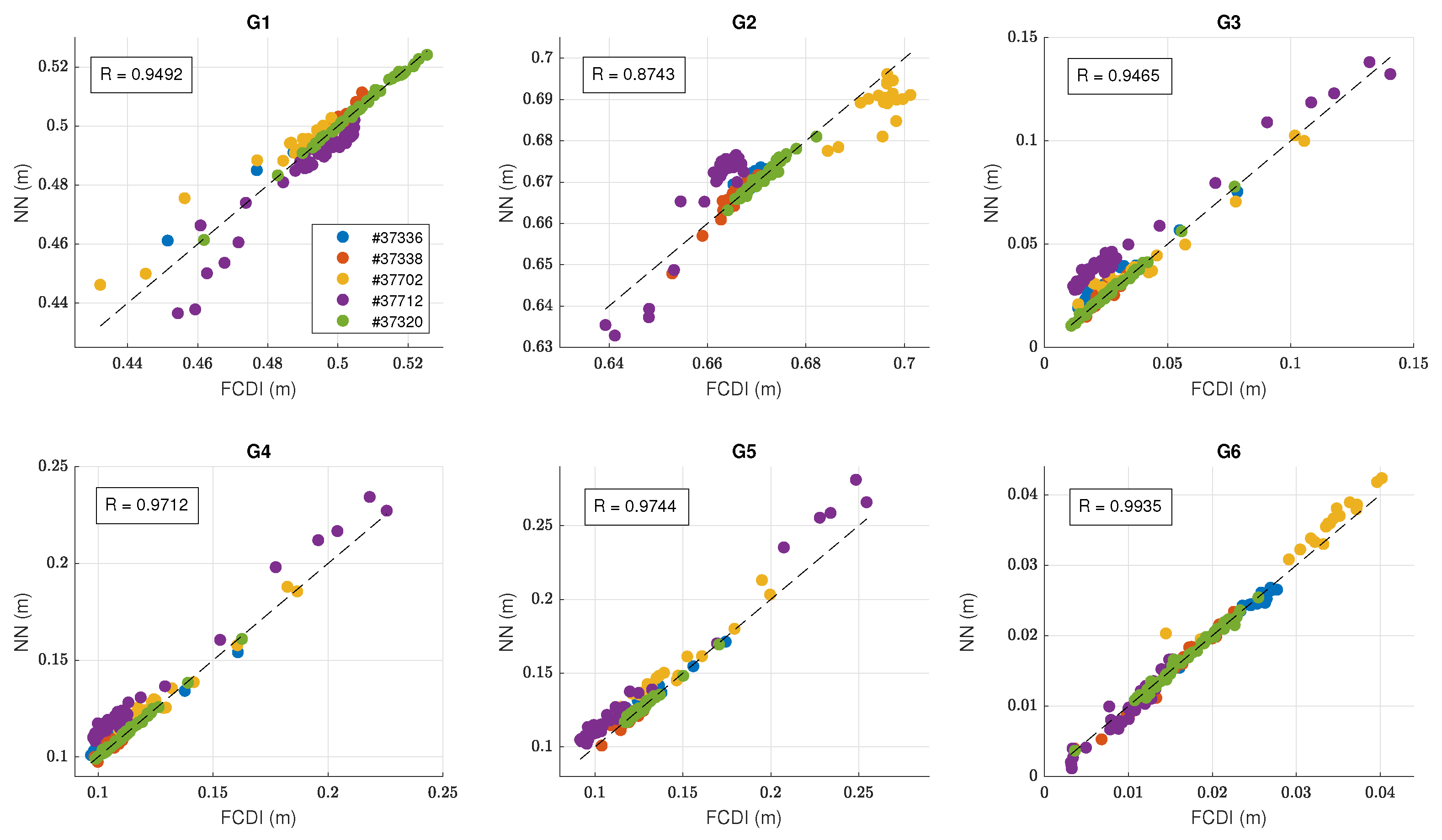
Training of the neural network involves finding values of weights and biases to obtain minimum of the loss-function between a real output signal and a signal predicted by the neural network. In case of FCDI identification, the MSE (Mean Square Error) loss is used. This is a multi-parameter non-linear optimization problem. The most widely used algorithm for training artificial neural networks is backpropagation with a gradient method [15]. The main idea rests in calculation of the gradient of the loss function with respect to weights from output to input. A gradient descent with backpropagation does not guarantee finding the global minimum of the loss function, but only a local minimum. For minimizing this problem, a stochastic gradient method with momentum is used. Furthermore, normalization of signals was made to improve performance of the backpropagation algorithm. Training of the neural network for the FCDI identification was achieved using the Adam [16] algorithm in PyTorch. The experimental data were divided into two parts: 46 training shots and 5 testing shots. Thus, the size of training data is 1795 points and the size of the test data is 145 points. Results are shown in Figure 5.
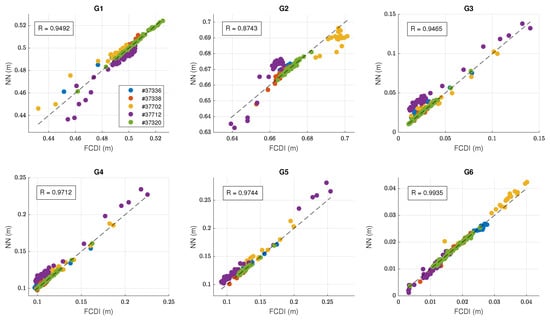
Figure 5.
Results of the FCDI identification by the fully connected feedforward neural network with one hidden layer of the size of 100 neurons and the LeakyReLU activation function. In total, 5 test signals from Globus-M2 shots #37336, #37338, #37702, #37712 and #37320 are shown.
3.2. Recurrent Neural Networks
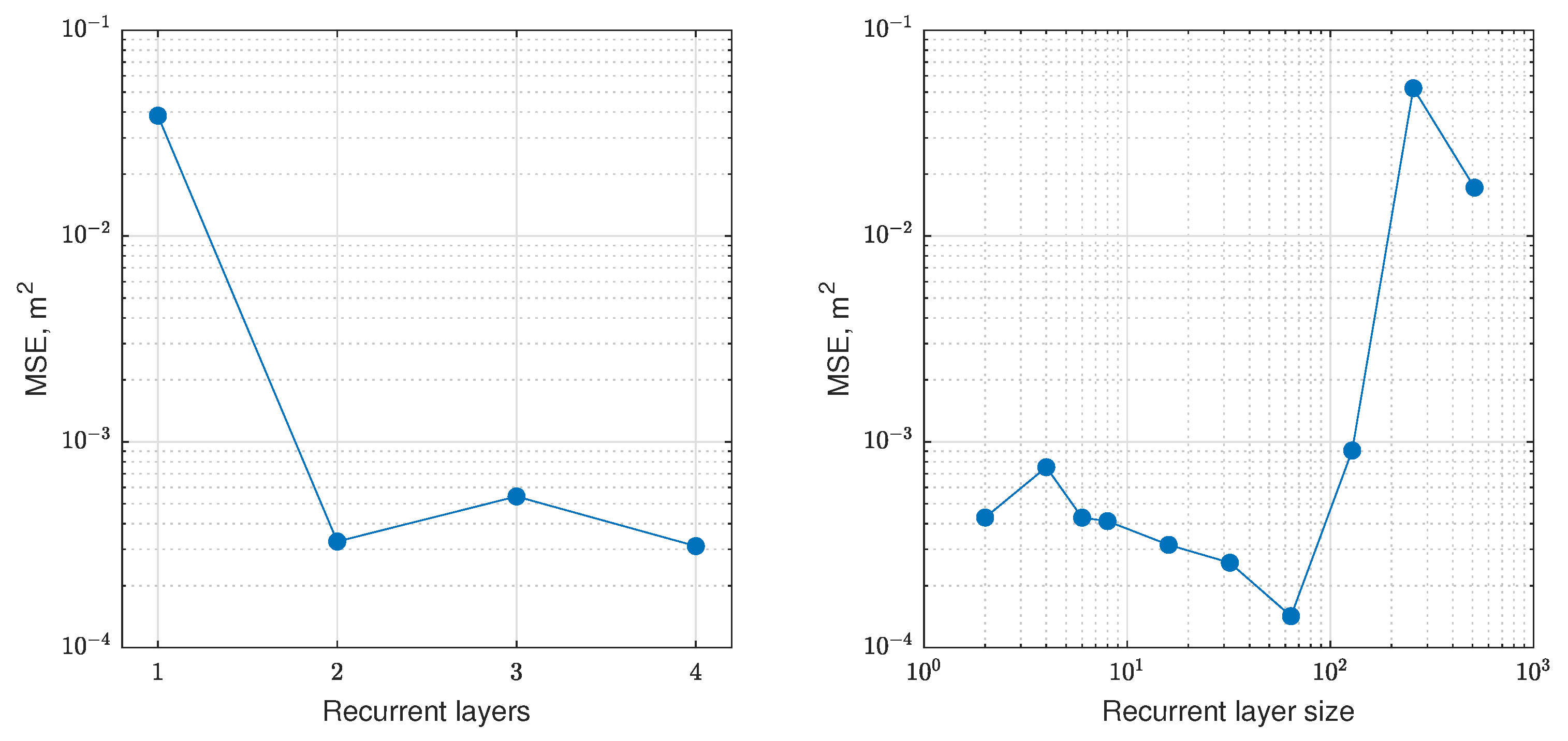
The feedforward neural network only uses a current input signal for calculation of the output signal. In the case of dynamic system identification, it could be useful to apply values from previous time moments. Recurrent neural networks use an additional hidden layer h. The values of the hidden layer on the time step uses for calculation next step . Accuracy of RNN in dependence of hyperparameters is shown in Figure 6.
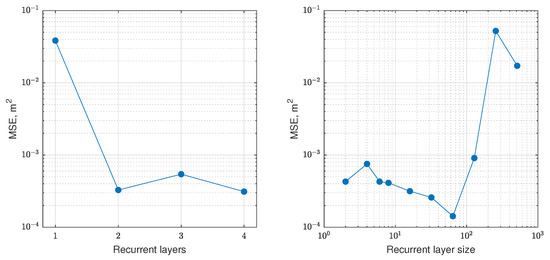
Figure 6.
Dependency of accuracy on hyperparameter values of the recurrent neural network. Accuracy is measured on test data.
3.3. Implementation of Neural Network Models in Real-Time Hardware
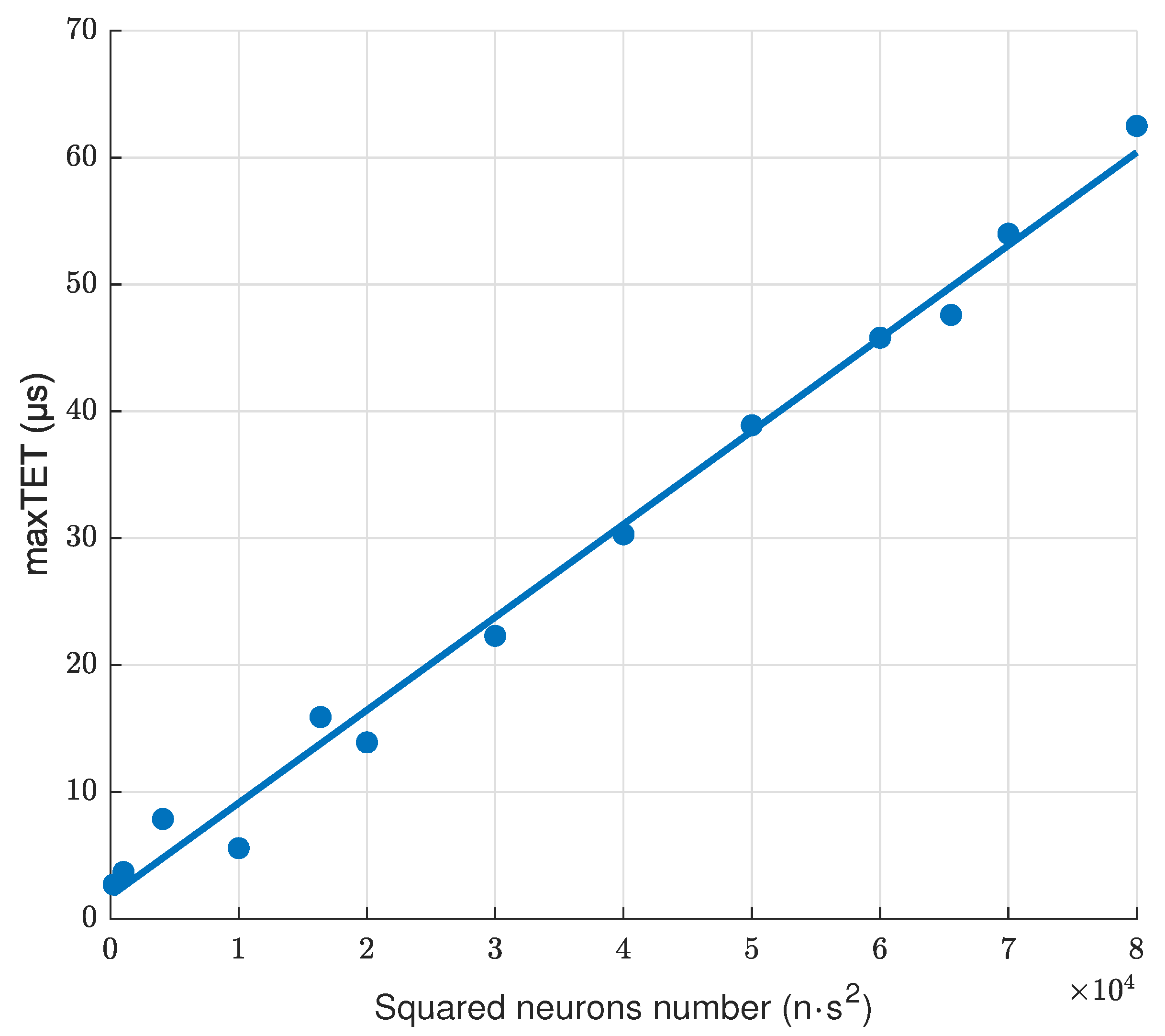
The imitation platform with Speedgoat computers is based on a SimulinkRT operation system. Real-time test bed for plasma control in tokamaks consists of two Speedgoat performance real-time target machines that are connected in feedback: one computer plays the role of the controlled plant model and the other one acts as the MIMO controller. PyTorch models were transferred to Matlab with the help of SciPy library. The neural networks with different structures were testified in real-time regime (Figure 7). Each neuron is connected with all neurons of adjacent layers. Because of this, the computation complexity of one layer of the neural network is proportional to the square of the layer size.
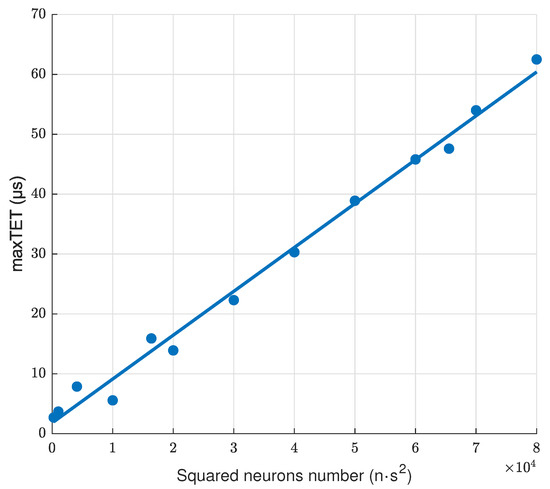
Figure 7.
Dependency of Task Execution Time (TET) on number of neurons.
Plasma shape control in Globus-M2 requires plasma-reconstruction works in about 10 s. Consequently, for real-time usage neural networks containing 100–150 neurons are applicable.
4. Conclusions
The artificial neural network model of the FCDI plasma reconstruction code was obtained along with an optimal structure and hyperparameters. The optimal model for FCDI algorithm identification is a fully connected feedforward neural network with one hidden layer and LeakyReLU activation function. Modeling on the imitation platform showed the possibility of using the neural network model for real-time high-performance control systems, with results demonstrating a Task Execution Time of 4.4 s and a Mean Square Error of 3.4 × 10 m.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.V.M.; methodology, Y.V.M.; funding acquisition, Y.V.M.; software, V.I.K.; supervision, Y.V.M.; validation, V.I.K.; visualization, V.I.K. and E.A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, V.I.K., Y.V.M. and E.A.P.; writing—review and editing, Y.V.M. and E.A.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was sponsored by the Russian Science Foundation (RSF), Grant No. 21-79-20180.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this paper are not currently publicly accessible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mitrishkin, Y.V.; Korenev, P.S.; Prokhorov, A.A.; Kartsev, N.M.; Patrov, M.I. Plasma control in tokamaks. Part 1. Controlled thermonuclear fusion problem. Tokamaks. Components of control systems. Adv. Syst. Sci. Appl. 2018, 18, 26–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrishkin, Y.V.; Kartsev, N.M.; Kuznetsov, E.A.; Korostelev, A.Y. Metodi i Sistemi Magnitnogo Upravleniya Plazmoi vs. Tokamakakh [Methods and Systems of Plasma Magnetic Control in Tokamaks]; KRASAND: Moscow, Russia, 2020. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Korenev, P.S.; Mitrishkin, Y.V.; Patrov, M.I. Rekonstruktsiya ravnovesnogo raspredeleniya parametrov plasmi tokamaka po vneshnim magnitnim izmereniyam i postroyeniye lineynikh plazmennikh modeley [Reconstruction of equilibrium distribution of plasma parameters on the base of external magnetic measurements and construction of plasma linear models]. Mechatron. Autom. Control 2016, 17, 254–265. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mitrishkin Yuri, V.; Korenev Pavel, S.; Konkov Artem, E.; Kruzhkov Valerii, I.; Ovsyannikov Nicolai, E. New Identification Approach and Methods for Plasma Equilibrium Reconstruction in D-Shaped Tokamaks. Mathematics 2022, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M.; Haynes, P.S.; Smith, M.E.U.; Todd, T.N.; Trotman, D.L. Real-Time Control of a Tokamak Plasma Using Neural Networks. Neural Comput. 1995, 7, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccorese, E.; Morabito, C.; Martone, R. Identification of noncircular plasma equilibria using a neural network approach. Nucl. Fusion 1994, 34, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, J.B.; Schnurrenberger, H. Fast non-linear extraction of plasma equilibrium parameters using a neural network mapping. Nucl. Fusion 1991, 31, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, R.; Coccorese, E.; Gruber, O.; Martone, R.; McCarthy, P.; Morabito, F.C. Identification of Plasma Equilibria in ITER from Magnetic Measurements Via Functional Parameterization and Neural Networks. Fusion Technol. 1996, 30, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, S.; Kim, J.; Kwak, S.; Bak, J.G.; Lee, S.; Han, H.; Ghim, Y. Deep neural network Grad-Shafranov solver constrained with measured magnetic signals. Nucl. Fusion 2019, 60, 016034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorov, A.; Mitrishkin, Y.; Korenev, P.; Patrov, M. The Plasma Shape Control System in the Tokamak with the Neural Network as a Plasma Equilibrium Reconstruction Algorithm; Elsevier Ltd.: London, UK, 2020; pp. 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrishkin, Y.V. Plasma magnetic control systems in D-shaped tokamaks and imitation digital computer platform in real time for controlling plasma current and shape. Adv. Syst. Sci. Appl. Int. Inst. Gen. Syst. Stud. 2022, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Minaev, V.B.; Gusev, V.K.; Sakharov, N.V.; Varfolomeev, V.I.; Bakharev, N.N.; Belyakov, V.A.; Bondarchuk, E.N.; Brunkov, P.N.; Chernyshev, F.V.; Davydenko, V.I.; et al. Spherical tokamak Globus-M2: Design, integration, construction. Nucl. Fusion 2017, 57, 066047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, F. The perceptron: A probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol. Rev. 1958, 65, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. Off. J. Int. Neural Netw. Soc. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep learning. Genet. Program. Evolvable Mach. 2018, 19, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).