Determination of Fatigue Crack Size in High-Strength Bolting Assemblies Using Hydrogen-Induced Cracking †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Requirement 1: Destructive tests must ensure that the failure occurs in the plane of the original fatigue crack (root of the first load bearing thread) to allow access for an optical crack size measurement;
- Requirement 2: The transition from original fatigue crack to residual fracture must be as clear as possible to reduce errors in the crack size measurement.
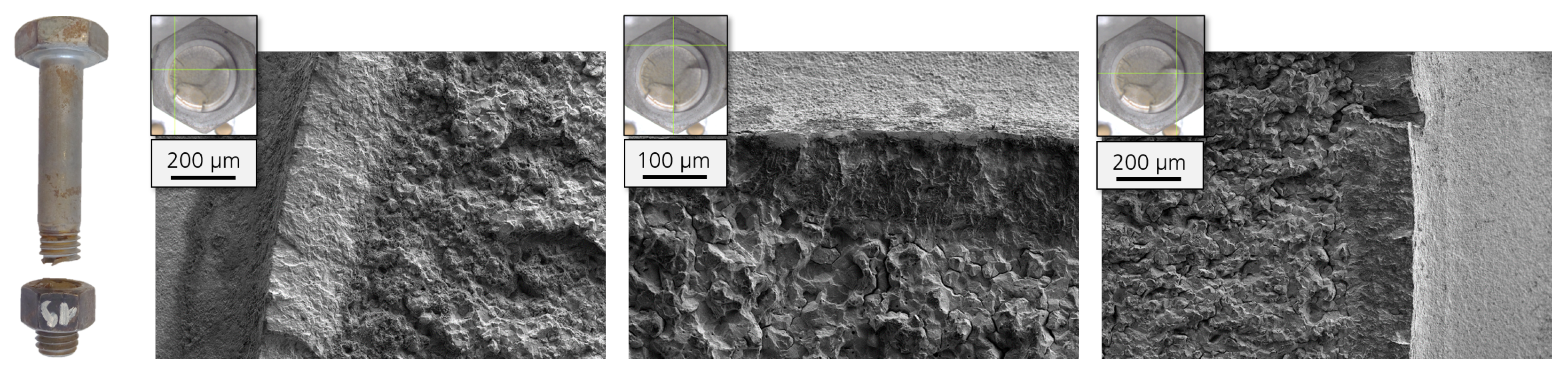
2. Materials and Methods
- Step 1: Fatigue testing of the bolting assembly up to a defined criterion (e.g., frequency drop, specified number of load cycles, …);
- Step 2: Removal of the bolting assembly from the fatigue testing machine and application of a suitable (e.g., hydrochloric) acid at the first load bearing thread;
- Step 3: Application of static load () to the bolting assembly until failure;
- Step 4: Determination of fatigue crack size by fracture surface assessment.
3. Results
3.1. Initial Crack Size Determination
3.1.1. Failure Locations
3.1.2. Initial Crack Size Measurement
3.2. Final Crack Size Determination
3.3. Validation of Fracture Mechanics Calculations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glienke, R.; Schwarz, M.; Johnston, C.; Hagemann, M.; Seidel, M. Update on the Fatigue Strength of Large-Size Bolting assemblies in Steel Construction. IJOPE 2023, 33, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, P.; Erdogan, F. A critical analysis of crack propagation laws. J. Basic Eng. 1963, 85, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forschungskuratorium Maschinenbau e.V. (FKM). FKM-Richtlinie: Bruchmechanischer Festigkeitsnachweis, 4th ed.; VDMA Verlag: Frankfurt am Main, Deutschland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pyttel, B.; Varfolomeyev, I.; Berger, C. Praktische Anwendung der FKM-Richtlinie “Bruchmechanischer Festigkeitsnachweis für Maschinenbauteile”. In Proceedings of the 40th Meeting of the DVM Working Group on Fracture Processes, Stuttgart, Germany, 19–20 February 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Eichstädt, R. Fatigue Assessment of Large-Size Bolting Assemblies for Wind Turbine Support Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität, Hannover, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- EN 14399-4:2015-04; High-Strength Structural Bolting Assemblies for Preloading—Part 4: System HV—Hexagon Bolt and Nut Assemblies. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2015.
- DIN EN ISO 4032:2023-12; Fasteners—Hexagon Regular Nuts (Style 1). Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2023.
- DIN EN ISO 7089:2000-11; Plain Washers—Normal Series, Product Grade A. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2000.
- DIN 969:2020-02; Threaded Fasteners—Axial Load Fatigue Testing—Test Methods and Evaluation of Results. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2020.
- Wiegand, H.; Kloos, K.-H.; Thomala, W. Schraubenverbindungen, 5th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 172–173. [Google Scholar]
- Hoche, H. Im Schatten der Schraube: Warum man die Mutter bei Wasserstoffversprödung nicht unterschätzen sollte. In Proceedings of the WAB-Innovationszirkel Gründungsstrukturen & Stahlbau, Bremen, Germany, 20 March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, M.; Wegener, F.; Hinrichs, J.; Stolle, C.; Güres, S.; Seidel, M.; Glienke, R.; Flügge, W. Remaining fatigue resistance of bolting assemblies in a wind turbine tower at the end of the planned service life. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Durability, Repair and Maintenance of Structures DRMS, Porto, Portugal, 13–14 March 2025. [Google Scholar]



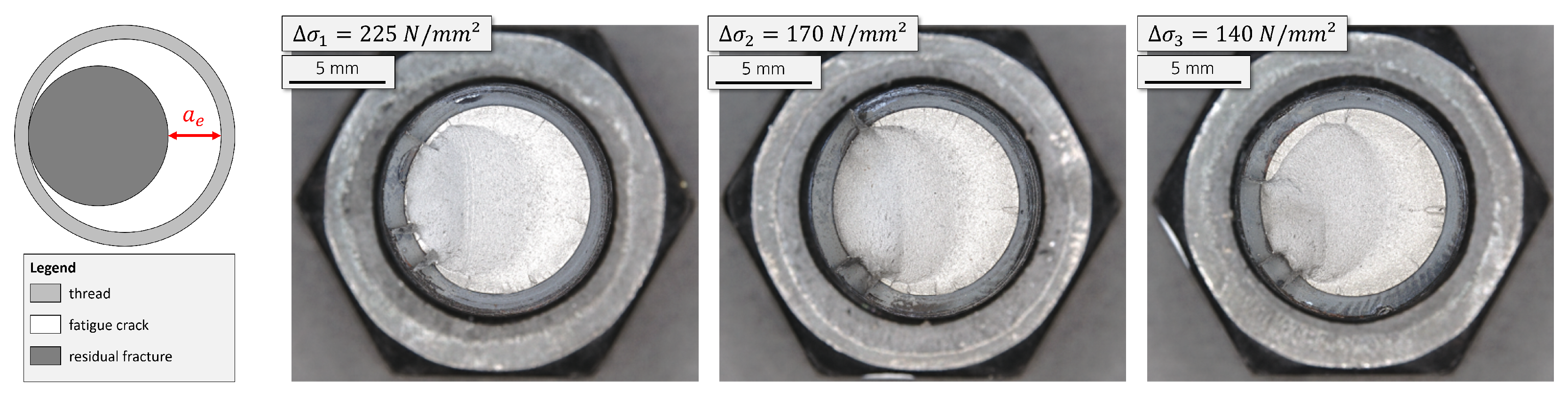

| Initial Crack Size | Final Crack Size | Fracture Mechanics Validation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | ||||||||
| [N/mm2] | [−] | [mm] | [−] | [−] | [mm] | [mm] | [−] | [−] | [%] | [%] |
| 225 | 32,337 | 0.35 | 61,163 | 63,922 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 31,585 | 30,771 | −8.8 | −3.7 |
| 43,382 | 0.35 | 67,718 | 1.6 | 20,540 | 30,771 | |||||
| 35,224 | 0.45 | 62,884 | 1.6 | 28,698 | 26,400 | |||||
| 170 | 79,723 | 0.30 | 105,253 | 135,673 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 55,950 | 75,366 | −23.3 | −9.8 |
| 61,050 | 0.30 | 154,794 | 2.5 | 74,623 | 75,366 | |||||
| 94,326 | 0.45 | 146,971 | 2.5 | 41,347 | 61,186 | |||||
| 140 | 167,409 | 0.50 | 237,509 | 240,767 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 73,358 | 89,285 | −29.0 | −10.0 |
| 149,117 | 0.35 | 233,539 | 1.9 | 91,650 | 111,400 | |||||
| 157,356 | 0.30 | 251,254 | 2.0 | 83,411 | 119,800 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wegener, F.; Glienke, R.; Schwerdt, D.; Lorenz, M.; Mantik, J.; Flügge, W. Determination of Fatigue Crack Size in High-Strength Bolting Assemblies Using Hydrogen-Induced Cracking. Eng. Proc. 2025, 119, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025119031
Wegener F, Glienke R, Schwerdt D, Lorenz M, Mantik J, Flügge W. Determination of Fatigue Crack Size in High-Strength Bolting Assemblies Using Hydrogen-Induced Cracking. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 119(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025119031
Chicago/Turabian StyleWegener, Fritz, Ralf Glienke, Daniela Schwerdt, Mathias Lorenz, Justus Mantik, and Wilko Flügge. 2025. "Determination of Fatigue Crack Size in High-Strength Bolting Assemblies Using Hydrogen-Induced Cracking" Engineering Proceedings 119, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025119031
APA StyleWegener, F., Glienke, R., Schwerdt, D., Lorenz, M., Mantik, J., & Flügge, W. (2025). Determination of Fatigue Crack Size in High-Strength Bolting Assemblies Using Hydrogen-Induced Cracking. Engineering Proceedings, 119(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025119031






